Abstract
Biopolymers, such as polysaccharides, polyphenols, alkaloids, and terpenoids, found in marine algae exhibit antiviral and anticancer properties. These compounds can inhibit viral replication, induce apoptosis in cancer cells, and enhance the immune response. Their diverse bioactive properties make marine algae a promising source for the development of sustainable antiviral and anticancer therapies. A major advantage of marine algae is that they do not require freshwater or arable land and can be cultivated in seawater, thus making them sustainable substitutes for conventional resources. Additionally, their ability to sequester carbon and recycle nutrients enhances their environmental sustainability. Despite their promising biomedical potential, challenges, such as compound extraction, large-scale production, and clinical validation, must be addressed for effective drug development. The vast biological diversity of marine algae across different ocean ecosystems is a largely unexplored source of distinct chemical structures, which may be the basis for new therapeutic schemes. Despite their therapeutic potential, the translation of marine algae-derived compounds into clinical applications faces significant hurdles, including challenges in large-scale extraction, bioavailability enhancement, and regulatory approval. The need to extract particular compounds to make them available for large-scale production and to overcome issues such as bioavailability and regulatory policies are formidable challenges. Marine algae represent innovative advances in antiviral and anticancer drug development, but only when combined with ecologically sound cultivation methods, interdisciplinary approaches, and understanding. The integration of advanced biotechnological approaches, innovative gene editing techniques, and environmentally sustainable aquaculture practices is pivotal for harnessing the full potential of marine algae for the development of next-generation antiviral and anticancer therapeutics.
1. Introduction
Marine algae have emerged as an important focus in biomedical research, owing to their rich content of bioactive compounds with potential antiviral and anticancer properties [1]. These compounds (polysaccharides, phenolics, terpenoids, alkaloids, and sulfated carbohydrates) have yielded remarkable pharmacological activities. The growing resistance to synthetic drugs and the demand for new, naturally derived therapeutics make marine algae a potential resource for drug discovery and an increasingly important subject [1,2]. Marine algae, microalgae (diatoms, dinoflagellates, and cyanobacteria), and macroalgae (green, brown, and red seaweeds) can withstand extreme oceanic conditions and, as defensive mechanisms, have evolved specialized secondary metabolites. These metabolites have attracted attention owing to their antiviral, anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory activities. Antigenic polysaccharides from red algae (carrageenans and fucoidans) have shown antiviral activities against human herpes simplex virus (HSV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and influenza virus. Similarly, brown algae metabolites such as phlorotannins and sulfated polysaccharides have also been reported to induce apoptosis and restrain cancer cell proliferation [3,4]. Antiviral activity of marine algae mainly relies on sulfated polysaccharides including carrageenans, fucoidans, and ulvans, which exert this effect by blocking viral binding and replication. Carrageenans isolated from Chondrus crispus and Kappaphycus alvarezii have shown suppressive activity against HIV, HSV, human papillomavirus (HPV), and dengue virus, inhibiting viral entry into the host cells [5,6]. Likewise, fucoidans from brown seaweeds like Fucus vesiculosus and Undaria pinnatifida can block the replication of viruses by binding to viral surface proteins, thereby blocking infection processes [6]. Research on ulvans from green algae has also shown potential activity against respiratory viruses, such as influenza A and coronaviruses [7]. However, there are some challenges in the standardization of extraction procedures, bioavailability optimization, and clinical trials to support the therapeutic activity of these compounds in human therapeutics. Further research should aim to increase the structural characterization of antiviral polysaccharides and optimize their formulation for therapeutic purposes [8]. Marine algae are also known to have anticancer activity, and reports on their tumor growth-inhibiting, apoptosis-inducing, and tumor metastasis-suppressing abilities have been presented. Cytotoxic properties of compounds (phlorotannins, bromophenols, and terpenoids) have been demonstrated in several cancers (including breast, lung, colon, and liver) [9]. Fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from brown algae, has received considerable attention because of its apoptosis activity in cancer cells via caspase activation and the inhibition of angiogenesis [8,9]. In addition, algae-derived alkaloids and flavonoids have demonstrated selective inhibitory effects on essential cellular activities such as cell cycle, migration, and invasion. Extracts from Ulva lactuca, Sargassum dentifolium, and Cystoseira myrica have exhibited potent antitumor activity, with studies indicating their ability to suppress tumor progression in vitro and in vivo [10,11]. Although promising results have been obtained, low bioavailability, structural complexity, and a lack of clinical trials limit the direct utilization of these compounds for cancer treatment [11]. Filling these gaps that have been achieved by biotechnological advances, nano-formulation tactics, as well as mechanistic studies of these gaps, are likely to play a critical role in incorporating marine algae bioactives into future oncology treatments. Marine algae contain a phenomenal library of bioactive compounds; however, the potential biomedical applications of these algae are poorly explored because of limitations in large-scale production, extraction efficacy, and clinical evidence (Figure 1) [9,10,11]. The requirements for sustainable extraction, upgraded techniques of purification, and extensive molecular characterization point to the need for further research. The need to understand structure–activity relationships (SARs) and optimize bioactive compound delivery systems will be a crucial factor in moving marine algae metabolite-based solutions for antiviral and anticancer therapeutics from the lab bench to patient use [8,9]. Marine algae are promising sources of modern medicine, offering a natural and sustainable source of antiviral and anticancer drugs. Future research at the frontier of this area would necessitate interdisciplinary teamwork between marine biology, pharmacology, and clinical sciences to explore the vast potential of these marine-derived compounds in human medicine [10,11].
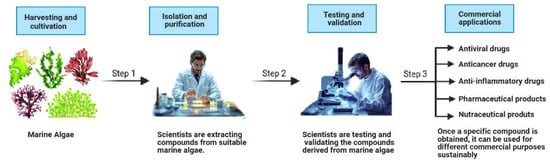
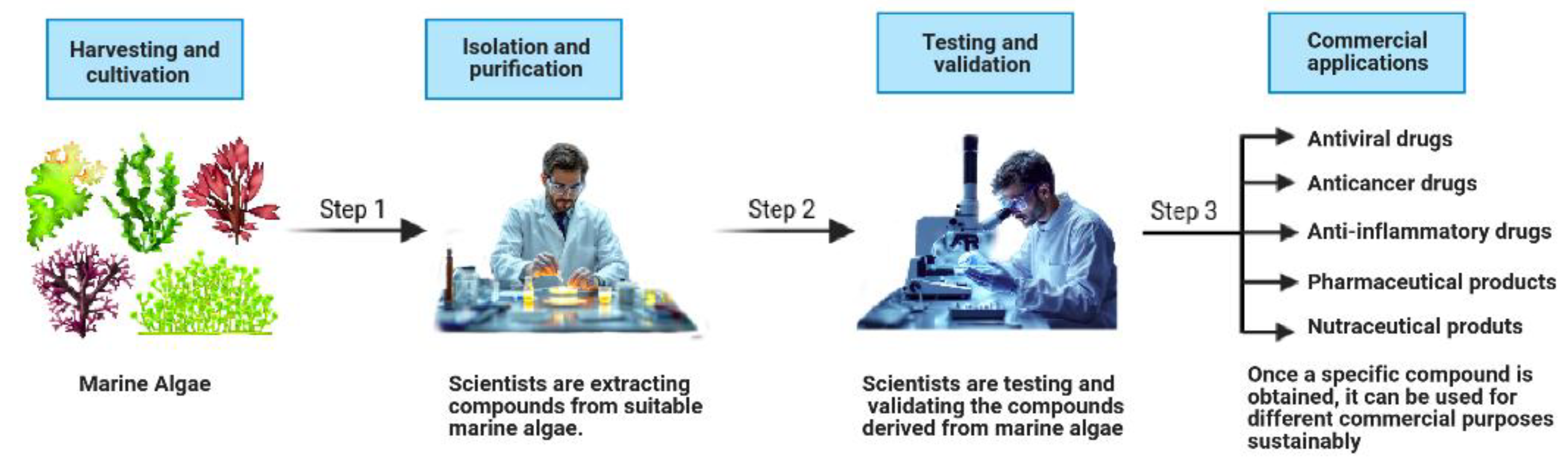
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the marine algae-derived bioactive compound development process. The process involves three key steps: (1) the harvesting and cultivation of marine algae, (2) the isolation and purification of bioactive compounds, and (3) the testing and validation of their efficacy, leading to commercial applications in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and therapeutic drugs.
Marine macroalgae and microalgae are eco-friendly and can be acquired as rich sources of bioactive molecules, which have promising biomedical and industrial applications for restoring properties of microorganisms, tissues, or cells. These bioactive compounds are carbohydrates, proteins, minerals, fatty acids, antioxidants, and pigments, depending on the content of these substances, which are under the control of biotic (plant and microorganism) and abiotic (temperature, pH, salinity, light intensity) factors [11,12]. Marine algae are promising anticancer and antiviral agents because of the vast amount of bioactive metabolites accumulated therein. Compounds including brominated metabolites, polysaccharides, terpenes, polyphenols, and phlorotannins have anticancer effects in vitro and in vivo by activating apoptosis, suppressing angiogenesis, and activating the immune system [13,14,15]. In addition, the anticancer effects of microalgae-derived pigments, lipids, and carotenoids have been demonstrated in many cell lines by targeting the anticancer-related molecular targets involved in cancer progression [15,16]. The specific antiviral activity of sulfated polysaccharides (SPs), fucoidans, carrageenans, and ulvans, is strong, and these offer potential for leading antiviral drugs. These SPs, along with other secondary metabolites, suppress viral replication and could be candidate therapeutic agents against viral infections [7,17]. In general, brown seaweeds are equipped with potent anti-biofilm compounds, including sulfated polysaccharides (fucoidan), carotenoids (zeaxanthin and lutein), lipids and fatty acids (γ-linolenic acid and linoleic acid), and phlorotannins. These species are used to inhibit bacterial adhesion, suppress proliferation, and denature extracellular polymeric substances, and are therefore important in preventing the development of biofilm. This is especially relevant for preventing the corrosion of metal components which can lead to substantial economic losses in many industries [17,18]. They are recognized in the food industry as a high-protein, nutrient-rich meal with vitamin and mineral components that can prevent chronic diseases such as obesity and cardiovascular disorders. Due to the presence of abundant n-3 fatty acids, essential amino acids, and dietary fibers that most of the usual algae-based food products contain, algae-based food items are helpful for human health and nutrition [16,17,18,19]. However, given the high diversity of bioactive compounds in marine algae, there are still many challenges in their extraction and practical applications.
Traditional solvent extraction procedures typically have poor efficiency, require high processing, and are extensive. To address these deficiencies, several high-tech extraction methods have been proposed, including enzyme-assisted, microwave-assisted, ultrasound-assisted, supercritical fluid, and pressurized liquid extractions. These novel methods enhance the efficiency, sustainability, and purity of compounds that are produced from algae-derived products, thereby enabling algae-derived products to be of use in production [18,19,20]. Brown, red, and green algae possess a wide variety of unique bioactive molecules such as sulfogalactofucans, fucoidans, carrageenans, and ulvans (Table 1); therefore, they have great potential in biomedical research and industry [21].

Table 1.
Different types of marine algae and their representative species.
Data Analysis
Keywords were used to search for articles in the following four databases: Google Scholar, SCOPUS, PubMed, and Web of Science. The domains were title, abstract, and keywords, which included “Marine algae, Antiviral compounds, Anticancer compounds, Bioactive compounds, Pharmaceutical applications, Algal secondary metabolites, Sustainable resources”. The duration for the search was limited to the years 2000–2024; however, two citations were taken from 1997 and four citations were taken from 1999, 1987, 1975, and 1981, respectively. A total of 70 citations were retrieved from SCOPUS, 70 from Google Scholar, 25 from PubMed, and 5 from Web of Science.
Publications were checked for duplication, and the publications whose scope was limited to applications of marine algae other than antiviral and anticancer compounds were excluded from the review. After screening, 62 publications from SCOPUS, 47 publications from Google Scholar, and 29 publications from PubMed, and 5 from Web of Science were retained for the review.
2. Classification and Distribution of Marine Algae
Marine algae are autotrophs that live in the ocean and can be either micro- or macro-sized (Figure 2). Microalgae, including diatoms, dinoflagellates, and cyanobacteria (blue–green algae), are single-celled organisms, whereas macroalgae, also known as seaweeds, are multicellular and comprise green, brown, and red algae, respectively. Cyanobacteria, diatoms, and dinoflagellates are examples of microalgae because they are unicellular. They are also essential components of and hold substantial importance in underwater biodiversity and oxygen production, and have a variety of industrial applications as basic living beings of underwater systems. They live in marine settings, and are classified into the following two main types: microalgae and macroalgae. In addition to their ecological importance, marine algae are used efficiently in the food, pharmaceutical, and biofuel sectors. However, they are also important reservoirs of blue carbon sequestration, which plays a role in mitigating climate change. Classification, bioactive compounds, and environmental and geographical distribution need to be understood to be sustainably utilized and conserved [22,23].
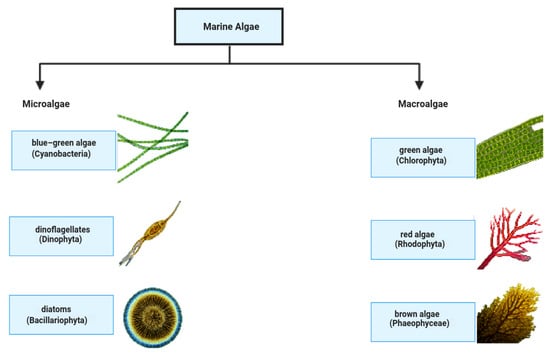
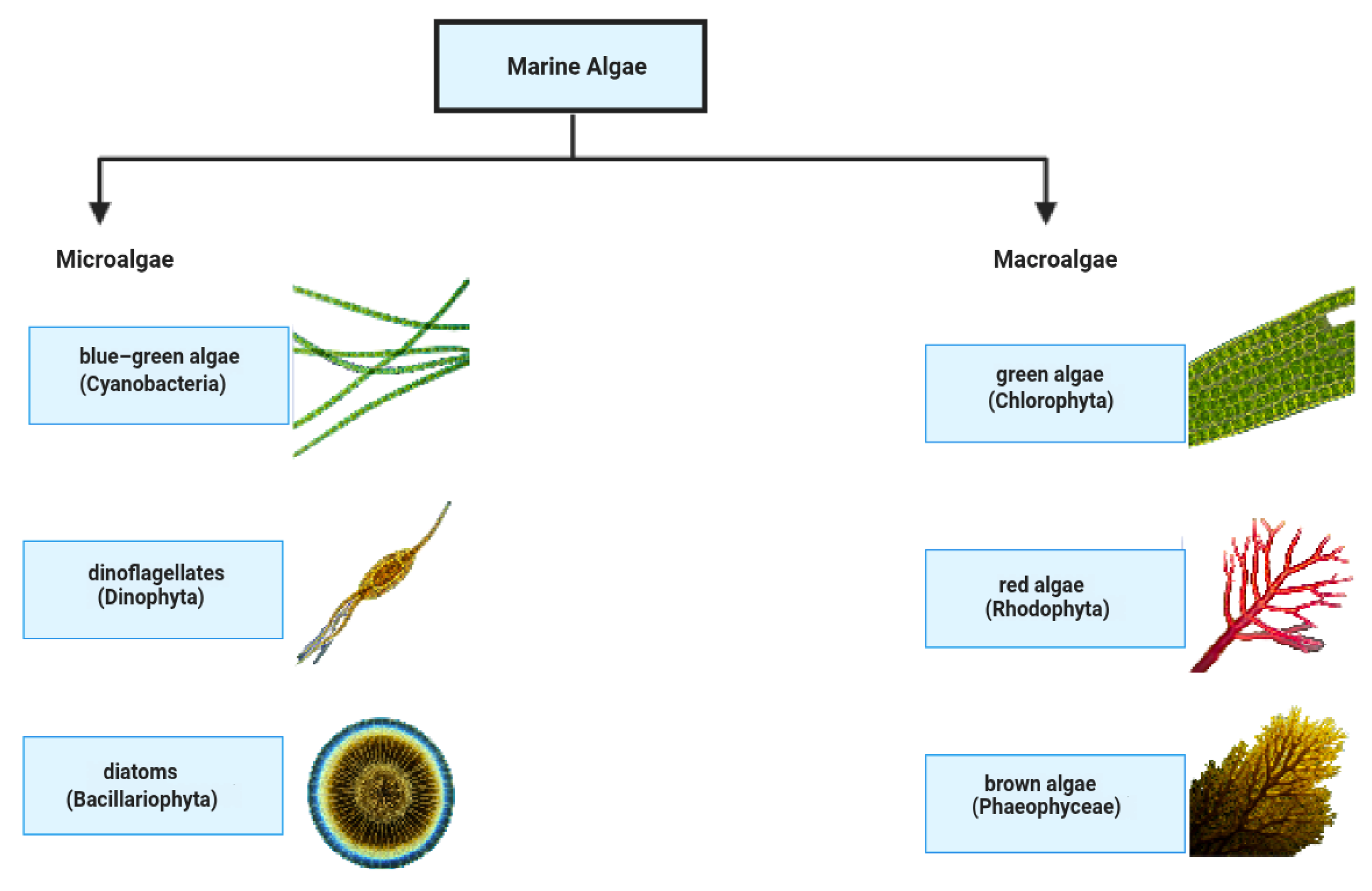
Figure 2.
Overview of marine algae categories: microalgae and macroalgae are shown with their examples.
2.1. Classification of Marine Algae
Microalgae are unicellular, nearly microscopic organisms, including cyanobacteria, diatoms, and dinoflagellates. These algae are the primary producers in the marine food chain in terms of organic synthesis via photosynthesis. Some of the most important microalgae species include Chlorella, Spirulina (Arthrospira platensis), Dunaliella salina, and Haematococcus pluvialis, some of which are beneficial for their nutritional and pharmacological properties [22,23,24]. In contrast, macroalgae and seaweeds are multicellular and are known to grow on macroscopic scales. Seaweeds also produce vast underwater forest habitats that provide both food and habitat for marine organisms. Examples include kelps (Laminaria, Macrocystis), Sargassum, and Gracilaria [24,25]. Macroalgae are commercially exploited in food and medicine because of the high content of polysaccharides and bioactive compounds in these taxa.
2.2. Bioactive Compounds and Industrial Applications
Marine algae are rich in bioactive compounds with significant applications in various fields. Microalgal lipids are abundant, and, as such, their potential use as biomass in biodiesel production is promising. The high lipid contents of species such as Nannochloropsis and Botryococcus braunii enables the extraction and conversion of the lipids into biofuels [24,25]. In addition, microalgae-derived antioxidants such as beta-carotene (Dunaliella salina) and astaxanthin (Haematococcus pluvialis) have been extensively utilized in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic fields due to their strong antioxidant activity [26]. However, macroalgae are also of interest for their high polysaccharide content (e.g., agar, carrageenan, and alginate), collectively known as phycolloids, which serve as gelling, thickening, and stabilizing agents in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. The natural origin compounds for Gracilaria, Gelidium, and Macrocystis, which might be present in dairy foods, cosmetics, and biomedical applications, are elaborated on in [27,28,29]. Furthermore, macroalgae are rich in bioactive compounds, including phlorotannins, bromophenols, and flavonoids with antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer activities. Brown seaweeds such as Turbinaria ornata and Hormopysa triquetra have extremely high contents of antioxidant activity and are beneficial for nutraceutical and pharmaceutical applications [30,31]. Marine algae also play an important role in aquaculture. Microalgae constitute a significant food source for larval fish, prawns, and bivalves, which have major importance in the sustainable development of the aquaculture industry. Species of Isochrysis galbana and Tetraselmis suecica are employed to enhance larval feeding, thereby enhancing the survival rate of larvae at hatcheries [26]. Additionally, algae-derived food supplements (e.g., Spirulina and Chlorella) are very commonly consumed due to their high protein, β-carotene, and vitamin contents, which are known to enhance the immune system and reduce neurodegeneration and cholesterol content [24,32].
2.3. Ecological Importance and Environmental Factors
Marine algae are fundamental to oceanic ecosystems, and serve as primary producers of organic matter and oxygen. They are responsible for over 90% of photochemical activity at the Earth’s surface and, accordingly, play an important role in carbon fixation and oxygen production. Macroalgal forests (e.g., kelp forests) provide a source of food, a refuge, and a breeding environment for a wide range of animal species [5,33]. Marine algae also function as regulators of natural climate. Macroalgal ecosystems, by providing blue carbon sequestration, absorb and store atmospheric CO2 to help limit global warming. As brown algae (e.g., Sargassum and Laminaria) are efficient at carbon storage, they play a key role in mitigation strategies for climate change [33]. However, not all algae have positive ecological impacts. Harmful algae blooms (HABs) resulting from toxic algae, such as Alexandrium, Karenia brevis and Pseudo-nitzschia, produce toxins and contaminate seafood through the pollution of shellfish and marine ecosystems, leading to ecosystem destabilization [34]. These blooms are highly indicative of excess nutrients in, warming of, and alterations in the oceanographic environment. Information on how algal growth is regulated in relation to environmental factors such as nutrients, temperature, light intensity, and wave action is helpful for algal growth inhibition and ecological balance [35].
2.4. Geographical Distribution and Environmental Impact
The distribution of marine algae is affected by a wide range of environmental factors such as temperature, salinity, and ocean currents. Microalgae such as Alexandrium are predominantly found in cold to temperate coastal waters, including the Northwest Pacific and the Mediterranean, where specific sea surface temperatures and oxygen levels favor their growth. These areas are especially susceptible to the rising frequency of HABs; therefore, surveillance and countermeasure actions are required [36]. By contrast, macroalgae, including kelps and fucoid seaweeds, are the key grazers of temperate coastal communities, especially in the Northeast Pacific and Southeast Australia. These macroalgal species can grow in areas with adequate light penetration and stable temperature. Their presence also plays a major role in marine biodiversity and coastal protection, decreases erosion, and provides important habitats for fish and invertebrates [37]. Recent reports indicate that up to 20.8 million km2 of ocean area can be farmed with marine algae, highlighting the scale at which the farming of macroalgae can occur and how the industry can be commercialized. The increased production of seaweed for farming can contribute to food security, carbon sequestration, and sustainable biofuel creation, extending marine algae’s involvement in the global economy [38]. Marine algae also engage with microorganisms to create holobionts composed of microbial communities that flourish with algae and play a role in nutrient cycling and ecological stability. Nevertheless, climate change, as well as its impacts on air quality and pollutant loss in habitats, interfere with these symbiotic relationships and disturbing dynamics of marine ecosystems [39].
Marine algae play an indispensable role in marine ecosystems as habitat providers and key contributors to global oxygen production. The bioactive compounds in marine algae have fueled innovations in pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and renewable energy. Moreover, their role in blue carbon sequestration positions them as vital components in climate change mitigation efforts [38,39]. Despite their benefits, harmful algae blooms pose ecological and economic threats, highlighting the importance of effective environmental management [33]. Additionally, geographical factors influence algal distribution, shaping biodiversity hotspots across different marine regions. The continued exploration of marine algae’s potential in food, medicine, and energy sectors, coupled with conservation efforts, is crucial for harnessing their benefits sustainably. Understanding marine algae’s functional diversity, environmental significance, and economic applications will ensure their effective utilization while maintaining ecological balance. Future research should focus on optimizing cultivation methods, exploring novel bioactive compounds, and mitigating the adverse effects of harmful blooms to maximize the potential of these marine organisms in a sustainable manner [5,33,40].
3. Bioactive Compounds in Marine Algae
Marine algae are potential sources of bioactive compounds that can be harnessed for therapeutic interventions, especially as anti-inflammatory agents, antioxidants and antimicrobials (Table 2). Secondary metabolites that are synthesized by both micro- and macroalgae, such as polyphenols, carotenoids, phlorotannins, and bromophenols, exhibit biological activities, including antioxidant, anticancer, and antibacterial properties. Marine algae are also potential sources for the manufacture of pharmaceutical drugs, biomedical products, nutraceuticals, and cosmeceuticals. Such compounds are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), pigments, antioxidants, terpenoids, carotenoids, tocopherol, phenolic compounds, polysaccharides, and mycosporine-like amino acids [41,42,43]. For example, phlorotannins derived from brown algae and carotenoids obtained from different algae types have been reported to alter inflammatory pathways as well as oxidative stress. Sulfated polysaccharides (SPs), particularly carrageenans, fucoidans, and ulvans, which are extracted from marine algae, are abundant and have significant health benefits, including antioxidant, anti-allergic, antiviral, anticancer, and anticoagulant activities [21,30]. Microalgae have been shown in recent studies to possess anticancer activity, with extracts having a considerable anti-proliferative impact on various cancer cell lineages. Fucoidans from brown seaweeds, such as Ecklonia cava, Sargassum horneri, and Costaria costata, inhibit colony formation in human melanoma and colon cancer cells by modulating key signaling pathways. They suppress the PI3K/Akt (Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B) pathway, which leads to reduced cell survival and promotes apoptosis. Fucoidans also inhibit NF-κB (Nuclear Factor-KappaB) activation, thereby downregulating the expression of inflammatory and pro-survival genes. Furthermore, fucoidans interfere with the MAPK (Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase) signaling cascade (comprising ERK(Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase), JNK,(c-Jun N-terminal Kinase) and p38), which further limits cancer cell proliferation and enhances apoptosis induction [44,45]. Additionally, research on Hawaiian algae revealed that the extract of Turbinaria ornata exhibited the highest antioxidant activity, with fucoxanthin identified as the primary bioactive antioxidant compound [43,46,47]. More specifically, some bioactive metabolites, such as halogenated mono- and sesquiterpenoids from red algae, have cytotoxic effects on tumor cells and exhibit antifeeding effects on marine animals [13]. Through the generation of cell toxicity, red algae produce brominated metabolites, including terpenoids and phenols, that possess anticancer activity. Furthermore, macromolecules, such as polysaccharides from green algae, are still being researched rather than existing as established treatments. While studies suggest they can block angiogenesis, stimulate immune responses, and trigger apoptosis, further preclinical and clinical trials are required to confirm their effectiveness and safety [48].

Table 2.
Biopolymers and bioactive compounds derived from marine algae and their biological activities.
Studies have shown that polysaccharides extracted from the green seaweed Enteromorpha (Ulva) prolifera have hypoglycemic activity; they have also been shown to modulate gut microbiota, boost the immune response, and possess antioxidant properties, as well as antidiabetic, antimicrobial, and hypolipidemic activities. These polysaccharides can be utilized to foster even more therapeutic potential through the degradation, carboxymethylation, or sulfonation of the polysaccharides, as indicated by recent work on molecular modification techniques. There is a growing trend of employing modern extraction techniques over those old trends because of the lack of suitable tools and techniques. Modern extraction methods, such as supercritical fluid extraction, subcritical water extraction, ultrasound-assisted extraction, and microwave-assisted extraction, are being used to isolate these compounds, as they present more benefits than the conventional methods. Marine algae bioactive compounds vary significantly based on species, environmental conditions, and growth parameters. These permissive conditions mean that algae grow under their most favorable conditions. Different species produce various compounds; some are specific to those types of algae and other compounds are common in all algae [54]. The following are general compounds found in marine algae.
3.1. Polysaccharides
Marine algae contain several important biopolymers, as follows:
- Fucoidan: Sulphated polysaccharides found in brown algae, with structural variations including U-fucoidan (contains glucuronic acid), F-fucoidan (sulfated fucose), and G-fucoidan (contains galactose). They have been shown to have anticoagulant, antiviral, and anticancer activities [55].
- Carrageenan: A sulfated polysaccharide classified into kappa, iota, and lambda types. It is extracted from red algae (Rhodophyceae) and is used as a gelling and thickening agent in the food industry [56].
- Porphyran: A sulfated polysaccharide from Rhodophyta, with a linear backbone of alternating β-D-galactose and α-L-galactose-6-sulfate units [56].
3.2. Proteins and Amino Acids:
Marine algae are rich in the following unique protein structures:
- Glycoproteins: Found in various marine algae, these are bound to carbohydrates, with approximately 36.24% composed of rhamnose, galactose, glucose, and mannose [12].
- Phycobiliproteins: Found in red algae and cyanobacteria, these are water-soluble proteins linked to chromophores like phycocyanin (PC) and phycoerythrin (PE), which demonstrate antioxidant and potential anticancer properties [12].
3.3. Lipids
Marine algae contain various bioactive lipids, including polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) and sterols, as follows:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in microalgae and some macroalgae, omega-3 fatty acids such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) have well-documented health benefits, including cardiovascular protection and anti-inflammatory effects [57].
- Fucosterol: Found in brown algae, fucosterol is a sterol with potential antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activities [58].
3.4. Secondary Metabolites
Marine algae produce a diverse array of secondary metabolites with various bioactivities, as follows:
- Phlorotannins: Found in brown algae, phlorotannins are polyphenolic compounds with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties [59].
- Fucoxanthin: A carotenoid found in brown algae, fucoxanthin has been studied for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-obesity effects [60].
5. Anticancer Compounds from Marine Algae
Marine algae are also a rich source of bioactive compounds displaying significant anticancer activities. These molecules have pleiotropic pharmacological effects (e.g., antiproliferative, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects) (Table 4). Sulfated polysaccharides (SPs), such as carrageenan, fucoidan, and laminarin, have demonstrated anticancer and antimetastatic activities [87]. Marine algae are receiving increased attention for their anticancer metabolites—for instance, red algae yield elatol from Callophycus serratus, which has cytotoxic effects, while brown algae provide pachydictyol A, bifurcarenone, and meroditerpenoids (e.g., stypolactone and atomaric acid), which are active against various cancer cell lines [88]. Microalgae, i.e., Acutodesmus obliquus and Desmodesmus perforates, have been previously reported to possess high antiproliferative activity against breast cancer cell line models with methanolic extracts, characterized by cell inhibition rates up to 87%. In addition, algal polysaccharides (fucoidan and alginate) have also been proposed for controlling tumor growth and enhancing the efficacy of current cancer therapies [14,89]. Over 60% of commercially available anticancer agents have been developed based on natural biomimetics, thereby underscoring the value of marine natural products for anticancer therapy. The anticancer effects of marine algae are not limited to direct cytotoxic activity; marine algae-derived bioactive substances can also exert inhibitory activities on major cellular events, for example, angiogenesis, migration, and invasion in vitro and vivo. In addition, the green alga Sphaerococcus coronopifolius is known to synthesize cytotoxic compounds and has possible anticancer applications. The multiple secondary metabolites in marine algae, such as phenolic compounds and polysaccharides, exert anticancer activity through activating the programmed cell death and immune response [8,13]. For example, Cladophora glomerata, harvested from the Hare Island–Tuticorin area, has shown potent anticancer activity on HT-29 colon cancer cell cultures, provided by the methanol extract. Its IC50 (half maximal inhibitory concentration), which represents the concentration needed to inhibit cell proliferation by 50%, was measured at 28.46 ± 0.65 µg/mL, demonstrating strong anticancer effects [90]. Extracts of polysaccharides and sulfated polysaccharides from Ulva lactuca, Sargassum dentifolium, and Cystoseiara myrica have demonstrated antitumor and antiviral activities with good activity profiles and without cytotoxicity [10]. These results indicate the possibility of using these natural substances for therapeutic uses. In particular, red algae are also recognized for the formation of brominated metabolites, including terpenoids and phenols components, which cause cell destruction. Non-toxic biological macromolecules, such as polysaccharides, produced by green algae, which can suppress tumor angiogenesis (the new blood vessel sprout-like supply for tumors), elicit an immune response, and elicit apoptosis. The marine-derived anticancer drug pipeline is one of the strongest in the industry, with four approved drugs and eighteen agents in late-stage development [13,14]. Many algal metabolites, including polysaccharides, terpenes, and phenols, exhibit anticancer activity by targeting key molecular pathways involved in cancer progression. They induce apoptosis, inhibit angiogenesis, and stimulate the immune system, thereby exerting proapoptotic, antiangiogenic, anti-invasive, and antimetastatic effects [13,91]. Macroalgal extracts and compounds also show potential as cancer chemopreventive agents due to their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimutagenic properties [91]. These kinds of compounds are also known to have a broad range of pharmacological activities including antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antiviral and anticancer properties. Marine algal peptides demonstrate anticancer properties, including, for example, apoptosis induction, cell cycle arrest inhibition, and angiogenesis inhibition [56,92]. In addition to showing great promise for cancer research, marine algae also show promising potential as drugs for the treatment of chronic diseases and neurodegenerative diseases. Additionally, marine algae carbohydrates have been shown to be useful in providing skin health benefits; therefore, they have appealing potential for cosmetics applications [56,93].

Table 4.
Anticancer compounds derived from marine algae and their mechanisms of action.
The clinical translation of marine algae-derived bioactive compounds faces several challenges, including complex extraction and purification, unclear mechanisms of action, and scalability issues. Marine algae are chemically diverse, requiring advanced extraction technologies to isolate specific bioactive molecules effectively [94]. Furthermore, many compounds exhibit promising anticancer properties in vitro, but their precise molecular targets and mechanisms remain poorly understood [1]. Another major barrier is the scalability of production, as sustainable harvesting and biotechnological synthesis are necessary to ensure a stable supply without overexploiting marine ecosystems [45]. Additionally, regulatory challenges related to toxicity, bioavailability, and clinical validation hinder the transition of these compounds into approved pharmaceuticals [8,56].
6. Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
The cultivation of marine algae presents great promise for sustainable development and ecological safeguards. Research has indicated that about 20.8 million km2 of ocean area is potentially available for the aquaculture of marine algae species, with the majority of potential sites lying within coastal zones. This agronomic potential relates to many United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)—food security and energy independence, carbon neutrality, and ecosystem restoration [38,98]. Seaweed cultivation demonstrates promising environmental benefits. It has the potential to contribute to carbon sequestration; a previous study found a net carbon emission of −1.11 kgCO2eq/kg for the production of agar using seaweed. Furthermore, seaweed cultivation can play a role in the removal of nitrogen, phosphorus, and heavy metals from sea areas [99]. Nevertheless, its negative effects should be considered, especially in terms of the impact of aquaculture on marine ecosystems without effective management [100]. Marine algae present great promise in terms of environmental sustainability and for tackling global issues. They can be applied to the fight against water contamination, ocean acidification, and global warming. Among others, microalgae in particular have potential as the feedstock for biofuels and fine chemicals [101,102]. Nevertheless, the economic viability of large-scale algae production represents one important challenge. To improve the viability, recent studies have focused on increasing productivity, multi-product situations, and developing the cultivation of algae within current industrial infrastructure [103]. The sustainable harvesting of marine algae integrates methods like offshore cultivation, rotational harvesting, and integrated multi-trophic aquaculture (IMTA) to minimize environmental impact. Offshore cultivation reduces coastal ecosystem degradation, while rotational harvesting allows regrowth before re-harvesting, maintaining biodiversity [104]. IMTA enhances sustainability by integrating algae with fish and shellfish farming, thereby recycling nutrients and reducing waste accumulation [105]. Additionally, spore-based seaweed propagation ensures long-term sustainability by reducing wild harvesting pressure [106]. These innovations help preserve marine ecosystems while ensuring a steady algae supply. Current progress in microalgae harvesting methods include bioflocculation, electrolytic coagulation, and ultrasonic aggregation, all of which have significantly lowered the energy consumption required for production and have the potential to exclude harmful chemicals, thereby making them sustainable engineering tools for food-grade microalgae production [107]. Furthermore, the environmental impacts of microalgae production have been critically evaluated via life cycle analysis and it has been concluded that the sustainability of microalgae production should not be taken for granted, particularly in the way inputs and emissions are managed in order to reduce environmental pollution [108]. In the context of wild seaweed harvesting, ecosystem-based management strategies are essential to maintain biodiversity and ecosystem functions; advocating for selective harvesting methods and the establishment of harvest-exclusion zones to protect habitats are important [109]. Technology for cultivating marine algae is being continuously refined, with different approaches introduced to achieve the best growth and yields. Standardized, routine, and economical large-scale seaweed cultivation has emerged as a result of progress in environmental regulation, due to studies on life histories and the asexual reproduction of the thalli. There are several taxa for which unique agronomy methods are necessary, and only a few dozen species are currently commercially farmed. The five family names Laminaria, Undaria, Porphyra, Eucheuma/Kappaphycus, and Gracilaria account for ~98% of global seaweed production [110]. Conventional approaches include bamboo raft, tube mesh, and stone techniques, whereas more sophisticated strategies include bio-refinery treatment [111]. New methods of planting have been devised to deal with environmental and economic issues. Land-based cultivation (e.g., segmental and ring-like channels) and tumble cultivation (circular tanks) have been contrasted. These systems offer benefits like a reduced cultivation medium volume, increased process control, and the separation of CO2 and nutrient supply from temperature control and agitation [112].
Marine algae play a crucial role in environmental sustainability by contributing to carbon sequestration, improving marine water quality through nutrient removal, and serving as a valuable source of bioactive compounds with applications in food, agriculture, and bioenergy. The cultivation of macroalgae, such as Gracilaria lemaneiformis, not only mitigates pollution and resource depletion but also supports carbon neutrality, with an overall negative carbon emission of −1.11 kgCO2eq/kg associated with agar production [99,113]. However, large-scale seaweed farming poses challenges, including the accumulation of litter that can lead to pollution if not properly managed. Implementing sound management practices like early sward harvesting and litter removal is essential to maximize ecological benefits while minimizing environmental risks [114]. Additionally, marine algae populations are under increasing threat due to over-exploitation, pollution, climate change, and unsustainable fishing practices, leading to biodiversity loss and the disappearance of certain algal species, challenging the notion that “everything is everywhere” in microalgae distribution [115]. Climate change, particularly ocean warming and marine heatwaves, has already had negative effects on key species such as canopy-forming brown algae, giant kelp, and bull kelp in regions like New Zealand, while also driving poleward range shifts in various seaweed species [116]. Future research should focus on improving sustainable cultivation techniques, developing policies for responsible exploitation, and understanding the impacts of climate change on algal biodiversity to enhance the ecological contributions of these technologies while minimizing risks to marine ecosystems.
7. Economic and Commercial Aspects
The global seaweed industry is projected to reach approximately USD 25.4 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 11% [117]. This surpasses earlier estimates of USD 11.7 billion, indicating rapid market expansion. For comparison, the global aquaculture industry is valued at approximately USD 376 billion, while the pharmaceutical algae market stands at USD 5 billion, and the functional food sector, which includes algae-based products, exceeds USD 300 billion [118]. Key drivers of the seaweed industry’s growth include a rising demand for plant-based foods and functional ingredients, expanded applications in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics, and the increasing use of seaweed for biofuel, bioplastics, and fertilizers, contributing to sustainability goals [98]. Commercial cultivation primarily involves species such as Gracilaria, Kappaphycus, and Porphyra, which are essential for producing agar, carrageenan, and nori [119]. In India, the total marine algae dry standing crop is estimated to be over 301,646 tons; it is a basic ingredient for food, fertilizers, and bioactive compounds.
Seaweeds include nutritive and polysaccharide components (agar and carrageenan), which are particularly important in several industries [120,121]. However, despite the potential of this product, large-scale algae cultivation is primarily restricted to Asian waters. Other continents demonstrate increasing interest, but there remains a considerable gap in the amount of relevant knowledge about the appropriate environmental conditions for further development. Moreover, agricultural developments are likely to play an important role in alleviating the increasing global demand and creating a reduction in production costs; this means that we are due to enter a new phase in which seaweed cultivation will become economically usable in areas such as the North Sea [38,122]. The industry has grown exponentially, with an 8.13% annual industry growth between 2003 and 2012 [123]. Bioactive compounds extracted from microalgae are being applied to nutraceuticals and pharmaceuticals, but there are still some challenges related to their large-scale production and commercialization. Seaweed aquaculture has the potential to be sustainable and efficient, with additional potential for biofuel production [124]. The rapidly expanding demand for algae-based biofuels and the lucrative market for cosmetics and pharmaceuticals based on algal natural products has fueled interest in the genetic toolset of marine algae [125]. Marine algae are now considered a potential feedstock for renewable fuels, such as biogas, in the energy sector. Their capacity to capture carbon dioxide, their increased rates of biomass production compared to terrestrial plant crops, and the absence of water and land resource competition make them very appealing as a source for producing industrial feedstocks. The food industry also considers marine algae a valuable nutrient source, with applications in food, beverages, fertilizers, and animal feed [82,126]. There has been a great deal of interest in marine algae-derived bioactive compounds from the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. The antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal properties of polysaccharides and polyphenols derived from seaweeds have already been substantiated, and thus they are of great interest for cosmeceuticals, nutraceuticals, and pharmacology. Rising environmental consumerism has further driven the need for eco-friendly products and, thereby, marine algae-derived nanocellulose has been employed for packaging, environmental, and biomedical purposes [42,127]. Marine algae-based aquaculture is expected to make a substantial contribution to the global demand for animal protein, which is estimated to rise from 263.8 Mt/yr to 286.5 Mt/yr by 2050 [128]. Nevertheless, it is imperative to deal with the problems of overexploitation and environmental factors in order to ensure the sustainable development of this industry [129]. These organisms are, to a certain extent, now known to be valuable to the pharmaceutical, cosmeceutical, nutraceutical, and energy industries and are providers of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial compounds. Moreover, marine algae are also being used as foodstuff, animal feed, and as a nutrient fertilizer that can boost agricultural production through their nutrient contents. The increasing interest in marine biotechnology has opened up new potential applications, particularly in biofuels and phycoremediation, which offer sustainable environmental solutions [130,131].
8. Future Perspectives
The biorefinery and market development of products derived from marine algae are attractive areas in which there is an increasing demand for economically feasible production schemes capable of outputting high-added value nutraceuticals products while using alternative nutrient sources (e.g., wastewater and flue gases) [132,133]. However, the large-scale metabolic engineering and industrial production of anti-fouling agents remain relatively unstudied. Climate change poses a significant threat to seaweeds, seaweed communities, and ecosystem services; thus, there is a need to carry out research on resistant strains and sustainable culture processes. Compared with terrestrial plants, damage to marine algae habitats is less pronounced due to the unique ecological characteristics of these algae. However, expanding the global algae farming industry depends on more research being performed on the selection of optimal cultivation grounds, as well as on the evaluation of the suitability of the nutrient supply, temporal fluctuations in temperature, and hydrodynamic conditions [134,135]. Advancements in state-of-the-art technology, including CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) -based bioengineering, synthetic biology, and nanomaterials, are currently transforming the field of algae research and commercialization. CRISPR-Cas9 genes are used in precise genetic manipulation, which can be expanded to algae to enhance their biomass yield, biofuel lipid contents, and high-potential value-added compound contents, including antioxidants and pharmaceuticals [21].
Synthetic biology contributes in this way by redesigning metabolic pathways for efficient nutraceutical, bioactive peptide, and industrial enzyme production, enhancing algae to act as bioreactors for pharmaceuticals and biofuels. Another significant innovation is the incorporation of algae in CO2 capture/sequestration applications; marine algae can effectively remove CO2 from industrial outgasses by acting as a biofilter of the treatment flue gas and enabling the development of biomass [21]. Through this approach, climate change impacts are mitigated and a circular economy is supported. In particular, bioplastics extracted from algae, for example, polysaccharide-based biopolyesters like carrageenan and alginate, can also be considered a green bioplastic alternative to plastics derived from fossil fuels, which contributes to reductions in plastic pollution and reductions in fossil fuel use. Nanotechnological applications are also being implemented in the study of algae, in the application of algae-derived nanomaterials to directed drug delivery, in biosensing, and in the decontamination of polluted water. The combination of nanotechnology and algae bioproducts improves the stability and bioavailability of pharmaceutical active substances and thus enables new medication uses. Metabolic engineering developments also enable the high-yield synthesis of antifouling compounds and environmentally friendly, toxic-free alternatives for anti-fouling coatings for the maritime sector [136]. In addition to industrial applications, marine algae play an important role in sustainable aquaculture development. Hence, proposing algae-based aquaculture as a green substitute for both the conventional and freshwater modes of production, one that does not require arable land and minimizes the pollution of the environment, is deemed suitable [111,137]. Some companies are leading the way in commercializing algae technologies for circular economy strategies and a variety of uses in food, pharmaceuticals and energy. Despite these advancements, research gaps persist. To achieve the most efficient large-scale production of commercially relevant macroalgae, their genome organization and metabolic pathways should be explored. High-throughput screening methods, e.g., Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) profiling, have revealed a number of antioxidative/anti-proliferative bioactive compounds; however, macroalgae pharmacological activity still needs to be studied [119]. Additionally, little research has been conducted regarding marine epiphytes, particularly macroalgae, within regions like Mexico and the Central American Pacific coast, indicating a need for further floristic and ecological studies [138,139]. To date, though bioactive compounds from marine algae, particularly as neuroprotective and anticancer agents [138,139,140], have already proven their therapeutic value, there is still a need for clinical studies that demonstrate the molecular mechanisms and therapeutic activity of these compounds in patients [141,142,143]. Closing these knowledge gaps is essential for the development of the sustainable exploitation of marine algae, biotechnologies, aquaculture, and drug discovery [74,140].
9. Conclusions
Marine algae offer an attractive, environmentally friendly, and valid platform for the production of biopolymers that contain antiviral and anticancer compounds with the potential to solve major global health issues. Their bioactive molecules, such as polysaccharides, polyphenols, alkaloids, and terpenoids, possess various mechanisms of action, including antiviral activity, the induction of cancer cell apoptosis, and immune modulation. However, the ecological benefits of algae farming, including the ability to grow them in uncultivated land and use seawater, contribute to making them a sustainable resource. Nevertheless, challenges remain, such as the difficulty in separating specific bioactive compounds, production scalability, and concerns regarding toxicity and bioavailability. Developments in biotechnology, including genetic manipulation and bioreactor systems, together with further understanding of the unique marine ecosystem, will be essential for the exploitation of the full pharmaceutical value of marine algae. Through the integration of interdisciplinary methods, marine algae may become the cornerstone of novel, potent, and environmentally friendly therapies for viral infections and cancer.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.A.V.M.; resources, A.S., A.K., S.K. and. B.A.V.M.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K. and A.S.; writing—review and editing, A.K., S.K., A.S. and B.A.V.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
This is a review article; requests for data can be discussed and data may be provided.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ahmed, N.; Sheikh, M.A.; Ubaid, M.; Chauhan, P.; Kumar, K.; Choudhary, S. Comprehensive exploration of marine algae diversity, bioactive compounds, health benefits, regulatory issues, and food and drug applications. Meas. Food 2024, 14, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-M.D.; Li, X.-C.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Potential biomedical applications of marine algae. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, S.; Ishida, K.-I.; Noda, M.; Abe, H. Marine algae and plants. In Japanese Marine Life: A Practical Training Guide in Marine Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashad, S.; El-Chaghaby, G.A. Marine Algae in Egypt: Distribution, phytochemical composition and biological uses as bioactive resources (a review). Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2020, 24, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbuchezhian, R.; Karuppiah, V.; Li, Z. Prospect of marine algae for production of industrially important chemicals. In Algal Biorefinery: An Integrated Approach; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 195–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.; Mathaiyan, M. Emerging Novel Anti HIV biomolecules from marine Algae: An overview. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veluchamy, C.; Palaniswamy, R. A review on marine algae and its applications. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2020, 13, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Silva, J.; Pinteus, S.; Gaspar, H.; Alpoim, M.C.; Botana, L.M.; Pedrosa, R. From Marine origin to therapeutics: The antitumor potential of Marine Algae-Derived compounds. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boopathy, N.S.; Kathiresan, K. Anticancer agents derived from marine algae. In Functional Ingredients from Algae for Foods and Nutraceuticals; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 307–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.M.; Hamdy, A.A.; Alshehri, B.M. Bioprospection of Antiviral and Antitumor Compounds from Some Marine Algae from Egyptian Shores. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 22, 1813–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvam, J.; Mal, J.; Singh, S.; Yadav, A.; Giri, B.S.; Pandey, A.; Sinha, R. Bioprospecting marine microalgae as sustainable bio-factories for value-added compounds. Algal Res. 2024, 79, 103444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menaa, F.; Wijesinghe, U.; Thiripuranathar, G.; Althobaiti, N.A.; Albalawi, A.E.; Khan, B.A.; Menaa, B. Marine Algae-Derived Bioactive Compounds: A new wave of nanodrugs? Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.; Chen, Y.; Shan, S.; Chen, Z.; Wen, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhao, C. Marine algae-derived characterized bioactive compounds as therapy for cancer: A review on their classification, mechanism of action, and future perspectives. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 4053–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, A.N.; Akhir, F.N.; Hara, H. Anticancer Potential of Bioactive Compounds from Microalgae. A Review. J. Adv. Res. Micro Nano Engieering 2024, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, A.G.; Juárez-Portilla, C.; Olivares-Bañuelos, T.; Zepeda, R.C. Anticancer activity of seaweeds. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 23, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, K.M.; Lauritano, C.; Romano, G.; Ianora, A. Marine Microalgae with Anti-Cancer Properties. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesekara, I.; Pangestuti, R.; Kim, S.-K. Biological activities and potential health benefits of sulfated polysaccharides derived from marine algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 84, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadnia, A.; Moosavi-Nasab, M.; Oliyaei, N. Anti-biofilm activity of marine algae-derived bioactive compounds. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1270174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaliaoui, N.; Hazzit, M.; Mokrane, H. Seaweeds as a potential source of bioactive compounds. Res. Biotechnol. Environ. Sci. 2024, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, S.U.; Tiwari, B.K.; O’Donnell, C.P. Application of Novel Extraction Technologies for Bioactives from Marine Algae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 4667–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, D.-H.; Kim, S.-K. Sulfated polysaccharides as bioactive agents from marine algae. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, P. Characteristics of algae. In Third Generation Biofuels; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titlyanov, E.A.; Titlyanova, T.V.; Li, X.; Huang, H. Marine plants of coral reefs. In Coral Reef Marine Plants of Hainan Island; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 5–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal, E.L.; Ali, A. Biological importance of marine algae. Saudi Pharm. J. 2010, 18, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumeerun, S.; Soulange-Govinden, J.; Driver, M.F.; Ranga, R.A.; Ravishankar, G.A.; Hudaa, N. Macroalgae and microalgae. In Handbook of Algal Technologies and Phytochemicals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitzka, M.A. Commercial production of microalgae: Ponds, tanks, tubes and fermenters. J. Biotechnol. 1999, 70, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyocak, H.; Kızılkaya, D.; Üstün, N.Ş. A Review about A Significant Source of Bioactive Compounds: Microalgae. Int. J. Innov. Approaches Agric. Res. 2023, 7, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kızılkaya, D.; Üstün, N.Ş.; Soyocak, H. A Review about Using Bioactive Compounds-Rich Microalgae as Pigments. Int. J. Innov. Approaches Agric. Res. 2023, 7, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eladl, S.N.; Elnabawy, A.M.; Eltanahy, E.G. Recent biotechnological applications of value-added bioactive compounds from microalgae and seaweeds. Bot. Stud. 2024, 65, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpena, M.; Pereira, C.S.G.P.; Silva, A.; Barciela, P.; Jorge, A.O.S.; Perez-Vazquez, A.; Pereira, A.G.; Barreira, J.C.M.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Prieto, M.A. Metabolite profiling of macroalgae: Biosynthesis and beneficial biological properties of active compounds. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiyasa, F.; Taringan, N.; Henggu, K.U.; Tega, Y.R.; Ndahawali, S.; Zulfamy, K.E.; Saputro, M.N.B.; Priyastiti, I. Biological activities of macroalgae in the Moudulung waters: Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity. Food Res. 2024, 8, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarruel-López, A.; Ascencio, F.; Nuño, K. Microalgae, a potential natural functional food source—A review. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2017, 67, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, T. Peranan Ekologi Makroalga Bagi Ekosistem Laut. Oseana 2019, 44, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, B.Y.; Elsaeed, I.; Youssef, H. Two shades of marine life. Med. Updates 2024, 17, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifian, S.; Mortazavi, M.S.; Nozar, S.L.M. Predicting present spatial distribution and habitat preferences of commercial fishes using a maximum entropy approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 75300–75313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Su, S.; Mohamed, H.F.; Xiao, J.; Kang, J.; Krock, B.; Xie, B.; Luo, Z.; Chen, B. Assessing the global distribution and risk of harmful microalgae: A focus on three toxic Alexandrium dinoflagellates. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 948, 174767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkopoulou, E.; Serrão, E.A.; De Clerck, O.; Costello, M.J.; Araújo, M.B.; Duarte, C.M.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Assis, J. Global biodiversity patterns of marine forests of brown macroalgae. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2022, 31, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, L.; Cheung, W.W.L.; Sumaila, U.R. Global estimates of suitable areas for marine algae farming. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 064028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Qin, S. The seaweed holobiont: From microecology to biotechnological applications. Microb. Biotechnol. 2022, 15, 738–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhard, C.T.; Planavsky, N.J.; Ward, B.A.; Love, G.D.; Hir, G.L.; Ridgwell, A. The impact of marine nutrient abundance on early eukaryotic ecosystems. Geobiology 2020, 18, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, M.; Koszarska, M.; Atanasov, A.G.; Król-Szmajda, K.; Jóźwik, A.; Stelmasiak, A.; Hejna, M. Bioactive potential of algae and Algae-Derived compounds: Focus on Anti-Inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant effects. Molecules 2024, 29, 4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dw, A.-K.S.M. Cosmeceuticals Derived from Bioactive Substances Found in Marine Algae. Oceanogr. Open Access 2013, 1, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathi, M.J. Bioactive Compounds from Algae. In Phycobiotechnology; Apple Academic Press: Waretown, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Antitumor effects of fucoidan on human colon cancer cells via activation of AKT signaling. Biomol. Ther. 2015, 23, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Gou, Z.; Wen, Y.; Luo, Q.; Huang, Z. Marine compounds targeting the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basha, A.N.; Akhir, F.N.M.; Othman, N.; Hara, H. Antioxidant And Anticancer Potential of Bioactive Compounds from Locally Isolated Microalgae. J. Health Qual. Life 2024, 3, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelman, D.; Posner, E.K.; McDermid, K.J.; Tabandera, N.K.; Wright, P.R.; Wright, A.D. Antioxidant activity of Hawaiian marine algae. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tringali, C. Bioactive metabolites from marine algae: Recent results. Curr. Org. Chem. 1997, 1, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senadheera, T.R.L.; Hossain, A.; Shahidi, F. Marine bioactives and their application in the food industry: A review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengasamy, K.R.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Aumeeruddy, M.Z.; Zengin, G.; Xiao, J.; Kim, D.H. Bioactive compounds in seaweeds: An overview of their biological properties and safety. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 135, 111013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Hassan, S.H.A.; Awasthi, M.K.; Gajendran, B.; Sharma, M.; Ji, M.-K.; Salama, E.-S. The recent progress on the bioactive compounds from algal biomass for human health applications. Food Biosci. 2022, 51, 102267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuru, P.; D′Auria, M.; Muller, C.; Tammela, P.; Vuorela, H.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J. Exploring marine resources for bioactive compounds. Planta Medica 2014, 80, 1234–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Melchor-Martínez, E.M.; Saxena, A.; Kapoor, N.; Singh, K.J.; Saldarriaga-Hernández, S.; Parra-Saldívar, R.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Therapeutic attributes and applied aspects of biological macromolecules (polypeptides, fucoxanthin, sterols, fatty acids, polysaccharides, and polyphenols) from diatoms—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 171, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.M.; Diab, M.H.; Elkomy, R.G. Algal Bioactive Compounds and Their biological activities. Int. J. Pharm. Res. 2021, 13, 09752366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negreanu-Pirjol, B.-S.; Negreanu-Pirjol, T.; Popoviciu, D.R.; Anton, R.-E.; Prelipcean, A.-M. Marine Bioactive Compounds Derived from Macroalgae as New Potential Players in Drug Delivery Systems: A Review. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Valado, A. Harnessing the power of seaweed: Unveiling the potential of marine algae in drug discovery. Explorationpub 2023, 1, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Tatsuno, I. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids focusing on eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaenoic acid in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases: A review of the state-of-the-art. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 14, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinita, M.D.N.; Harwanto, D.; Tirtawijaya, G.; Negara, B.F.S.P.; Sohn, J.-H.; Kim, J.-S.; Choi, J.-S. Fucosterol of marine macroalgae: Bioactivity, safety and toxicity on organism. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, W.; Mu, T.; Sun, H.; Garcia-Vaquero, M. Phlorotannins: A review of extraction methods, structural characteristics, bioactivities, bioavailability, and future trends. Algal Res. 2021, 60, 102484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohibbullah; Haque, N.; Sohag, A.A.M.; Hossain, T.; Zahan, S.; Uddin, J.; Hannan, A.; Moon, I.S.; Choi, J.-S. A Systematic Review on Marine Algae-Derived Fucoxanthin: An Update of Pharmacological Insights. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Aroca, Á.; Ferrandis-Montesinos, M.; Wang, R. Antiviral Properties of Alginate-Based Biomaterials: Promising Antiviral Agents against SARS-CoV-2. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 5897–5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballantine, D.L.; Gerwick, W.H.; Velez, S.M.; Alexander, E.; Guevara, P. Antibiotic activity of lipid-soluble extracts from Caribbean marine algae. Hydrobiologia 1987, 151, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliyaei, N.; Moosavi-Nasab, M.; Mazloomi, S.M. Therapeutic activity of fucoidan and carrageenan as marine algal polysaccharides against viruses. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, N.; Kim, E.-A.; Park, A.; Heo, S.-Y.; Heo, J.-H.; Lee, W.-K.; Ryu, Y.-K.; Heo, S.-J. Antiviral Activity of Chlorophyll Extracts from Tetraselmis sp., a Marine Microalga, Against Zika Virus Infection. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassen, B.M.; Rashedy, S.H.; Mostafa, A.; Mahrous, N.; Nafie, M.S.; Elebeedy, D.; Azeiz, A.Z.A. Identification of potential antiviral compounds from Egyptian marine algae against influenza A virus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 38, 4411–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardee, K.I.; Ellis, P.; Bouthillier, M.; Towers, G.H.; French, C.J. Plant virus inhibitors from marine algae. Can. J. Bot. 2004, 82, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Macena, L.d.G.P.d.; Amorim, L.d.S.C.; Souza, K.F.C.d.S.e.; Pereira, L.D.; dos Santos, C.C.C.; Barros, C.d.S.; Ramos, C.J.B.; Santana, M.V.; Castro, H.C.; Teixeira, V.L.; et al. Antiviral activity of terpenes isolated from marine brown seaweeds against herpes simplex virus type 2. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023, 39, 712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, C.; Félix, C.; Lemos, M. The antiviral potential of algal lectins. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krylova, N.V.; Kravchenko, A.O.; Iunikhina, O.V.; Pott, A.B.; Likhatskaya, G.N.; Volod’ko, A.V.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Shchelkanov, M.Y.; Yermak, I.M. Influence of the Structural Features of Carrageenans from Red Algae of the Far Eastern Seas on Their Antiviral Properties. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Hao, C.; Zhao, X.; Jiao, G.; Shan, X.; Tai, W.; Yu, G. Inhibition of influenza a virus infection by fucoidan targeting viral neuraminidase and cellular EGFR pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besednova, N.N.; Andryukov, B.G.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Kryzhanovsky, S.P.; Fedyanina, L.N.; Kuznetsova, T.A.; Zvyagintseva, T.N.; Shchelkanov, M.Y. Antiviral Effects of Polyphenols from Marine Algae. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomartire, S.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Antiviral Activity and Mechanisms of Seaweeds Bioactive Compounds on Enveloped Viruses—A Review. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.G.; Tuvikene, R. Potential antiviral properties of industrially important marine algal polysaccharides and their significance in fighting a future viral pandemic. Viruses 2021, 13, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venmathi Maran, B.A.; Iqbal, M.; Gangadaran, P.; Ahn, B.-C.; Rao, P.V.; Shah, M.D. Hepatoprotective potential of Malaysian medicinal plants: A review on phytochemicals, oxidative stress, and antioxidant mechanisms. Molecules 2022, 27, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Parra-Saldivar, R.; Bilal, M.; Afroze, C.A.; Ahmed, N.; Iqbal, H.M.; Xu, J. Algae-Derived bioactive molecules for the potential treatment of SARS-CoV-2. Molecules 2021, 26, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, I.D.; Mariottini, G.L. Glycans with Antiviral Activity from Marine Organisms. In Marine Organisms as Model Systems in Biology and Medicine; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 439–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niccolai, A. Antiviral products derived from microalgae. In Sustainable Industrial Processes Based on Microalgae; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 265–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besednova, N.N.; Andryukov, B.G.; Kuznetsova, T.A.; Zaporozhets, T.S.; Kryzhanovsky, S.P.; Ermakova, S.P.; Shchelkanov, M.Y. Antiviral effects and mechanisms of action of water extracts and polysaccharides of microalgae and cyanobacteria. J. Pharm. Nutr. Sci. 2022, 12, 54–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.I.; Ahmed, S.S.; Habib, N.; Ferdous, M.A.; Sanjida, S.; Mou, M.J. High-throughput virtual screening of marine algae metabolites as high-affinity inhibitors of ISKNV major capsid protein: An analysis of in-silico models and DFT calculation to find novel drug molecules for fighting infectious spleen and kidney necrosis virus (ISKNV). Heliyon 2023, 9, e16383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosik, M.N.; Krylova, N.V.; Usoltseva, R.V.; Surits, V.V.; Kireev, D.E.; Shchelkanov, M.Y.; Svitich, O.A.; Ermakova, S.P. In Vitro Anti-HIV-1 Activity of Fucoidans from Brown Algae. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaeffer, D.J.; Krylov, V.S. Anti-HIV Activity of Extracts and Compounds from Algae and Cyanobacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2000, 45, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Healy, L.; Zhang, Z.; Maguire, J.; Sun, D.; Tiwari, B.K. Novel postharvest processing strategies for value-added applications of marine algae. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 4444–4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.-Y.; Huang, X.; Cheong, K.-L. Recent advances in marine algae polysaccharides: Isolation, structure, and activities. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, M.W.F.S.; da Cunha, N.B.; Carneiro, J.A.; da Costa, R.A.; de Alencar, S.A.; Cardoso, M.H.; Franco, O.L.; Dias, S.C. Marine organisms as a rich source of biologically active peptides. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 667764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusto, A.; Lemos, M.F.L.; Silva, S.F.J. Exploring Marine-Based Food Production: The challenges for a sustainable and fast Biotechnology-Based Development. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzaro, G.; Vatland, A.K.; Pampanin, D.M. The One-Health approach in seaweed food production. Environ. Int. 2021, 158, 106948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khotimchenko, M.; Tiasto, V.; Kalitnik, A.; Begun, M.; Khotimchenko, R.; Leonteva, E.; Bryukhovetskiy, I.; Khotimchenko, Y. Antitumor potential of carrageenans from marine red algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 246, 116568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Pereira, A.R.; Gerwick, W.H. The chemistry of marine algae and cyanobacteria. In Handbook of Marine Natural Products; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 55–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomaa, M. Algal polysaccharides as promising anticancer agents. In Frontiers in Clinical Drug Research-Anti-Cancer Agents: Volume 9; Bentham Science Publishers: Oak Park, IL, USA, 2024; pp. 78–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadik, D.M.; Mohammed, I.H. Evaluation of anticancer effect of Cladophora glomerata algae extract. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2024, 16, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopeechund, A.; Bhagooli, R.; Neergheen, V.S.; Bolton, J.J.; Bahorun, T. Anticancer activities of marine macroalgae: Status and future perspectives. In Biodiversity and Biomedicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visuddho, V.; Halim, P.; Helen, H.; Muhar, A.M.; Iqhrammullah, M.; Mayulu, N.; Surya, R.; Tjandrawinata, R.R.; Ribeiro, R.I.M.A.; Tallei, T.E.; et al. Modulation of apoptotic, cell cycle, DNA repair, and senescence pathways by marine algae peptides in cancer therapy. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.-E.; Kim, K.H.; Kang, N.J. Beneficial effects of Marine Algae-Derived carbohydrates for skin health. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minhas, L.A.; Kaleem, M.; Farooqi, H.M.U.; Kausar, F.; Waqar, R.; Bhatti, T.; Aziz, S.; Jung, D.W.; Mumtaz, A.S. Algae-derived bioactive compounds as potential pharmaceuticals for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review. Algal Res. 2024, 78, 103396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, R.; Devi, K.P. Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticancer potential of natural bioactive compounds from seaweeds. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 113–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppusamy, S.; Rajauria, G.; Fitzpatrick, S.; Lyons, H.; McMahon, H.; Curtin, J.; Tiwari, B.K.; O’Donnell, C. Biological Properties and Health-Promoting Functions of Laminarin: A Comprehensive Review of preclinical and Clinical studies. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Beltagi, H.S.; Mohamed, A.A.; Mohamed, H.I.; Ramadan, K.M.A.; Barqawi, A.A.; Mansour, A.T. Phytochemical and potential properties of seaweeds and their recent applications: A review. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias, D.; Guillen, J.; Duteil, O.; Garcia-Gorriz, E.; Ferreira-Cordeiro, N.; Miladinova, S.; Parn, O.; Piroddi, C.; Polimene, L.; Serpetti, N.; et al. Assessing the potential for seaweed cultivation in EU seas through an integrated modelling approach. Aquaculture 2024, 594, 741353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Q.; Shen, H.; Yang, Y.; Liu, P.; Dong, Y. Environmental benefits of macroalgae products: A case study of agar based on life cycle assessment. Algal Res. 2024, 78, 103384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillias, S.; Cottrell, R.S.; Kelly, R.; O’Brien, K.R.; Adams, J.; Bellgrove, A.; Kelly, B.; Kilpatrick, C.; Layton, C.; Macleod, C.; et al. Expert perceptions of seaweed farming for sustainable development. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 368, 133052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Poza, S.; Pacheco, D.; Cotas, J.; Marques, J.C.; Pereira, L.; Gonçalves, A.M.M. Marine macroalgae as a feasible and complete resource to address and promote Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2022, 18, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuppaladadiyam, A.K.; Prinsen, P.; Raheem, A.; Luque, R.; Zhao, M. Sustainability Analysis of Microalgae Production Systems: A Review on Resource with Unexploited High-Value Reserves. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 14031–14049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, J.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, R.; Ma, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Integrated marine microalgae biorefineries for improved bioactive compounds: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 817, 152895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaat, L.M.; Burg, S.W.K.v.D.; Ketelaar, T.; Koppenberg, M.; Möhring, N.; Meuwissen, M.P.M. Prospective seaweed systems for North-West European waters. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2025, 82, fsaf010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, A.; Entrena-Barbero, E.; Ilmjärv, T.; Paoli, R.; Romagnoli, F.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T. Conceptual design and environmental evaluation of the Biorefinery approach for R-phycoerythrin extraction and purification. New Biotechnol. 2025, 86, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundarraj, D.K.; Majumder, A.; Suhail Haq, R.; Eswar, I.; Shek, M.I.S. Spore-Based seaweed propagation for germplasm selection and cultivation. In Biotechnological Interventions to Aid Commercial Seaweed Farming; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2025; pp. 257–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wakisaka, M.; Omura, T.; Yang, Z.; Yin, Y.; Fang, W. Advances in industrial harvesting techniques for edible microalgae: Recent insights into sustainable, efficient methods and future directions. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 436, 140626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechsiri, J.S. Sustainability of microalgae-based industrial processes. In Sustainable Industrial Processes Based on Microalgae; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotze, H.K.; Milewski, I.; Fast, J.; Kay, L.; Worm, B. Ecosystem-based management of seaweed harvesting. Bot. Mar. 2019, 62, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Yarish, C. Mass production of marine macroalgae. In Encyclopedia of Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 2236–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margal, P.B.; Thakare, R.S.; Kamble, B.M.; Patil, V.S.; Patil, K.B.; Titirmare, N.S. Effect of seaweed extracts on crop growth and soil: A review. J. Exp. Agric. Int. 2023, 45, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebök, S.; Herppich, W.B.; Hanelt, D. Development of an innovative ring-shaped cultivation system for a land-based cultivation of marine macroalgae. Aquac. Eng. 2017, 77, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eluvathingal; Aleena, B.; Amitha, T.V.; Rosario, J.; Carolin, J. A review on Potentiality of marine algae in environmental sustainability. Int. J. Pharm. Bio-Med. Sci. 2023, 3, 501–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Yang, Y.; Xie, S. The ecological effect of large-scale coastal natural and cultivated seaweed litter decay processes: An overview and perspective. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 341, 118091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, J.; Andersen, R.A.; Kawachi, M.; Millar, A.J.K. Endangered algal species and how to protect them. Phycologia 2009, 48, 423–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornwall, C.E.; Nelson, W.A.; Aguirre, J.D.; Blain, C.O.; Coyle, L.; D’Archino, R.; Desmond, M.J.; Hepburn, C.D.; Liggins, L.; Shears, N.T.; et al. Predicting the impacts of climate change on New Zealand’s seaweed-based ecosystems. N. Z. J. Bot. 2023, 63, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samoraj, M.; Çalış, D.; Trzaska, K.; Mironiuk, M.; Chojnacka, K. Advancements in algal biorefineries for sustainable agriculture: Biofuels, high-value products, and environmental solutions. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2024, 58, 103224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, P.; Somers, N.K.; Thilsted, S.H. Seaweed’s contribution to food security in low- and middle-income countries: Benefits from production, processing and trade. Glob. Food Secur. 2023, 37, 100686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, K.G.; Abomohra, A.; French, C.E.; Zaky, A.S. Recent advances in seaweed biorefineries and assessment of their potential for carbon capture and storage. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeragurunathan, V.; Ramalingam, D.; Bhayani, A.; Grace, P.G. Constraints and Challenges on Large-Scale cultivation of economically important algae. In Algal Biotechnology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, A.; Shanmugam, M. Seaweeds as agricultural crops in India: New vistas. In Innovative Saline Agriculture; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 441–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Den Burg, S.; Wakenge, C.; Berkhout, P. Economic Prospects for Large-scale Seaweed Cultivation in the North Sea. Wagening. Econ. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, R.; Gachon, C.M.M.; Rebours, C. Seaweed cultivation: Potential and challenges of crop domestication at an unprecedented pace. New Phytol. 2015, 206, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehariya, S.; Goswami, R.K.; Karthikeysan, O.P.; Verma, P. Microalgae for high-value products: A way towards green nutraceutical and pharmaceutical compounds. Chemosphere 2021, 280, 130553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Lin, H.; Jiang, P. Advances in genetic engineering of marine algae. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 1602–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanegas, C.H.; Bartlett, J. Green energy from marine algae: Biogas production and composition from the anaerobic digestion of Irish seaweed species. Environ. Technol. 2013, 34, 2277–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, M.; Hps, A.K.; Sabaruddin, F.A.; Bairwan, R.D.; Oyekanmi, A.A.; Alfatah, T.; Danish, M.; Mistar, E.M.; Abdullah, C.K. Microbial treatment for nanocellulose extraction from marine algae and its applications as sustainable functional material. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 16, 100811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, C.; Scott-Buechler, C.; Hausner, A.; Johnson, Z.; Lei, X.G.; Huntley, M. Transforming the Future of Marine Aquaculture: A Circular Economy approach. Oceanography 2022, 35, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, C.W. Bioeconomics of the ocean. Bioscience 1981, 31, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarasinghe, H.S.; Gunathilaka, T.L.; Jayasooriya, R.G.P.T.; Samarakoon, K.W. Impact of Algal Research and its Potential for Industrial Applications: A Review. Sri Lankan J. Biol. 2023, 8, 4–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhan, K.; Iffat, Z.A. Seaweed biotechnology: An answer to environmental issues and human health problems. In Seaweed Biotechnology; Apple Academic Press: Waretown, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 311–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishshanka, G.K.S.H.; Anthonio, R.A.D.P.; Nimarshana, P.H.V.; Ariyadasa, T.U.; Chang, J.-S. Marine microalgae as sustainable feedstock for multi-product biorefineries. Biochem. Eng. J. 2022, 187, 108593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, M.; Goecke, F.; Bhadury, P. Minireview: Algal natural compounds and extracts as antifoulants. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 30, 1859–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, M.E.; Firth, L.B.; Foggo, A. Victim of changes? Marine macroalgae in a changing world. Ann. Bot. 2023, 133, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renn, D. Biotechnology and the red seaweed polysaccharide industry: Status, needs and prospects. Trends Biotechnol. 1997, 15, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priya, K.S. Exploring the Bioactive Potential of Marine Algae: Insights from Phytochemical Analysis, GC-MS Profiling, and Antioxidant Evaluation. Pharmacogn. J. 2024, 16, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fal, S.; Smouni, A.; Arroussi, H.E. Integrated microalgae-based biorefinery for wastewater treatment, industrial CO2 sequestration and microalgal biomass valorization: A circular bioeconomy approach. Environ. Adv. 2023, 12, 100365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz-González, N.; Aguilar-Estrada, L.G.; Acosta-Calderón, J.A.; Álvarez-Castillo, L.; Arriola-Álvarez, F. Biodiversity of epiphytic marine macroalgae in Mexico: Composition and current status. Bot. Mar. 2023, 66, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.; Venmathi Maran, B.A.; Shaleh, S.; Zuldin, W.; Gnanaraj, C.; Yong, Y. Therapeutic Potential and nutraceutical Profiling of North Bornean seaweeds: A review. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-García, C.; Riosmena-Rodríguez, R.; Wysor, B.; Tejada, O.L.; Cortés, J. Checklist of the Pacific marine macroalgae of Central America. Bot. Mar. 2011, 54, 53–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soratur, A.; Venmathi Maran, B.A.; Kamarudin, A.S.; Rodrigues, K.F. Microbial Diversity and Nitrogen Cycling in Peat and Marine Soils: A Review. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 15, 806–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, M.S.; Gangadaran, P.; Jackson, A.; Venmathi Maran, B.A.; Kurita, T.; Ahn, B.-C. Deep Neural Network Models for Colon Cancer Screening. Cancers 2022, 14, 3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venmathi Maran, B.A.; Josmeh, D.; Tan, J.K.; Yong, Y.S.; Shah, M.D. Efficacy of the Aqueous Extract of Azadirachta indica Against the Marine Parasitic Leech and Its Phytochemical Profiling. Molecules 2021, 26, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).