Polystyrene–Carbon Nanotube Composites: Interaction Mechanisms, Preparation Methods, Structure, and Rheological Properties—A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fundamentals of PS/CNT Composites
2.1. Structure and Properties of Polystyrene (PS)
2.2. Structure and Characteristics of Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)
2.3. Interaction Mechanisms Between Polystyrene (PS) and Carbon Nanotubes (CNT)
2.3.1. Van der Waals Forces
2.3.2. π-π Stacking Interactions
2.3.3. Covalent Bonding
2.3.4. Interfacial Polarization
2.4. Dispersion and Entanglement
3. PS/CNT Composite Preparation Methods
3.1. Melt Mixing
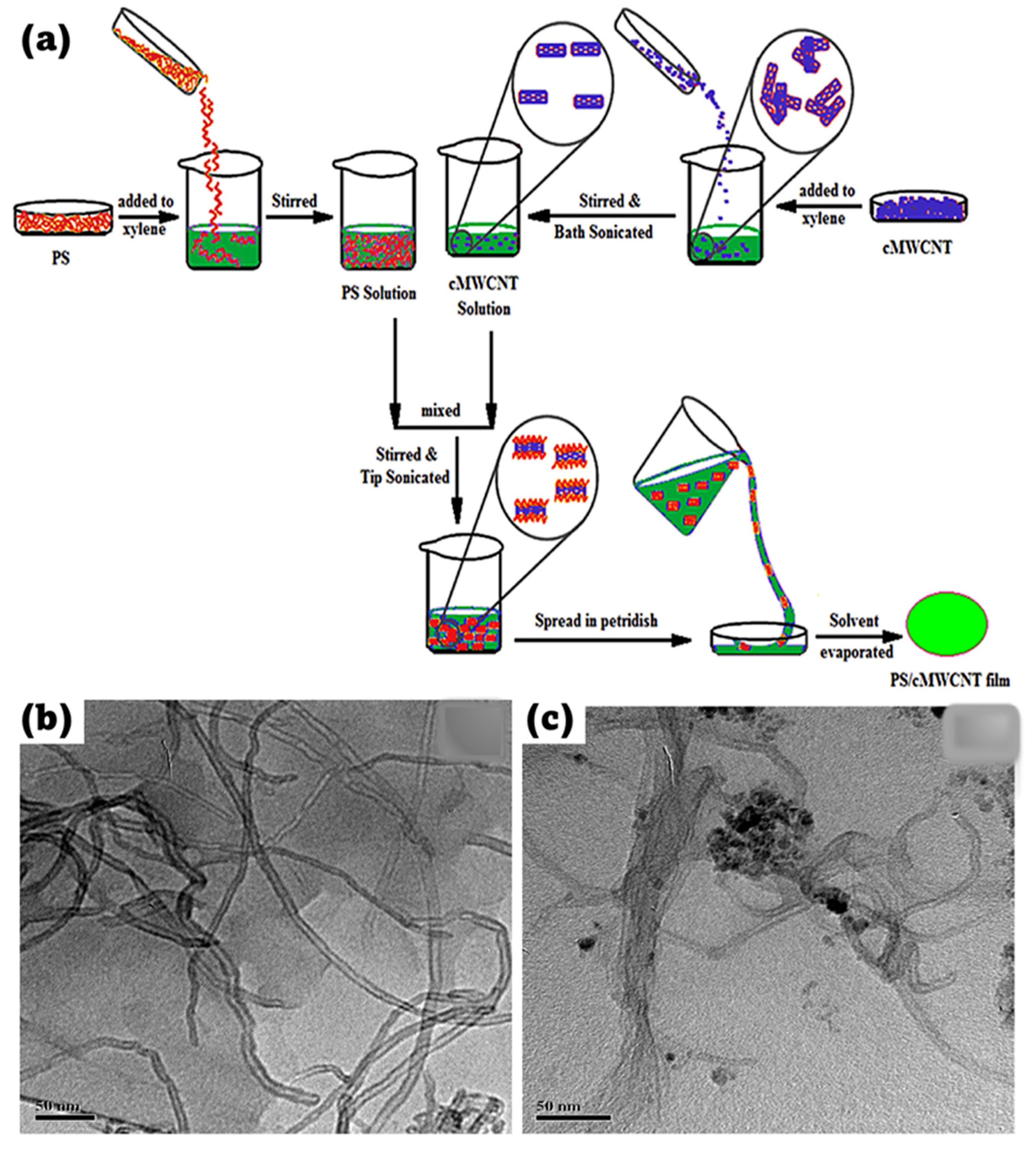
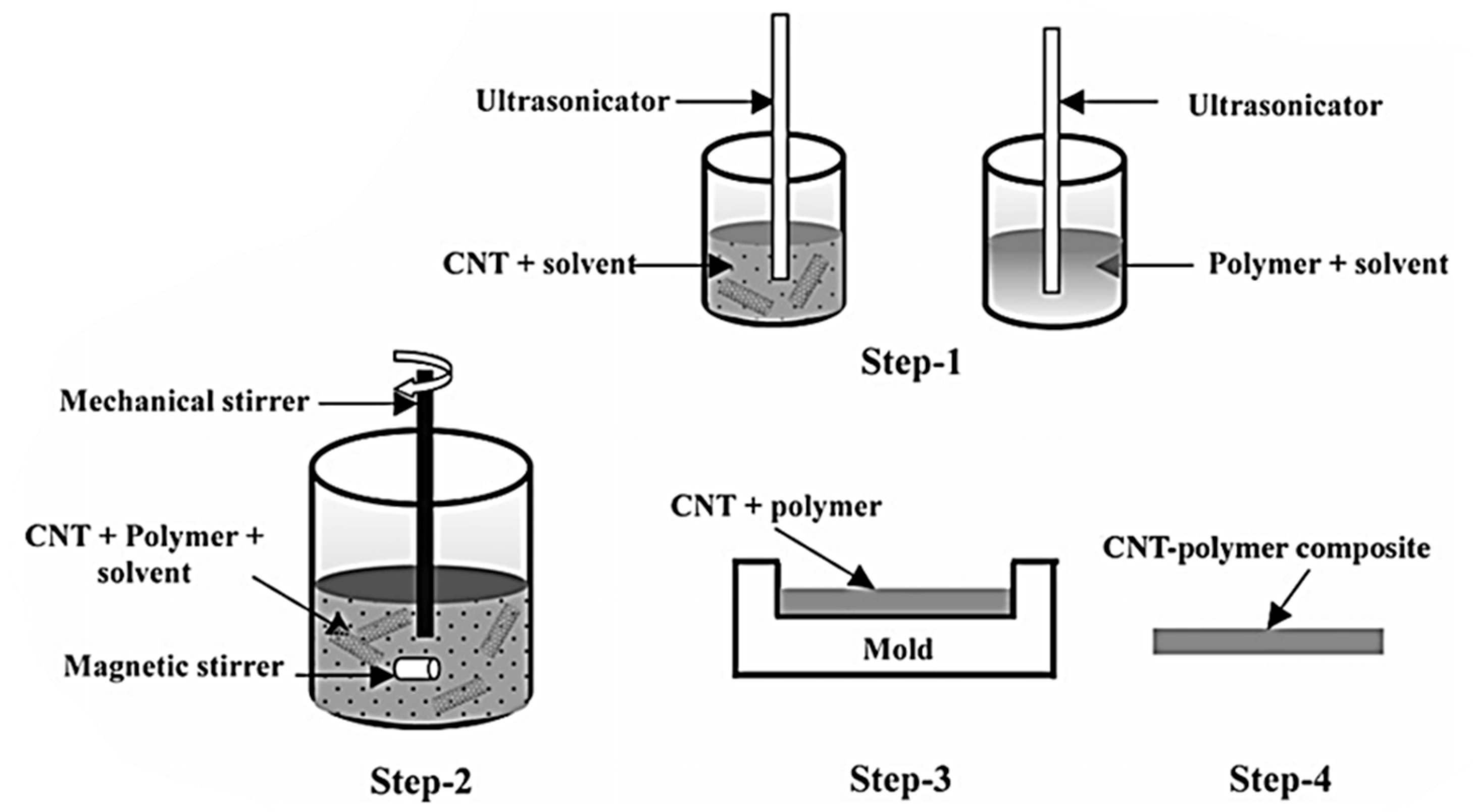
3.2. Solution Mixing
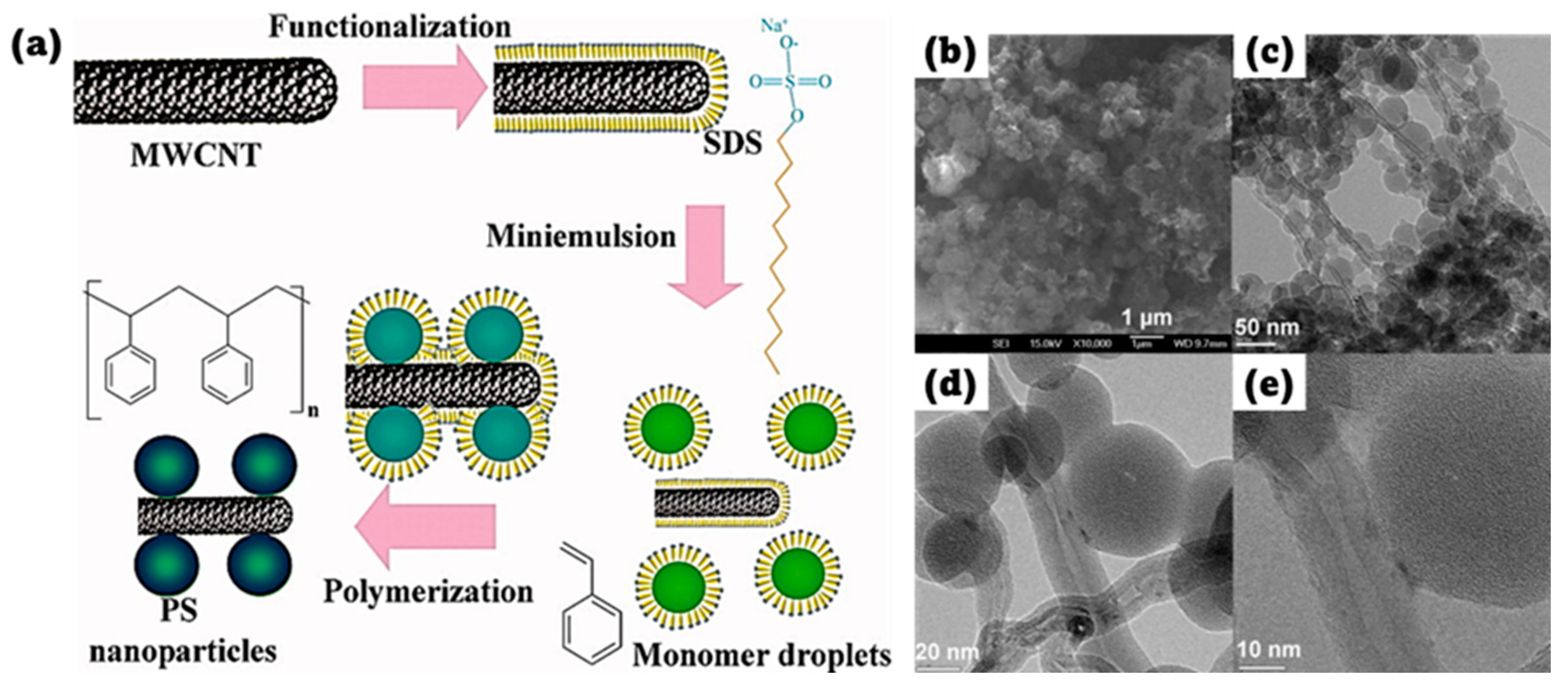
3.3. In Situ Polymerization
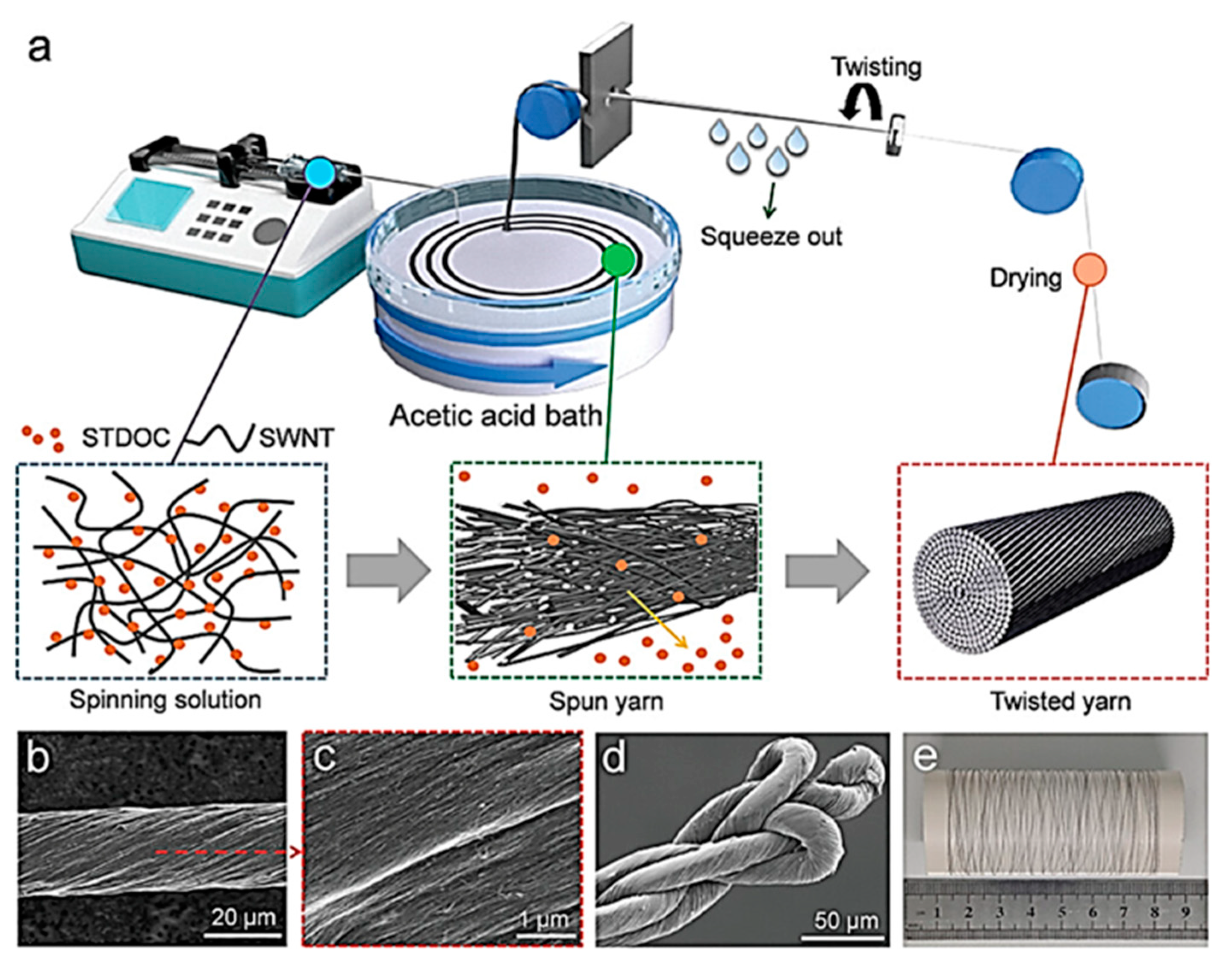
3.4. Wet Spinning
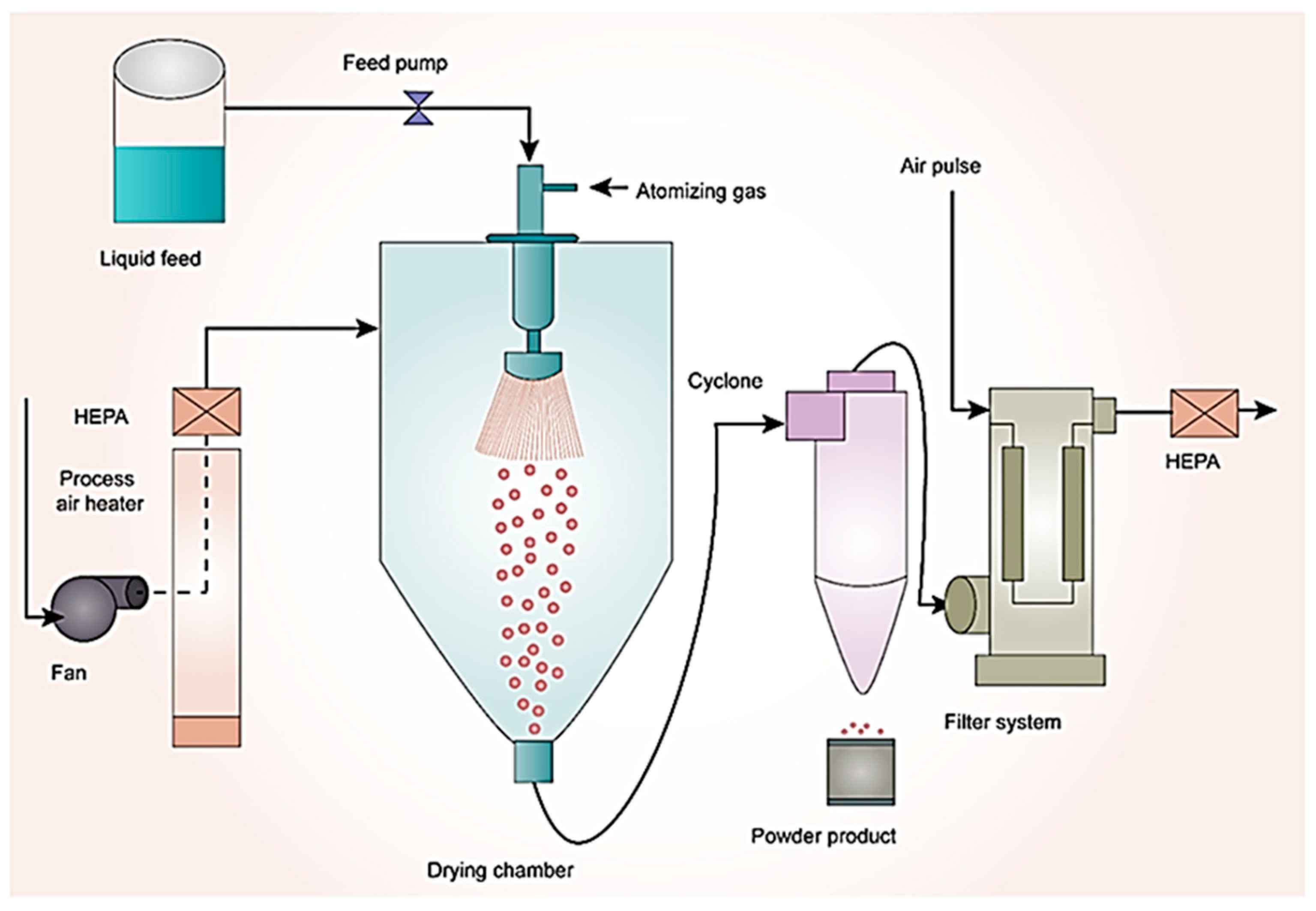
3.5. Spray Drying
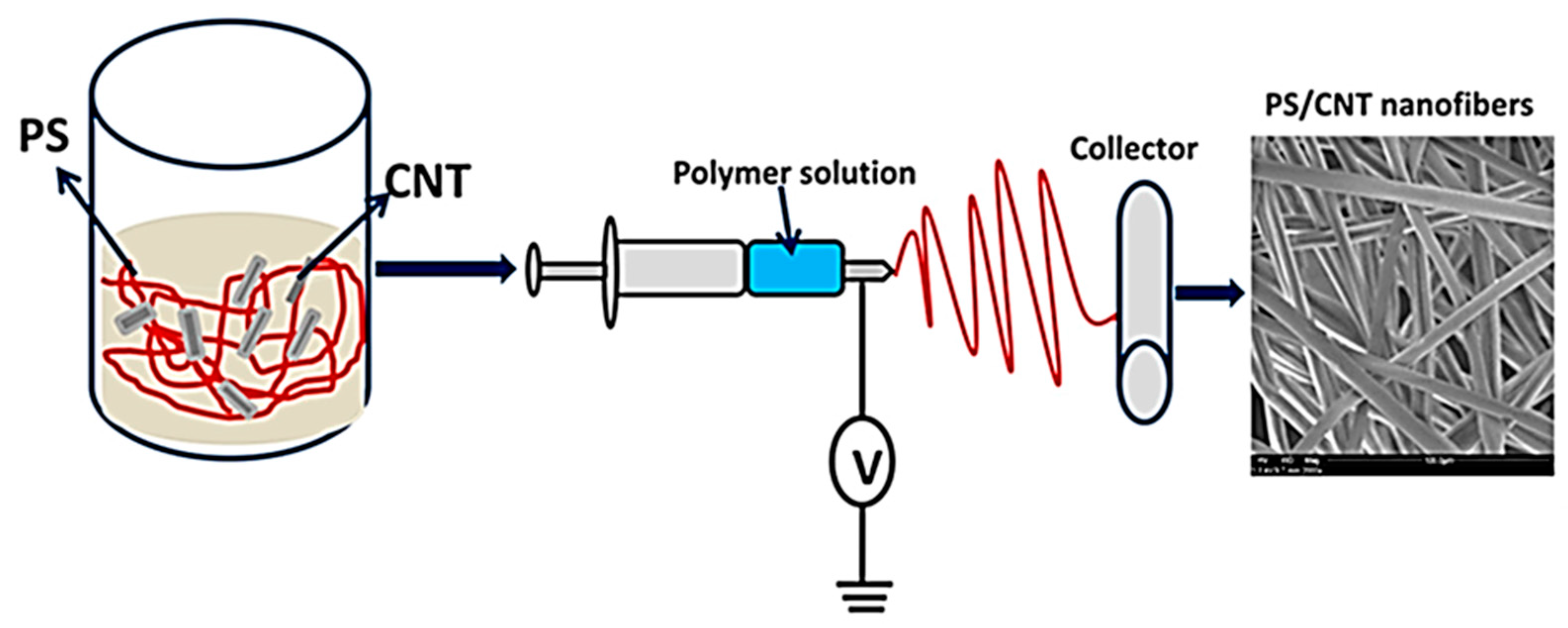
3.6. Electrospinning
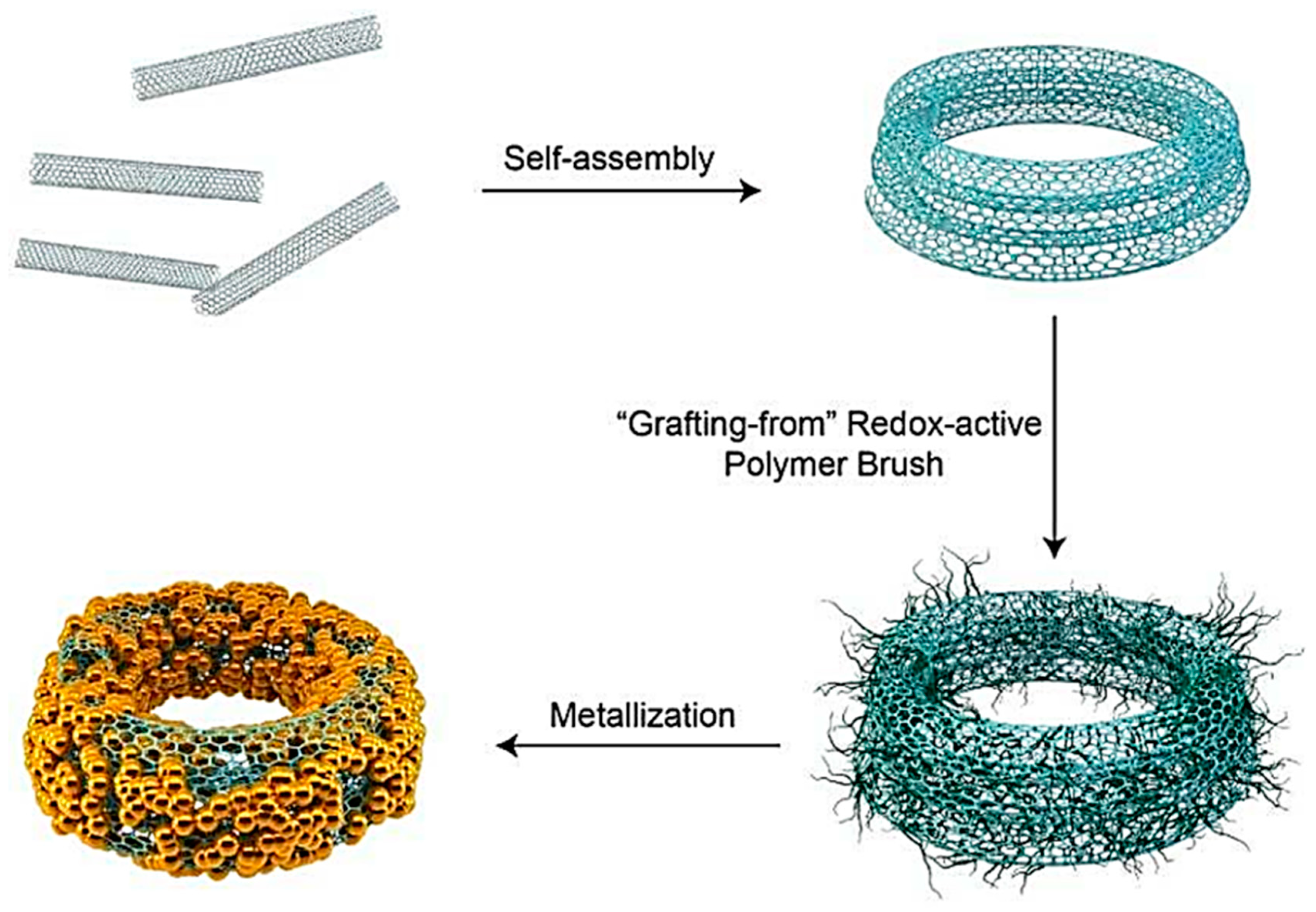
3.7. Self-Assembly Techniques
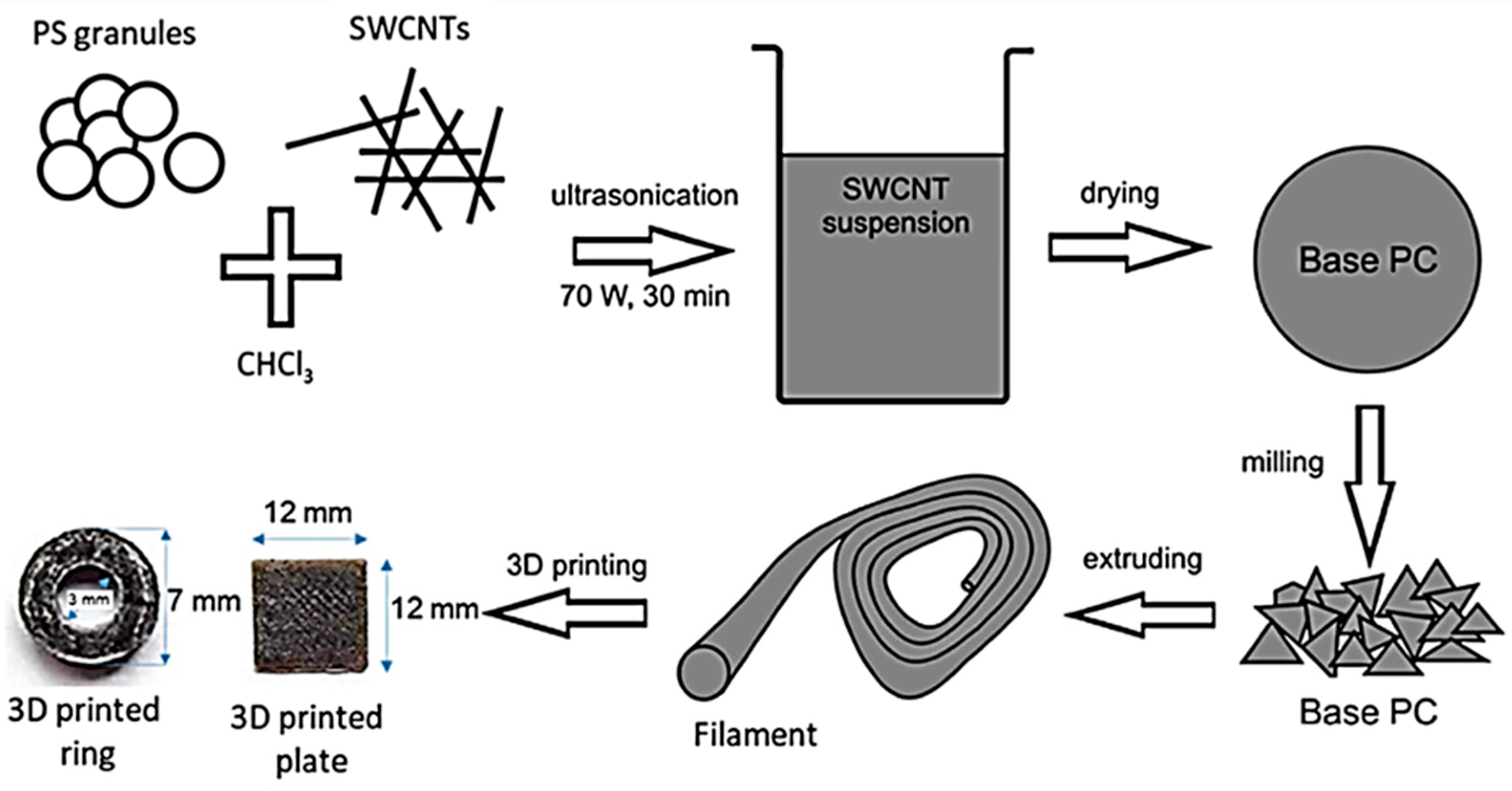
3.8. Three-Dimensional Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
3.9. Layer-by-Layer (LbL) Assembly
3.10. Co-Solvent Method
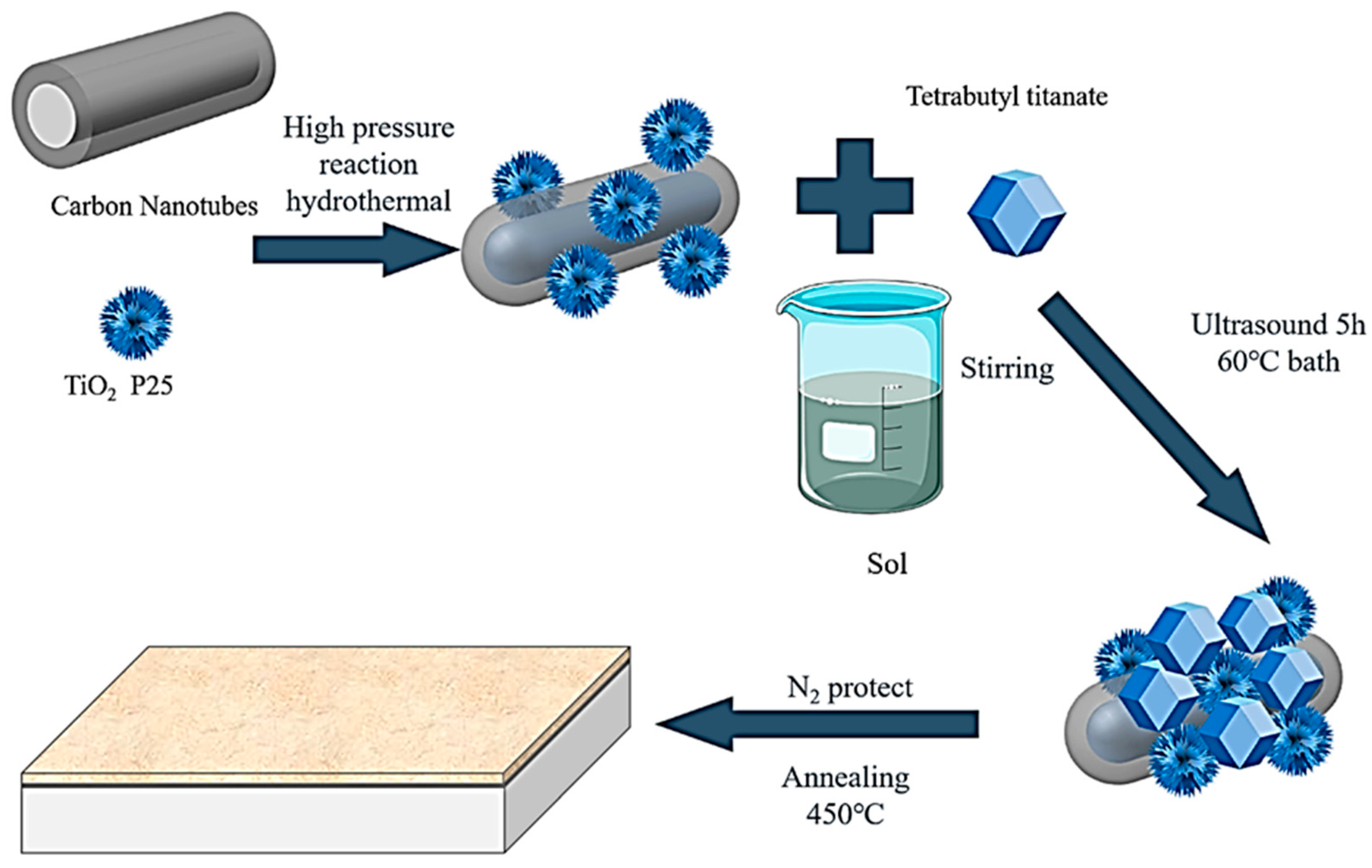
3.11. Sol–Gel Method
3.12. Microwave-Assisted Processing
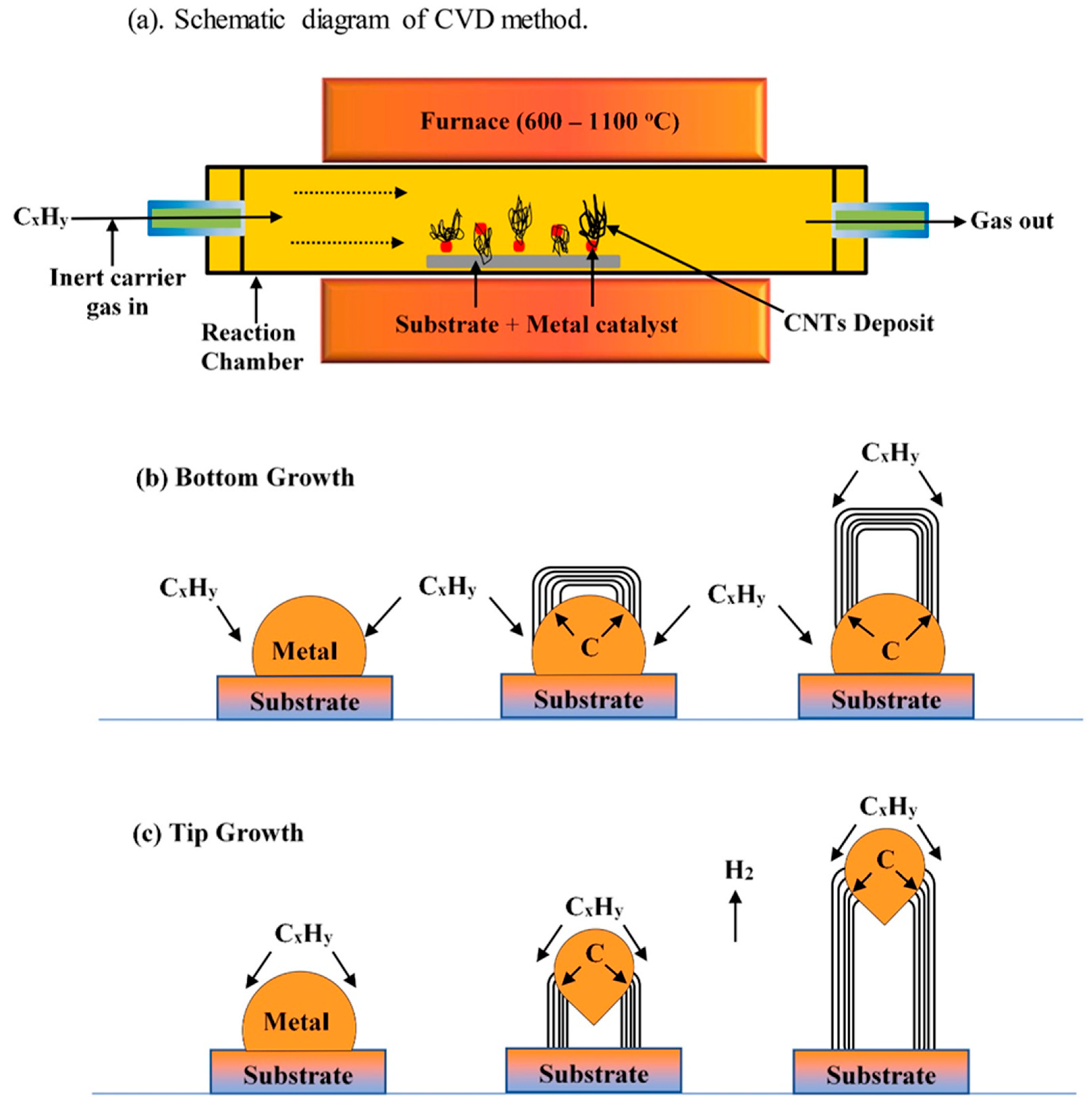
3.13. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) with PS Deposition
4. Rheological Properties of PS/CNT Composites
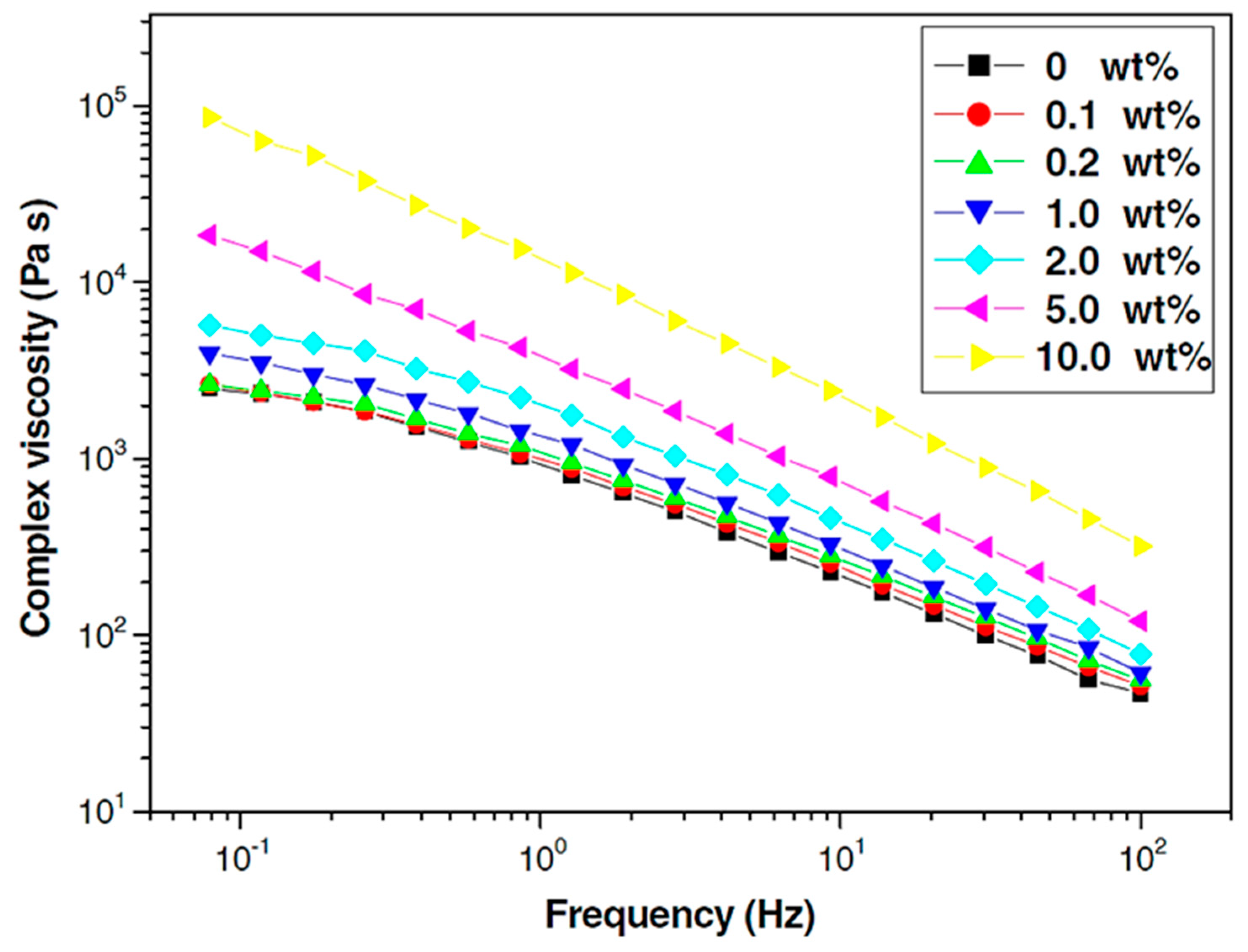
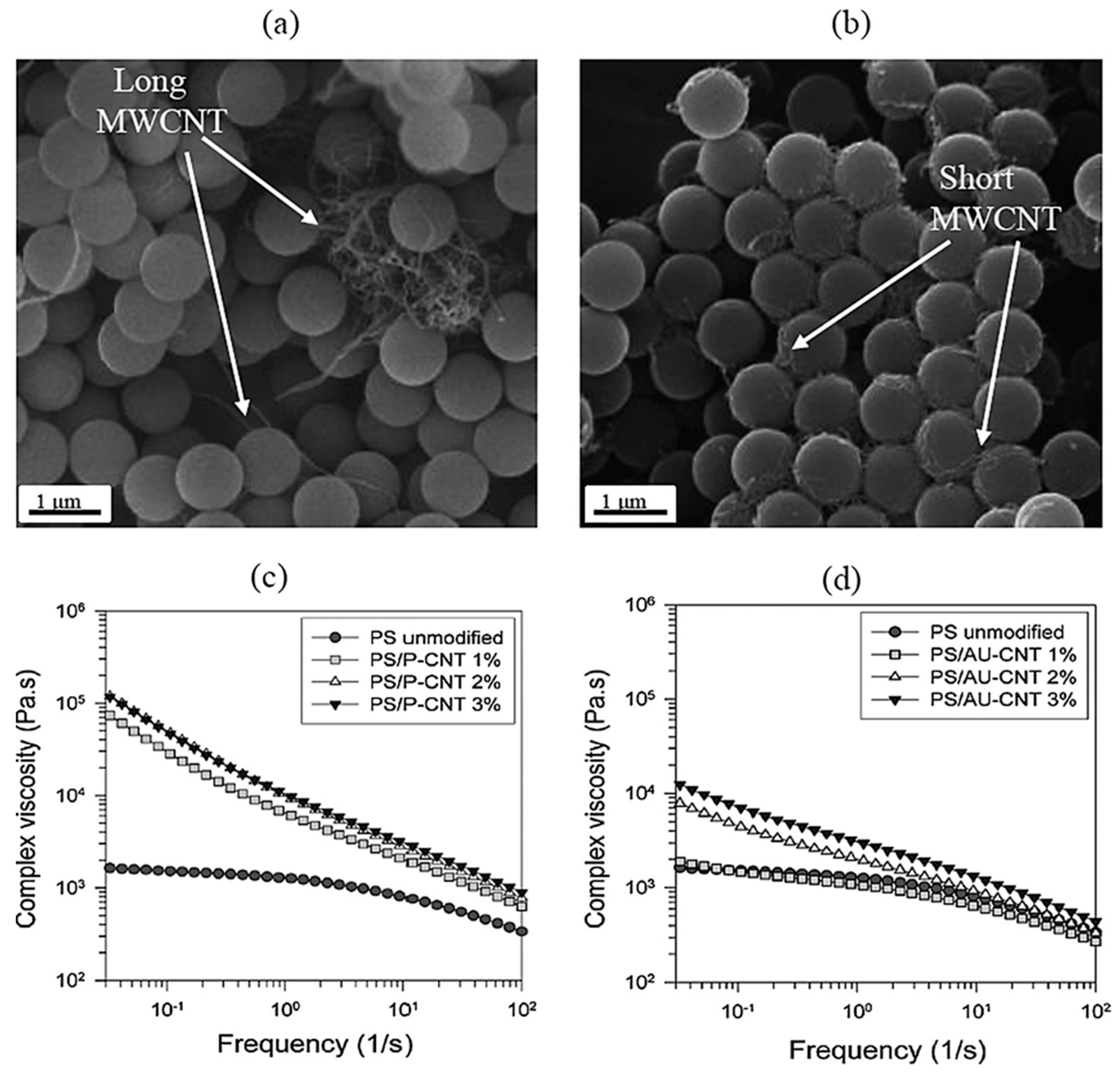
4.1. Steady-Shear and Oscillatory-Shear Viscosity
4.2. Shear Thinning and Flow Behavior
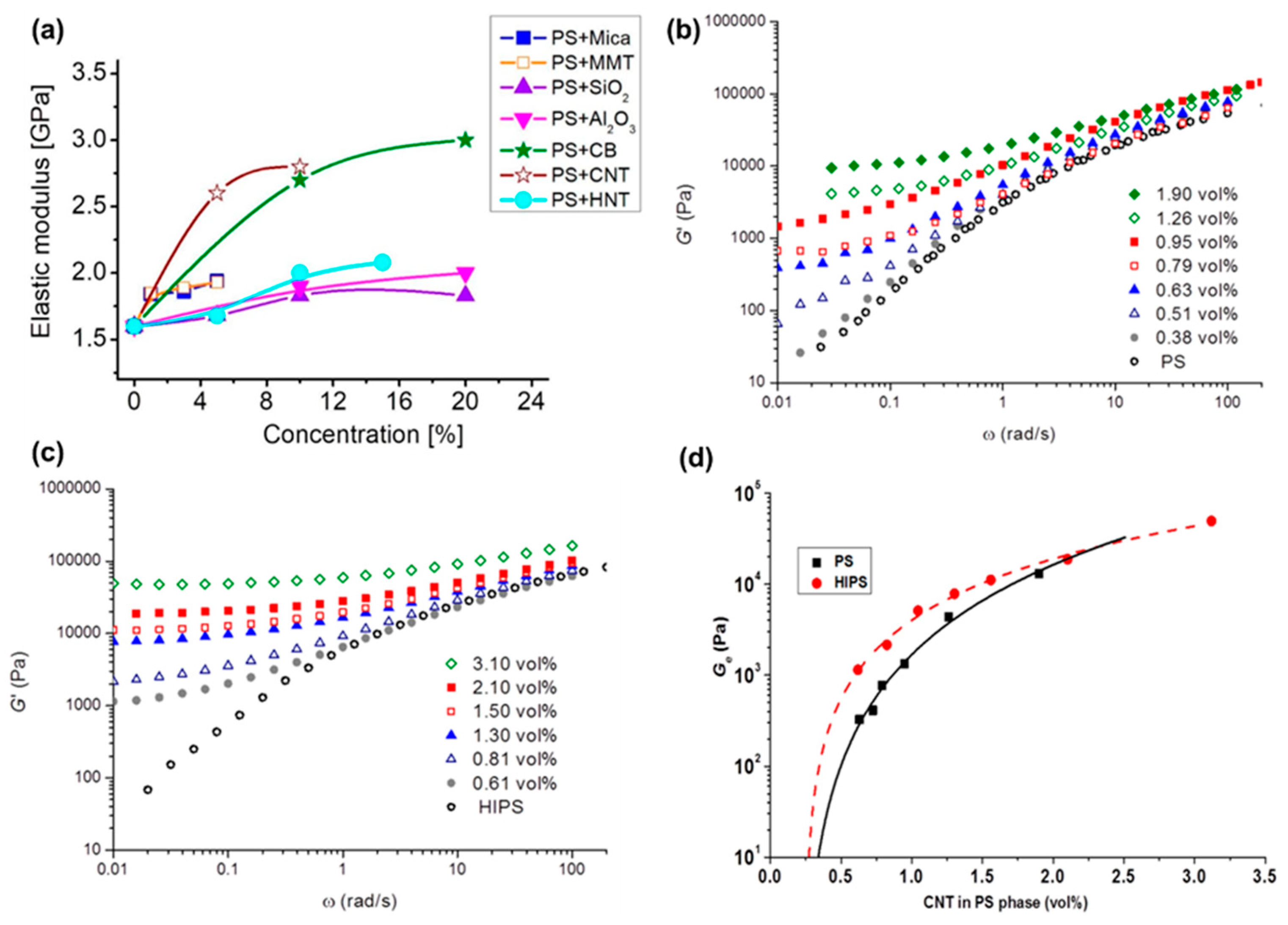
4.3. Elasticity
5. Challenges and Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oladele, I.O.; Omotosho, T.F.; Adediran, A.A. Polymer-based composites: An indispensable material for present and future applications. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2020, 2020, 8834518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashfipour, M.A.; Mehra, N.; Zhu, J. A review on the role of interface in mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of polymer composites. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. 2018, 1, 415–439. [Google Scholar]
- Mergen, Ö.B.; Arda, E.; Evingür, G.A. Electrical, optical, and mechanical percolations of multi-walled carbon nanotube and carbon mesoporous-doped polystyrene composites. J. Compos. Mater. 2020, 54, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantano, A. Mechanical properties of CNT/polymer. In Carbon Nanotube-Reinforced Polymers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 201–232. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Niu, K. Functionalization of Carbon Nanotubes in Polystyrene and Properties of Their Composites: A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; An, J.H.; Jang, K.-S.; Lee, S.J. Rheological and electrical properties of polystyrene nanocomposites via incorporation of polymer-wrapped carbon nanotubes. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2019, 31, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H. Rheological properties and phase structure of polypropylene/polystyrene/multiwalled carbon nanotube composites. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2020, 32, 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Khaksar, M.-R.; Ghazi-Khansari, M. Determination of migration monomer styrene from GPPS (general purpose polystyrene) and HIPS (high impact polystyrene) cups to hot drinks. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2009, 19, 257–261. [Google Scholar]
- Alfarraj, A.; Nauman, E.B. Super HIPS: Improved high impact polystyrene with two sources of rubber particles. Polymer 2004, 45, 8435–8442. [Google Scholar]
- Ramli Sulong, N.H.; Mustapa, S.A.S.; Abdul Rashid, M.K. Application of expanded polystyrene (EPS) in buildings and constructions: A review. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksit, M.; Zhao, C.; Klose, B.; Kreger, K.; Schmidt, H.-W.; Altstädt, V. Extruded polystyrene foams with enhanced insulation and mechanical properties by a benzene-trisamide-based additive. Polymers 2019, 11, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baugh, L.S.; Schulz, D.N. Discovery of syndiotactic polystyrene: Its synthesis and impact. Polymer 2020, 53, 3627–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniruzzaman, M.; Winey, K.I. Polymer nanocomposites containing carbon nanotubes. Macromolecules 2006, 39, 5194–5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.; Yaqoob, S.; Yu, J.; D’Amore, A. Critical review on the characterization, preparation, and enhanced mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties of carbon nanotubes and their hybrid filler polymer composites for various applications. Composites Part C Open Access 2024, 13, 100434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dervishi, E.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Saini, V.; Biris, A.R.; Lupu, D.; Biris, A.S. Carbon nanotubes: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Part. Sci. Technol. 2009, 27, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigo, R.; Malucelli, G. Rheological behavior of polymer/carbon nanotube composites: An overview. Materials 2020, 13, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Fang, F.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Chen, D. Use of dynamic rheological behavior to estimate the dispersion of carbon nanotubes in carbon nanotube/polymer composites. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 12606–12611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Nurazzi, N.; Asyraf, M.M.; Khalina, A.; Abdullah, N.; Sabaruddin, F.A.; Kamarudin, S.H.; Ahmad, S.b.; Mahat, A.M.; Lee, C.L.; Aisyah, H. Fabrication, functionalization, and application of carbon nanotube-reinforced polymer composite: An overview. Polymers 2021, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grady, B.P. Effects of carbon nanotubes on polymer physics. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2012, 50, 591–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaseem, M.; Hamad, K.; Ko, Y.G. Fabrication and materials properties of polystyrene/carbon nanotube (PS/CNT) composites: A review. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 79, 36–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnian, P.; D’Amore, A. Investigating the electrical and mechanical properties of polystyrene (PS)/untreated SWCNT nanocomposite films. J. Compos. Sci. 2024, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, A.H.A.; Arjmand, M.; Sundararaj, U.; Trifkovic, M. Significance of interfacial interaction and agglomerates on electrical properties of polymer-carbon nanotube nanocomposites. Mater. Des. 2017, 125, 126–134. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, E.M.; Martín, N. π–π interactions in carbon nanostructures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6425–6433. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guadagno, L.; Raimondo, M.; Vertuccio, L.; Naddeo, C.; Barra, G.; Longo, P.; Lamberti, P.; Spinelli, G.; Nobile, M. Morphological, rheological and electrical properties of composites filled with carbon nanotubes functionalized with 1-pyrenebutyric acid. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 147, 12–21. [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler, S.E.; Bloom, J.W. Toward a more complete understanding of noncovalent interactions involving aromatic rings. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 6133–6147. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Li, N.; Ren, K.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, Q. Exploring interfacial enhancement in polystyrene/multiwalled carbon nanotube monofilament induced by stretching. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2014, 61, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, H.; Lyu, W. Enhancing the reinforcing efficiency in CNT nanocomposites via the development of pyrene-based active dispersants. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 23892–23900. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.U.; Gomes, V.G.; Altarawneh, I.S. Synthesizing polystyrene/carbon nanotube composites by emulsion polymerization with non-covalent and covalent functionalization. Carbon 2010, 48, 2925–2933. [Google Scholar]
- Erkmen, B. Polystyrene-Based and Carbon Fabric-Reinforced Polymer composites Containing Carbon Nanotubes: Preparation, Modification and Characterization. Ph.D. Thesis, Middle East Technical University, Cankaya, Turkey, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Keshmiri, N.; Hoseini, A.H.A.; Najmi, P.; Liu, J.; Milani, A.S.; Arjmand, M. Highly conductive polystyrene/carbon nanotube/PEDOT: PSS nanocomposite with segregated structure for electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 2023, 212, 118104. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, N.K.; Khatua, B. Development of electrical conductivity with minimum possible percolation threshold in multi-wall carbon nanotube/polystyrene composites. Carbon 2011, 49, 4571–4579. [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava, N.; Maiti, S.; Suin, S.; Khatua, B. Influence of selective dispersion of MWCNT on electrical percolation of in-situ polymerized high-impact polystyrene/MWCNT nanocomposites. Express Polym. Lett. 2014, 8, 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- Navas, I.O.; Kamkar, M.; Arjmand, M.; Sundararaj, U. Morphology evolution, molecular simulation, electrical properties, and rheology of carbon nanotube/polypropylene/polystyrene blend nanocomposites: Effect of molecular interaction between styrene-butadiene block copolymer and carbon nanotube. Polymers 2021, 13, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Terentjev, E. Dispersion and rheology of carbon nanotubes in polymers. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2008, 1, 63–74. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, K.A.; Higgins, L.J.; Nahil, M.A.; Mishra, B.; Williams, P.T. Structural comparison of multi-walled carbon nanotubes produced from polypropylene and polystyrene waste plastics. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 161, 105396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbie, E.K. Shear rheology of carbon nanotube suspensions. Rheol. Acta 2010, 49, 323–334. [Google Scholar]
- Yousfi, M.; Alix, S.; Lebeau, M.; Soulestin, J.; Lacrampe, M.-F.; Krawczak, P. Evaluation of rheological properties of non-Newtonian fluids in micro rheology compounder: Experimental procedures for a reliable polymer melt viscosity measurement. Polym. Test. 2014, 40, 207–217. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Guo, B.-H.; Guo, Z.-X.; Yu, J. Electrical conductivity of carbon nanotube-filled miscible poly (phenylene oxide)/polystyrene blends prepared by melt compounding. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 176, 107213. [Google Scholar]
- Papageorgiou, D.G.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Kinloch, I.A.; Young, R.J. Mechanisms of mechanical reinforcement by graphene and carbon nanotubes in polymer nanocomposites. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 2228–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J. Mechanics of carbon nanotube scission under sonication. J. Chem. Phys. 2014, 140, 244908. [Google Scholar]
- Ishak, K.A.; Annuar, M.S.M.; Aris, M.H. Chain scission by ultrasonication of polycaprolactone with different initial molecular weight and concentration. J. Polym. Res. 2022, 29, 134. [Google Scholar]
- Erkmen, B.; Bayram, G. Influence of nanocomposite preparation techniques on the multifunctional properties of carbon fabric-reinforced polystyrene-based composites with carbon nanotubes. SPE Polym. 2022, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.; Suresh, K.; Kumar, R.V.; Kumar, M.; Pugazhenthi, G. A simple solvent blending coupled sonication technique for synthesis of polystyrene (PS)/multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) nanocomposites: Effect of modified MWCNT content. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2016, 1, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riolo, D.; Piazza, A.; Cottini, C.; Serafini, M.; Lutero, E.; Cuoghi, E.; Gasparini, L.; Botturi, D.; Marino, I.G.; Aliatis, I. Raman spectroscopy as a PAT for pharmaceutical blending: Advantages and disadvantages. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 149, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azubuike, L.; Sundararaj, U. Interface strengthening of PS/APA polymer blend nanocomposites via in situ compatibilization: Enhancement of electrical and rheological properties. Materials 2021, 14, 4813. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patole, A.S.; Patole, S.; Yoo, J.B.; Ahn, J.H.; Kim, T.H. Effective in situ synthesis and characteristics of polystyrene nanoparticle-covered multiwall carbon nanotube composite. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2009, 47, 1523–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, A.V.; Kanny, K.; Abitha, V.; Thomas, S. Methods for synthesis of nanoparticles and fabrication of nanocomposites. In Synthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 121–139. [Google Scholar]
- Quijano, J.R.B. Mechanical, Electrical and Sensing Properties of Melt-Spun Polymer Fibers Filled with Carbon Nanoparticles. Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University of Dresden, Dresden, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Farha, F.I.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, W.; Chen, W.; Liu, L.; Xu, F. Microstructural tuning of twisted carbon nanotube yarns through the wet-compression process: Implications for multifunctional textiles. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 11071–11079. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Kong, D.; Tao, J.; Kong, N.; Mota-Santiago, P.; Lynch, P.A.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, J. Wet Twisting in spinning for rapid and cost-effective fabrication of superior carbon nanotube yarns. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2400197. [Google Scholar]
- Prasad, G.; Chakradhar, R.; Bera, P.; Anand Prabu, A. UV and thermally stable polystyrene-MWCNT superhydrophobic coatings. Surf. Interface Anal. 2017, 49, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, J.; Yu, S. New fabrication of Styrene-Butadiene Rubber/Carbon Nanotubes nanocomposite and corresponding mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 26, 1127. [Google Scholar]
- Tambe, S.; Jain, D.; Meruva, S.K.; Rongala, G.; Juluri, A.; Nihalani, G.; Mamidi, H.K.; Nukala, P.K.; Bolla, P.K. Recent advances in amorphous solid dispersions: Preformulation, formulation strategies, technological advancements and characterization. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozmen, L.; Langrish, T. A study of the limitations to spray dryer outlet performance. Dry. Technol. 2003, 21, 895–917. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, S.; Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Jeong, S. Reusable carbon nanotube-embedded polystyrene/polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous sorbent for managing oil spills. Desalination 2022, 537, 115865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parangusan, H.; Ponnamma, D.; Hassan, M.K.; Adham, S.; Al-Maadeed, M.A.A. Designing carbon nanotube-based oil absorbing membranes from gamma irradiated and electrospun polystyrene nanocomposites. Materials 2019, 12, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, E.Y.; Bode, R.; Escárcega-Bobadilla, M.V.; Zelada-Guillén, G.A.; Maier, G. Polymer nanocomposites from self-assembled polystyrene-grafted carbon nanotubes. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 4625–4634. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, G.-J. A novel method for well-organized polystyrene-grafted multi-walled carbon nanotube bundles via self-assembly in tetrahydrofuran. Fibers Polym. 2013, 14, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, T.; Lu, X. Facile fabrication of polystyrene/carbon nanotube composite nanospheres with core-shell structure via self-assembly. Polymer 2010, 51, 3715–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.; Ning, B.; Harp, M.G.; Culp, S.H.; Hu, S.; Huang, P.; Nie, L.; Chen, J. Gold nanoparticle coated carbon nanotube ring with enhanced raman scattering and photothermal conversion property for theranostic applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 7005–7015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Tao, X.; Shi, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, N. From materials to components: 3D-printed architected honeycombs toward high-performance and tunable electromagnetic interference shielding. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 230, 109500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskakova, K.I.; Okotrub, A.V.; Bulusheva, L.G.; Sedelnikova, O.V. Manufacturing of carbon nanotube-polystyrene filament for 3D printing: Nanoparticle dispersion and electromagnetic properties. Nanomanufacturing 2022, 2, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Huang, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. A review of conductive carbon materials for 3D printing: Materials, technologies, properties, and applications. Materials 2021, 14, 3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Park, J.G.; Cheng, Q.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, B. The fabrication of single-walled carbon nanotube/polyelectrolyte multilayer composites by layer-by-layer assembly and magnetic field assisted alignment. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 335601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Caruso, F.; Dähne, L.; Decher, G.; De Geest, B.G.; Fan, J.; Feliu, N.; Gogotsi, Y.; Hammond, P.T.; Hersam, M.C. The future of layer-by-layer assembly: A tribute to ACS nano associate editor Helmuth Mohwald. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6151–6169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zeng, J.; Groll, J.; Matsusaki, M. Layer-by-layer assembly methods and their biomedical applications. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 4077–4094. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.; Han, J.Y.; Yoon, H.; Joo, P.; Lee, T.; Seo, E.; Char, K.; Kim, B.-S. Carbon-based layer-by-layer nanostructures: From films to hollow capsules. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 4515–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Kotov, N.A. Composite layer-by-layer (LBL) assembly with inorganic nanoparticles and nanowires. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H. Layer-by-layer assembly: From conventional to unconventional methods. Chem. Commun. 2007, 8, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Lubineau, G.; Rahaman, A. A review of strategies for improving the degradation properties of laminated continuous-fiber/epoxy composites with carbon-based nanoreinforcements. Carbon 2012, 50, 2377–2395. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Qian, X.; Jing, J.; Che, H. Functionalized CNTs with DOPO and silicon containing agents: Effective reinforcer for thermal and flame retardant properties of polystyrene nanocomposites. Front. Chem. 2021, 8, 627642. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, C.-H.; Hung, P.-S.; Cheng, Y.; Wu, P.-W. Combination of microspheres and sol-gel electrophoresis for the formation of large-area ordered macroporous SiO2. Electrochem. Commun. 2017, 85, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Chen, G.Z.; Puma, G.L. Carbon nanotubes/titanium dioxide (CNTs/TiO2) nanocomposites prepared by conventional and novel surfactant wrapping sol–gel methods exhibiting enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2009, 89, 503–509. [Google Scholar]
- Toyama, N.; Takahashi, T.; Terui, N.; Furukawa, S. Synthesis of polystyrene@ TiO2 core–shell particles and their photocatalytic activity for the decomposition of methylene blue. Inorganics 2023, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, W.; Lin, Y.; Feng, Z. Physicochemical and Antibacterial Evaluation of TiO2/CNT Mesoporous Nanomaterials Prepared by High-Pressure Hydrothermal Sol–Gel Method under an Ultrasonic Composite Environment. Molecules 2023, 28, 3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modan, E.M.; PLĂIAȘU, A.G. Advantages and disadvantages of chemical methods in the elaboration of nanomaterials. Ann. “Dunarea De Jos” Univ. Galati. Fascicle IX Metall. Mater. Sci. 2020, 43, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Rybakov, K.I.; Olevsky, E.A.; Krikun, E.V. Microwave sintering: Fundamentals and modeling. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 96, 1003–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Tang, J.; Li, P.; Chen, W.; Liu, P.; Li, L.; Zheng, Z. Microwave-assisted foaming and sintering to prepare lightweight high-strength polystyrene/carbon nanotube composite foams with an ultralow percolation threshold. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 9702–9711. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbazi, M.; Aghvami-Panah, M.; Panahi-Sarmad, M.; Seraji, A.A.; Zeraatkar, A.; Ghaffarian Anbaran, R.; Xiao, X. Fabricating bimodal microcellular structure in polystyrene/carbon nanotube/glass-fiber hybrid nanocomposite foam by microwave-assisted heating: A proof-of-concept study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 52125. [Google Scholar]
- Rezvanpanah, E.; Anbaran, S.R.G.; Di Maio, E. Carbon nanotubes in microwave foaming of thermoplastics. Carbon 2017, 125, 32–38. [Google Scholar]
- Zubair, M.; Ferrari, R.; Alagha, O.; Mu’azu, N.D.; Blaisi, N.I.; Ateeq, I.S.; Manzar, M.S. Microwave foaming of materials: An emerging field. Polymers 2020, 12, 2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghel, P.; Sakhiya, A.K.; Kaushal, P. Ultrafast growth of carbon nanotubes using microwave irradiation: Characterization and its potential applications. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10943. [Google Scholar]
- Granados-Martínez, F.G.; Domratcheva-Lvova, L.; Flores-Ramírez, N.; García-González, L.; Zamora-Peredo, L.; de Mondragón-Sánchez, M.L. Composite films from polystyrene with hydroxyl end groups and carbon nanotubes. Mater. Res. 2017, 19, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Guzenko, N.; Godzierz, M.; Kurtyka, K.; Hercog, A.; Nocoń-Szmajda, K.; Gawron, A.; Szeluga, U.; Trzebicka, B.; Yang, R.; Rümmeli, M.H. Flexible Piezoresistive Polystyrene Composite Sensors Filled with Hollow 3D Graphitic Shells. Polymers 2023, 15, 4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicerano, J.; Douglas, J.F.; Brune, D.A. Model for the viscosity of particle dispersions. J. Macromol. Sci. Part C Polym. Rev. 1999, 39, 561–642. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, T.; Krishnamoorti, R. Rheology of polymer carbon nanotubes composites. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 9515–9529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, M.K.; Bazilevsky, A.V.; Yarin, A.L.; Megaridis, C.M. Elongational and shear rheology of carbon nanotube suspensions. Rheol. Acta 2009, 48, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.W.; Mackley, M.R.; Chinesta, F. The microstructure and rheology of carbon nanotube suspensions. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2008, 1, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, A.W.; Chinesta, F.; Mackley, M.R.; Ammar, A. The rheological modelling of carbon nanotube (CNT) suspensions in steady shear flows. Int. J. Mater. Form. 2008, 1, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Münstedt, H. Extensional rheology and processing of polymeric materials. Int. Polym. Process. 2018, 33, 594–618. [Google Scholar]
- Miyazono, K.; Kagarise, C.D.; Koelling, K.W.; Mahboob, M.; Bechtel, S.E. Shear and extensional rheology and flow-induced orientation of carbon nanofiber/polystyrene melt composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 119, 1940–1951. [Google Scholar]
- Rizvi, A.; Bae, S.S.; Mohamed, N.M.; Lee, J.H.; Park, C.B. Extensional flow resistance of 3D fiber networks in plasticized nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 6467–6473. [Google Scholar]
- Kamkar, M.; Aliabadian, E.; Shayesteh Zeraati, A.; Sundararaj, U. Application of nonlinear rheology to assess the effect of secondary nanofiller on network structure of hybrid polymer nanocomposites. Phys. Fluids 2018, 30, 023102. [Google Scholar]
- Kamkar, M.; Sultana, S.N.; Pawar, S.P.; Eshraghian, A.; Erfanian, E.; Sundararaj, U. The key role of processing in tuning nonlinear viscoelastic properties and microwave absorption in CNT-based polymer nanocomposites. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 24, 101010. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, H.T.; Ahn, K.H.; Hong, J.S.; Hyun, K. Nonlinear viscoelasticity of polymer nanocomposites under large amplitude oscillatory shear flow. J. Rheol. 2013, 57, 767–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.G.; Wei, Y. A review of thixotropy and its rheological modeling. J. Rheol. 2019, 63, 477–501. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, C.A.; Bahr, J.L.; Arepalli, S.; Tour, J.M.; Krishnamoorti, R. Dispersion of functionalized carbon nanotubes in polystyrene. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8825–8830. [Google Scholar]
- Garmestani, H.; Al-Haik, M.S.; Dahmen, K.; Tannenbaum, R.; Li, D.; Sablin, S.S.; Hussaini, M.Y. Polymer-mediated alignment of carbon nanotubes under high magnetic fields. Adv. Mater. 2003, 15, 1918–1921. [Google Scholar]
- Pötschke, P.; Fornes, T.; Paul, D. Rheological behavior of multiwalled carbon nanotube/polycarbonate composites. Polymer 2002, 43, 3247–3255. [Google Scholar]
- Vodnik, V.V.; Dzunuzovic, E.; Dzunuzovic, J. Synthesis and characterization of polystyrene based nanocomposites. In Polystyrene: Synthesis, Characteristics and Applications, 1st ed.; Lynwood, C., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 201–240. [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein, M.; Colby, R.H. Polymer Physics; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, R.G. The Structure and Rheology of Complex Fluids; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 150. [Google Scholar]
- Sukumaran, A.; Das, K.; Rawat, K.; Bohidar, H. Universal Validity of Einstein Relation and Size-Dependent Viscosity and Surface-Active Characteristics of Nanofluids. Int. J. Nanosci. 2018, 17, 1850006. [Google Scholar]
- Banfill, P.F.G. Concentration effects in the rheology of cement pastes: Krieger-Dougherty revisited. In Proceedings of the 13th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement, Madrid, Spain, 5 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Guillot, P.; Colin, A. Determination of the flow curve of complex fluids using the Rabinowitsch–Mooney equation in sensorless microrheometer. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2014, 17, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PAL, R. Evaluation of the Mooney viscosity/concentration equation for liquid-liquid emulsions. Chem. Eng. Commun. 1990, 89, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Ferry, J. Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1980; Volume 264. [Google Scholar]
- Tadros, T.F. Rheology of Dispersions: Principles and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.-D.; Han, D.-H.; Teng, D.; Kwon, Y. Rheological properties and dispersion of multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) in polystyrene matrix. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2008, 8, 482–485. [Google Scholar]
- Saasen, A.; Ytrehus, J.D. Viscosity models for drilling fluids—Herschel-bulkley parameters and their use. Energies 2020, 13, 5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negishi, H.; Kondo, M.; Amakawa, H.; Obara, S.; Kurose, R. Bingham fluid simulations using a physically consistent particle method. J. Fluid. Sci. Technol. 2023, 18, JFST0035. [Google Scholar]
- Yusufi, B.; Kapelan, Z.; Mehta, D. Advances in modeling the flow of Herschel–Bulkley fluids in pipes: A review. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 021302. [Google Scholar]
- Massoudi, M.; Phuoc, T.X. Remarks on constitutive modeling of nanofluids. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2012, 4, 927580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagarise, C.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Mahboob, M.; Koelling, K.W.; Bechtel, S.E. Transient shear rheology of carbon nanofiber/polystyrene melt composites. J. Non-Newton. Fluid Mech. 2010, 165, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarali, C.S.; Patil, S.F.; Pilli, S.C.; Lu, Y.C. Modeling the effective elastic properties of nanocomposites with circular straight CNT fibers reinforced in the epoxy matrix. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 3160–3172. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D.; Tong, X.; Liu, H.; Lv, S.; Srivatsan, T.; Gao, X. A modified Halpin–Tsai model for predicting the elastic modulus of composite materials. AIP Adv. 2024, 14, 015157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.P.; Brisard, S.; Guilleminot, J.; Sab, K. Mori–Tanaka estimates of the effective elastic properties of stress-gradient composites. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2018, 146, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornes, T.; Paul, D. Modeling properties of nylon 6/clay nanocomposites using composite theories. Polymer 2003, 44, 4993–5013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragneaud, B.; Masenelli-Varlot, K.; Gonzalez-Montiel, A.; Terrones, M.; Cavaille, J.-Y. Mechanical behavior of polystyrene grafted carbon nanotubes/polystyrene nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 3265–3271. [Google Scholar]
- Faraguna, F.; Jukic, A.; Vidovic, E. Synthesis and characterization of polystyrene composites with oxidized and ethylbenzene functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes. J. Compos. Biodegrad. Polym. 2013, 1, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serenko, O.A.; Roldughin, V.I.; Askadskii, A.A.; Serkova, E.S.; Strashnov, P.V.; Shifrina, Z.B. The effect of size and concentration of nanoparticles on the glass transition temperature of polymer nanocomposites. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 50113–50120. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.A.A.; Qi, H.-K.; Huang, J.-H.; Luo, M.-B. A simulation study on the effect of nanoparticle size on the glass transition temperature of polymer nanocomposites. Soft Matter 2021, 17, 8095–8104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moskalyuk, O.A.; Belashov, A.V.; Beltukov, Y.M.; Ivan’kova, E.M.; Popova, E.N.; Semenova, I.V.; Yelokhovsky, V.Y.; Yudin, V.E. Polystyrene-based nanocomposites with different fillers: Fabrication and mechanical properties. Polymers 2020, 12, 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcourt, M.; Cassagnau, P.; Fulchiron, R.; Rousseaux, D.; Lhost, O.; Karam, S. High Impact Polystyrene/CNT nanocomposites: Application of volume segregation strategy and behavior under extensional deformation. Polymer 2018, 157, 156–165. [Google Scholar]


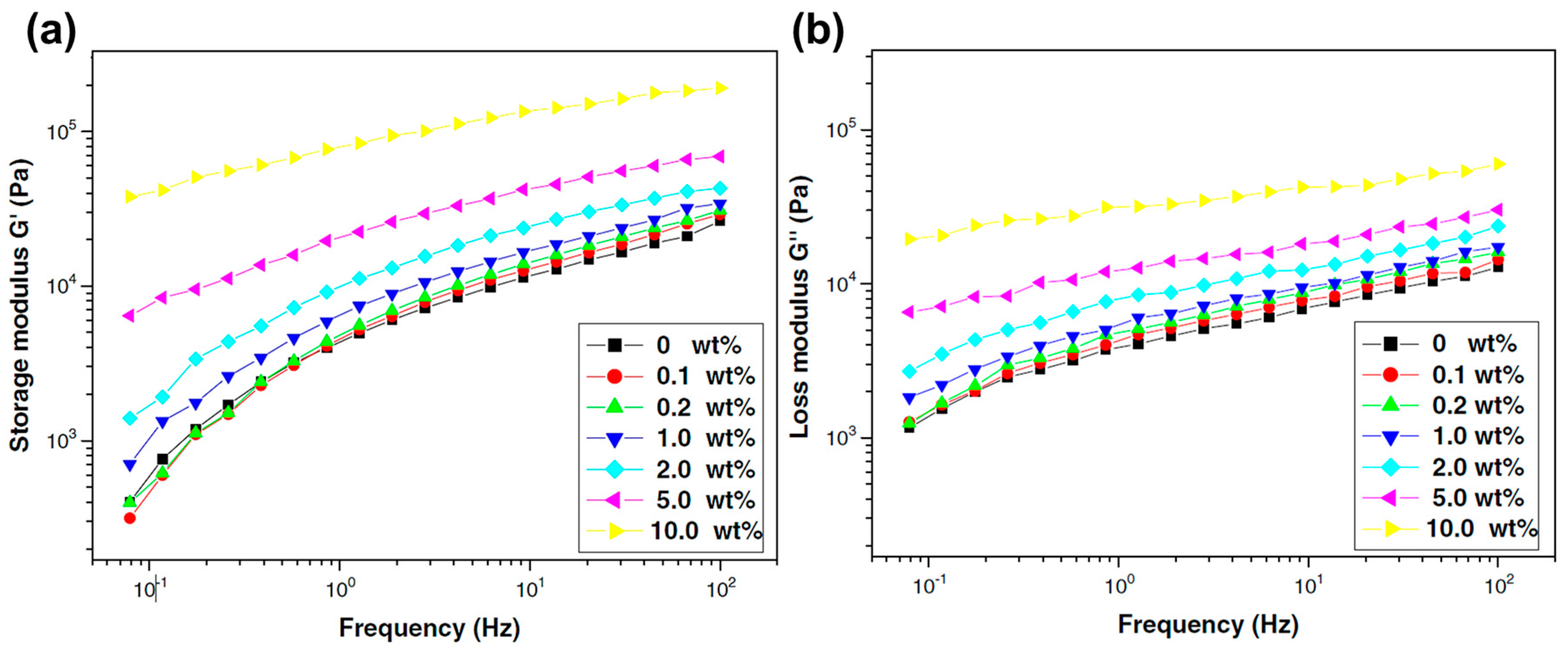
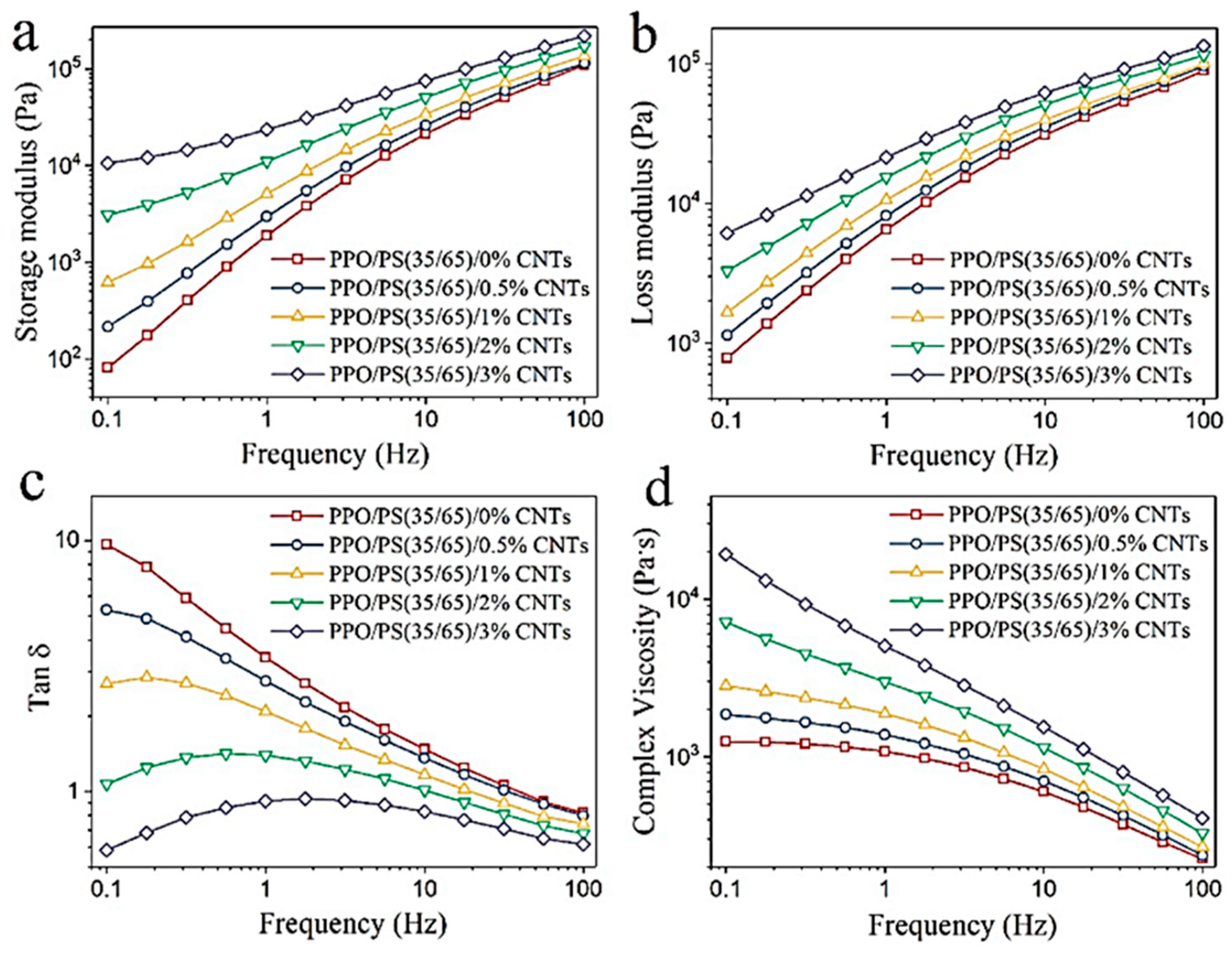

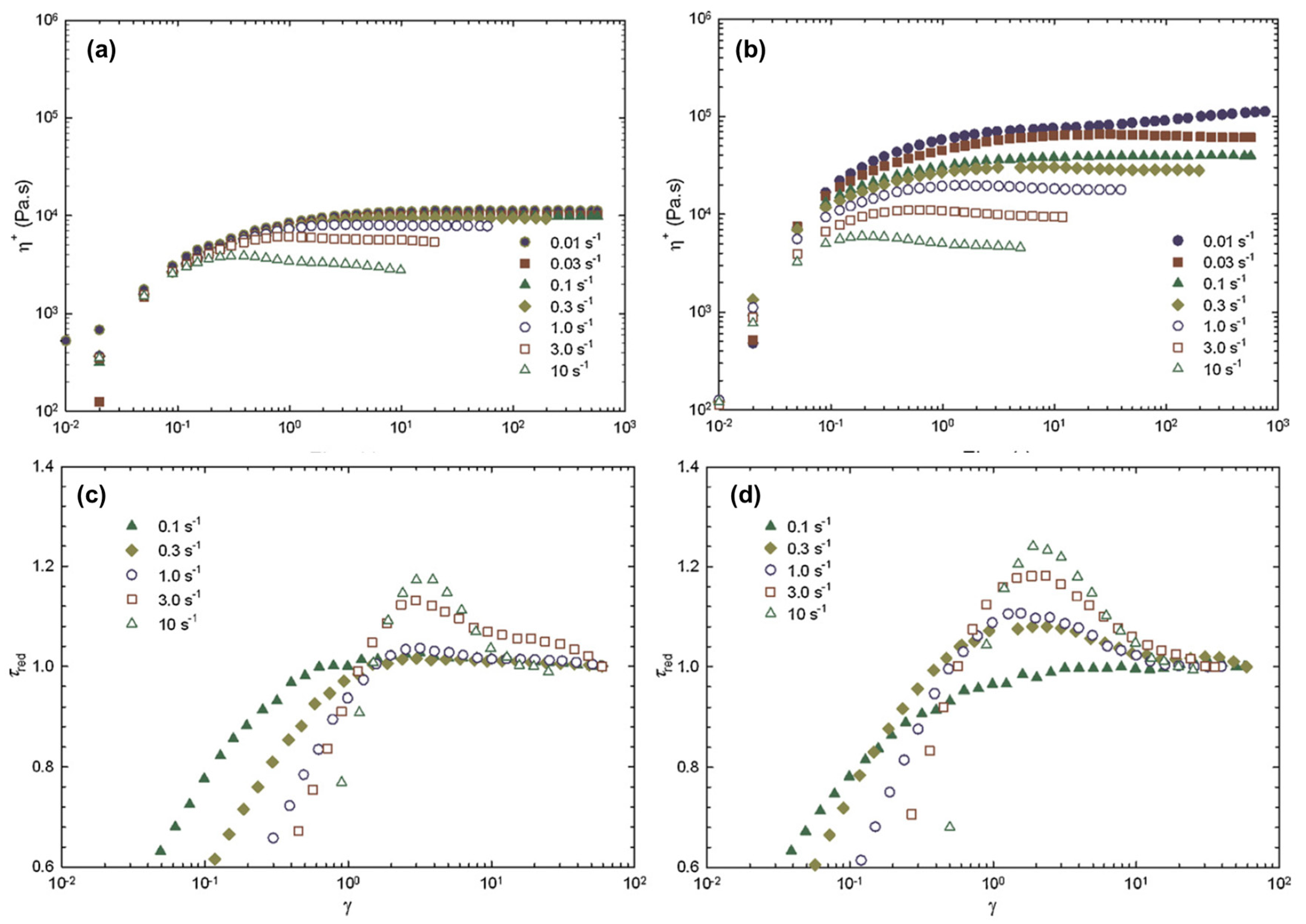
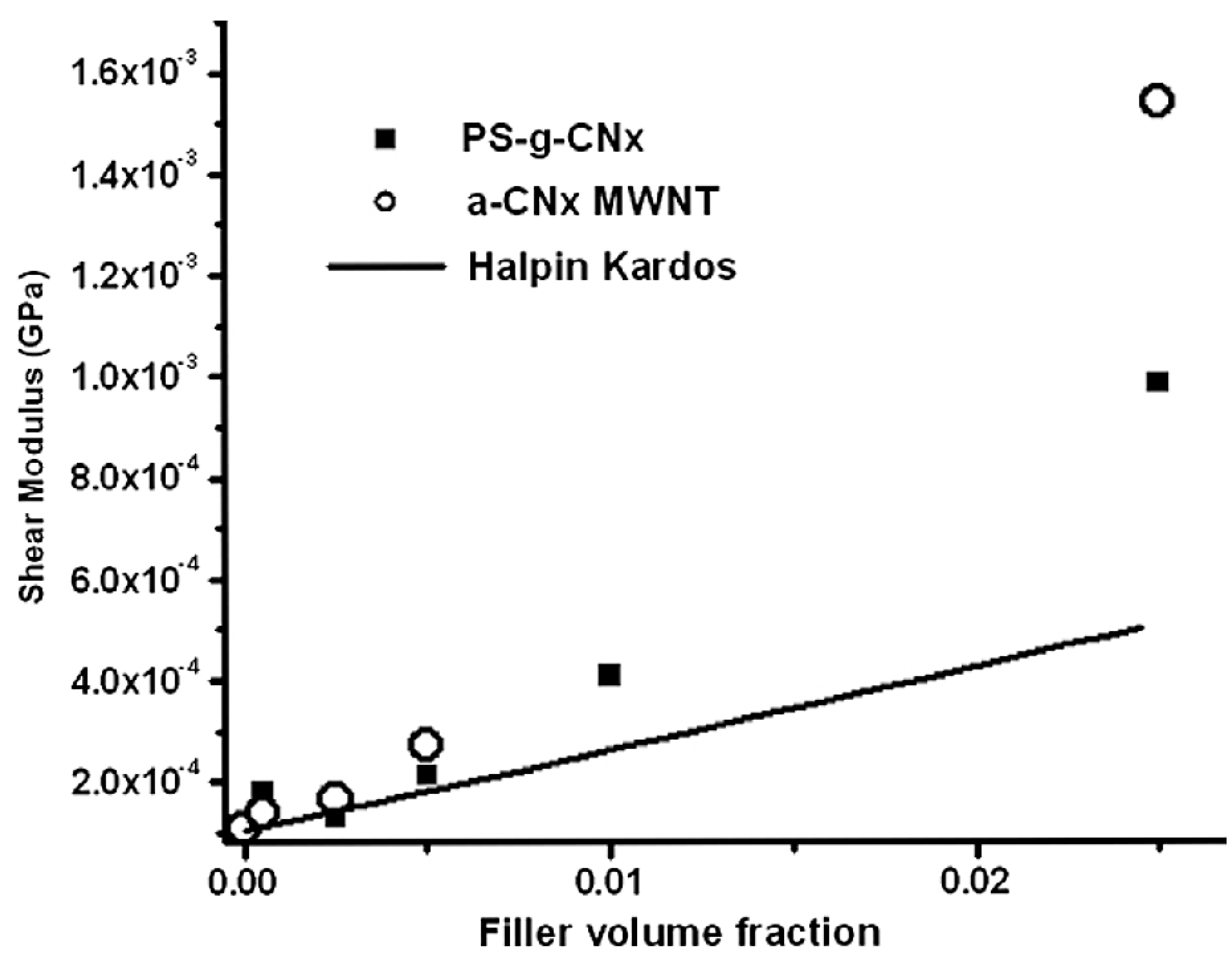
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yaqoob, S.; Ali, Z.; Ali, S.; D’Amore, A. Polystyrene–Carbon Nanotube Composites: Interaction Mechanisms, Preparation Methods, Structure, and Rheological Properties—A Review. Physchem 2025, 5, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5020014
Yaqoob S, Ali Z, Ali S, D’Amore A. Polystyrene–Carbon Nanotube Composites: Interaction Mechanisms, Preparation Methods, Structure, and Rheological Properties—A Review. Physchem. 2025; 5(2):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5020014
Chicago/Turabian StyleYaqoob, Saba, Zulfiqar Ali, Sajjad Ali, and Alberto D’Amore. 2025. "Polystyrene–Carbon Nanotube Composites: Interaction Mechanisms, Preparation Methods, Structure, and Rheological Properties—A Review" Physchem 5, no. 2: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5020014
APA StyleYaqoob, S., Ali, Z., Ali, S., & D’Amore, A. (2025). Polystyrene–Carbon Nanotube Composites: Interaction Mechanisms, Preparation Methods, Structure, and Rheological Properties—A Review. Physchem, 5(2), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/physchem5020014





