Burkitt Lymphoma Incidence in Five Continents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Age-Standardized Incidence Rates
2.2. Age-Specific Incidence Rates
3. Results
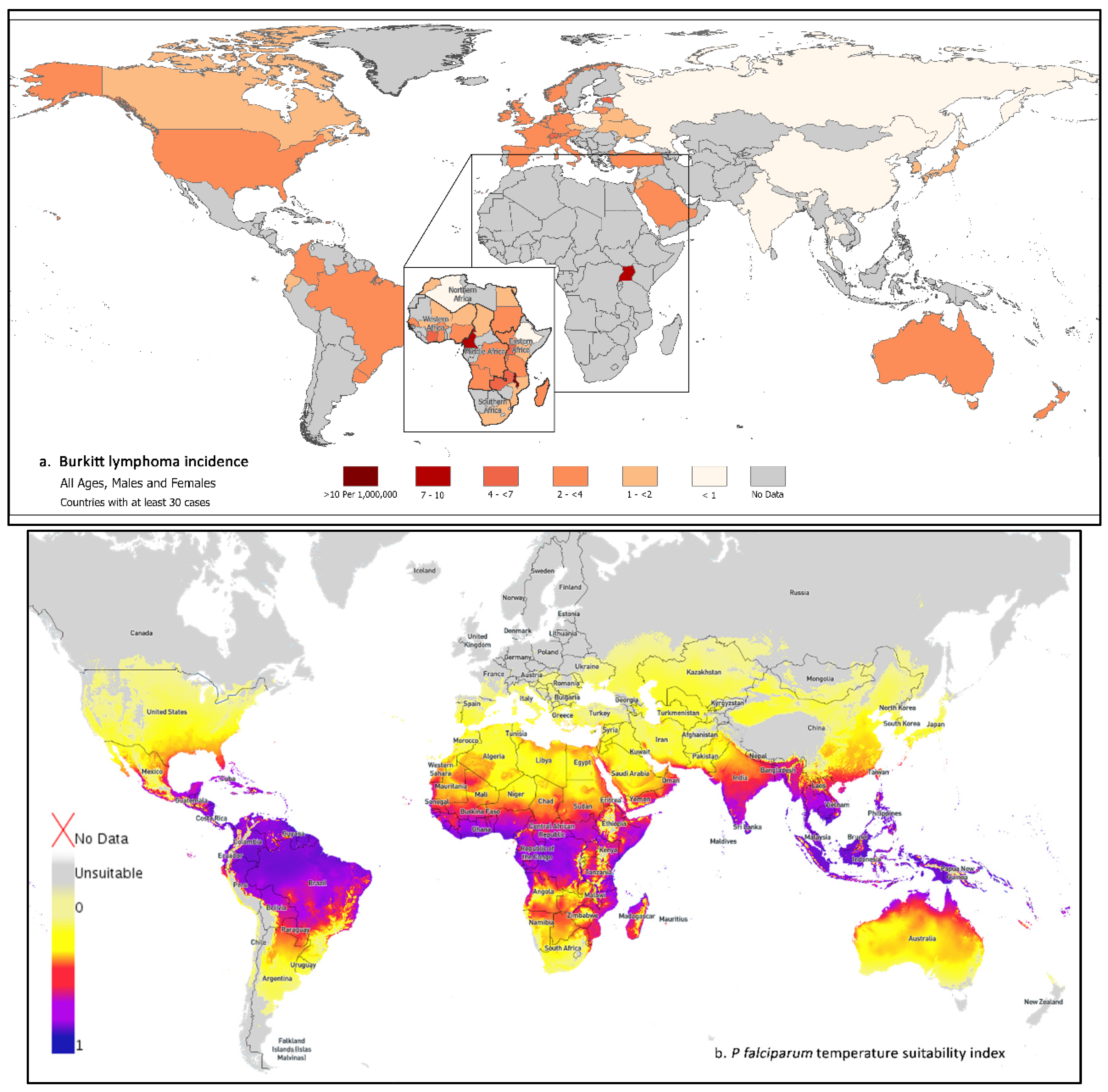
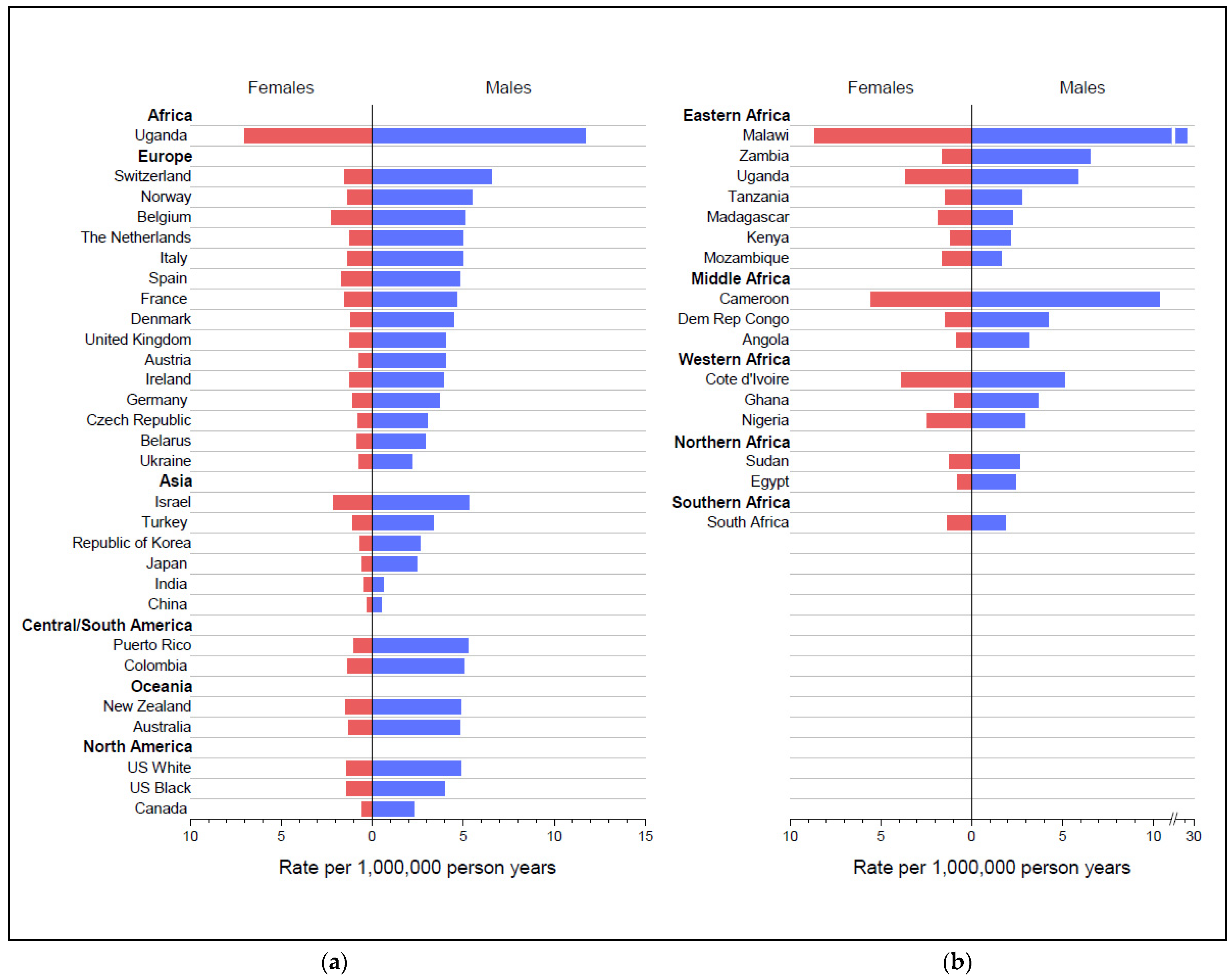
3.1. Worldwide Geographic Patterns of BL
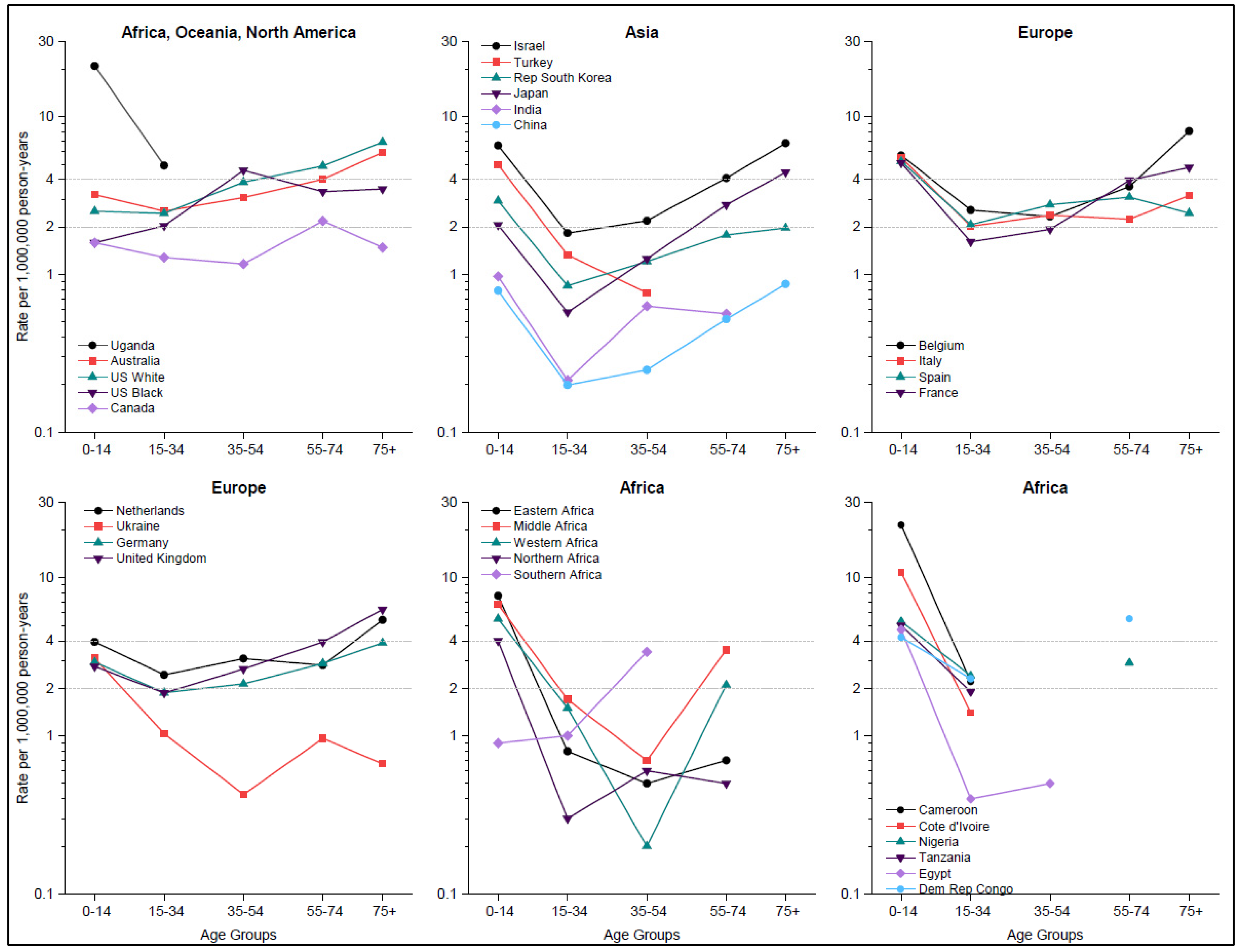
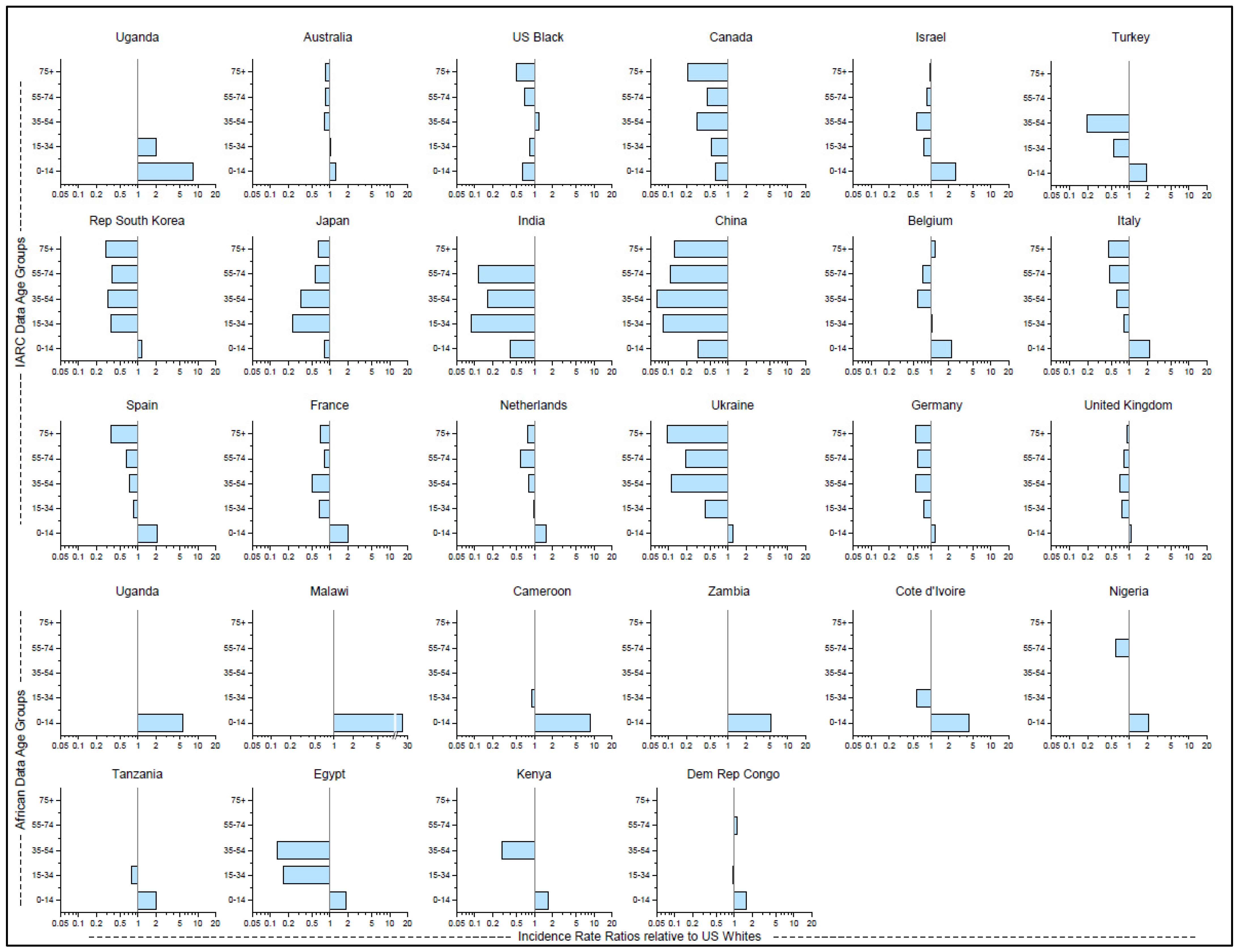
3.2. Age-Specific Incidence Rates Relative to BL Rates in US White Individuals
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basso, K.; Dalla-Favera, R. Germinal centres and B cell lymphomagenesis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkitt, D. A sarcoma involving the jaws in African children. Br. J. Surg. 1958, 46, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutt, M.S.; Wright, D.H. Central African lymphomas. Lancet 1963, 1, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.H. Cytology and histochemistry of the Burkitt lymphoma. Br. J. Cancer 1963, 17, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorfman, R.F. Childhood Lymphosarcoma in St. Louis, Missouri, Clinically and Histologically Resembling Burkitt’s Tumor. Cancer 1965, 18, 418–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkitt, D. Burkitt’s lymphoma outside the known endemic areas of Africa and New Guinea. Int. J. Cancer 1967, 2, 562–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.H. Burkitt’s tumour in England. A comparison with childhood lymphosarcoma. Int. J. Cancer 1966, 1, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, K.; Burkitt, D.P.; Bassett, D.J.; Cooke, R.A.; Biddulph, J. Burkitt Lymphoma in Papua New Guinea. Br. J. Cancer 1967, 21, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Conor, G.T.; Davies, J.N. Malignant tumors in African children. With special reference to malignant lymphoma. J. Pediatr. 1960, 56, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Conor, G.T. Malignant lymphoma in African children. II. A pathological entity. Cancer 1961, 14, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.B.; O’Keefe, C.D. Sarcoma of the ovary with unusual oral metastases. Ann. Surg. 1928, 87, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berard, C. Histopathological definition of Burkitt’s tumour. Bull World Health Organ 1969, 40, 601–607. [Google Scholar]
- Burkitt, D. A tumour syndrome affecting children in tropical Africa. Postgrad. Med. J. 1962, 38, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkitt, D. A Children’s Cancer with Geographical Limitations. Cancer Prog. 1963, 92, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burkitt, D. A “tumour safari” in East and Central Africa. Br. J. Cancer 1962, 16, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalldorf, G.; Linsell, C.A.; Barnhart, F.E.; Martyn, R. An Epidemiologic Approach to the Lymphomas of African Children and Burkitt’s Sacroma of the Jaws. Perspect. Biol. Med. 1964, 7, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, M.A.; Achong, B.G.; Barr, Y.M. Virus Particles in Cultured Lymphoblasts from Burkitt’s Lymphoma. Lancet 1964, 1, 702–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henle, G.; Henle, W.; Diehl, V. Relation of Burkitt’s tumor-associated herpes-ytpe virus to infectious mononucleosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1968, 59, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geser, A.; Brubaker, G.; Olwit, G.W. The frequency of Epstein-Barr virus infection and Burkitt’s lymphoma at high and low altitudes in East Africa. Rev. Epidemiol. Sante Publique 1980, 28, 307–321. [Google Scholar]
- Bouvard, V.; Baan, R.A.; Grosse, Y.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Benbrahim-Tallaa, L.; Guha, N.; Straif, K. Carcinogenicity of malaria and of some polyomaviruses. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkitt, D.P. Etiology of Burkitt’s lymphoma—An alternative hypothesis to a vectored virus. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1969, 42, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Torgbor, C.; Awuah, P.; Deitsch, K.; Kalantari, P.; Duca, K.A.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. A multifactorial role for P. falciparum malaria in endemic Burkitt’s lymphoma pathogenesis. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMaio, D.; Emu, B.; Goodman, A.L.; Mothes, W.; Justice, A. Cancer Microbiology. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2021, 114, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, J.L.; Drew, W.L.; Miner, R.C.; Mintz, L.; Rosenbaum, E.; Gershow, J.; Lennette, E.T.; Greenspan, J.; Shillitoe, E.; Beckstead, J.; et al. Outbreak of Burkitt’s-like lymphoma in homosexual men. Lancet 1982, 2, 631–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control. Diffuse, undifferentiated non-Hodgkins lymphoma among homosexual males—United States. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1982, 31, 277–279. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, K.G.; John, W.M.D.; Ward, M.D.; Slutsker, M.D.L.; James, W.M.P.H.; Buehler, M.D.; Jaffe, M.D.H.W.; Berkelman, M.D.R.L. 1993 revised classification system for HIV infection and expanded surveillance case definition for AIDS among adolescents and adults. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 1992, 41, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolov, G.; Manolova, Y. Marker band in one chromosome 14 from Burkitt lymphomas. Nature 1972, 237, 33–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla-Favera, R.; Bregni, M.; Erikson, J.; Patterson, D.; Gallo, R.C.; Croce, C.M. Human c-myc onc gene is located on the region of chromosome 8 that is translocated in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 7824–7827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oettgen, H.F.; Clifford, P.; Burkitt, D. Malignant Lymphoma Involving the Jaw in African Children—Treatment with Alkylating Agents and Actinomycin-D. Cancer Chemother. Rep. 1963, 28, 25–34. [Google Scholar]
- Oettgen, H.F.; Burkitt, D.; Burchenal, J.H. Malignant lymphoma involving the jaw in African children: Treatment with Methotrexate. Cancer 1963, 16, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkitt, D.; Hutt, M.S.; Wright, D.H. The African Lymphoma: Preliminary Observations on Response to Therapy. Cancer 1965, 18, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.H.; Bennett, J.M.; Berard, C.W.; Ziegler, J.L.; Vogel, C.L.; Sheagren, J.N.; Carbone, P.P. Burkitt’s tumor in the United States. Cancer 1969, 23, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, J.L. Treatment results of 54 American patients with Burkitt’s lymphoma are similar to the African experience. N. Engl. J. Med. 1977, 297, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, J.L. Research projects in Burkitt’s lymphoma. JAMA 1972, 222, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchenal, J.H. Geographic chemotherapy--Burkitt’s tumor as a stalking horse for leukemia: Presidential address. Cancer Res. 1966, 26, 2393–2405. [Google Scholar]
- Risks to Humans. Epstein-Barr Virus and Kaposi’s Sarcoma Herpesvirus/Human Herpesvirus 8. In Proceedings of the IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic, Lyon, France, 17–24 June 1997; Volume 70, pp. 1–492.
- de Martel, C.; Georges, D.; Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Clifford, G.M. Global burden of cancer attributable to infections in 2018: A worldwide incidence analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e180–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkitt, D.P. Observations on the geography of malignant lymphoma. E. Afr. Med. J. 1961, 38, 511–514. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, D.H. Burkitt’s Tumour. A Post-Mortem Study of 50 Cases. Br. J. Surg. 1964, 51, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Conor, G.T.; Rappaport, H.; Smith, E.B. Childhood Lymphoma Resembling “Burkitt Tumor” in the United States. Cancer 1965, 18, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogwang, M.D.; Zhao, W.; Ayers, L.W.; Mbulaiteye, S.M. Accuracy of Burkitt lymphoma diagnosis in constrained pathology settings: Importance to epidemiology. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2011, 135, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leoncini, L.; Raphael, M.; Stein, H.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Kluin, P.M. Burkitt Lymphoma, 4th ed.; International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC): Lyon, France, 2008; pp. 262–264.
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.F.; Ghazawi, F.M.; Le, M.; Lagace, F.; Roy, C.F.; Rahme, E.; Savin, E.; Zubarev, A.; Sasseville, D.; Popradi, G.; et al. Epidemiology of adult and pediatric Burkitt lymphoma in Canada: Sequelae of the HIV epidemic. Curr. Oncol. 2020, 27, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caetano Dos Santos, F.L.; Michalek, I.M.; Wojciechowska, U.; Didkowska, J.; Walewski, J. Improved survival of Burkitt lymphoma/leukemia patients: Observations from Poland, 1999–2020. Ann. Hematol. 2022, 101, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbulaiteye, S.M.; Anderson, W.F.; Bhatia, K.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Linet, M.S.; Devesa, S.S. Trimodal age-specific incidence patterns for Burkitt lymphoma in the United States, 1973–2005. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 1732–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guech-Ongey, M.; Simard, E.P.; Anderson, W.F.; Engels, E.A.; Bhatia, K.; Devesa, S.S.; Mbulaiteye, S.M. AIDS-related Burkitt lymphoma in the United States: What do age and CD4 lymphocyte patterns tell us about etiology and/or biology? Blood 2010, 116, 5600–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerma, E.G.; van Imhoff, G.W.; Appel, I.M.; Veeger, N.J.; Kluin, P.M.; Kluin-Nelemans, J.C. Gender and age-related differences in Burkitt lymphoma--epidemiological and clinical data from The Netherlands. Eur. J. Cancer 2004, 40, 2781–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orem, J.; Mbidde, E.K.; Lambert, B.; de Sanjose, S.; Weiderpass, E. Burkitt’s lymphoma in Africa, a review of the epidemiology and etiology. Afr. Health Sci. 2007, 7, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hammerl, L.; Colombet, M.; Rochford, R.; Ogwang, D.M.; Parkin, D.M. The burden of Burkitt lymphoma in Africa. Infect. Agents Cancer 2019, 14, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de-The, G. Is Burkitt’s lymphoma related to perinatal infection by Epstein-Barr virus? Lancet 1977, 1, 335–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwanda, O.W.; Rochford, R.; Moormann, A.M.; Macneil, A.; Whalen, C.; Wilson, M.L. Burkitt’s lymphoma in Kenya: Geographical, age, gender and ethnic distribution. East Afr. Med. J. 2004, S68–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkitt, D.P. Epidemiology of Brukitts Lymphoma. Proc. R. Soc. Med. Lond. 1971, 64, 909. [Google Scholar]
- Muchengeti, M.; Bartels, L.; Olago, V.; Dhokotera, T.; Chen, W.C.; Spoerri, A.; Rohner, E.; Bütikofer, L.; Ruffieux, Y.; Singh, E.; et al. Cohort profile: The South African HIV Cancer Match (SAM) Study, a national population-based cohort. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e053460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbulaiteye, S.M.; Katabira, E.T.; Wabinga, H.; Parkin, D.M.; Virgo, P.; Ochai, R.; Workneh, M.; Coutinho, A.; Engels, E.A. Spectrum of cancers among HIV-infected persons in Africa: The Uganda AIDS-Cancer Registry Match Study. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akarolo-Anthony, S.N.; Maso, L.D.; Igbinoba, F.; Mbulaiteye, S.M.; Adebamowo, C.A. Cancer burden among HIV-positive persons in Nigeria: Preliminary findings from the Nigerian AIDS-cancer match study. Infect. Agent. Cancer 2014, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godbole, S.V.; Nandy, K.; Gauniyal, M.; Nalawade, P.; Sane, S.; Koyande, S.; Toyama, J.; Hegde, A.; Virgo, P.; Bhatia, K.; et al. HIV and cancer registry linkage identifies a substantial burden of cancers in persons with HIV in India. Medicine 2016, 95, e4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbulaiteye, S.M.; Anderson, W.F.; Ferlay, J.; Bhatia, K.; Chang, C.; Rosenberg, P.S.; Devesa, S.S.; Parkin, D.M. Pediatric, elderly, and emerging adult-onset peaks in Burkitt’s lymphoma incidence diagnosed in four continents, excluding Africa. Am. J. Hematol. 2012, 87, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.C.M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Zanetti, R.; Ferlay, J. (Eds.) Cancer Incidence in Five Continents, Vol. XI (Electronic Version); International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2017.
- International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problem, 10th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, The Switzerland, 1992.
- Doll, R.; Payne, P.; Waterhouse, J.A.H. Cancer Incidence In Five Continents; Union Internationale Contre le Cancer: Geneva, The Switzerland, 1966; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Mbulaiteye, S.M.; Anderson, W.F. Age-related heterogeneity of Burkitt lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.-M.; Liu, H.; Chin, P.-J.; Li, B.; Hung, G.-C.; Tsai, S.; Otim, I.; Legason, I.D.; Ogwang, M.D.; Reynolds, S.J.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus in Burkitt Lymphoma in Africa Reveals a Limited Set of Whole Genome and LMP-1 Sequence Patterns: Analysis of Archival Datasets and Field Samples From Uganda, Tanzania, and Kenya. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 812224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bosch, C.A. Is endemic Burkitt’s lymphoma an alliance between three infections and a tumour promoter? Lancet Oncol. 2004, 5, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aka, P.; Vila, M.C.; Jariwala, A.; Nkrumah, F.; Emmanuel, B.; Yagi, M.; Palacpac, N.M.; Periago, M.V.; Neequaye, J.; Kiruthu, C.; et al. Endemic Burkitt lymphoma is associated with strength and diversity of Plasmodium falciparum malaria stage-specific antigen antibody response. Blood 2013, 122, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravell, J.; Otim, I.; Nabalende, H.; Legason, I.D.; Reynolds, S.J.; Ogwang, M.D.; Ndugwa, C.M.; Marshall, V.; Whitby, D.; Goedert, J.J.; et al. Plasma magnesium is inversely associated with Epstein-Barr virus load in peripheral blood and Burkitt lymphoma in Uganda. Cancer Epidemiol. 2018, 52, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Linet, M.S.; Brown, L.M.; Mbulaiteye, S.M.; Check, D.; Ostroumova, E.; Landgren, A.; Devesa, S.S. International long-term trends and recent patterns in the incidence of leukemias and lymphomas among children and adolescents ages 0–19 years. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 1862–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkitt, D. A children’s cancer dependent on climatic factors. Nature 1962, 194, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kafuko, G.W.; Burkitt, D.P. Burkitt’s lymphoma and malaria. Int. J. Cancer 1970, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, M.H.; Snow, R.W.; le Sueur, D. A climate-based distribution model of malaria transmission in sub-Saharan Africa. Parasitol. Today 1999, 15, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkitt, D.; Wright, D. Geographical and tribal distribution of the African lymphoma in Uganda. Br. Med. J. 1966, 1, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbulaiteye, S.M. Burkitt Lymphoma: Beyond discoveries. Infect. Agent. Cancer 2013, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, B.; Kawira, E.; Ogwang, M.D.; Wabinga, H.; Magatti, J.; Nkrumah, F.; Neequaye, J.; Bhatia, K.; Brubaker, G.; Biggar, R.J.; et al. African Burkitt Lymphoma: Age-Specific Risk and Correlations with Malaria Biomarkers. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 84, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisue, N.; Chagaluka, G.; Palacpac, N.M.Q.; Johnston, W.T.; Mutalima, N.; Peprah, S.; Bhatia, K.; Borgstein, E.; Liomba, G.N.; Kamiza, S.; et al. Assessment of Mixed Plasmodium falciparumsera5 Infection in Endemic Burkitt Lymphoma: A Case-Control Study in Malawi. Cancers 2021, 13, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, W.T.; Mutalima, N.; Sun, D.; Emmanuel, B.; Bhatia, K.; Aka, P.; Wu, X.; Borgstein, E.; Liomba, G.N.; Kamiza, S.; et al. Relationship between Plasmodium falciparum malaria prevalence, genetic diversity and endemic Burkitt lymphoma in Malawi. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Band, G.; Leffler, E.M.; Jallow, M.; Sisay-Joof, F.; Ndila, C.M.; Macharia, A.W.; Hubbart, C.; Jeffreys, A.E.; Rowlands, K.; Nguyen, T.; et al. Malaria protection due to sickle haemoglobin depends on parasite genotype. Nature 2022, 602, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Diaz, E.; Ranford-Cartwright, L. Evolutionary race: Malaria evolves to evade sickle cell protection. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Cardoso, J.D.C.; Chies, J.A.B. Variability in human attractiveness to mosquitoes. Curr. Res. Parasitol. Vector Borne Dis. 2021, 1, 100058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumba, P.O.; Kabiru, E.W.; Namuyenga, E.; Fiore, N.; Otieno, R.O.; Moormann, A.M.; Orago, A.S.; Rosenbaum, P.F.; Rochford, R. Microgeographic variations in Burkitt’s lymphoma incidence correlate with differences in malnutrition, malaria and Epstein-Barr virus. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macmahon, B. Epidemiological evidence of the nature of Hodgkin’s disease. Cancer 1957, 10, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, L.A.G.; Devesa, S.S. Cancer incidence, mortality, and patient survival in the United States. In Cancer Epidemiology and Prevention, 3rd ed.; Schottenfeld, D., Fraumeni, J.F., Jr., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 139–167. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, J.; John, K.; Staiger, A.M.; Rosenwald, A.; Kurz, K.; Michgehl, U.; Ott, G.; Franzenburg, S.; Kohler, C.; Finger, J.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus status of sporadic Burkitt lymphoma is associated with patient age and mutational features. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, B.M.; Gerhard, D.S.; Jiang, A.; Griner, N.B.; Abramson, J.S.; Alexander, T.B.; Allen, H.; Ayers, L.W.; Bethony, J.M.; Bhatia, K.; et al. Genome-wide discovery of somatic coding and noncoding mutations in pediatric endemic and sporadic Burkitt lymphoma. Blood 2019, 133, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, N.; Dreval, K.; Gerhard, D.S.; Hilton, L.K.; Abramson, J.S.; Bartlett, N.L.; Bethony, J.; Bowen, J.; Bryan, A.C.; Casper, C.; et al. Genetic Subgroups Inform on Pathobiology in Adult and Pediatric Burkitt Lymphoma. Medrxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbulaiteye, S.M.; Biggar, R.J.; Bhatia, K.; Linet, M.S.; Devesa, S.S. Sporadic childhood Burkitt lymphoma incidence in the United States during 1992-2005. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2009, 53, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osunkoya, B.O. Burkitt’s Lymphoma. In Critical Reviews in Tropical Medicine: Volume 1; Chandra, R.K., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1982; pp. 367–393. [Google Scholar]
- Dunford, A.; Weinstock, D.M.; Savova, V.; Schumacher, S.E.; Cleary, J.P.; Yoda, A.; Sullivan, T.J.; Hess, J.M.; Gimelbrant, A.A.; Beroukhim, R.; et al. Tumor-suppressor genes that escape from X-inactivation contribute to cancer sex bias. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Blain, A.E.; Newman, A.M.; Zaka, M.; Chagaluka, G.; Adlar, F.R.; Offor, U.T.; Broadbent, C.; Chaytor, L.; Whitehead, A.; et al. Sporadic and endemic Burkitt lymphoma have frequent FOXO1 mutations but distinct hotspots in the AKT recognition motif. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 2118–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, D.J.; Lucas, T.C.D.; Nguyen, M.; Nandi, A.K.; Bisanzio, D.; Battle, K.E.; Cameron, E.; Twohig, K.A.; Pfeffer, D.A.; Rozier, J.A.; et al. Mapping the global prevalence, incidence, and mortality of Plasmodium falciparum, 2000–2017: A spatial and temporal modelling study. Lancet 2019, 394, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Lourenco, J.; Kraemer, M.; He, Q.; Cazelles, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; et al. The relationship between rising temperatures and malaria incidence in Hainan, China, from 1984 to 2010: A longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Planet Health 2022, 6, e350–e358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de-The, G.; Day, N.E.; Geser, A.; Lavoue, M.F.; Ho, J.H.; Simons, M.J.; Sohier, R.; Tukei, P.; Vonka, V.; Zavadova, H. Sero-epidemiology of the Epstein-Barr virus: Preliminary analysis of an international study—A review. IARC Sci. Publ. 1975, 11, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- de-The, G.; Lavoue, M.F.; Muenz, L. Differences in EBV antibody titres of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma originating from high, intermediate and low incidence areas. IARC Sci. Publ. 1978, 20, 471–481. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.C. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Epidemiology and dietary factors. IARC Sci. Publ. 1991, 105, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, Y.; Meehan, M.T.; Burrows, S.R.; Doolan, D.L.; Miles, J.J. Estimating the global burden of Epstein-Barr virus-related cancers. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol 2022, 148, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, L.; Riquelme, I.; Buchegger, K.; Abanto, M.; Ili, C.; Brebi, P. A reliable Epstein-Barr Virus classification based on phylogenomic and population analyses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, R.; Correia, S.; Wegner, F.; Venturini, C.; Palser, A.; White, R.E.; Kellam, P.; Breuer, J.; Farrell, P.J. Essential role of inverted repeat in Epstein-Barr virus IR-1 in B cell transformation; geographical variation of the viral genome. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2019, 374, 20180299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, S.; Bridges, R.; Wegner, F.; Venturini, C.; Palser, A.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Cohen, J.I.; Lorenzetti, M.A.; Bassano, I.; White, R.E.; et al. Sequence Variation of Epstein-Barr Virus: Viral Types, Geography, Codon Usage, and Diseases. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e01132-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, S.S.; Fu, K.; Wright, G.W.; Lam, L.T.; Kluin, P.; Boerma, E.J.; Greiner, T.C.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Rosenwald, A.; Ott, G.; et al. Molecular diagnosis of Burkitt’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 2431–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, R.; Young, R.M.; Ceribelli, M.; Jhavar, S.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, M.; Wright, G.; Shaffer, A.L.; Hodson, D.J.; Buras, E.; et al. Burkitt lymphoma pathogenesis and therapeutic targets from structural and functional genomics. Nature 2012, 490, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.; Schlesner, M.; Hoffmann, S.; Kreuz, M.; Leich, E.; Burkhardt, B.; Rosolowski, M.; Ammerpohl, O.; Wagener, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; et al. Recurrent mutation of the ID3 gene in Burkitt lymphoma identified by integrated genome, exome and transcriptome sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1316–1320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dunleavy, K.; Pittaluga, S.; Shovlin, M.; Steinberg, S.M.; Cole, D.; Grant, C.; Widemann, B.; Staudt, L.M.; Jaffe, E.S.; Little, R.F.; et al. Low-intensity therapy in adults with Burkitt’s lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1915–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, E.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Harris, N.L.; Pileri, S.; Stein, H.; Jaffe, E.S. The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid neoplasms and beyond: Evolving concepts and practical applications. Blood 2011, 117, 5019–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Diebold, J.; Flandrin, G.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K.; Vardiman, J.; Lister, T.A.; Bloomfield, C.D. The World Health Organization classification of neoplastic diseases of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Report of the Clinical Advisory Committee meeting, Airlie House, Virginia, November, 1997. Ann. Oncol. 1999, 10, 1419–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Stein, H.; Banks, P.M.; Chan, J.K.; Cleary, M.L.; Delsol, G.; De Wolf-Peeters, C.; Falini, B.; Gatter, K.C.; et al. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: A proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group. Blood 1994, 84, 1361–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.d.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, E.S.; Harris, N.L.; Diebold, J.; Muller-Hermelink, H.K. World Health Organization classification of neoplastic diseases of the hematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. A progress report. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1999, 111, S8–S12. [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Cook, J.R. As the world turns, evolving lymphoma classifications-past, present and future. Hum. Pathol. 2020, 95, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathwani, B.N.; Sasu, S.J.; Ahsanuddin, A.N.; Hernandez, A.M.; Drachenberg, M.R. The critical role of histology in an era of genomics and proteomics: A commentary and reflection. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2007, 14, 375–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naresh, K.N.; Ibrahim, H.A.H.; Lazzi, S.; Rince, P.; Onorati, M.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Bilhou-Nabera, C.; Amen, F.; Reid, A.; Mawanda, M.; et al. Diagnosis of Burkitt lymphoma using an algorithmic approach—Applicable in both resource-poor and resource-rich countries. Br. J. Haematol. 2011, 154, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orem, J.; Sandin, S.; Weibull, C.E.; Odida, M.; Wabinga, H.; Mbidde, E.; Wabwire-Mangen, F.; Meijer, C.J.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Weiderpass, E. Agreement between diagnoses of childhood lymphoma assigned in Uganda and by an international reference laboratory. Clin. Epidemiol. 2012, 4, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Westmoreland, K.D.; Montgomery, N.D.; Stanley, C.C.; El-Mallawany, N.K.; Wasswa, P.; van der Gronde, T.; Mtete, I.; Butia, M.; Itimu, S.; Chasela, M.; et al. Plasma Epstein-Barr virus DNA for pediatric Burkitt lymphoma diagnosis, prognosis and response assessment in Malawi. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 2509–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, R.H., Jr.; Levine, P.H.; Ziegler, J.L.; Berard, C. Letter: What is Burkitt’s lymphoma? Lancet 1974, 2, 1268–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.H. What is Burkitt’s lymphoma and when is it endemic? Blood 1999, 93, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderuccio, J.P.; Olszewski, A.J.; Evens, A.M.; Collins, G.P.; Danilov, A.V.; Bower, M.; Jagadeesh, D.; Zhu, C.; Sperling, A.; Kim, S.H.; et al. HIV-associated Burkitt lymphoma: Outcomes from a US-UK collaborative analysis. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2852–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewski, A.J.; Jakobsen, L.H.; Collins, G.P.; Cwynarski, K.; Bachanova, V.; Blum, K.A.; Boughan, K.M.; Bower, M.; Dalla Pria, A.; Danilov, A.; et al. Burkitt Lymphoma International Prognostic Index. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evens, A.M.; Danilov, A.; Jagadeesh, D.; Sperling, A.; Kim, S.H.; Vaca, R.; Wei, C.; Rector, D.; Sundaram, S.; Reddy, N.; et al. Burkitt lymphoma in the modern era: Real-world outcomes and prognostication across 30 US cancer centers. Blood 2021, 137, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudson, A.G., Jr. Heredity and human cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 1974, 77, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.P.; Fraumeni, J.F., Jr. Rhabdomyosarcoma in children: Epidemiologic study and identification of a familial cancer syndrome. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1969, 43, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Global Retinoblastoma Study, G.; Fabian, I.D.; Abdallah, E.; Abdullahi, S.U.; Abdulqader, R.A.; Adamou Boubacar, S.; Ademola-Popoola, D.S.; Adio, A.; Afshar, A.R.; Aggarwal, P.; et al. Global Retinoblastoma Presentation and Analysis by National Income Level. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Zou, Z.Q.; Pirollo, K.; Blattner, W.; Chang, E.H. Germ-line transmission of a mutated p53 gene in a cancer-prone family with Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Nature 1990, 348, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malkin, D.; Li, F.P.; Strong, L.C.; Fraumeni, J.F., Jr.; Nelson, C.E.; Kim, D.H.; Kassel, J.; Gryka, M.A.; Bischoff, F.Z.; Tainsky, M.A.; et al. Germ line p53 mutations in a familial syndrome of breast cancer, sarcomas, and other neoplasms. Science 1990, 250, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablin, A.; Stephens, B.G.; Hirata, T.; Wilson, K.; Williams, H.E. Nephropathy, xanthinuria, and orotic aciduria complicating Burkitt’s lymphoma treated with chemotherapy and allopurinol. Metabolism 1972, 21, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbulaiteye, S.M.; Talisuna, A.O.; Ogwang, M.D.; McKenzie, F.E.; Ziegler, J.L.; Parkin, D.M. African Burkitt’s lymphoma: Could collaboration with HIV-1 and malaria programmes reduce the high mortality rate? Lancet 2010, 375, 1661–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, R.R.; Kinyera, T.; Otim, I.; Sampson, J.N.; Nabalende, H.; Legason, I.D.; Stone, J.; Ogwang, M.D.; Reynolds, S.J.; Kerchan, P.; et al. Plasma EBV DNA: A Promising Diagnostic Marker for Endemic Burkitt Lymphoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 804083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Region | Country 1 | Total Cases 2 | Total Rate 3 | Incidence Rate Ratio 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| International CI5(XI) data for 2008–2012: | ||||
| Africa | ||||
| Uganda | 124 | 9.28 | 2.91 | |
| Central/South America | ||||
| Colombia | 60 | 3.19 | 1.00 | |
| Puerto Rico | 60 | 3.13 | 0.98 | |
| Uruguay | 48 | 2.82 | 0.88 | |
| Brazil | 41 | 2.23 | 0.70 | |
| Ecuador | 33 | 1.15 | 0.36 | |
| North America | ||||
| US white people (referent) | 4482 | 3.19 | 1.00 | |
| United States (US) | 5405 | 3.09 | 0.97 | |
| US black people | 611 | 2.68 | 0.84 | |
| Canada | 194 | 1.47 | 0.46 | |
| Asia | ||||
| Israel | 143 | 3.77 | 1.18 | |
| Saudi Arabia: Saudi | 54 | 2.41 | 0.76 | |
| Turkey | 115 | 2.30 | 0.72 | |
| Republic of Korea | 376 | 1.72 | 0.54 | |
| Japan | 276 | 1.55 | 0.49 | |
| Jordan: Jordanians | 39 | 1.17 | 0.37 | |
| Thailand | 44 | 0.88 | 0.28 | |
| India | 128 | 0.59 | 0.18 | |
| China | 120 | 0.45 | 0.14 | |
| Europe | ||||
| Estonia | 35 | 5.67 | 1.78 | |
| Switzerland | 96 | 4.12 | 1.29 | |
| Belgium | 199 | 3.72 | 1.16 | |
| Norway | 90 | 3.49 | 1.10 | |
| Spain | 153 | 3.34 | 1.05 | |
| Italy | 347 | 3.23 | 1.01 | |
| The Netherlands | 265 | 3.16 | 0.99 | |
| France | 172 | 3.13 | 0.98 | |
| Lithuania | 37 | 3.00 | 0.94 | |
| Denmark | 77 | 2.92 | 0.91 | |
| United Kingdom | 950 | 2.68 | 0.84 | |
| Ireland | 67 | 2.64 | 0.83 | |
| Austria | 99 | 2.44 | 0.77 | |
| Germany | 676 | 2.43 | 0.76 | |
| Czech Republic | 91 | 1.97 | 0.62 | |
| Belarus | 70 | 1.96 | 0.61 | |
| Ukraine | 252 | 1.52 | 0.48 | |
| Poland | 37 | 0.88 | 0.27 | |
| Russian Federation | 30 | 0.72 | 0.22 | |
| Oceania | ||||
| New Zealand | 80 | 3.21 | 1.01 | |
| Australia | 363 | 3.12 | 0.98 | |
| African AFRCN data for 2018: | ||||
| Eastern Africa | ||||
| Malawi | 521 | 19.3 | 6.05 | |
| Uganda | 307 | 4.8 | 1.50 | |
| Zambia | 105 | 4.2 | 1.32 | |
| Rwanda | 42 | 3.5 | 1.10 | |
| Burundi | 37 | 3.4 | 1.07 | |
| South Sudan | 39 | 2.5 | 0.78 | |
| Tanzania | 171 | 2.2 | 0.69 | |
| Madagascar | 71 | 2.1 | 0.66 | |
| Kenya | 102 | 1.7 | 0.53 | |
| Mozambique | 72 | 1.7 | 0.53 | |
| Ethiopia | 56 | 0.4 | 0.13 | |
| Middle Africa | ||||
| Cameroon | 251 | 8.0 | 2.51 | |
| Congo, Democratic People Republic of | 261 | 2.9 | 0.91 | |
| Angola | 86 | 2.1 | 0.66 | |
| Chad | 38 | 1.7 | 0.53 | |
| Northern Africa | ||||
| Sudan | 90 | 2.0 | 0.63 | |
| Egypt | 178 | 1.7 | 0.53 | |
| Morocco | 55 | 1.7 | 0.53 | |
| Algeria | 37 | 0.9 | 0.28 | |
| Southern Africa | ||||
| South Africa | 94 | 1.6 | 0.50 | |
| Western Africa | ||||
| Cote d’Ivoire | 138 | 4.6 | 1.44 | |
| Nigeria | 647 | 2.8 | 0.88 | |
| Ghana | 86 | 2.4 | 0.75 | |
| Senegal | 48 | 2.4 | 0.75 | |
| Burkina Faso | 58 | 2.2 | 0.69 | |
| Mali | 41 | 1.4 | 0.44 | |
| Niger | 45 | 1.2 | 0.38 | |
| MALES | FEMALES | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region | Country 1 | Cases 2 | Rate 3 | Cases 2 | Rate 3 | Male-to-Female Rate Ratio 4 |
| International CI5(XI) data for 2008–2012: | ||||||
| Africa | ||||||
| Uganda | 71 | 11.74 | 53 | 7.05 | 1.67 | |
| Central/South America | ||||||
| Puerto Rico | 49 | 5.32 | 11 | 1.03 | 5.14 | |
| Colombia | 47 | 5.10 | 13 | 1.38 | 3.71 | |
| North America | ||||||
| US white people | 3344 | 4.94 | 1138 | 1.45 | 3.41 | |
| United States (US) | 3997 | 4.75 | 1408 | 1.46 | 3.25 | |
| US black people | 433 | 4.04 | 178 | 1.45 | 2.79 | |
| Canada | 151 | 2.35 | 43 | 0.58 | 4.02 | |
| Asia | ||||||
| Israel | 99 | 5.36 | 44 | 2.17 | 2.47 | |
| Turkey | 87 | 3.42 | 28 | 1.12 | 3.07 | |
| Republic of Korea | 289 | 2.71 | 87 | 0.70 | 3.86 | |
| Japan | 205 | 2.54 | 71 | 0.57 | 4.45 | |
| India | 80 | 0.70 | 48 | 0.47 | 1.47 | |
| China | 77 | 0.55 | 43 | 0.34 | 1.63 | |
| Europe | ||||||
| Switzerland | 71 | 6.63 | 25 | 1.54 | 4.31 | |
| Norway | 69 | 5.53 | 21 | 1.37 | 4.03 | |
| Belgium | 129 | 5.16 | 70 | 2.26 | 2.28 | |
| The Netherlands | 202 | 5.02 | 63 | 1.25 | 4.02 | |
| Italy | 255 | 5.02 | 92 | 1.38 | 3.65 | |
| Spain | 108 | 4.89 | 45 | 1.72 | 2.84 | |
| France | 122 | 4.70 | 50 | 1.56 | 3.02 | |
| Denmark | 57 | 4.56 | 20 | 1.23 | 3.72 | |
| United Kingdom | 695 | 4.12 | 255 | 1.25 | 3.30 | |
| Austria | 76 | 4.10 | 23 | 0.75 | 5.47 | |
| Ireland | 48 | 3.98 | 19 | 1.29 | 3.09 | |
| Germany | 485 | 3.75 | 191 | 1.09 | 3.43 | |
| Czech Republic | 66 | 3.06 | 25 | 0.84 | 3.65 | |
| Belarus | 47 | 3.00 | 23 | 0.87 | 3.47 | |
| Ukraine | 166 | 2.22 | 86 | 0.78 | 2.84 | |
| Oceania | ||||||
| New Zealand | 60 | 4.94 | 20 | 1.52 | 3.25 | |
| Australia | 279 | 4.90 | 84 | 1.33 | 3.70 | |
| African AFRCN data for 2018: | ||||||
| Eastern Africa | ||||||
| Malawi | 405 | 29.7 | 116 | 8.7 | 3.41 | |
| Zambia | 84 | 6.6 | 21 | 1.7 | 3.88 | |
| Uganda | 201 | 5.9 | 106 | 3.7 | 1.59 | |
| Tanzania | 114 | 2.8 | 57 | 1.5 | 1.87 | |
| Madagascar | 39 | 2.3 | 32 | 1.9 | 1.21 | |
| Kenya | 67 | 2.2 | 35 | 1.2 | 1.83 | |
| Mozambique | 36 | 1.7 | 36 | 1.7 | 1.00 | |
| Middle Africa | ||||||
| Cameroon | 159 | 10.4 | 92 | 5.6 | 1.86 | |
| Congo, Democratic People Republic of | 179 | 4.3 | 82 | 1.5 | 2.87 | |
| Angola | 68 | 3.2 | 18 | 0.9 | 3.56 | |
| Northern Africa | ||||||
| Sudan | 63 | 2.7 | 27 | 1.3 | 2.08 | |
| Egypt | 137 | 2.5 | 41 | 0.8 | 3.13 | |
| Southern Africa | ||||||
| South Africa | 52 | 1.9 | 42 | 1.4 | 1.36 | |
| Western Africa | ||||||
| Cote d’Ivoire | 76 | 5.2 | 62 | 3.9 | 1.33 | |
| Ghana | 68 | 3.7 | 18 | 1.0 | 3.70 | |
| Nigeria | 379 | 3.0 | 268 | 2.5 | 1.20 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mbulaiteye, S.M.; Devesa, S.S. Burkitt Lymphoma Incidence in Five Continents. Hemato 2022, 3, 434-453. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato3030030
Mbulaiteye SM, Devesa SS. Burkitt Lymphoma Incidence in Five Continents. Hemato. 2022; 3(3):434-453. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato3030030
Chicago/Turabian StyleMbulaiteye, Sam M., and Susan S. Devesa. 2022. "Burkitt Lymphoma Incidence in Five Continents" Hemato 3, no. 3: 434-453. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato3030030
APA StyleMbulaiteye, S. M., & Devesa, S. S. (2022). Burkitt Lymphoma Incidence in Five Continents. Hemato, 3(3), 434-453. https://doi.org/10.3390/hemato3030030







