Cell-Type-Specific Effect of Innate Immune Signaling on Stress Granules
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
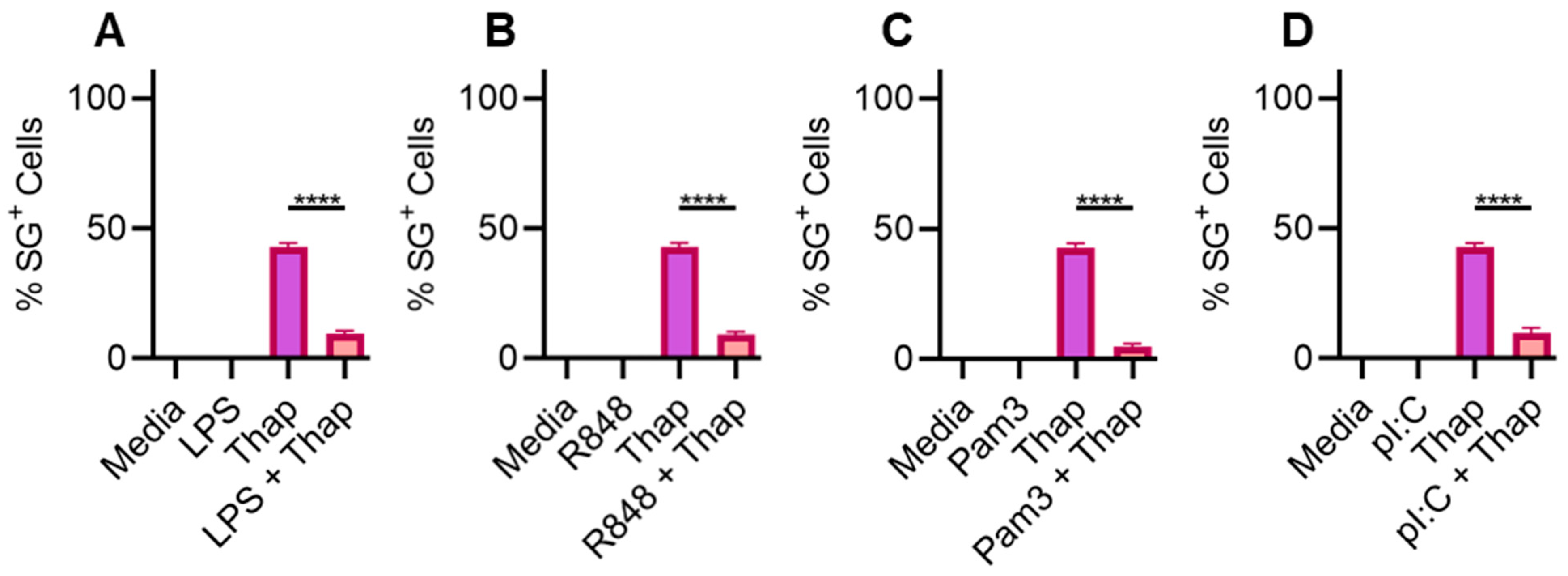
2.1. TLR Signaling Inhibits SGs in Bone-Marrow-Derived Macrophages
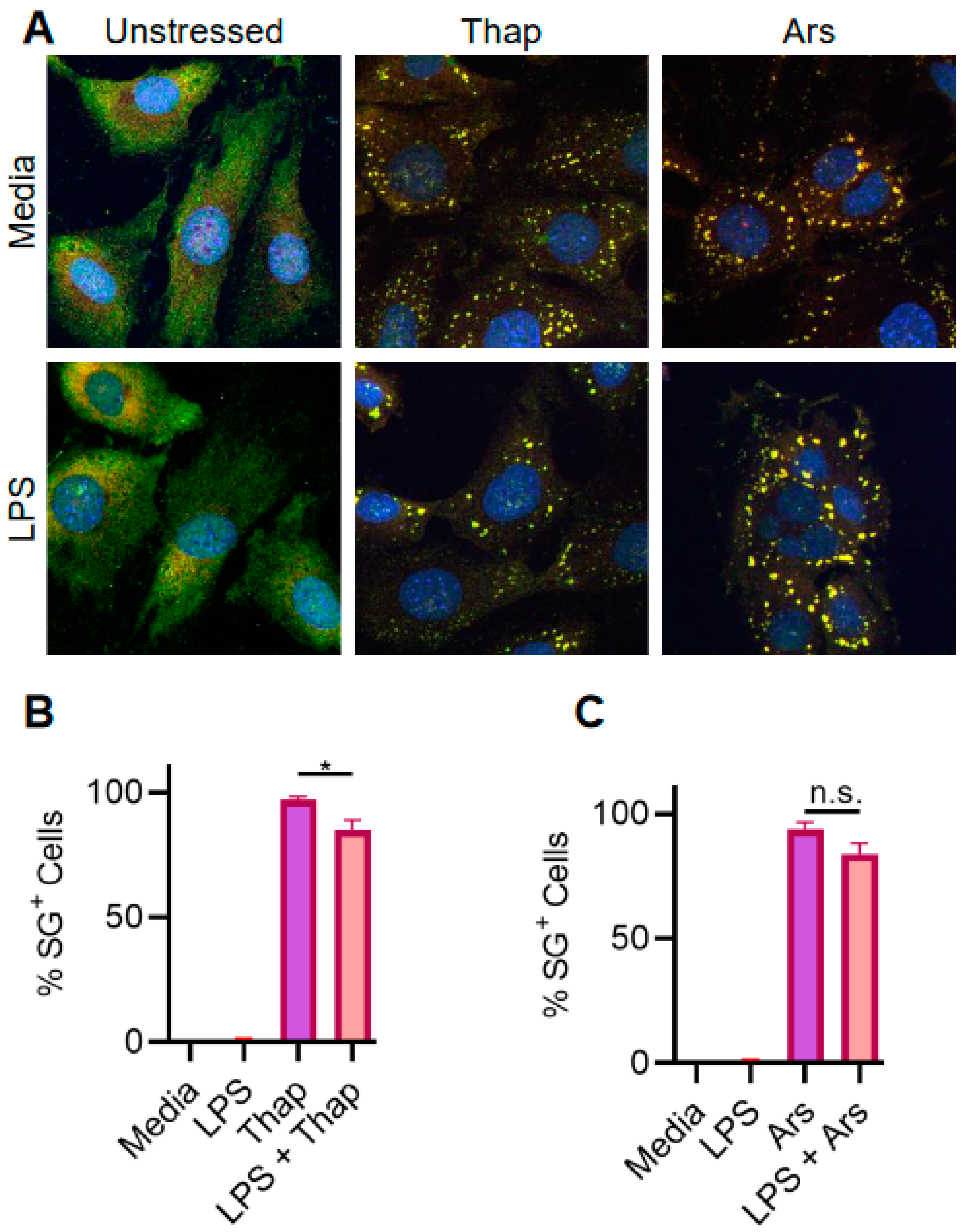
2.2. TLR4 Signaling Has a Very Weak Effect on ER Stress-Induced SGs in A549 Lung Cancer Cells
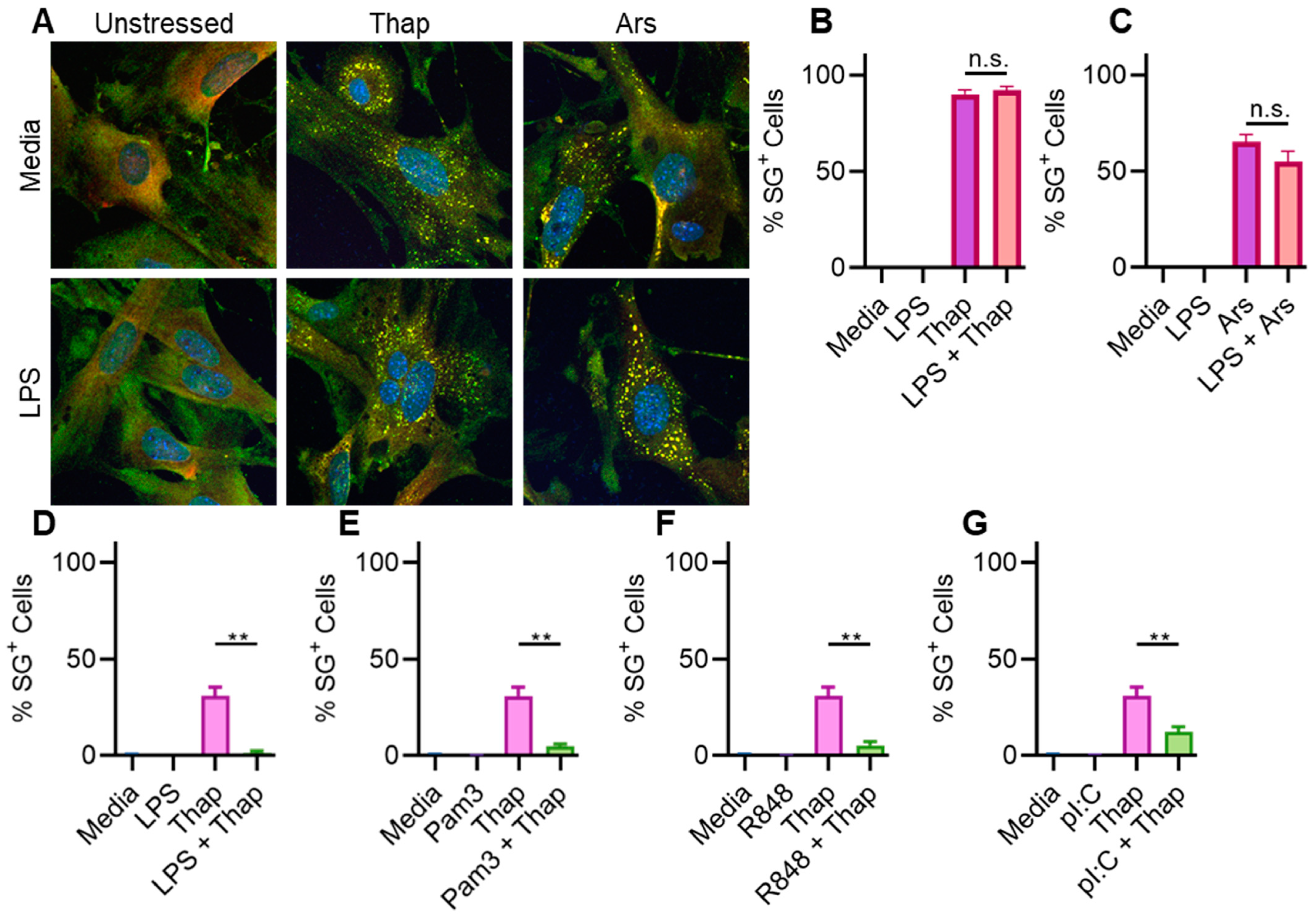
2.3. TLR4 Signaling Has a Very Weak Effect on ER Stress-Induced SGs in Immortalized Mouse Lung Fibroblasts
2.4. TLR4 Signaling Does Not Significantly Affect ER Stress-Induced SGs in Immortalized Mouse Lung Fibroblasts
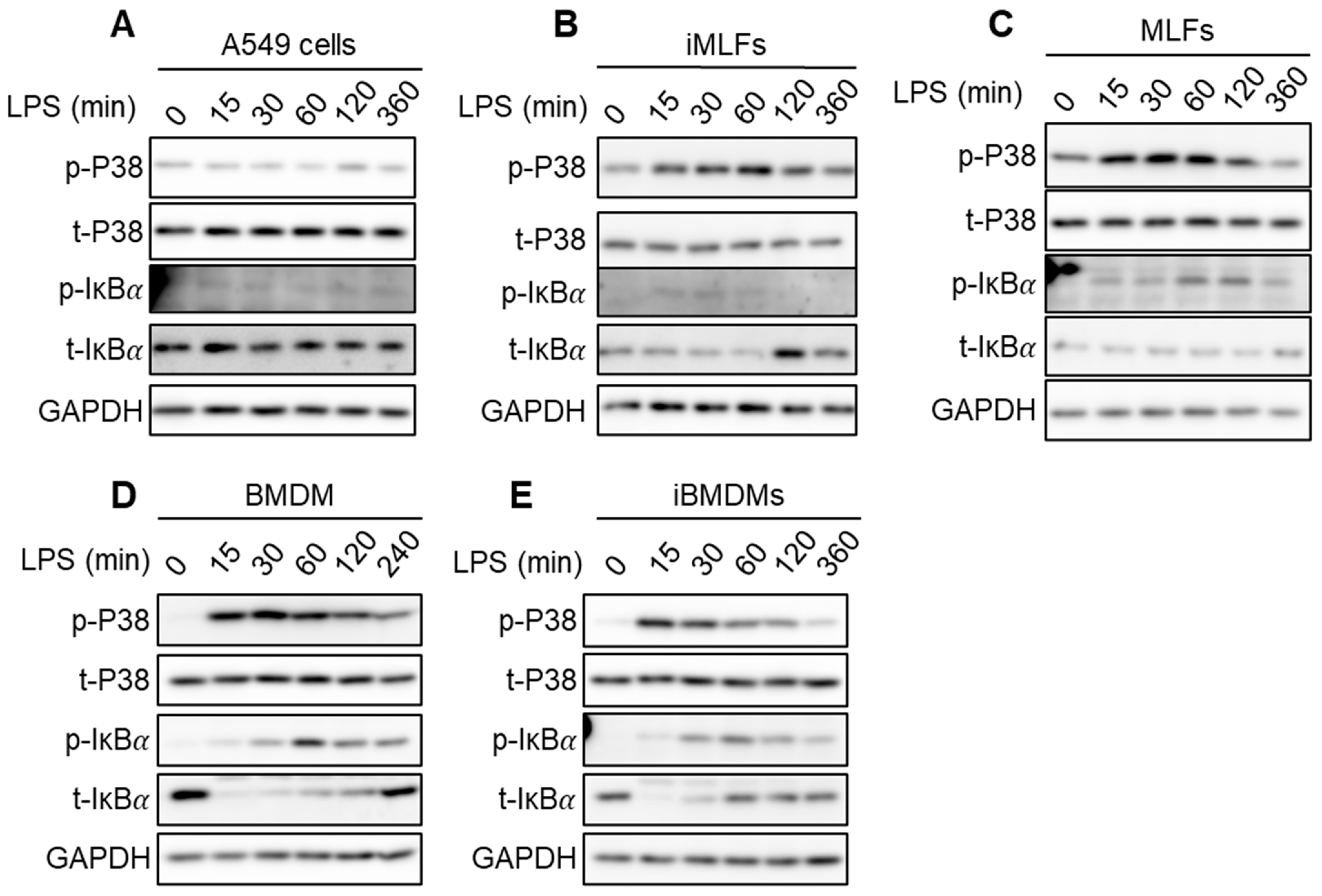
2.5. Strength of IKK Complex Kinase Activity Induction Is Weak in Cells Where It Fails to Inhibit SGs
2.6. Discussion and Conclusions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Mice
3.2. Cell Culture and Stimulations
3.3. Western Blot Analysis
3.4. Confocal Microscopy Imaging and Analysis
3.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Protter, D.S.W.; Parker, R. Principles and Properties of Stress Granules. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedersha, N.L.; Gupta, M.; Li, W.; Miller, I.; Anderson, P. RNA-Binding Proteins Tia-1 and Tiar Link the Phosphorylation of Eif-2α to the Assembly of Mammalian Stress Granules. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 147, 1431–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nover, L.; Scharf, K.D.; Neumann, D. Formation of Cytoplasmic Heat Shock Granules in Tomato Cell Cultures and Leaves. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1983, 3, 1648–1655. [Google Scholar]
- Collier, N.C.; Schlesinger, M.J. The Dynamic State of Heat Shock Proteins in Chicken Embryo Fibroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 1986, 103, 1495–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyle, N.P.; Castelli, L.M.; Campbell, S.G.; Holmes, L.E.A.; Ashe, M.P. Stress-Dependent Relocalization of Translationally Primed mRNPs to Cytoplasmic Granules That Are Kinetically and Spatially Distinct from P-Bodies. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 179, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedersha, N.; Cho, M.R.; Li, W.; Yacono, P.W.; Chen, S.; Gilks, N.; Golan, D.E.; Anderson, P. Dynamic Shuttling of Tia-1 Accompanies the Recruitment of mRNA to Mammalian Stress Granules. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 151, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilliker, A.; Gao, Z.; Jankowsky, E.; Parker, R. The DEAD-Box Protein Ded1 Modulates Translation by the Formation and Resolution of an eIF4F-mRNA Complex. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 962–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedersha, N.; Ivanov, P.; Anderson, P. Stress Granules and Cell Signaling: More than Just a Passing Phase? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 38, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedersha, N.; Anderson, P. Chapter 4 Regulation of Translation by Stress Granules and Processing Bodies. In Translational Control in Health and Disease; Hershey, J.W.B., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2009; Volume 90, pp. 155–185. [Google Scholar]
- Buchan, J.R.; Parker, R. Eukaryotic Stress Granules: The Ins and Outs of Translation. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, P.; Kedersha, N.; Ivanov, P. Stress Granules, P-Bodies and Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Gene Regul. Mech. 2015, 1849, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabocka, E.; Bar-Sagi, D. Mutant KRAS Enhances Tumor Cell Fitness by Upregulating Stress Granules. Cell 2016, 167, 1803–1813.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ash, P.E.A.; Vanderweyde, T.E.; Youmans, K.L.; Apicco, D.J.; Wolozin, B. Pathological Stress Granules in Alzheimer’s Disease. Brain Res. 2014, 1584, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.R.; King, O.D.; Shorter, J.; Gitler, A.D. Stress Granules as Crucibles of ALS Pathogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 201, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewey, C.M.; Cenik, B.; Sephton, C.F.; Johnson, B.A.; Herz, J.; Yu, G. TDP-43 Aggregation in Neurodegeneration: Are Stress Granules the Key? Brain Res. 2012, 1462, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimoto, K.; Fukuda, H.; Imajoh-Ohmi, S.; Saito, H.; Takekawa, M. Formation of Stress Granules Inhibits Apoptosis by Suppressing Stress-Responsive MAPK Pathways. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samir, P.; Kesavardhana, S.; Patmore, D.M.; Gingras, S.; Malireddi, R.S.; Karki, R.; Guy, C.S.; Briard, B.; Place, D.E.; Bhattacharya, A. DDX3X Acts as a Live-or-Die Checkpoint in Stressed Cells by Regulating NLRP3 Inflammasome. Nature 2019, 573, 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamichhane, P.P.; Samir, P. Cellular Stress: Modulator of Regulated Cell Death. Biology 2023, 12, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.P.; Lloyd, R.E. Regulation of Stress Granules in Virus Systems. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eiermann, N.; Haneke, K.; Sun, Z.; Stoecklin, G.; Ruggieri, A. Dance with the Devil: Stress Granules and Signaling in Antiviral Responses. Viruses 2020, 12, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reineke, L.C.; Lloyd, R.E. Diversion of Stress Granules and P-Bodies during Viral Infection. Virology 2013, 436, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesavardhana, S.; Samir, P.; Zheng, M.; Malireddi, R.S.; Karki, R.; Sharma, B.R.; Place, D.E.; Briard, B.; Vogel, P.; Kanneganti, T.-D. DDX3X Coordinates Host Defense against Influenza Virus by Activating the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Type I Interferon Response. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samir, P.; Place, D.E.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; Kanneganti, T.-D. TLR and IKK Complex–Mediated Innate Immune Signaling Inhibits Stress Granule Assembly. J. Immunol. 2021, 207, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kedersha, N.; Stoecklin, G.; Ayodele, M.; Yacono, P.; Lykke-Andersen, J.; Fritzler, M.J.; Scheuner, D.; Kaufman, R.J.; Golan, D.E.; Anderson, P. Stress Granules and Processing Bodies Are Dynamically Linked Sites of mRNP Remodeling. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 169, 871–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasi, E.; Mathieson, B.J.; Varesio, L.; Cleveland, J.L.; Borchert, P.A.; Rapp, U.R. Selective Immortalization of Murine Macrophages from Fresh Bone Marrow by a Raf/Myc Recombinant Murine Retrovirus. Nature 1985, 318, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israël, A. The IKK Complex, a Central Regulator of NF-κB Activation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K. Toll-like Receptor Signalling. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2004, 4, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitzgerald, K.A.; Kagan, J.C. Toll-like Receptors and the Control of Immunity. Cell 2020, 180, 1044–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbet, G.A.; Parker, R. RNP Granule Formation: Lessons from P-Bodies and Stress Granules. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2019, 84, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An Open-Source Platform for Biological-Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, U.; Weigert, M.; Broaddus, C.; Myers, G. Cell Detection with Star-Convex Polygons. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2018; Frangi, A.F., Schnabel, J.A., Davatzikos, C., Alberola-López, C., Fichtinger, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 265–273. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lamichhane, P.P.; Aditi; Xie, X.; Samir, P. Cell-Type-Specific Effect of Innate Immune Signaling on Stress Granules. Stresses 2024, 4, 411-420. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses4030027
Lamichhane PP, Aditi, Xie X, Samir P. Cell-Type-Specific Effect of Innate Immune Signaling on Stress Granules. Stresses. 2024; 4(3):411-420. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses4030027
Chicago/Turabian StyleLamichhane, Prem Prasad, Aditi, Xuping Xie, and Parimal Samir. 2024. "Cell-Type-Specific Effect of Innate Immune Signaling on Stress Granules" Stresses 4, no. 3: 411-420. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses4030027
APA StyleLamichhane, P. P., Aditi, Xie, X., & Samir, P. (2024). Cell-Type-Specific Effect of Innate Immune Signaling on Stress Granules. Stresses, 4(3), 411-420. https://doi.org/10.3390/stresses4030027





