Stochastic Models Applied to the Forecasting and Management of Residual Woody Forest Biomass: Approaches, Challenges, and Practical Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bastos, T.; Teixeira, L.C.; Nunes, L.J. Forest 4.0: Technologies and digitalization to create the residual biomass supply chain of the future. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 467, 143041. [Google Scholar]
- Ezejiofor, T.I.N.; Enebaku, U.E.; Ogueke, C. Waste to wealth-value recovery from agro-food processing wastes using biotechnology: A review. Br. Biotechnol. J. 2014, 4, 418–481. [Google Scholar]
- Garvie, L.C.; Roxburgh, S.H.; Ximenes, F.A. Greenhouse gas emission offsets of forest residues for bioenergy in Queensland, Australia. Forests 2021, 12, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casau, M.; Dias, M.F.; Matias, J.C.; Nunes, L.J. Residual biomass: A comprehensive review on the importance, uses and potential in a circular bioeconomy approach. Resources 2022, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivello, V.R.; Vieira, I.; Christianini, A.V.; Ribeiro, D.B.; da Silva Menezes, L.; Berlinck, C.N.; Melo, F.P.; Marengo, J.A.; Tornquist, C.G.; Tomas, W.M. Understanding Brazil’s catastrophic fires: Causes, consequences and policy needed to prevent future tragedies. Perspect. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 19, 233–255. [Google Scholar]
- Agarwal, F.; Chakraborty, I.; Banerjee, S. Impact of Forest Fire on Climate Change. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Manag. (IJAEM) 2024, 6, 391–398. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, P.; Thakur, N. Sustainable farming practices and soil health: A pathway to achieving SDGs and future prospects. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5, 250. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, R.; Zinda, J.A.; Ke, S. Designating tree crops as forest: Land competition and livelihood effects mediate tree crops impact on natural forest cover in south China. Land Use Policy 2020, 96, 104702. [Google Scholar]
- Saravanakumar, A.; Vijayakumar, P.; Hoang, A.T.; Kwon, E.E.; Chen, W.-H. Thermochemical conversion of large-size woody biomass for carbon neutrality: Principles, applications, and issues. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 370, 128562. [Google Scholar]
- Titus, B.D.; Brown, K.; Helmisaari, H.-S.; Vanguelova, E.; Stupak, I.; Evans, A.; Clarke, N.; Guidi, C.; Bruckman, V.J.; Varnagiryte-Kabasinskiene, I. Sustainable forest biomass: A review of current residue harvesting guidelines. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2021, 11, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Zahraee, S.M.; Shiwakoti, N.; Stasinopoulos, P. Biomass supply chain environmental and socio-economic analysis: 40-Years comprehensive review of methods, decision issues, sustainability challenges, and the way forward. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 142, 105777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, F.; Mafakheri, F.; Nasiri, F. Biomass supply chain resilience: Integrating demand and availability predictions into routing decisions using machine learning. Smart Sci. 2023, 11, 293–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moallemi, E.A.; Kwakkel, J.; de Haan, F.J.; Bryan, B.A. Exploratory modeling for analyzing coupled human-natural systems under uncertainty. Glob. Environ. Change 2020, 65, 102186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antar, M.; Lyu, D.; Nazari, M.; Shah, A.; Zhou, X.; Smith, D.L. Biomass for a sustainable bioeconomy: An overview of world biomass production and utilization. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.L.Y.; How, B.S.; Teng, S.Y.; Lam, H.L.; Lim, C.H.; Rhamdhani, M.A.; Sunarso, J. Stochastic techno-economic evaluation model for biomass supply chain: A biomass gasification case study with supply chain uncertainties. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 152, 111644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores Hernández, U.; Jaeger, D.; Samperio, J.I. Modeling forest woody biomass availability for energy use based on short-term forecasting scenarios. Waste Biomass Valor. 2020, 11, 2137–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, D.N.; Meejaroen, P.; Nananukul, N. Multi-objective models for biomass supply chain planning with economic and carbon footprint consideration. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 6833–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noa-Yarasca, E.; Osorio Leyton, J.M.; Angerer, J.P. Extending multi-output methods for long-term aboveground biomass time series forecasting using convolutional neural networks. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2024, 6, 1633–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.J.; Silva, S. Optimization of the Residual Biomass Supply Chain: Process Characterization and Cost Analysis. Logistics 2023, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Anderson, N. Machine learning applications in forest and biomass supply chain management: A review. Int. J. For. Eng. 2024, 35, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Beer, M.; Cogan, S.; Mottershead, J. Stochastic model updating with uncertainty quantification: An overview and tutorial. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2023, 204, 110784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaria, A.; Ismail, F.B.; Lipu, M.H.; Hannan, M.A. Uncertainty models for stochastic optimization in renewable energy applications. Renew. Energy 2020, 145, 1543–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, F.R.; Csala, D. A seasonal autoregressive integrated moving average with exogenous factors (SARIMAX) forecasting model-based time series approach. Inventions 2022, 7, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulay, E.; Sen, M.; Akgun, O.B. Forecasting electricity production from various energy sources in Türkiye: A predictive analysis of time series, deep learning, and hybrid models. Energy 2024, 286, 129566. [Google Scholar]
- Si, X.-S.; Wang, W.; Hu, C.-H.; Zhou, D.-H. Remaining useful life estimation–a review on the statistical data driven approaches. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2011, 213, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, J. Modeling Risk: Applying Monte Carlo Simulation, Real Options Analysis, Forecasting, and Optimization Techniques; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; Volume 347. [Google Scholar]
- Lindner, M.; Maroschek, M.; Netherer, S.; Kremer, A.; Barbati, A.; Garcia-Gonzalo, J.; Seidl, R.; Delzon, S.; Corona, P.; Kolström, M. Climate change impacts, adaptive capacity, and vulnerability of European forest ecosystems. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 259, 698–709. [Google Scholar]
- Dale, V.H.; Joyce, L.A.; McNulty, S.; Neilson, R.P.; Ayres, M.P.; Flannigan, M.D.; Hanson, P.J.; Irland, L.C.; Lugo, A.E.; Peterson, C.J. Climate change and forest disturbances: Climate change can affect forests by altering the frequency, intensity, duration, and timing of fire, drought, introduced species, insect and pathogen outbreaks, hurricanes, windstorms, ice storms, or landslides. BioScience 2001, 51, 723–734. [Google Scholar]
- Khashei, M.; Bijari, M. A novel hybridization of artificial neural networks and ARIMA models for time series forecasting. Appl. Soft Comput. 2011, 11, 2664–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, E.M.; Santo, F.D.E.; Wulder, M.A.; Júnior, F.W.A.; Carvalho, M.C.; Mello, C.R.; Mello, J.M.; Shimabukuro, Y.E.; Terra, M.C.N.S.; Carvalho, L.M.T. Pre-stratified modelling plus residuals kriging reduces the uncertainty of aboveground biomass estimation and spatial distribution in heterogeneous savannas and forest environments. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 445, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, H.; Aranha, J.; Lopes, D.; Cohen, W.B. Estimation of crown biomass of Pinus pinaster stands and shrubland above-ground biomass using forest inventory data, remotely sensed imagery and spatial prediction models. Ecol. Model. 2012, 226, 22–35. [Google Scholar]
- Shabani, N.; Akhtari, S.; Sowlati, T. Value chain optimization of forest biomass for bioenergy production: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 23, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirkouei, A.; Haapala, K.R.; Sessions, J.; Murthy, G.S. A review and future directions in techno-economic modeling and optimization of upstream forest biomass to bio-oil supply chains. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.R.; Foster, D.R.; Scheller, R.; Kittredge, D. The influence of land use and climate change on forest biomass and composition in Massachusetts, USA. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 2425–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulo, H.; Azcue, X.; Barbosa-Póvoa, A.P.; Relvas, S. Supply chain optimization of residual forestry biomass for bioenergy production: The case study of Portugal. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 83, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, T.; Mutanga, O.; Adam, E.; Ismail, R. Intra-and-inter species biomass prediction in a plantation forest: Testing the utility of high spatial resolution spaceborne multispectral rapideye sensor and advanced machine learning algorithms. Sensors 2014, 14, 15348–15370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, H.; Pishvaee, M.S.; Moini, A. Biomass supply chain network design: An optimization-oriented review and analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 94, 972–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosofske, K.D.; Froese, R.E.; Falkowski, M.J.; Banskota, A. A review of methods for mapping and prediction of inventory attributes for operational forest management. For. Sci. 2014, 60, 733–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elavarasan, D.; Vincent, D.R.; Sharma, V.; Zomaya, A.Y.; Srinivasan, K. Forecasting yield by integrating agrarian factors and machine learning models: A survey. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 155, 257–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ummenhofer, C.C.; Meehl, G.A. Extreme weather and climate events with ecological relevance: A review. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, A.; Hong, T. Vulnerability and resilience of urban energy ecosystems to extreme climate events: A systematic review and perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 173, 113038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, A. Forest damage and forest supply chains: A literature review and reflections. Int. J. For. Eng. 2023, 34, 330–339. [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez Camargo, L.; Stoeglehner, G. Spatiotemporal modelling for integrated spatial and energy planning. Energy Sustain. Soc. 2018, 8, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Goodchild, M.F. Geographic information science and systems for environmental management. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2003, 28, 493–519. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelmajeed, A.Y.A.; Juszczak, R. Challenges and Limitations of Remote Sensing Applications in Northern Peatlands: Present and Future Prospects. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Han, L.; Liu, L.; Bai, C.; Ao, J.; Hu, H.; Li, R.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Wei, Y. Advancements and Perspective in the Quantitative Assessment of Soil Salinity Utilizing Remote Sensing and Machine Learning Algorithms: A Review. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokityanskiy, D.; Benítez, P.C.; Kraxner, F.; McCallum, I.; Obersteiner, M.; Rametsteiner, E.; Yamagata, Y. Geographically explicit global modeling of land-use change, carbon sequestration, and biomass supply. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2007, 74, 1057–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Macías-Escrivá, F.D.; Haber, R.; Del Toro, R.; Hernandez, V. Self-adaptive systems: A survey of current approaches, research challenges and applications. Expert Syst. Appl. 2013, 40, 7267–7279. [Google Scholar]
- Luthra, S.; Sharma, M.; Kumar, A.; Joshi, S.; Collins, E.; Mangla, S. Overcoming barriers to cross-sector collaboration in circular supply chain management: A multi-method approach. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2022, 157, 102582. [Google Scholar]
- Merghadi, A.; Yunus, A.P.; Dou, J.; Whiteley, J.; ThaiPham, B.; Bui, D.T.; Avtar, R.; Abderrahmane, B. Machine learning methods for landslide susceptibility studies: A comparative overview of algorithm performance. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2020, 207, 103225. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.S.-H.; Yao, Y. Machine learning for sustainable development and applications of biomass and biomass-derived carbonaceous materials in water and agricultural systems: A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 190, 106847. [Google Scholar]
- Valipour, M.; Mafakheri, F.; Gagnon, B.; Prinz, R.; Bergström, D.; Brown, M.; Wang, C. Integrating bio-hubs in biomass supply chains: Insights from a systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 467, 142930. [Google Scholar]
- Ciesielski, P.N.; Pecha, M.B.; Lattanzi, A.M.; Bharadwaj, V.S.; Crowley, M.F.; Bu, L.; Vermaas, J.V.; Steirer, K.X.; Crowley, M.F. Advances in multiscale modeling of lignocellulosic biomass. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 3512–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.; Causer, T.; Ciolkosz, D. Biomass for energy: A review on supply chain management models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 120, 109658. [Google Scholar]
- Wassie, S.B. Natural resource degradation tendencies in Ethiopia: A review. Environ. Syst. Res. 2020, 9, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Arrogante-Funes, F.; Mouillot, F.; Moreira, B.; Aguado, I.; Chuvieco, E. Mapping and assessment of ecological vulnerability to wildfires in Europe. Fire Ecol. 2024, 20, 98. [Google Scholar]
- Rijal, B.; Gautam, S.H.; LeBel, L. The impact of forest disturbances on residual biomass supply: A long-term forest level analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119278. [Google Scholar]
- Ngan, S.L.; How, B.S.; Teng, S.Y.; Leong, W.D.; Loy, A.C.M.; Yatim, P.; Promentilla, M.A.B.; Lam, H.L. A hybrid approach to prioritize risk mitigation strategies for biomass polygeneration systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 121, 109679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potrč, S.; Čuček, L.; Martin, M.; Kravanja, Z. Sustainable renewable energy supply networks optimization–The gradual transition to a renewable energy system within the European Union by 2050. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 146, 111186. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Christensen, T.; Panoutsou, C. Policy review for biomass value chains in the European bioeconomy. Glob. Transit. 2021, 3, 13–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramoniam, R.; Huisingh, D.; Sundin, E.; Chinnam, R.B.; Bayulken, B.; Gaur, J.; Govindan, K.; Viegas, C. Special issue editorial: Supply chain planning & management challenges and opportunities driven by climate change and other disruptions and how to accelerate societal transition to equitable, sustainable and livable societies. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 481, 144129. [Google Scholar]
- Hiloidhari, M.; Sharno, M.A.; Baruah, D.; Bezbaruah, A.N. Green and sustainable biomass supply chain for environmental, social and economic benefits. Biomass Bioenergy 2023, 175, 106893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.; Piazzullo, D.; Di Battista, D.; De Vita, A. Sustainability assessment of the whole biomass-to-energy chain of a combined heat and power plant based on biomass gasification: Biomass supply chain management and life cycle assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshilalu, A.Z. Sustainability meets scalability: Transforming energy infrastructure projects into economic catalysts through supply chain innovation. Int. J. Res. Publ. Rev. 2024, 5, 762–779. [Google Scholar]
- Salehi, S.; Mehrjerdi, Y.Z.; Sadegheih, A.; Hosseini-Nasab, H. Designing a resilient and sustainable biomass supply chain network through the optimization approach under uncertainty and the disruption. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 359, 131741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Jain, R.; Brennan-Tonetta, P.; Swartz, E.; Silver, D.; Paolini, J.; Mamonov, S.; Hill, C. Impact of big data and artificial intelligence on industry: Developing a workforce roadmap for a data driven economy. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2021, 22, 197–217. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, M.S.; Hwang, S.-J. Developing sustainable, resilient, and responsive biofuel production and distribution management system: A neutrosophic fuzzy optimization approach based on artificial intelligence and geographic information systems. Appl. Energy 2024, 372, 123683. [Google Scholar]


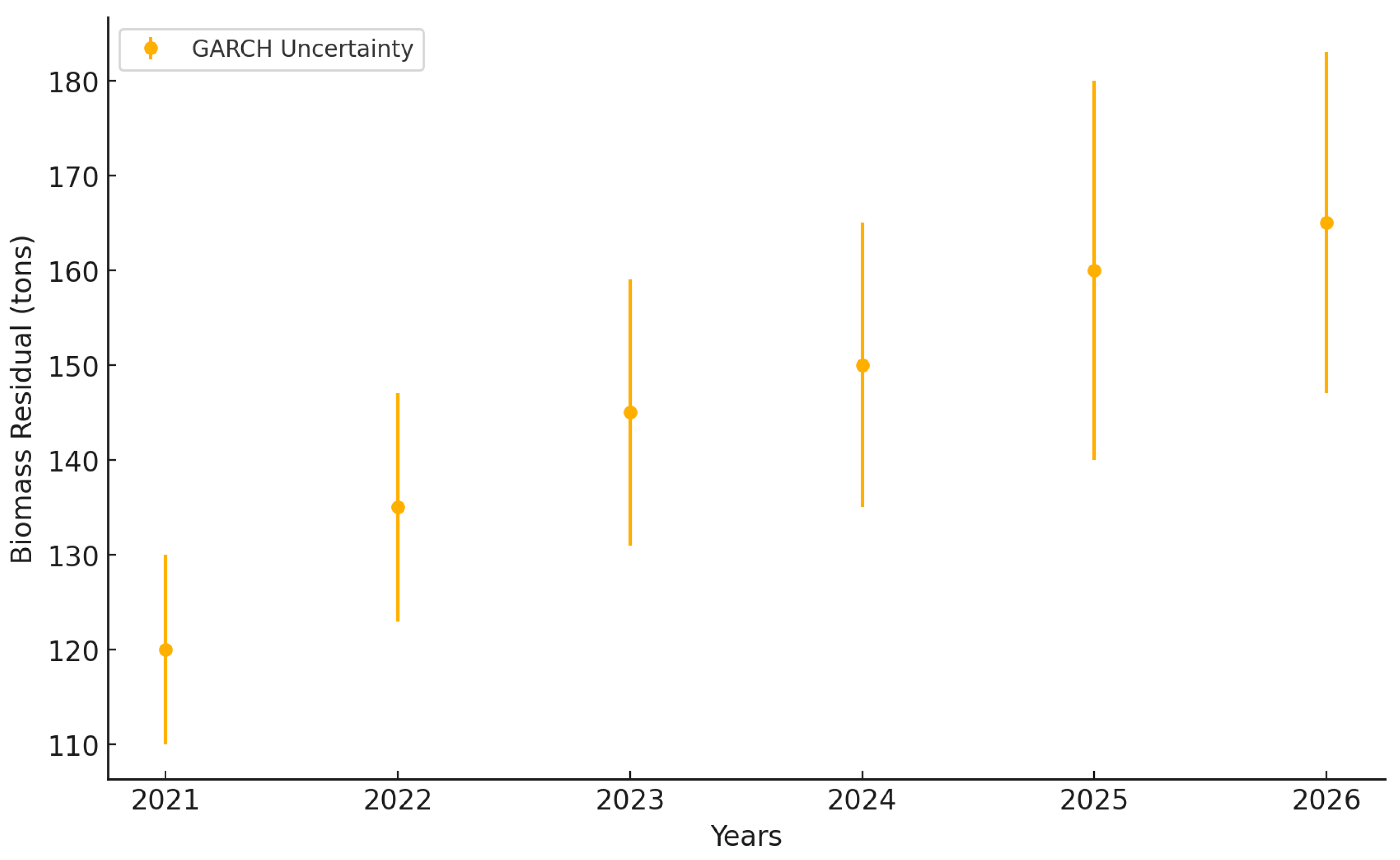
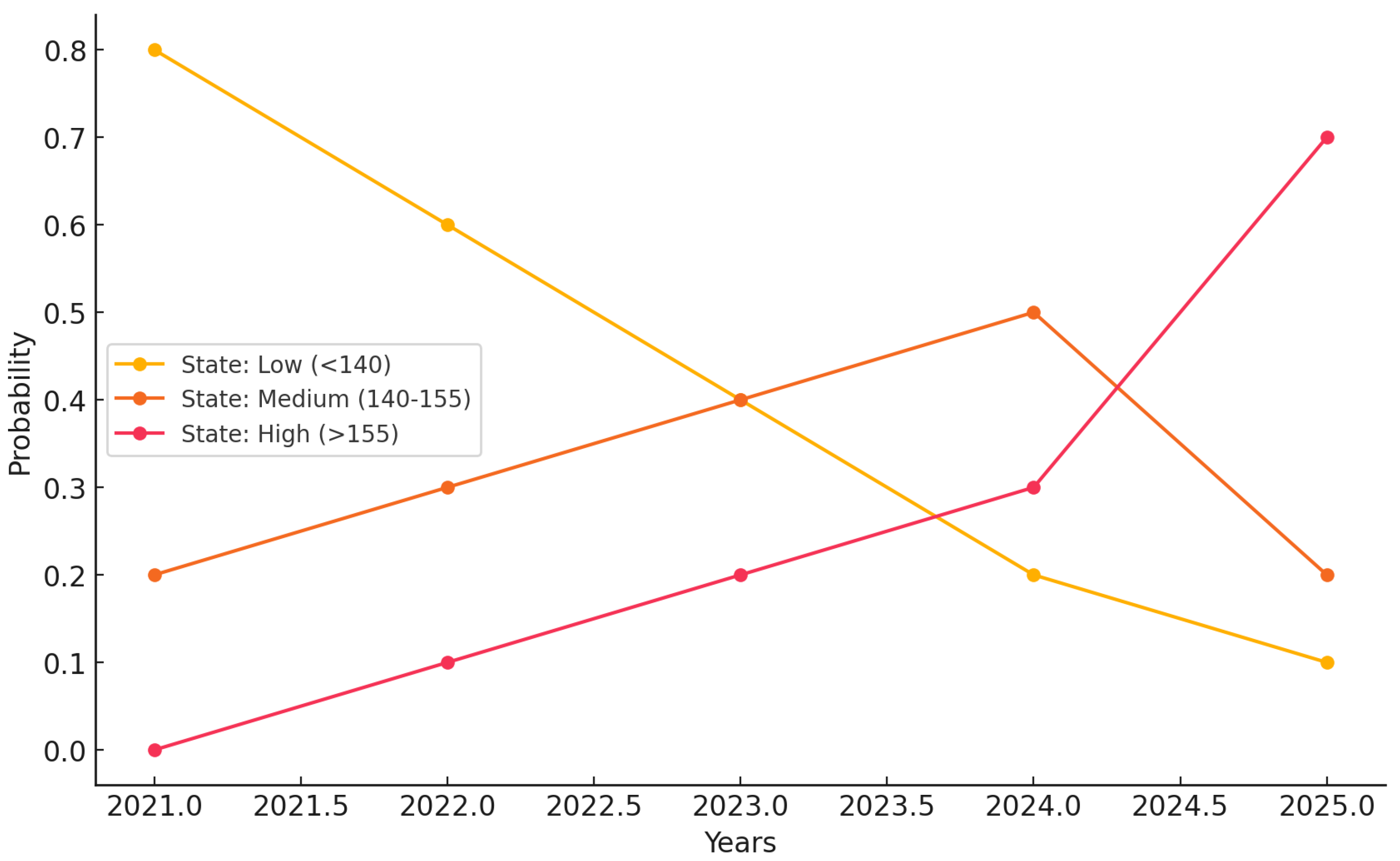


| Model | Strengths | Weaknesses | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARIMA | Captures trends and seasonality with high accuracy. | Limited in capturing nonlinear dynamics. | Forecasting residuals with regular seasonal patterns. |
| ARIMAX | Integrates exogenous variables for greater flexibility. | Highly dependent on consistent exogenous data. | Scenarios strongly influenced by external variables. |
| Markov Chains | Useful for discrete events and probabilistic forecasting. | Limited performance for continuous data. | Prediction of events such as harvests and interruptions. |
| Monte Carlo Simulation | Models complex uncertainties and generates multiple scenarios. | Demands high computational resources. | Analysis of climatic and economic uncertainties. |
| Hybrid Models | Combines machine learning with statistical techniques, suitable for high variability. | Requires large amounts of data and specific configurations. | Complex scenarios with high variability. |
| Model | RMSE (Tons) | MAPE (%) | R2 | Reliability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARIMA | 6.2 | 5.3 | 0.92 | High |
| GARCH | 7.8 | 6.5 | 0.88 | Moderate |
| State Transition | 8.9 | 7.2 | 0.85 | Moderate |
| Monte Carlo Simulation | 5.4 | 4.7 | 0.94 | High |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nunes, L.J.R. Stochastic Models Applied to the Forecasting and Management of Residual Woody Forest Biomass: Approaches, Challenges, and Practical Applications. Biomass 2025, 5, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5020020
Nunes LJR. Stochastic Models Applied to the Forecasting and Management of Residual Woody Forest Biomass: Approaches, Challenges, and Practical Applications. Biomass. 2025; 5(2):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleNunes, Leonel J. R. 2025. "Stochastic Models Applied to the Forecasting and Management of Residual Woody Forest Biomass: Approaches, Challenges, and Practical Applications" Biomass 5, no. 2: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5020020
APA StyleNunes, L. J. R. (2025). Stochastic Models Applied to the Forecasting and Management of Residual Woody Forest Biomass: Approaches, Challenges, and Practical Applications. Biomass, 5(2), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass5020020






