Machine Learning Regression to Predict Pollen Concentrations of Oleaceae and Quercus Taxa in Thessaloniki, Greece †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
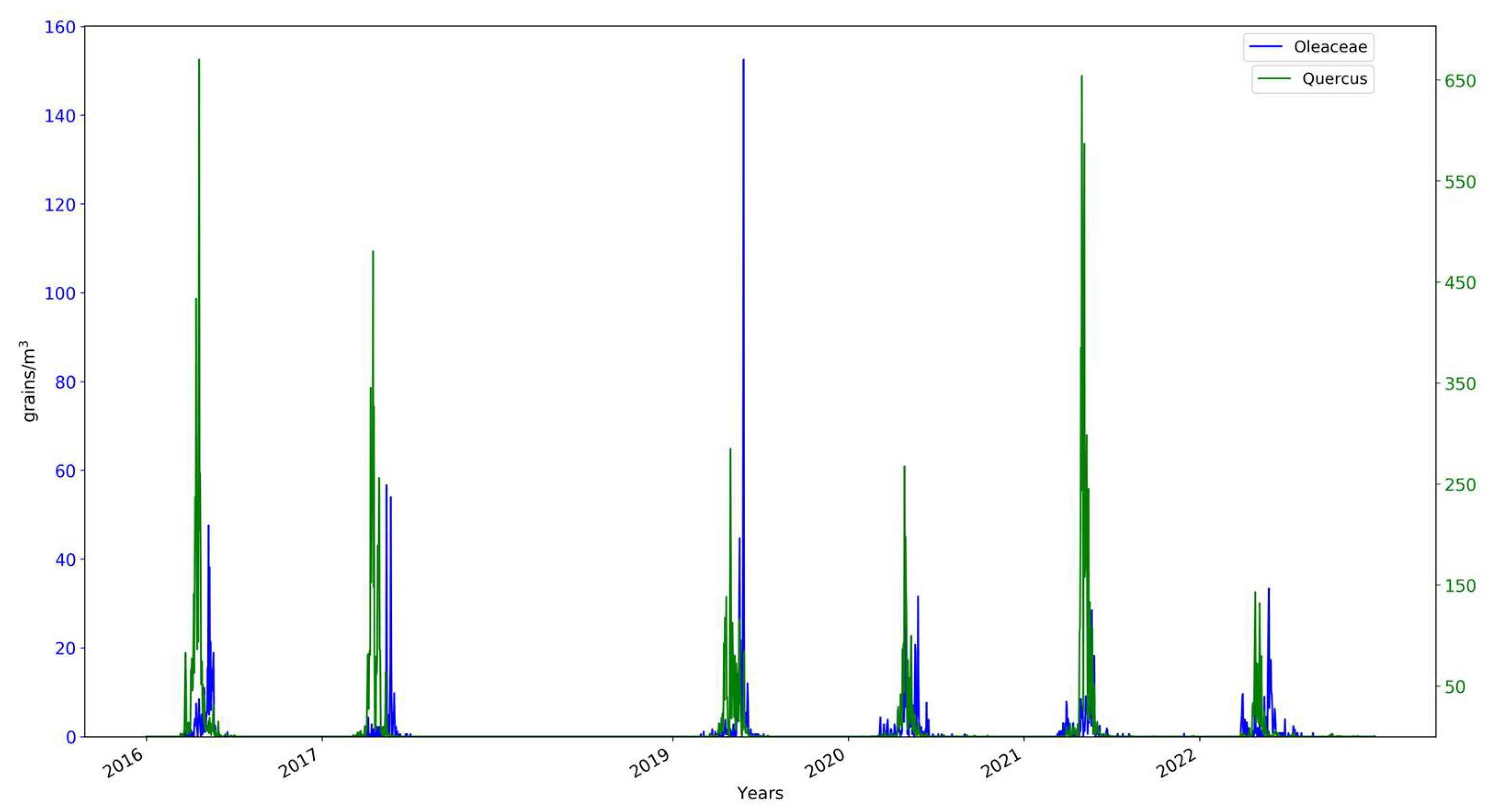
2.1. Pollen Data
2.2. ECMWF Data
2.3. GBR and Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- Mean Bias (MB):
- Mean Absolute Error (MAE):
- Normalized Mean Absolute Error (NMAE):
- Index of Agreement (IoA):where N is the number of values, Pi is the predicted values, Oi is the observed values, and is the observation’s mean. The MB ranges from −∞ to +∞ with an optimal value of 0, while MAE and NMAE range from 0 to +∞ with an optimal value of 0. IoA ranges from 0 to 1, with an optimal value above 0.7 indicating a good performance of the predictions. The optimal value is 1 [29,30].
References
- D’Amato, G.; Cecchi, L.; Bonini, S.; Nunes, C.; Annesi-Maesano, I.; Behrendt, H.; Liccardi, G.; Popov, T.; Van Cauwenberge, P. Allergenic pollen and pollen allergy in Europe. Allergy Allerg. Immunother. 2017, 62, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, J.; Schünemann, H.; Samolinski, B.; Demoly, P.; Baena-Cagnani, C.; Bachert, C.; Bonini, S.; Boulet, L.; Bousquet, P.; Brozek, J.; et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA): Achievements in 10 years and future needs. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 1049–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawankar, R. Allergic diseases and asthma: A global public health concern and a call to action. World Allergy Organ. J. 2014, 7, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’amato, G.; Holgate, S.T.; Pawankar, R.; Ledford, D.K.; Cecchi, L.; Al-Ahmad, M.; Al-Enezi, F.; Al-Muhsen, S.; Ansotegui, I.; Baena-Cagnani, C.E.; et al. Meteorological conditions, climate change, new emerging factors, and asthma and related allergic disorders. A statement of the World Allergy Organization. World Allergy Organ. J. 2015, 8, 25–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Academy of Allergy And Clinical Immunology. Advocacy Manifesto, Tackling the Allergy Crisis in Europe—Concerted Policy Action Needed. Brussels. 2015. Available online: https://www.veroval.info/-/media/diagnostics/files/knowledge/eaaci_advocacy_manifesto.pdf (accessed on 24 April 2023).
- Blaiss, M.S. Pediatric allergic rhinitis: Physical and mental complications. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2008, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, E.O.; Nathan, R.; Derebery, J.; Stang, P.E.; Campbell, U.B.; Yeh, W.-S.; Corrao, M.; Stanford, R. Sleep, quality of life, and productivity impact of nasal symptoms in the United States: Findings from the Burden of Rhinitis in America survey. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2009, 30, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damialis, A.; Halley, J.M.; Gioulekas, D.; Vokou, D. Long-term trends in atmospheric pollen levels in the city of Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 7011–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, I.R.; Jones, N.R.; Agnew, M.; Goodess, C.M.; Giorgi, F.; Hamaoui-Laguel, L.; Semenov, M.A.; Solomon, F.; Storkey, J.; Vautard, R.; et al. Climate Change and Future Pollen Allergy in Europe. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, D.; Zewdie, G.K.; Wijerante, L.; Timms, C.I.; Riley, A.; Levetin, E.; Lary, D.J. Using machine learning to estimate atmospheric Ambrosia pollen concentrations in Tulsa, OK. Environ. Health Insights 2017, 11, 1178630217699399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewdie, G.K.; Lary, D.J.; Levetin, E.; Garuma, G.F. Applying Deep Neural Networks and Ensemble Machine Learning Methods to Forecast Airborne Ambrosia Pollen. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, F.; Bitz, C.M.; Hess, J.J. Development of a Random Forest model for forecasting allergenic pollen in North America. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 773, 145590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, J.M.; Rojo, J.; Gutiérrez-Bustillo, A.M.; Narros, A.; Borge, R. Predicting the Olea pollen concentration with a machine learning algorithm ensemble. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2020, 65, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rajo, F.; Astray, G.; Ferreiro-Lage, J.; Aira, M.; Jato-Rodriguez, M.; Mejuto, J. Evaluation of atmospheric Poaceae pollen concentration using a neural network applied to a coastal Atlantic climate region. Neural Netw. 2010, 23, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Mesa, J.A.; Galan, C.; Martínez-Heras, J.A.; Hervás-Martínez, C. The use of a neural network to forecast daily grass pollen concentration in a Mediterranean region: The southern part of the Iberian Peninsula. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 1606–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, J.A.; Astray, G.; Fernández-González, M.; Aira, M.J.; Rodríguez-Rajo, F.J. Assessment of neural networks and time series analysis to forecast airborne Parietaria pollen presence in the Atlantic coastal regions. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2019, 63, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makra, L.; Sánta, T.; Matyasovszky, I.; Damialis, A.; Karatzas, K.; Bergmann, K.-C.; Vokou, D. Airborne pollen in three European cities: Detection of atmospheric circulation pathways by applying three-dimensional clustering of backward trajectories. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D24220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioulekas, D.; Papakosta, D.; Damialis, A.; Spieksma, F.; Giouleka, P.; Patakas, D. Allergenic pollen records (15 years) and sensitization in patients with respiratory allergy in Thessaloniki, Greece. Allergy 2004, 59, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damialis, A.; Kaimakamis, E.; Konoglou, M.; Akritidis, I.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Gioulekas, D. Estimating the abundance of airborne pollen and fungal spores at variable elevations using an aircraft: How high can they fly? Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalampopoulos, A.; Damialis, A.; Lazarina, M.; Halley, J.M.; Vokou, D. Spatiotemporal assessment of airborne pollen in the urban environment: The pollenscape of Thessaloniki as a case study. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 247, 118185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voukantsis, D.; Niska, H.; Karatzas, K.; Riga, M.; Damialis, A.; Vokou, D. Forecasting daily pollen concentrations using data-driven modeling methods in Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 5101–5111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, J.M. An automatic volumetric spore trap. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1952, 39, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, C.; Smith, M.; Thibaudon, M.; Frenguelli, G.; Oteros, J.; Gehrig, R.; Berger, U.E.; Clot, B.; Brandao, R.; EAS QC Working Group. Pollen monitoring: Minimum requirements and reproducibility of analysis. Aerobiologia 2014, 30, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T.B. A model to predict the beginning of the pollen season. Grana 1991, 30, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. Boosting and additive trees. In The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 337–387. [Google Scholar]
- Natekin, A.; Knoll, A. Gradient boosting machines, a tutorial. Front. Neurorobotics 2013, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python. JMLR 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Emery, C.; Tai, E.; Yarwood, G. Enhanced Meteorological Modeling and Performance Evaluation for Two Texas Ozone Episodes. Final Report Submitted to Texas Natural Resources Conservation Commission, Prepared by ENVIRON 2001; International Corp.: Novato, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kontos, S.; Papadogiannaki, S.; Parliari, D.; Steiner, A.L.; Melas, D. High resolution modeling of Quercus pollen with an Eulerian modeling system: A case study in Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 268, 118816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
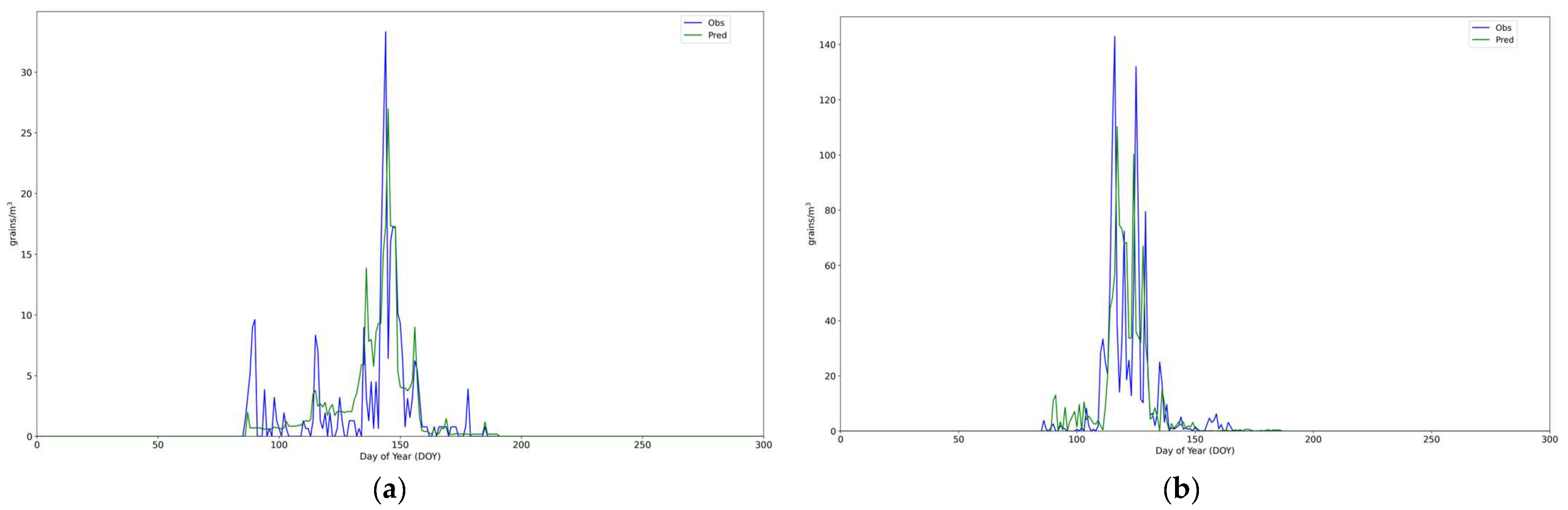
| ΜΒ | ΜAΕ | ΝΜAΕ | ΙοA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oleaceae | 0.28 | 2.81 | 0.55 | 0.86 |
| Quercus | −0.38 | 11.02 | 0.64 | 0.78 |
| Actual Date | Expected Date | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Start | End | Peak | Start | End | Peak | |
| Oleaceae | 89 (30 March) | 196 (15 July) | 145 (25 May) | 96 (6 April) | 185 (4 July) | 146 (26 May) |
| Quercus | 111 (21 April) | 165 (14 June) | 117 (27 April) | 101 (11 April) | 171 (20 June) | 118 (28 April) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papadogiannaki, S.; Kontos, S.; Parliari, D.; Melas, D. Machine Learning Regression to Predict Pollen Concentrations of Oleaceae and Quercus Taxa in Thessaloniki, Greece. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 26, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2023026002
Papadogiannaki S, Kontos S, Parliari D, Melas D. Machine Learning Regression to Predict Pollen Concentrations of Oleaceae and Quercus Taxa in Thessaloniki, Greece. Environmental Sciences Proceedings. 2023; 26(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2023026002
Chicago/Turabian StylePapadogiannaki, Sofia, Serafeim Kontos, Daphne Parliari, and Dimitrios Melas. 2023. "Machine Learning Regression to Predict Pollen Concentrations of Oleaceae and Quercus Taxa in Thessaloniki, Greece" Environmental Sciences Proceedings 26, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2023026002
APA StylePapadogiannaki, S., Kontos, S., Parliari, D., & Melas, D. (2023). Machine Learning Regression to Predict Pollen Concentrations of Oleaceae and Quercus Taxa in Thessaloniki, Greece. Environmental Sciences Proceedings, 26(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/environsciproc2023026002









