Rheology and Phase Behavior of Surfactant–Oil–Water Systems and Their Relationship with O/W Nano-Emulsion’s Characteristics Obtained by Dilution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Phase Diagram
2.2.2. Emulsion Formation
2.2.3. Electrical Conductivity
2.2.4. Droplet Size and Stability
2.2.5. Rheology of Initial Dispersions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Phase Diagram
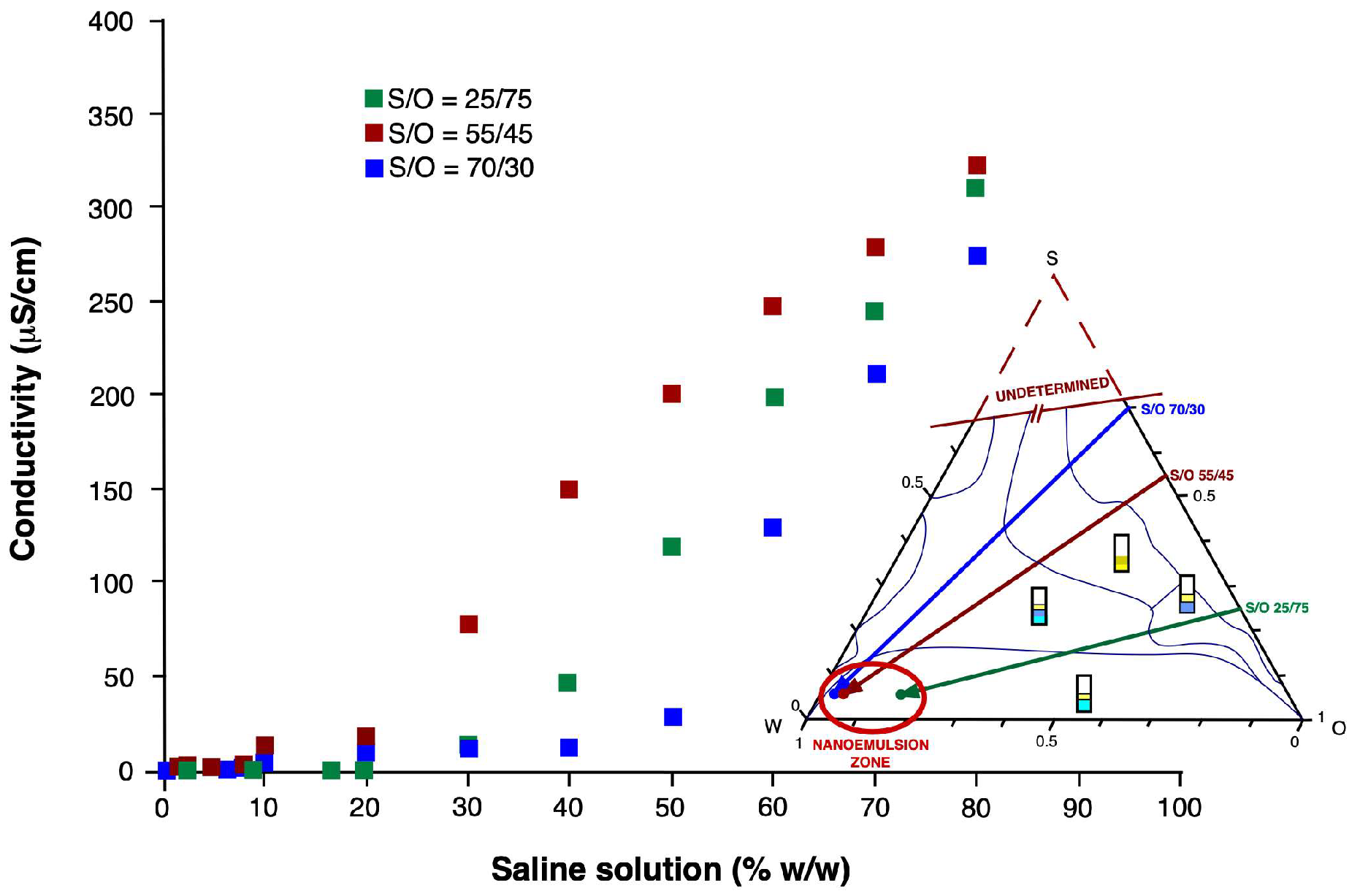
3.2. Electrical Conductivity
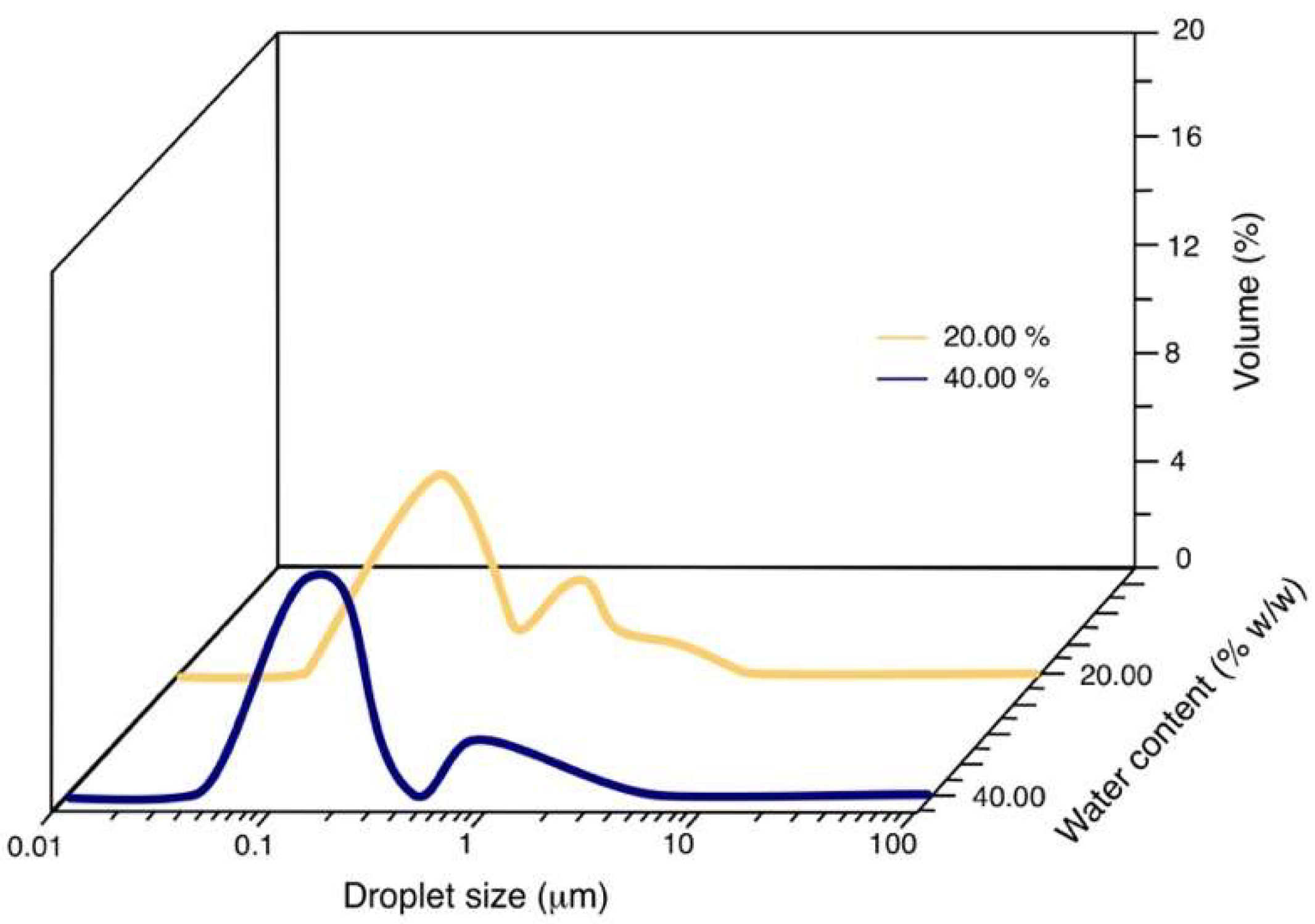
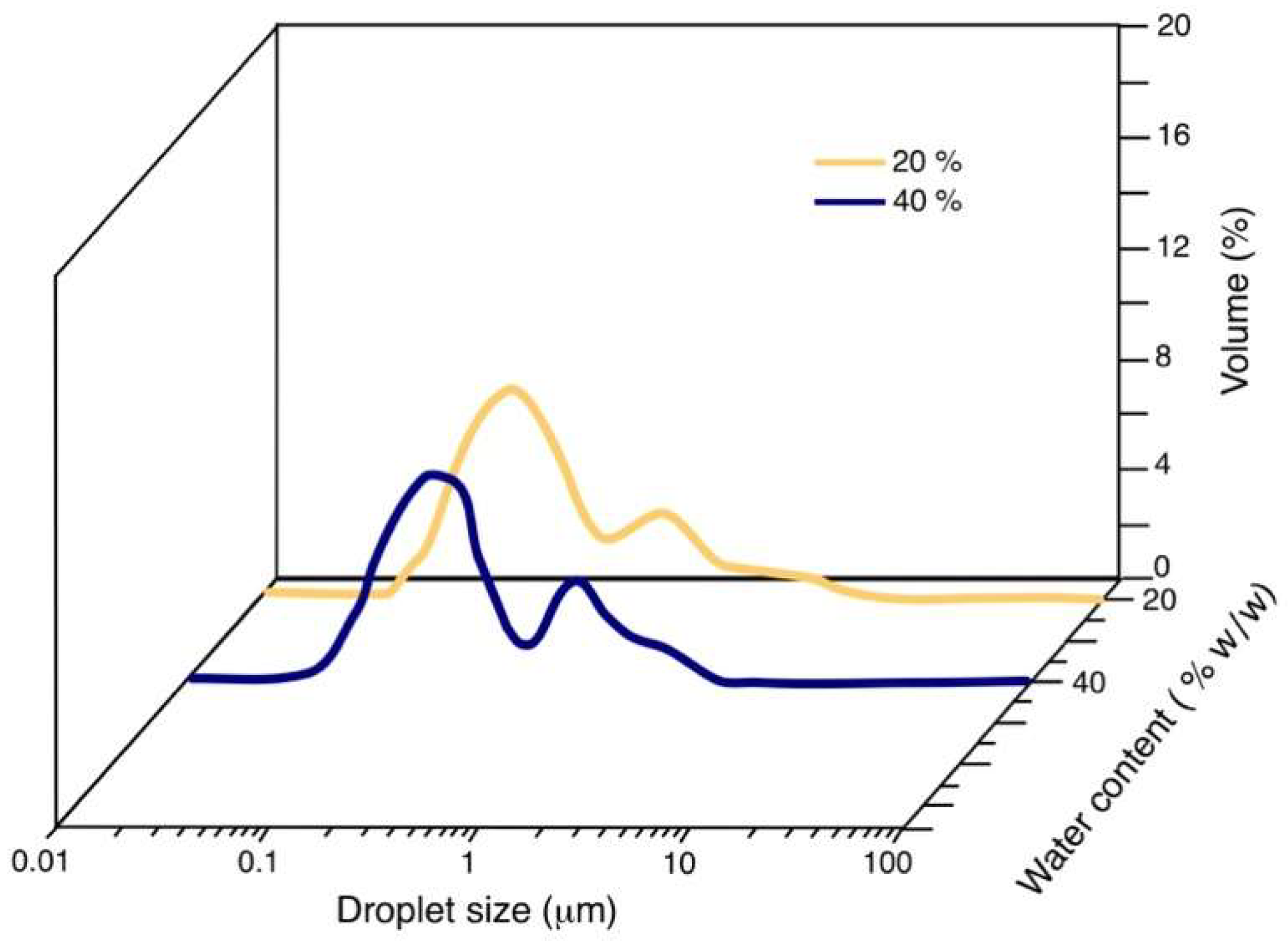
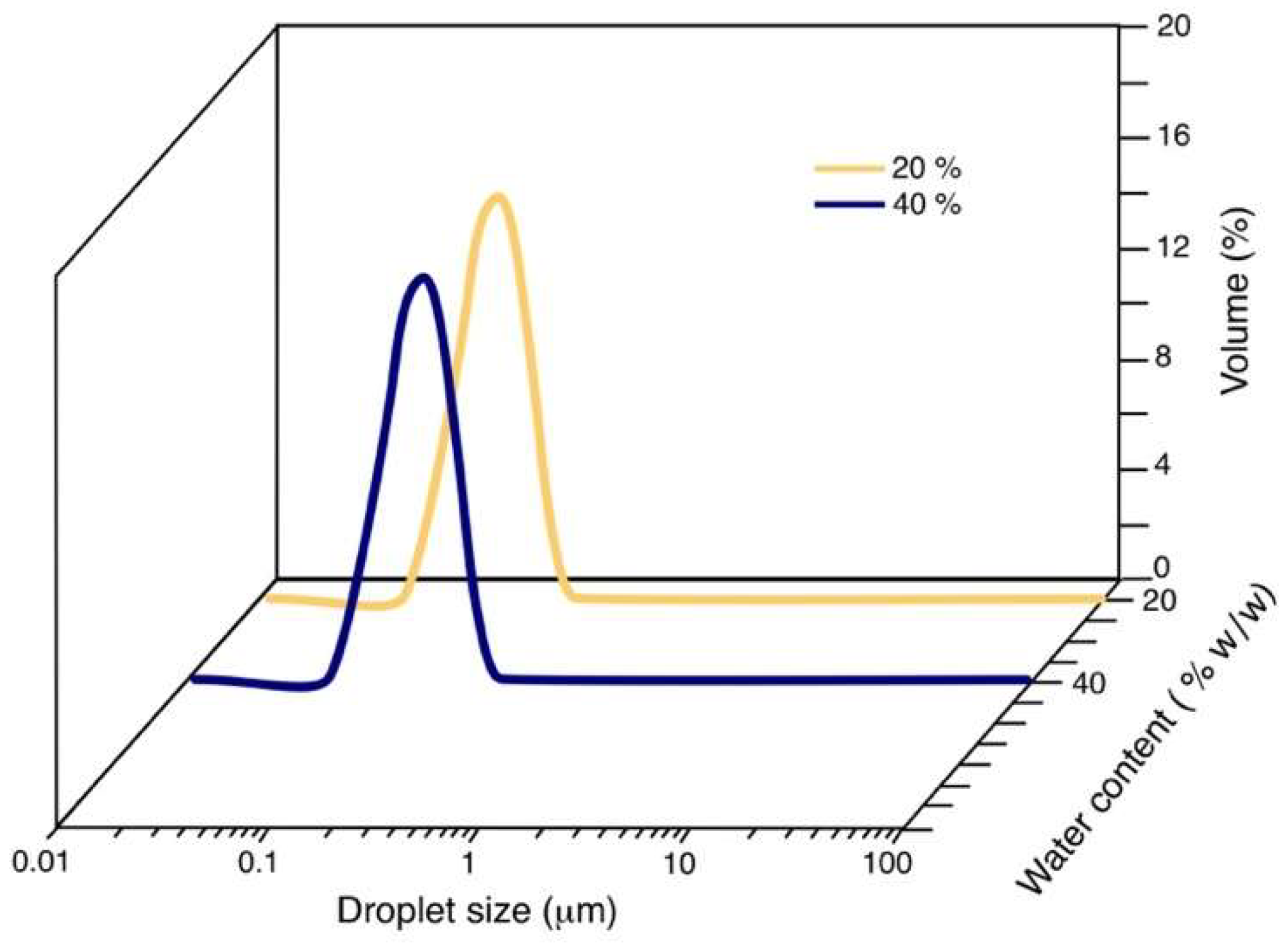
3.3. Droplet Size
3.4. Type of Liquid Crystal
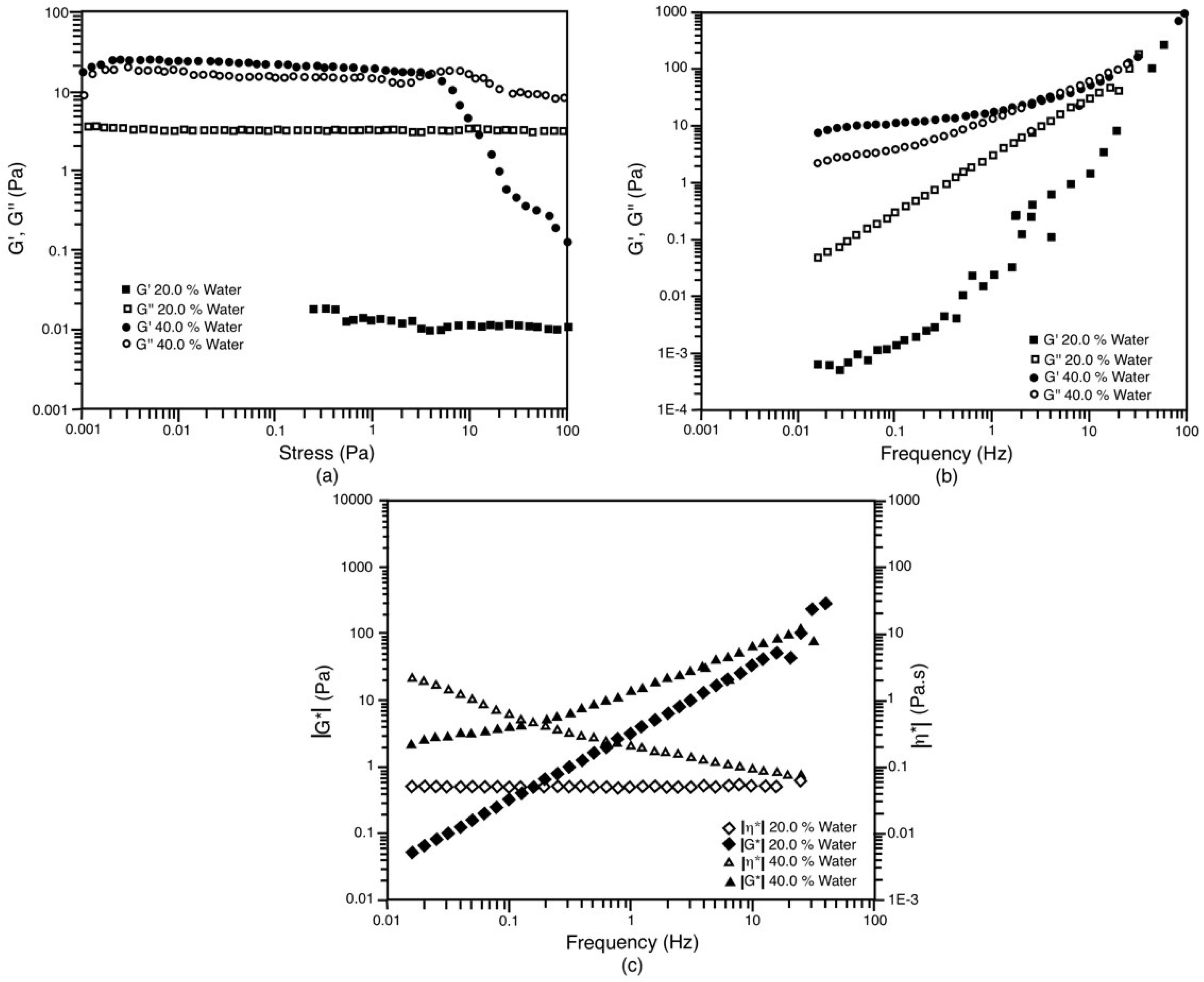
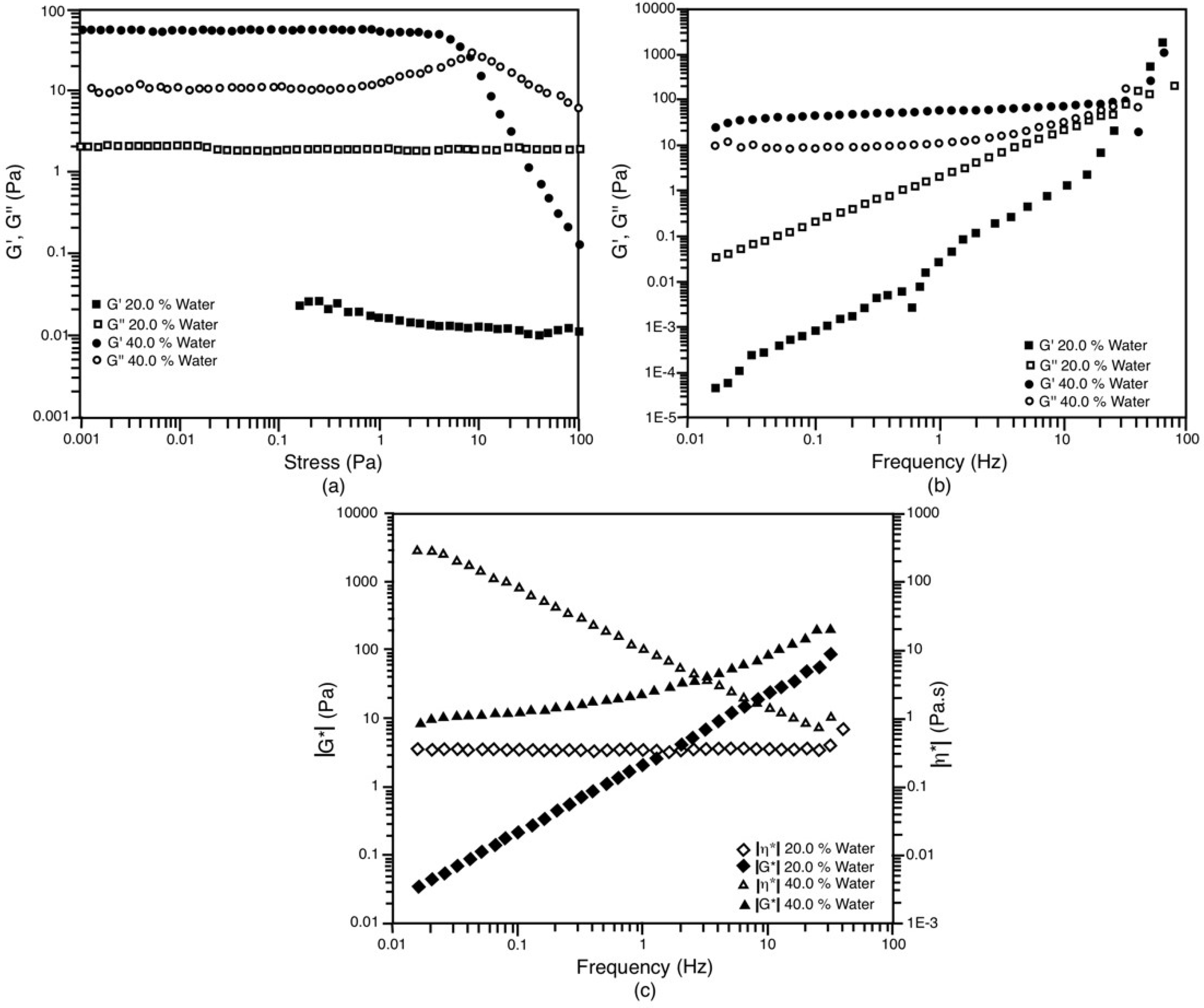
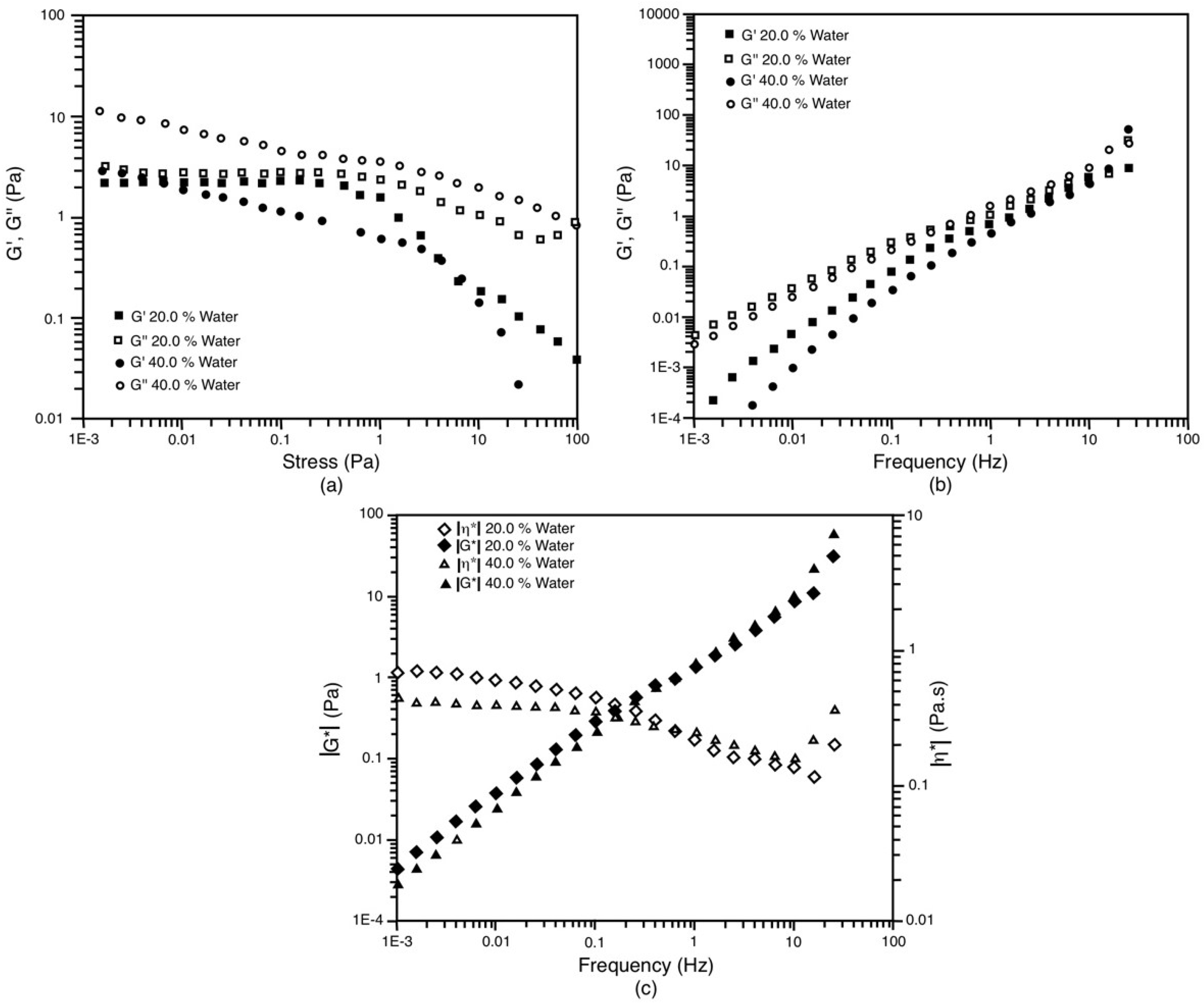
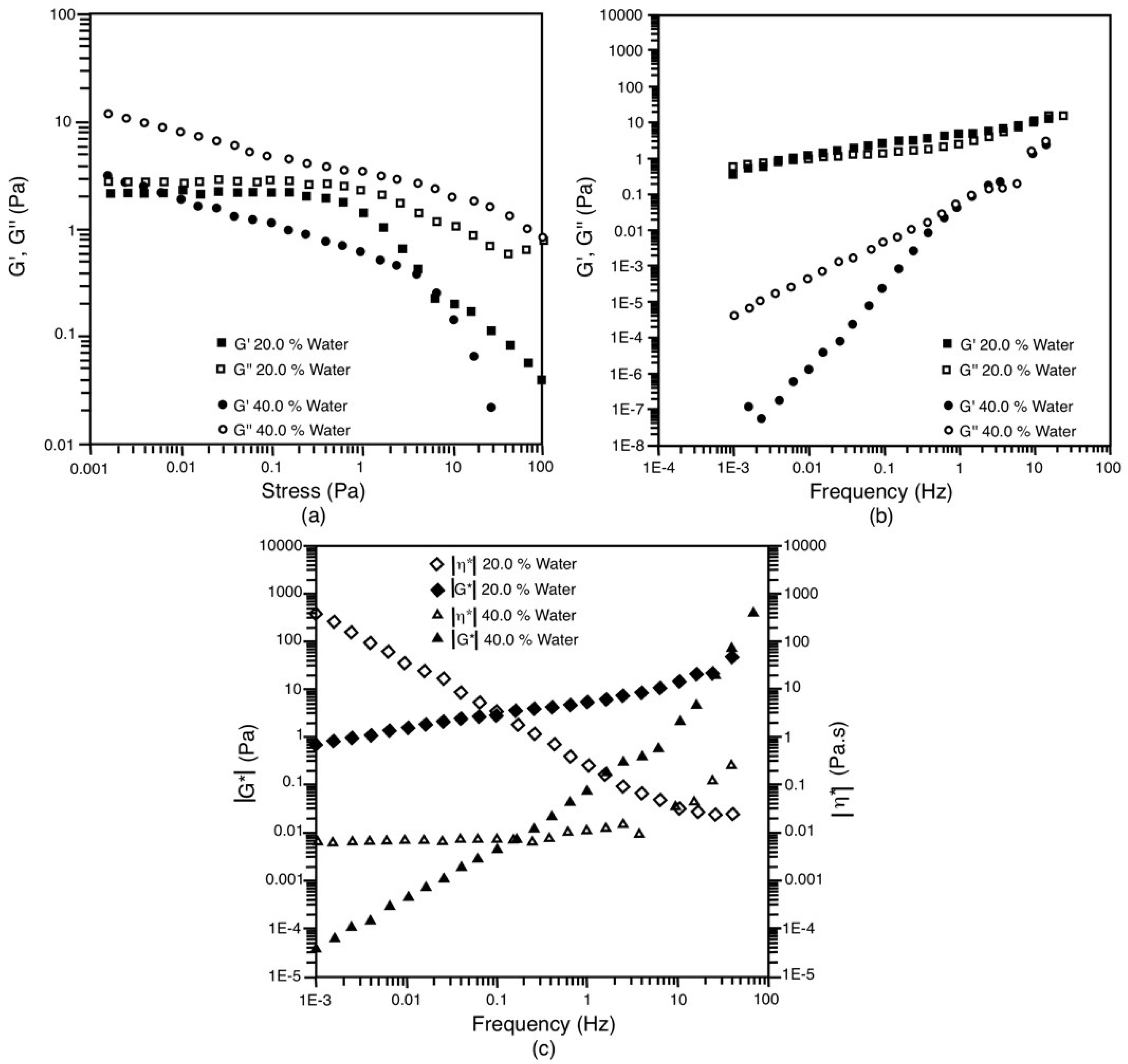
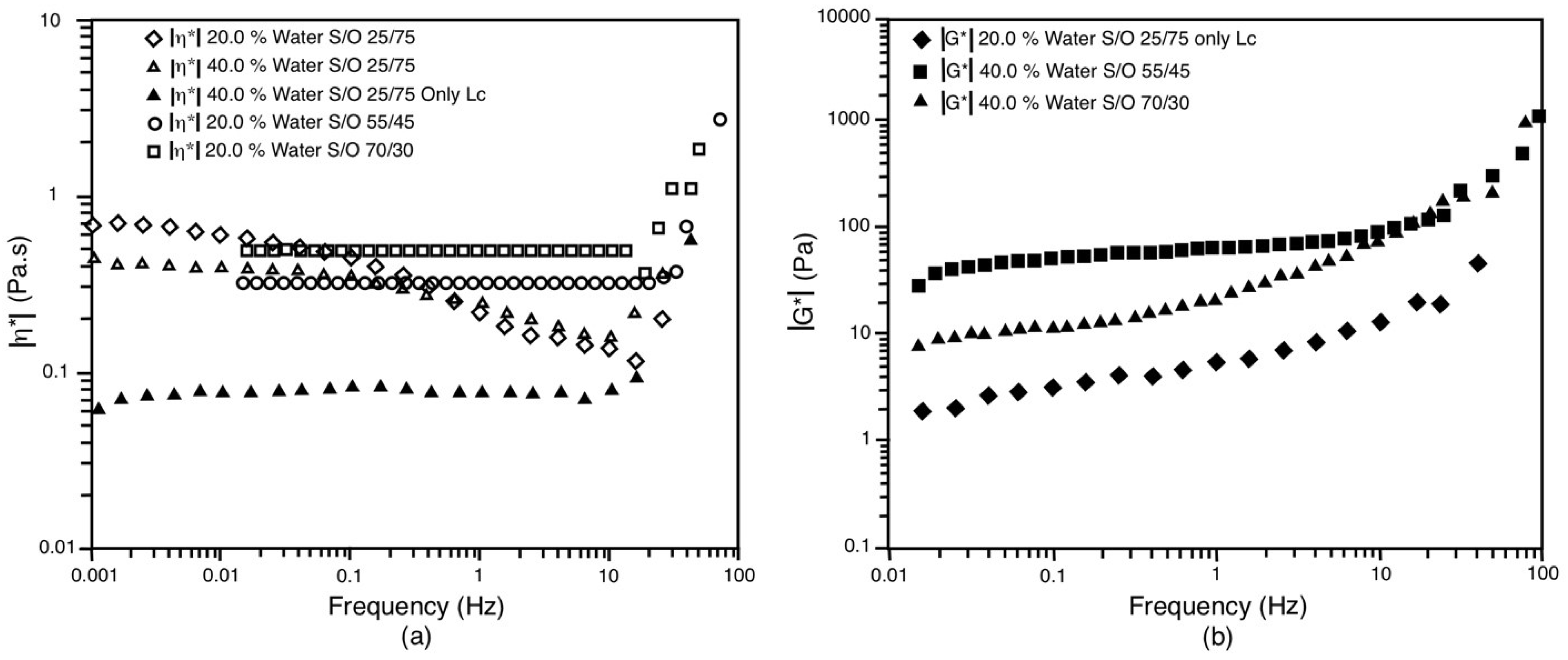
3.5. Rheological Behavior
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Forgiarini, A.; Esquena, J.; González, C.; Solans, C. Studies of the Relation between Phase Behavior and Emulsification Methods with NE Formation. In Trends in Colloid and Interface Science XIV; Buckin, V., Ed.; Progress in Colloid and Polymer Science; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volume 115, pp. 36–39. ISBN 978-3-540-67128-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, S.M.; McClements, D.J. (Eds.) NE. Formulation, Applications, and Characterization; Academic Press: London, UK, 2018; ISBN 978-0-12-811838-2. [Google Scholar]
- Sagitani, H. Making Homogeneous and Fine Droplet O/W Emulsions Using Nonionic Surfactants. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1981, 58, 738–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Verma, A.; Mandal, A. Formation, Characteristics and Oil Industry Applications of NE: A Review. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 206, 109042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariyate, J.; Bera, A. A Critical Review on Selection of Microemulsions or NE for Enhanced Oil Recovery. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 353, 118791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, N.; Mandal, A. Enhanced Oil Recovery Performance of Gemini Surfactant-Stabilized NE Functionalized with Partially Hydrolyzed Polymer/Silica Nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 226, 115887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.D.; Kapila, S.; Ganesan, N.G.; Rangarajan, V. A Review on Green NE for Cosmetic Applications with Special Emphasis on Microbial Surfactants as Impending Emulsifying Agents. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2022, 25, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oca-Ávalos, J.M.M.; Candal, R.J.; Herrera, M.L. NE: Stability and Physical Properties. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmi, N.A.N.; Elgharbawy, A.A.M.; Motlagh, S.R.; Samsudin, N.; Salleh, H.M. NE: Factory for Food, Pharmaceutical and Cosmetics. Processes 2019, 7, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashaolu, T.J. NE for Health, Food, and Cosmetics: A Review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 3381–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aasser, M.S.; Miller, C.M. Preparation of Latexes Using Miniemulsions. In Polymeric Dispersions: Principles and Applications; Asua, J.M., Ed.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 109–126. ISBN 978-94-010-6321-0. [Google Scholar]
- Lovell, P.A.; El-Aasser, M.S. (Eds.) Emulsion Polymerization and Emulsion Polymers; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-0-471-96746-0. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, L.J.; Alves, F.C.; de França, F.P. A Review of the Technological Solutions for the Treatment of Oily Sludges from Petroleum Refineries. Waste Manag. Res. 2012, 30, 1016–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solè, I.; Solans, C.; Maestro, A.; González, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Study of Nano-Emulsion Formation by Dilution of Microemulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 376, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostertag, F.; Weiss, J.; McClements, D.J. Low-Energy Formation of Edible NE: Factors Influencing Droplet Size Produced by Emulsion Phase Inversion. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 388, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perazzo, A.; Preziosi, V.; Guido, S. Phase Inversion Emulsification: Current Understanding and Applications. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 581–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, K.; Cabane, B.; Olsson, U. Emulsification through Surfactant Hydration: The PIC Process Revisited. Langmuir 2011, 27, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonneville-Aubrun, O.; Babayan, D.; Bordeaux, D.; Lindner, P.; Rata, G.; Cabane, B. Phase Transition Pathways for the Production of 100 Nm Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2009, 11, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.J. Low-Energy Emulsification—I—Principles and Applications. J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. 1978, 29, 117–125. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Mutch, K.J.; Eastoe, J.; Heenan, R.K.; Dong, J. NE Prepared by a Two-Step Low-Energy Process. Langmuir 2008, 24, 6092–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagitani, H. Formation of O/W Emulsions by Surfactant Phase Emulsification and the Solution Behavior of Nonionic Surfactant System in the Emulsification Process. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 1988, 9, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagitani, H.; Friberg, S.E. Microemulsion Systems with a Nonionic Cosurfactant. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 1980, 1, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagitani, H.; Hirai, Y.; Nabeta, K.; Nagai, M. Effect of Types Polyols on Surfactant Phase Emulsification. J. Jpn. Oil Chem. Soc. 1986, 35, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.J.; Lim, C.K.; Ee, G.C.L.; Basri, M. Formation of Liquid Crystal/Gel Emulsions to Nano-Emulsions Constructed by Polyalkoxylated Fatty Alcohol (PAFA)-Based Mixed Surfactant Systems. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 40, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, X. The Effects of Some Factors on the Rheological Properties of the Lyotropic Liquid Crystals Formed in Brij97/NaDC/IPM/Water System: Compositions, Temperature and Polyphenols. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2019, 40, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo, G.; Valiente, M.; Rodenas, E. Rheological Properties of the L Phase and the Hexagonal, Lamellar, and Cubic Liquid Crystals of the CTAB/Benzyl Alcohol/Water System. Langmuir 1996, 12, 5202–5208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezzenga, R.; Meyer, C.; Servais, C.; Romoscanu, A.I.; Sagalowicz, L.; Hayward, R.C. Shear Rheology of Lyotropic Liquid Crystals: A Case Study. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3322–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordobés, F.; Franco, J.M.; Gallegos, C. Rheology of the Lamellar Liquid-Crystalline Phase in Polyethoxylated Alcohol/Water/Heptane Systems. Grasas Y Aceites 2005, 56, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mislan, A.A.; Foong, J.L.N.; Saharin, S.M.; Zahid, N.I. Rheological Behaviour of Thermotropic and Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Phases of Guerbet Branched Chain Glycolipids. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2019, 502, 112305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biradar, S.V.; Dhumal, R.S.; Paradkar, A. Rheological Investigation of Self-Emulsification Process. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 12, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biradar, S.V.; Dhumal, R.S.; Paradkar, A.R. Rheological Investigation of Self-Emulsification Process: Effect of Co-Surfactant. J Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 12, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanun, M.; Al-Diyn, W.S. Structural Transitions in the System Water/Mixed Nonionic Surfactants/R (+)-Limonene Studied by Electrical Conductivity and Self-Diffusion-NMR. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2007, 28, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidich, N.; Aserin, A.; Garti, N. Structural Characteristics of Oil-Poor Dilutable Fish Oil Omega-3 Microemulsions for Ophthalmic Applications. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 463, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Esquena, J.; Rodriguez-Abreu, C.; Solans, C. Key Features of Nano-Emulsion Formation by the Phase Inversion Temperature Method. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2021, 42, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, C.; Kunieda, H. Phase Behavior and Microstructure of Liquid Crystals in Mixed Surfactant Systems. In Mixed Surfactant Systems; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-0-429-12030-5. [Google Scholar]
- Forgiarini, A.; Esquena, J.; González, C.; Solans, C. Formation of Nano-Emulsions by Low-Energy Emulsification Methods at Constant Temperature. Langmuir 2001, 17, 2076–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.; Zhao, C.; Sun, Z.; Sun, D. Formation of Concentrated NE by W/O Microemulsion Dilution Method: Biodiesel, Tween 80, and Water System. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 3299–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, K.L.; Shah, D.O. Adsorption and Aggregation of Surfactants in Solution; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-203-91057-3. [Google Scholar]
- Solè, I.; Maestro, A.; González, C.; Solans, C.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Optimization of Nano-Emulsion Preparation by Low-Energy Methods in an Ionic Surfactant System. Langmuir 2006, 22, 8326–8332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.M.; Hoshida, S.; Arima, S.; Aramaki, K. Lyotropic Behavior of Nonionic Sugar Surfactant and Rheology of the Liquid Crystal. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2013, 34, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.O.; Hamlin, R.M. Structure of Water in Microemulsions: Electrical, Birefringence, and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Studies. Science 1971, 171, 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strey, R.; Schomäcker, R.; Roux, D.; Nallet, F.; Olsson, U. Dilute Lamellar and L3 Phases in the Binary Water–C12E5 System. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1990, 86, 2253–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayali, I.; Karaein, M.; Qamhieh, K.; Wadaah, S.; Ahmad, W.; Olsson, U. Phase Behavior of Bicontinuous and Water/Diesel Fuel Microemulsions Using Nonionic Surfactants Combined with Hydrophilic Alcohol Ethoxylates. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2015, 36, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasert, W.; Gohtani, S. Effect of Temperature on Low-Energy Nano-Emulsification and Phase Behavior in Water/Polyoxyethylene Sorbitan Fatty Acid Ester (Tweens®)/Vegetable Oil Systems. J. Food Eng. 2016, 180, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlweit, M.; Busse, G.; Winkler, J. Electric Conductivity in Microemulsions. J. Chem. Phys. 1993, 99, 5605–5614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquali, R.C.; Bregni, C.; Serrao, R. Características e identificación de los cristales líquidos liotrópicos. Rev. Mex. De Cienc. Farm. 2006, 37, 38–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ouaer, H.; Gareche, M. The Rheological Behaviour of a Water-Soluble Polymer (HEC) Used in Drilling Fluids. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2018, 40, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macosko, C.w. Rheology Principles; Wiley VCH: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994; ISBN 1-56081-579-5. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, H.A. An Introduction to Rheology, 1st ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2000; Volume 3, ISBN 0-9538032-0-1. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, H.A. Rheology of Emulsions—A Review. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1994, 91, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni, M.G.; Lawrence, C.J.; Machin, D. A Review of the Rheology of the Lamellar Phase in Surfactant Systems. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 98, 217–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


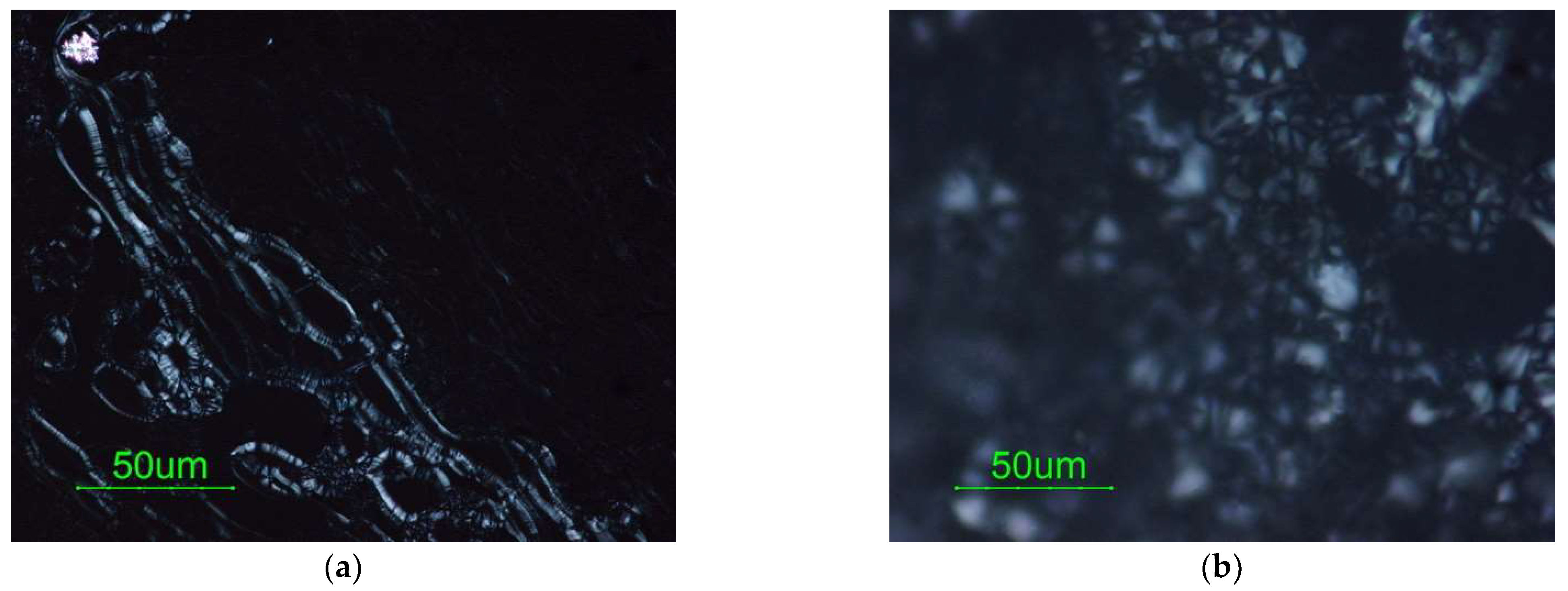
| Water Amount in the Initial System (wt.%) S/O = 25/75 | ||
|---|---|---|
| 20% | 40% | |
| Phases at equilibrium | O + Liquid Crystal (LC) | O + LC + O/W microemulsion (Wm) |
| Water amount in the initial system (wt.%) S/O = 55/45 | ||
| 20% | 40% | |
| Phases at equilibrium | W/O microemulsion (Om) + LC | O + LC + Wm |
| Water amount in the initial system (wt.%) S/O = 70/30 | ||
| 20% | 40% | |
| Phases at equilibrium | Om + LC | O + LC + Wm |
 | ||
| S/O | %wt. Water | D(0.5) µm |
|---|---|---|
| 25/75 | 20 | 0.185 |
| 25/75 | 40 | 0.151 |
| 55/45 | 20 | 0.118 |
| 55/45 | 40 | 0.111 |
| 70/30 | 20 | 0.173 |
| 70/30 | 40 | 0.170 |
| S/O | Water (%wt) | G’ (Pa) | G’’ (Pa) | |G*| (Pa) | |η*| (Pa.s) | D (0.5) (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25/75 (only Lc) | 20 | 4.772 | 2.561 | 5.416 | 0.862 | 0.117 |
| 25/75 (only Lc) | 40 | 0.053 | 0.052 | 0.074 | 0.012 | 0.121 |
| 25/75 (All) | 20 | 0.436 | 1.005 | 1.095 | 0.174 | 0.185 |
| 25/75 (All) | 40 | 0.487 | 1.428 | 1.509 | 0.240 | 0.151 |
| 55/45 | 20 | 0.002 | 2.109 | 2.109 | 0.334 | 0.118 |
| 55/45 | 40 | 60.81 | 11.09 | 61.81 | 9.796 | 0.111 |
| 70/30 | 20 | 0.024 | 3.258 | 3.258 | 0.516 | 0.173 |
| 70/30 | 40 | 17.86 | 13.34 | 22.29 | 3.533 | 0.173 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guevara, M.; Mercado, R.; Vega, K.; Cardenas, A.; Forgiarini, A. Rheology and Phase Behavior of Surfactant–Oil–Water Systems and Their Relationship with O/W Nano-Emulsion’s Characteristics Obtained by Dilution. Nanomanufacturing 2023, 3, 20-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing3010002
Guevara M, Mercado R, Vega K, Cardenas A, Forgiarini A. Rheology and Phase Behavior of Surfactant–Oil–Water Systems and Their Relationship with O/W Nano-Emulsion’s Characteristics Obtained by Dilution. Nanomanufacturing. 2023; 3(1):20-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing3010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuevara, Mairis, Ronald Mercado, Katty Vega, Antonio Cardenas, and Ana Forgiarini. 2023. "Rheology and Phase Behavior of Surfactant–Oil–Water Systems and Their Relationship with O/W Nano-Emulsion’s Characteristics Obtained by Dilution" Nanomanufacturing 3, no. 1: 20-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing3010002
APA StyleGuevara, M., Mercado, R., Vega, K., Cardenas, A., & Forgiarini, A. (2023). Rheology and Phase Behavior of Surfactant–Oil–Water Systems and Their Relationship with O/W Nano-Emulsion’s Characteristics Obtained by Dilution. Nanomanufacturing, 3(1), 20-35. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanomanufacturing3010002






