Monitoring of Corrosion in Reinforced E-Waste Concrete Subjected to Chloride-Laden Environment Using Embedded Piezo Sensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
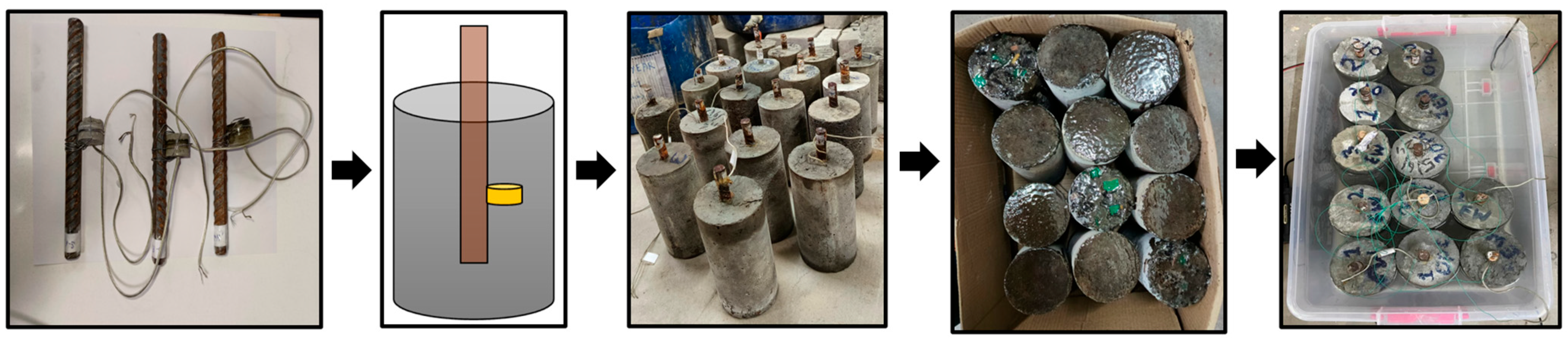
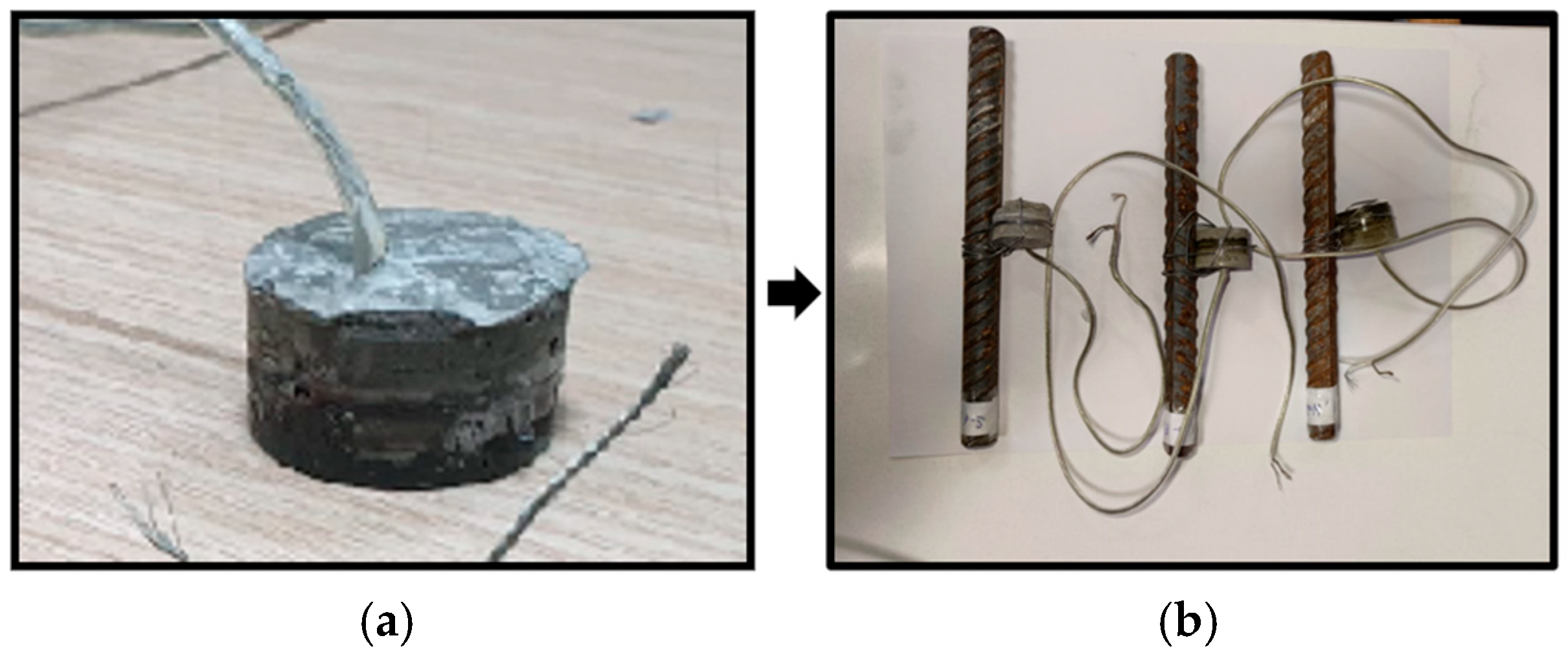
2.1. Preparation of Embedded Piezo Sensor (EPS)
2.2. Electro-Mechanical Impedance (EMI) Technique
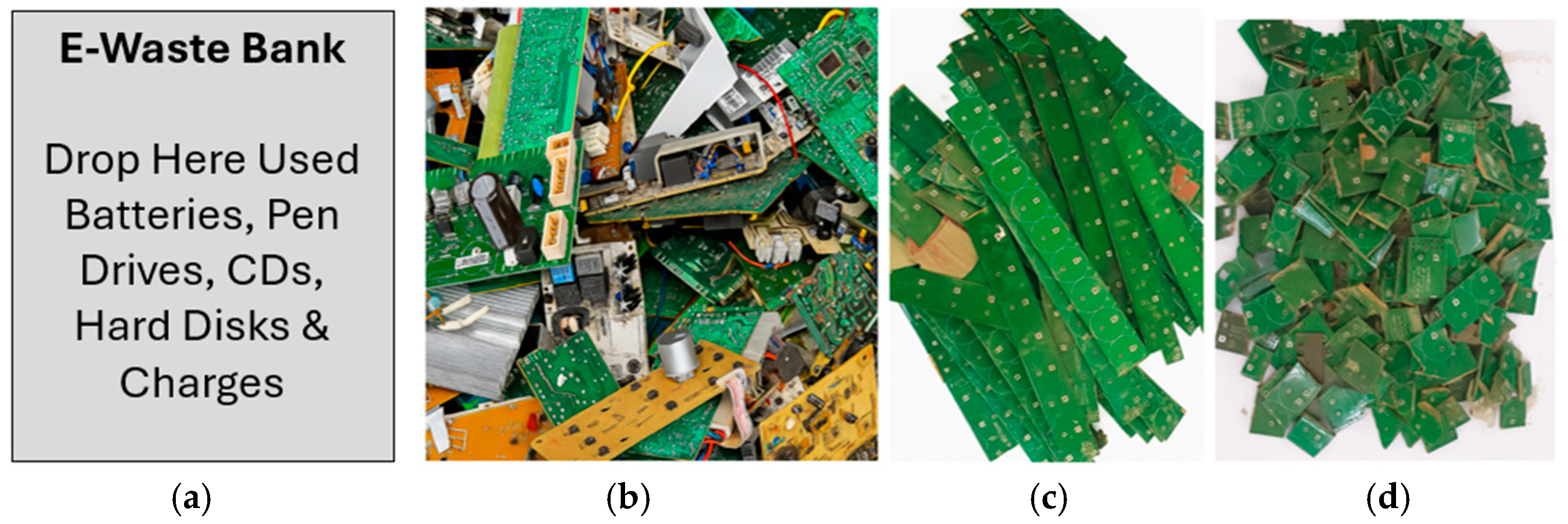
2.3. Preparation of E-Waste Material and Mix Design Details
2.4. Sample Preparation
2.5. Experimental Setup and Corrosion Monitoring
3. Results and Discussion
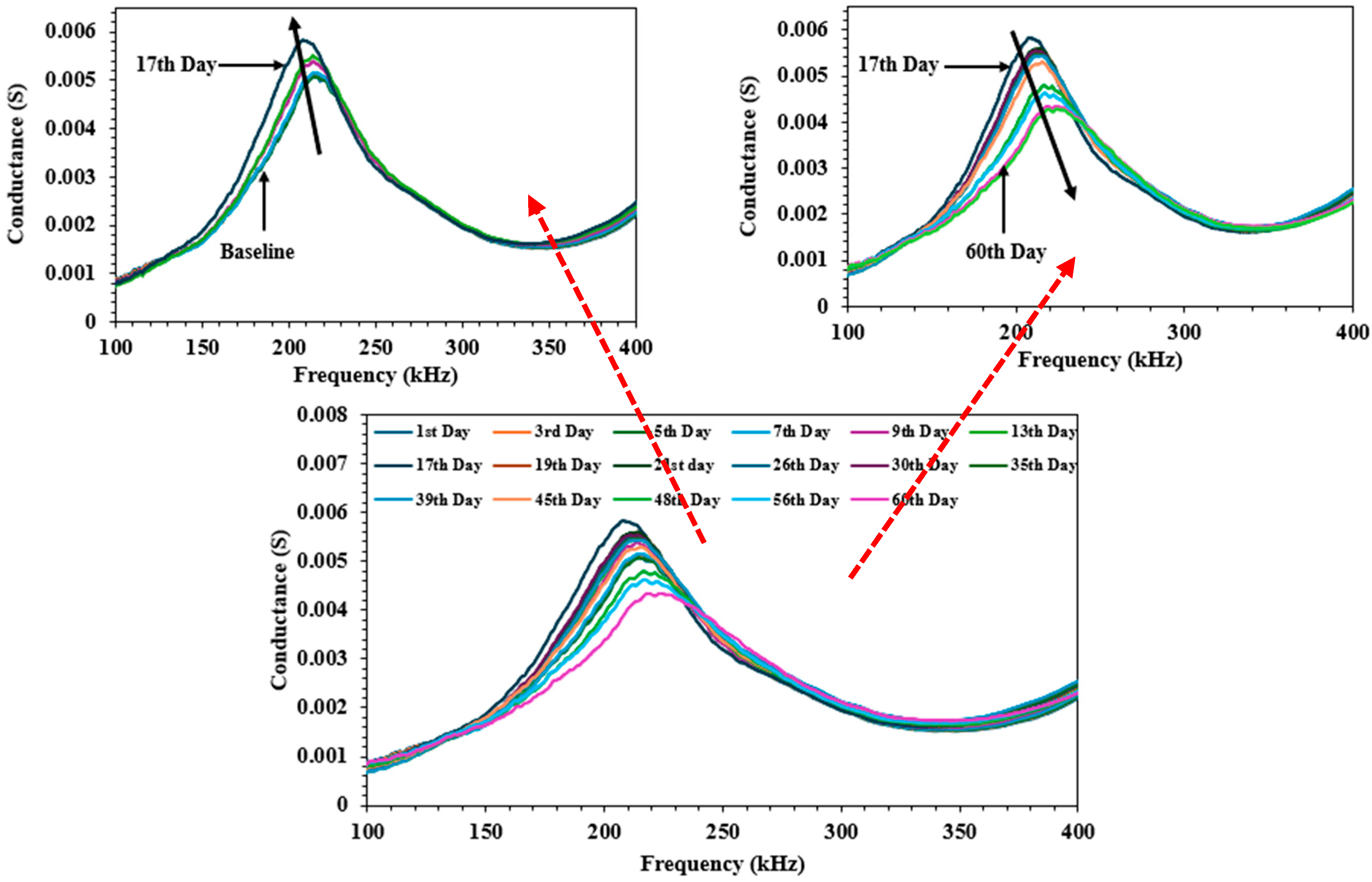
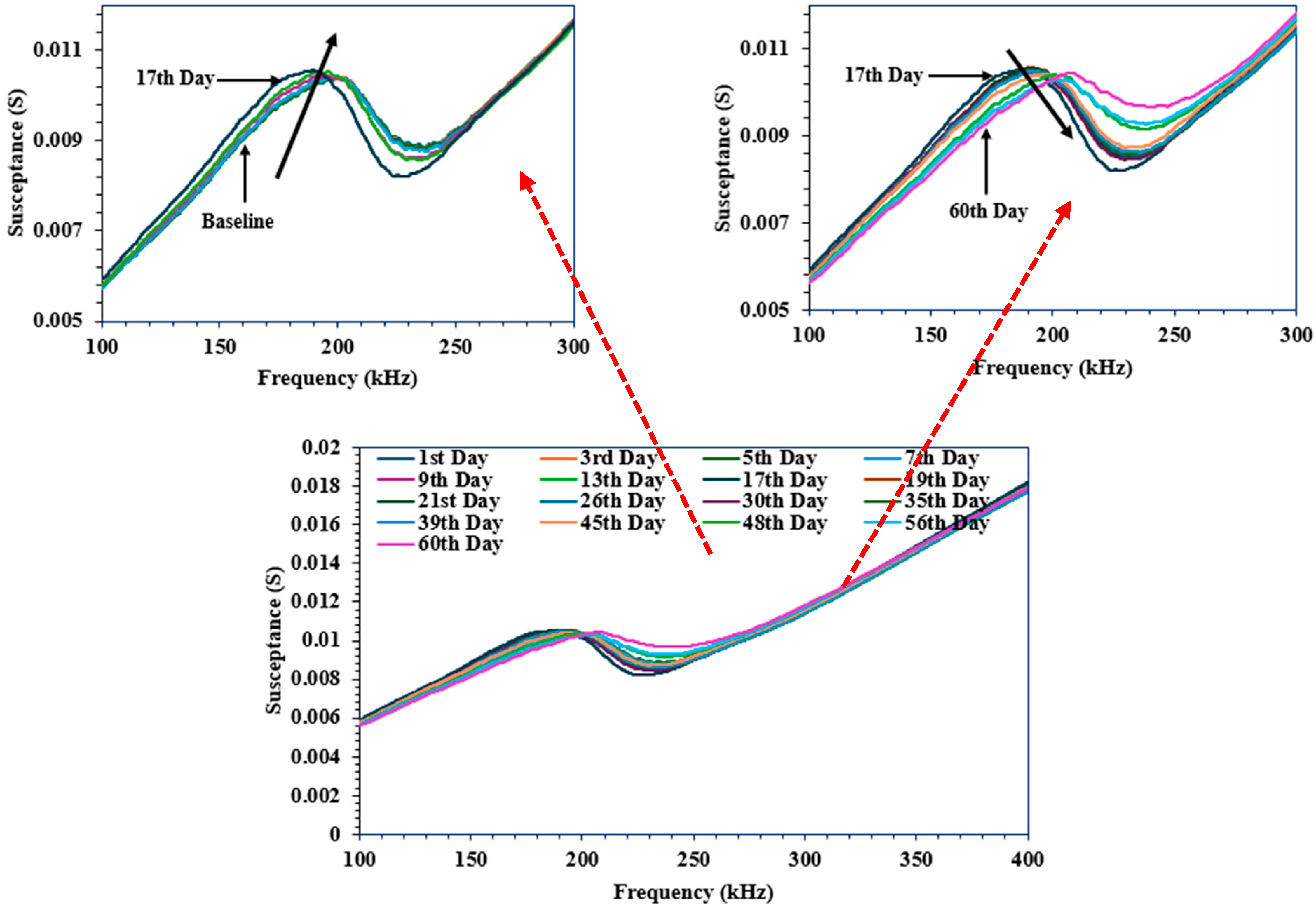
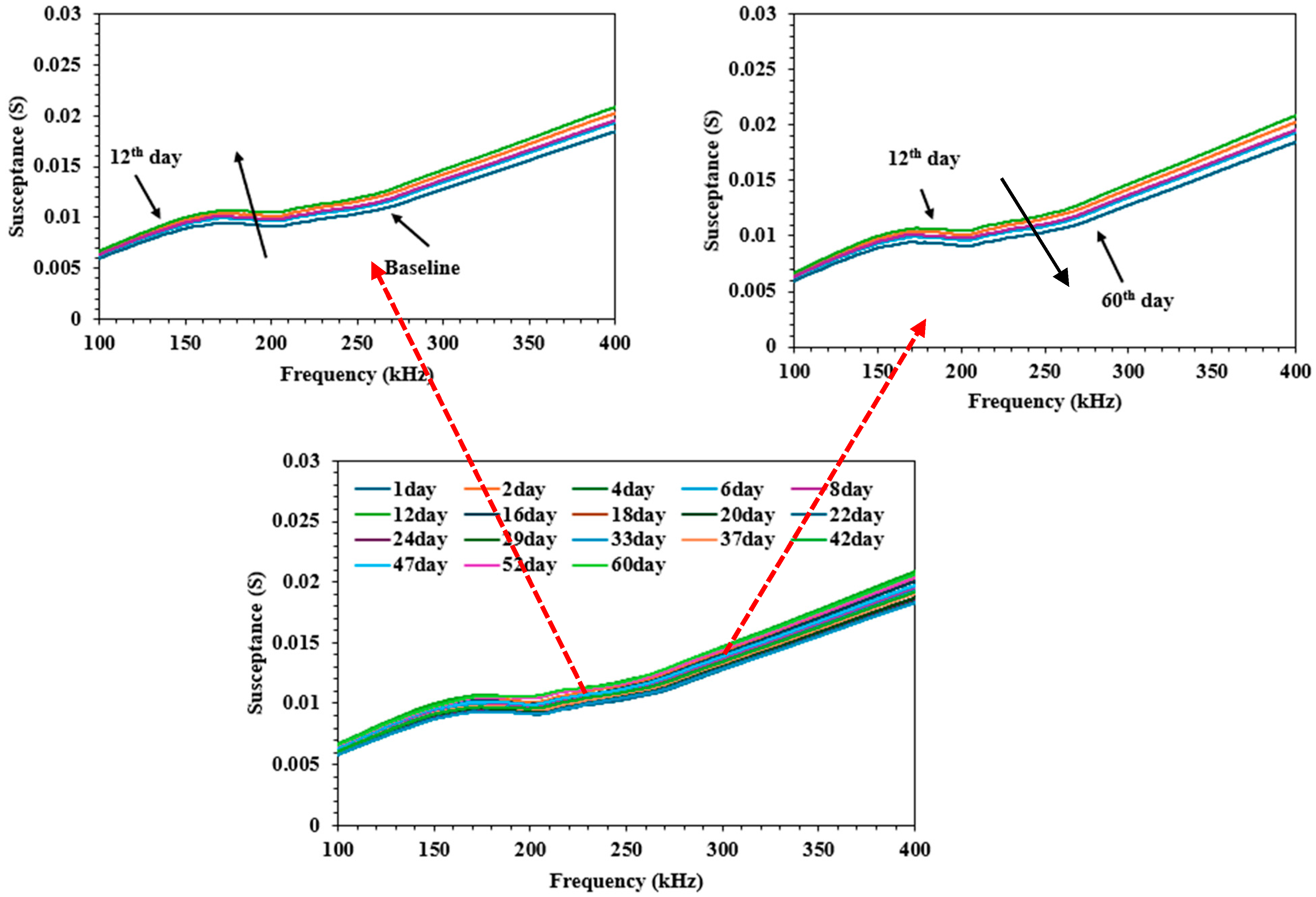
3.1. Qualitative Analysis
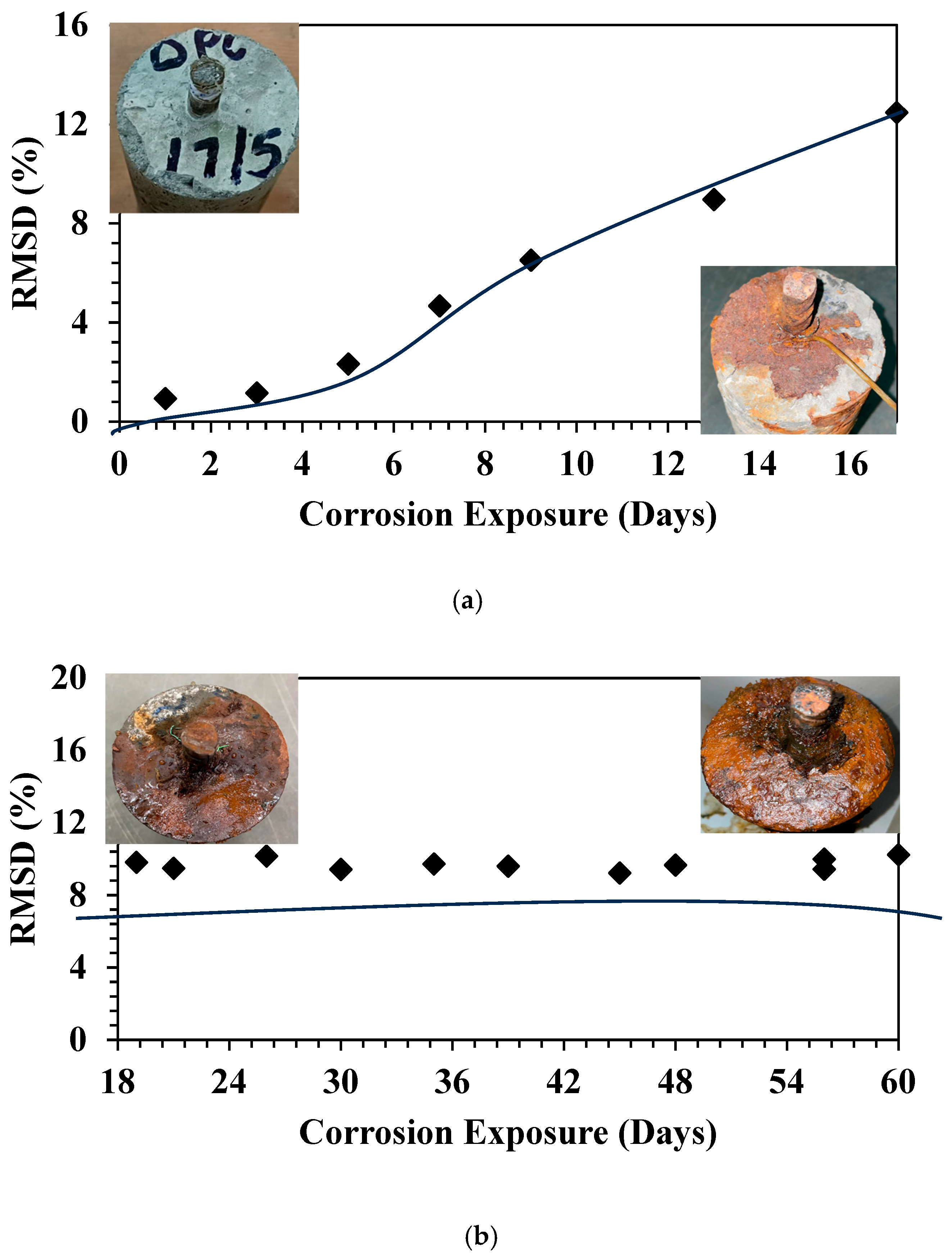
3.2. Quantitative Analysis
3.3. Gravimetric Mass Loss Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tuutti, K. Corrosion of Steel in Concrete; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1977; ISBN 9781032120980. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Ash, F. Protection of steel reinforcement for concrete—A review. Corros. Rev. 1998, 16, 317–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mukherjee, A. Longitudinal Guided Waves for Monitoring Chloride Corrosion in Reinforcing Bars in Concrete. Struct. Health Monit. 2010, 9, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, G.K.; Page, C.L. Factors affecting the corrosion rate of steel in carbonated mortars. Corros. Sci. 1991, 32, 1283–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagwan, W.A. Electronic Waste (E-Waste) Generation and Management Scenario of India, and ARIMA Forecasting of E-Waste Processing Capacity of Maharashtra State till 2030. Waste Manag. Bull. 2024, 1, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetriwal, D.S. E-Waste Management in India. In Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Handbook; Elsevier, Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 541–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sua-iam, G.; Chatveera, B. A Study on Workability and Mechanical Properties of Eco-Sustainable Self-Compacting Concrete Incorporating PCB Waste and Fly Ash. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 329, 129523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakkar, J.; Dave, N.; Thaker, T. Influence of Additive on Mechanical, Durability, and Microstructural Properties of Concrete Containing Printed Circuit Board (PCB) E-Waste as Coarse Aggregates: A Review. In Smart Cities and Sustainable Manufacturing: Innovations for a Greener Future; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 175–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramteke, J.; Rathore, K.; Supe, J.D. Green Concrete Incorporating Industrial Waste and E-Waste: A Review of Compressive Strength, CO2 Emissions, and Replacement Levels. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2025, 26, 1881–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almohana, A.I.; Abdulwahid, M.Y.; Galobardes, I.; Mushtaq, J.; Almojil, S.F. Producing Sustainable Concrete with Plastic Waste: A Review. Environ. Chall. 2022, 9, 100626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, Z.; Qureshi, M.I.; Ahmad, A.; Khan, S.U.; Javaid, M.F. An Experimental Study on the Mechanical and Durability Properties Assessment of E-Waste Concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 38, 102177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Bansal, T.; Sharma, D. Effect of E-Waste on Concrete during Combined Chlorination and Compression Loading Using Electro-Mechanical Impedance Technique. Measurement 2025, 253, 117832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu Gopu, G.; Sofi, A. Corrosion-Induced Bond Behaviour of Steel, E-Glass, And E-Waste Copper Wire Fiber Reinforced Concrete. Rom. J. Mater. 2022, 52, 404. [Google Scholar]
- Pagadala, M.; Mundra, S.; Bansal, S. Corrosion Monitoring Techniques for Concrete in Corrosive Environments. Corros. Rev. 2022, 40, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talakokula, V.; Bhalla, S.; Gupta, A. Corrosion Assessment of Reinforced Concrete Structures Based on Equivalent Structural Parameters Using Electro-Mechanical Impedance Technique. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2014, 25, 484–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talakokula, V.; Bhalla, S. Reinforcement Corrosion Assessment Capability of Surface Bonded and Embedded Piezo Sensors for Reinforced Concrete Structures. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 2304–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, G.; Yun, C.B.; Farrar, C.R. Sensor Self-Diagnosis Using a Modified Impedance Model for Active Sensing-Based Structural Health Monitoring. Struct. Health Monit. 2009, 8, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, T.; Talakokula, V.; Saravanan, T.J. EMI-Based Monitoring of Prestressed Concrete Beam under Chloride-Induced Corrosion Using an Embedded Piezo Sensor. Meas. Sens. 2024, 33, 101158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SSDL|Home. Available online: https://ssdl.iitd.ac.in/ (accessed on 2 June 2025).
- Bhalla, S.; Gupta, A. An Embeddable Piezo Composite Concrete Vibration Sensor for Structural Health Monitoring of Reinforced Concrete Structures and Process of Preparation Thereof. Indian Patent No. 412929, 29 November 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, T.; Talakokula, V.; Rama Jyosyula, S.K.; Vicente, R.; Ascensão, G. Embedded Piezo-Sensor-Based Automatic Performance Monitoring of Chloride-Induced Corrosion in Alkali-Activated Concrete. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, T.; Talakokula, V.; Sathujoda, P. A Machine Learning Approach for Predicting the Electro-Mechanical Impedance Data of Blended RC Structures Subjected to Chloride Laden Environment. Smart Mater. Struct. 2021, 31, 015036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Bansal, T.; Sharma, D. Monitoring Hydration and Strength Development of E-Waste Concrete: A Passive Sensing Approach Using Piezo Sensors. Clean. Mater. 2025, 17, 100326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hire, J.H.; Hosseini, S.; Moradi, F. Optimum Pzt Patch Size for Corrosion Detection in Reinforced Concrete Using the Electromechanical Impedance Technique. Sensors 2021, 21, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parida, L.; Moharana, S. Mechanical and Corrosion Investigations of Bond Behavior in Reinforced Concrete with Varying Parameters. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2024, 24, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, L.; Moharana, S. Monitoring the Bond Zone Mechanism between Reinforced Steel & Concrete for Electromechanical Impedance Technique through a Multi-Attached Piezo Sensor-Based Diagnostic Approach. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 2025, 223, 111897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, I.; Dev, N.; Pal, S. Impedance Based Damage Assessment of Concrete under the Combined Effect of Impact and Temperature Using Different Piezo Configurations. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 345, 113763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, P.; Chhabra, R.; Kaur, N.; Bhalla, S. Health Monitoring of Reinforced Concrete Structures under Impact Using Multiple Piezo-Based Configurations. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 222, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, M.; Bhalla, S.; Naqvi, T. Fatigue Damage and Residual Fatigue Life Assessment in Reinforced Concrete Frames Using PZT-Impedance Transducers. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 114, 103771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.; Parida, L.; Moharana, S. Influence of Adhesive Bonding and Debonding Detection on Aluminum Beam Using Electro-Mechanical Impedance (EMI) Technique. In International Workshop on Civil Structural Health Monitoring; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.F.; Han, G.; Amran, A.; Nantung, T.; Lu, N. Instantaneous Monitoring the Early Age Properties of Cementitious Materials Using PZT-Based Electromechanical Impedance (EMI) Technique. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Panda, G.P.; Yan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Vipulanandan, C.; Song, G. Monitoring Early-Age Hydration and Setting of Portland Cement Paste by Piezoelectric Transducers via Electromechanical Impedance Method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 258, 120348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Agha, W.; Pal, S.; Dev, N. Challenges for Structural Health Monitoring of Concrete Curing Using Piezoelectric Sensor and Electromechanical Impedance (EMI) Technique: A Critical Review. Mater. Today Proc. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Agha, W.; Pal, S.; Dev, N. Electro-Mechanical Impedance-Based Equivalent Structural Health Monitoring of Steel Fibre Cementitious Materials under Long Curing Age Effect. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 489, 142296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, P.; Chakraborty, T.; Kaur, N.; Bhalla, S. Investigations on Effectiveness of Embedded PZT Patches at Varying Orientations for Monitoring Concrete Hydration Using EMI Technique. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, C.K.; Bhalla, S. Calibration of Piezo-Impedance Transducers for Strength Prediction and Damage Assessment of Concrete. Smart Mater. Struct. 2005, 14, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, T.; Zou, D.; Wang, J.; Yi, T.H. PZT Based Smart Corrosion Coupon Using Electromechanical Impedance. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 2019, 129, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalla, S. A Mechanical Impedance Approach for Structural Identification, Health Monitoring and Non-Destructive Evaluation Using Piezo-Impedance Transducers. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, G.; Bansal, T.; Haq, M.; Sharma, U.; Kumar, A.; Jha, P.; Sharma, D.; Kamyab, H.; Valencia, E.A.V. Utilizing E-Waste as a Sustainable Aggregate in Concrete Production: A Review. Buildings 2024, 14, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caré, S.; Raharinaivo, A. Influence of Impressed Current on the Initiation of Damage in Reinforced Mortar Due to Corrosion of Embedded Steel. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 1598–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S. Techniques for Inducing Accelerated Corrosion of Steel in Concrete. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2009, 34, 95. [Google Scholar]







| Mix Proportion | Cement Content (kg/m3) | Coarse Aggregate Replacement (%) | Fine Aggregate (kg/m3) | Coarse Aggregate (kg/m3) | Water (kg/m3) | E-Waste |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CC Concrete | 386.36 | 0 | 672.84 | 1196 | 170 | 0 |
| E-waste Concrete | 386.36 | 15 | 672.84 | 1016.6 | 170 | 179.4 |
| S.No | Sample ID | Initial Mass (gm) | Final Mass (gm) | Mass Loss (gm) | Exposure Days (hours) | Corrosion Rate (mm/year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CC-1 | 310 | 240 | 70 | 1440 | 10.00 |
| 2 | CC-2 | 309 | 245 | 64 | 1440 | 9.14 |
| 3 | CC-3 | 310 | 247 | 63 | 1440 | 9.00 |
| 4 | E-waste-1 | 294 | 212 | 82 | 1440 | 11.71 |
| 5 | E-waste-2 | 298 | 212 | 86 | 1440 | 12.28 |
| 6 | E-waste-3 | 302 | 214 | 88 | 1440 | 12.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumar, G.; Bansal, T.; Sharma, D. Monitoring of Corrosion in Reinforced E-Waste Concrete Subjected to Chloride-Laden Environment Using Embedded Piezo Sensor. Constr. Mater. 2025, 5, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/constrmater5030046
Kumar G, Bansal T, Sharma D. Monitoring of Corrosion in Reinforced E-Waste Concrete Subjected to Chloride-Laden Environment Using Embedded Piezo Sensor. Construction Materials. 2025; 5(3):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/constrmater5030046
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumar, Gaurav, Tushar Bansal, and Dayanand Sharma. 2025. "Monitoring of Corrosion in Reinforced E-Waste Concrete Subjected to Chloride-Laden Environment Using Embedded Piezo Sensor" Construction Materials 5, no. 3: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/constrmater5030046
APA StyleKumar, G., Bansal, T., & Sharma, D. (2025). Monitoring of Corrosion in Reinforced E-Waste Concrete Subjected to Chloride-Laden Environment Using Embedded Piezo Sensor. Construction Materials, 5(3), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/constrmater5030046





