Rotating Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Their Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
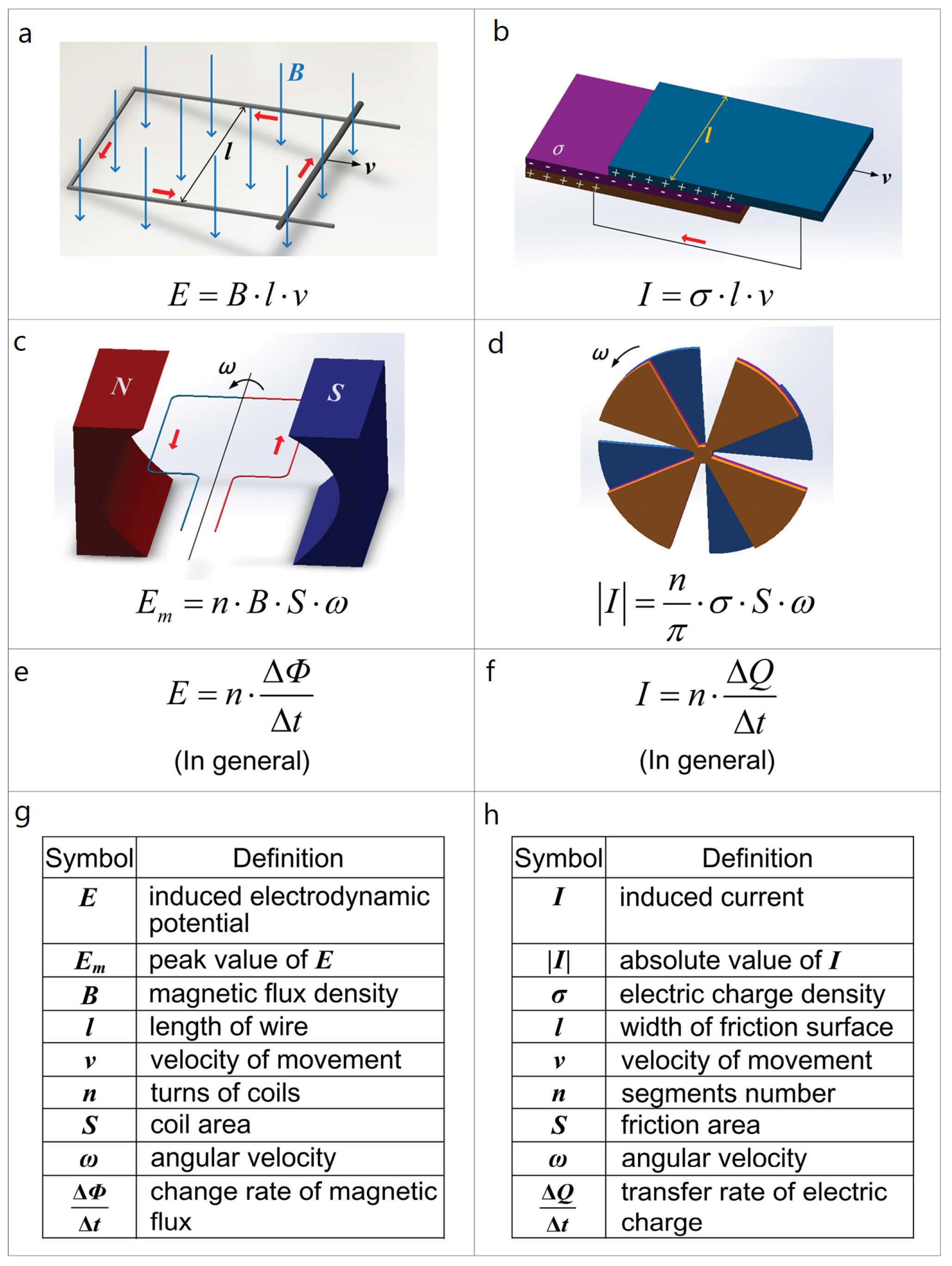
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Operating Principles of (Rotary) TENGs
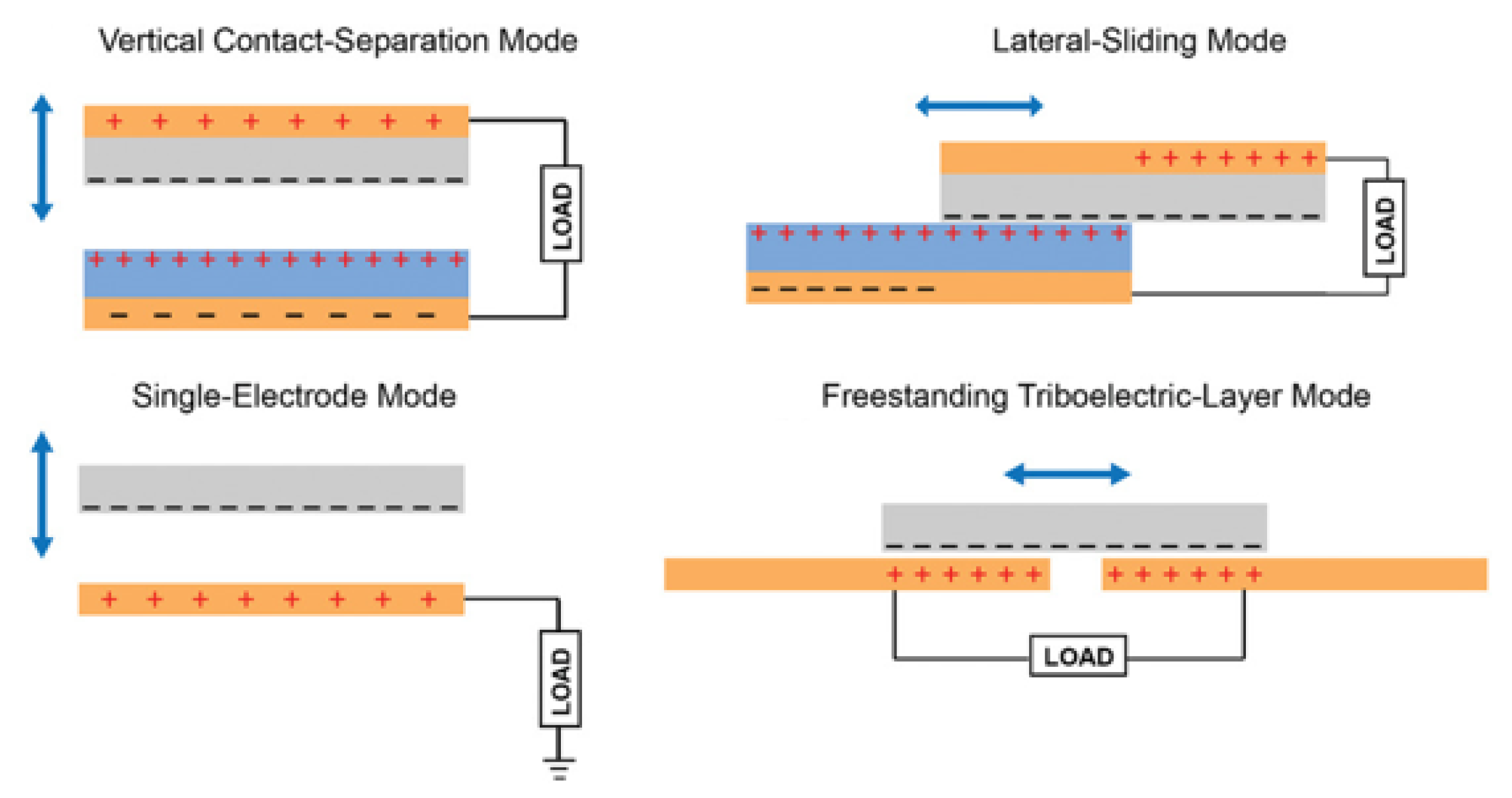
2.2. Classification of TENGs
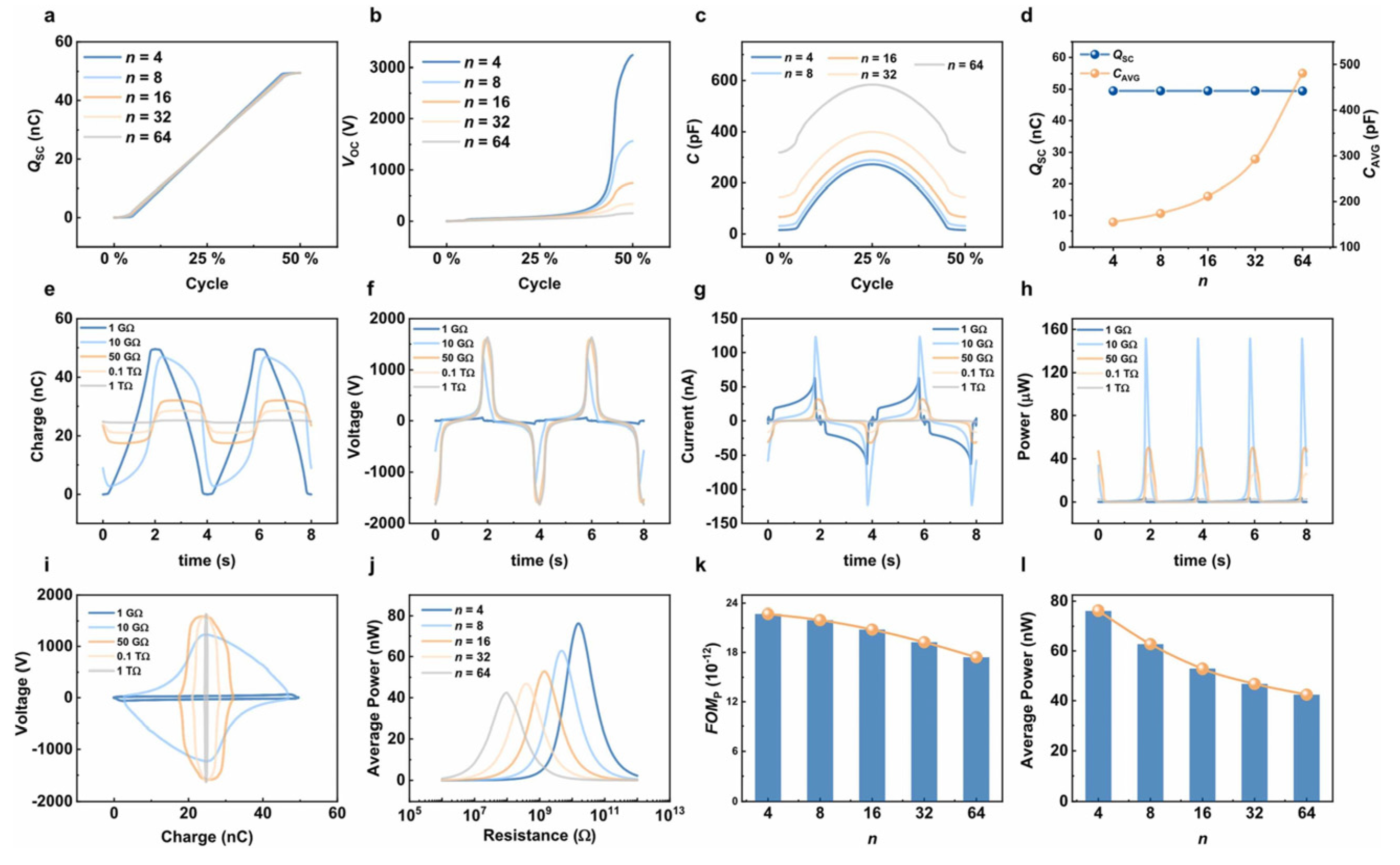
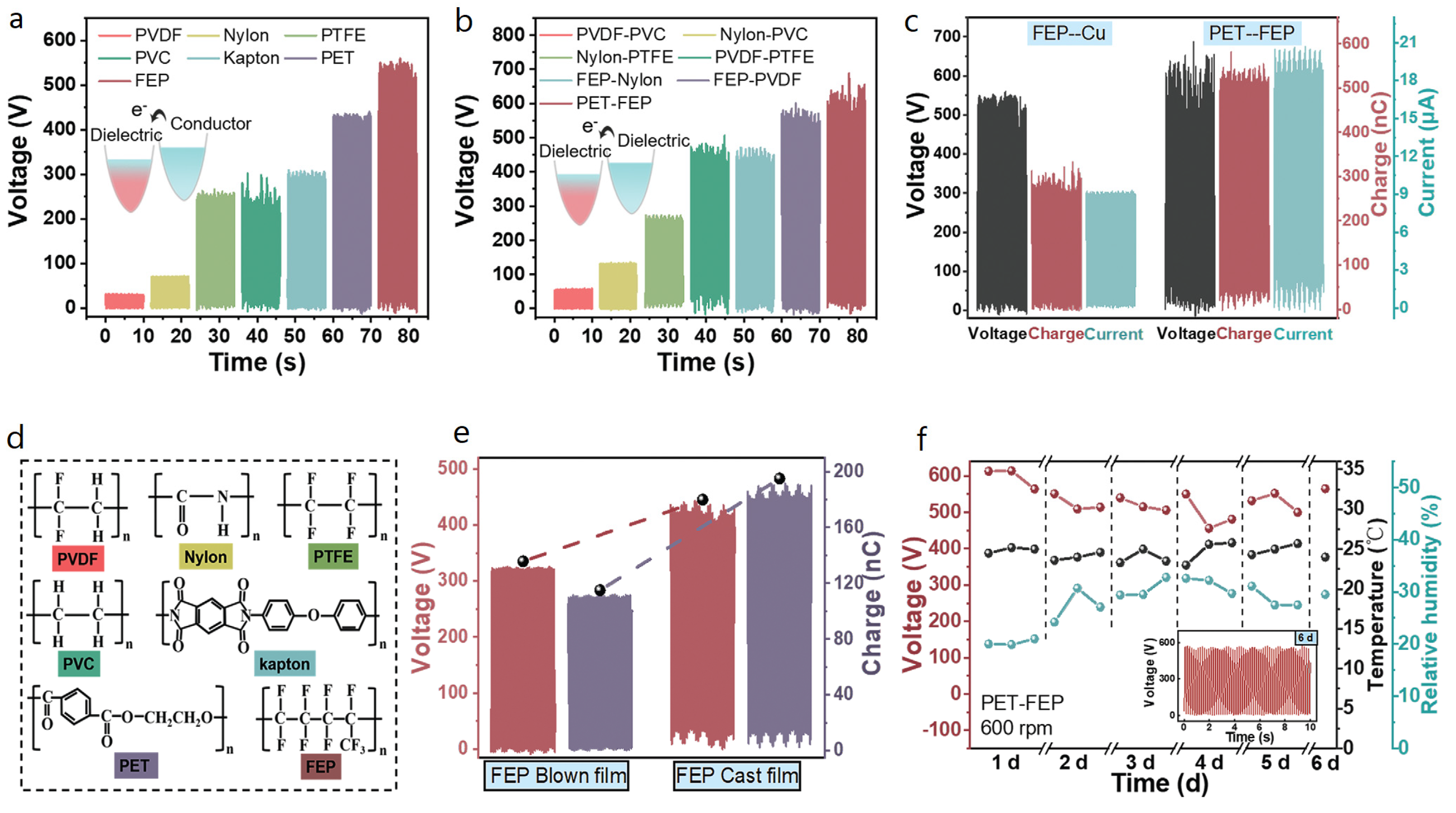
2.3. Design Parameters, Operating Conditions, and Electrical Output
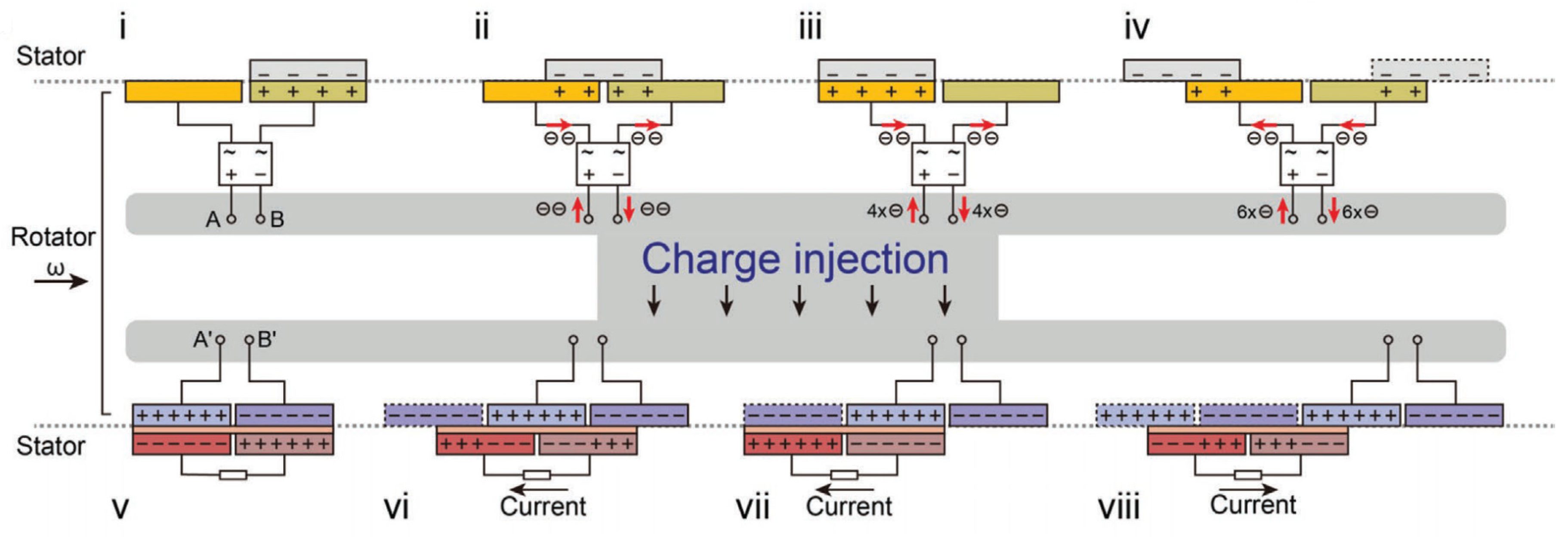
2.4. Enhancing the Electrical Output of R-TENGs
3. R-TENGs for Energy Harvesting Applications
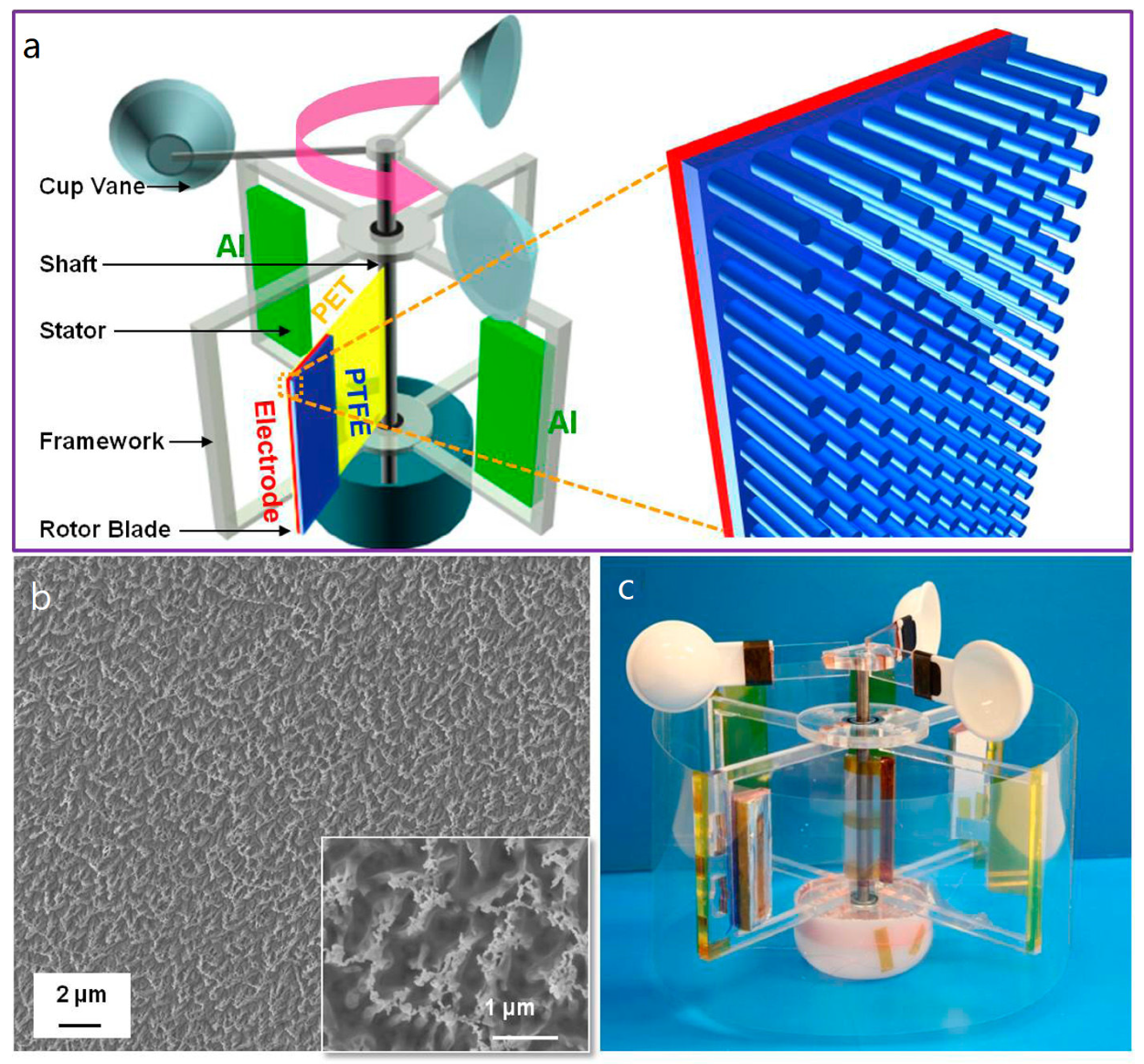
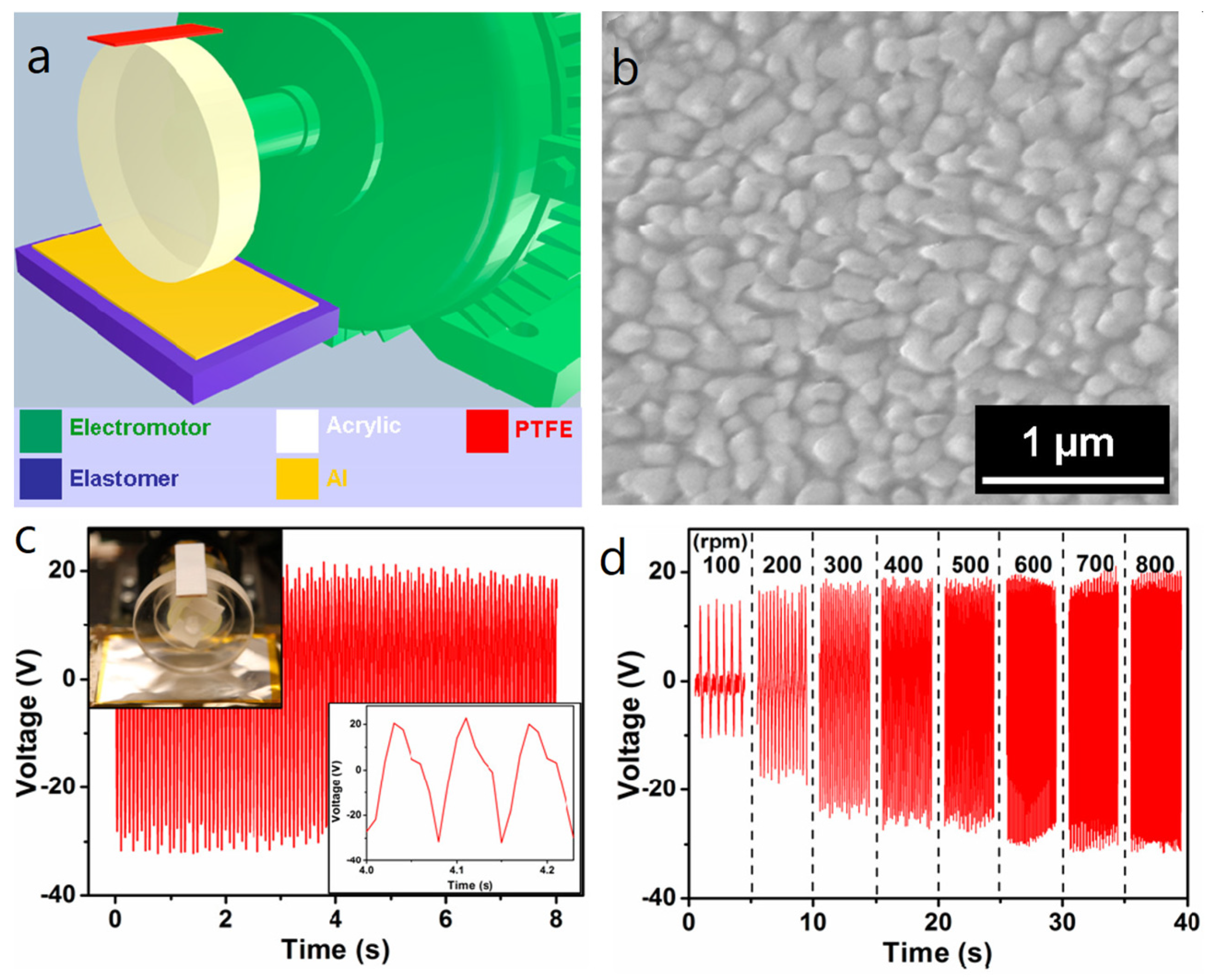
3.1. Radial Flaps
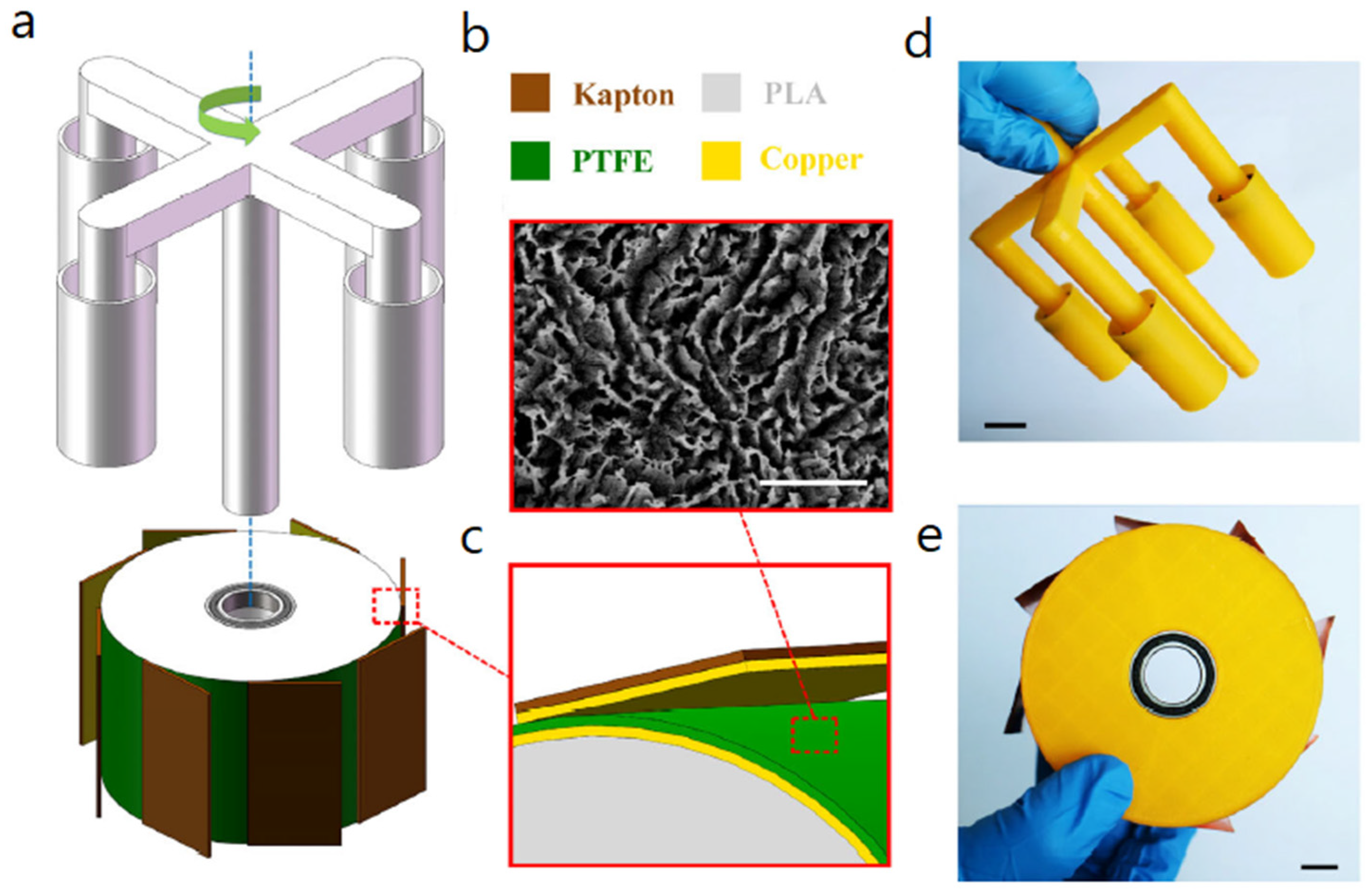
3.2. Coaxial Cylinders
3.3. Liquid-Solid Contact
3.4. Radially Segmented Disk
3.5. Hybrid Nanogenerators
4. R-TENGs as Sensors and Actuators
4.1. R-TENGs for Sensing Applications
4.2. R-TENGs as Actuators
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amin, F.; Abbasi, R.; Mateen, A.; Abid, M.A.; Khan, S. A Step toward Next-Generation Advancements in the Internet of Things Technologies. Sensors 2022, 22, 8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yildizbasi, A.; Wang, Y.; Sarkis, J. Safety Concerns for the Management of End-of-Life Lithium-Ion Batteries. Glob. Chall. 2022, 6, 2200049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farghali, M.; Osman, A.I.; Mohamed, I.M.A.; Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Ihara, I.; Yap, P.-S.; Rooney, D.W. Strategies to save energy in the context of the energy crisis: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2023, 21, 2003–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, L.; Mariappan, S.; Parameswaran, P.; Rajendran, J.; Nitesh, R.S.; Kumar, N.; Nathan, A.; Yarman, B.S. The Advancement of Radio Frequency Energy Harvesters (RFEHs) as a Revolutionary Approach for Solving Energy Crisis in Wireless Communication Devices: A Review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 106107–106139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoman, M.; Aldrigo, M.; Dinescu, A.; Vasilache, D.; Iordanescu, S.; Dragoman, D. Nanomaterials and Devices for Harvesting Ambient Electromagnetic Waves. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozariasbmarz, A.; Collins, H.; Dsouza, K.; Polash, M.H.; Hosseini, M.; Hyland, M.; Liu, J.; Malhotra, A.; Ortiz, F.M.; Mohaddes, F.; et al. Review of wearable thermoelectric energy harvesting: From body temperature to electronic systems. Appl. Energy 2020, 258, 114069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanad, M.F.; Shalan, A.E.; Abdellatif, S.O.; Abu Serea, E.S.; Adly, M.S.; Ahsan, A. Thermoelectric Energy Harvesters: A Review of Recent Developments in Materials and Devices for Different Potential Applications. Top. Curr. Chem. 2020, 378, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massetti, M.; Jiao, F.; Ferguson, A.J.; Zhao, D.; Wijeratne, K.; Würger, A.; Blackburn, J.L.; Crispin, X.; Fabiano, S. Unconventional Thermoelectric Materials for Energy Harvesting and Sensing Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 12465–12547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J.V.; Slabov, V.; Kholkin, A.L.; dos Santos, M.P.S. Hybrid Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Nanogenerators for Mechanical Energy Harvesting: A Review. Nano-Micro Lett. 2021, 13, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, M.; Shi, Q.; Wen, F.; Liu, L.; Dong, B.; Haroun, A.; Yang, Y.; Vachon, P.; Guo, X.; et al. Progress in TENG technology—A journey from energy harvesting to nanoenergy and nanosystem. Ecomat 2020, 2, e12058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementi, G.; Cottone, F.; Di Michele, A.; Gammaitoni, L.; Mattarelli, M.; Perna, G.; López-Suárez, M.; Baglio, S.; Trigona, C.; Neri, I. Review on Innovative Piezoelectric Materials for Mechanical Energy Harvesting. Energies 2022, 15, 6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Guo, X.; Lee, C. Promoting smart cities into the 5G era with multi-field Internet of Things (IoT) applications powered with advanced mechanical energy harvesters. Nano Energy 2021, 88, 106304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezer, N.; Koç, M. A comprehensive review on the state-of-the-art of piezoelectric energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Tang, L.; Liang, J.; Lan, C.; Das, R. Acoustic-Elastic Metamaterials and Phononic Crystals for Energy Harvesting: A Review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 30, 085025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.T.; Mandale, M.B. Recent acoustic energy harvesting methods and mechanisms: A review. Noise Vib. Worldw. 2021, 52, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, F.; Mandal, D.; Banerjee, S. Metamaterials for Acoustic Noise Filtering and Energy Harvesting. Sensors 2023, 23, 4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. On Maxwell’s displacement current for energy and sensors: The origin of nanogenerators. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. On the first principle theory of nanogenerators from Maxwell’s equations. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Willatzen, M.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical modeling of triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs). J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 111101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Shao, J.; Willatzen, M.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical model and optimal output of a cylindrical triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2022, 92, 106762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical systems of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 161–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, C.; Wang, A.C.; Ding, W.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator: A Foundation of the Energy for the New Era. Adv. Energy Mater. 2019, 9, 1802906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Chen, X.; Yang, K.; Han, C.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical study on rotary-sliding disk triboelectric nanogenerators in contact and non-contact modes. Nano Res. 2016, 9, 1057–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorsand, M.; Tavakoli, J.; Guan, H.; Tang, Y. Artificial intelligence enhanced mathematical modeling on rotary triboelectric nanogenerators under various kinematic and geometric conditions. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.; You, Z. Numerical analysis and structural optimization of cylindrical grating-structured triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, S.; Zou, Y.; Xu, J.; Yeh, M.-H.; Guo, H.; Chen, J. Ternary Electrification Layered Architecture for High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 9050–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wei, X.; Wang, B.; Li, R.; Sun, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.L. Design Optimization of Soft-Contact Freestanding Rotary Triboelectric Nanogenerator for High-Output Performance. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2102106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, M.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Cao, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Ma, X.; Ye, X. Optimization of structural parameters for rotary freestanding-electret generators and wind energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tang, W.; Han, C.; Fan, F.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical Comparison, Equivalent Transformation, and Conjunction Operations of Electromagnetic Induction Generator and Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Mechanical Energy. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3580–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Xu, L.; Lin, S.; Luo, J.; Qin, H.; Han, K.; Wang, Z.L. Charge Pumping Strategy for Rotation and Sliding Type Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, Q.; Long, L.; Yang, Q.; Fu, S.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H.; Hu, C.; Xi, Y. Matching Mechanism of Charge Excitation Circuit for Boosting Performance of a Rotary Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 48636–48646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Guo, H.; Zi, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, J.; Li, S.; Hu, C.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.L. Multifunctional TENG for Blue Energy Scavenging and Self-Powered Wind-Speed Sensor. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Pan, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Dai, G.; Zou, H.; Dong, K.; Wang, Z.L. An Ultra-Low-Friction Triboelectric–Electromagnetic Hybrid Nanogenerator for Rotation Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Wind Speed Sensor. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9433–9440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, R.; Zhang, R.; Jie, Y.; Zhao, W.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z. Natural cotton-based triboelectric nanogenerator as a self-powered system for efficient use of water and wind energy. Nano Energy 2022, 92, 106685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Jing, Q.; Lin, Z.-H.; Niu, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Rotary Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on a Hybridized Mechanism for Harvesting Wind Energy. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7119–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.; Alves, C.A.; Puga, J.; Pereira, A.; Ventura, J.O. Triboelectric driven turbine to generate electricity from the motion of water. Nano Energy 2016, 30, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Li, N.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Z.; Yin, Y.; Cao, R.; Zhao, S.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.L.; et al. Ultra-robust triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting rotary mechanical energy. Nano Res. 2018, 11, 2862–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Zhang, C.; Han, C.B.; Wang, Z.L. Enhancing Output Power of Cylindrical Triboelectric Nanogenerators by Segmentation Design and Multilayer Integration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6684–6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Fully Enclosed Cylindrical Single-Electrode-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Chen, S.; An, J.; Wang, K.; Deng, Y.; Benard, A.; Lajnef, N.; Cao, C. Multilayered Cylindrical Triboelectric Nanogenerator to Harvest Kinetic Energy of Tree Branches for Monitoring Environment Condition and Forest Fire. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2003598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Su, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Single-Electrode-Based Rotating Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Energy from Tires. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 680–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Jing, Q.; Yang, W.; Ma, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.L. Cylindrical Rotating Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6361–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Qin, C.; Feng, T.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Sun, X.; Liang, E.; Mao, Y.; Wang, X. Non-contact cylindrical rotating triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting kinetic energy from hydraulics. Nano Res. 2020, 13, 1903–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Jiang, T.; Liang, X.; An, J.; Wang, Z.L. Cylindrical triboelectric nanogenerator based on swing structure for efficient harvesting of ultra-low-frequency water wave energy. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2020, 7, 021401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Ouro-Koura, H.; Salalila, A.; Salalila, M.; Deng, Z.D. Frequency-multiplied cylindrical triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting low frequency wave energy to power ocean observation system. Nano Energy 2022, 99, 107365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Burman, S.R.; Khan, I.; Saha, S.; Choi, D.; Lee, S.; Lin, Z.-H. Recent advancements in solid–liquid triboelectric nanogenerators for energy harvesting and self-powered applications. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 17663–17697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Xu, L.; Zhan, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Wang, Z.L. Dripping Channel Based Liquid Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Sensing. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 10510–10517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Wang, N.; Yang, D.; Wang, J.; Lu, W.; Wang, D. Robust Solid-Liquid Triboelectric Nanogenerators: Mechanisms, Strategies and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2300764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Chung, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Moon, J.H.; Lee, S.; Cho, M.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S. Design and optimization of rotating triboelectric nanogenerator by water electrification and inertia. Nano Energy 2016, 27, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.-D.; Vo, C.-P.; Nguyen, T.-H.; Vu, D.-L.; Ahn, K.K. Liquid-solid contact electrification based on discontinuous-conduction triboelectric nanogenerator induced by radially symmetrical structure. Nano Energy 2021, 80, 105571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, T.; Tang, W.; Han, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.L. Rotating-Disk-Based Direct-Current Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1301798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Lee, J.H.; Khan, U.; Kwak, S.S.; Hinchet, R.; Kim, S.-W. Sustainable direct current powering a triboelectric nanogenerator via a novel asymmetrical design. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2057–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; An, J.; Cheng, R.; Shu, S.; Berbille, A.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Rationally segmented triboelectric nanogenerator with a constant direct-current output and low crest factor. Energy Environ. Sci. 2021, 14, 4523–4532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Jing, Q.; Niu, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Segmentally Structured Disk Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Rotational Mechanical Energy. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2916–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Jing, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Radial-arrayed rotary electrification for high performance triboelectric generator. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, G.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C. Dual Mode Rotary Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Collecting Kinetic Energy from Bicycle Brake. Adv. Energy Sustain. Res. 2021, 2, 2000113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, S.Y.; Chen, J.; Cheng, X.B.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Z.L. Two-dimensional rotary triboelectric nanogenerator as a portable and wearable power source for electronics. Nano Energy 2015, 17, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Luo, H.; Liao, R.; Wang, Z.L. Auto-Switching Self-Powered System for Efficient Broad-Band Wind Energy Harvesting Based on Dual-Rotation Shaft Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2101194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wei, X.; Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z. Thermal-mechanical-electrical energy conversion system based on Curie effect and soft-contact rotary triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 2502–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wei, X.; Shi, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, B.; Xu, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Low-grade heat energy harvesting system based on the shape memory effect and hybrid triboelectric-electromagnetic nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2022, 96, 107106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, B.; Zou, H.; Wu, Z.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Rationally designed rotation triboelectric nanogenerators with much extended lifetime and durability. Nano Energy 2020, 68, 104378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, O.; Yuan, W.; He, L.; Wei, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting Wind Energy by a Triboelectric Nanogenerator for an Intelligent High-Speed Train System. ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 1490–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Bai, Y.; Qiao, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, E.; Chao, S.; Qu, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Han, X.; et al. An Ultra-Simple Charge Supplementary Strategy for High Performance Rotary Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Small 2021, 17, e2101430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Liu, W.; Yang, H.; He, W.; Long, L.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Xi, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Ultra-stability high-voltage triboelectric nanogenerator designed by ternary dielectric triboelectrification with partial soft-contact and non-contact mode. Nano Energy 2021, 90, 106585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; He, W.; Li, G.; Tang, Q.; Guo, H.; Pu, X.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C. High performance floating self-excited sliding triboelectric nanogenerator for micro mechanical energy harvesting. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Kim, J.; Rajabi-Abhari, A.; Bui, V.; Kim, J.; Choi, D.; Oh, I. Long-Lasting and Steady Triboelectric Energy Harvesting from Low-Frequency Irregular Motions Using Escapement Mechanism. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2002929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, Y.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y.; Cao, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.L. Efficient Delivery of Power Generated by a Rotating Triboelectric Nanogenerator by Conjunction of Wired and Wireless Transmissions Using Maxwell’s Displacement Currents. Adv. Energy Mater. 2018, 8, 1802084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhang, M.; Huang, J.; Jiang, T.; Zou, J.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.L. Inductor-Free Wireless Energy Delivery via Maxwell’s Displacement Current from an Electrodeless Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Derakhshani, M.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Cao, C. Hybrid Energy-Harvesting Systems Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Matter 2021, 4, 116–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ren, Z.; Han, M.; Wan, J.; Zhang, H. Hybrid energy cells based on triboelectric nanogenerator: From principle to system. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Qu, J.; Chu, P.K.; Shin, D.-M.; Luo, Y.; Feng, S.-P. Hybrid photovoltaic-triboelectric nanogenerators for simultaneously harvesting solar and mechanical energies. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriphan, S.; Vittayakorn, N. Hybrid piezoelectric-triboelectric nanogenerators for flexible electronics: Recent advances and perspectives. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2022, 7, 100461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Zhou, T.; Wang, B.; Yin, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.L. Rotating-Sleeve Triboelectric–Electromagnetic Hybrid Nanogenerator for High Efficiency of Harvesting Mechanical Energy. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 8370–8378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Liang, X.; An, J.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Z.L. Soft-contact cylindrical triboelectric-electromagnetic hybrid nanogenerator based on swing structure for ultra-low frequency water wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2021, 81, 105625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, Z.; Liao, X.; Qiao, L.; Li, Y.; Dong, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B. A heaving point absorber-based ocean wave energy convertor hybridizing a multilayered soft-brush cylindrical triboelectric generator and an electromagnetic generator. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Tang, T.; Li, Y.; Hou, C.; Wen, F.; Yang, Z.; Chen, T.; Sun, L.; Liu, H.; Lee, C. A high-performance triboelectric-electromagnetic hybrid wind energy harvester based on rotational tapered rollers aiming at outdoor IoT applications. iScience 2021, 24, 102300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhu, H.; Cao, X.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting wind energy: A hybridized design of pinwheel by coupling triboelectrification and electromagnetic induction effects. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Jin, L.; Deng, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, M.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Rotating-Disk-Based Hybridized Electromagnetic–Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Sustainably Powering Wireless Traffic Volume Sensors. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6241–6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Du, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, S.; Ren, K.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Hybrid piezo/triboelectric nanogenerator for highly efficient and stable rotation energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as self-powered active sensors. Nano Energy 2015, 11, 436–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator (TENG)—Sparking an Energy and Sensor Revolution. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 2000137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jin, T.; Sun, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, G.; Chen, T.; Tian, Y.; Hou, X.; et al. Triboelectric nanogenerator sensors for soft robotics aiming at digital twin applications. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tat, T.; Libanori, A.; Au, C.; Yau, A.; Chen, J. Advances in triboelectric nanogenerators for biomedical sensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Pan, J.; Deng, S.; Xia, F.; Kim, T. Triboelectric Nanogenerator-Based Sensor Systems for Chemical or Biological Detection. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2008276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yu, A.; Zhai, J.; Wang, Z.L. Recent Progress of Functional Fiber and Textile Triboelectric Nanogenerators: Towards Electricity Power Generation and Intelligent Sensing. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2021, 3, 394–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Wang, S.; Niu, S.; Liu, C.; Xie, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Noncontact Free-Rotating Disk Triboelectric Nanogenerator as a Sustainable Energy Harvester and Self-Powered Mechanical Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 3031–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, S.; Gao, L.; Chen, X.; Tong, D.; Lei, W.; Yuan, P.; Mu, X.; Yu, H. Simultaneous energy harvesting and signal sensing from a single triboelectric nanogenerator for intelligent self-powered wireless sensing systems. Nano Energy 2020, 75, 104813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Gu, L.; Song, B.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric rotational speed sensor integrated into a bearing: A solid step to industrial application. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2020, 34, 100595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Z.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, N.; Cao, X. Thermal-Driven Soft-Contact Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting and Industrial Cooling Water Monitoring. Small 2022, 19, 2206269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.S.; Li, H.Y.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Z.L. Fully enclosed bearing-structured self-powered rotation sensor based on electrification at rolling interfaces for multi-tasking motion measurement. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Du, T.; Liu, C.; Hu, Z.; Sun, P.; Xu, M. A Ring-Type Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Rotational Mechanical Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Rotational Speed Sensing. Micromachines 2022, 13, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Kang, S.G.; Jeong, J. A self-powered absolute shaft encoder based on triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2022, 98, 107230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jing, Q.; Chen, J.; Bai, P.; Bai, J.; Zhu, G.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z.L. A Self-Powered Angle Measurement Sensor Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2166–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Tang, X.; Fang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Chen, X.; Zheng, L. Self-driven real-time angle vector sensor as security dialer based on bi-directional backstop triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2022, 99, 107430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; An, J.; Nie, J.; Luo, J.; Shao, J.; Jiang, T.; Chen, B.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.L. A Self-Powered Angle Sensor at Nanoradian-Resolution for Robotic Arms and Personalized Medicare. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2001466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Chen, B.D.; Jiang, T.; Xu, L.; Han, C.B.; Gu, G.Q.; Wang, Z.L. Radial-Grating Pendulum-Structured Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting and Tilting-Angle Sensing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, Z.; Pan, L.; Gao, R.; Zhang, B.; Yang, L.; Guo, H.; Liao, R.; Wang, Z.L. Direct-Current Rotary-Tubular Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Liquid-Dielectrics Contact for Sustainable Energy Harvesting and Chemical Composition Analysis. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 2587–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tang, W.; Pang, Y.; Han, C.; Wang, Z.L. Active Micro-Actuators for Optical Modulation Based on a Planar Sliding Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Huang, X.; Xu, L.; Lai, Y.-C.; Zhang, C.; Wu, H. Triboelectric nanogenerators enabled sensing and actuation for robotics. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 104005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, M.; Huang, B.; Liu, H.; Hu, W.; Shao, L.-H.; Wang, Z.L. Nanoporous-Gold-Based Hybrid Cantilevered Actuator Dealloyed and Driven by A Modified Rotary Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, X.; Fan, H.; Wang, C.; Ma, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, M.; Lei, S.; Wang, W. Wind energy harvester based on coaxial rotatory freestanding triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered water splitting. Nano Energy 2018, 50, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yin, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhou, T.; Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Tang, W.; Cao, R.; Yuan, Z.; Li, N.; et al. Self-Powered Electrospinning System Driven by a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10439–10445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wei, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Rui, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, S.; Wang, P. Self-powered droplet manipulation system for microfluidics based on triboelectric nanogenerator harvesting rotary energy. Lab Chip 2021, 21, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, Q.; Feng, X.; Kuang, S.; Panwar, N.; Song, P.; Yang, C.; Yang, G.; Hemu, X.; Zhang, G.; Yoon, H.S.; et al. Self-powered, on-demand transdermal drug delivery system driven by triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 62, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wei, X.; Zhu, L.; Yin, D.; Wei, A.; Bi, X.; Liu, T.; Zhou, G.; Qiang, Y.; Sun, X.; et al. Enhancing proliferation and migration of fibroblast cells by electric stimulation based on triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, E.; Kong, X.; Gai, Y.; Qu, X.; Li, Q.; Xue, S.; Guo, P.; et al. Chemical warfare agents decontamination via air mircoplasma excited by a triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2022, 95, 106992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, P.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Peng, Y.; Wang, B.; Wu, Z. Self-powered antifouling UVC pipeline sterilizer driven by the discharge stimuli based on the modified freestanding rotary triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2022, 95, 106969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Kim, D.Y. Rotating Gate-Driven Solution-Processed Triboelectric Transistors. Sensors 2022, 22, 3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

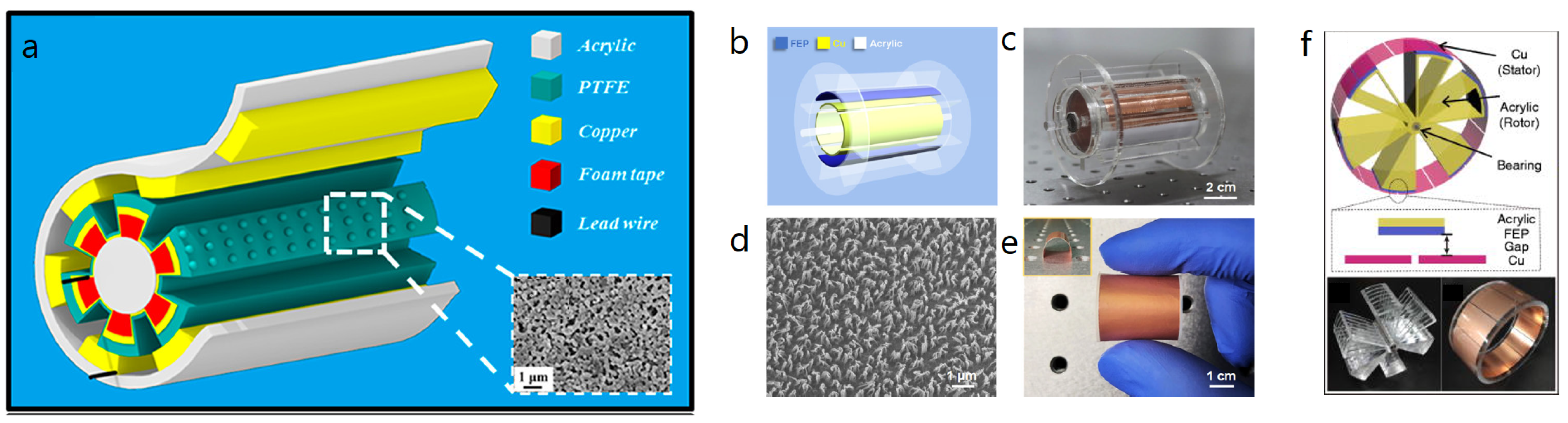
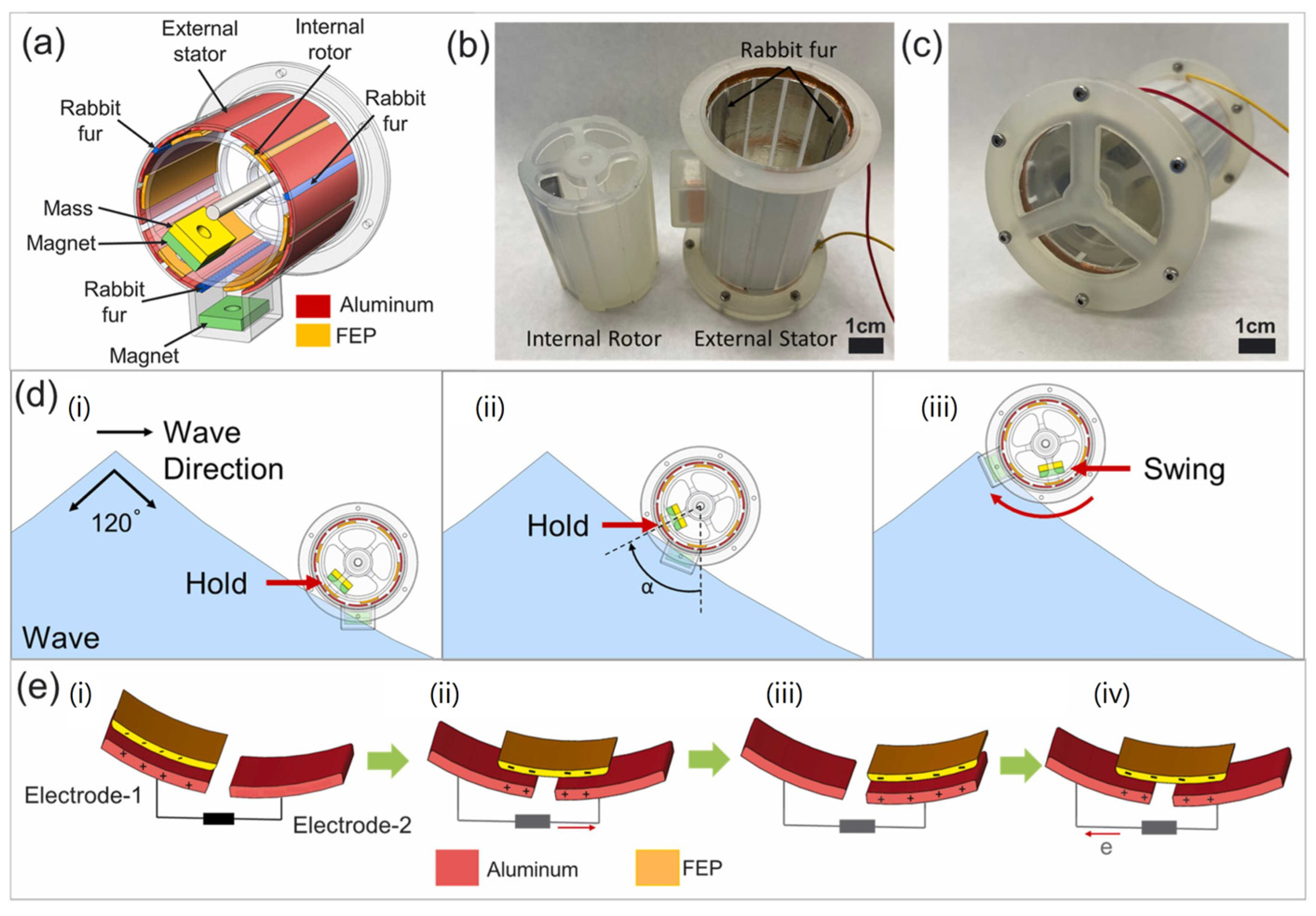
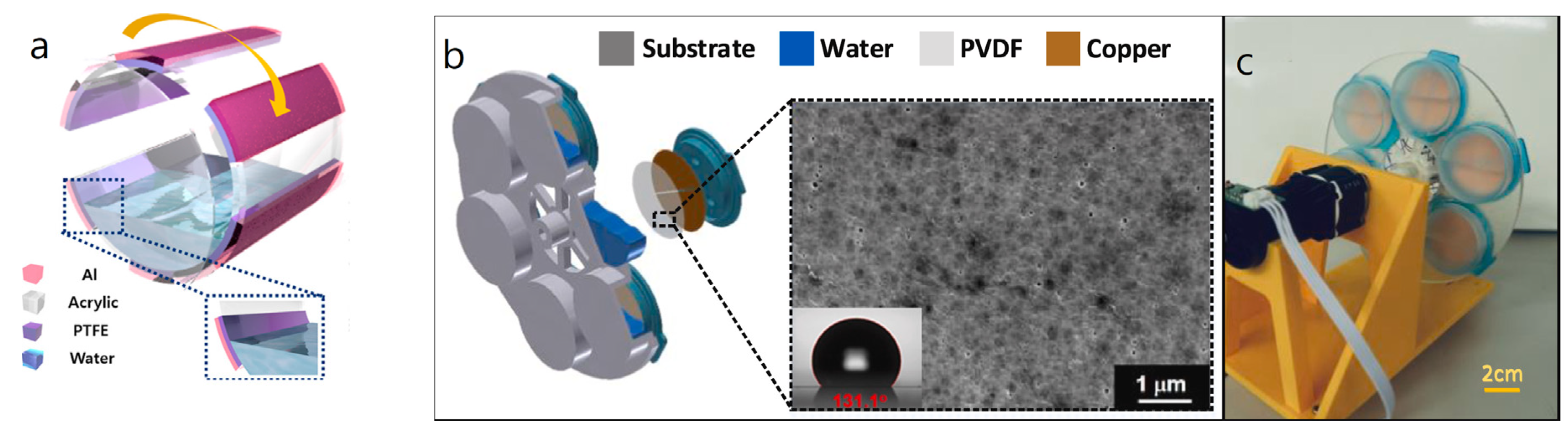
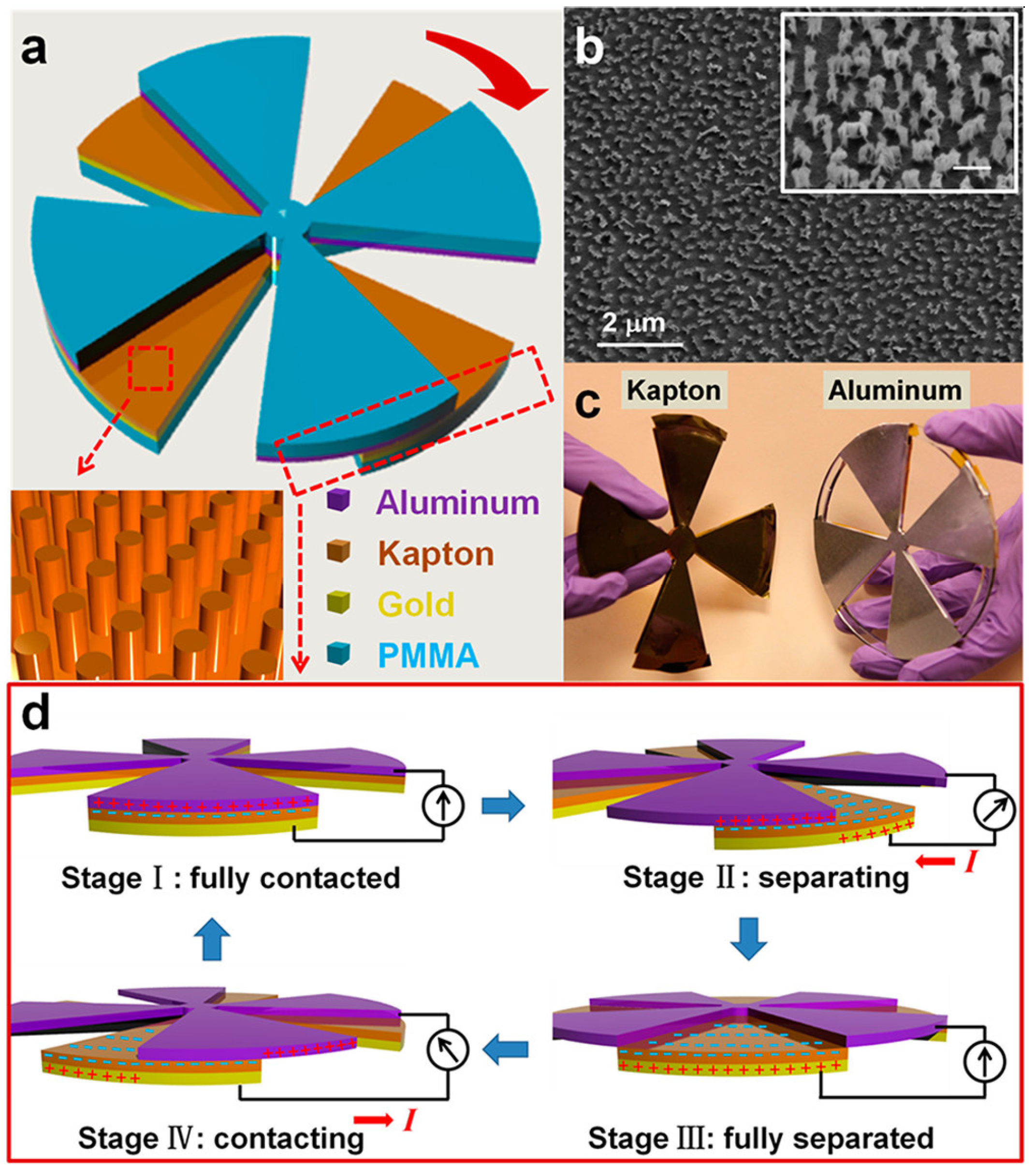
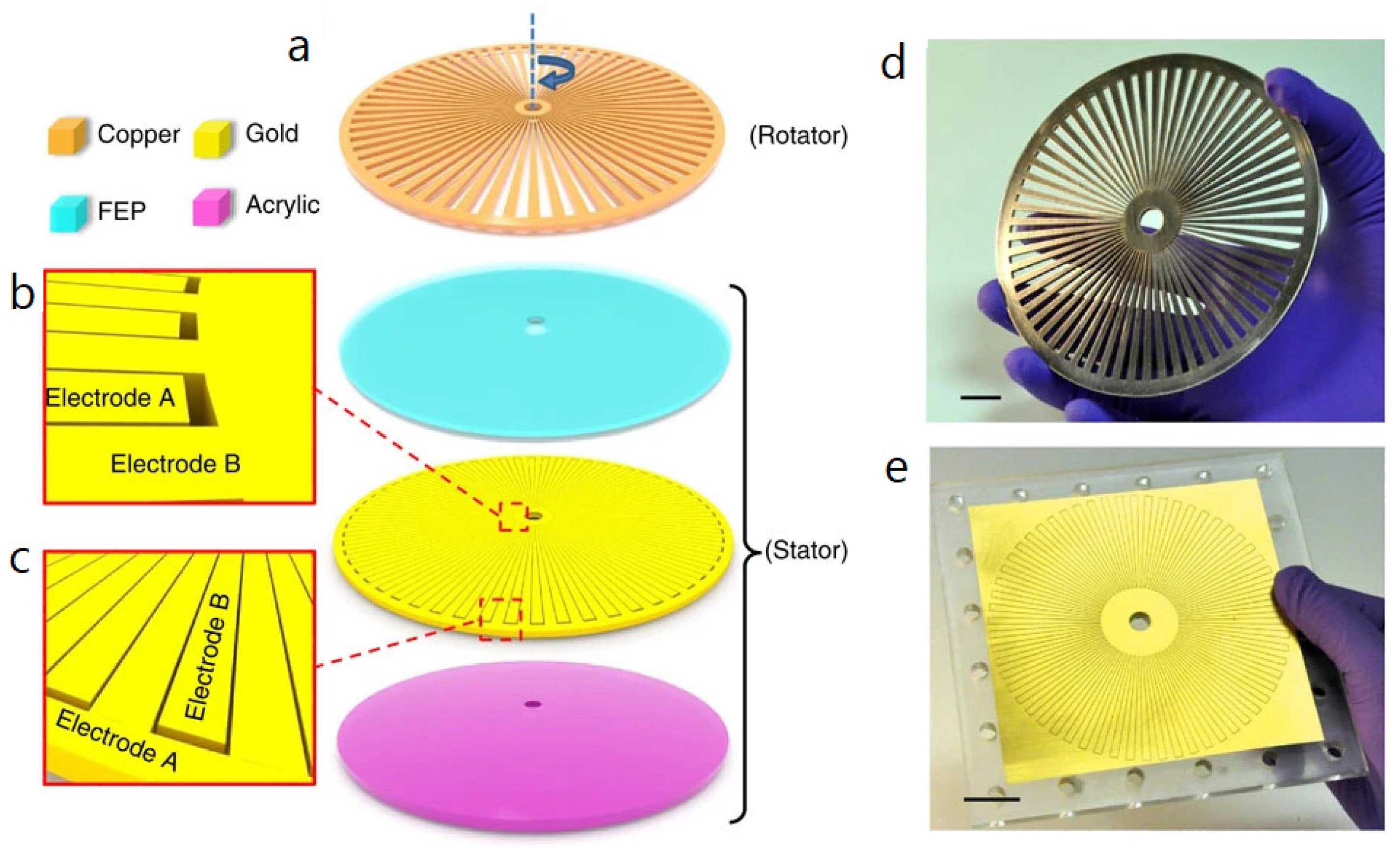

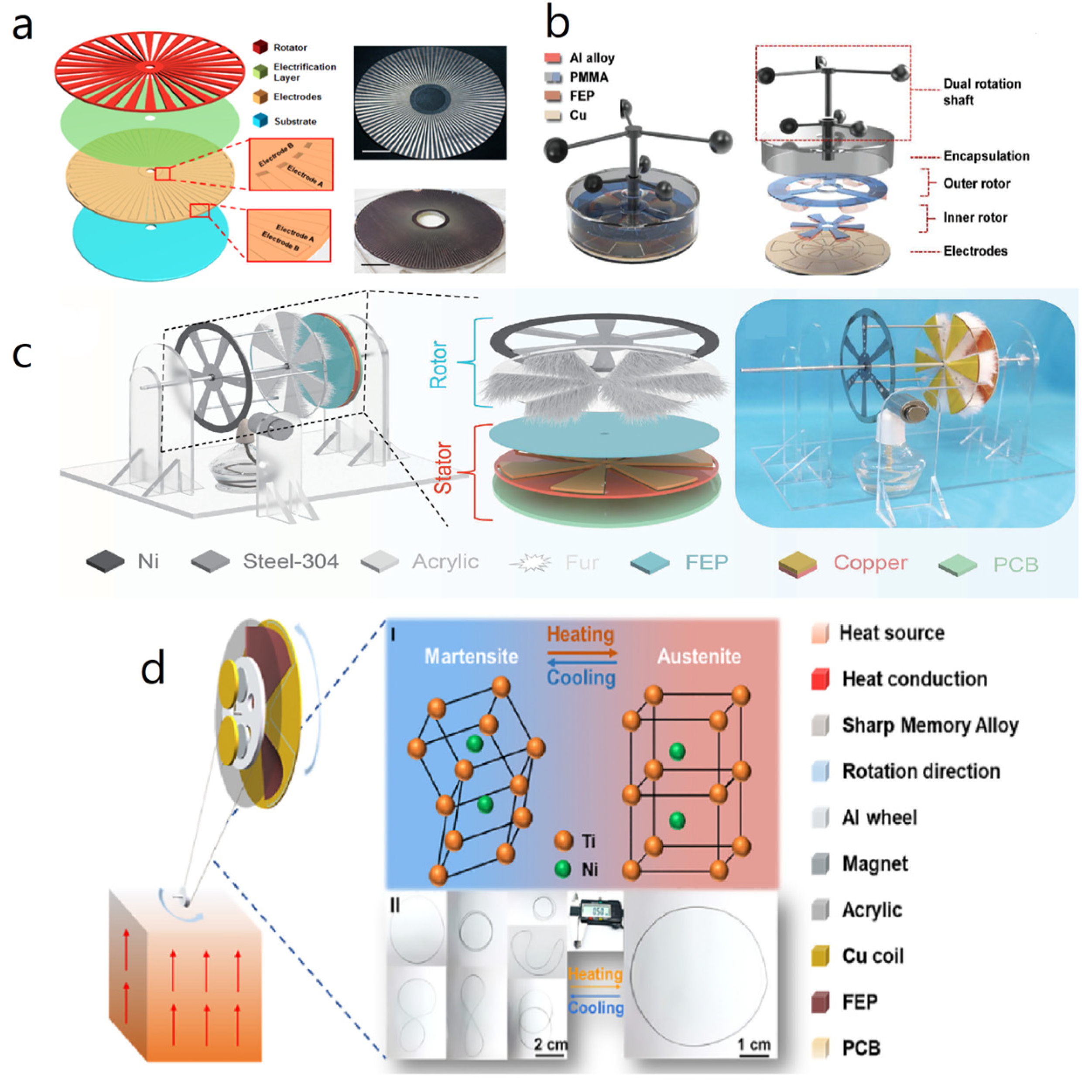
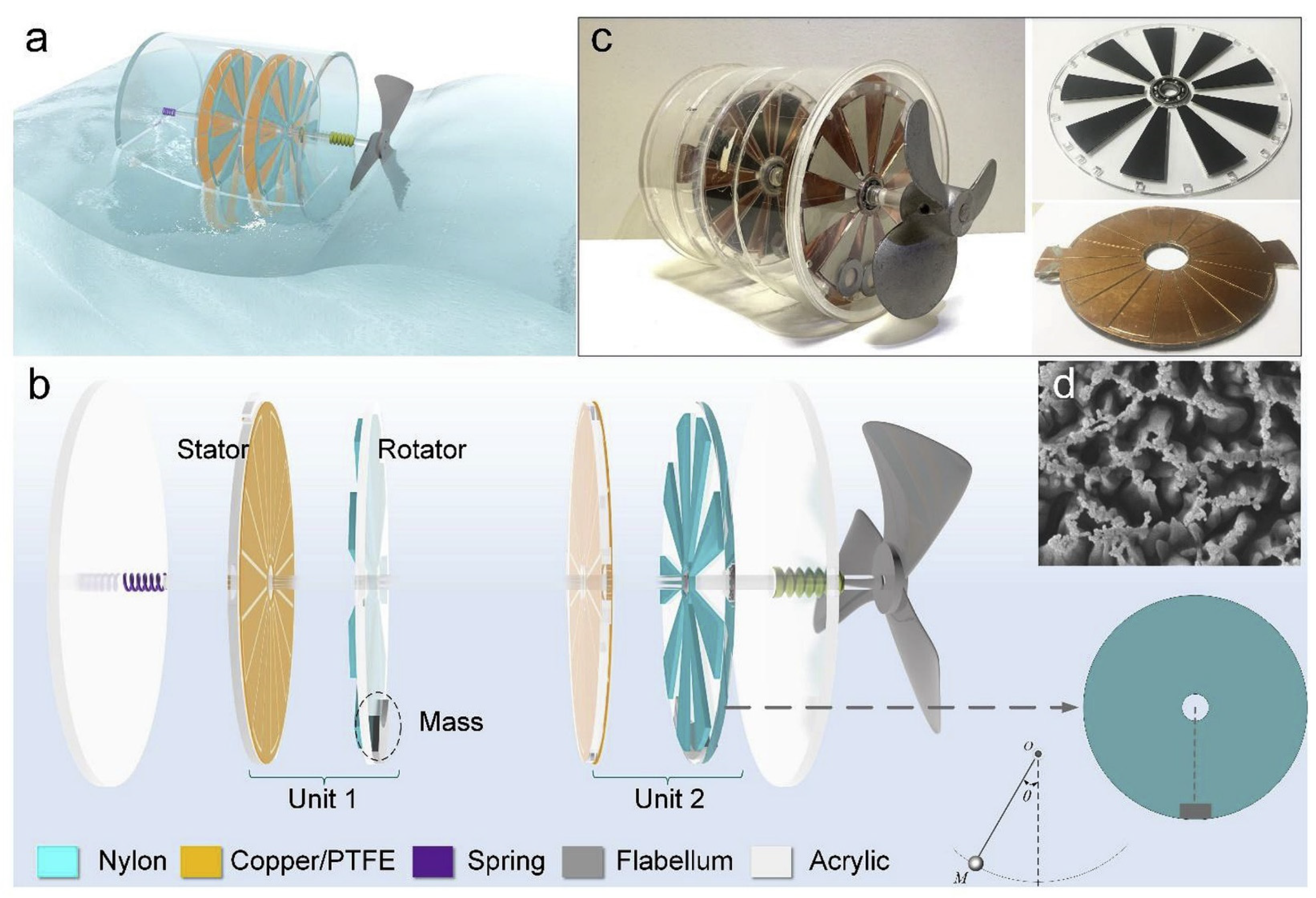
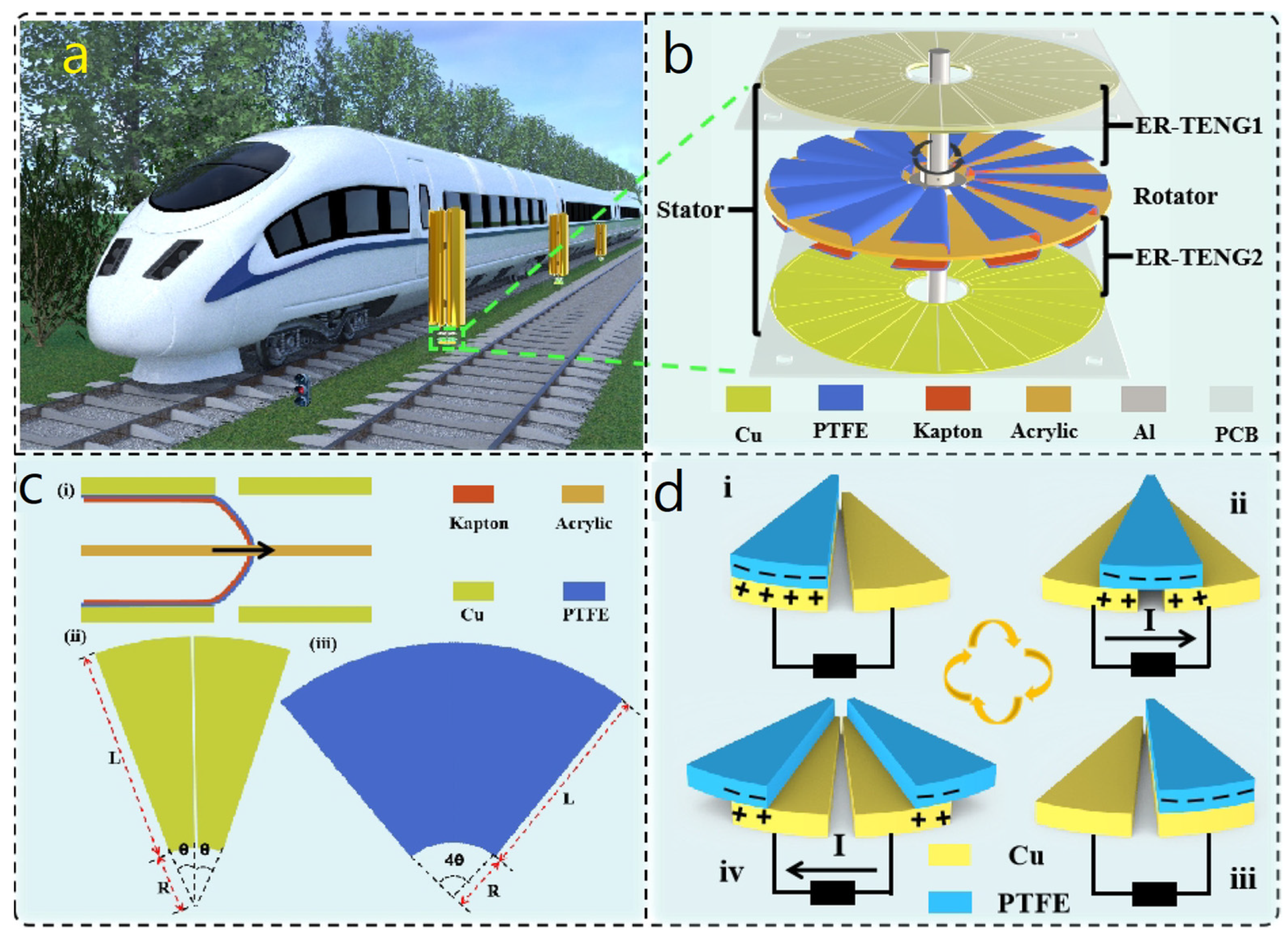
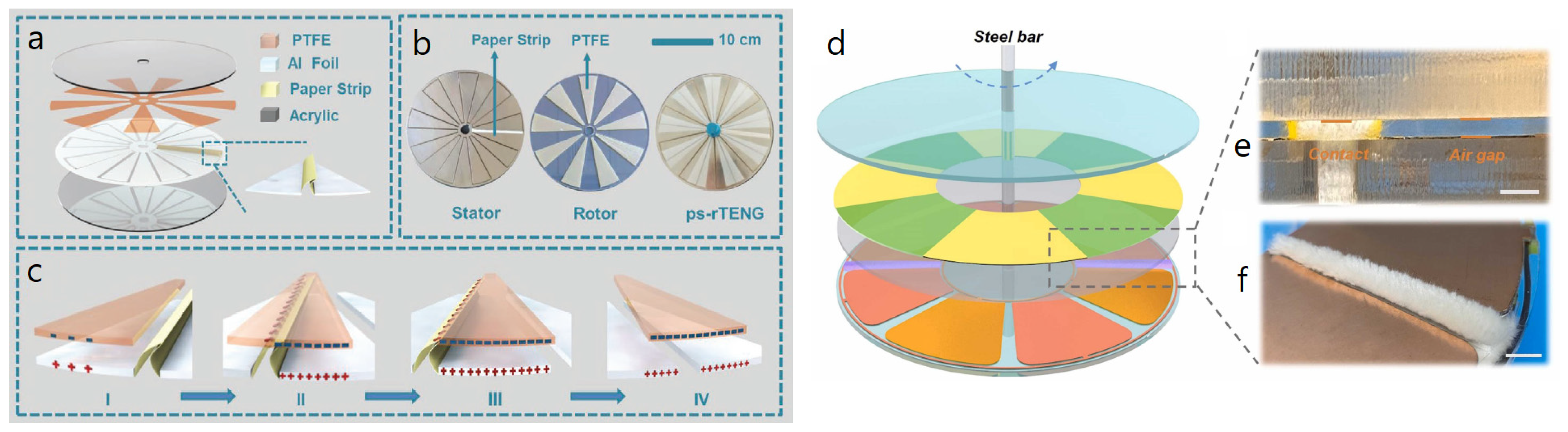
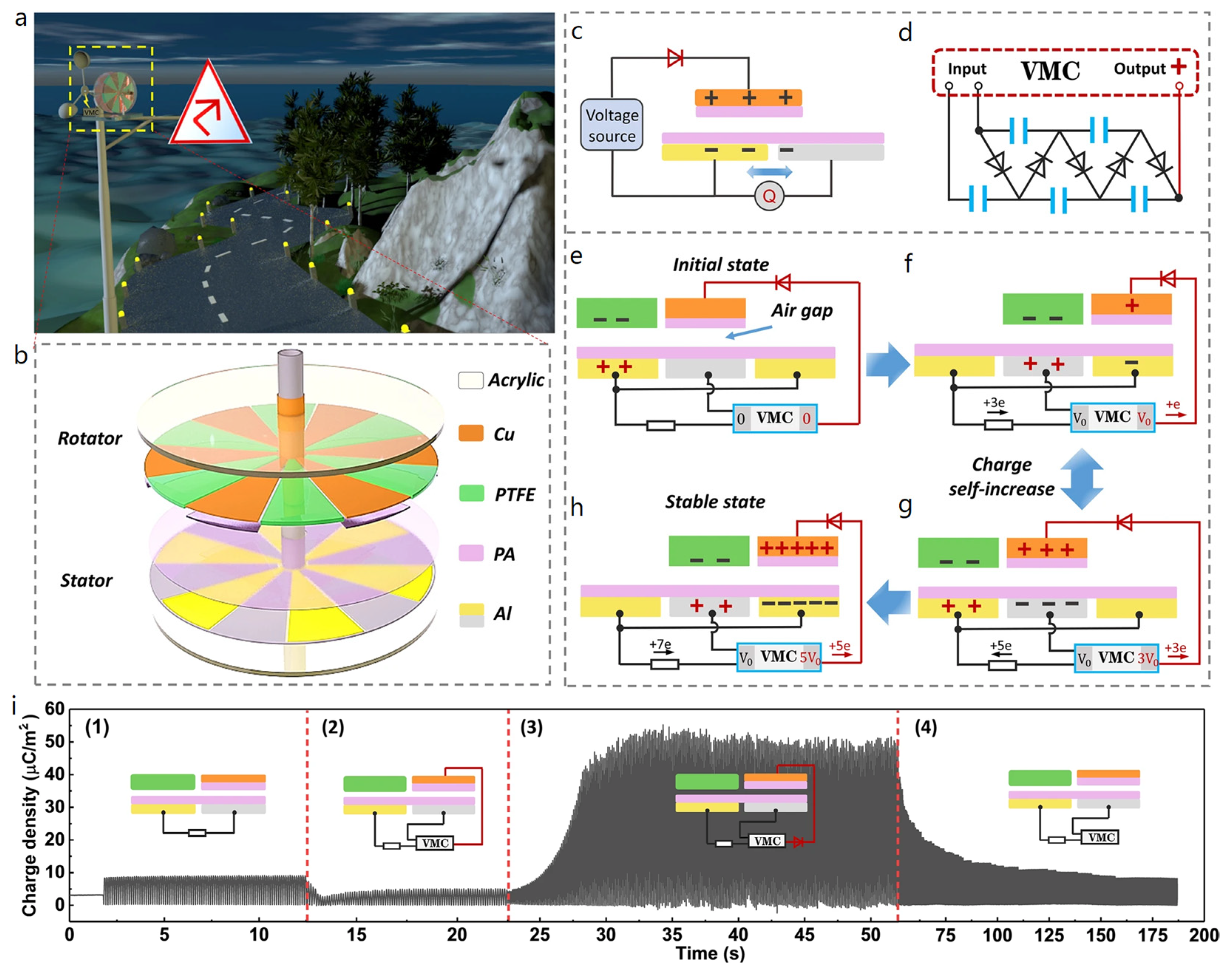

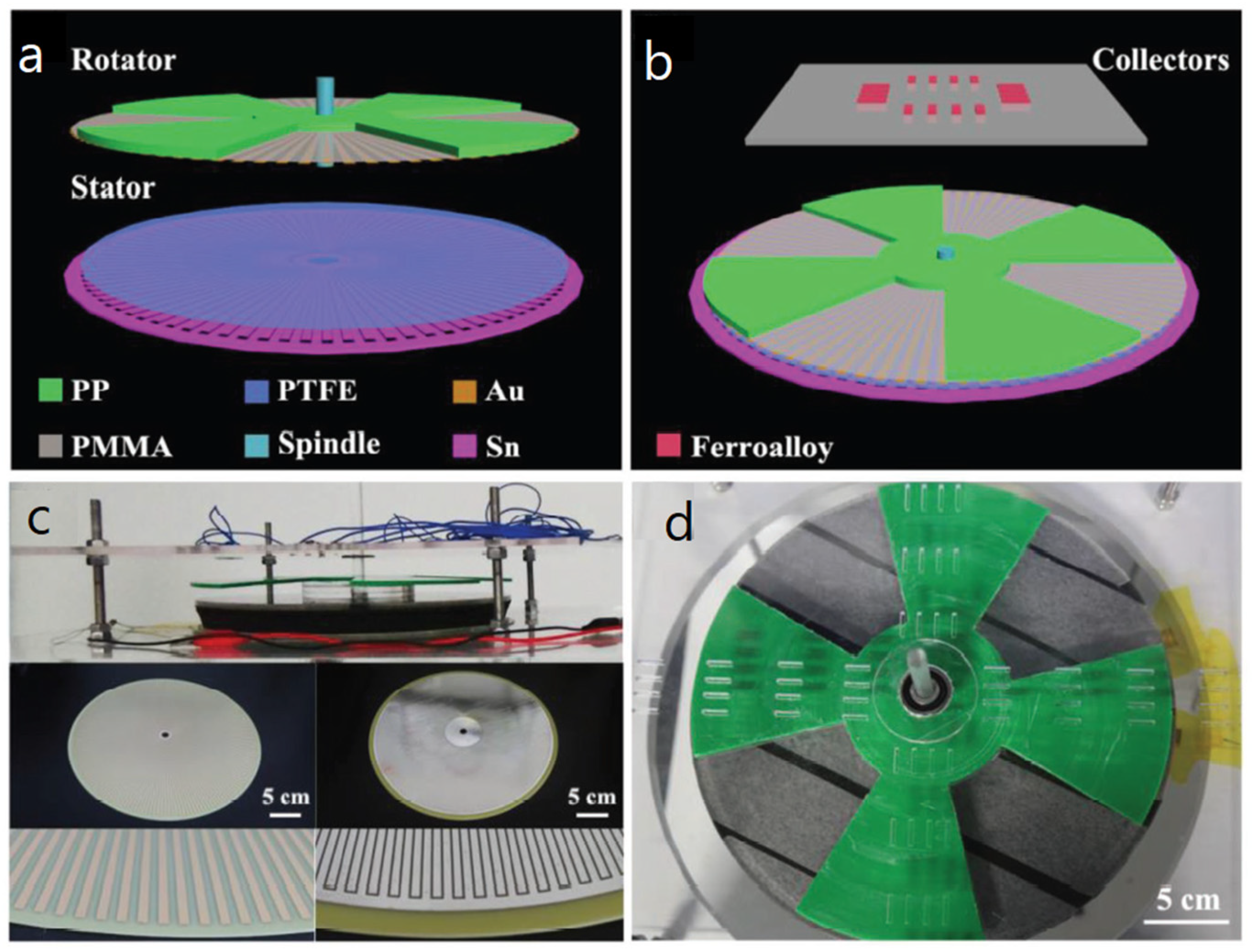
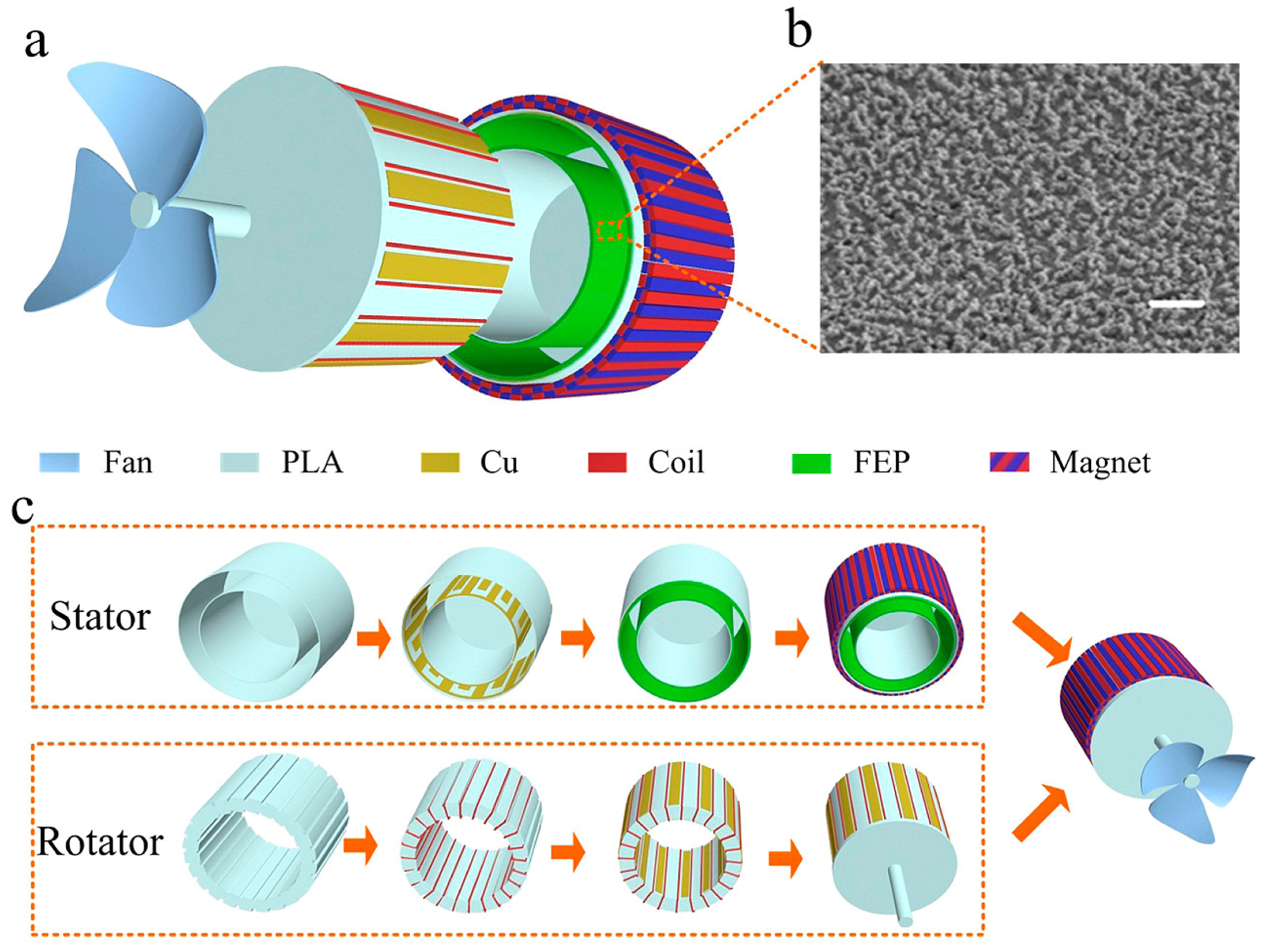
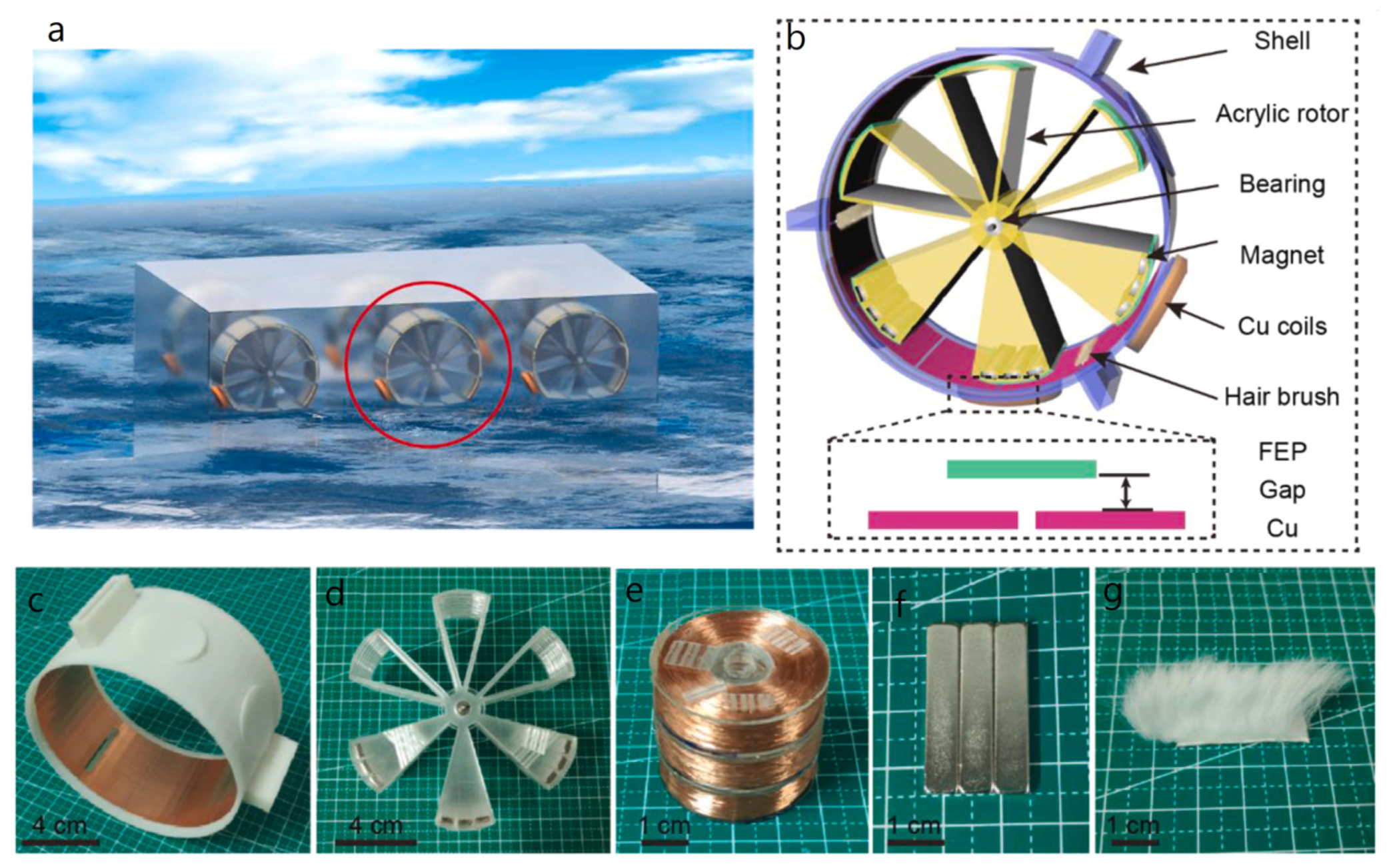
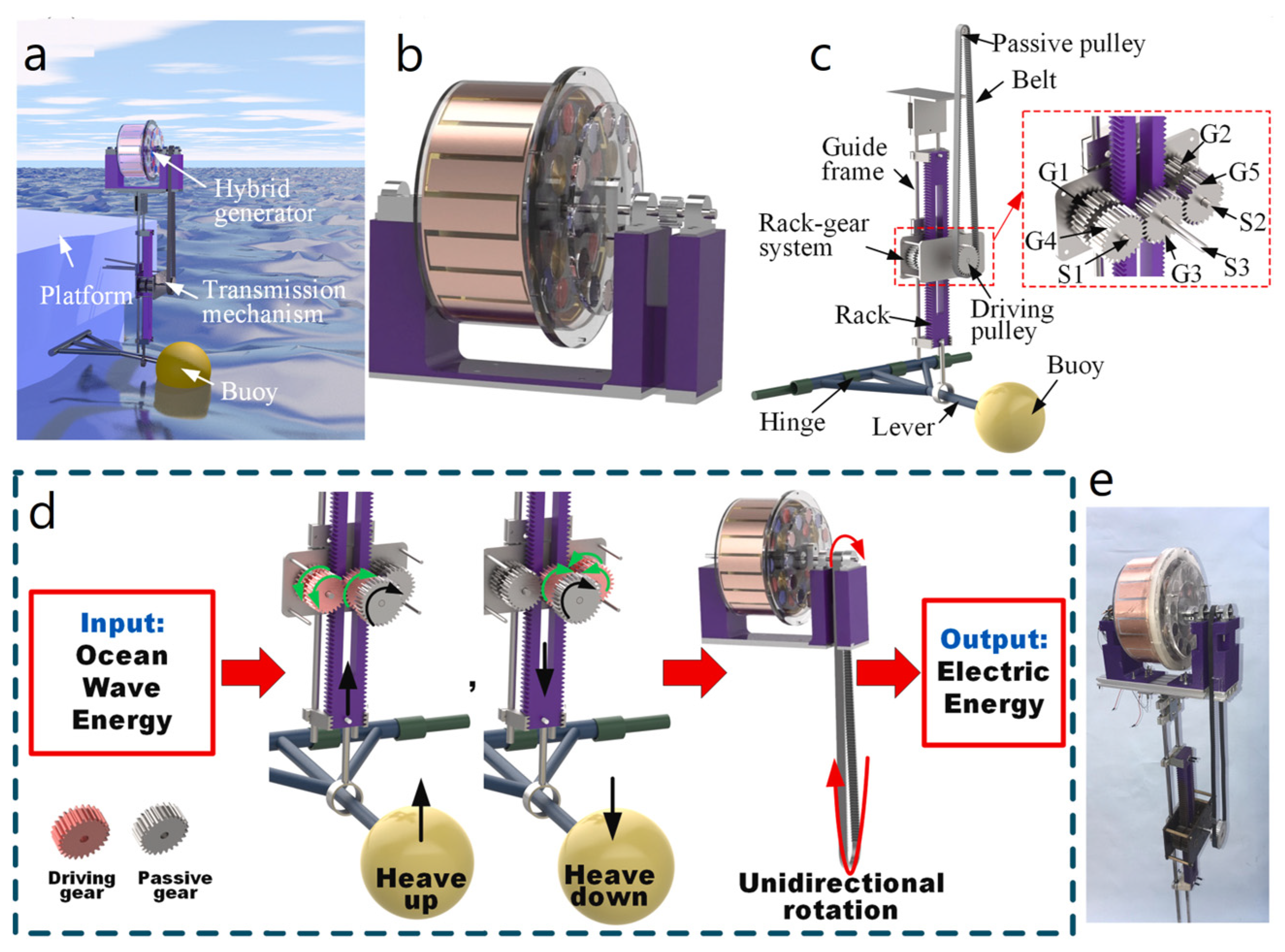
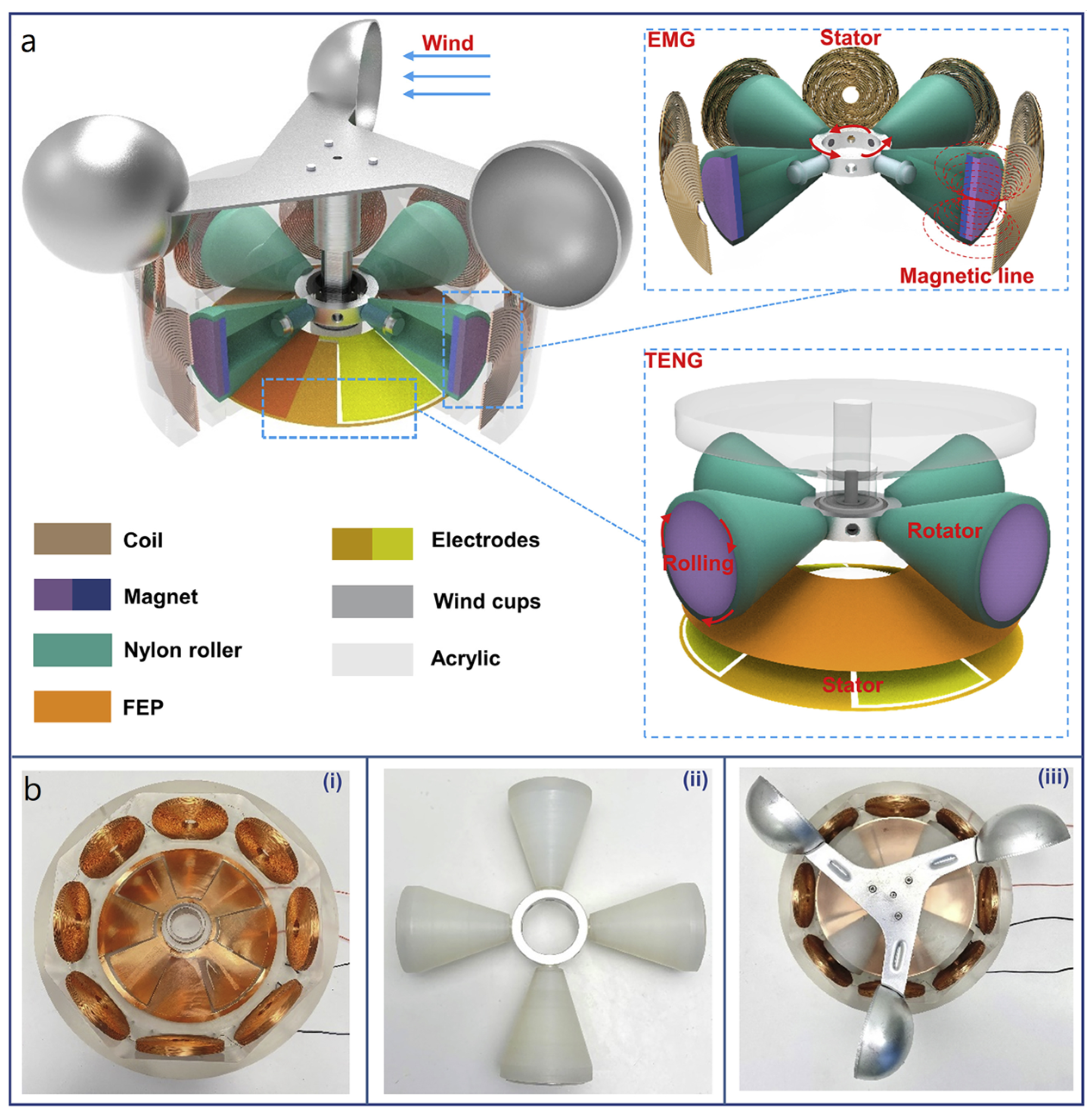
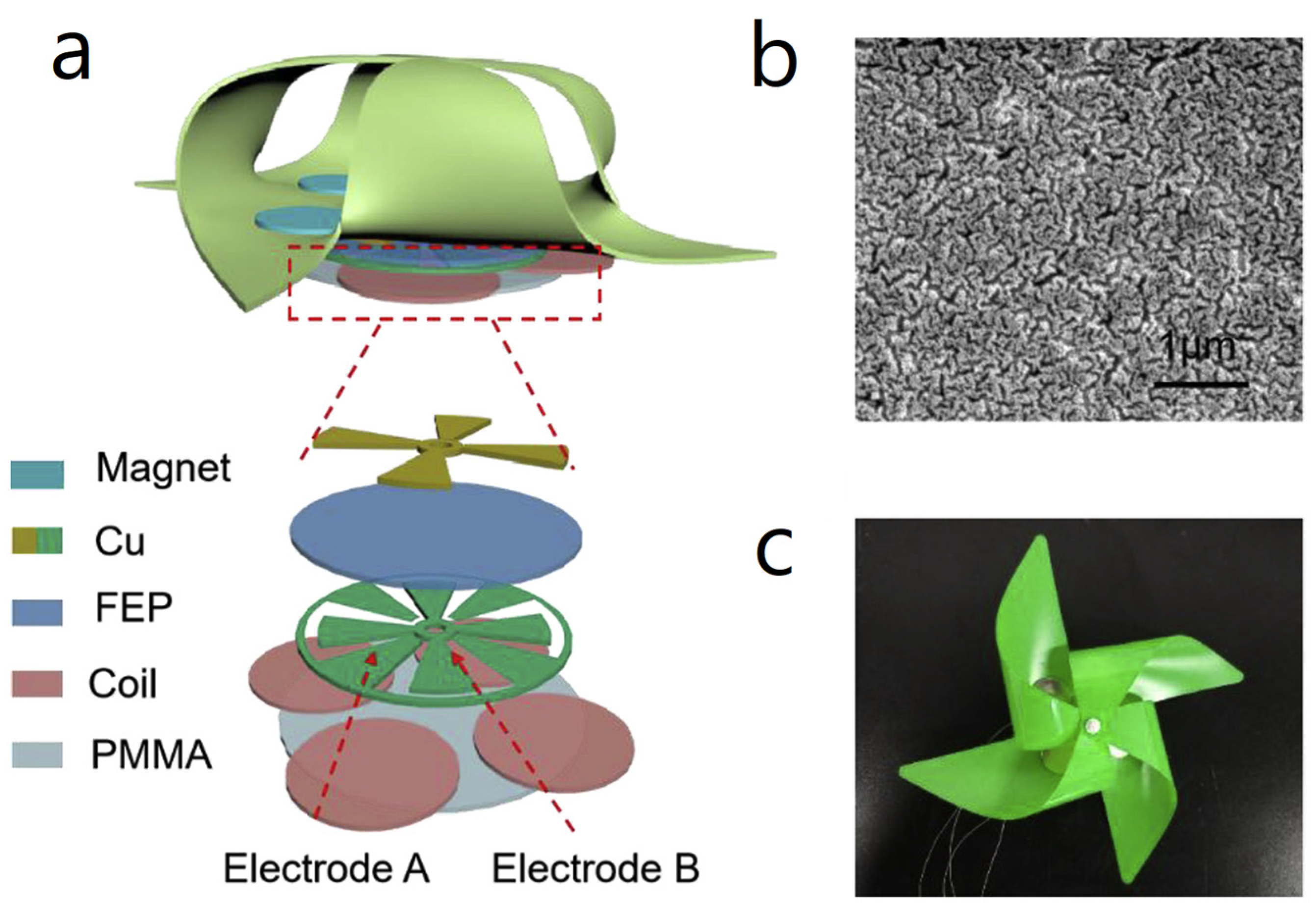
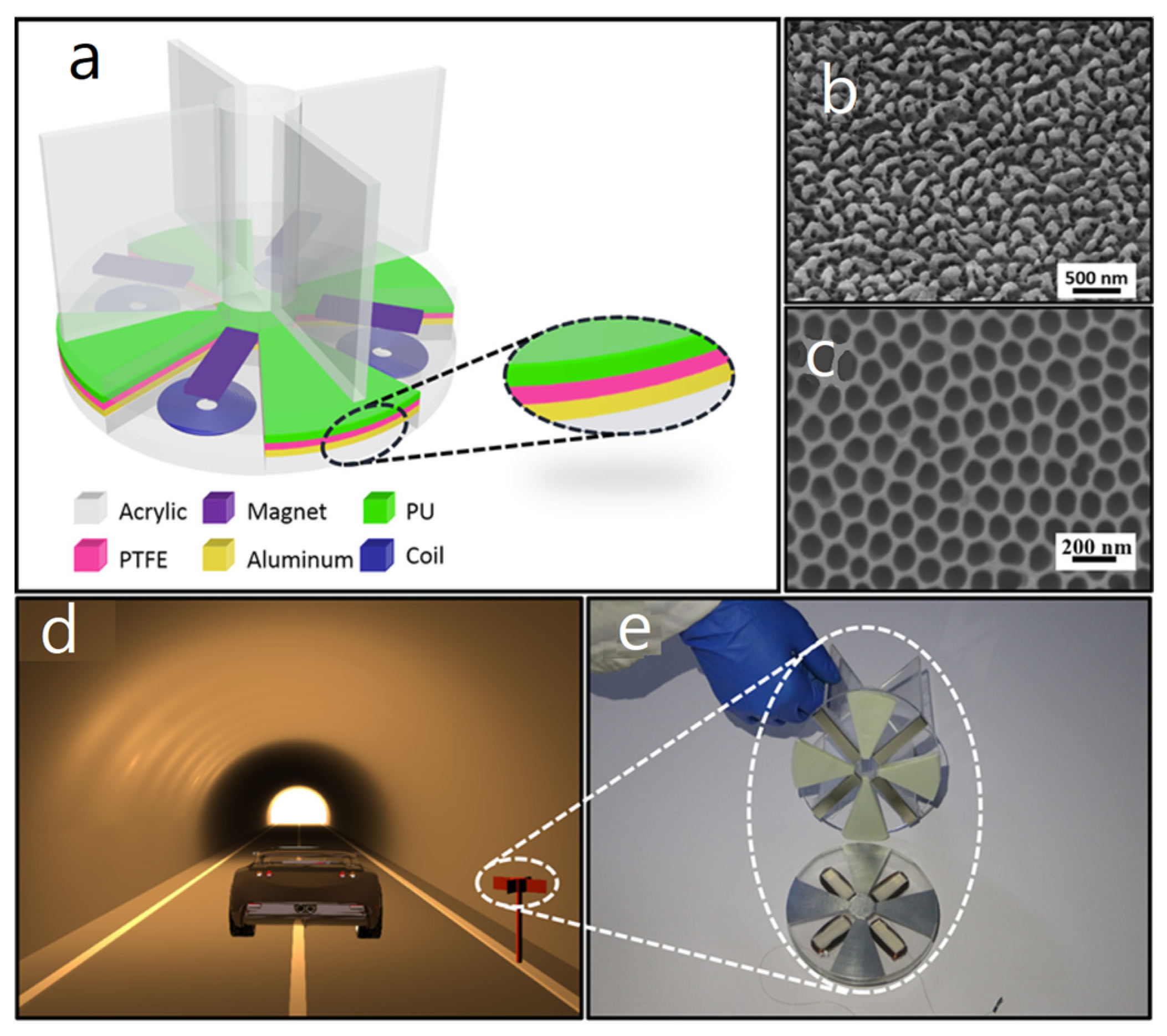
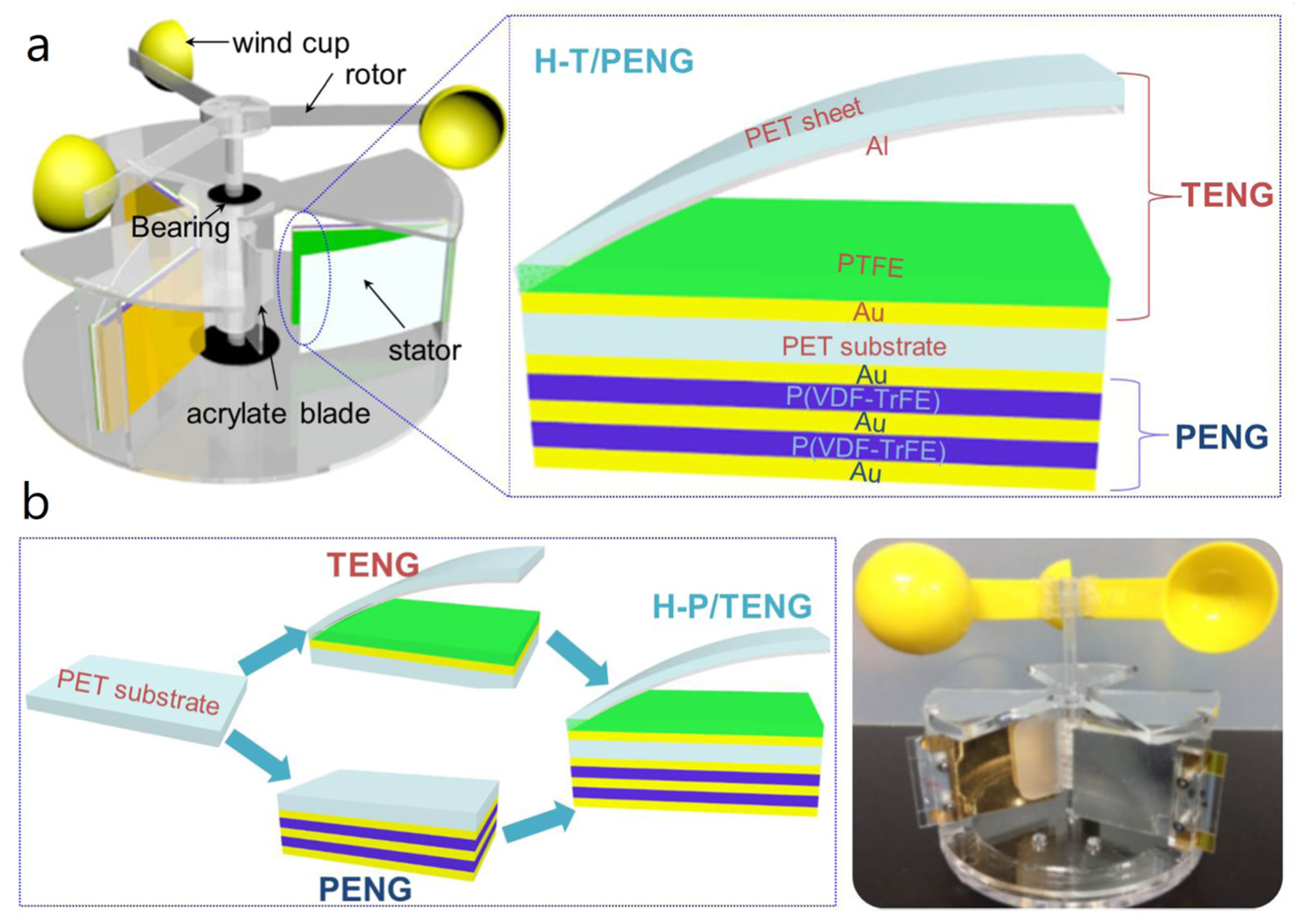
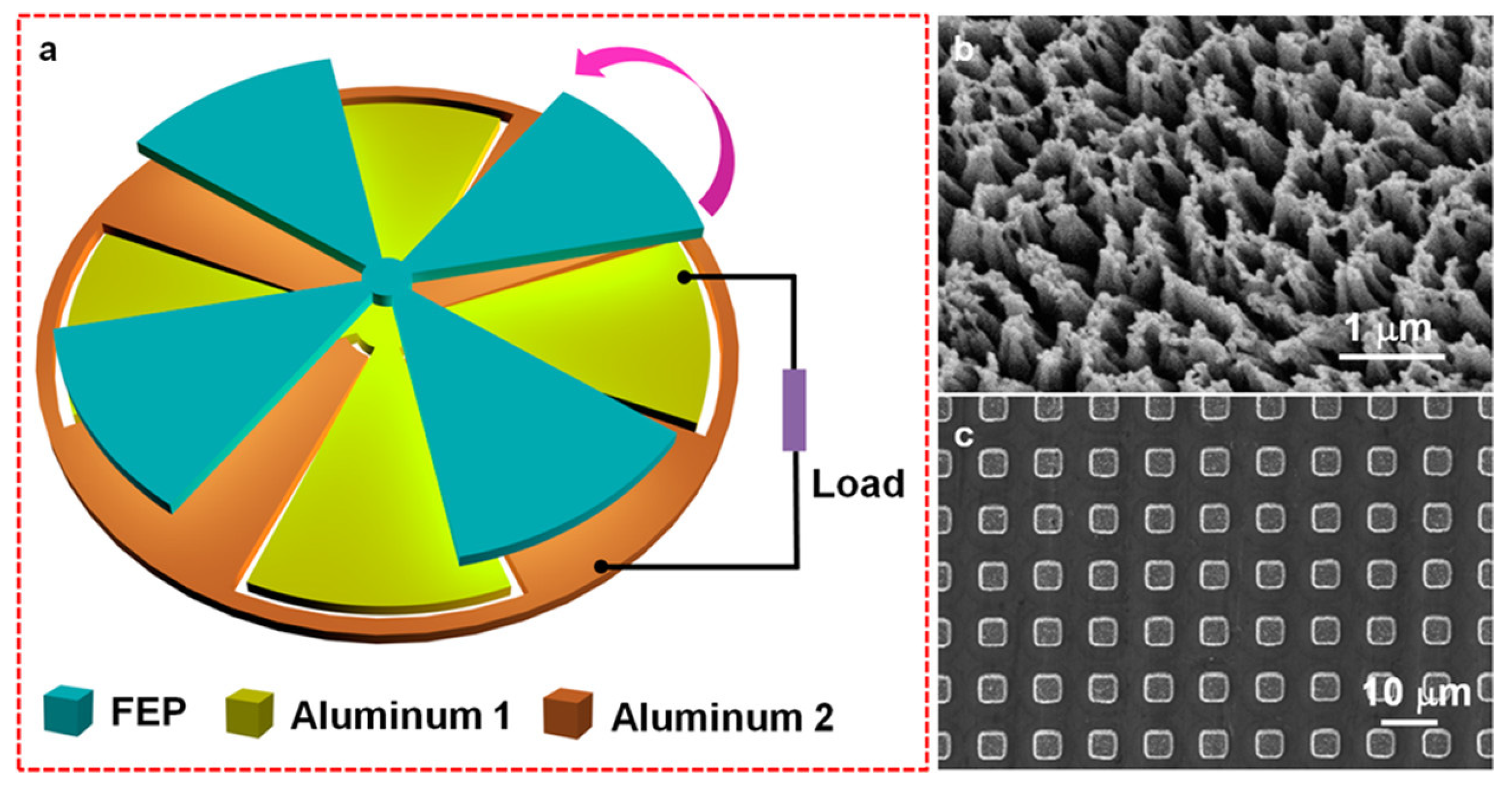
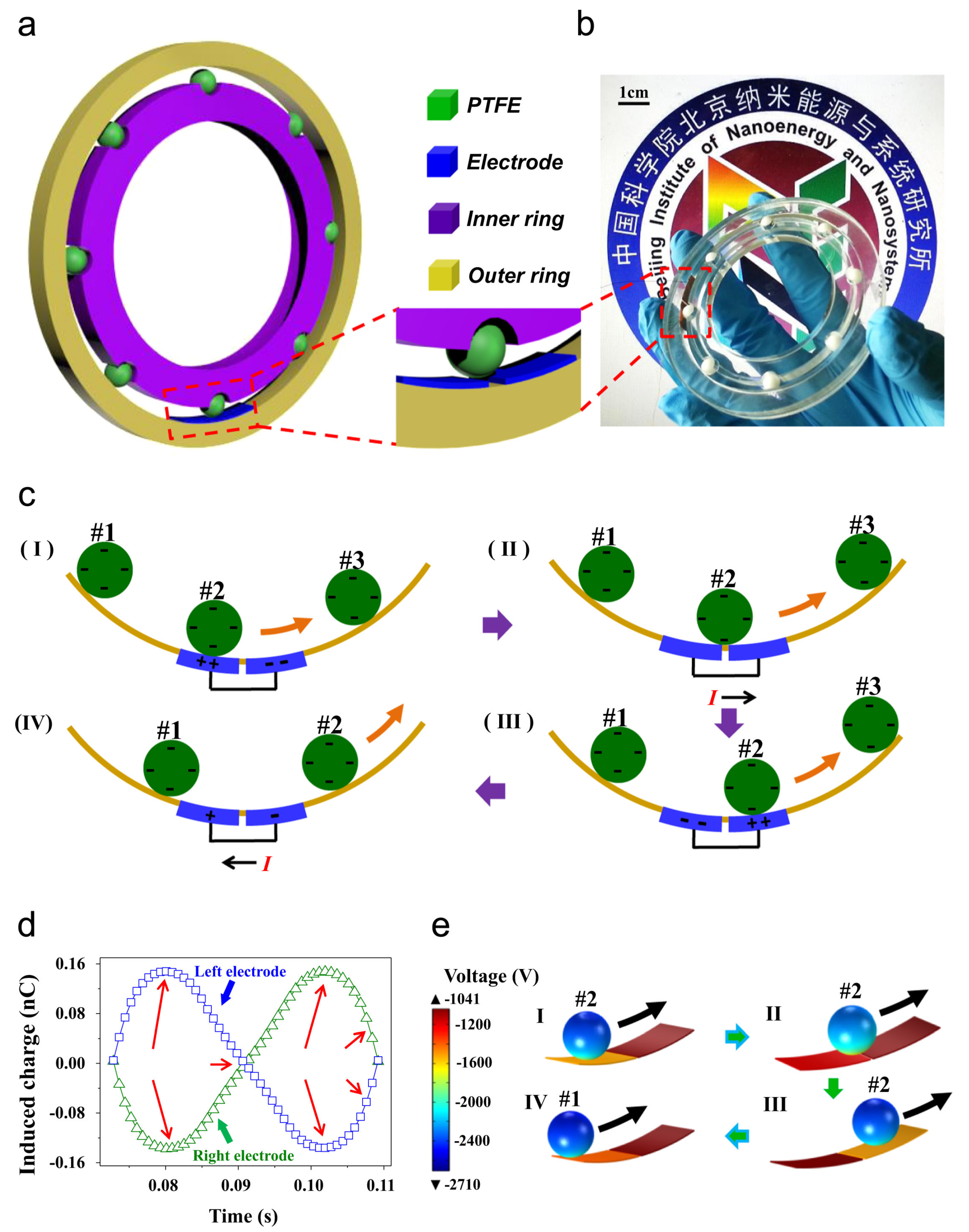

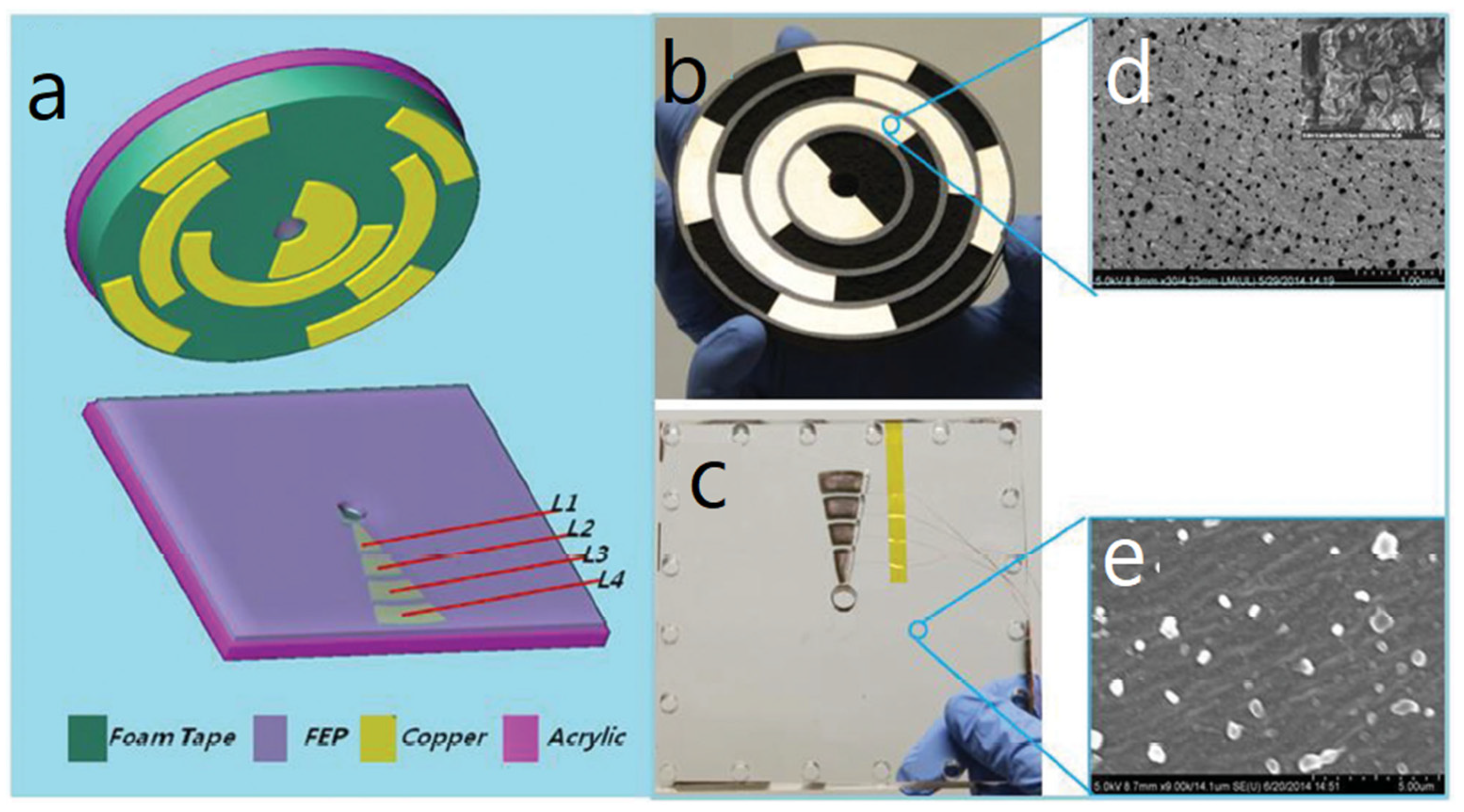

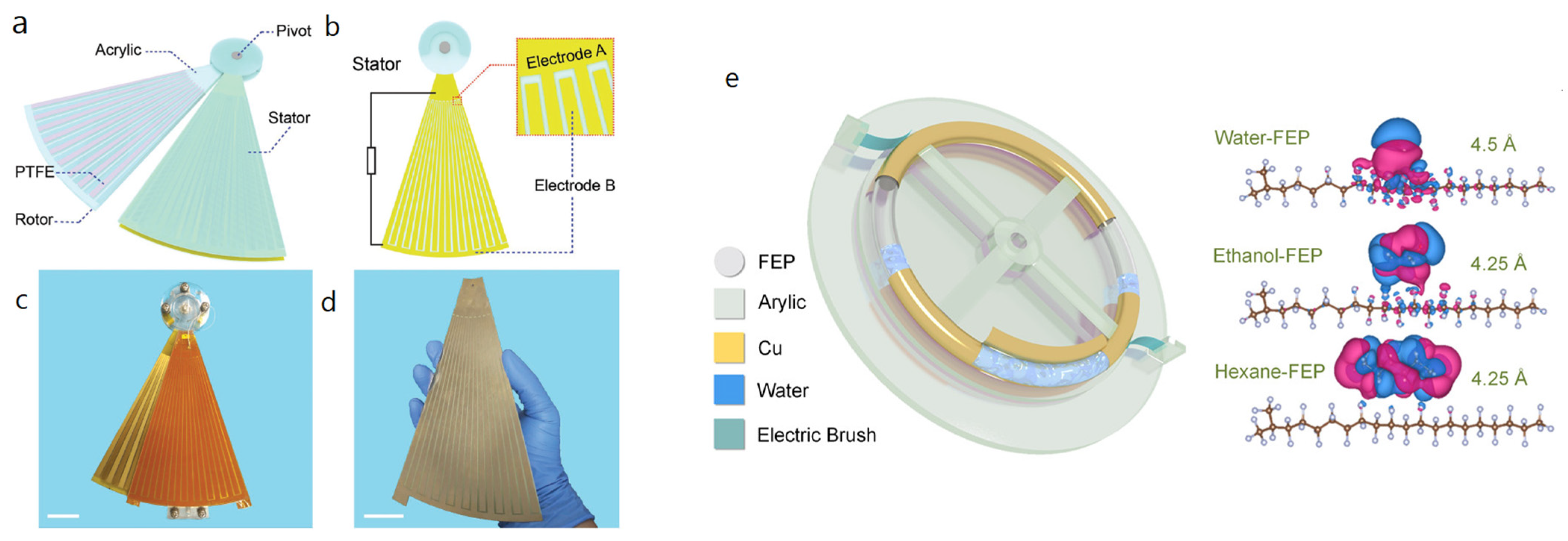
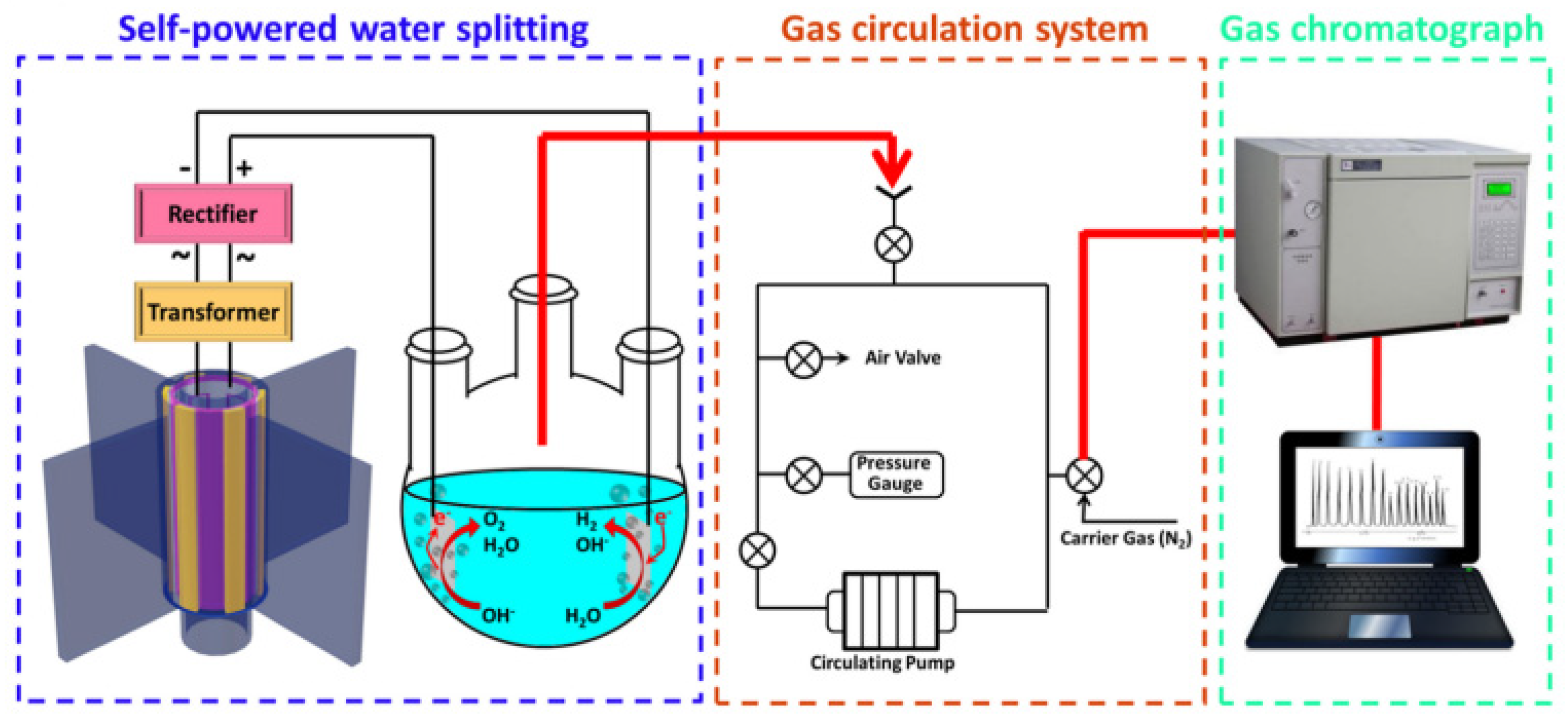
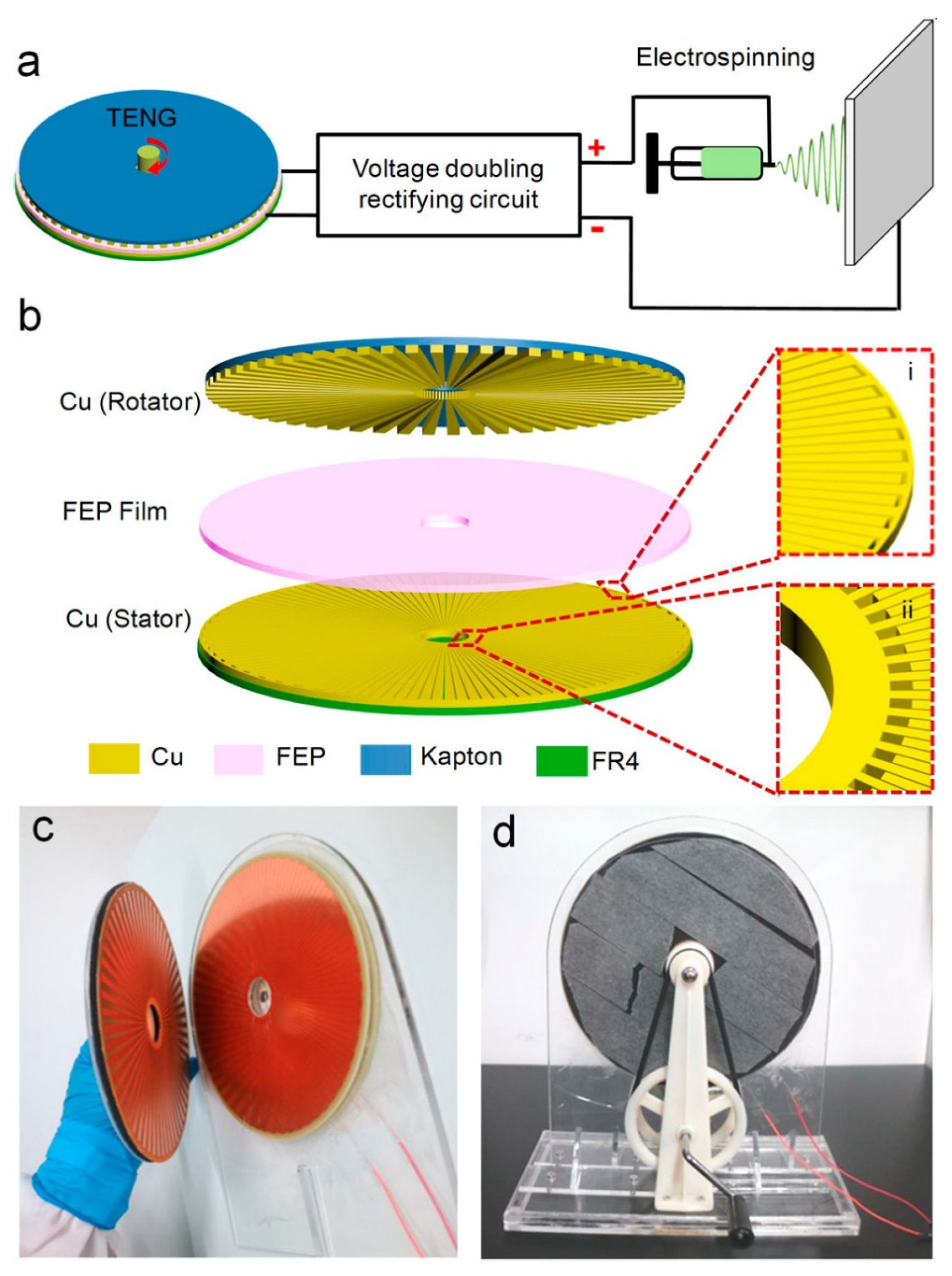
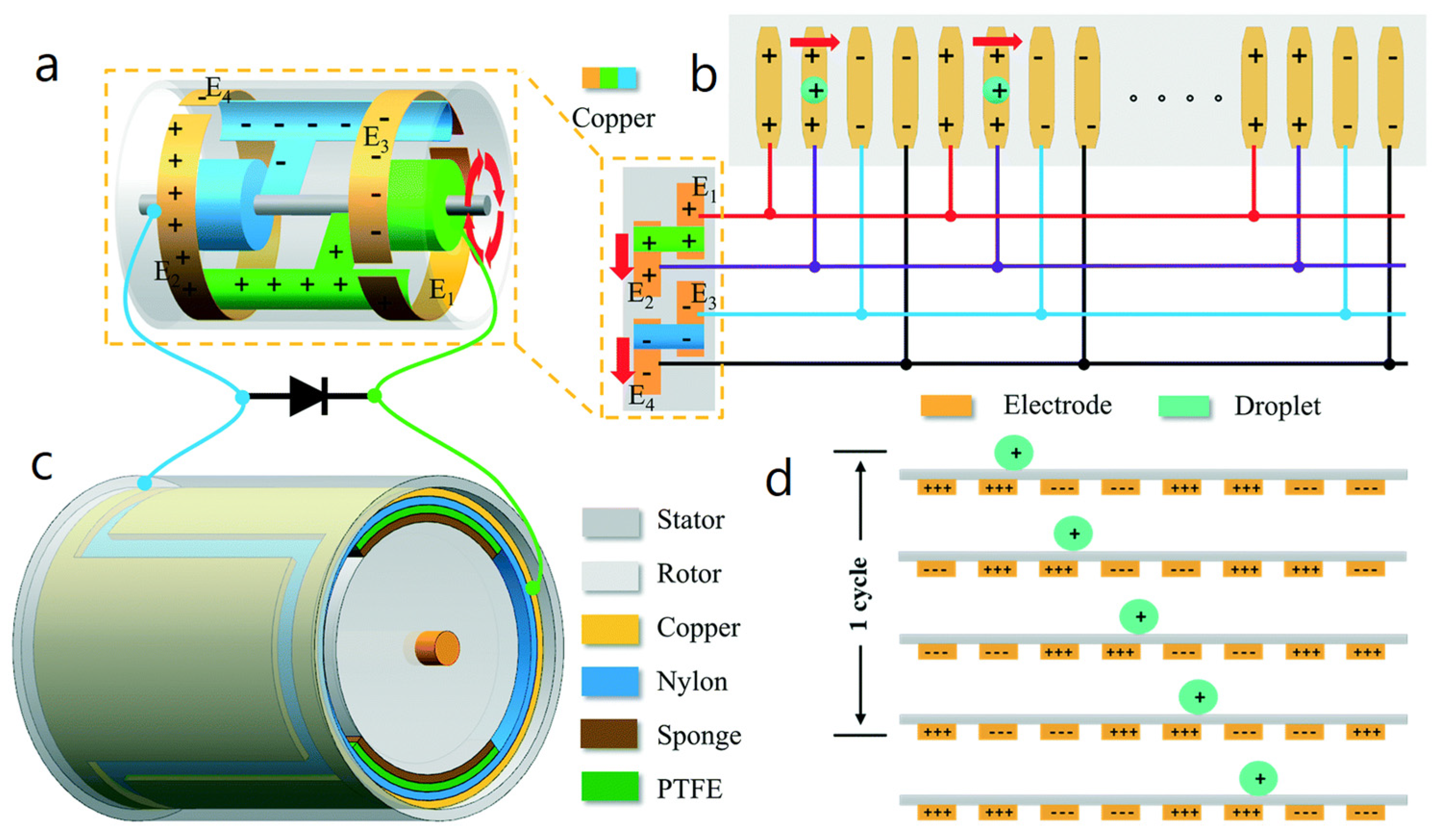
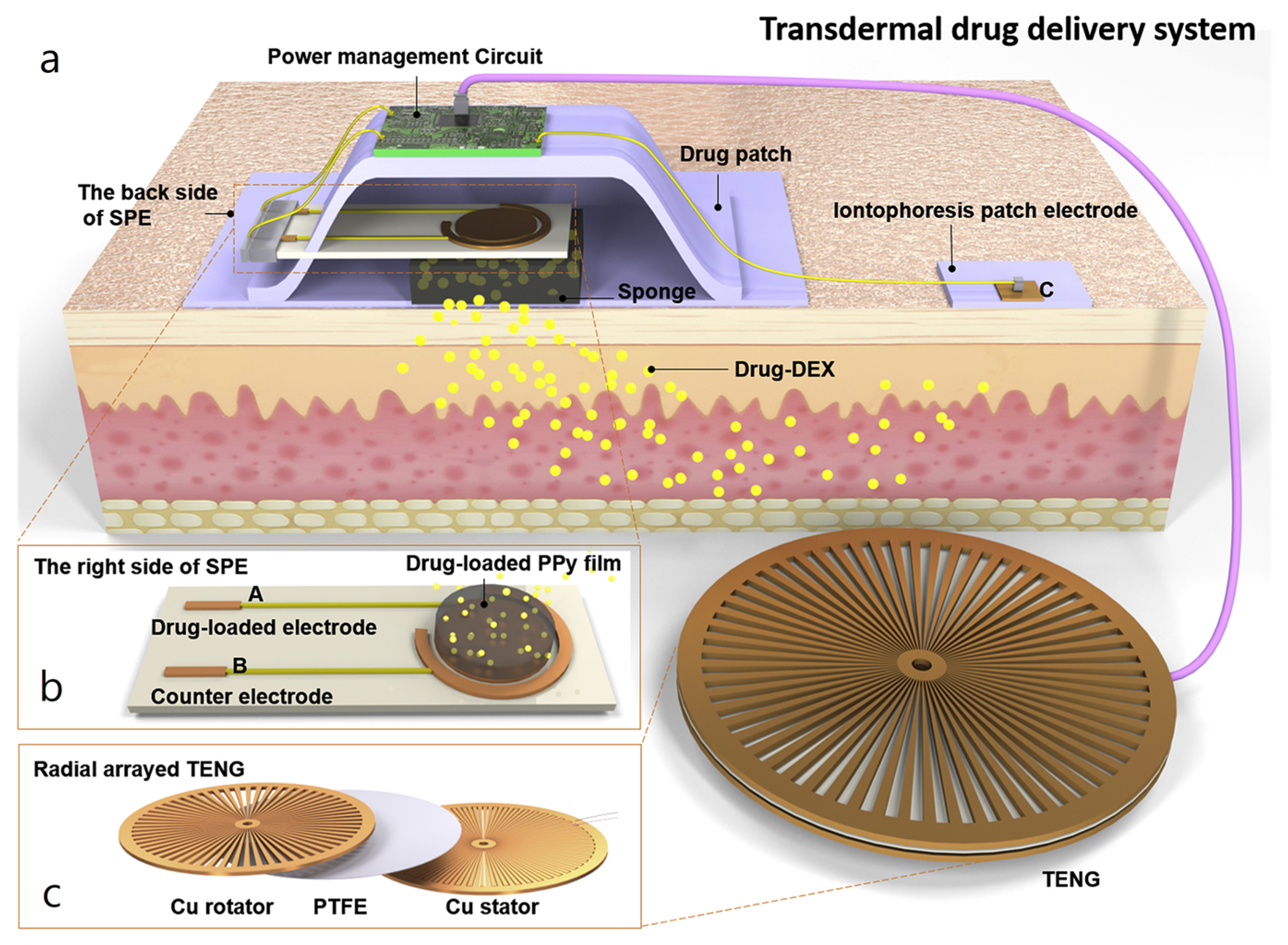

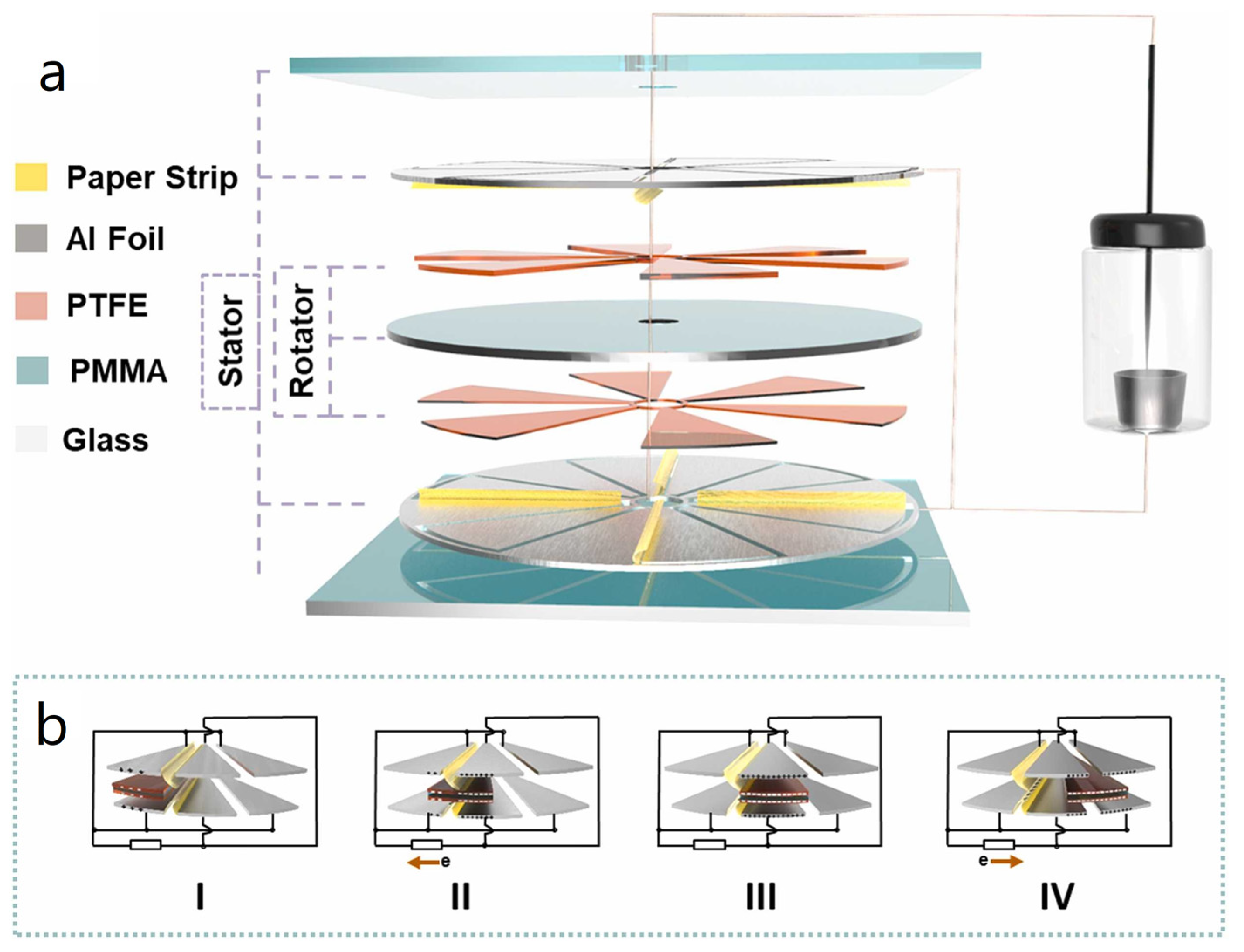

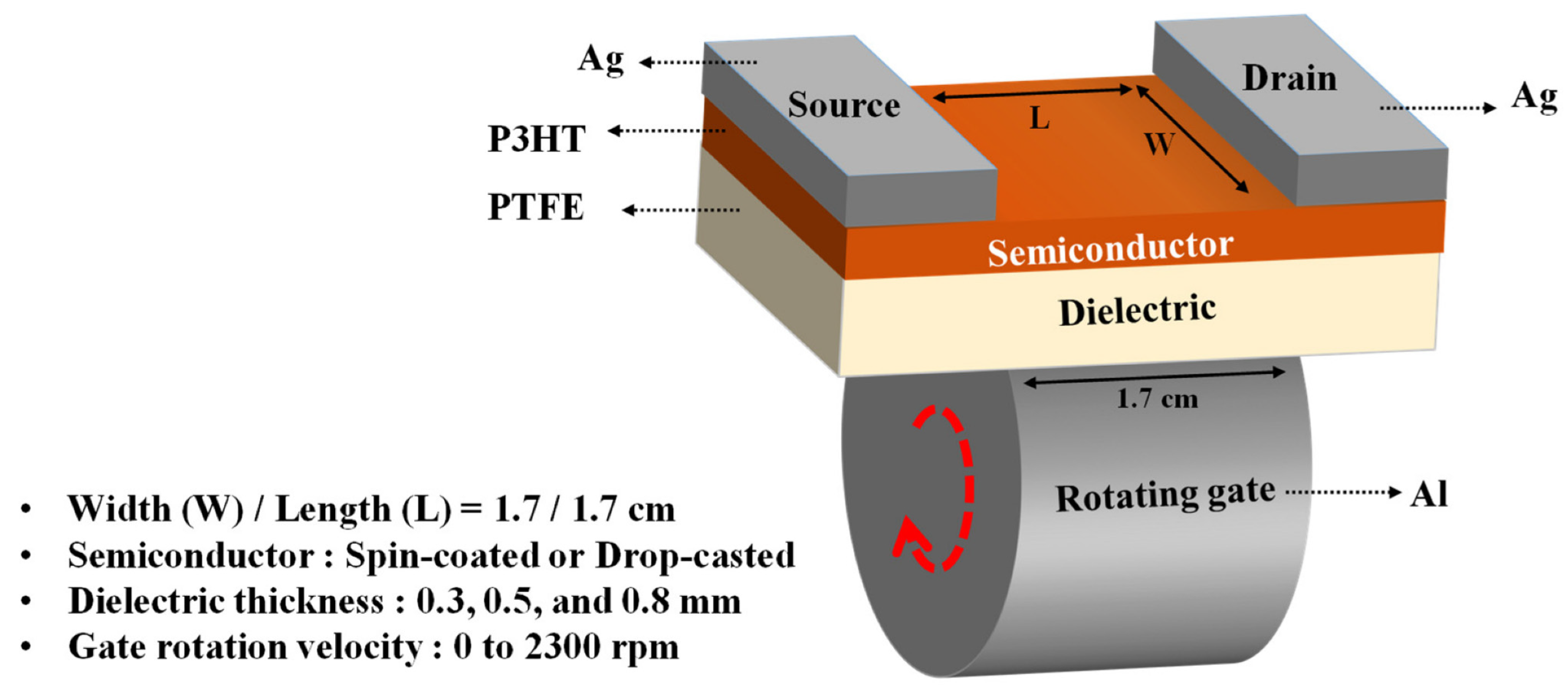
| Reference | Dielectrics | Electrodes | Mode of Operation | Electrical Output Characteristics |
| Xie et al. [12] | PTFE (ICP) PET | Aluminum | Contact | Voc: 250 V Qsc: 140 nC Isc: 0.25 mA (1 GΩ) P: 12 mW (1 MΩ) |
| Rodrigues et al. [37] | PTFE Nylon 6.6 Kapton | Aluminum | Contact | Voc: 102.2 V (44 L/min) Qsc: 8.1 μC (44 L/min) Isc: 120 mA/m2 (44 L/min) Pd: 6.1 W/m2 (44 L/min) |
| Du et al. [38] | Kapton PTFE (ICP) | Copper | Contact | Voc: 280 V (120 rpm) Qsc: - Isc: 78 μA (120 rpm) Pd: 2.54 W/m2 (120 rpm, 5 MΩ) |
| Zhang et al. [42] | PTFE (ICP) | Aluminum | Contact | Voc: 55 V (800 rpm) Qsc: - Isc: 20 μA (800 rpm) Pd: 3.1 mW/m2 (800 rpm) |
| Bai et al. [16] | PTFE (PTFE nanoparticles) | Copper | Contact | Voc: 400 V (1000 rpm) Qdsc: 24.5 μC Jsc: 90 μA (1000 rpm) Pd: 36.9 W/m2 (1000 rpm) |
| Zhang et al. [44] | FEP (ICP) | Copper | Non-Contact | Voc: 1661 V (2000 rpm) Qsc: 46 nC Isc: 12 μA (2000 rpm) Pd: 16.5 mW/m2 (2000 rpm) |
| Feng et al. [45] | FEP | Copper | Non-Contact | Voc: 120 V Qsc: 46 nC Isc: 1.52 μA P: 159 μW (100 MΩ) |
| Jung et al. [46] | FEP | Aluminum | Non-Contact | Voc: 395 V (0.33 Hz) Qsc: 46 nC Isc: 7.3 μA (0.33 Hz) Pd: 117 μW (0.33 Hz, 70 MΩ) |
| Kim et al. [50] | PTFE Water | Aluminum | Contact | Voc: 27.2 V (200 rpm) Qsc: - Isc: 3.84 μA (200 rpm) P: 19.1 μW (200 rpm, 20 MΩ) |
| Le et al. [51] | PVDF (phase inversion) Water | Copper | Contact | Voc: 1.5 V (18 rpm) Qsc: 2.03 nC (18 rpm) Jsc: 11.94 nA/cm2 (18 rpm) Pd: 18.48 nW/cm2 (18 rpm, 20 MΩ) |
| Lin et al. [55] | Kapton (ICP) | Gold Aluminum | Contact | Voc: 230 V (500 rpm) Qdsc: 40 μC/m2 (500 rpm) Jsc: 29 mA/m2 (1000 rpm) Pd: 1 W/m2 (10 MΩ) |
| Zhu el al. [56] | FEP | Gold Copper | Contact | Voc: 850 V (3000 rpm) Qsc: 0.32 μC Isc: 3 mA (3000 rpm) Pd: 19 mW/m2 (3000 rpm, 0.8 MΩ) |
| Zhou et al. [57] | PTFE | Copper Steel | Contact & Non-Contact | Voc: 300 V (150 rpm) Qsc: 24 μC/m2 (150 rpm) Isc: 60 μA (150 rpm) P: 2.29 mW (150 rpm, 20 MΩ) |
| Kuang et al. [58] | PTFE | - | Contact | Voc: 200 V (500 rpm) Qsc: - Isc: 0.75 mA (500 rpm) Pd: - |
| Yong et al. [59] | FEP | Copper | Contact | Voc: 306 V Qsc: - Isc: 32 μA P: 5.2 mW |
| Cao et al. [60] | FEP Rabbit fur | Copper | Contact | Voc: - Qsc: 389 nC (30 rpm) Ιsc: 3.23 μA (30 rpm) P: 14. 8 μW (30 rpm, 1.1 GΩ) |
| Lin et al. [62] | PTFE (ICP) Nylon | Copper | Non-Contact | Voc: 160 V Qsc: 75 nC Isc: 1.5 μA P: 74 μW (100 MΩ) |
| Zhang et al. [63] | PTFE Kapton | Copper Aluminum | Contact | Voc: 1200 V (600 rpm) Qsc: 2.2 μC Isc: 0.35 mA (600 rpm) Pavg: 47 mW (1 MΩ) |
| Feng et al. [64] | PTFE Paper | Aluminum | Non-Contact | Voc: 2352 V (600 rpm) Qsc: 197 nC (600 rpm) Isc: 133 μA (600 rpm) P: 120 mW (600 rpm, 30 MΩ) |
| Li et al. [65] | PTFE Nylon Polyester fur | Copper | Non-Contact | VAC: 10 kV (900 rpm) Qsc: 516 nC (900 rpm) Isc: 71 μA (900 rpm) P: 201.8 mW (600 rpm, 110 MΩ) |
| Long et al. [66] | PTFE Nylon | Copper Aluminum | Non-Contact | VR: 470 V (300 rpm, 10 MΩ) Qsc: 1 μC (300 rpm) Isc: 76 μA (300 rpm) P: 34.68 mW (300 rpm, 30 MΩ) |
| Han et al. [67] | PTFE (nanopatterned) Nylon (nanopatterned) | Aluminum | Non-Contact | Voc: 320 V (0.067 Hz) Qdsc: 2.84 μC/m2 (0.067 Hz) Jsc: 0.59 mA/m2 (0.067 Hz) Pd: 41 mW/m2 (0.067 Hz, 33 MΩ) |
| Jie et al. [68] | PTFE PP | Tin Gold | Non-Contact | Voc: 17.5 V (500 rpm) Qsc: - Isc: 3 μA (500 rpm) Pd: 21.8 mW/m2 (500 rpm, 7 MΩ) |
| Hybrid Energy Harvester Designs | ||||
| Reference | Combination | Dielectrics | Electrodes | Maximum electrical output characteristics |
| Li et al. [61] | R-TENG and EMG | FEP | Copper | Voc: - Ιsc: - PdTENG: 313 μW (6 ΜΩ) PdEMG: 4.3 mW (680 Ω) |
| Cao et al. [74] | R-TENG and EMG | FEP | Copper | Voc: 48 V (250 rpm) Ιsc: 1 mA (250 rpm) PHybrid: 13 mW (250 rpm, 8 kΩ) |
| Feng et al. [75] | R-TENG and EMG | FEP Rabbit fur | Copper | Voc: - Ιsc: - PdHybrid: 0.23 W/m3 (0.1 Hz, ~100 ΜΩ) |
| Zhao et al. [76] | R-TENG and EMG | PTFE Nylon | Copper | Voc: - Ιsc: - PdTENG: 10 W/m3 (8 MΩ) PdEMG: 4.19 W/m3 (100 Ω) |
| Fang et al. [77] | R-TENG and EMG | FEP Nylon | Aluminum | Voc: 683 V (47.4 V) Ιsc: - PdHybrid: 0.27 W/m3 (267 rpm, 60 MΩ) |
| Guo et al. [78] | R-TENG and EMG | FEP | Copper | Voc: - Ιsc: - PdTENG: 0.12 mW/g PdEMG: 0.26 mW/g |
| Zhang et al. [79] | R-TENG and EMG | PTFE (ICP) Polyurethane | Aluminum | VR: 3.5 V (700 Ω) ΙR: 5 mA (700 Ω) PHybrid: 55.7 W/m3 (1000 rpm, 700 Ω) |
| Zhao et al. [80] | R-TENG and Piezoelectric | PTFE PET | Gold Aluminum | Voc: 210 V (100 rpm) Ιsc: 395 μA (100 rpm) PdHybrid: 6.04 mW/cm2 (100 rpm, ~250 kΩ) |
| Reference | Type of R-TENG | Type of Sensor | Parameters | Mode of Operation | Electrical Output Characteristics |
| Lin et al. [87] | Radially segmented sliding disk | Displacement and Rotation speed | Jsc amplitude and frequency | Non-contact | Voc: 220 V Jsc: 13 mA/m2 Pd: 1.22 W/m2 (2 MΩ) |
| Lu et al. [88] | Radially segmented sliding disk | Rotation speed | Isc frequency | Contact | Voc: 39 V Isc: 15.6 μA (AC amplitude) Pmax: 377.7 μW (600 kΩ) |
| Xie et al. [89] | Radially segmented sliding disk | Rotation speed | Voc frequency Isc frequency | Contact | Voc: 130 V Isc: 150 μA (AC amplitude) |
| Xuan et al. [90] | Radially segmented sliding disk | Rotation speed (Temperature) | Isc amplitude and frequency | Non-contact | Voc: 226.2 V Isc: 12.3 μA (AC amplitude) Qsc: 78.4 nC Pmax: 538.6 nW (40 ΜΩ) |
| Meng et al. [91] | Bearings | Rotation speed | Isc frequency | Contact | Isc: 70 nA (AC amplitude) Qsc: 2.7 μC |
| Xin et al. [92] | Bearings | Rotation speed | Voc frequency | Contact | Voc: 150 V Isc: 2 μA (AC amplitude) Pmax: 107 μW (~700 ΜΩ) |
| Lee et al. [93] | Radially segmented sliding disk | Angle | Voc frequency | Contact | Voc: 180 V Isc: 0.4 μA (AC amplitude) Qsc: 65 nC |
| Wu et al. [94] | Radially arrayed sliding disk | Angle | Voc amplitude | Contact | Voc: 20 V |
| Hou et al. [95] | Radially segmented pendulum | Angle | Voc frequency | Contact | Voc: 150 V Isc: 0.4 μA (AC amplitude) |
| Wang et al. [96] | Radially segmented sliding disk | Angle | Voc frequency Phase difference | Contact | Voc: 123.09 V |
| He et al. [97] | Radially segmented pendulum | Angle | Voc amplitude Isc amplitude | Contact | Voc: 83.6 V Isc: 8.46 μA (AC amplitude) Pmax: 35.2 mW/m2 (10 ΜΩ) |
| Wang et al. [98] | Tubular | Chemical composition | Voc amplitude | Contact | Voc: 228 V Isc: 11.5 μA (AC amplitude) Pmax: 37 mW (120 ΜΩ) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Segkos, A.; Tsamis, C. Rotating Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Their Applications. Nanoenergy Adv. 2023, 3, 170-219. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv3030010
Segkos A, Tsamis C. Rotating Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Their Applications. Nanoenergy Advances. 2023; 3(3):170-219. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv3030010
Chicago/Turabian StyleSegkos, Apostolos, and Christos Tsamis. 2023. "Rotating Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Their Applications" Nanoenergy Advances 3, no. 3: 170-219. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv3030010
APA StyleSegkos, A., & Tsamis, C. (2023). Rotating Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Their Applications. Nanoenergy Advances, 3(3), 170-219. https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv3030010










