Using Large Language Models for Microbiome Findings Reports in Laboratory Diagnostics
Abstract
1. Introduction, Motivation, Problem Statement, Research Question, and Approach
2. State of the Art in Science and Technology
2.1. Metagenomic Data Analysis in Laboratory Diagnostics
2.2. Bioinformatics and Diagnostics Platforms
2.3. AI Methods
2.4. Regulatory Landscape and Responsible AI
3. Design and Conceptual Modeling
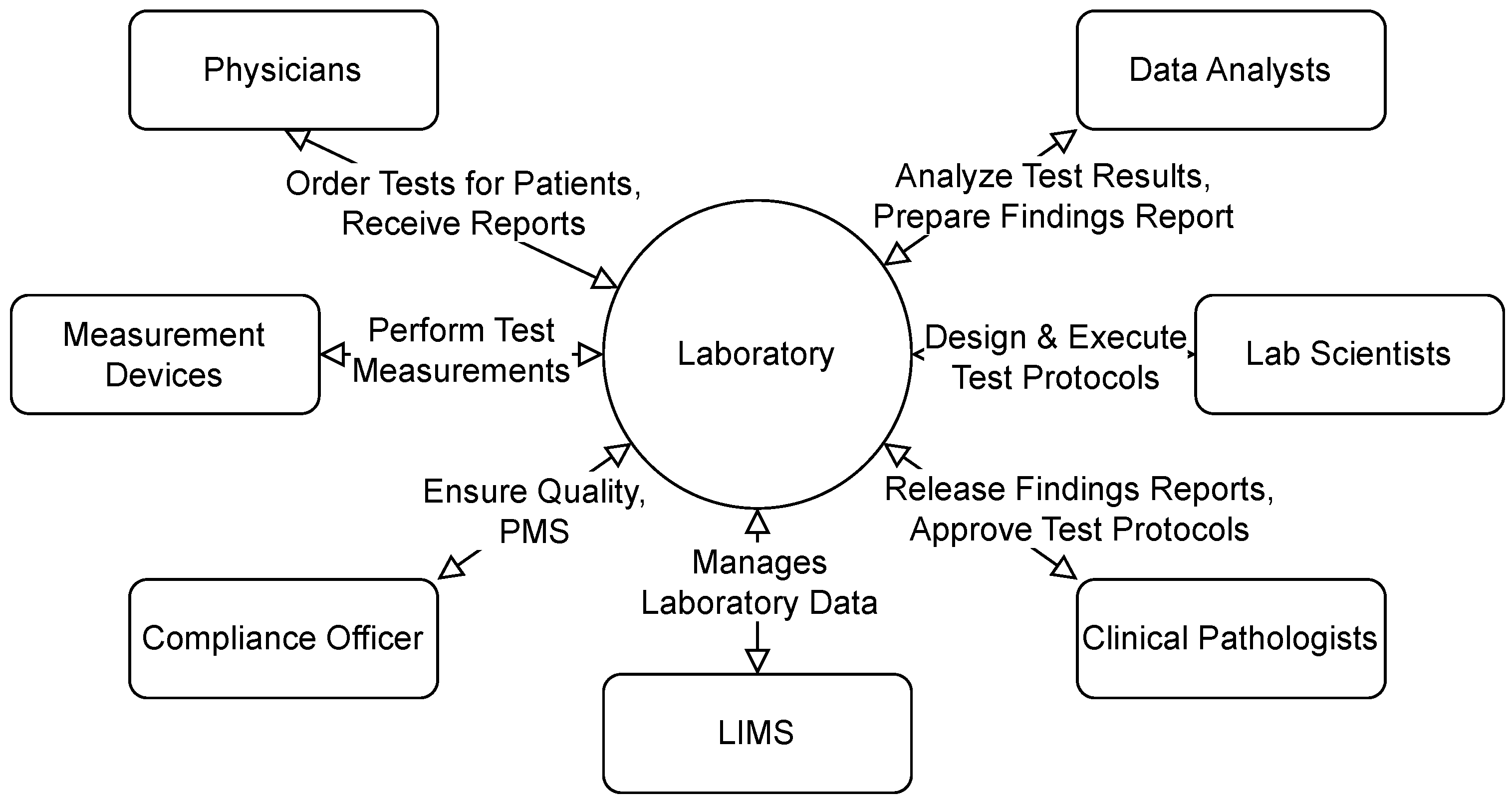
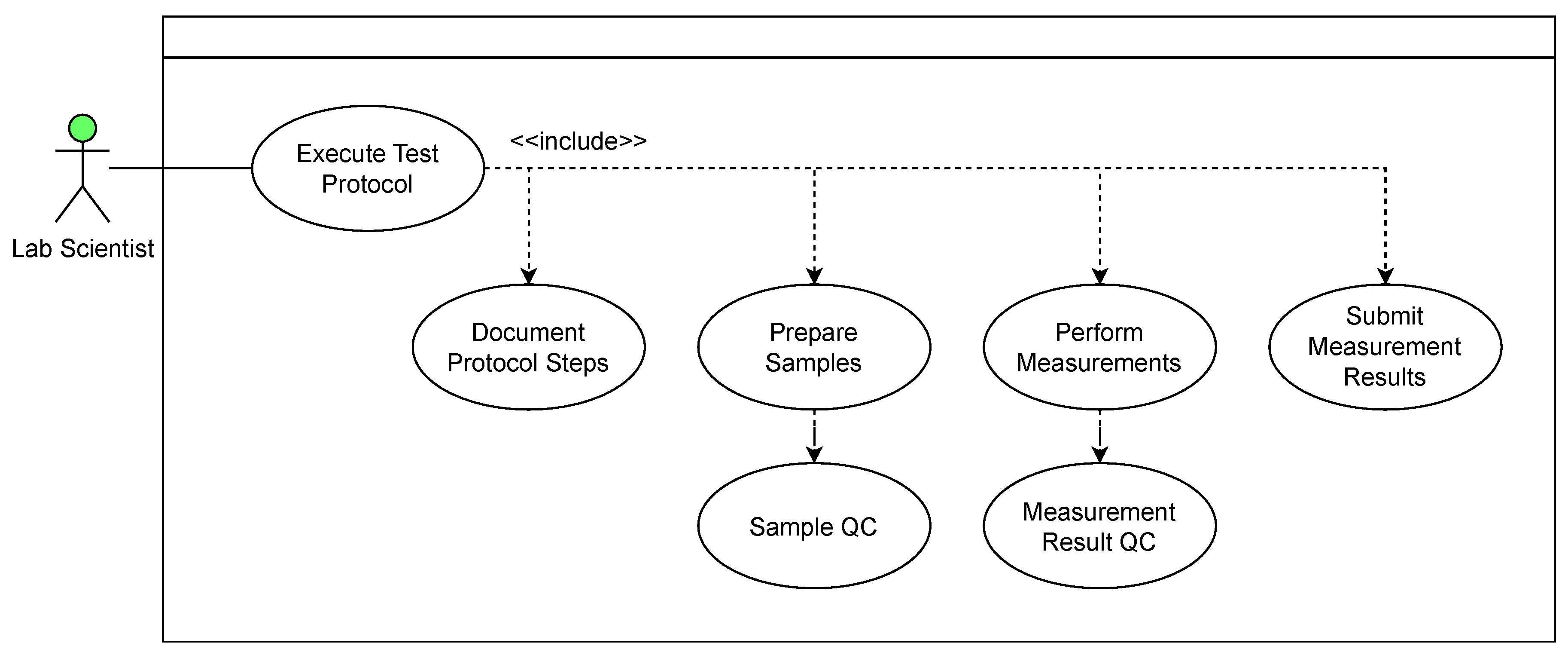
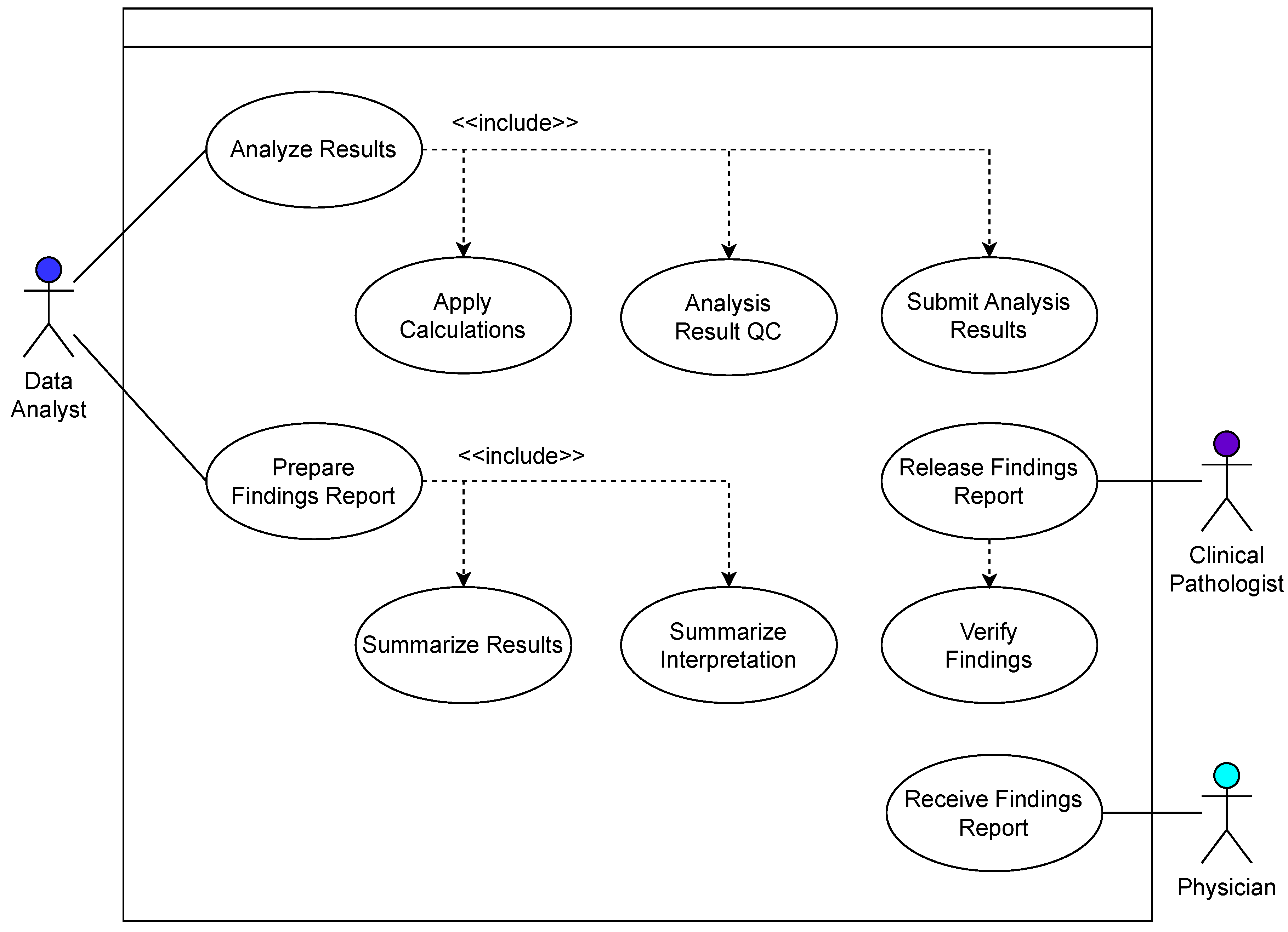
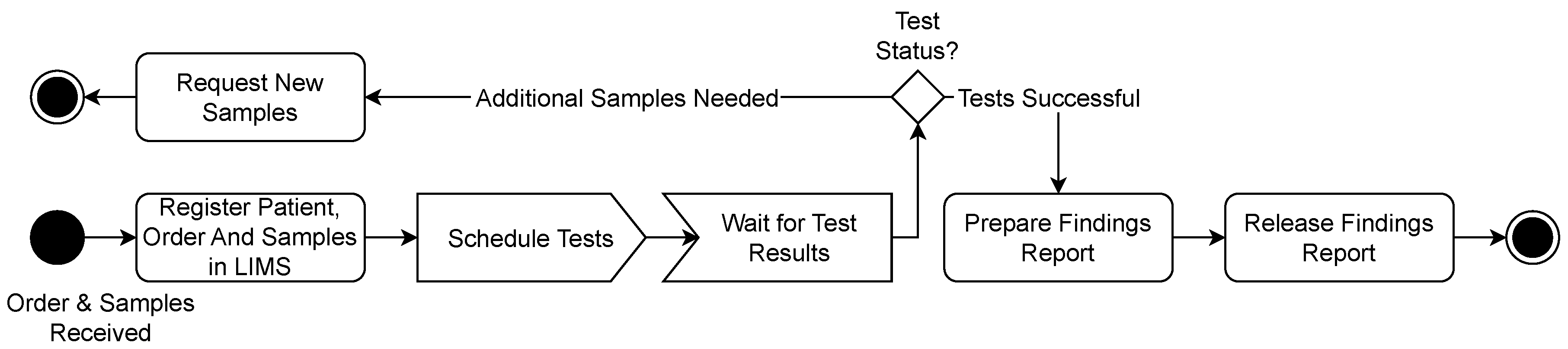
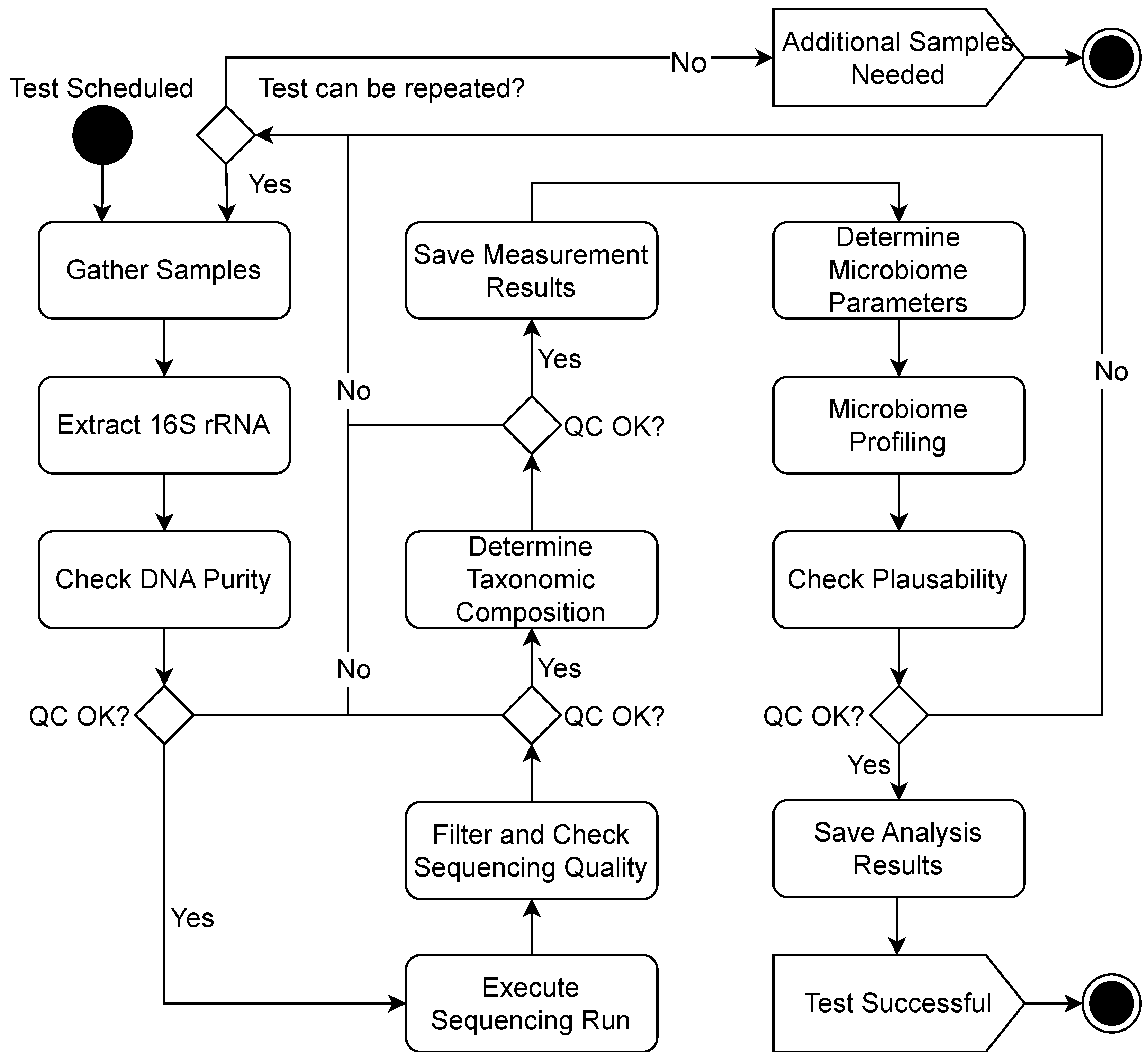
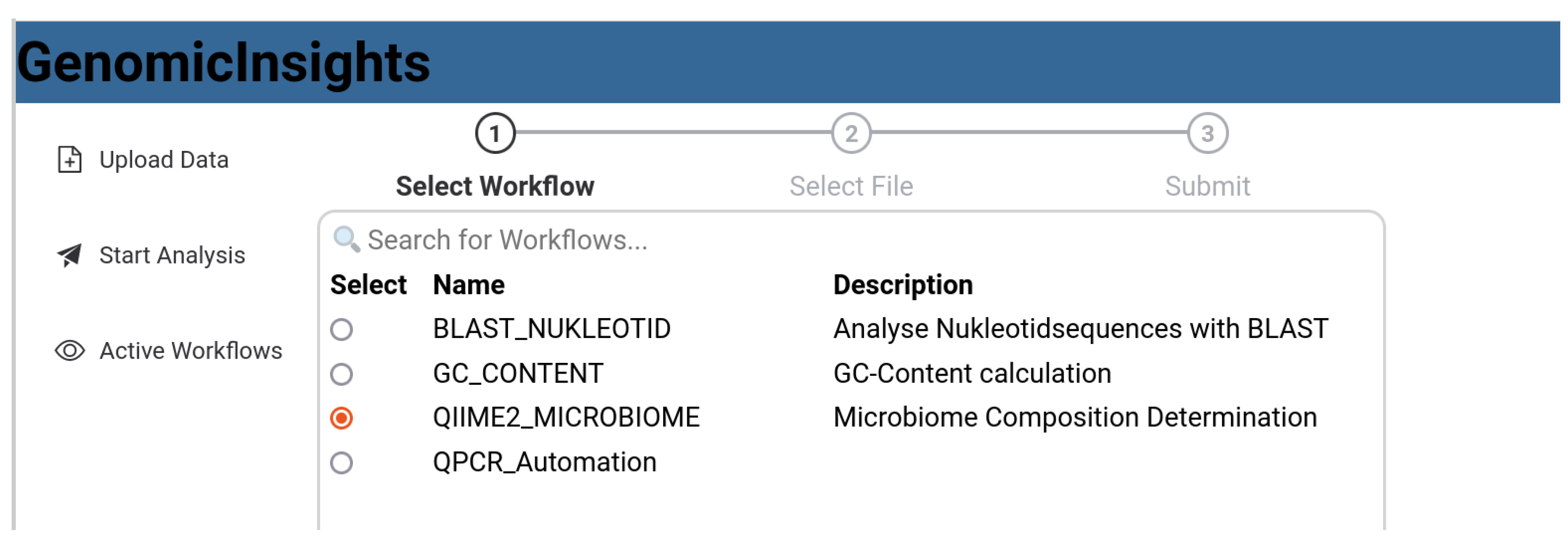
3.1. Use Cases
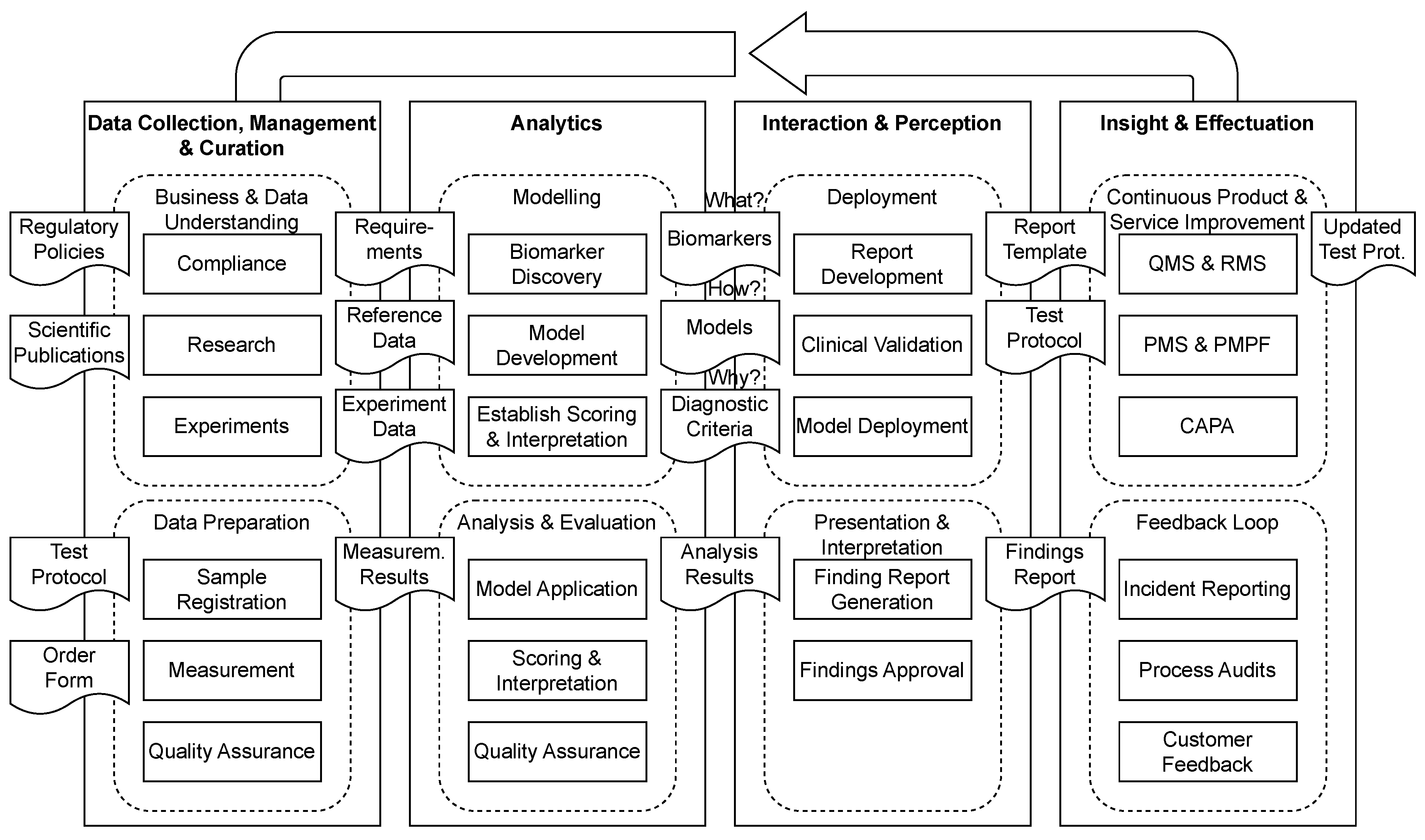
3.2. Conceptual Model
3.3. AI Integration
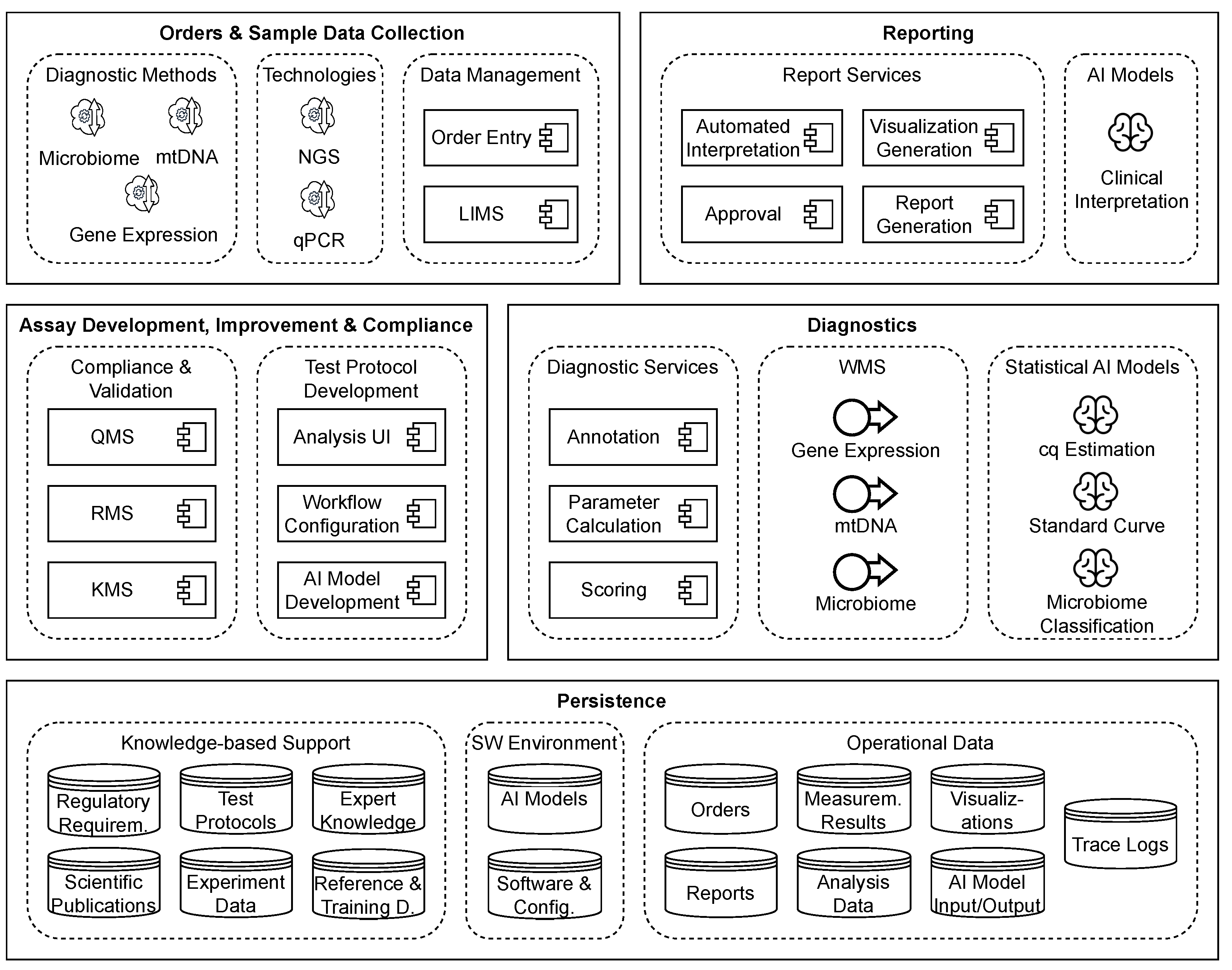
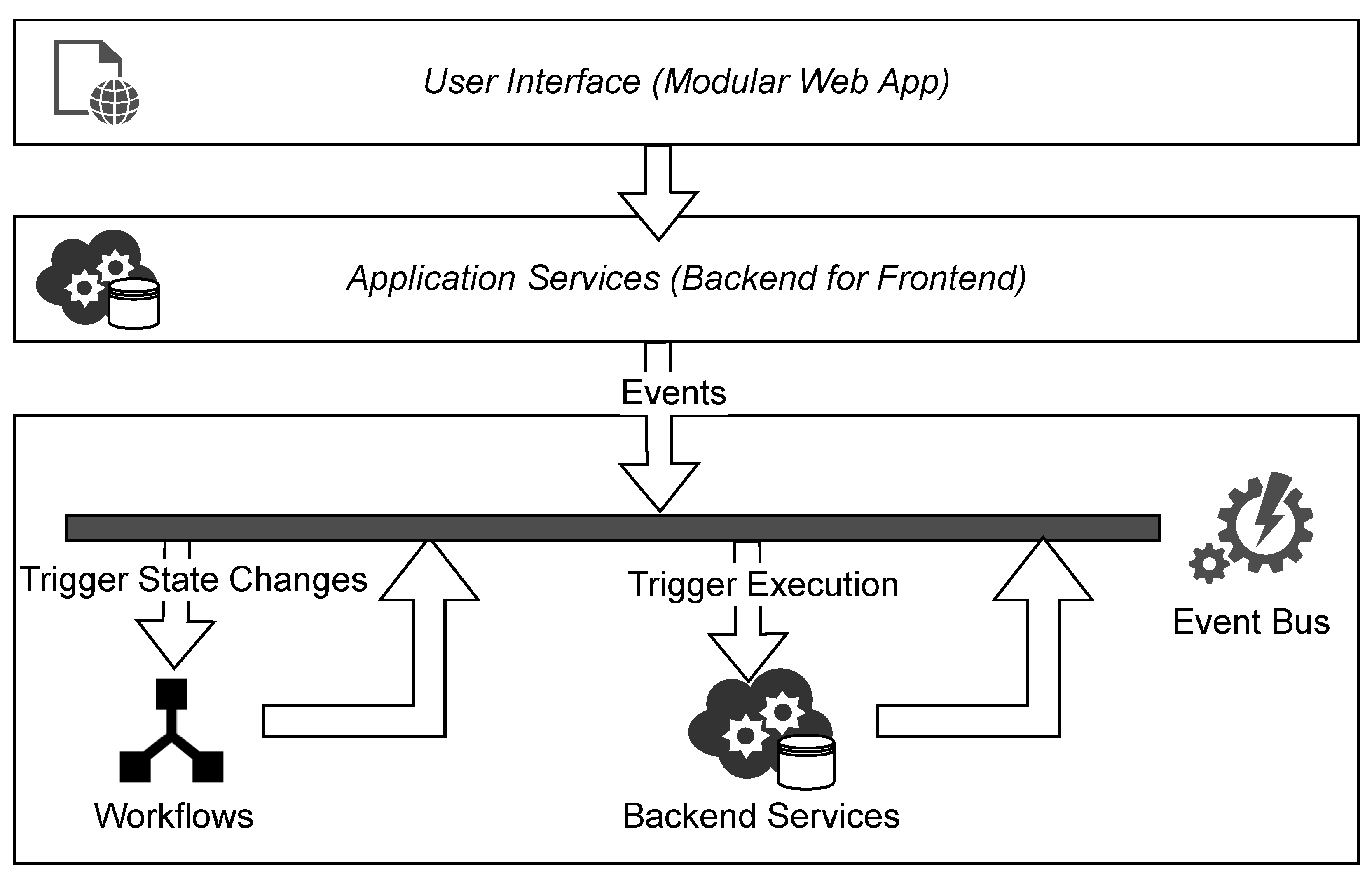
3.4. Conceptual Architecture
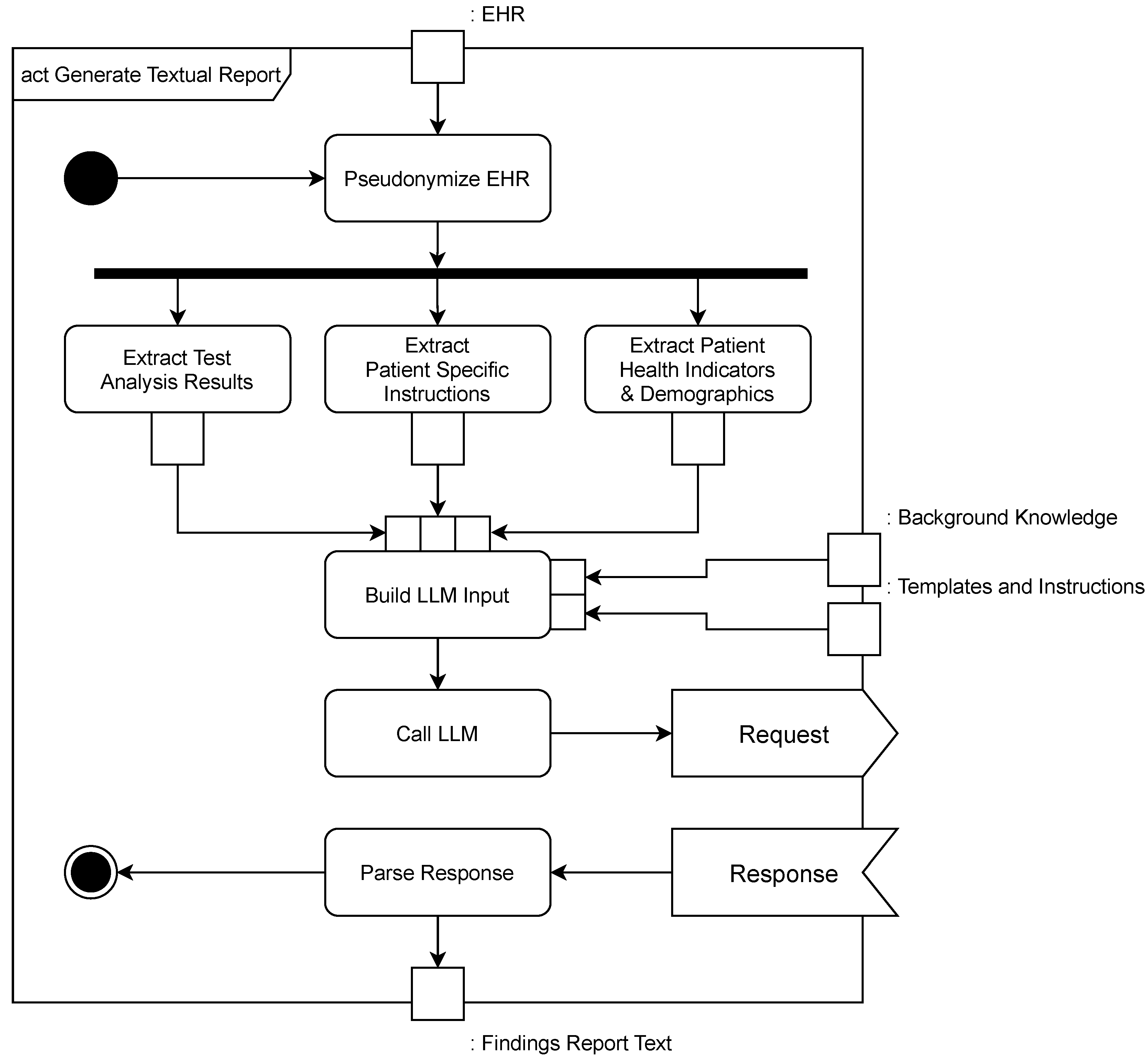
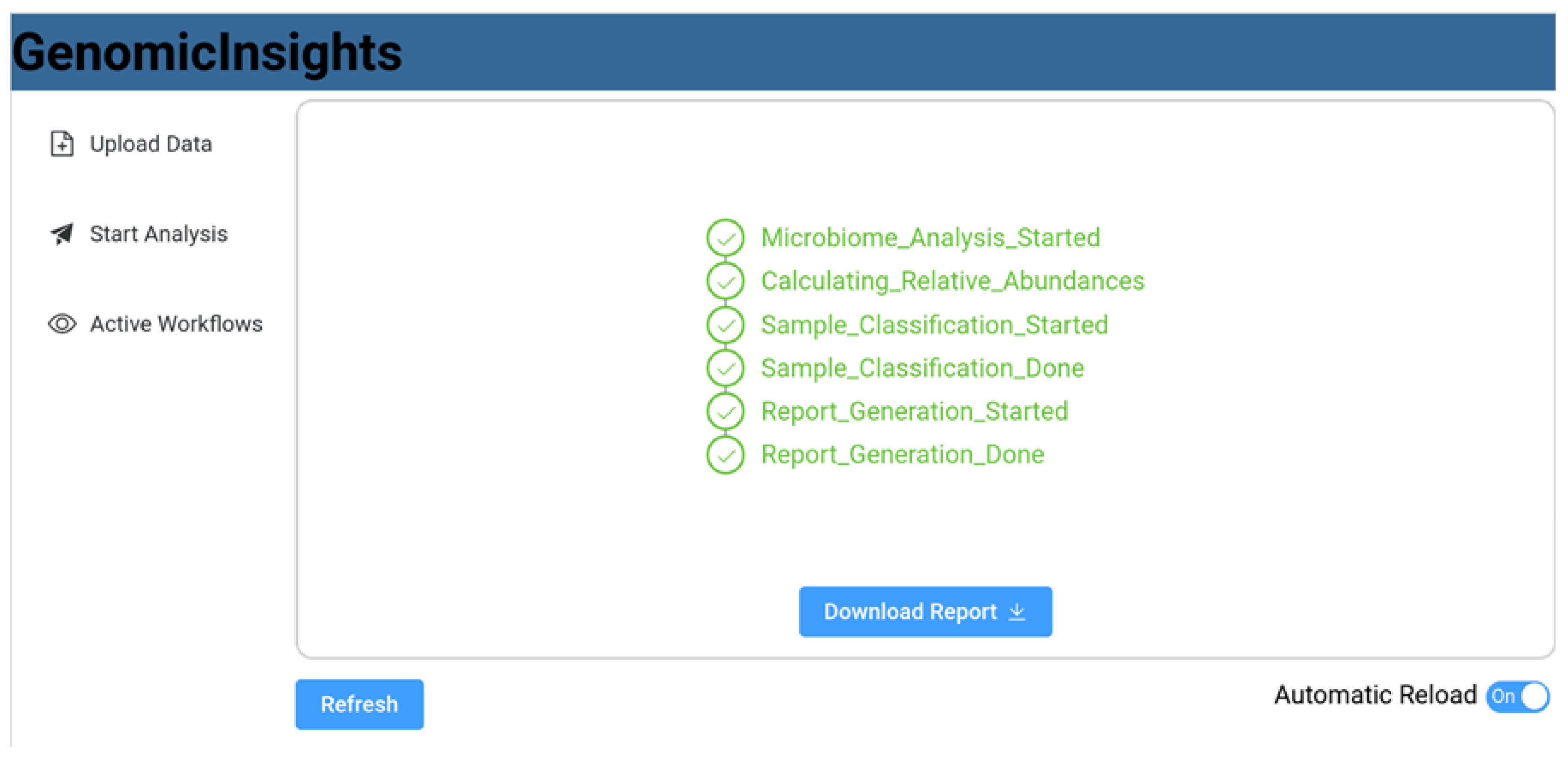
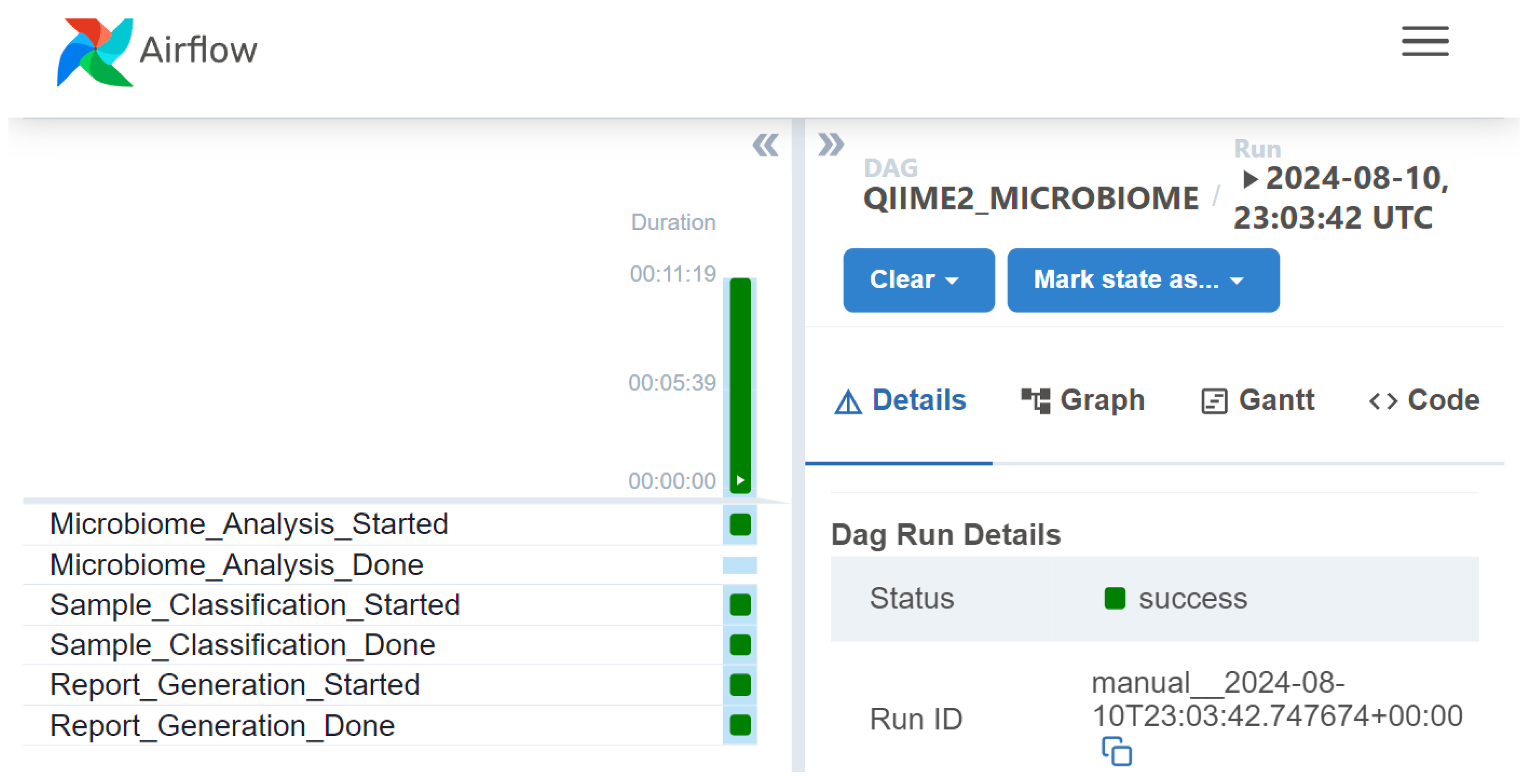
4. Implementation
| Listing 1. MicroFlow Prompt Template (Translated). |
|
5. Evaluation
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogunrinola, G.A.; Oyewale, J.O.; Oshamika, O.O.; Olasehinde, G.I. The Human Microbiome and Its Impacts on Health. Int. J. Microbiol. 2020, 2020, 8045646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, T.; Jolkver, E.; Mc Kevitt, P.; Kramer, M.; Hemmje, M. A Systematic Approach to Diagnostic Laboratory Software Requirements Analysis. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, T.; Jolkver, E.; Bruchhaus, S.; Kramer, M.; Hemmje, M. GenDAI—AI-Assisted Laboratory Diagnostics for Genomic Applications. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM), Houston, TX, USA, 9–12 December 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, T.; Glau, L.; Jolkver, E.; Leonardi-Essmann, F.; Mc Kevitt, P.; Kramer, M.; Hemmje, M. Design and Development of a qPCR-based Mitochondrial Analysis Workflow for Medical Laboratories. BioMedInformatics 2022, 2, 643–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nori, H.; King, N.; McKinney, S.M.; Carignan, D.; Horvitz, E. Capabilities of GPT-4 on Medical Challenge Problems. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.13375. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wright, A.P.; Patterson, B.L.; Wanderer, J.P.; Turer, R.W.; Nelson, S.D.; McCoy, A.B.; Sittig, D.F.; Wright, A. Assessing the Value of ChatGPT for Clinical Decision Support Optimization. medRxiv 2023, 2023.02.21.23286254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunamaker, J.F.; Chen, M.; Purdin, T.D. Systems Development in Information Systems Research. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 1990, 7, 89–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-García, C.; Bargiela, R.; Martínez-Martínez, M.; Ferrer, M. Metagenomic Protocols and Strategies. In Metagenomics; Nagarajan, M., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 15–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, K.G.; Olsen, G.J.; Lane, D.J.; Giovannoni, S.J.; Ghiselin, M.T.; Raff, E.C.; Pace, N.R.; Raff, R.A. Molecular phylogeny of the animal kingdom. Science 1988, 239, 748–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarello, M.; McCauley, M.; Villéger, S.; Jackson, C.R. Ranking the biases: The choice of OTUs vs. ASVs in 16S rRNA amplicon data analysis has stronger effects on diversity measures than rarefaction and OTU identity threshold. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Gregory Caporaso, J. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, T.; Zickfeld, M.; Bruchhaus, S.; Reis, T.; Bornschlegl, M.X.; Buono, P.; Kramer, M.; Mc Kevitt, P.; Hemmje, M. An Event-Driven Architecture for Genomics-Based Diagnostic Data Processing. Appl. Biosci. 2023, 2, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balvočiūtė, M.; Huson, D.H. SILVA, RDP, Greengenes, NCBI and OTT—How do these taxonomies compare? BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolkver, E. Verarbeitung von RT-qPCR Daten in der Labordiagnostik. Bachelor’s Thesis, FernUniversität Hagen, Hagen, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Glau, L. Validation of qPCR Data in the Field of Medical Diagnostics; University Project; FernUniversität Hagen: Hagen, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Glau, L. Development of a System for Automated Microbiome Analysis and Subsequent LLM-Supported Report Generation in the Field of Medical Diagnostics. Master’s Thesis, FernUniversität Hagen, Hagen, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, T.; Andrade, B.G.N.; Afli, H.; Wang, H.; Zheng, H.; Hemmje, M. Understanding the Role of (Advanced) Machine Learning in Metagenomic Workflows. In Proceedings of the Advanced Visual Interfaces, Ischia, Italy, 9 June and 29 September 2020; Reis, T., Bornschlegl, M.X., Angelini, M., Hemmje, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 56–82. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, B.; Galley, M.; He, P.; Cheng, H.; Xie, Y.; Hu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liden, L.; Yu, Z.; Chen, W.; et al. Check Your Facts and Try Again: Improving Large Language Models with External Knowledge and Automated Feedback. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.12813v3. [Google Scholar]
- Bubeck, S.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Eldan, R.; Gehrke, J.; Horvitz, E.; Kamar, E.; Lee, P.; Lee, Y.T.; Li, Y.; Lundberg, S.; et al. Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.12712v5. [Google Scholar]
- McDuff, D.; Schaekermann, M.; Tu, T.; Palepu, A.; Wang, A.; Garrison, J.; Singhal, K.; Sharma, Y.; Azizi, S.; Kulkarni, K.; et al. Towards Accurate Differential Diagnosis with Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00164v1. [Google Scholar]
- Truhn, D.; Weber, C.D.; Braun, B.J.; Bressem, K.; Kather, J.N.; Kuhl, C.; Nebelung, S. A pilot study on the efficacy of GPT-4 in providing orthopedic treatment recommendations from MRI reports. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.Y.; Miao, B.Y.; Butte, A.J. Evaluating the use of GPT-3.5-turbo to provide clinical recommendations in the Emergency Department. medRxiv 2023, 2023.10.19.23297276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buiten, M.C. Towards Intelligent Regulation of Artificial Intelligence. Eur. J. Risk Regul. 2019, 10, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smuha, N.A. From a ‘race to AI’ to a ‘race to AI regulation’: Regulatory competition for artificial intelligence. Law Innov. Technol. 2021, 13, 57–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High-Level Expert Group on AI. Ethics Guidelines for Trustworthy AI; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High-Level Expert Group on AI. Assessment List for Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence (ALTAI); Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- High-Level Expert Group on AI. Sectoral Considerations on Policy and Investment Recommendations for Trustworthy AI; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, L. The EU AI Act: A Summary of Its Significance and Scope; Ada Lovelace Institute: London, UK, 2022; Available online: https://www.adalovelaceinstitute.org/resource/eu-ai-act-explainer/ (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Gillespie, N.; Lockey, S.; Curtis, C.; Pool, J.; Akbari, A. Trust in Artificial Intelligence: A Global Study; The University of Queensland: Brisbane, Australia; KPMG: Sydney, Australia, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornschlegl, M.X. Towards Trustworthiness in AI-Based Big Data Analysis; FernUniversität Hagen: Hagen, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation; Official Journal of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, T.; Wassan, J.T.; Mc Kevitt, P.; Wang, H.; Zheng, H.; Hemmje, M. Analyzing Large Microbiome Datasets Using Machine Learning and Big Data. BioMedInformatics 2021, 1, 138–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plevkova, J.; Brozmanova, M.; Harsanyiova, J.; Sterusky, M.; Honetschlager, J.; Buday, T. Various aspects of sex and gender bias in biomedical research. Physiol. Res. 2020, 69, S367–S378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, D.A.; Draper, S.W. (Eds.) User Centered System Design; Erlbaum: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI; Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; Almeida, D.; Altenschmidt, J.; Altman, S.; et al. GPT-4 Technical Report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 14971:2019; Medical Devices—Application of Risk Management to Medical Devices. ISO International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- ISO 22367:2020; Medical Laboratories—Application of Risk management to Medical Laboratories. ISO International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.
- Krause, T.; Zickfeld, M.; Müller, K.; Glau, L. GenomicInsights GitHub Repository. Available online: https://github.com/aKzenT/GenomicInsights (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Krause, T.; Jolkver, E.; Kramer, M.; Mc Kevitt, P.; Hemmje, M. A Scalable Architecture for Smart Genomic Data Analysis in Medical Laboratories. In Applied Data Science; Blum, L., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Soulter. HuggingChat Python API GitHub Repository. Available online: https://github.com/Soulter/hugging-chat-api (accessed on 20 August 2024).
- Mahatody, T.; Sagar, M.; Kolski, C. State of the Art on the Cognitive Walkthrough Method, Its Variants and Evolutions. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2010, 26, 741–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutylowski, J. DeepL. Available online: https://www.deepl.com/ (accessed on 20 August 2024).

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krause, T.; Glau, L.; Newels, P.; Reis, T.; Bornschlegl, M.X.; Kramer, M.; Hemmje, M.L. Using Large Language Models for Microbiome Findings Reports in Laboratory Diagnostics. BioMedInformatics 2024, 4, 1979-2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4030108
Krause T, Glau L, Newels P, Reis T, Bornschlegl MX, Kramer M, Hemmje ML. Using Large Language Models for Microbiome Findings Reports in Laboratory Diagnostics. BioMedInformatics. 2024; 4(3):1979-2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4030108
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrause, Thomas, Laura Glau, Patrick Newels, Thoralf Reis, Marco X. Bornschlegl, Michael Kramer, and Matthias L. Hemmje. 2024. "Using Large Language Models for Microbiome Findings Reports in Laboratory Diagnostics" BioMedInformatics 4, no. 3: 1979-2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4030108
APA StyleKrause, T., Glau, L., Newels, P., Reis, T., Bornschlegl, M. X., Kramer, M., & Hemmje, M. L. (2024). Using Large Language Models for Microbiome Findings Reports in Laboratory Diagnostics. BioMedInformatics, 4(3), 1979-2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedinformatics4030108





