Recyclability Perspectives of the Most Diffused Biobased and Biodegradable Plastic Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Recycling of PLA
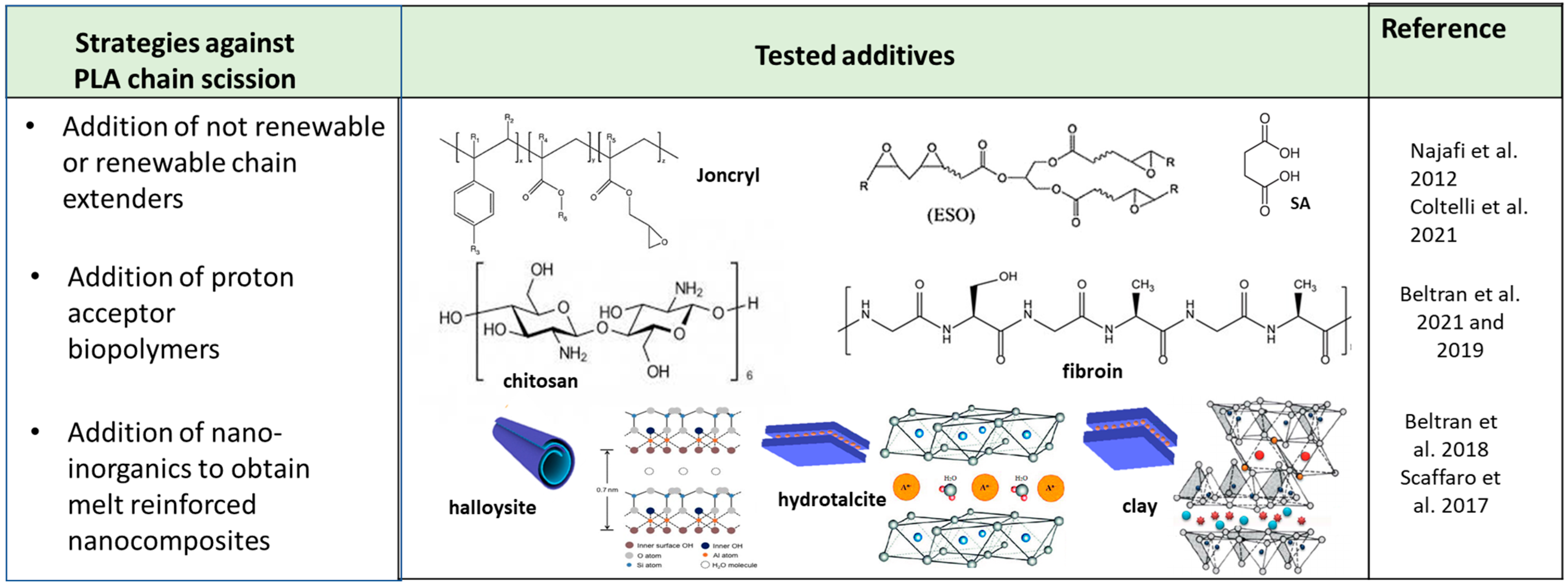
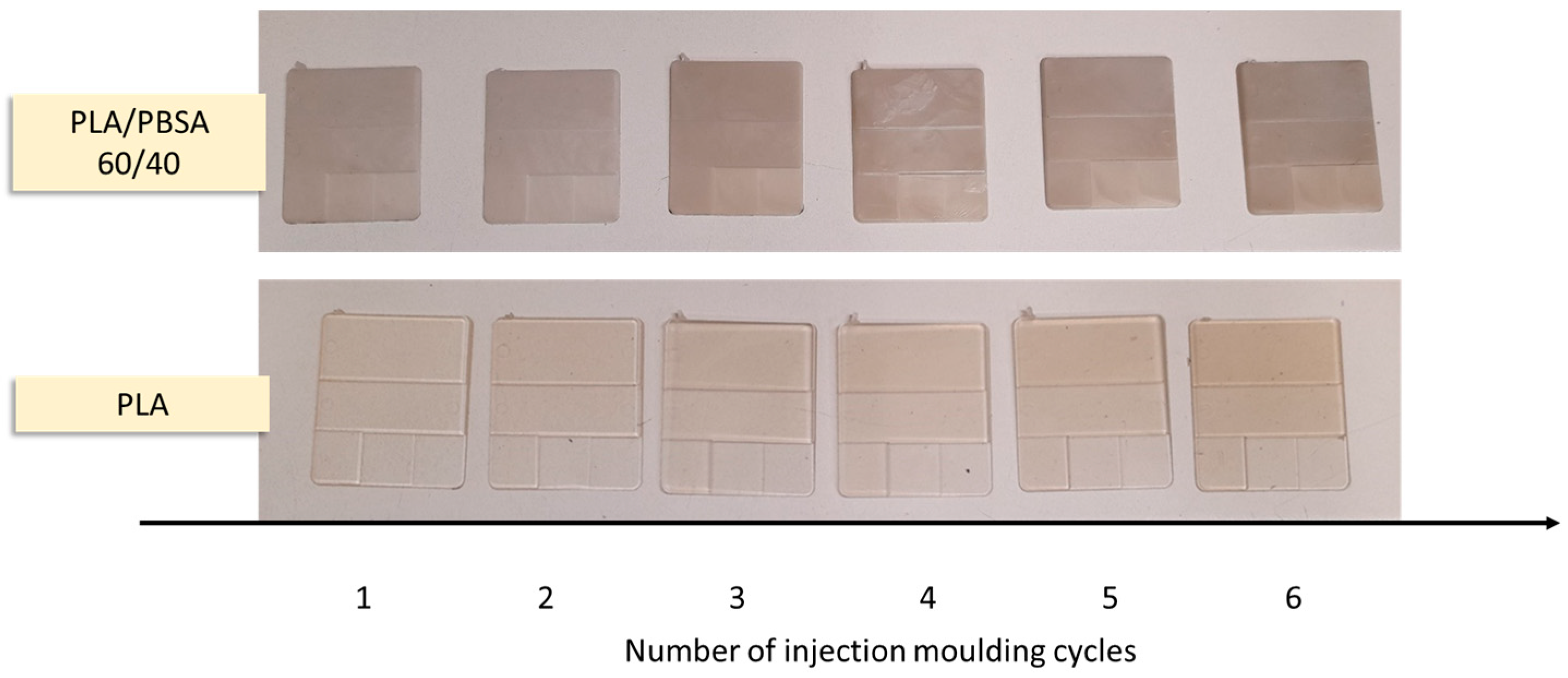
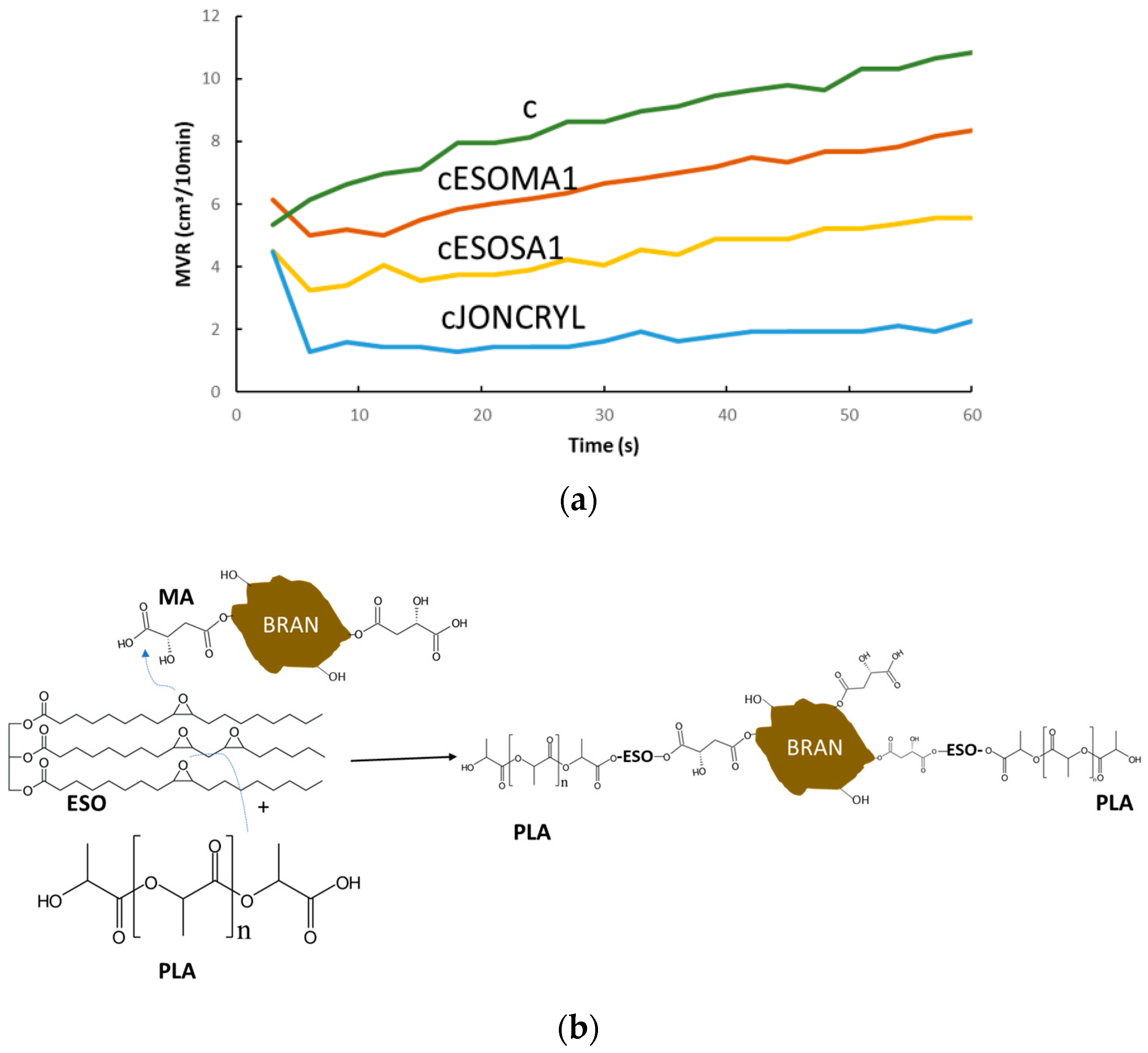
2.1. Mechanical Recycling
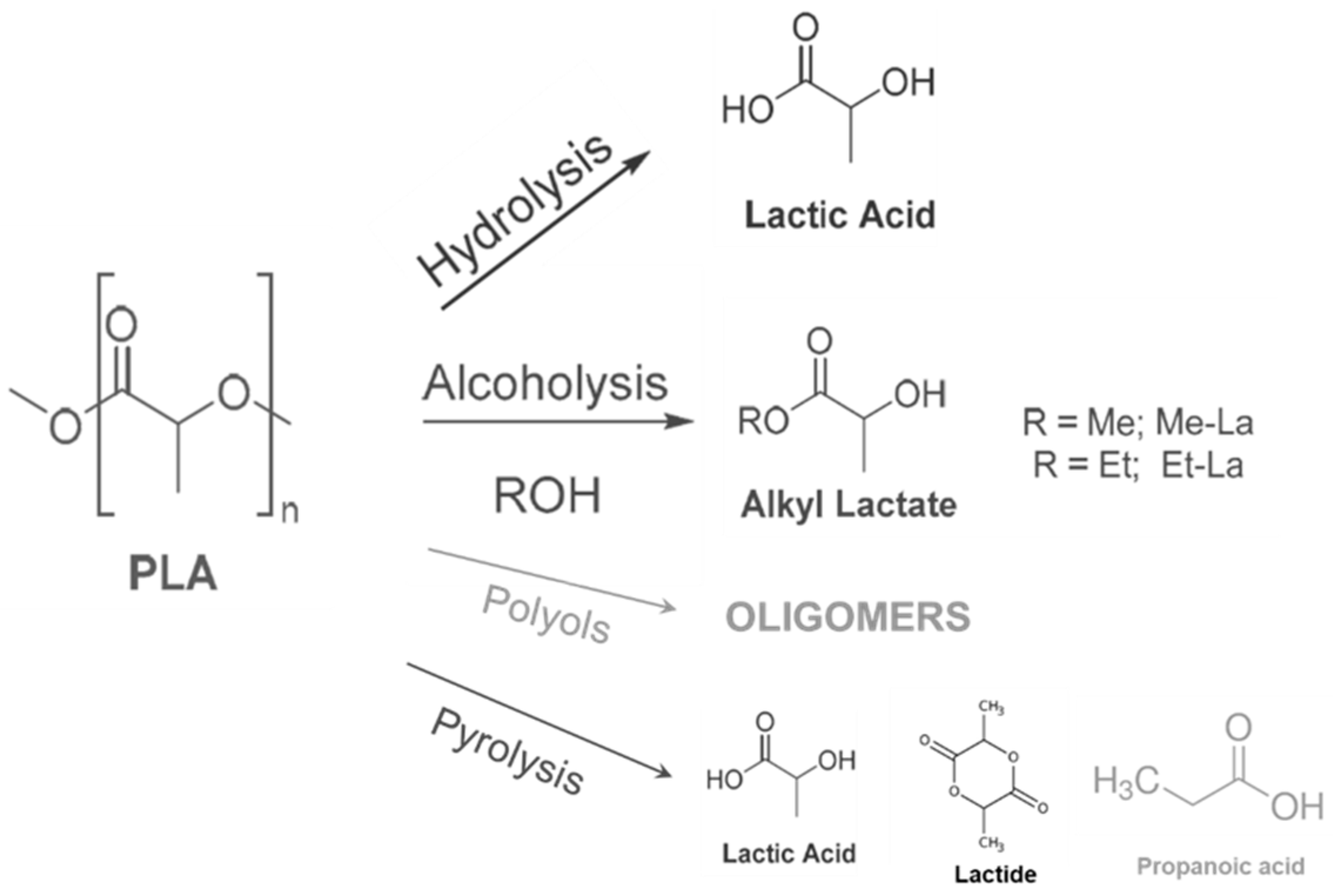
2.2. Chemical Recycling
3. Recycling of Other Biodegradable Bioplastics
3.1. Poly(Hydroxy Alcanoate)
3.2. Poly(Butylene Succinate)
3.3. Poly(Butylene Adipate-co-Terephathalate)
4. Recycling of Starch-Based Materials
5. Recycling of Blends
6. Recycling of Natural-Fiber-Reinforced Composites
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwarz, A.E.; Ligthart, T.N.; Godoi Bizarro, D.; De Wild, P.; Vreugdenhil, B.; van Harmelen, T. Plastic recycling in a circular economy; determining environmental performance through an LCA matrix model approach. Waste Manag. 2021, 121, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Hui, D.; Singh, R.; Ahuja, I.P.S.; Feo, L.; Fraternali, F. Recycling of plastic solid waste: A state of art review and future applications. Compos. Part B Eng. 2017, 115, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltelli, M.B.; Aglietto, M. Riutilizzo dei Materiali Polimerici; Testi, A.I.M., Ed.; Nuova Cultura: Rome, Italy, 2015; pp. 6–24. [Google Scholar]
- Schyns, Z.O.G.; Shaver, M.P. Mechanical Recycling of Packaging Plastics: A Review. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2021, 42, 2000415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalali, E.N.; Lotfian, S.; Shabestari, M.E.; Khayatzadeh, S.; Zhao, C.; Nezhad, H.Y. A critical review of the current progress of plastic waste recycling technology in structural materials. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2023, 40, 100763. [Google Scholar]
- Ambrus, M.; Mucsi, G. Open-loop recycling of end-of-life textiles as geopolymer fibre reinforcement. Waste Manag. Res. 2024, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, F.; Wei, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, S.; Deng, D.; Wang, Y.-Z. From trash to treasure: Chemical recycling and upcycling of commodity plastic waste to fuels, high-valued chemicals and advanced materials. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 69, 369–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min Soo Kim, M.S.; Chang, H.; Zheng, L.; Yan, Q.; Pfleger, B.F.; Klier, J.; Nelson, K.; Majumder, E.L.-W.; Huber, G.W. A Review of Biodegradable Plastics: Chemistry, Applications, Properties, and Future Research Needs. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 9915–9939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeisinger, C. Material recycling of post-consumer polyolefin bulk plastics: Influences on waste sorting and treatment processes in consideration of product qualities achievable. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Tuladhar, R.; Shi, F.; Shanks, R.A.; Combe, M.; Collister, T. Mechanical Reprocessing of Polyolefin Waste: A Review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 2899–2909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicogna, F.; Coiai, S.; Moliterni, D.; Ruggeri, G.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Lazzeri, A.; Passaglia, E. Co-agent mediated functionalizationof LDPE/iPP mixtures for compatibilization of WEEE-recovered polyvinylchloride. Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedada, W.; Karltun, E.; Lemenih, M.; Tolera, M. Long-term addition of compost and NP fertilizer increases crop yield and improves soil quality in experiments on smallholder farms. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 195, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donn, S.; Wheatley, R.E.; McKenzie, B.M.; Loades, K.W.; Hallett, P.D. Improved soil fertility from compost amendment increases root growth and reinforcement of surface soil on slopes. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Encarnação, T.; Tavares, R.; Todo Bom, T.; Mateus, A. Bioplastics: Innovation for Green Transition. Polymers 2023, 15, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Seggiani, M.; Lazzeri, A.; Gigante, V.; Cinelli, P. A Brief Review of Poly (Butylene Succinate) (PBS) and Its Main Copolymers: Synthesis, Blends, Composites, Biodegradability, and Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wu, G.; Bian, X.; Zeng, J.; Weng, Y. Biodegradation Behavior of Poly(Butylene Adipate-Co-Terephthalate) (PBAT), Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA), and Their Blend in Freshwater with Sediment. Molecules 2020, 25, 3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouhoubi, R.; Lasschuijt, M.; Ramon Carrasco, S.; Gojzewski, H.; Wurm, F.R. End-of-life biodegradation? how to assess the composting of polyesters in the lab and the field. Waste Manag. 2022, 154, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narancic, T.; Verstichel, S.; Reddy Chaganti, S.; Morales-Gamez, L.; Kenny, S.T.; De Wilde, B.; Babu Padamati, R.; O’Connor, K.E. Biodegradable Plastic Blends Create New Possibilities for End-of-Life Management of Plastics but They Are Not a Panacea for Plastic Pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10441–10452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Gigante, V.; Geerinck, R.; Coltelli, M.B.; Lazzeri, A. Micromechanical analysis and fracture mechanics of Poly(lactic acid) (PLA)/Polycaprolactone (PCL) binary blends. Polym. Test. 2023, 121, 107984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaore, V.; Chadwick, D.; Shah, N. Sustainable production of chemical intermediates for nylon manufacture: A techno-economic analysis for renewable production of caprolactone. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 135, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Fernandez, M.; Heckmann, C.M.; Paradisi, F. Biocatalytic Production of a Nylon 6 Precursor from Caprolactone in Continuous Flow. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202200811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, N.; Misra, M.; Mohanty, A.K. Durable Polylactic Acid (PLA)-Based Sustainable Engineered Blends and Biocomposites: Recent Developments, Challenges, and Opportunities. ACS Eng. Au 2021, 1, 7–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balla, E.; Daniilidis, V.; Karlioti, G.; Kalamas, T.; Stefanidou, M.; Bikiaris, N.D.; Vlachopoulos, A.; Koumentakou, I.; Bikiaris, D.N. Poly(lactic Acid): A Versatile Biobased Polymer for the Future with Multifunctional Properties—From Monomer Synthesis, Polymerization Techniques and Molecular Weight Increase to PLA Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, V.; Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M. Perspective on Polylactic Acid (PLA) based Sustainable Materials for Durable Applications: Focus on Toughness and Heat Resistance. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 2899–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pretula, J.; Slomkowski, S.; Penczek, S. Polylactides—Methods of synthesis and characterization. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Pandey, P.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Toughening of Polylactic Acid: An Overview of Research Progress. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2016, 55, 1623–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, S.; Anderson, D.G.; Langer, R. Physical and mechanical properties of PLA, and their functions in widespread applications—A comprehensive review. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Aguirre, E.; Iñiguez-Franco, F.; Samsudin, H.; Fang, X.; Auras, R. Poly(lactic acid)—Mass production, processing, industrial applications, and end of life. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 107, 333–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Signori, F.; Coltelli, M.B.; Bronco, S. Thermal degradation of poly (lactic acid)(PLA) and poly (butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)(PBAT) and their blends upon melt processing. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2009, 94, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmann, C.; Schippers, S.; Höfs, C. Influence of Recycling of Poly(lactic acid) on Packaging Relevant Properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41532–41538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsawy, M.A.; Kim, K.-H.; Park, J.-W.; Deep, A. Hydrolytic degradation of polylactic acid (PLA) and its composites. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 79, 1346–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.D.; Ribes-Greus, A. Mechanical recycling of polylactide, upgrading trends and combination of valorization techniques. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 84, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocca-Smith, J.R.; Chau, N.; Champion, D.; Brachais, C.-H.; Marcuzzo, E.; Sensidoni, A.; Piasente, F.; Karbowiak, T.; Debeaufort, F. Effect of the state of water and relative humidity on ageing of PLA films. Food Chem. 2017, 236, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.D.; Stromberg, E.; Karlsson, S.; Ribes-Greus, A. Material valorisation of amorphous polylactide. Influence of thermo-mechanical degradation on the morphology, segmental dynamics, thermal and mechanical performance. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüster, B.; Addiego, F.; Hassouna, F.; Ruch, D.; Raquez, J.-M.; Dubois, P. Thermo-mechanical degradation of plasticized poly(lactide) after multiple reprocessing to simulate recycling: Multi-scale analysis and underlying mechanisms. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 131, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, F.R.; Lorenzo, V.; Acosta, J.; de la Orden, M.U.; Martínez Urreag, J. Effect of simulated mechanical recycling processes on the structure and properties of poly(lactic acid). J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 216, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piemonte, V. Bioplastic wastes: The best final disposition for energy saving. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavanaie, M.A. Melt Recycling of Poly(lactic Acid) Plastic Wastes to Produce Biodegradable Fibers. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2014, 53, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, N.; Heuzey, M.C.; Carreau, P.J.; Wood-Adams, P.M. Control of thermal degradation of polylactide (PLA)-clay nanocomposites using chain extenders. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatani, M.; Ikeda, K.; Sakamoto, K.; Okamoto, T. Cellulose esters as compatibilizers in wood/poly(lactic acid) composite. J. Wood Sci. 2008, 54, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Loi, J.; Delgado, P.; Topolkaraev, V.; McEneany, R.J.; Macosko, C.W.; Hillmyer, M.A. Reactive Compatibilization of Polylactide/Polypropylene Blends. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 6108–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltelli, M.-B.; Bertolini, A.; Aliotta, L.; Gigante, V.; Vannozzi, A.; Lazzeri, A. Chain Extension of Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA)–Based Blends and Composites Containing Bran with Biobased Compounds for Controlling Their Processability and Recyclability. Polymers 2021, 13, 3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkita, T.; Lee, S.-H. Thermal Degradation and Biodegradability of Poly (lactic acid)/Corn Starch Biocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 100, 3009–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Hakkarainen, M. Recycling PLA to multifunctional oligomeric compatibilizers for PLA/starch composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 64, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltelli, M.-B.; Aliotta, L.; Vannozzi, A.; Morganti, P.; Panariello, L.; Danti, S.; Neri, S.; Fernandez-Avila, C.; Fusco, A.; Donnarumma, G.; et al. Properties and Skin Compatibility of Films Based on Poly(Lactic Acid) (PLA) Bionanocomposites Incorporating Chitin Nanofibrils (CN). J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Vannozzi, A.; Bonacchi, D.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Lazzeri, A. Analysis, Development, and Scaling-Up of Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) Biocomposites with Hazelnuts Shell Powder (HSP). Polymers 2021, 13, 4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panariello, L.; Coltelli, M.-B.; Vannozzi, A.; Bonacchi, D.; Aliotta, L.; Lazzeri, A. Fully Biobased Reactive Extrusion of Biocomposites Based on PLA Blends and Hazelnut Shell Powders (HSP). Chemistry 2021, 3, 1464–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, F.R.; Gaspar, G.; Chomachayi, M.D.; Jalali-Arani, A.; Lozano-Pérez, A.A.; Cenis, J.L.; de la Orden, M.U.; Pérez, E.; Martínez Urreaga, J.M. Influence of addition of organic fillers on the properties of mechanically recycled PLA. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 24291–24304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, F.R.; Infante, C.; de la Orden, M.U.; Martínez Urreaga, J. Mechanical recycling of poly(lactic acid): Evaluation of a chain extender and a peroxide as additives for upgrading the recycled plastic. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Beltrán, F.R.; de la Orden, M.U.; Martínez Urreaga, J. Aminomodified halloysite nanotubes to reduce polymer degradation and improve the performance of mechanically recycled poly(lactic acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 4046–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Sutera, F.; Mistretta, M.C.; Botta, L.; La Mantia, F.P. Structure-properties relationships in melt reprocessed PLA/hydrotalcites nanocomposites. Express Polym. Lett. 2017, 11, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrán, F.R.; Ortega, E.; Solvoll, A.M. Effects of Aging and Different Mechanical Recycling Processes on the Structure and Properties of Poly(lactic acid)-clay Nanocomposites. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 2142–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piemonte, V.; Sabatini, S.; Gironi, F. Chemical Recycling of PLA: A Great Opportunity Towards the Sustainable Development? J. Polym. Environ. 2013, 21, 640–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeown, P.; Jones, M.D. The Chemical Recycling of PLA: A Review. Sustain. Chem. 2020, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gironi, F.; Frattari, S.; Piemonte, V. PLA Chemical Recycling Process Optimization: PLA Solubilization in Organic Solvents. J. Polym. Environ. 2016, 24, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iñiguez-Franco, F.; Auras, R.; Dolan, K.; Selke, S.; Holmes, D.; Rubino, M.; Soto-Valdez, H. Chemical recycling of poly(lactic acid) by water-ethanol solutions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 149, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, J.; McKeown, P.; Mahon, M.F.; Emanuelsson, E.A.C.; Jones, M.D. Mono- and dimeric zinc(II) complexes for PLA production and degradation into methyl lactate—A chemical recycling method. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majgaonkar, P.; Hanich, R.; Malz, F.; Brüll, R. Chemical Recycling of Post-Consumer PLA Waste for Sustainable Production of Ethyl Lactate. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 423, 129952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plichta, A.; Lisowska, P.; Kundys, A.; Zychewicz, A.; Debowski, M.; Florjanczyk, Z. Chemical recycling of poly(lactic acid) via controlled degradation with protic (macro)molecules. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2014, 108, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nim, B.; Opaprakasit, M.; Petchsuk, A.; Opaprakasit, P. Microwave-assisted chemical recycling of polylactide (PLA) by alcoholysis with various diols. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 181, 109363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undri, A.; Rosi, L.; Frediani, M.; Frediani, P. Conversion of poly(lactic acid) to lactide via microwave assisted pyrolysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2014, 110, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeaung, K.; Phusunti, N.; Phetwarotai, W.; Assabumrungrat, S.; Cheirsilp, B. Catalytic pyrolysis of petroleum-based and biodegradable plastic waste to obtain high-value chemicals. Waste Manag. 2021, 127, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.H.; Åkesson, D.; Taherzadeh, M.J.; Ferreira, J.A. Recycling strategies for polyhydroxyalkanoate-based waste materials: An overview. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 298, 122393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, L.F.; Casarin, S.A.; Nepomuceno, N.C.; Alencar, M.I.; Agnelli, J.A.M.; Souto de Medeiros, E.; de Oliveira Wanderley Neto, A.; Pinheiro de Oliveira, M.; de Medeiros, A.M.; Severino Ferreira e Santos, A. Reprocessability of PHB in extrusion: ATR-FTIR, tensile tests and thermal studies. Polímeros 2017, 27, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnenfant, C.; Gontard, N.; Aouf, C. Active Packaging: Incorporation of Polyphenols in Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): Thermal Stabilization and Antioxidant Properties. Biopolymers and Sustainable Composites. March 2020, Valencia, Spain. hal-02943213f. Available online: https://hal.inrae.fr/hal-02943213 (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Ariffin, H.; Nishida, H.; Hassan, M.A.; Shirai, Y. Chemical recycling of polyhydroxyalkanoates as a method towards sustainable development. Biotechnol. J. 2010, 5, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiqah, S.A.; Khalina, A.; Harmaen, A.S.; Tawakkal, I.A.; Zaman, K.; Asim, M.; Nurrazi, M.N.; Lee, C.H. A Review on Properties and Application of Bio-Based Poly(Butylene Succinate). Polymers 2021, 13, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgousopoulou, I.-N.; Vouyiouka, S.; Dole, P.; Papaspyrides, C.D. Thermo-mechanical degradation and stabilization of poly(butylene succinate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 128, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemura, C.; Nakashima, S.; Hotta, A. Mechanical properties and chemical structures of biodegradable poly(butylenesuccinate) for material reprocessing. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2012, 97, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Zeng, X.; Huang, X. An overview on synthesis, properties and applications of poly(butylene-adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT). Adv. Ind. Eng. Polym. Res. 2020, 3, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gigante, V.; Canesi, I.; Cinelli, P.; Coltelli, M.B.; Lazzeri, A. Rubber Toughening of Polylactic Acid (PLA) with Poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT): Mechanical Properties, Fracture Mechanics and Analysis of Ductile-to-Brittle Behavior while Varying Temperature and Test Speed. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 115, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mantia, F.P.; Botta, L.; Mistretta, M.C.; Di Fiore, A.; Titone, V. Recycling of a Biodegradable Polymer Blend. Polymers 2020, 12, 2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffaro, R.; Maio, A.; Sutera, F.; Gulino, E.F.; Morreale, M. Degradation and Recycling of Films Based on Biodegradable Polymers: A Short Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accinelli, C.; Saccà, M.L.; Mencarelli, M.; Vicari, A. Deterioration of bioplastic carrier bags in the environment and assessment of a new recycling alternative. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saieh, S.E.; Eslam, H.K.; Ghasemi, E.; Bazyar, B.; Rajabi, M. Biodegradable composites of recycled thermoplastic starch and sawdust: The effect of cellulose nanofbers, nanoclay and temperature. Iran. Polym. J. 2019, 28, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hejna, A.; Lenża, J.; Formela, K.; Korol, J. Studies on the Combined Impact of Starch Source and Multiple Processing on Selected Properties of Thermoplastic Starch/EthyleneVinyl Acetate Blends. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 1112–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinho, V.A.D.; Pereira, C.A.B.; Vitorino, M.B.C.; Silva, A.S.; Carvalho, L.H.; Canedo, E.L. Degradation and recovery in poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/thermoplastic starch blends. Polym. Test. 2017, 58, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, T.A.; Oliveira, R.R.; Barbosa, R.; Azevedo, J.B.; Alves, T.S. Effect of reprocessing cycles on the degradation ofPP/PBAT-thermoplastic starch blendsThainá. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 168, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo de Oliveira, T.; Barbosa, R.; Mesquita, A.B.S.; Ferreira, J.H.L.; Hecker de Carvalho, L.; Soares Alves, T. Fungal degradation of reprocessed PP/PBAT/thermoplastic starch blends. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 2338–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zembouai, I.; Bruzaud, S.; Kaci, M.; Benhamida, A.; Corre, Y.M.; Grohens, Y. Mechanical Recycling of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-co-3-Hydroxyvalerate)/Polylactide Based Blends. J. Polym. Environ. 2014, 22, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plavec, R.; Hlaváčiková, S.; Omaníková, L.; Feranc, J.; Vanovčanová, Z.; Tomanová, K.; Bočkaj, J.; Kruželák, J.; Medlenová, E.; Gálisová, I.; et al. Recycling possibilities of bioplastics based on PLA/PHB blends. Polym. Test. 2020, 92, 106880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Kopitzky, R.; Tolga, S.; Kabasci, S. Polylactide (PLA) and Its Blends with Poly(butylene succinate) (PBS): A Brief Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuneizumi, Y.; Kuwahara, M.; Okamoto, K.; Matsumura, S. Chemical recycling of poly(lactic acid)-based polymer blends using environmentally benign catalysts. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1387–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltelli, M.B.; Aliotta, L.; Fasano, G.; Miketa, F.; Brkić, F.; Alonso, R.; Romei, M.; Cinelli, P.; Canesi, I.; Gigante, V.; et al. Recyclability Studies on Poly(lactic acid)/Poly(butylene succinate-co-adipate) (PLA/PBSA) Biobased and Biodegradable Films. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2023, 308, 2300136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, J.P.; Girones, J.; Mendez, J.A.; Puig, J.; Pelach, M.A. Recycling Ability of Biodegradable Matrices and Their Cellulose-Reinforced Composites in a Plastic Recycling Stream. J. Polym. Environ. 2012, 20, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.R.M.; Reul, L.T.A.; Sousa, F.M.; Ito, E.N.; Carvalho, L.H.; Canedo, E.L. Degradation during processing of vegetable fiber compounds based on PBAT/PHB blends. Polym. Test. 2018, 69, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliotta, L.; Sergi, C.; Dal Pont, B.; Coltelli, M.B.; Gigante, V.; Lazzeri, A. Sustainable 3D printed poly (lactic acid) (PLA)/Hazelnut shell powder bio composites for design applications. Mater. Today Sustain. 2024, 26, 100780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akesson, D.; Vrignaud, T.; Tissot, C.; Skrifvars, M. Mechanical Recycling of PLA Filled with a High Level of Cellulose Fibres. J. Polym. Environ. 2016, 24, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Duigou, A.; Pillin, I.; Bourmaud, A.; Davies, P.; Baley, C. Effect of recycling on mechanical behaviour of biocompostable flax/poly(l-lactide) composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grozdanov, A.; Avella, M.; Buzarovska, A.; Gentile, G.; Errico, M.E. Reuse of Natural Fiber Reinforced Eco-Composites in Polymer Mortars. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2010, 50, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coltelli, M.-B.; Gigante, V.; Aliotta, L.; Lazzeri, A. Recyclability Perspectives of the Most Diffused Biobased and Biodegradable Plastic Materials. Macromol 2024, 4, 401-419. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4020023
Coltelli M-B, Gigante V, Aliotta L, Lazzeri A. Recyclability Perspectives of the Most Diffused Biobased and Biodegradable Plastic Materials. Macromol. 2024; 4(2):401-419. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleColtelli, Maria-Beatrice, Vito Gigante, Laura Aliotta, and Andrea Lazzeri. 2024. "Recyclability Perspectives of the Most Diffused Biobased and Biodegradable Plastic Materials" Macromol 4, no. 2: 401-419. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4020023
APA StyleColtelli, M.-B., Gigante, V., Aliotta, L., & Lazzeri, A. (2024). Recyclability Perspectives of the Most Diffused Biobased and Biodegradable Plastic Materials. Macromol, 4(2), 401-419. https://doi.org/10.3390/macromol4020023








