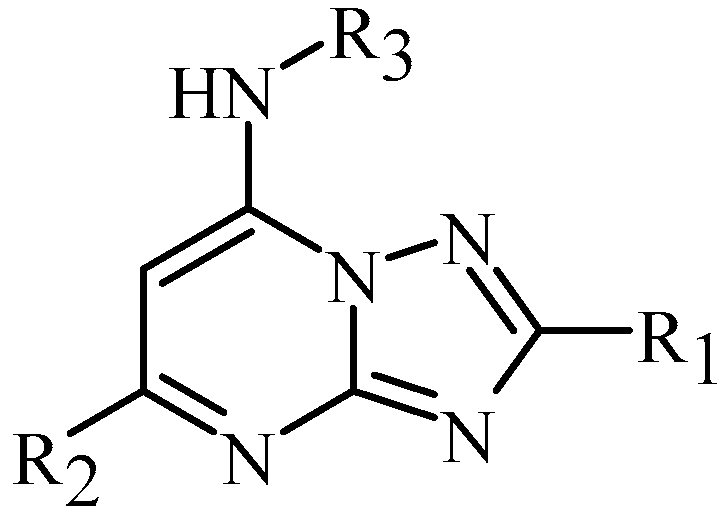
Modeling the Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationships of 1,2,4-Triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-amine Analogs in the Inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Computational Tools
2.2. Dataset
2.3. Preparation of Dataset
2.4. Selecting Significant Variables
2.5. Data Split
2.6. Residual Analysis of the Model
2.7. Building Regression Models
2.8. Evaluation of Model
3. Results and Discussion
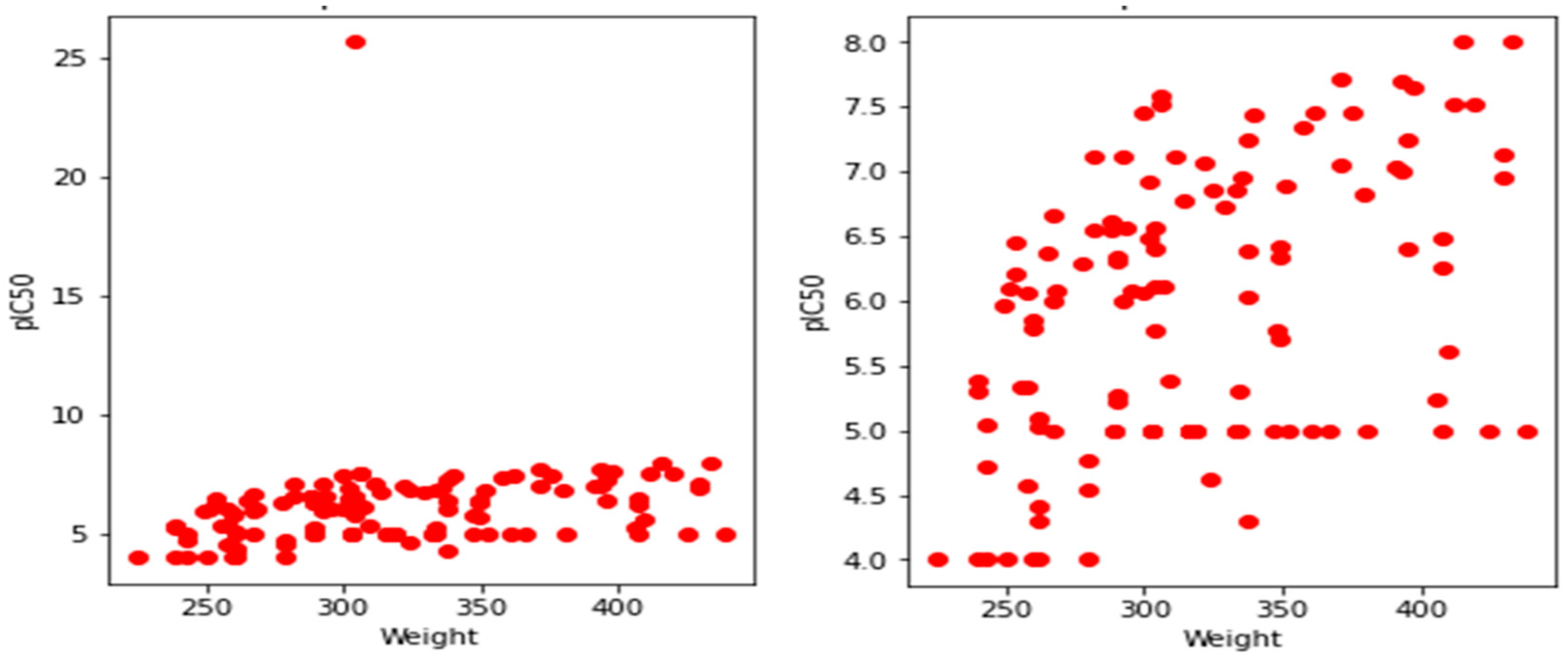
3.1. Exploratory Data Analysis
3.2. Feature Selection Using RFE
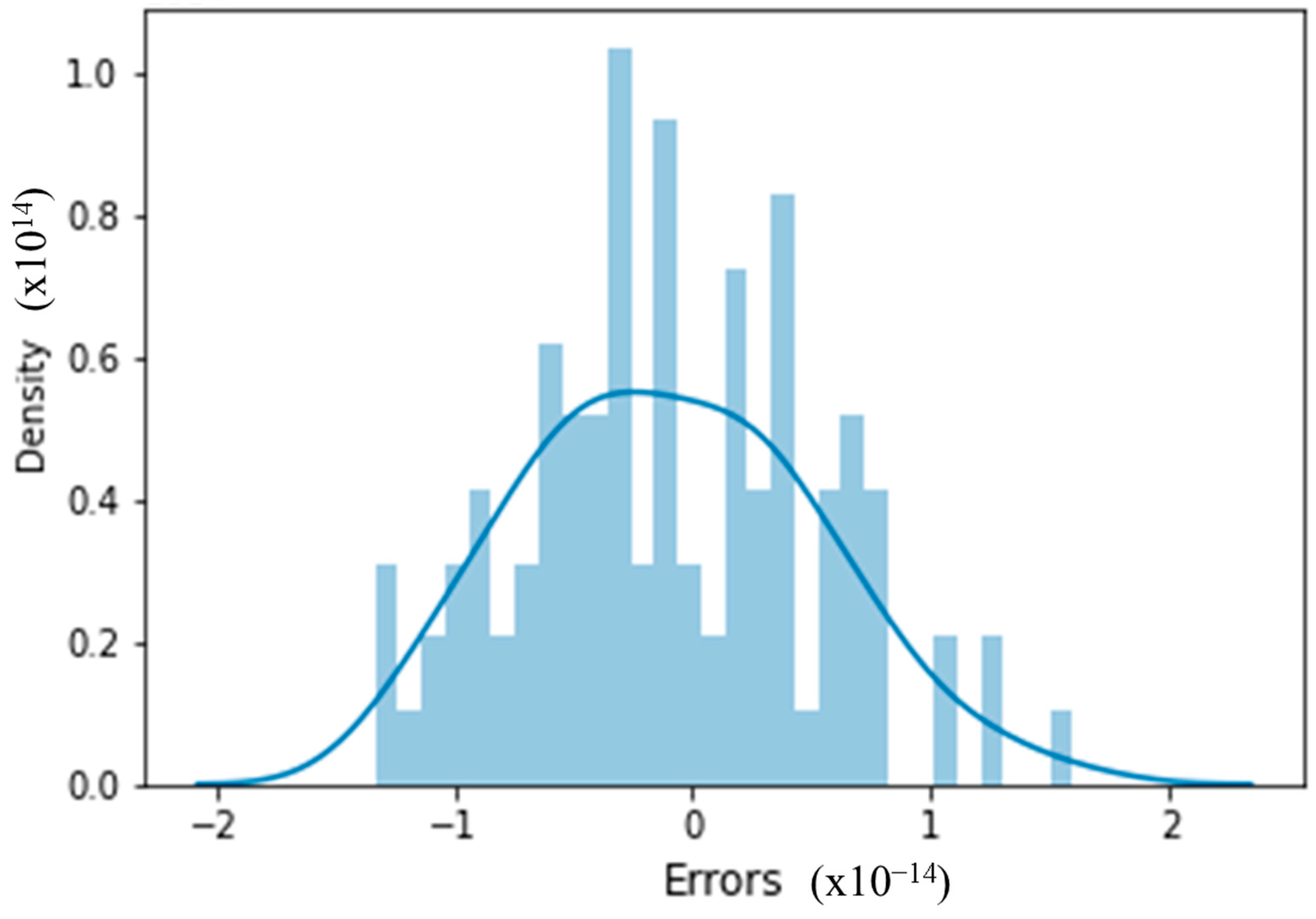
3.3. Model Residual Analysis
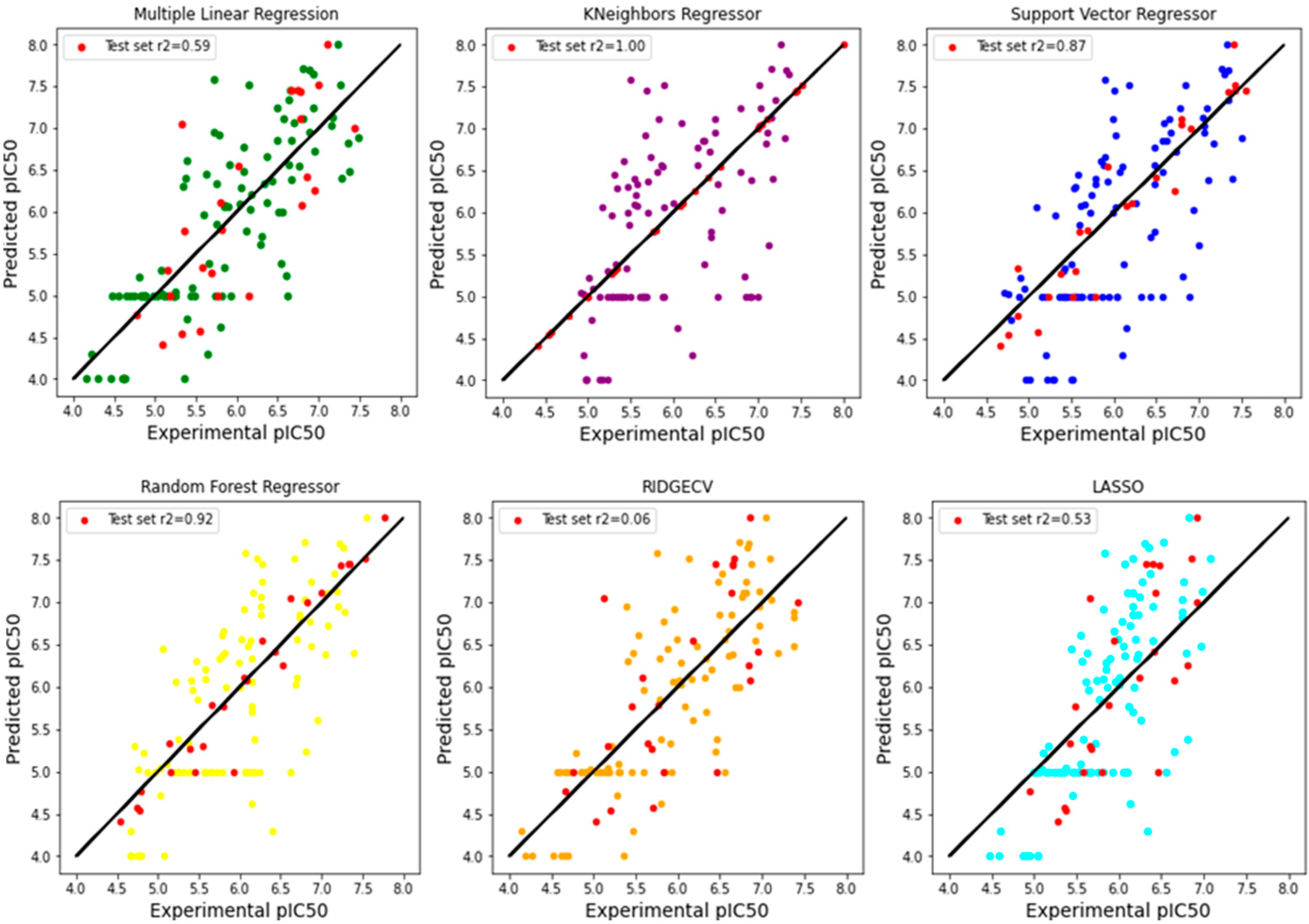
3.4. Building Models with ML Algorithms
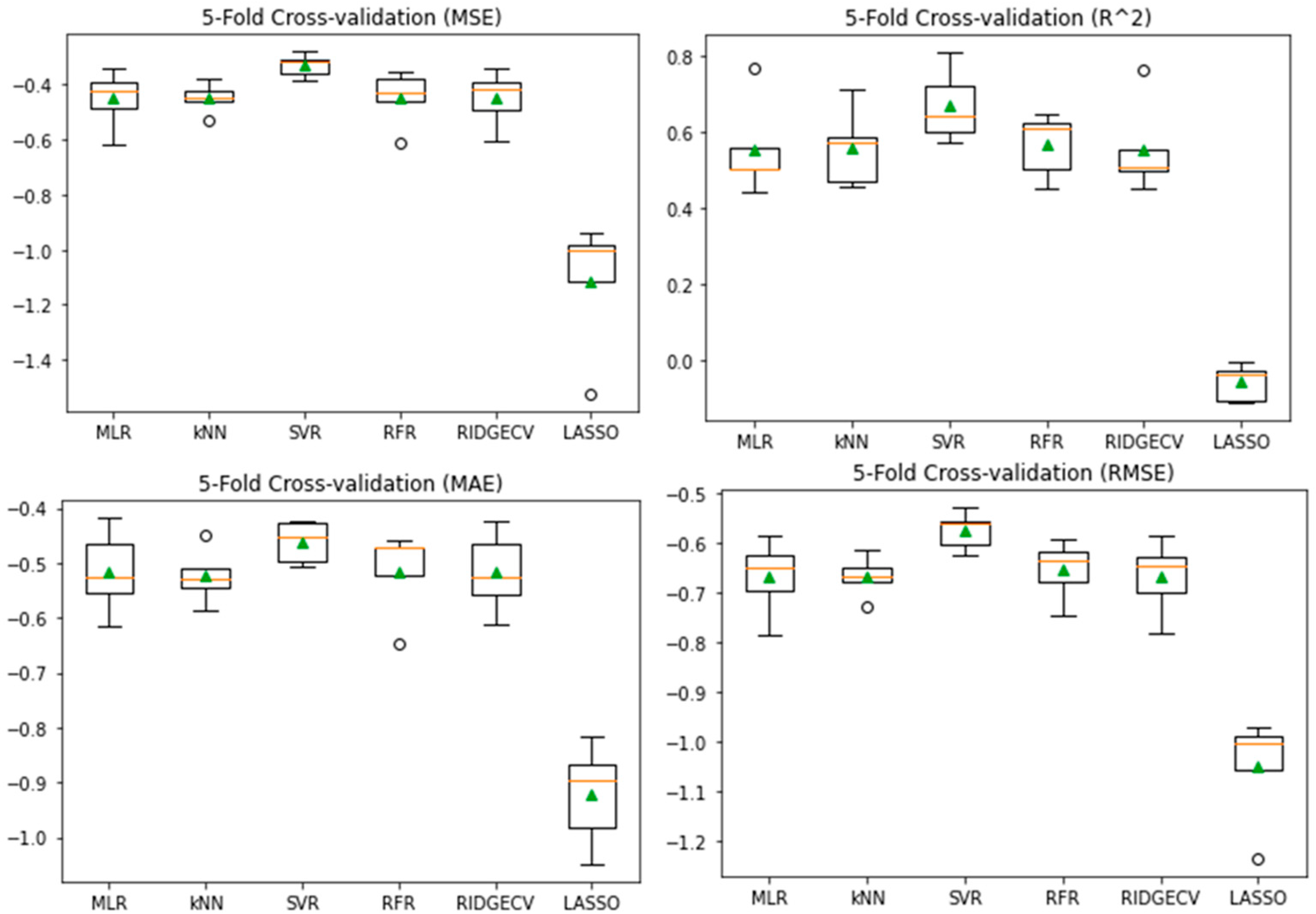
3.5. Model Evaluation and Comparison
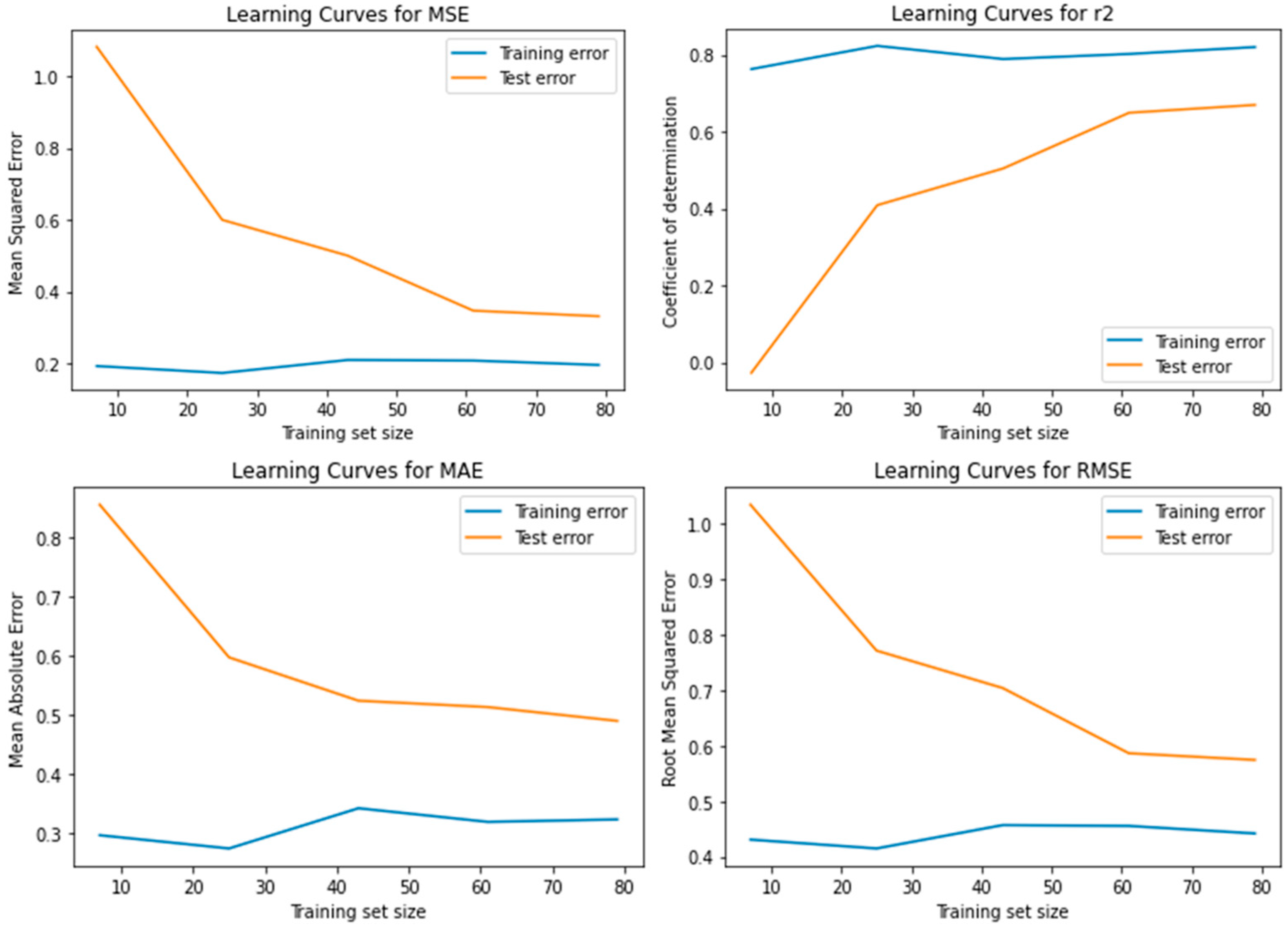
3.6. Learning Curves for Model Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ikerionwu, C.; Ugwuishiwu, C.; Okpala, I.; James, I.; Okoronkwo, M.; Nnadi, C.O.; Orji, U.; Ebem, D.; Ike, A. Application of machine and deep learning algorithms in optical microscopic detection of Plasmodium: A malaria diagnostic tool for the future. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2022, 40, 103198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguike, E.O.; Ugwuishiwu, C.H.; Asogwa, C.N.; Nnadi, C.O.L.; Obonga, W.O.; Attama, A.A. Systematic review on the application of machine learning to quantitative structure-activity relationship modelling against Plasmodium falciparum. Molec. Divers 2022, 26, 3447–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikwuka, C.E.; Asogwa, C.M.; Ikwuka, O.J.; Ogbonna, J.E.; Onah, C.E.; Ohama, C.C.; Nnadi, C.O. Insights into the in-vivo antiplasmodial activity of trisdimethylamino pyrimidine derivative in Plasmodium berghei Infected Mouse Model. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2022, 34, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlhodi, T.; Makatsela, L.P.; Dongola, T.H.; Simelane, M.B.C.; Shonhai, A.; Gumede, N.J.; Mokoena, F. Auto QSAR-based active learning docking for hit identification of potential inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum Hsp90 as antimalarial agents. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0308969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojha, P.K.; Kumar, V.; Roy, J.; Roy, K. Recent advances in quantitative structure-activity relationship models of antimalarial drugs. Exp. Opin. Drug Discov. 2021, 16, 659–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoka, T.O.; Uchegbu, U.J.; Alabuike, C.C.; Nnadi, C.O. Efficient classification and regression models for the QSAR of chloroquine analogues against chloroquine-sensitive and chloroquine-resistant. Lett. Appl. NanoBioSci. 2024, 13, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umoette, K.S.; Nnadi, C.O.; Obonga, W.O. A robust regression-based modelling to predict the antiplasmodial activity of thiazolyl–pyrimidine hybrid derivatives against Plasmodium falciparum. Chem. Proc. 2023, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibot, A.; Oumessaoud, A.; Hafid, A.; Khouili, M.; Pujol, M.D. Different synthetic methods for the preparation of triazolopyrimidines and their biological profile. ChemSelect 2023, 8, e202301654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkhalek, A.S.; Attia, M.S.; Kamal, M.A. Triazolopyrimidine derivatives: An updated review on recent advances in synthesis, biological activities and drug delivery aspects. Curr. Med. Chem. 2024, 31, 1896–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tee, E.H.; Karoli, T.; Ramu, S.; Huang, J.X.; Butler, M.S.; Cooper, M.A. Synthesis of essramycin and comparison of its antibacterial activity. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1940–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oukoloff, K.; Lucero, B.; Francisco, K.R.; Brunden, K.R.; Ballatore, C. 1,2,4-Triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines in drug design. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 165, 332–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trianaa, M.A.H.; Huynhb, M.H.; Garavitoa, M.F.; Foxc, B.A.; Bzikc, D.J.; Carruthers, V.B.; Lofflerd, M.; Zimmermanna, B.H. Biochemical and molecular characterization of the pyrimidine biosynthetic enzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase from Toxoplasma gondii. Mol. Biochem. Parasit. 2012, 184, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaulton, A.; Bellis, L.J.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Davies, M.; Hersey, A.; Light, Y.; McGlinchey, S.; Michalovich, D.; Al-Lazikani, B.; et al. ChEMBL: A large-scale bioactivity database for drug discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1100–D1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, C.W. PaDEL-descriptor: An open-source software to calculate molecular descriptors and fingerprints. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 32, 1466–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sydow, D.; Morger, A.; Driller, M.; Volkamer, A. TeachOpenCADD: A teaching platform for computer-aided drug design using open-source packages and data. J. Cheminform. 2019, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Features | Coeff | SE | t | p > |t| | [0.025–0.975] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| constant | 5.8964 | 0.060 | 98.522 | 0.000 | 5.778 | 6.015 |
| npr1 * | −0.7146 | 0.085 | −8.360 | 0.000 | −0.884 | −0.545 |
| pmi3 * | −1.5210 | 0.281 | −5.407 | 0.000 | −2.078 | −0.964 |
| SlogP ** | 0.8752 | 0.094 | 9.349 | 0.000 | 0.690 | 1.061 |
| vsurf_CW2 * | −0.5733 | 0.204 | −2.808 | 0.006 | −0.978 | −0.169 |
| vsurf_W2 * | 1.1120 | 0.312 | 3.570 | 0.001 | 0.495 | 1.729 |
| ML Models | MLR | kNN | SVR | RFR | RIDGECV | LASSO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test MSE | 0.48 | 0.0 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.62 | 0.56 |
| five-fold CV | 0.45 ± 0.10 | 0.46 ± 0.07 | 0.33 ± 0.04 | 0.43 ± 0.07 | 0.45 ± 0.09 | 0.62 ± 0.12 |
| Test R2 | 0.59 | 1.0 | 0.87 | 0.92 | 0.06 | 0.53 |
| five-fold CV | 0.56 ± 0.11 | 0.54 ± 0.10 | 0.67 ± 0.09 | 0.58 ± 0.05 | 0.56 ± 0.11 | 0.40 ± 0.11 |
| Test MAE | 0.58 | 0.0 | 0.27 | 0.19 | 0.66 | 0.62 |
| five-fold CV | 0.52 ± 0.07 | 0.54 ± 0.04 | 0.46 ± 0.04 | 0.51 ± 0.06 | 0.52 ± 0.07 | 0.64 ± 0.10 |
| Test RMSE | 0.69 | 0.0 | 0.34 | 0.27 | 0.78 | 0.75 |
| five-fold CV | 0.67 ± 0.07 | 0.68 ± 0.05 | 0.57 ± 0.03 | 0.66 ± 0.05 | 0.67 ± 0.07 | 0.79 ± 0.08 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apeh, I.S.; Ayoka, T.O.; Nnadi, C.O.; Obonga, W.O. Modeling the Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationships of 1,2,4-Triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-amine Analogs in the Inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum. Eng. Proc. 2025, 87, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087052
Apeh IS, Ayoka TO, Nnadi CO, Obonga WO. Modeling the Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationships of 1,2,4-Triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-amine Analogs in the Inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 87(1):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087052
Chicago/Turabian StyleApeh, Inalegwu S., Thecla O. Ayoka, Charles O. Nnadi, and Wilfred O. Obonga. 2025. "Modeling the Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationships of 1,2,4-Triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-amine Analogs in the Inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum" Engineering Proceedings 87, no. 1: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087052
APA StyleApeh, I. S., Ayoka, T. O., Nnadi, C. O., & Obonga, W. O. (2025). Modeling the Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationships of 1,2,4-Triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidin-7-amine Analogs in the Inhibition of Plasmodium falciparum. Engineering Proceedings, 87(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025087052






