Abstract
Erinaceus europaeus is a cosmopolitan mammalian species broadly distributed in Europe, from natural to suburban areas. Due to its ecological role and susceptibility to distinct zoonotic agents, E. europaeus could be a suitable sentinel candidate for many global problems that negatively affect human and animal health. Hedgehogs can work as bioindicators to environmental contamination and can be hosts for multiple tickborne zoonotic agents. Thus, people who directly or indirectly make physical contact with this species are exposed to a variety of threats. Moreover, it has also been studied as an indicator for antibiotic resistance, which was already confirmed for tetracyclines. Additionally, it was also reported as a reservoir for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). More recently, hedgehogs have been recently recognised as potential reservoirs of MERS-CoV-like strains. Among other animals, this species can possibly represent an intermediate reservoir for SARS-CoV-2. The aim of this review is to briefly expose the scientific attainments about hedgehog health, namely agents, diseases, and threats that significantly affect general health concerns and that contribute to achieve One Health principles.
1. Introduction
Erinaceus europaeus, also known as the European hedgehog or western-European hedgehog, classified under “Least Concern” by the International Union Conservation of Nature (IUCN), is broadly distributed in continental Europe (including Russia) [1]. It is also present on some Mediterranean islands, the Azores, and New Zealand [2]. Hedgehog habitats are very diverse, from very natural spaces to rural and urban areas. Though they usually prefer areas with rich food supply and large amounts of vegetation, they have recently been found in high densities in green city parks, which demonstrates their adaptability and resilience [3].
The presence of predators, such as badgers (Meles meles) and foxes (Vulpes vulpes), and the massive changes in agricultural and rural landscapes (the use of pesticides) have had a severe impact on the hedgehog population size, particularly in the UK [3,4]. Nevertheless, the current hedgehog abundance and general distribution are generally stable in most European countries [5,6].
Hedgehogs are hibernators, mainly nocturnal, and insectivorous. Visually, they are known for their spines and back muscles, which allow them to roll up. Their diet is primarily composed of earthworms, caterpillars, slugs, earwigs, millipedes, and beetles. Very rarely, they may also eat mice, snakes, small birds, bird eggs, and pet food found in private gardens [7].
One Health is defined as the assumption that human health is strongly connected with animal health and the environment. Even though it is not a new concept, One Health principles and approaches are becoming more and more important in recent years due to human population growth, global movement of people and food, wildlife habitat loss, and climate change, among others [8].
Wildlife disease surveillance represents a crucial tool to achieve One Health principles and prevents us from the remarkable consequences of an epidemic or pandemic disease in the human population. The Ebola virus epidemic and the SARS-CoV2 pandemic perfectly illustrate how important it is to improve the basic knowledge of wildlife infectious agents and threats to prevent a world catastrophe. In fact, most emerging infectious diseases are zoonotic (which means they affect humans and at least one other vertebrate species). Zoonoses result in thousands of human deaths per year [9], not to mention economic losses, making the overall consequences of a single outbreak extraordinary. Prevention and early control of disease outbreaks and environmental changes could be the keys to reduce the impact of these situations, which requires transdisciplinary research approaches [10].
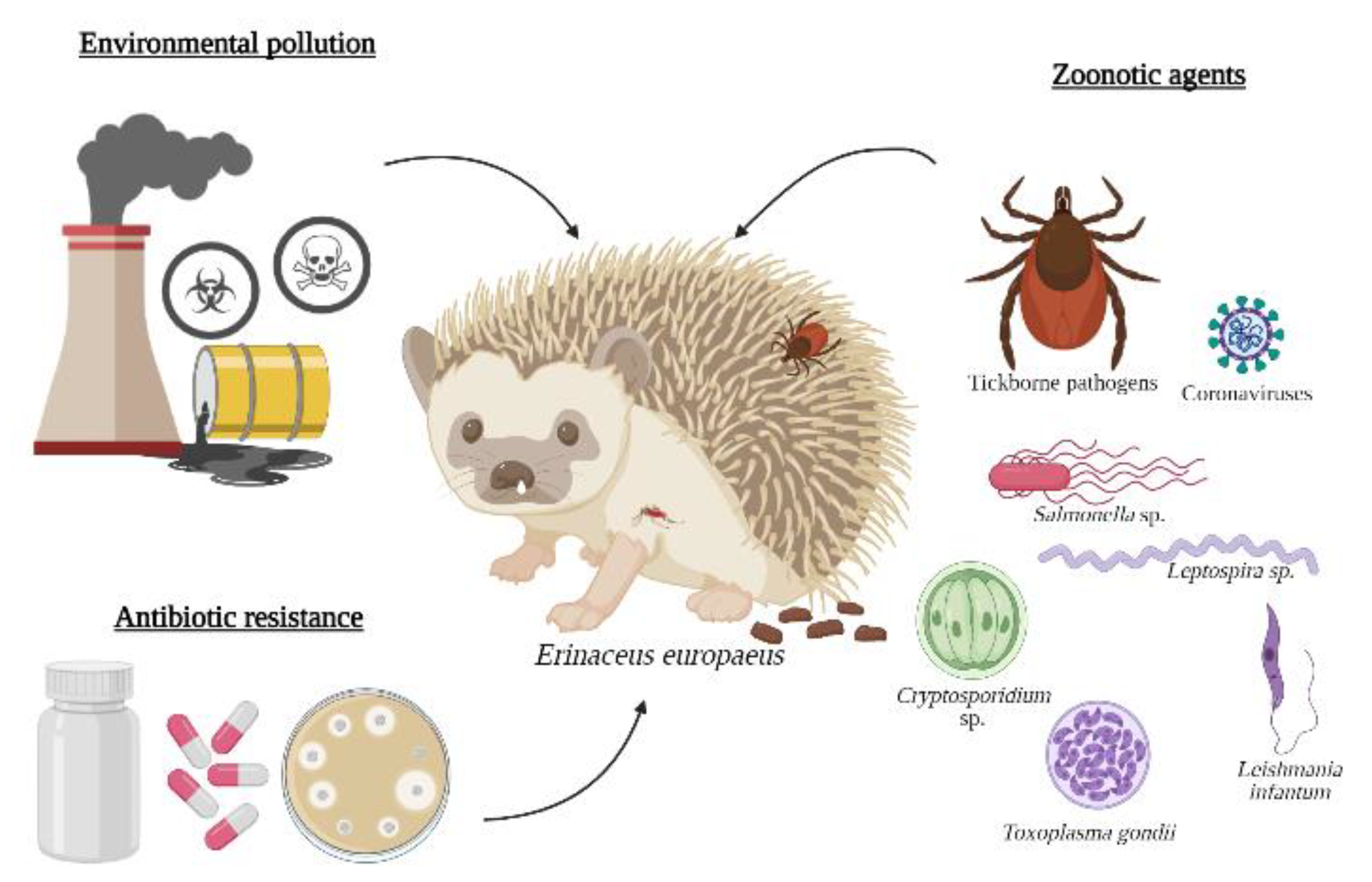
A sentinel species is an organism that provides an advance warning of a threat that potentially represents a risk to humans or other species, namely infectious agents or environmental changes [11]. The biology of some hedgehogs and aspects of ecology should raise awareness for the possible involvement of E. europaeus in several potentially emerging pathogens and diseases [12], namely their frequently occupied trophic levels and their extensive geographical distribution. Consequently, this review aims to summarise information about the hedgehog that is directly related to the One Health concept, indicating that it may be a possible sentinel for health hazards. Some interactions between hedgehogs, zoonotic agents, and environmental conditions are illustrated in Figure 1.
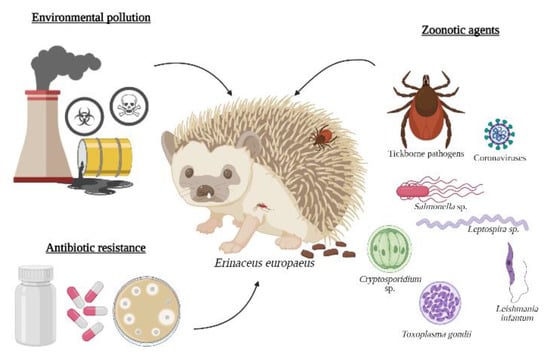
Figure 1.
One Health threats related to the European hedgehog: environmental contamination, zoonotic agents, and antibiotic resistance.
2. Methodology
To produce this literature review, the Scopus® search tool was used with the key words ((european AND hedgehog) OR (erinaceus AND europaeus)) AND (zoonotic OR zoonosis OR pollution OR disease OR one AND health OR parasite OR bacteria OR virus OR rodenticide OR poison OR contamination)). The 86 documents obtained were the base of this review. Some of them were unrelated to the field (e.g., the sonic hedgehog factor; embriology) and were excluded for this reason.
3. Zoonotic Agents
The potential zoonotic agents that have already been reported in E.europeaus are mentioned in Table 1.

Table 1.
Agents detected in E. europaeus with public health importance.
Hedgehogs are considered by some as “melting pots” for tickborne zoonoses [16]. Lyme borreliosis is one of the most common vector-borne zoonotic diseases in Europe, caused by the Borrelia burgdorferi sensu latum (s.l.) complex and transmitted by Ixodes ricinus and I. hexagonus. Improving knowledge about the cycle of these pathogens between ticks and their vertebrate hosts is epidemiologically relevant. Some authors suggest that hedgehogs influence the epidemiology of some species of the B. burgdorferi s.l., affecting their abundance and distribution in distinct habitats. The younger and immunocompromised are the most important reservoirs for B. afzelii, B. spielmanii, and B. bavariensis [32,33]. Another pathogen transmitted by I. ricinus is Anaplasma phagocytophilum. This pathogen is responsible for granulocytic anaplasmosis in horses, dogs, and humans and tickborne fever in ruminants [34]. In Hungary, a survey that analysed the ticks of road-killed hedgehogs showed a prevalence of 74% A. phagocytophilum, 26% B. burgdorferi s.l., and 52% Rickettsia helvetica [26], even though they might not be representative of the population. Furthermore, in Switzerland, tickborne encephalitis virus (TBEV) antibodies were detected for the first time in a European hedgehog. TBEV antibodies and virus RNA were detected in the same individual, which means that the European hedgehog is a suitable host for the disease and leads to the reasonable assumption that it is a reservoir. However, its occurrence at the population level is not known [20].
Salmonellosis is a complex of some of the most common zoonotic diseases worldwide, whose nomenclature is often complex due to the variety of species, subspecies, and phage types [35]. On the European continent, E. europaeus have been reported with different phages of Salmonella enteritidis as well as with S. typhimurium and S. kottbus. The prevalence of infection is generally low (3–4%), particularly when determined by fecal samples or rectal swabs. Nevertheless, in feeding areas shared with humans and birds, this value increases substantially (71%), possibly due to cross-contamination [14]. In Norway, some outbreaks and sporadic human cases were investigated, and salmonella-infected hedgehogs and birds were proposed as a primary source of infection in some of them [36]. Hedgehogs, which are normally asymptomatic, can also carry these bacteria in their coat and spines and can get infected through the ingestion of contaminated food, such as beetles or maggots, easily spreading it in the environment. High mortalities in recovery centers are normally restricted to immunosuppressed or young individuals, who can show clinical signs of enteritis, hepatitis, or peritonitis, and whose differential diagnosis could include Klebsiella sp., Yersinia pseudotuberculosis, and coccidiosis, all of which are zoonotic [14].
Leptospirosis is a clinically relevant zoonotic disease, caused by spirochete bacteria. In France, some species, namely hedgehogs and mustelids, were investigated as carriers of leptospirosis. In this study, hedgehogs were considered as a potential reservoir for L. interrogans Australis [37]. In Azores, where leptospirosis is already recognized in humans and in bovines, several insectivorous species, including the E. europaeus, have been identified as reservoir hosts. On São Miguel island, the hedgehog seems to carry L. serovar copenhageni (from the Icterohaemorrhagiae group). In contrast, in New Zealand, where hedgehogs were also positive for this disease, the reported serovar is ballum [18,38].
Furthermore, in one study, 5 out of 26 E. europaeus brain tissue samples (19.2%) were positive for Toxoplasma gondii [29]. Although not showing high prevalence in hedgehogs, Cryptosporidium parvum, a zoonotic coccidian parasite, was already detected in hedgehogs, in places such as Great Britain [28] and the Netherlands [13]. In the same way, Giardia sp., a flagellated protozoan parasite responsible for a considerable number of human cases of enteritis worldwide, had already been detected in hedgehogs, at least in the Netherlands [13] and New Zealand [27]. Moreover, in 2013, in northern Spain, Leishmania infantum was identified in the European hedgehog for the first time, adding to the list of wildlife reservoirs for this disease that affects humans and domestic dogs [30].
Coronaviruses can affect a variety of animal species and usually cause respiratory, enteric, or neurological diseases. Over the last two decades, it has become more than clear that potentially zoonotic betacoronaviruses can represent massive public health threats, such as those related to Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), or more recently and globally with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). Recent findings of MERS-related CoVs in hedgehogs from Germany [39], France [24], and Great Britain [40] suggest that E. europaeus represents a wild reservoir of betacoronaviruses named as Erinaceus CoVs (EriCoVs) [12,41]. In 2020, a study that analysed virological and epidemiological data of COVID-19 outbreaks in Wuhan, China, comparing it with SARS-2002 and MERS-2012 outbreaks concluded that, among other findings, the responsible agent was genetically close to SARS-related viruses isolated from bats. However, an additional reservoir of the virus could work as an intermediate host, perpetuating and helping to spread the disease. The geographical distribution and usual eating habits of the hedgehog make this species an improbable candidate to this role, even though it is mentioned by the authors [42]. Moreover, genomic, structural, biological, antigenic, and pathogenic properties were detected between hedgehog (and other mammalian species) hepatoviruses and the human hepatitis A virus, suggesting a common evolutionary origin [43].
4. Environmental Pollution
In addition to measuring the level of pollutants in soil or water, biomonitoring animal species is helpful to quantify the amount of hazardous substances that the animal has been exposed to, to determine how much has been absorbed, to predict and describe the consequent organic lesions, and eventually, to develop exposure mitigation strategies. Different studies have been performed to analyse the organs of European hedgehogs, namely the blood, liver, kidneys, hair, and spines for trace elements and organic pollutants (such as organochlorines and organobromines). While hair and spines can be used to evaluate exposure, internal organs and blood may provide information on its distribution, accumulation, and induced damages [44,45,46,47].
The leading causes for the admission of E. europeaus in rehabilitation centres are collisions and traumas, but poisoning is also reported [48]. In general, insectivores (hedgehogs) and carnivores tend to show higher levels of pollutant residues and subsequent clinical signs than herbivorous animals due to the bioaccumulation effects between trophic levels [49].
Hedgehogs tend to have higher levels of lead (Pb) than omnivores or herbivores due to the consumption of insects and earthworms, which bioaccumulate notably high levels of Pb and, consequently, represent a potential way of perpetuating Pb in distinct food chains [50]. Moreover, they usually occupy areas with a high level of urbanisation, where this compound is more frequently present [49]. In contrast, in more natural and unpolluted areas, the amount of heavy metals and metalloids found in hedgehog organs is usually lower and strongly related with the individual age of the hedgehog, which is directly linked with exposure time [51].
Traditionally, the rodenticide poisoning cases in wildlife were only attributed to the ingestion of contaminated rodent carcasses. However, significant detections of brodifacoum, bromadiolone, and difenacoum in urban hedgehogs may suggest other sources of contamination since the ingestion of rodents by hedgehogs is not common. Explanations for these results include the use of rodenticides in urban areas, leading to hedgehog exposure and ingestion of sub-lethal levels in baiting stations [52].
However, environmental pollution is not only chemical. A pilot study performed in Berlin was designed to understand how a music festival, with all of the associated sound pollution and high density of people, affected the hedgehog population of that urban park. Some individual hedgehogs were monitored with different non-invasive technology equipment before and during the festival, and they exhibited particular behaviour patterns and translocations as individual strategies to deal with that environmental aggression. This study allows us to understand how wildlife, especially urban wildlife, adapts to human disturbance [53].
5. Antibiotic Resistance
When bacteria selectively change in response to the use of antibiotic drugs, they become antibiotic-resistant. Consequently, those antibiotics are no longer effective to treat the same bacterial infections, as they were in the past [54]. Antibiotic resistance is a critical worldwide problem that is becoming increasingly prevalent among wildlife studies. The presence of bacteria carrying genes for antimicrobial resistance in wildlife is an indicator that a problem of human and domestic species origin has spread to wild environments and has become global. Furthermore, it represents an additional One Health challenge since wild animals could act as effective reservoirs and links between environments, humans, and domestic animals. Consequently, hedgehogs not only indicate that this worldwide problem is happening, but indeed represent a reservoir of microbes with antibiotic resistance genes, perpetuating this situation [55,56]. In Germany, other mammalian species, such as the wild boar (Sus scrofa) and roe deer (Capreolus capreolus), have been identified as having the potential to be reservoirs for zoonotic agents and sentinels for threats to One Health [56].
Tetracyclines comprise one of the most globally used groups of antimicrobials in human and veterinary medicine due to their large spectrum of activity, facility of administration, and low cost [57]. Consequently, resistances to tetracyclines have been reported since 1953 [58]. In 2020, a study aimed to find tetracycline resistance genes in different tissues of European hedgehogs and crested porcupines (Hystrix cristata) reported that all hedgehogs tested from Italy and 50% of the hedgehogs tested from Switzerland had at least one resistance gene. According to these authors, small mammals may work as reservoirs, sentinels, or potential vectors for resistance genes or antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the environment and transmission to other hosts, such as humans [59].
Moreover, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) represents a significant problem for infection control and antibiotic treatment worldwide. In Sweden, two hedgehogs with severe infections caused by MRSA—one with lethal septicemia and bacterial presence in the kidneys and brain and the other with severe dermatitis—were considered reservoirs for different precursors of resistant genes [60].
As mentioned above, Salmonella spp. is one of the bacterial zoonotic diseases registered in hedgehogs, mainly in recovery centers. In Catalonia, Spain, different admitted animal species were tested for different Salmonella species and serovars. Its antibiotic resistance pattern was determined before the initiation of any treatment. One of the tested E. europeaus was positive for S. enterica subsp. enterica serovar kottbus and showed resistance to ampicillin, streptomycin, tetracycline, sulphamethoxazole, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, and nalidixic acid [61].
6. Conclusions
Nowadays, the impact and difficulty to control certain human health problems and infectious diseases, namely SARS-CoV or Ebola, can be interpreted as an urgent call for more transdisciplinary approaches in their prediction, prevention, and management, considering the One Health principles. A variety of researchers, mainly focused on wildlife surveillance and disease control among wild populations, have simultaneously improved our baseline knowledge of infectious zoonotic agents and the subsequent risk of exposure [10].
Nevertheless, there is a significant knowledge gap that might function as a stimulus for developing future projects in this area. Given the variety and prevalence of zoonotic agents in hedgehogs and their proximity to humans, they could indeed be a sentinel candidate for human threats to One Health. However, it remains necessary to quantify the actual threat it represents and to evaluate its quality as a sentinel. In other words, are they a main source of infection for humans regarding the aforementioned zoonotic diseases? Are there any better species to evaluate the aforementioned problems? Can they give practical and consistent information to predict an epidemic or a pandemic disease? Some authors specifically suggest, for instance, that comparisons between isolates obtained from wildlife (namely hedgehogs) and human isolates should be made [13].
Thus, the answer to the title is currently unknown, but the information shared in this review should act as encouragement for future research on the role of mammals, including E. europeaus, in One Health problems.
Author Contributions
C.V.J.B. wrote the paper. F.S., J.M.G.-O., and P.A.O. supported the first author in correcting and revising the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Funds by FCT—Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, under the project UIDB/04033/2020 and UIDB/CVT/00772/2020.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Amori, G. Erinaceus europaeus. IUCN Red List Threat. Species 2016, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.L.; Larsen, J.; Van Wijk, R.E.; Jones, O.R.; Berg, T.B.; Angen, O.; Larsen, A.R. European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) as a natural reservoir of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying mecC in Denmark. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, B.M.; Baker, P.J.; Thomas, E.; Wilson, G.; Judge, J.; Yarnell, R.W. Reduced occupancy of hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in rural England and Wales: The influence of habitat and an asymmetric intra-guild predator. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettett, C.E.; Johnson, P.J.; Moorhouse, T.P.; Macdonald, D.W. National predictors of hedgehog Erinaceus europaeus distribution and decline in Britain. Mamm. Rev. 2018, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencatel, J.; Sabino-Marques, H.; Álvares, F.; Moura, A.E.; Barbosa, A.M. Atlas de Mamíferos de Portugal, 2nd ed.; Universidade de Évora: Évora, Portugal, 2019; ISBN 9789898550804. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell-Jones, A.J.; Amori, G.; Bogdanowicz, W.; Krystufek, B.; Reijnders, P.J.H.; Spitzenberger, F.; Stubbe, M.; Thissen, J.B.M.; Vohralik, V.; Zima, J. The Atlas of European Mammals; Poyser: London, UK, 1999; ISBN 9780856611308. [Google Scholar]
- European Hedgehog (Erinaceus Europaeus)|Natural History Museum. Available online: https://www.nhm.ac.uk/discover/hedgehog-erinaceus-europaeus.html (accessed on 24 April 2021).
- One Health Basics. One Health|CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/onehealth/basics/index.html (accessed on 3 June 2021).
- World Bank. People, Pathogens and our Planet; Agriculture and Rural Development: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Available online: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/2012/06/16360943/people-pathogens-planet-economics-one-healt (accessed on 25 May 2021).
- Kelly, T.R.; Karesh, W.B.; Johnson, C.K.; Gilardi, K.V.K.; Anthony, S.J.; Goldstein, T.; Olson, S.H.; Machalaba, C.; Mazet, J.A.K.; Aguirre, A.; et al. One Health proof of concept: Bringing a transdisciplinary approach to surveillance for zoonotic viruses at the human-wild animal interface. Prev. Vet. Med. 2017, 137, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council (US) Committee on Animals as Monitors of Environmental Hazards. Animals as Sentinels of Environmental Health Hazards; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Delogu, M.; Cotti, C.; Lelli, D.; Sozzi, E.; Trogu, T.; Lavazza, A.; Garuti, G.; Castrucci, M.R.; Vaccari, G.; De Marco, M.A.; et al. Eco-virological preliminary study of potentially emerging pathogens in hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) recovered at a wildlife treatment and rehabilitation center in Northern Italy. Animals 2020, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, A.I.; Van Leeuwen, A.D.; Jacobs-Reitsma, W.; Wijnands, L.M.; Bouw, E.; Jahfari, S.; Van Hoek, A.H.A.M.; Van Der Giessen, J.W.B.; Roelfsema, J.H.; Kroes, M.; et al. Presence of zoonotic agents in engorged ticks and hedgehog faeces from Erinaceus europaeus in (sub) urban areas. Parasites Vectors 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeble, E.; Koterwas, B. Salmonellosis in Hedgehogs. Vet. Clin. North. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2020, 23, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.Q.; Xiao, X.; Liu, J.W.; Han, H.J.; Qin, X.R.; Lei, S.C.; Yu, X.J. Occurrence and Genotyping of Coxiella burnetii in Hedgehogs in China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 20, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahfari, S.; Ruyts, S.C.; Frazer-Mendelewska, E.; Jaarsma, R.; Verheyen, K.; Sprong, H. Melting pot of tick-borne zoonoses: The European hedgehog contributes to the maintenance of various tick-borne diseases in natural cycles urban and suburban areas. Parasites Vectors 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hydeskov, H.B.; Amar, C.F.L.; Fernandez, J.R.-R.; John, S.K.; MacGregor, S.K.; Cunningham, A.A.; Lawson, B. Listeria monocytogenes infection of free-living western european hedgehogs (erinaceus Europaeus). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2019, 50, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collares-Pereira, M.; Korver, H.; Terpstra, W.J.; Santos-Reis, M.; Ramalhinho, M.G.; Mathias, M.L.; Oom, M.M.; Fons, R.; Libois, R.; Petrucci-Fonseca, F. First epidemiological data on pathogenic leptospires isolated on the Azorean islands. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 13, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sixl, W.; Kock, M.; Withalm, H.; Stunzner, D. Serological investigations of the hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) in Styria. Geogr. Med. Suppl. 1989, 2, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schönbächler, K.; Hatt, J.-M.; Silaghi, C.; Merz, N.; Fraefel, C.; Bachofen, C. Confirmation of tick-borne encephalitis virus in an european hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus)|Détection du virus de la méningo-encéphalite verno-estivale chez le hérisson d’europe (Erinaceus europaeus)|Frühsommer-meningoenzephalitis-virus nachweis beim. Schweiz. Arch. Tierheilkd. 2018, 161, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spengler, J.R.; Bergeron, É.; Rollin, P.E. Seroepidemiological Studies of Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Virus in Domestic and Wild Animals. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medlock, J.M.; Snow, K.R.; Leach, S. Possible ecology and epidemiology of medically important mosquito-borne arboviruses in Great Britain. Epidemiol. Infect. 2021, 135, 466–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubálek, Z.; Rödl, P.; Juricová, Z. Experimental infection of hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) with Bhanja virus. Folia Parasitol. 1984, 31, 189–190. [Google Scholar]
- Monchatre-Leroy, E.; Boué, F.; Boucher, J.M.; Renault, C.; Moutou, F.; Gouilh, M.A.; Umhang, G. Identification of alpha and beta coronavirus in wildlife species in france: Bats, rodents, rabbits, and hedgehogs. Viruses 2017, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bao, C.; Hu, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Ji, Z.; Feng, Z.; Li, L.; Shen, A.; et al. Ecology of the Tick-Borne Phlebovirus Causing Severe Fever with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome in an Endemic Area of China. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekeres, S.; Docters van Leeuwen, A.; Tóth, E.; Majoros, G.; Sprong, H.; Földvári, G. Road-killed mammals provide insight into tick-borne bacterial pathogen communities within urban habitats. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilvers, B.L.; Cowan, P.E.; Waddington, D.C.; Kelly, P.J.; Brown, T.J. The prevalence of infection of Giardia spp. and Cryptosporidium spp. in wild animals on farmland, southeastern North Island, New Zealand. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 1998, 8, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangster, L.; Blake, D.P.; Robinson, G.; Hopkins, T.C.; Sa, R.C.C.; Cunningham, A.A.; Chalmers, R.M.; Lawson, B. Detection and molecular characterisation of Cryptosporidium parvum in British European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus). Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 217, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmannová, L.; Juránková, J. Survey of Toxoplasma gondii and Trichinella spp. in hedgehogs living in proximity to urban areas in the Czech Republic. Parasitol. Res. 2019, 118, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Madrid, R.; Belinchón-Lorenzo, S.; Iniesta, V.; Fernández-Cotrina, J.; Parejo, J.C.; Serrano, F.J.; Monroy, I.; Baz, V.; Gómez-Luque, A.; Gómez-Nieto, L.C. First detection of Leishmania infantum kinetoplast DNA in hair of wild mammals: Application of qPCR method to determine potential parasite reservoirs. Acta Trop. 2013, 128, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingmueller, G.; Heymer, T.; Sobich, E. Trichophyton mentagrophytes var. erinacei-infection of hedgehog. Trichophyton-mentagrophytes-var.-erinacei-infektion VOM IGEL. Hautarzt 1979, 30, 140–143. [Google Scholar]
- Majerová, K.; Hönig, V.; Houda, M.; Papežík, P.; Fonville, M.; Sprong, H.; Rudenko, N.; Golovchenko, M.; Bolfíková, B.Č.; Hulva, P.; et al. Hedgehogs, squirrels, and blackbirds as sentinel hosts for active surveillance of borrelia miyamotoi and borrelia burgdorferi complex in urban and rural environments. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skuballa, J.; Petney, T.; Pfäffle, M.; Oehme, R.; Hartelt, K.; Fingerle, V.; Kimmig, P.; Taraschewski, H. Occurrence of different Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato genospecies including B. afzelii, B. bavariensis, and B. spielmanii in hedgehogs (Erinaceus spp.) in Europe. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silaghi, C.; Skuballa, J.; Thiel, C.; Pfister, K.; Petney, T.; Pfäffle, M.; Taraschewski, H.; Passos, L.M.F. The European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus)-A suitable reservoir for variants of Anaplasma phagocytophilum? Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, B.; Franklinos, L.H.V.; Rodriguez-Ramos Fernandez, J.; Wend-Hansen, C.; Nair, S.; Macgregor, S.K.; John, S.K.; Pizzi, R.; Núñez, A.; Ashton, P.M.; et al. Salmonella Enteritidis ST183: Emerging and endemic biotypes affecting western European hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) and people in Great Britain. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heir, E.; Lindstedt, B.A.; Nygård, I.; Vardund, T.; Hasseltvedt, V.; Kapperud, G. Molecular epidemiology of Salmonella typhimurium isolates from human sporadic and outbreak cases. Epidemiol. Infect. 2002, 128, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayral, F.; Djelouadji, Z.; Raton, V.; Zilber, A.-L.; Gasqui, P.; Faure, E.; Baurier, F.; Vourc’h, G.; Kodjo, A.; Combes, B. Hedgehogs and Mustelid Species: Major Carriers of Pathogenic Leptospira, a Survey in 28 Animal Species in France (20122015). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hathaway, S.C.; Hathaway, S.C. Leptospirosis in New Zealand: An ecological view. N. Z. Vet. J. 1981, 29, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corman, V.M.; Kallies, R.; Philipps, H.; Gopner, G.; Muller, M.A.; Eckerle, I.; Brunink, S.; Drosten, C.; Drexler, J.F. Characterization of a Novel Betacoronavirus Related to Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus in European Hedgehogs. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldanha, I.F.; Lawson, B.; Goharriz, H.; Rodriguez-Ramos Fernandez, J.; John, S.K.; Fooks, A.R.; Cunningham, A.A.; Johnson, N.; Horton, D.L. Extension of the known distribution of a novel clade C betacoronavirus in a wildlife host. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sabato, L.; Di Bartolo, I.; De Marco, M.A.; Moreno, A.; Lelli, D.; Cotti, C.; Delogu, M.; Vaccari, G. Can Coronaviruses Steal Genes from the Host as Evidenced in Western European Hedgehogs by EriCoV Genetic Characterization? Viruses 2020, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lvov, D.K.; Alkhovsky, S.V.; Kolobukhina, L.V.; Burtseva, E.I. Etiology of epidemic outbreaks COVID-19 in Wuhan, Hubei province, Chinese People Republic associated with 2019-nCoV (Nidovirales, Coronaviridae, Coronavirinae, Betacoronavirus, Subgenus Sarbecovirus): Lessons of SARS-CoV outbreak. Vopr. Virusol. 2020, 65, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drexler, J.F.; Corman, V.M.; Lukashev, A.N.; Van Den Brand, J.M.A.; Gmyl, A.P.; Brünink, S.; Rasche, A.; Seggewiβ, N.; Feng, H.; Leijten, L.M.; et al. Evolutionary origins of hepatitis A virus in small mammals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Havé, H.; Scheirs, J.; Mubiana, V.K.; Verhagen, R.; Blust, R.; De Coen, W. Nondestructive pollution exposure assessment in the European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus): I. Relationships between concentrations of metals and arsenic in hair, spines, and soil. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 2356–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, F.; Covaci, A.; D’Havé, H.; Van den Brink, N.W.; Blust, R.; De Coen, W.; Bervoets, L. Accumulation of background levels of persistent organochlorine and organobromine pollutants through the soil-earthworm-hedgehog food chain. Environ. Int. 2010, 36, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Covaci, A.; Voorspoels, S.; Schepens, P. The distribution of octachlorostyrene (OCS) in environmental samples from Europe. J. Environ. Monit. 2003, 5, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, F.; D’Havé, H.; Mubiana, V.K.; Van den Brink, N.W.; Blust, R.; Bervoets, L.; De Coen, W. Relevance of hair and spines of the European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus) as biomonitoring tissues for arsenic and metals in relation to blood. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcês, A.; Soeiro, V.; Lóio, S.; Sargo, R.; Sousa, L.; Silva, F.; Pires, I. Outcomes, Mortality Causes, and Pathological Findings in European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europeus, Linnaeus 1758): A Seventeen Year Retrospective Analysis in the North of Portugal. Animals 2020, 10, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleva, E.; Francia, N.; Pandolfi, M.; De Marinis, A.M.; Chiarotti, F.; Santucci, D. Organochlorine and heavy-metal contaminants in wild mammals and birds of Urbino-Pesaro Province, Italy: An analytic overview for potential bioindicators. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 51, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinecke, A.J.; Reinecke, S.A.; Musilbono, D.E.; Chapman, A. The transfer of lead (Pb) from earthworms to shrews (Myosorex varius). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 39, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rautio, A.; Kunnasranta, M.; Valtonen, A.; Ikonen, M.; Hyvärinen, H.; Holopainen, I.J.; Kukkonen, J.V.K. Sex, age, and tissue specific accumulation of eight metals, arsenic, and selenium in the European Hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 59, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowding, C.V.; Shore, R.F.; Worgan, A.; Baker, P.J.; Harris, S. Accumulation of anticoagulant rodenticides in a non-target insectivore, the European hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus). Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rast, W.; Barthel, L.M.F.; Berger, A. Music festival makes Hedgehogs move: How individuals cope behaviorally in response to human-induced stressors. Animals 2019, 9, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Antibiotic Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/antibiotic-resistance (accessed on 3 June 2021).
- Martin, J.F.; Liras, P. Organization and expression of genes involved in the biosynthesis of antibiotics and other secondary metabolites. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1989, 43, 173–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza-Rodríguez, C.; Alt, K.; Grobbel, M.; Hammerl, J.A.; Irrgang, A.; Szabo, I.; Stingl, K.; Schuh, E.; Wiehle, L.; Pfefferkorn, B.; et al. Wildlife as Sentinels of Antimicrobial Resistance in Germany? Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 7, 7821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bucur, I.; Dumitrescu, V.; Imre, K.; Herman, V.; Nichita, I.; Cristina, R.T.; Tirziu, E. Research on the Frequency of Resistance Phenotypes in Bacterial Strains Isolated From Chamois (Rupicapra Rupicapra Carpatica). Rev. Rom. Med. Vet. 2020, 30, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, M.C. Tetracycline Resistance Determinants: Mechanisms of Action, Regulation of Expression, Genetic Mobility, and Distribution. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1996, 19, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Francesco, A.; Renzi, M.; Borel, N.; Marti, H.; Salvatore, D. Detection of tetracycline resistance genes in european hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) and crested porcupines (Hystrix cristata). J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monecke, S.; Gavier-Widen, D.; Mattsson, R.; Rangstrup-Christensen, L.; Lazaris, A.; Coleman, D.C.; Shore, A.C.; Ehricht, R. Detection of mecC-Positive Staphylococcus aureus (CC130-MRSA-XI) in Diseased European Hedgehogs (Erinaceus europaeus) in Sweden. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-López, R.A.; Vidal, A.; Obón, E.; Martín, M.; Darwich, L. Multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium monophasic variant 4,12:i:- Isolated from asymptomatic wildlife in a catalonian wildlife rehabilitation center, Spain. J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).