Painful Legs and Moving Toes
Definition
:1. History
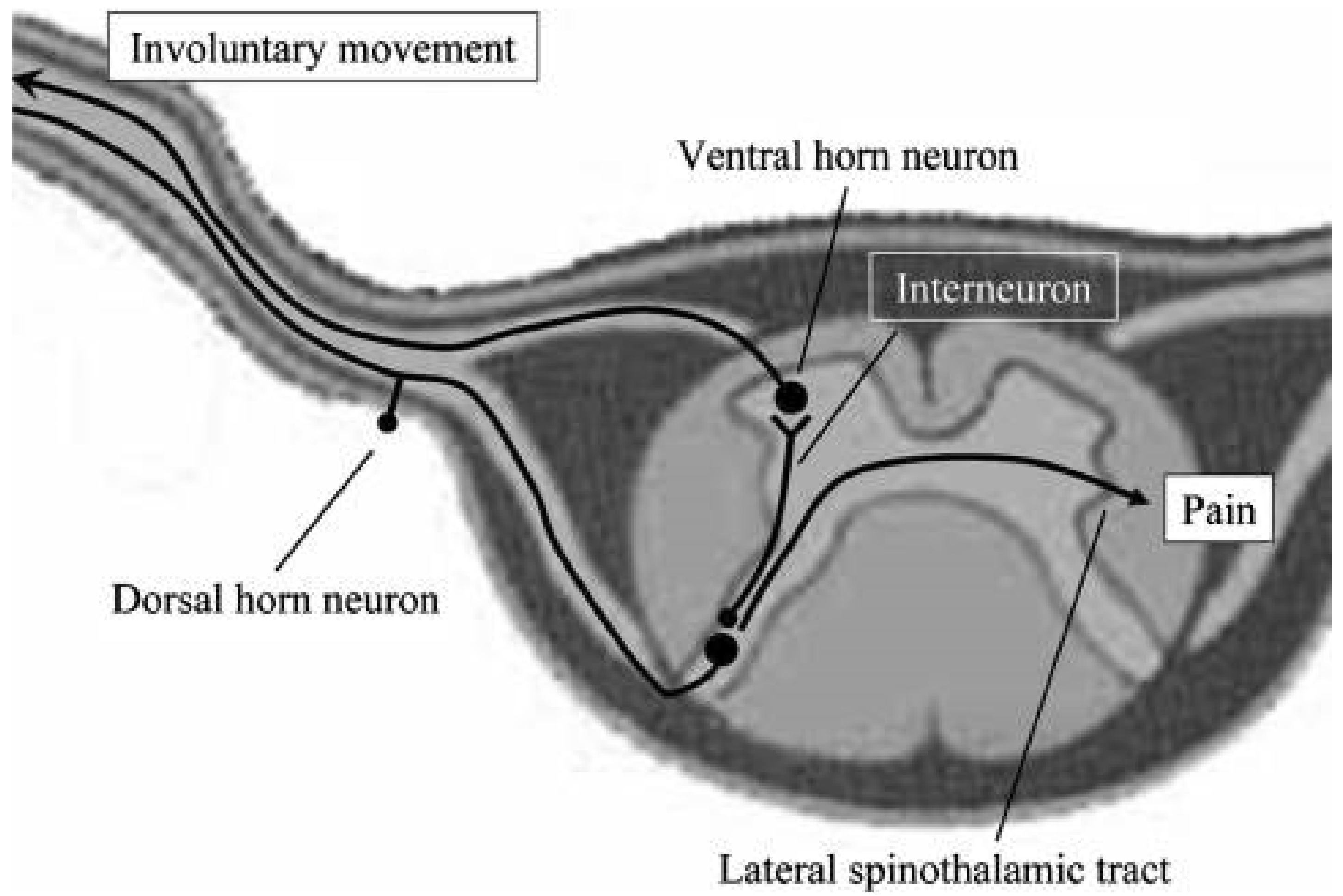
2. Etiology of PLMT
3. Diagnostics of PLMT
3.1. Medical History of Possible Pathological Conditions of PLMT
3.2. Clinical and Neurophysiological Diagnostics
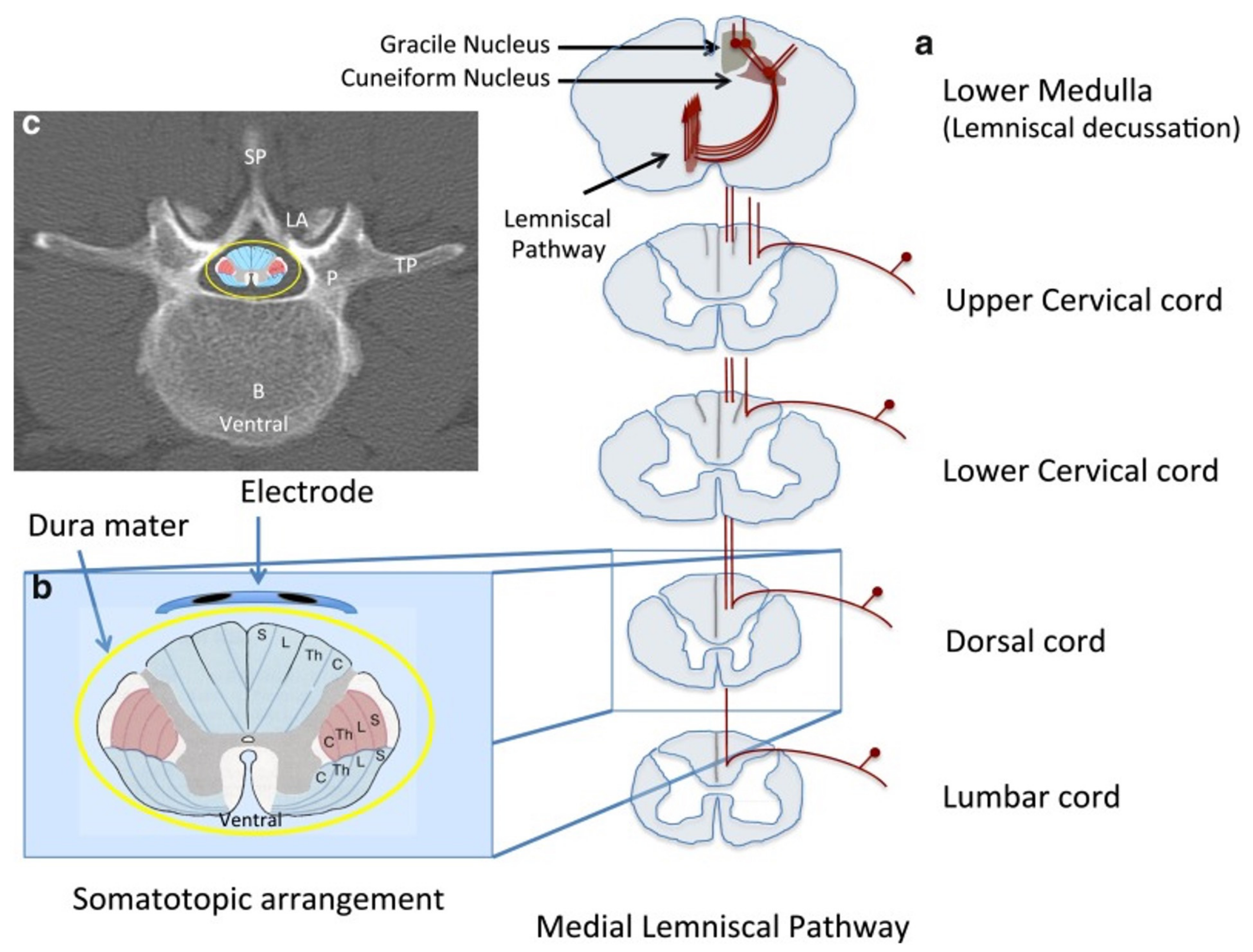
3.3. Neurophysiological Examination
- -
- the first type with short duration (10–80 ms) and a higher frequency of 4–6 Hz
- -
- the second type with longer duration (160–500 ms) and lower frequency of 1.5–3 Hz.
3.4. Differential Diagnoses
- -
- Restless leg syndrome with pain and movement of feet and legs;
- -
- Painful radiculopathy or plexopathy;
- -
- Complex regional pain syndrome;
- -
- Akathisia with leg movements;
- -
- Cramps with unilateral involuntary muscle hardening, usually calf muscle;
- -
- Spinal segmental myoclonus with leg movement;
- -
- EPC with continuous toes/foot or leg movement;
- -
- Focal or polyneuropathy with feet numbness, tingling, and/or pain;
- -
- Dystonia with sustained involuntary movements of feet and legs;
- -
- Periodic-limb-movement disorder (PLMD);
- -
- Parkinson with tremor;
- -
- Chorea;
- -
- Pseudoathetosis;
- -
- Epilepsia partialis continua with toes/foot movements; and
- -
- Psychogenic movement disorder.
4. Management of PLMT
4.1. Pharmacological Therapy
4.1.1. Oral Medication
4.1.2. Interventions
4.2. Nonpharmacological Therapeutic Interventions
4.3. Other Surgical Treatments
5. Conclusions and Prospects
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Entry Link on the Encyclopedia Platform
References
- Termsarasab, P.; Thammongkolchai, T.; Frucht, S.J. Spinal-generated movement disorders: A clinical review. J. Clin. Mov. Disord. 2015, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillane, J.D.; Nathan, P.W.; Kelly, R.E.; Marsden, C.D. Painful legs and moving toes. Brain 1971, 94, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, F.H.; Liu, W.; Geigel, E.; Castaneda, S.; Rossi, E.M.; Schnacky, K. Painful legs and moving toes syndrome responsive to pregabalin. J. Postgrad. Med. 2015, 61, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, S.; Takegami, T.; Mano, T. Peculiar involuntary movement of the toes associated with discomfort of the foot, a case of so-called “painful legs and moving toes”. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 1974, 14, 829–834. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nathan, P.W. Painful legs and moving toes: Evidence on the site of the lesion. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1978, 41, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schott, G.D. Painful legs and moving toes: The role of trauma. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1981, 44, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, W.I.; Horstink, M.W.; Notermans, S.L. Painful arm and moving fingers. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1985, 48, 384–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funakawa, I.; Mano, Y.; Takayanagi, T. Painful hand and moving fingers. A case report. J. Neurol. 1987, 234, 342–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walters, A.S.; Hening, W.A.; Shah, S.K.; Chokroverty, S. Painless legs and moving toes: A syndrome related to painful legs and moving toes? Mov. Disord. 1993, 8, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressler, D.; Thompson, P.D.; Gledhill, R.F.; Marsden, C.D. The syndrome of painful legs and moving toes. Mov. Disord. 1994, 9, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supiot, F.; Gazagnes, M.D.; Blecic, S.A.; Zegers de Beyl, D. Painful arm and moving fingers: Clinical features of four new cases. Mov. Disord. 2002, 17, 616–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papapetropoulos, S.; Singer, C. Painless legs moving toes in a patient with Wilson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2006, 21, 579–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, A.; Mateen, F.J.; Coon, E.A.; Ahlskog, J.E. Painful legs and moving toes syndrome: A 76-patient case series. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 1032–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.Y.; Xu, Y.; Gao, X.G. Spontaneous aching pain and peculiar involuntary movements: A case report of painful legs and moving toes and review of the literature. Case Rep. Med. 2014, 2014, 581402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, S.G. Painful legs and moving toes. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2011, 100, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebersbach, G.; Schelosky, L.; Schenkel, A.; Scholz, U.; Poewe, W. Unilateral painful legs and moving toes syndrome with moving fingers--evidence for distinct oscillators. Mov. Disord. 1998, 13, 965–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosek, A.; Rabey, J.M.; Kushnir, M.; Korczyn, A.D. Painful calf, moving foot. Mov. Disord. 1996, 11, 339–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziewas, R.; Kuhlenbäumer, G.; Okegwo, A.; Lüdemann, P. Painless legs and moving toes in a mother and her daughter. Mov. Disord. 2003, 18, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, C.; Papapetropoulos, S. A case of painless arms/moving fingers responsive to botulinum toxin a injections. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2007, 13, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrawashdeh, O. Painless legs and moving toes syndrome associated with a sacral Tarlov cyst: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2016, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermejo, P.E.; Zabala, J.A. Painless legs and moving toes” syndrome due to spinal cord compression. Eur. Spine J. 2008, 17 (Suppl. S2), S294–S295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwingenschuh, P.; Bhatia, K.P. Painful moving tongue in a patient with the painful legs moving toes syndrome. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 1324–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, J.; Santos, L.; Bugalho, P. Painful legs and moving toes syndrome associated with Hashimoto’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2007, 14, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renard, D.; Taieb, G.; Castelnovo, G.; Labauge, P. Teaching Video NeuroImages: Painful legs, moving toes associated with partial transverse myelitis. Neurology 2010, 75, e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, K.; Deguchi, K.; Touge, T.; Sasaki, I.; Tsukaguchi, M.; Shimamura, M.; Komatsu, E.; Takeuchi, H.; Kuriyama, S. Painful legs and moving toes syndrome associated with herpes zoster myelitis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2004, 219, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guieu, R.; Sampiéri, F.; Pouget, J.; Guy, B.; Rochat, H. Adenosine in painful legs and moving toes syndrome. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 1994, 17, 460–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinnuroglu, M.; Ozkayran, T. Painful legs and moving toes following a traumatic medial plantar nerve injury. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 133–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsumoto, H.; Levin, K.H.; Wilbourn, A.J.; Chou, S.M. Hypertrophic mononeuritis clinically presenting with painful legs and moving toes. Muscle Nerve 1990, 13, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pla, M.E.; Dillingham, T.R.; Spellman, N.T.; Colon, E.; Jabbari, B. Painful legs and moving toes associates with tarsal tunnel syndrome and accessory soleus muscle. Mov. Disord. 1996, 11, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagna, P.; Cirignotta, F.; Sacquegna, T.; Martinelli, P.; Ambrosetto, G.; Lugaresi, E. “Painful legs and moving toes” associated with polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1983, 46, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touge, T.; Ishibashi, T.; Kamoda, M.; Tsukaguchi, M.; Takeuchi, H. Painful legs and moving toes” and muscle cramps spreading to the bilateral legs in a patient with alcoholic polyneuropathy. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 1998, 38, 762–766. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pitágoras de Mattos, J.; Oliveira, M.; André, C. Painful legs and moving toes associated with neuropathy in HIV-infected patients. Mov. Disord. 1999, 14, 1053–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Fabio, R.; Casali, C.; Pierelli, F. Quetiapine: An alternative treatment in painless legs and moving toes. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 1326–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, S.; Soni, G. Painful leg and moving toes syndrome in secondary tethered cord syndrome. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2016, 39, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.J.; Kim, J.M.; Jeon, B.S. A case report of painless moving toes syndrome. J. Clin. Neurol. 2008, 4, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, C.H. Painful legs and moving toes. A report of 3 cases with neurophysiological studies. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1982, 66, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Otmani, H.; Moutaouakil, F.; Fadel, H.; Slassi, I. Syndrome de jambe douloureuse et orteils instables associé à une radiculopathie lombaire [Painful legs and moving toes syndrome associated with lumbar radiculopathy]. Rev. Neurol. 2009, 165, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahashi, K.; Tsuchiya, I.; Iwase, S.; Ibi, T.; Mano, T. Clinical analyses on moving toes in “painful legs and moving toes”. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 1989, 29, 849–853. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Okuda, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Kitajima, T.; Masuda, R.; Asai, T. Lumbar epidural block for ‘painful legs and moving toes’ syndrome: A report of three cases. Pain 1998, 78, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakawa, T.; Yoshimoto, M.; Takebayashi, T.; Yamashita, T. Case reports: Painful limbs/moving extremities: Report of two cases. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 3419–3425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchihara, T.; Ichikawa, T.; Furukawa, T.; Tsukagoshi, H. Myoclonus with burning sensation in legs that remits with sympathetic blockade. J. Neurol. Sci. 1990, 100, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seipelt, M.; Zerr, I.; Nau, R.; Mollenhauer, B.; Kropp, S.; Steinhoff, B.J.; Wilhelm-Gössling, C.; Bamberg, C.; Janzen, R.W.; Berlit, P.; et al. Hashimoto’s encephalitis as a differential diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1999, 66, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, H.; Saitoh, C.; Iwata, O.; Nanbu, T.; Takada, S.; Morita, S. Epidural spinal cord stimulation for the treatment of painful legs and moving toes syndrome. Pain 2002, 96, 343–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shime, N.; Sugimoto, E. Lumbar sympathetic ganglion block in a patient with painful legs and moving toes syndrome. Anesth. Analg. 1998, 86, 1056–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, P.D.; Finch, P.M. Sympathetic nervous system involvement in the syndrome of painful legs and moving toes. Clin. J. Pain 2004, 20, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Török, N.; Tóth, F.; Szabó, Á.; Vécsei, L. Co-Players in Chronic Pain: Neuroinflammation and the Tryptophan-Kynurenine Metabolic Pathway. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guieu, R.; Tardy-Gervet, M.F.; Blin, O.; Pouget, J. Pain relief achieved by transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation and/or vibratory stimulation in a case of painful legs and moving toes. Pain 1990, 42, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.V.; Driver-Dunckley, E.E.; Caviness, J.N.; Adler, C.H.; Evidente, V.G. Case series of painful legs and moving toes: Clinical and electrophysiologic observations. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 2062–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, K.; Suzuki, M.; Nakajima, M.; Hara, T.; Iseki, M.; Hattori, N. Painful legs and moving toes syndrome evaluated through brain single photon emission computed tomography: A case series. J. Neurol. 2019, 266, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, N.L.; Hanspal, E.K.; Mazzoni, P. Painless legs and moving toes: Symptom reduction during pregnancy. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 328–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiriez, C.; Gurruchaga, J.M.; Goujon, C.; Fénelon, G.; Palfi, S. Spinal stimulation for movement disorders. Neurotherapeutics 2014, 11, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, P.; Waddy, H.M.; Thompson, P.D. An ‘annoying’ foot: Unilateral painful legs and moving toes syndrome. Pain 1999, 82, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenen, J.; Gonce, M.; Delwaide, P.J. Painful legs and moving toes: A syndrome with different physiopathologic mechanisms. Neurology 1984, 34, 1108–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugaresi, E.; Cirignotta, F.; Coccagna, G.; Montagna, P. Nocturnal myoclonus and restless legs syndrome. Adv. Neurol. 1986, 43, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jankovic, J.; Pardo, R. Segmental myoclonus. Clinical and pharmacologic study. Arch. Neurol. 1986, 43, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Moizuddin, M.; Hung, S. Painful legs and moving toes: Case report and review of literature. Br. J. Med. Pract. 2011, 4, a431. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, A.K.; Tan, C.B. The syndrome of painful legs and moving toes—A case report. Singap. Med. J. 1996, 37, 446–447. [Google Scholar]
- Gastaut, J.L. Jambes douloureuses et orteils instables. Un cas d’origine médicamenteuse [Painful legs and moving toes. A drug-induced case]. Rev. Neurol. 1986, 142, 641–642. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Malapert, D.; Degos, J.D. Jambes douloureuses et orteils instables. Neuropathie induite par la cytarabine [Painful legs and moving toes. Neuropathy caused by cytarabine]. Rev. Neurol. 1989, 145, 869–871. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzman, R.J.; Kerrigan, J. The movement disorder of reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Neurology 1990, 40, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, K.P.; Bhatt, M.H.; Marsden, C.D. The causalgia-dystonia syndrome. Brain 1993, 116, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandyk, R. Neuroleptic-induced “painful legs and moving toes” syndrome: Successful treatment with clonazepam and baclofen. Ital. J. Neurol. Sci. 1990, 11, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarejo, A.; Porta-Etessam, J.; Camacho, A.; De La Aleja, J.G.; Martínez-Salio, A.; Penas, M. Gabapentin for painful legs and moving toes syndrome. Eur. Neurol. 2004, 51, 180–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizawa, H. Gabapentin for painful legs and moving toes syndrome. Intern. Med. 2007, 46, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, P.; Pandav, V.; Peche, S. A pediatric case of painful legs and moving toes syndrome. Pediatr. Neurol. 2013, 49, 298–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisa, M.; Singer, C.; Sengun, C.; Russel, A.; Jabbari, B.; Papapetropoulos, S. Treatment of painful limbs/moving extremities with botulinum toxin type A injections. Eur. Neurol. 2008, 60, 104–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, E.; Llanero, M. Painful legs and moving toes syndrome associated with a sacral Tarlov cyst. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 645–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovier, P.; Hilleret, H.; Tissot, R. Traitement par le progabide d’un cas de syndrome des jambes douloureuses et orteils instables [Progabide treatment of a case of the syndrome of painful legs and moving toes]. Rev. Neurol. 1985, 141, 422–424. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Azzi, J.; Atweh, S.; Saade, N.; Jabbour, R. Neuroleptics as a cause of painful legs and moving toes syndrome. BMJ Case Rep. 2014, 2014, bcr2014205117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, M.F.; Diaz-Olivo, R.; Hunt, A.L.; Fahn, S. Therapeutic trial of milacemide in patients with myoclonus and other intractable movement disorders. Mov. Disord. 1993, 8, 484–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ri, S.; Kivi, A.; Wissel, J. The Safety and Effect of Local Botulinumtoxin a Injections for Long-Term Management of Chronic Pain in Post-Herpetic Neuralgia: Literature Review and Cases Report Treated with Incobotulinumtoxin A. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durham, P.L.; Cady, R.; Cady, R. Regulation of calcitonin gene-related peptide secretion from trigeminal nerve cells by botulinum toxin type A: Implications for migraine therapy. Headache 2004, 44, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucioni, A.; Bales, G.T.; Lotan, T.L.; McGehee, D.S.; Cook, S.P.; Rapp, D.E. Botulinum toxin type A inhibits sensory neuropeptide release in rat bladder models of acute injury and chronic inflammation. BJU Int. 2008, 101, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, H.T.; Foran, P.; Dolly, J.O.; Verhage, M.; Wiegant, V.M.; Nicholls, D.G. Tetanus toxin and botulinum toxins type A and B inhibit glutamate, gamma-aminobutyric acid, aspartate, and met-enkephalin release from synaptosomes. Clues to the locus of action. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 21338–21343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wissel, J.; Ri, S. Assessment, goal setting, and botulinum neurotoxin a therapy in the management of post-stroke spastic movement disorder: Updated perspectives on best practice. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2021, 30, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, R.L.; Fernandez, H.H. Sustained benefit of painful legs moving toes syndrome with botulinum toxin type A. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2013, 20, 1031–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyriou, A.A.; Papapetropoulos, S. Botulinum toxin type A for painful limbs moving extremities. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoffer, K. Painful leg moving toes treated with botulinum toxin type A: A video report. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 784–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivi, A.; Ri, S.; Wissel, J. What clinicians and patients want: The past, the presence, and the future of the botulinum toxins. Toxicon 2020, 177, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, G.B.; Piedimonte, F.; Micheli, F. Posterior spinal cord stimulation in a case of painful legs and moving toes. Stereotact Funct. Neurosurg. 2007, 85, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wider, C.; Kuntzer, T.; Olivier, P.; Debatisse, D.; Nancoz, R.; Maeder, P.; Bogousslavsky, J.; Vingerhoets, F. Painful hand and moving finger treated by wearing a glove. Neurology 2006, 67, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cauda equina trauma Radiculopathy Plexus injury Focal neuropathy (e.g., tarsal tunnel syndrome) Polyneuropathy (large fiber, small fiber) Herpes zoster myelitis Spinal cord compression Traumatic spinal cord injury Postsurgical complication Hashimoto’s Encephalopathy Morbus Wilson Morbus Parkinson Stroke Neuroleptics Endocrinologic condition, e.g., Hashimoto thyroiditis and Hypophysenadenome Local trauma without neurologic injury (at least not found) Dupuytren’s contracture |
| Oral medications, e.g., gabapentin, pregabalin, baclofen, clonazepam, carbamazepine, amitriptyline, citalopram, duloxetine, Levodopa, Tramadol, Fentanyl citrate, quetiapine, progabide, beta-blockers, corticosteroids, cannabis, calcitonin, adenosine, etc. Spinal cord stimulation Botulinum neurotoxin injection Local vibration Sympathetic blockade Epidural blockade Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation Massage Local cold, warm, or tactile stimulation Sympathectomy Surgical decompression Other surgical treatments according to possible causes of PLMT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ri, S. Painful Legs and Moving Toes. Encyclopedia 2022, 2, 325-335. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia2010020
Ri S. Painful Legs and Moving Toes. Encyclopedia. 2022; 2(1):325-335. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia2010020
Chicago/Turabian StyleRi, Songjin. 2022. "Painful Legs and Moving Toes" Encyclopedia 2, no. 1: 325-335. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia2010020
APA StyleRi, S. (2022). Painful Legs and Moving Toes. Encyclopedia, 2(1), 325-335. https://doi.org/10.3390/encyclopedia2010020






