Characterization of Critical Quality Attributes of an Anti-PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibody
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Anti-PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibody Expression and Purification
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Mathematical Methods for Quantitative Data Comparison
2.3.1. Statistical Analysis
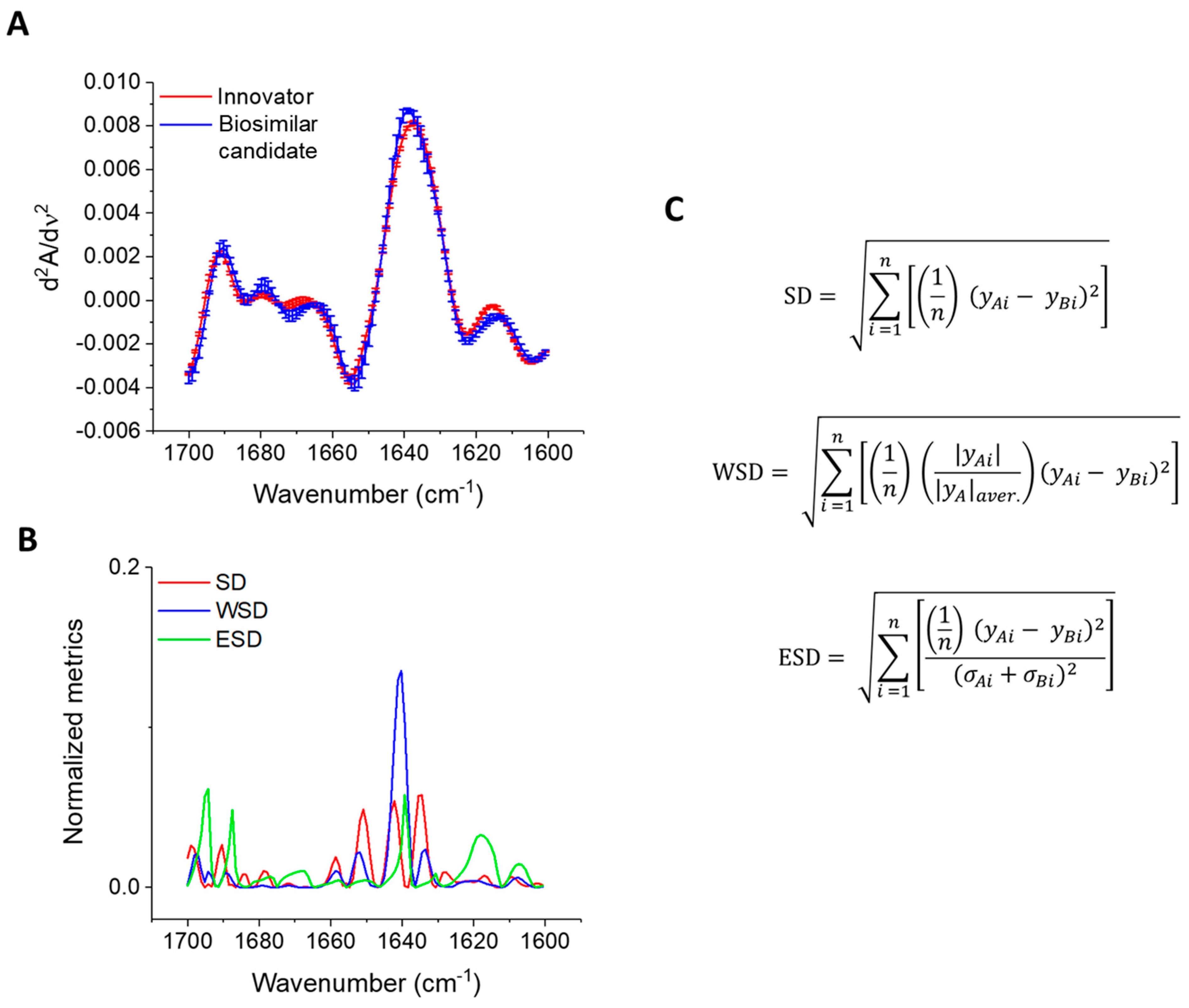
2.3.2. Error Spectral Difference (ESD)
2.4. Analytical Assays
3. Results
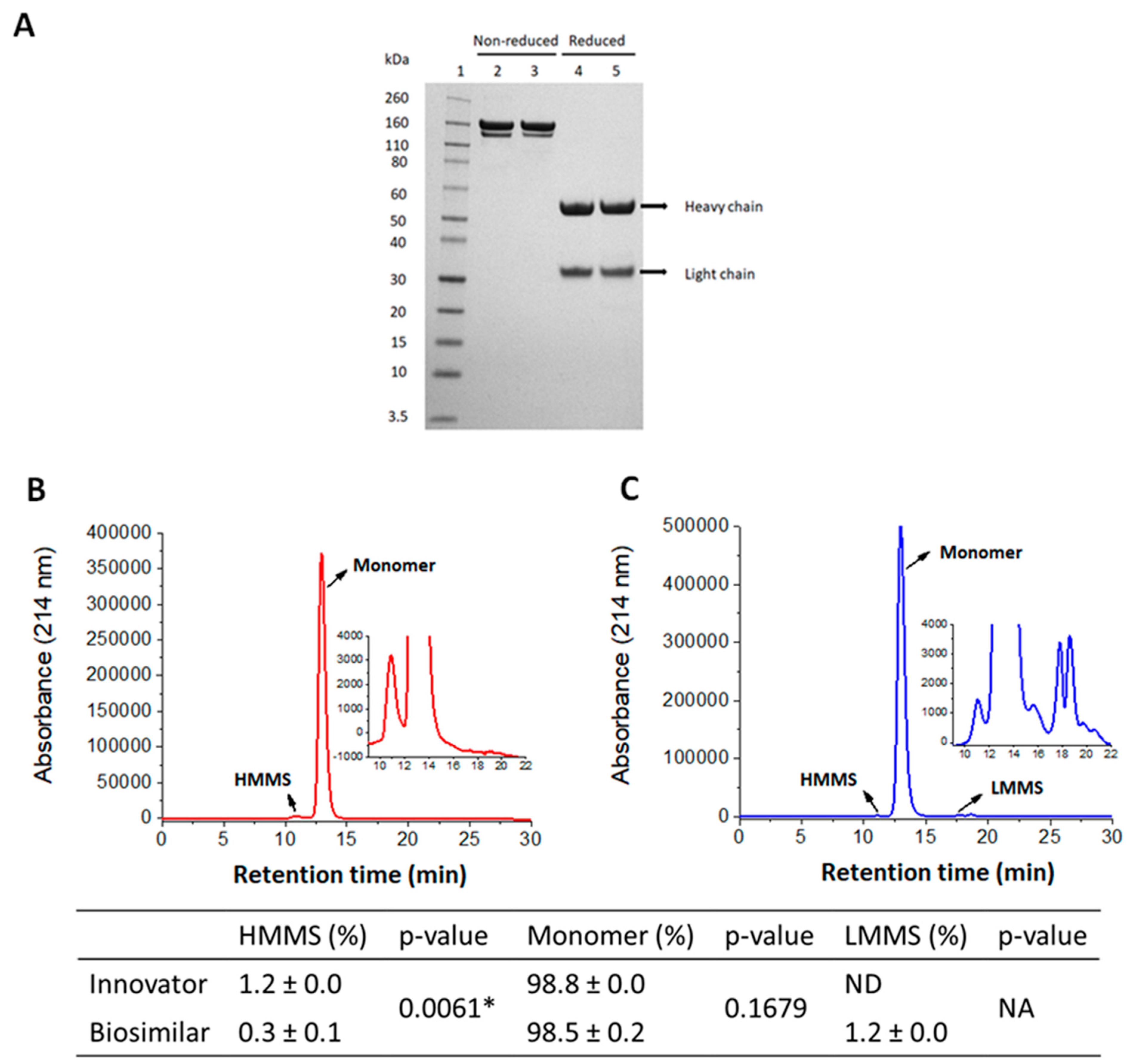
3.1. Purity and Size Distribution
3.2. Peptide Mapping Analysis
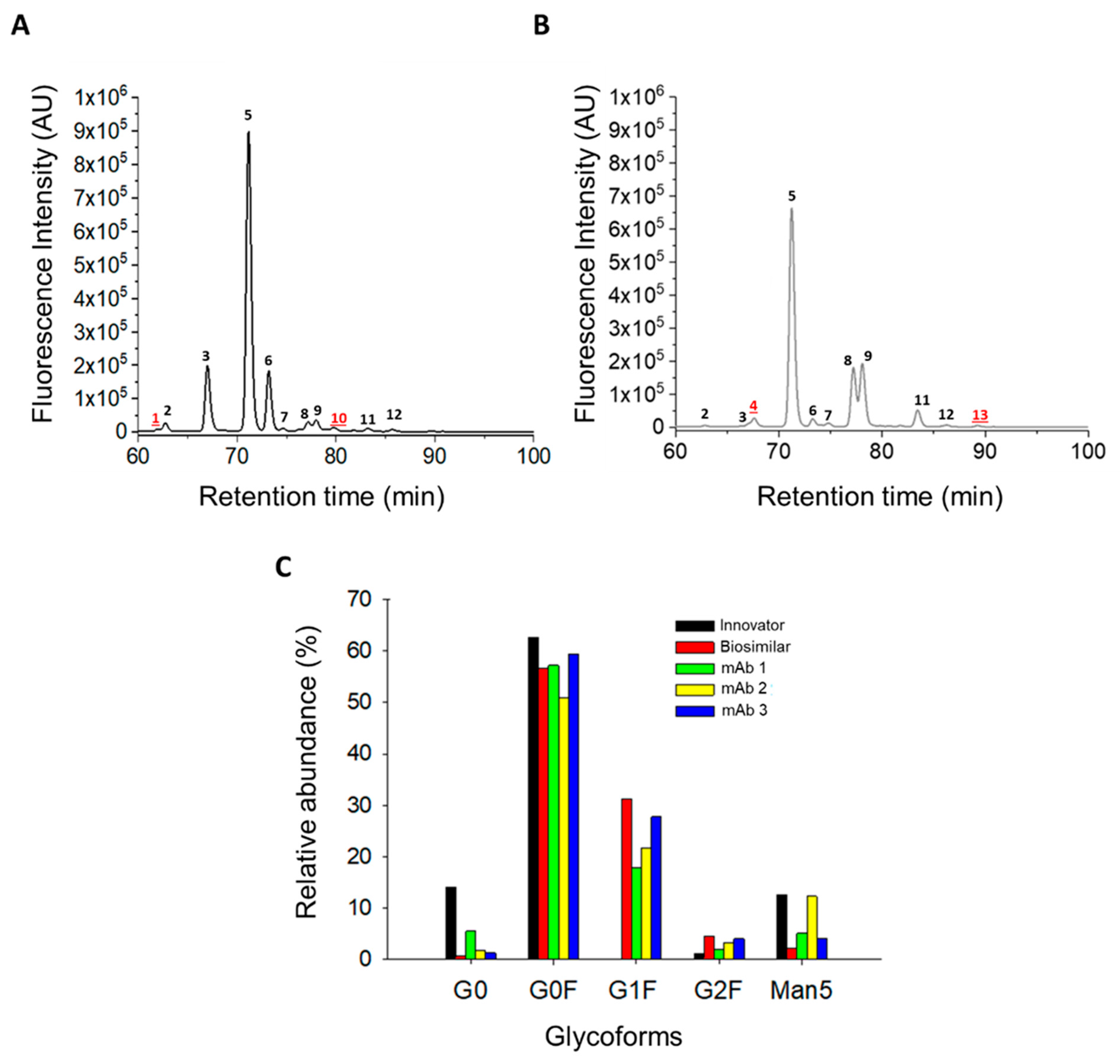
3.3. N-Glycosylation Profile
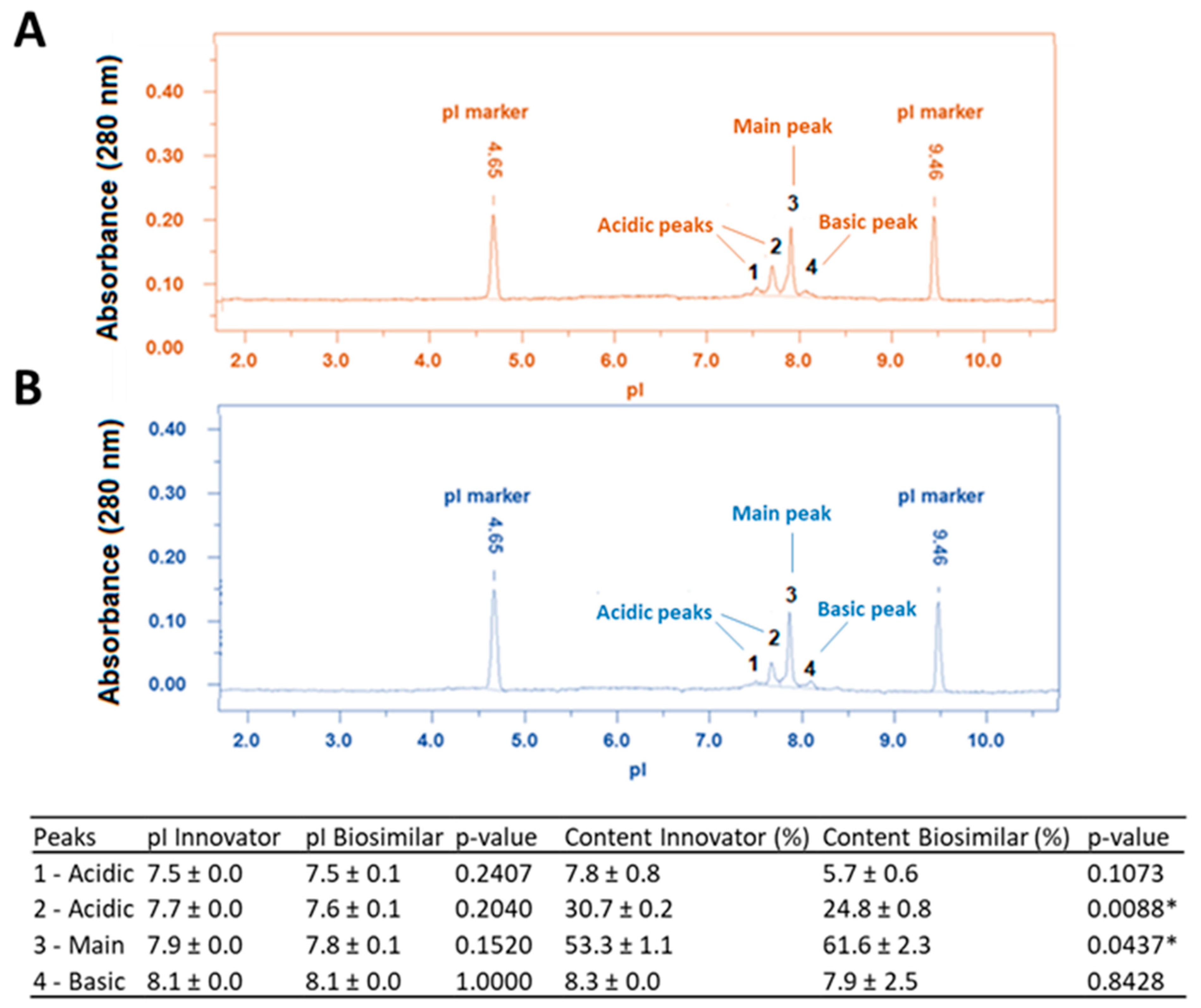
3.4. Charge Heterogeneity
3.5. Relative Solubility Analysis
3.6. Higher-Order Structure (HOS)
3.7. Aggregation Propensity and Overall Conformational Stability
3.8. Physical Stability Profiles (pH versus Temperature)
3.9. In-Vitro Binding Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADCC | antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity |
| ADCP | antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis |
| BLI | bio-layer interferometry |
| CD | circular dichroism |
| CDC | complement-dependent cytotoxicity |
| CHO | Chinese hamster ovary cells |
| CP | citrate-phosphate |
| CQAs | critical quality attributes |
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
| DSC | differential scanning calorimetry |
| DTT | dithiothreitol |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| EPD | empirical phase diagram |
| ESI-TOF | electrospray ionization time-of-flight |
| ESD | error spectral difference |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| G-CSF | human granulocyte-colony stimulation factor |
| GU | glucose units |
| HC | heavy chain |
| HILIC | hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography |
| HMMS | high-molecular mass species |
| HOS | higher-order structure |
| HPLC | high-performance liquid chromatography |
| HT | hypoxanthine and thymidine |
| IAA | iodoacetamide |
| icIEF | imaged capillary isoelectric focusing |
| IGF | insulin-like growth factor |
| IgG | immunoglobulin |
| IRES | internal ribosome entry site |
| ka | kinetic association rate |
| KD | equilibrium dissociation constant or binding affinity |
| kdis | dissociation rate |
| LC | light chain |
| LC-MS | liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry |
| LDL | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LDLR | LDL receptor |
| LMMS | low molecular mass species |
| mAbs | monoclonal antibodies |
| MM | molecular mass |
| MOA | mode of action |
| MRME | mean residual molar ellipticity |
| MSM | mean spectral center of mass |
| PK/PD | pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PCSK9 | proprotein convertase subtilsin kexin type 9 |
| PEG | polyethylene glycol |
| pI | isoelectric point |
| SD | spectral difference |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| SEC | size-exclusion chromatography |
| Tm | thermal unfolding temperature or melting temperature |
| Tonset | onset temperature |
| Trp | tryptophan |
| Tyr | tyrosine |
| UPLC | ultra-performance liquid chromatography |
| US | United States |
| UV | ultraviolet |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| WSD | weighted spectral difference |
| χ2 | chi-squared test |
| ya | innovator data point |
| yb | biosimilar data point |
| σa | innovator standard deviation |
| σb | biosimilar standard deviation |
References
- Walsh, G.; Walsh, E. Biopharmaceutical benchmarks 2022. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1722–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.L.; Xiao, L.L.; Tang, Z.H.; Jiang, Z.S.; Liu, M.H. Role of PCSK9 in lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, R.; Garg, J.; Shah, N.; Sumner, A. PCSK9 inhibitors: A new era of lipid lowering therapy. World J. Cardiol. 2017, 9, 76–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, T.A.; Pinho, M.B.; Castilho, L.R. Evaluation of different IRES-mediated tricistronic plasmid designs for expression of an anti-PCSK9 biosimilar monoclonal antibody in CHO cells. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 2511–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Guidelines on Evaluation of Monoclonal Antibodies as Similar Biotherapeutic Products (SBPs). In WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardization: Sixty-Seventh Report; WHO Technical Report Series, No. 1004, Annex 2; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/biologicals/who_trs_1004_web_annex_2.pdf (accessed on 24 August 2024).
- Ishii-Watabe, A.; Kuwabara, T. Biosimilarity assessment of biosimilar therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2019, 34, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkowitz, S.A.; Engen, J.R.; Mazzeo, J.R.; Jones, G.B. Analytical tools for characterizing biopharmaceuticals and the implications for biosimilars. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, J.; Feuerstein, I.; Stangler, T.; Schmiederer, T.; Fritsch, C.; Schiestl, M. Physicochemical and functional comparability between the proposed biosimilar rituximab GP2013 and originator rituximab. BioDrugs 2013, 27, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Lee, J.; Bae, J.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, H.A.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.J.; Lim, K.J.; Lee, J.W.; Jung, S.K.; et al. Analytical similarity assessment of rituximab biosimilar CT-P10 to reference medicinal product. MAbs 2018, 10, 380–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Lee, J.J.; Yang, H.; Baek, S.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, T.; Song, D.; Park, G. Evaluation of similar quality attribute characteristics in SB5 and reference product of adalimumab. MAbs 2019, 11, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velayudhan, J.; Amanda, Y.C.; Christina, R.; Maher, G.; Thomas, H.; Brown, R.; Born, T.L. Demonstration of functional similarity of proposed biosimilar ABP 501 to adalimumab. BioDrugs 2016, 30, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, C.; Eo, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, N.; Park, J.; Park, S.; Seo, D.; Jeong, M.; et al. Physicochemical and biological characterization of SB2, a biosimilar of Remicade® (infliximab). MAbs 2016, 9, 364–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, B.; Walch, N.; Jungbauer, A.; Lingg, N. How similar is biosimilar? A comparison of infliximab therapeutics in regard to charge variant profile and antigen binding affinity. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 14, 1800340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.H.; Lee, N.; Song, D.; Jung, S.Y.; Bou-Assaf, G.; Sosic, Z.; Zhang, W.; Lyubarskaya, Y. Evaluation of the structural, physicochemical, and biological characteristics of SB4, a biosimilar of etanercept. MAbs 2016, 8, 1136–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Postapproval Manufacturing Changes to Biosimilar and Interchangeable Biosimilar Products Questions and Answers Guidance for Industry. 2024. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/180206/download (accessed on 24 August 2024).
- Castilho, L.R.; Anspach, F.B.; Deckwer, W. An integrated process for mammalian cell perfusion cultivation and product purification using a dynamic filter. Biotechnol. Prog. 2002, 18, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ExPASy. Protparam. 2024. Available online: https://web.expasy.org/protparam/ (accessed on 24 August 2024).
- Teska, B.M.; Li, C.; Winn, B.C.; Arthur, K.K.; Jiang, Y.; Gabrielson, J.P. Comparison of quantitative spectral similarity analysis methods for protein higher-order structure confirmation. Anal. Biochem. 2013, 434, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Committee for Medicinal Products for Human use (CHMP) Assessment Report Repatha. May 2015. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/assessment-report/repatha-epar-public-assessment-report_en.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2023).
- Wypych, J.; Li, M.; Guo, A.; Zhang, Z.; Martinez, T.; Allen, M.J.; Fodor, S.; Kelner, D.N.; Flynn, G.C.; Liu, Y.D.; et al. Human IgG2 antibodies display disulfide-mediated structural isoforms. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 16194–16205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossler, P.; Khattak, S.F.; Li, Z.J. Optimal and consistent protein glycosylation in mammalian cell culture. Glycobiology 2009, 19, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Walsh, I.; Abrahams, J.L.; Royle, L.; Nguyen-Khuong, T.; Spencer, D.; Fernandes, D.L.; Packer, N.H.; Rudd, P.M.; Campbell, M.P. GlycoStore: A database of retention properties for glycan analysis. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3231–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetze, A.M.; Liu, Y.D.; Zhang, Z.; Shah, B.; Lee, E.; Bondarenko, P.V.; Flynn, G.C. High-mannose glycans on the Fc region of therapeutic IgG antibodies increase serum clearance in humans. Glycobiology 2011, 21, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A. N-Glycan Analysis of Biotherapeutic Proteins. BioPharm Int. 2017, 30, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, C.; Cheung, J.K.; Dellatore, S.M.; Katiyar, A.; Bhat, R.; Sun Ponniah, G.; Neill, A.; Mason, B.; Beck, A.; Liu, H. Forced degradation of recombinant monoclonal antibodies: A practical guide. MAbs 2017, 9, 1217–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- More, A.S.; Toprani, V.M.; Okbazghi, S.Z.; Kim, J.H.; Joshi, S.B.; Middaugh, C.R.; Tolbert, T.J.; Volkin, D.B. Correlating the impact of well-defined oligosaccharide structures on physical stability profiles of IgG1-Fc glycoforms. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 588–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Larson, N.R.; Angalakurthi, S.K.; Middaugh, C.R. Improved fluorescence methods for high-throughput protein formulation screening. SLAS Technol. 2018, 23, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Joshi, S.B.; He, F.; Brems, D.N.; He, B.; Kerwin, B.A.; Volkin, D.B.; Middaugh, C.R. Comparison of high-throughput biophysical methods to identify stabilizing excipients for a model IgG2 monoclonal antibody: Conformational stability and kinetic aggregation measurements. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 1701–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, J.; Hickey, J.M.; Majumdar, R.; Esfandiary, R.; Bishop, S.M.; Samra, H.S.; Middaugh, C.R.; Weis, D.D.; Volkin, D.B. Hydrogen exchange mass spectrometry reveals protein interfaces and distant dynamic coupling effects during the reversible self-association of an IgG1 monoclonal antibody. MAbs 2015, 7, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Tsumoto, K. Effects of subclass change on the structural stability of chimeric, humanized, and human antibodies under thermal stress. Protein Sci. 2013, 22, 1542–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, N.N.; Winn, B.C.; Arthur, K.K.; Gabrielson, J.P. Quantitative spectral comparison by weighted spectral difference for protein higher order structure confirmation. Anal. Biochem. 2014, 464, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Singh, A.; Wu, H.; Kroe-Barrett, R. Comparison of biosensor platforms in the evaluation of high affinity antibody-antigen binding kinetics. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 508, 78–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidarsson, G.; Dekkers, G.; Rispens, T. IgG subclasses and allotypes: From structure to effector functions. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferis, R. Recombinant antibody therapeutics: The impact of glycosylation on mechanisms of action. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Doneanu, C.; Alley, W.R., Jr.; Yu, Y.Q.; Beck, A.; Chen, W. Advanced assessment of the physicochemical characteristics of Remicade® and Inflectra® by sensitive LC/MS techniques. MAbs 2016, 8, 1021–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lee, C.; Jeong, M.; Lee, J.J.; Seo, S.; Cho, S.C.; Zhang, W.; Jaquez, O. Glycosylation profile and biological activity of Remicade® compared with Flixabi® and Remsima®. MAbs 2017, 9, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgetti, J.; D’Atri, V.; Canonge, J.; Lechner, A.; Guillarme, D.; Colas, O.; Wagner-Rousset, E.; Beck, A.; Leize-Wagner, E.; François, Y.N. Monoclonal antibody N-glycosylation profiling using capillary electrophoresis—Mass spectrometry: Assessment and method validation. Talanta 2018, 178, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuhrer, M.; Stam, J.C.; van de Geijn, F.E.; Koeleman, C.A.M.; Verrips, C.T.; Dolhain, R.J.E.M.; Hokke, C.G.; Deelder, A.M. Glycosylation profiling of immunoglobulin G (IgG) subclasses from human serum. Proteomics 2007, 7, 4070–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielson, J.P.; Weiss, W.F., 4th. Technical decision-making with higher order structure data: Starting a new dialogue. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, W.F., 4th; Gabrielson, J.P.; Al-Azzam, W.; Chen, G.; Davis, D.L.; Das, T.K.; Hayes, D.B.; Houde, D.; Singh, S.K. Technical Decision Making with Higher Order Structure Data: Perspectives on Higher Order Structure Characterization from the Biopharmaceutical Industry. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 3465–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, T.; Patchett, M.L.; Norris, G.E.; Lott, J.S. Using secretion to solve a solubility problem: High-yield expression in Escherichia coli and purification of the bacterial glycoamidase PNGase F. Protein Expr. Purif. 2002, 98, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisa, J.M.A. Avaliação do Padrão de Glicosilação de um Anticorpo Monoclonal Produzido por Células CHO. Master’s Thesis, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Toprani, V.M.; Joshi, S.B.; Kueltzo, L.A.; Schwartz, R.M.; Middaugh, C.R.; Volkin, D.B. A micro-polyethylene glycol precipitation assay as a relative solubility screening tool for monoclonal antibody design and formulation development. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2319–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middaugh, C.R.; Tisel, W.A.; Haire, R.N.; Rosenberg, A. Determination of the apparent protein solutions thermodynamic activities. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leoz, M.L.A.; Duewer, D.L.; Fung, A.; Liu, L.; Yau, H.K.; Potter, O.; Staples, G.O.; Furuki, K.; Frenkel, R.; Hu, Y.; et al. NIST Interlaboratory study on glycosylation analysis of monoclonal antibodies: Comparison of results from diverse analytical methods. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2020, 19, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Tm 1 (°C) | Tm 2 (°C) | Tm 3 (°C) | Tonset (°C) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical Method/pH | Innovator | Biosimilar Candidate | p-Value | Innovator | Biosimilar Candidate | p-Value | Innovator | Biosimilar Candidate | p-Value | Innovator | Biosimilar Candidate | p-Value |
| CD | ||||||||||||
| pH 3.5 | 52.63 ± 0.89 | 53.82 ± 1.16 | 0.3688 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 4.5 | 67.01 ± 1.10 | 66.51 ± 0.11 | 0.5879 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 5.5 | 66.23 ± 0.35 | 66.80 ± 0.81 | 0.4574 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 6.5 | 66.86 ± 0.37 | 67.12 ± 0.35 | 0.5453 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 7.5 | 69.13 ± 0.00 | 69.00 ± 0.72 | 0.8283 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Intrinsic FL | ||||||||||||
| pH 3.5 | 51.58 ± 0.30 | 52.42 ± 0.11 | 0.0653 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 4.5 | 62.60 ± 0.39 | 64.12 ± 0.20 | 0.0391 * | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 5.5 | 66.47 ± 0.19 | 68.56 ± 0.20 | 0.0086 * | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 6.5 | 67.87 ± 0.21 | 67.79 ± 0.11 | 0.6803 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 7.5 | 67.38 ± 0.09 | 67.79 ± 0.11 | 0.0552 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Extrinsic FL | ||||||||||||
| pH 3.5 | 34.87 ± 1.29 | 36.81 ± 0.00 | 0.1673 | 51.44 ± 1.60 | 51.44 ± 1.52 | 1.0000 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 4.5 | 59.48 ± 4.64 | 56.84 ± 1.52 | 0.5844 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 5.5 | 66.17 ± 0.07 | 66.17 ± 0.07 | 1.0000 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 6.5 | 67.41 ± 2.61 | 68.03 ± 2.52 | 0.8315 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 7.5 | 67.49 ± 2.56 | 66.72 ± 1.32 | 0.7417 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| DSC | ||||||||||||
| pH 3.5 | 36.63 ± 0.47 | 37.45 ± 0.08 | 0.1355 | 54.17 ± 0.59 | 54.27 ± 0.04 | 0.8333 | 59.13 ± 0.21 | 59.33 ± 0.08 | 0.3352 | 24.85 ± 0.58 | 26.69 ± 0.06 | 0.0467 * |
| pH 4.5 | 59.16 ± 0.08 | 59.04 ± 0.01 | 0.1699 | 66.68 ± 0.02 | 66.62 ± 0.03 | 0.1429 | 74.26 ± 0.05 | 74.08 ± 0.01 | 0.0379 * | 51.44 ± 2.23 | 51.90 ± 0.28 | 0.7995 |
| pH 5.5 | 68.57 ± 0.02 | 68.67 ± 0.01 | 0.0241 * | 77.74 ± 0.04 | 77.57 ± 0.02 | 0.0329* | NA | NA | NA | 59.99 ± 0.39 | 61.14 ± 0.29 | 0.0789 |
| pH 6.5 | 69.45 ± 0.12 | 69.56 ± 0.01 | 0.3255 | 77.84 ± 0.01 | 77.81 ± 0.01 | 0.0955 | NA | NA | NA | 61.58 ± 0.25 | 61.44 ± 0.07 | 0.5254 |
| pH 7.5 | 69.26 ± 0.01 | 69.50 ± 0.01 | 0.0017 | 77.58 ± 0.03 | 77.56 ± 0.06 | 0.7143 | NA | NA | NA | 61.80 ± 0.30 | 61.75 ± 0.14 | 0.8507 |
| DLS | ||||||||||||
| pH 3.5 | 78.83 ± 0.88 | 79.62 ± 0.09 | 0.3339 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 4.5 | 73.95 ± 0.86 | 73.10 ± 0.33 | 0.3218 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 5.5 | 73.83 ± 1.05 | 72.16 ± 1.93 | 0.3949 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 6.5 | 70.66 ± 0.39 | 70.16 ± 2.73 | 0.8216 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| pH 7.5 | 74.57 ± 2.41 | 74.47 ± 0.00 | 0.9585 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Error Spectral Difference (ESD) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank Position | Biophysical Assay | pH 3.5 | pH 4.5 | pH 5.5 | pH 6.5 | pH 7.5 | Average |
| 1 | Dynamic Light Scattering | 4.8 | 251.2 | 48.1 | 7.5 | 387.2 | 139.8 |
| 2 | MSM Intrinsic Trp Fluorescence | 22.8 | 8.0 | 7.5 | 4.7 | 7.4 | 10.1 |
| 3 | Circular Dichroism | 5.2 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 2.1 |
| 4 | Differential Scanning Calorimetry | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.3 |
| 5 | Extrinsic SYPRO Orange Fluorescence | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cruz, T.A.; Larson, N.R.; Wei, Y.; Subelzu, N.; Wu, Y.; Schöneich, C.; Castilho, L.R.; Middaugh, C.R. Characterization of Critical Quality Attributes of an Anti-PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibody. Biologics 2024, 4, 294-313. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics4030019
Cruz TA, Larson NR, Wei Y, Subelzu N, Wu Y, Schöneich C, Castilho LR, Middaugh CR. Characterization of Critical Quality Attributes of an Anti-PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibody. Biologics. 2024; 4(3):294-313. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics4030019
Chicago/Turabian StyleCruz, Thayana A., Nicholas R. Larson, Yangjie Wei, Natalia Subelzu, Yaqi Wu, Christian Schöneich, Leda R. Castilho, and Charles Russell Middaugh. 2024. "Characterization of Critical Quality Attributes of an Anti-PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibody" Biologics 4, no. 3: 294-313. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics4030019
APA StyleCruz, T. A., Larson, N. R., Wei, Y., Subelzu, N., Wu, Y., Schöneich, C., Castilho, L. R., & Middaugh, C. R. (2024). Characterization of Critical Quality Attributes of an Anti-PCSK9 Monoclonal Antibody. Biologics, 4(3), 294-313. https://doi.org/10.3390/biologics4030019







