Advancing Early Detection of Breast Cancer: A User-Friendly Convolutional Neural Network Automation System
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Problem Definition and Deep Learning Model
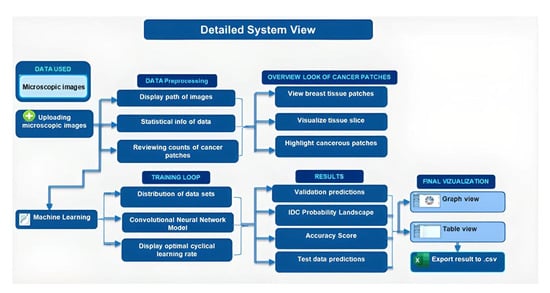
3.1. Proposed Research Methodology
3.2. Deep Learning Model
3.2.1. The Functionality and Operations of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
3.2.2. Mathematical Foundation of Conventional Neural Networks (CNNs)
- W is the size of the input volume (width and height);
- D is the depth of the input volume (number of channels);
- F is the spatial size of the kernels;
- S is the stride with which the kernels are convolved across the input volume;
- P is the amount of padding used.
- input is the flattened activation map (512 elements);
- W is the weight matrix with dimensions of (1024,512);
- B is the bias term with dimensions of (1024,1);
- activation is a non-linear function applied on the output.
3.2.3. Technical Aspects of Conventional Neural Networks (CNNs)
| Algorithm 1: Conventional Neural Networks (CNN) Model |
|
4. Experimental Evaluation
4.1. Data
4.2. Results
4.2.1. Descriptive Analysis
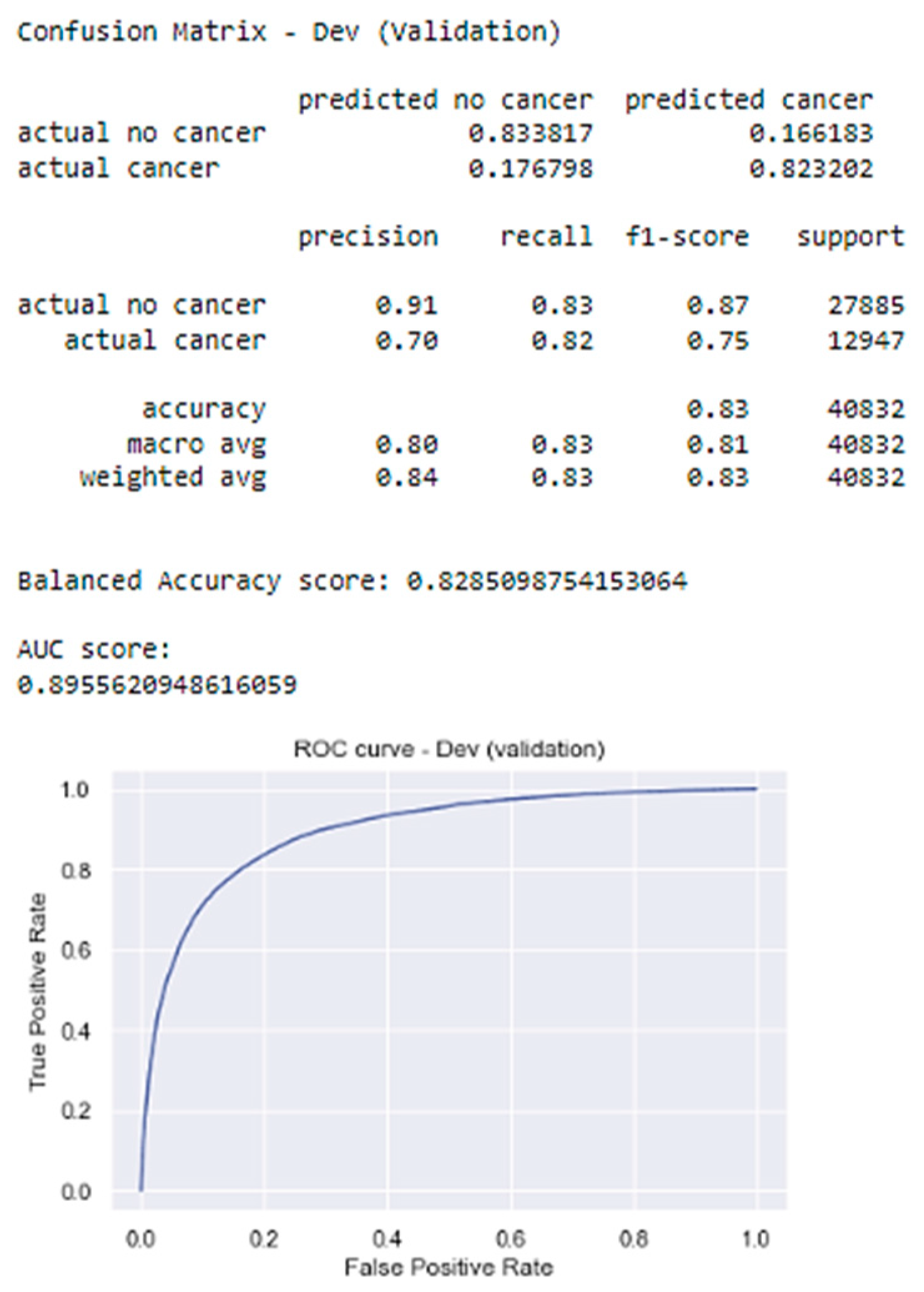
4.2.2. Model Performance
5. Limitations
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Cancer Society. Breast Cancer Facts & Figures 2021–2022. Available online: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/breast+cancer+wisconsin+(diagnostic) (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Esteva, A.; Kuprel, B.; Novoa, R.A.; Ko, J.; Swetter, S.M.; Blau, H.M.; Thrun, S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 2017, 542, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, S.M.; Sieniek, M.; Godbole, V.; Godwin, J.; Antropova, N.; Ashrafian, H.; Back, T.; Chesus, M.; Corrado, G.S.; Darzi, A.; et al. International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening. Nature 2020, 577, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Giger, M.L.; Olopade, O.I. Margins of breast cancer in mammography and whole-slide histopathology images. In Proceedings of the Signal Processing in Medicine and Biology Symposium (SPMB), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2 December 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, P. Applying XGBoost Machine Learning Tool to Digitized Images of Fine Needle Aspirates (FNA) of the Breast. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelrahman, L.; Al Ghamdi, M.; Collado-Mesa, F.; Abdel-Mottaleb, M. Convolutional neural networks for breast cancer detection in mammography: A survey. Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 131, 104248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, M.; Sharma, A. Breast cancer detection in mammogram images using fuzzy k-means clustering, c-means clustering and edge detection techniques. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2023, 181, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Pawar, S. Evaluation of different machine learning algorithms for breast cancer prediction using Wisconsin Breast Cancer Dataset. Int. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 10, 339–344. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Yang, N.; Pan, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z. Synchronous Medical Image Augmentation framework for deep learning-based image segmentation. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2023, 104, 102161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.; Wang, H.; Pu, B.; Tao, L.; Chen, J.; Philip, S.Y. A hybrid two-stage teaching-learning-based optimization algorithm for feature selection in bioinformatics. In IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Yang, N.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X. A configurable deep learning framework for medical image analysis. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 7375–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulsun, I.; Acikalin, T.; Ekici, S. Transfer learning-based breast cancer classification using pre-trained convolutional neural networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Han, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y. Attention-based convolutional neural network for breast cancer metastasis prediction on whole-slide images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2023, 166, 272–278. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S. Deep learning ensemble with data augmentation for breast cancer diagnosis on ultrasound images. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 209, 118353. [Google Scholar]
- Amira, A.; Mahmood, A.; Ali, E.M. Generative Adversarial Networks for data augmentation in breast cancer detection. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 144, 105320. [Google Scholar]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.A.W.M.; van Ginneken, B.; Sánchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Nat. Methods 2016, 14, 863–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, N.; Huynh, V.; Nguyen, V.; Pham, T.; Nam, H. A review on deep learning methods for breast cancer detection. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2297. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Shen, L.; Zhou, X.; Yang, J.; Feng, Y. Explainable deep learning for breast cancer diagnosis. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 12–18 July 2020; pp. 11741–11751. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Roa, A.; Basavanhally, A.; González, F.; Gilmore, H.; Feldman, M.; Ganesan, S.; Shih, N.; Tomaszewski, J.; Madabhushi, A. Automatic detection of invasive ductal carcinoma in whole-slide images with convolutional neural networks. In Medical Imaging 2014: Digital Pathology; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9041, p. 904103. [Google Scholar]
- Zotin, A.; Simonov, K.; Kurako, M.; Hamad, Y.; Kirillova, S. Edge detection in MRI brain tumor images based on fuzzy C-means clustering. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2018, 126, 1261–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakradeo, K.; Vyawahare, S.; Pawar, P. Breast cancer recurrence prediction using machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Information and Communication Technology, Allahabad, India, 6–8 December 2019; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]


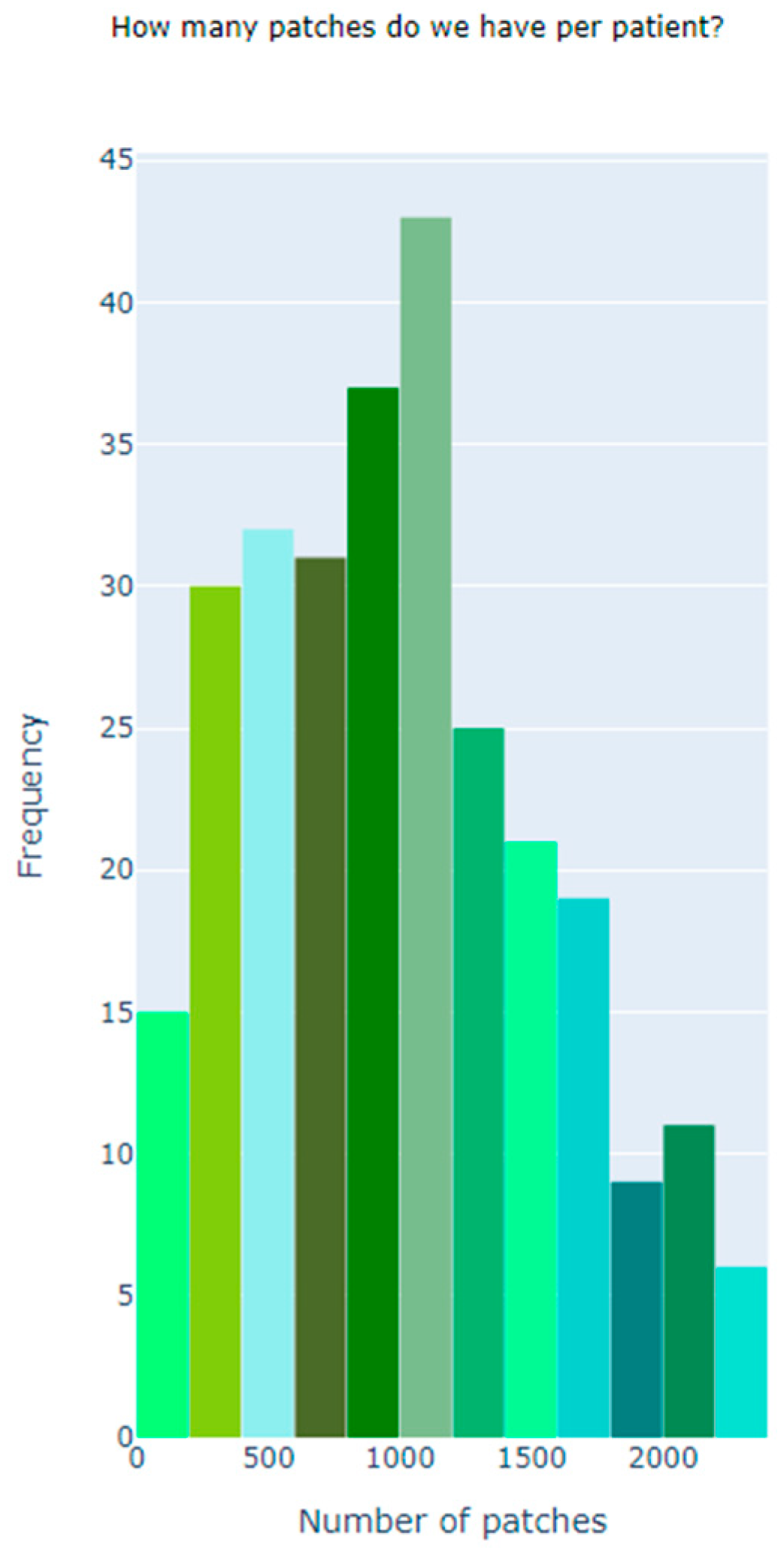
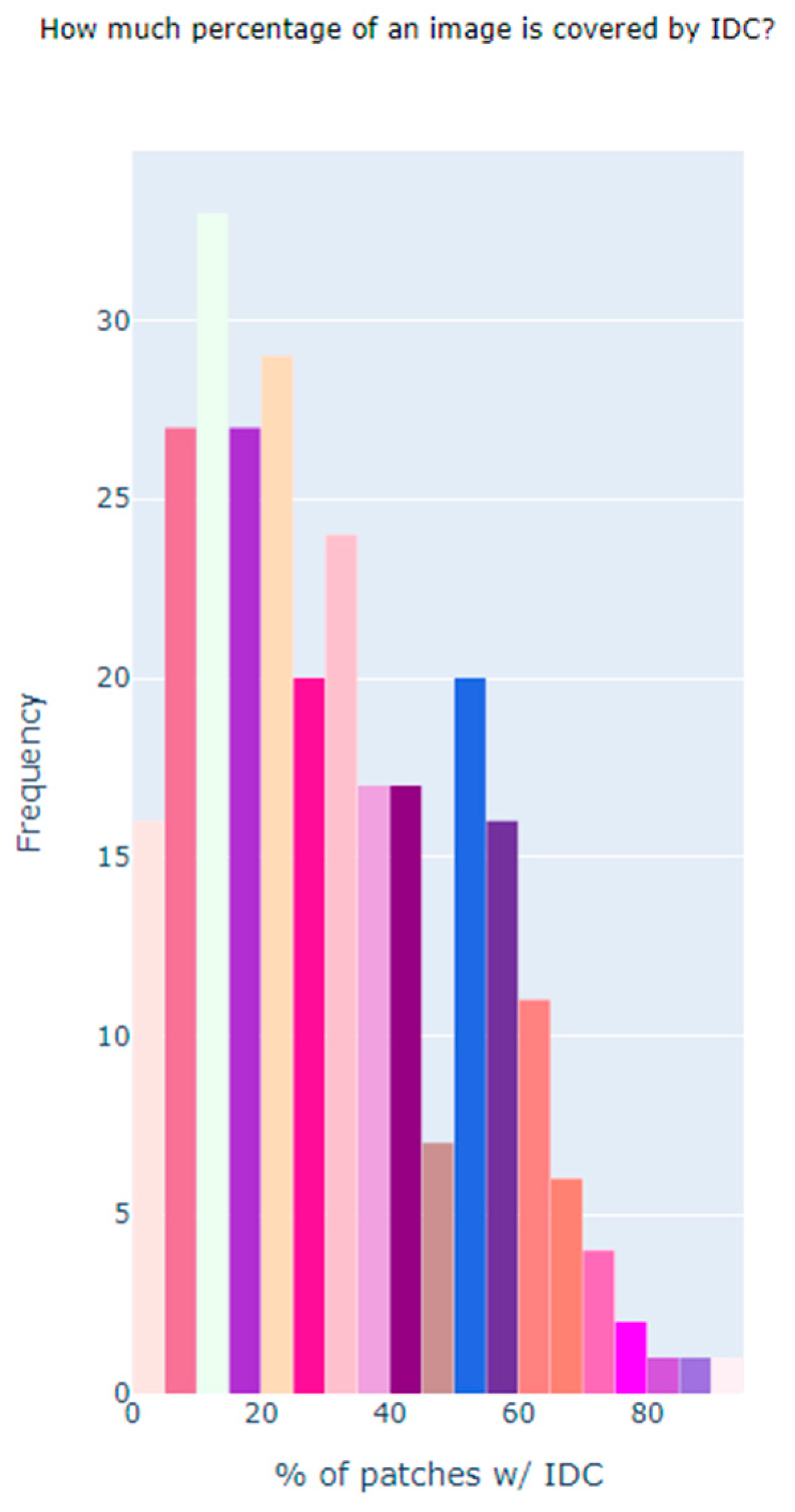
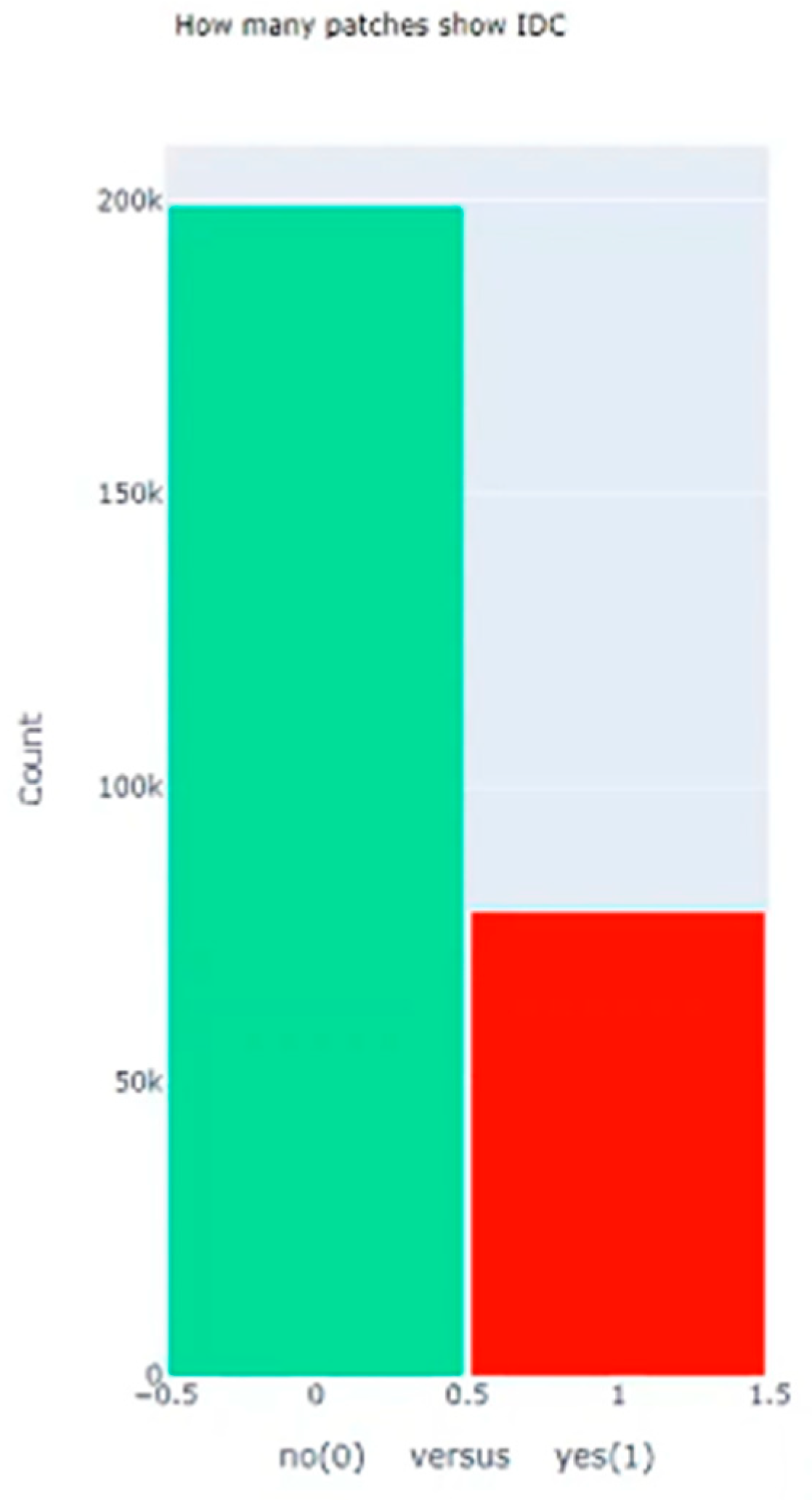

| Dataset | Size |
|---|---|
| Size of the data | Roughly 4.14 GB |
| Total Number of Images | 277,524 |
| Total Number of Features | 512 |
| Total Number of Patient | 162 |
| Total Number of Images without Cancer | 198,738 |
| Total Number of Images with Cancer | 78,786 |
| Total Number of Images in Training data | 210,602 |
| Total Number of Images in Testing data | 33,013 |
| Total Number of Images in Developing data | 33,909 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dequit, A.; Nafa, F. Advancing Early Detection of Breast Cancer: A User-Friendly Convolutional Neural Network Automation System. BioMedInformatics 2024, 4, 992-1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4020055
Dequit A, Nafa F. Advancing Early Detection of Breast Cancer: A User-Friendly Convolutional Neural Network Automation System. BioMedInformatics. 2024; 4(2):992-1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4020055
Chicago/Turabian StyleDequit, Annie, and Fatema Nafa. 2024. "Advancing Early Detection of Breast Cancer: A User-Friendly Convolutional Neural Network Automation System" BioMedInformatics 4, no. 2: 992-1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4020055
APA StyleDequit, A., & Nafa, F. (2024). Advancing Early Detection of Breast Cancer: A User-Friendly Convolutional Neural Network Automation System. BioMedInformatics, 4(2), 992-1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4020055