Assessment of Mathematical Approaches for the Estimation and Comparison of Efficiency in qPCR Assays for a Prokaryotic Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Biological Model and Experimental Analyses
2.2. Estimation of qPCR Efficiency Using Different Mathematical Models
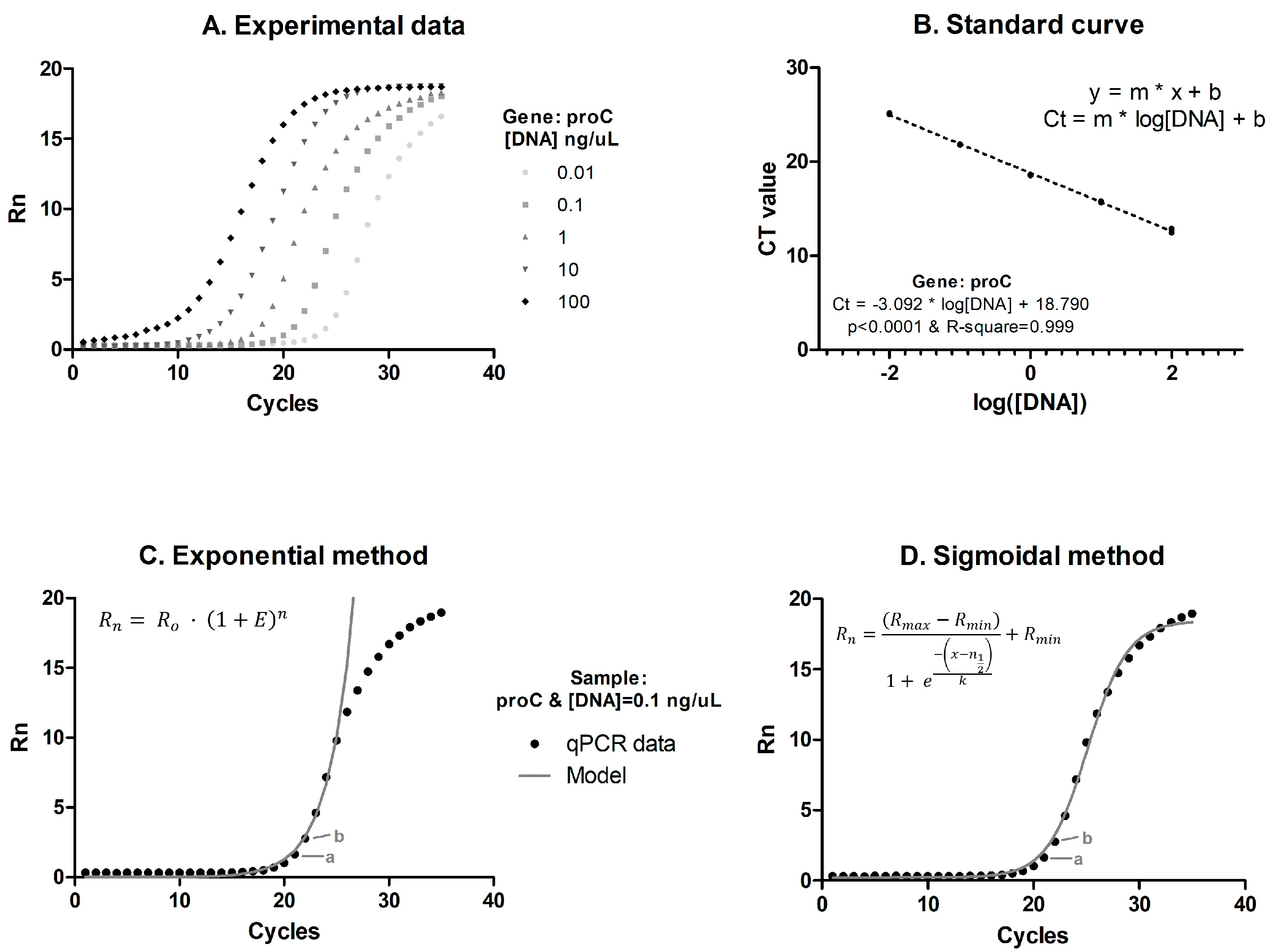
2.2.1. Calibration or Standard Curves
2.2.2. Individual-Curve-Based Approaches (Exponential and Sigmoidal Methods)
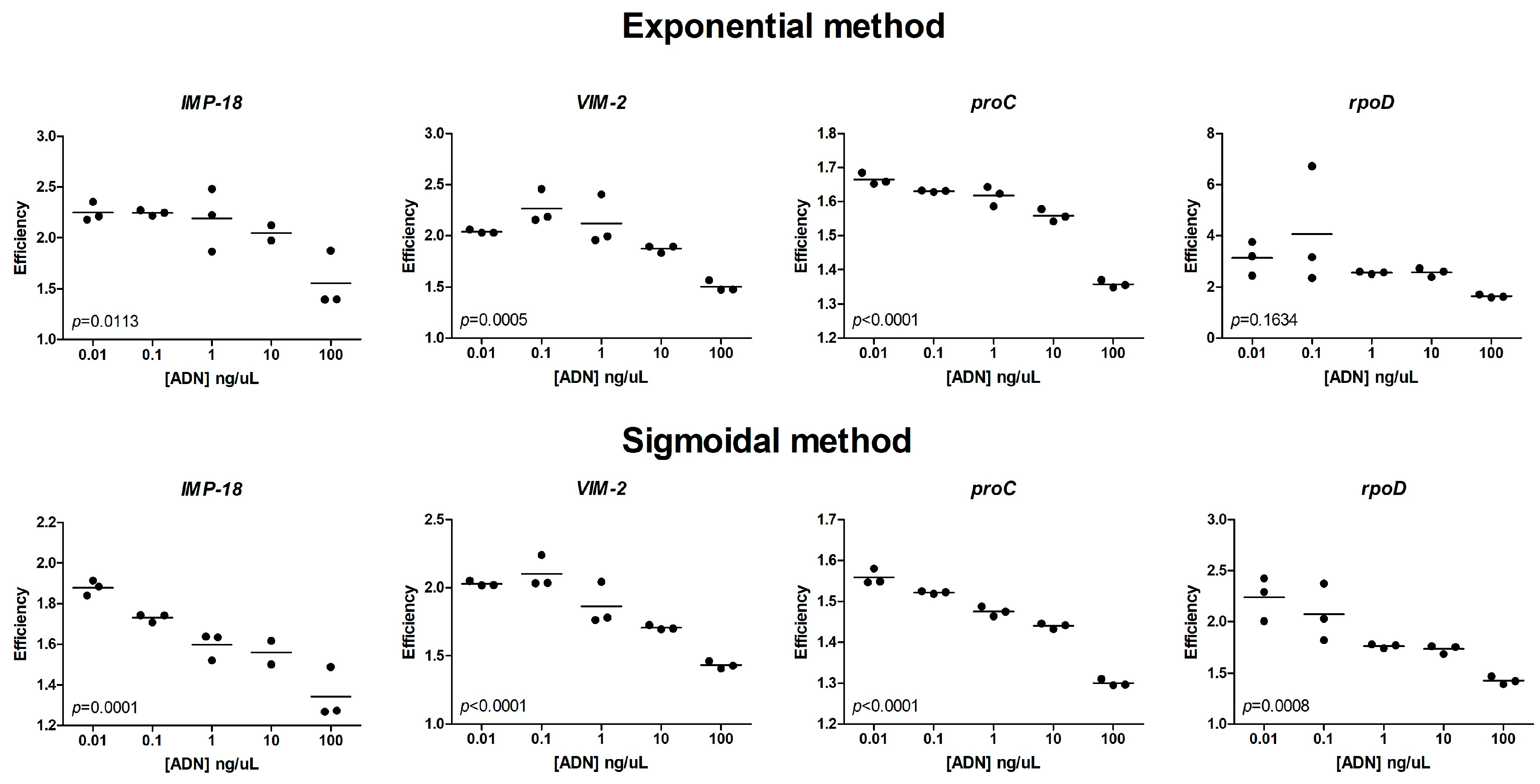
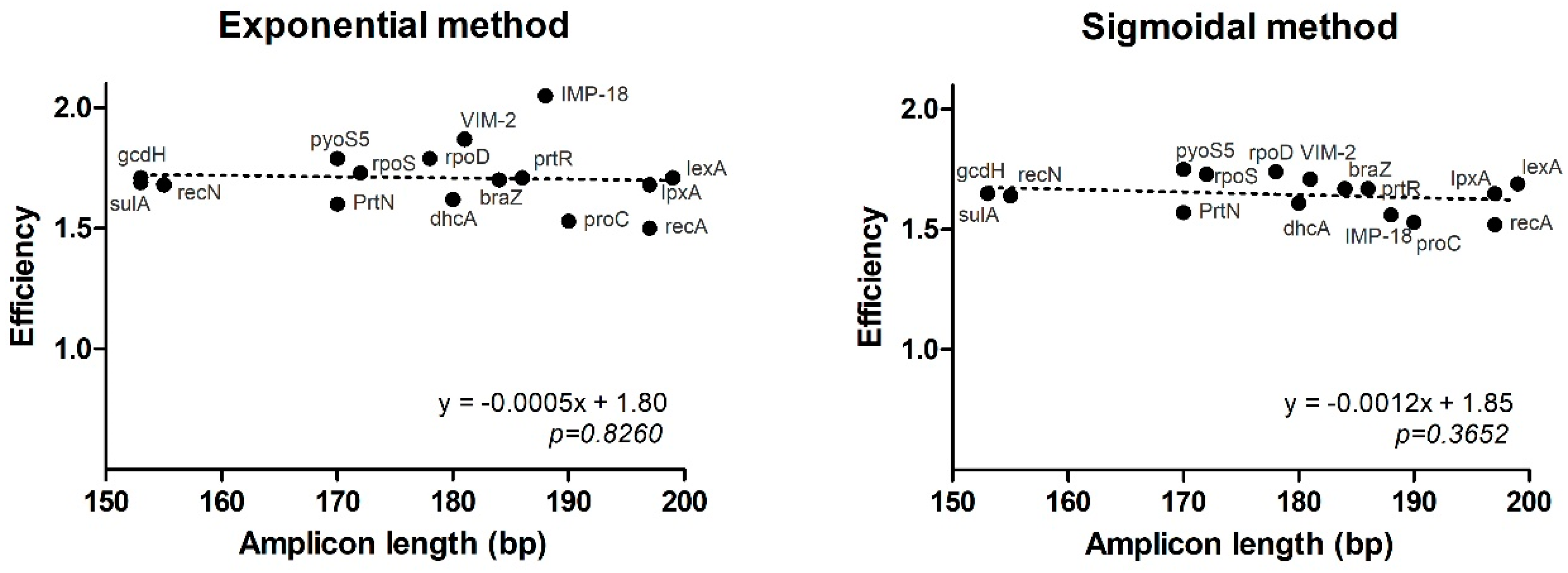
2.3. Comparison of Mathematical Approaches for the Estimation of qPCR Efficiency
2.4. Fold Change between Points of the Standard Curve
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dymond, J.S. Explanatory Chapter: Quantitative PCR. Methods Enzymol. 2013, 529, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panina, Y.; Germond, A.; David, B.G.; Watanabe, T.M. Pairwise efficiency: A new mathematical approach to qPCR data analysis increases the precision of the calibration curve assay. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcher, C.; Malinge, M.C.; Picat, C.; Grandchamp, B. A simplified method for determination of specific DNA or RNA copy number using quantitative PCR and an automatic DNA sequencer. Biotechniques 1992, 13, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patrone, P.N.; Romsos, E.L.; Cleveland, M.H.; Vallone, P.M.; Kearsley, A.J. Affine analysis for quantitative PCR measurements. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 7977–7988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruijter, J.M.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Zhao, S.; Spiess, A.N.; Boggy, G.; Blom, J.; Rutledge, R.G.; Sisti, D.; Lievens, A.; De Preter, K.; et al. Evaluation of qPCR curve analysis methods for reliable biomarker discovery: Bias, resolution, precision, and implications. Methods 2013, 59, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Shang, S.; Meng, S.; Lin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Evaluation validation of a qPCR curve analysis method and conventional approaches. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svec, D.; Tichopad, A.; Novosadova, V.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Kubista, M. How good is a PCR efficiency estimate: Recommendations for precise and robust qPCR efficiency assessments. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2015, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutledge, R.G. Sigmoidal curve-fitting redefines quantitative real-time PCR with the prospective of developing automated high-throughput applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, e178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez Sánchez, P.A.; Rodríguez Fuerte, V.; Marín Montoya, M. A Sigmoidal Model for the interpretation of Quantitative PCR (QPCR) Experiments. Rev. Fac. De Cienc. Básicas 2012, 8, 244–253. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Saint, D.A. A new quantitative method of real time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay based on simulation of polymerase chain reaction kinetics. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 302, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. Relative quantification. In Real-Time PCR; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2006; pp. 63–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. Quantification strategies in real-time PCR. In Quantification Strategies in Real-Time PCR; Citeseer: Princetonm, HJ, USA, 2004; pp. 87–112. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X. An improvement of the 2^(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat. Bioinform. Biomath. 2013, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- VanGuilder, H.D.; Vrana, K.E.; Freeman, W.M. Twenty-five years of quantitative PCR for gene expression analysis. Biotechniques 2008, 44, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Mora, J.A.; García, F. Molecular Determinants of Antibiotic Resistance in the Costa Rican Pseudomonas aeruginosa AG1 by a Multi-omics Approach: A Review of 10 Years of Study. Phenomics 2021, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina Mora, J.A.; Montero-Manso, P.; García-Batán, R.; Campos-Sánchez, R.; Fernández, J.V.; García, F. A first perturbome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Identification of core genes related to multiple perturbations by a machine learning approach. Biosystems 2021, 205, 104411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Mora, J.A.; Chinchilla, D.; Chavarría, M.; Ulloa, A.; Campos-Sanchez, R.; Mora-Rodríguez, R.A.; Shi, L.; García, F. Transcriptomic determinants of the response of ST-111 Pseudomonas aeruginosa AG1 to ciprofloxacin identified by a top-down systems biology approach. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Mora, J.A.; Chinchilla-Montero, D.; García-Batán, R.; García, F. Genomic context of the two integrons of ST-111 Pseudomonas aeruginosa AG1: A VIM-2-carrying old-acquaintance and a novel IMP-18-carrying integron. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 89, 104740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Mora, J.-A.; Campos-Sánchez, R.; Rodríguez, C.; Shi, L.; García, F. High quality 3C de novo assembly and annotation of a multidrug resistant ST-111 Pseudomonas aeruginosa genome: Benchmark of hybrid and non-hybrid assemblers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savli, H.; Karadenizli, A.; Kolayli, F.; Gundes, S.; Ozbek, U.; Vahaboglu, H. Expression stability of six housekeeping genes: A proposal for resistance gene quantification studies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by real-time quantitative RT-PCR. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 52, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Cao, X.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Xie, H.; Shi, J.; Han, M.; Shen, H.; Liu, C. Housekeeping gene stability in Pesudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 under the pressure of commonly used antibiotics in molecular microbiology assays. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1140515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqarni, B.; Colley, B.; Klebensberger, J.; McDougald, D.; Rice, S.A. Expression stability of 13 housekeeping genes during carbon starvation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Microbiol. Methods 2016, 127, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Saint, D.A. Validation of a quantitative method for real time PCR kinetics. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 294, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakers, C.; Ruijter, J.M.; Lekanne Deprez, R.H.; Moorman, A.F.M. Assumption-free analysis of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) data. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 339, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogva, H.K.; Rudi, K. Potential influence of the first PCR cycles in real-time comparative gene quantifications. Biotechniques 2004, 37, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustin, S.A.; Benes, V.; Garson, J.A.; Hellemans, J.; Huggett, J.; Kubista, M.; Mueller, R.; Nolan, T.; Pfaffl, M.W.; Shipley, G.L.; et al. The MIQE Guidelines: Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments. Clin. Chem. 2009, 55, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conte, J.; Potoczniak, M.J.; Tobe, S.S. Using synthetic oligonucleotides as standards in probe-based qPCR. Biotechniques 2018, 64, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čikoš, Š.; Bukovská, A.; Koppel, J. Relative quantification of mRNA: Comparison of methods currently used for real-time PCR data analysis. BMC Mol. Biol. 2007, 8, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidstedt, M.; Rådström, P.; Hedman, J. PCR inhibition in qPCR, dPCR and MPS—Mechanisms and solutions. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2009–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, C.S.; Pienaar, E.; Termaat, J.R.; Whitney, S.E.; Louw, T.M.; Viljoen, H.J. Efficiency of the polymerase chain reaction. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 4996–5006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreedharan, S.P.; Kumar, A.; Giridhar, P. Primer design and amplification efficiencies are crucial for reliability of quantitative PCR studies of caffeine biosynthetic N-methyltransferases in coffee. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, W.; Byrne-Steele, M.; Wang, C.; Lu, S.; Clemmons, S.; Zahorchak, R.J.; Han, J. DNA polymerase preference determines PCR priming efficiency. BMC Biotechnol. 2014, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.Y.; Ugozzoli, L.; Pal, B.K.; Qian, J.; Wallace, R.B. The Effect of Temperature and Oligonucleotide Primer Length on the Specificity and Efficiency of Amplification by the Polymerase Chain Reaction. DNA Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mar, J.; Kimura, Y.; Schroder, K.; Irvine, K.M.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Hume, D.; Quackenbush, J. Data-driven normalization strategies for high-throughput quantitative RT-PCR. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Mora, J.A.; Campos-Sanchez, R.; Garcia, F. Gene Expression Dynamics Induced by Ciprofloxacin and Loss of Lexa Function in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Using Data Mining and Network Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Work Conference on Bioinspired Intelligence (IWOBI), San Carlos, Costa Rica, 18–20 July 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
| Gene | Concentration (uM) | Primer Name | Sequence 5′ → 3′ | Amplicon Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IMP-18 Imipenemase MBL | 1 | IMP-F | GAATAG(A/G)(A/G)TGGCTTAA(C/T)TCTC | 188 bp |
| IMP-R | CCAAAC(C/T)ACTA(G/C)GTTATC | |||
| VIM-2 Verona integron–encoded MBL | 1 | VIM2-F | CCGCGTCTATCATGGCTATT | 181 bp |
| VIM2-R | ATGAGACCATTGGACGGGTA | |||
| rpoD RNA polymerase sigma factor | 1 | rpoD-F | GGGCGAAGAAGGAAATGGTC | 178 pb |
| rpoD-R | CAGGTGGCGTAGGTGGAGAA | |||
| proC Pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase | 1 | proC-F | CAGGCCGGGCAGTTGCTGTC | 190 pb |
| proC-R | GGTCAGGCGCGAGGCTGTCT | |||
| gcdH Glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase | 1 | gcdH-F | ATGTGGATCACCAACAGCCC | 153 pb |
| gcdH-R | TCTCTTCCGGAACGAACACG | |||
| dhcA Dehydrocarnitine CoA transferase | 1 | gcdH-F | ATTCCCGAGAACCTGATCGC | 180 pb |
| gcdH-R | GTTCTCGCCGACATAGGAGG | |||
| braZ branched-chain AA transporter | 1 | braZ-F | TGCCTACGTGCAACATACCT | 184 pb |
| braZ-R | ACGATGAAGGAGAACCCTGC | |||
| PrtN Transcription regulatory protein | 0.1 | PrtN-F | GGAAAACTTCAGCAAGGCCC | 170 pb |
| PrtN-R | TCAGGATGCGATGCTGTCA | |||
| pyoS5 Pyocin S5 | 0.1 | pyoS5-F | GCCAGCCTGTACCAAGAGTT | 170 pb |
| pyoS5-R | ATTACCAGTGCGAACCCCAG | |||
| prtR HTH-type transcriptional regulator | 0.1 | prtR-F | CCGCTGTACAAGGAAGTGGA | 186 pb |
| prtR-R | ATGATCAGCGGTTCCATGCT | |||
| rpoS RNA polymerase sigma factor | 1 | rpoS-F | TGGTCAAGGAGCTCAACGTC | 172 pb |
| rpoS-R | GACGTCTACCGAAGTCACCC | |||
| lexA SOS repressor protein | 0.1 | lexA-F | TCCCGCCTTCTTCAATCCTC | 199 pb |
| lexA-R | GAAGCGTTTCACCGTGACCT | |||
| recA Recombinase A | 1 | recA-F | GAGATCGAAGGCGAGATGGG | 197 pb |
| recA-R | AGGCGTAGAACTTCAGTGCG | |||
| recN DNA repair protein RecN | 0.1 | recN-F | GTGGAAATGTGCAGCGAGAG | 155 pb |
| recN-R | TTGGGATCGGCATCGAAGTG | |||
| sulA Cell division inhibitor | 1 | sulA-F | GAGGAACCCGCTGCCTTTAG | 153 pb |
| sulA-R | AGCCATTCATGGGTCAGGC | |||
| lpxA Acetylglucosamine acyltransferase | 1 | lpxA-F | AAGCACAACCGCATCTACCA | 197 pb |
| lpxA-R | ATGTGCGCATAGGCCATGAT |
| GENE Conditions | Efficiency by Approach (Estimated by Amplification Rate) | Normalization by Mathematical Approach * | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene Type | Gene Name | Amplicon Size (bp) | [DNA] (ng/μL) | Ct | Standard Curve ** | Exponential Method | Sigmoidal Method | Condition for Normalization: Name and [DNA] | Used Efficiency for Normalization | CV | |||
| 2-delta-Ct | Standard Curve | Exponential Method | Sigmoidal Method | ||||||||||
| Target genes (gene of interest) *** | IMP-18 | 188 | 0.01 | 24.73 | 2.00 | 2.25 | 1.88 | proC-0.01 | 1.2924 | 1.2924 | 0.0007 | 0.0115 | 114.4 |
| 0.1 | 21.26 | 2.25 | 1.73 | proC-0.1 | 1.4948 | 1.4948 | 0.0015 | 0.0832 | 109.2 | ||||
| 1 | 17.92 | 2.19 | 1.60 | proC-1 | 1.5764 | 1.5764 | 0.0060 | 0.3107 | 95.5 | ||||
| 10 | 15.01 | 2.05 | 1.56 | proC-10 | 1.6320 | 1.6320 | 0.0228 | 0.3954 | 90.8 | ||||
| 100 | 12.64 | 1.55 | 1.34 | proC-100 | 1.0305 | 1.0305 | 0.1848 | 0.6731 | 54.9 | ||||
| VIM-2 | 181 | 0.01 | 26.17 | 1.90 | 2.04 | 2.03 | proC-0.01 | 0.4752 | 1.8191 | 0.0028 | 0.0006 | 149.6 | |
| 0.1 | 22.71 | 2.27 | 2.10 | proC-0.1 | 0.5459 | 1.7501 | 0.0004 | 0.0005 | 143.7 | ||||
| 1 | 19.02 | 2.12 | 1.86 | proC-1 | 0.7354 | 1.9509 | 0.0048 | 0.0100 | 135.8 | ||||
| 10 | 15.70 | 1.87 | 1.71 | proC-10 | 1.0116 | 2.2634 | 0.0563 | 0.0700 | 122.6 | ||||
| 100 | 12.90 | 1.50 | 1.43 | proC-100 | 0.8606 | 1.6678 | 0.2515 | 0.2705 | 87.4 | ||||
| rpoD | 178 | 0.01 | 24.96 | 2.00 | 2.43 | 2.24 | proC-0.01 | 1.10 | 1.10 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 115.45 | |
| 0.1 | 21.89 | 2.34 | 2.08 | proC-0.1 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.0004 | 0.0011 | 115.30 | ||||
| 1 | 18.30 | 2.55 | 1.76 | proC-1 | 1.2086 | 1.2086 | 0.0003 | 0.0426 | 111.5 | ||||
| 10 | 15.84 | 2.57 | 1.73 | proC-10 | 0.9181 | 0.9181 | 0.0003 | 0.0505 | 109.3 | ||||
| 100 | 12.70 | 1.63 | 1.43 | proC-100 | 0.9908 | 0.9908 | 0.0969 | 0.3081 | 77.6 | ||||
| braZ | 184 | 10 | 21.00 | - | 1.70 | 1.67 | proC-10 * | 0.0115 | - | 0.0070 | 0.0112 | 25.7 | |
| dhcA | 180 | 10 | 15.32 | - | 1.62 | 1.61 | 0.5905 | - | 0.3118 | 0.3374 | 37.3 | ||
| gcdH | 153 | 10 | 17.00 | - | 1.71 | 1.65 | 0.1836 | - | 0.0523 | 0.0977 | 60.0 | ||
| lpxA | 197 | 10 | 18.00 | - | 1.68 | 1.65 | 0.0918 | - | 0.0432 | 0.0615 | 37.5 | ||
| lexA | 199 | 10 | 19.02 | - | 1.71 | 1.69 | 0.0454 | - | 0.0183 | 0.0240 | 48.9 | ||
| PrtN | 170 | 10 | 23.03 | - | 1.60 | 1.57 | 0.0028 | - | 0.0093 | 0.0155 | 69.1 | ||
| prtR | 186 | 10 | 14.96 | - | 1.71 | 1.67 | 0.7552 | - | 0.1702 | 0.2295 | 83.6 | ||
| pyoS5 | 170 | 10 | 16.35 | - | 1.79 | 1.75 | 0.2888 | - | 0.0377 | 0.0555 | 110.0 | ||
| recA | 197 | 10 | 10.61 | - | 1.50 | 1.52 | 15.4015 | - | 6.5567 | 5.9561 | 56.8 | ||
| recN | 155 | 10 | 15.97 | - | 1.68 | 1.64 | 0.3750 | - | 0.1260 | 0.1927 | 55.8 | ||
| rpoD | 178 | 10 | 14.69 | - | 1.79 | 1.74 | 0.9086 | - | 0.0983 | 0.1544 | 116.9 | ||
| rpoS | 172 | 10 | 17.52 | - | 1.73 | 1.73 | 0.1278 | - | 0.0336 | 0.0354 | 82.1 | ||
| sulA | 153 | 10 | 15.97 | - | 1.69 | 1.65 | 0.3750 | - | 0.1193 | 0.1686 | 61.4 | ||
| Reference gene | proC | 190 | 0.01 | 25.10 | 2.00 | 1.66 | 1.56 | proC-0.01 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.0 |
| 0.1 | 21.84 | 1.63 | 1.52 | proC-0.1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.0 | ||||
| 1 | 18.58 | 1.62 | 1.48 | proC-1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.0 | ||||
| 10 | 15.72 | 1.56 | 1.44 | proC-10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.0 | ||||
| 100 | 12.68 | 1.36 | 1.30 | proC-100 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.0 | ||||
| proC * | 190 | 10 | 14.56 | - | 1.53 | 1.53 | proC-10 * | 1 | - | 1 | 1 | 0.0 | |
| Statistics by column | Min | 153 | 0.01 | 10.61 | 1.90 | 1.36 | 1.30 | - | 0.0028 | 0.9181 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0 |
| Max | 199 | 100 | 26.17 | 2.00 | 2.57 | 2.24 | - | 15.4015 | 2.2634 | 6.5567 | 5.9561 | 149.6 | |
| Mean | 178.3 | 17.2 | 17.93 | 1.98 | 1.85 | 1.67 | - | 1.2058 | 1.3331 | 0.4180 | 0.4579 | 72.9 | |
| Gen | [DNA] (ng/μL) | Ct Value | Efficiency Estimation | Fold Respect to the Lower Concentration 0.01 ng/μL | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical (Ideal) | Standard Curve | Exponential Method | Sigmoidal Method | Expected Fold | Ideal Efficiency | Standard Curve | Exponential Method | Sigmoidal Method | |||
| IMP-18 | 0.01 | 24.7 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.25 | 1.88 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.1 | 21.3 | 2.00 | 2.25 | 1.73 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 17 | 51 | ||
| 1 | 17.9 | 2.00 | 2.19 | 1.60 | 100 | 112 | 112 | 400 | 1343 | ||
| 10 | 15.0 | 2.00 | 2.05 | 1.56 | 1000 | 841 | 841 | 10,754 | 7617 | ||
| 100 | 12.6 | 2.00 | 1.55 | 1.34 | 10,000 | 4350 | 4350 | 1,927,012 | 142,801 | ||
| VIM-2 | 0.01 | 26.2 | 2.00 | 1.90 | 2.04 | 2.03 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.1 | 22.7 | 2.00 | 2.27 | 2.10 | 10 | 11 | 9 | 1 | 5 | ||
| 1 | 19.0 | 2.00 | 2.12 | 1.86 | 100 | 142 | 98 | 79 | 807 | ||
| 10 | 15.7 | 2.00 | 1.87 | 1.71 | 1000 | 1418 | 829 | 6667 | 25,206 | ||
| 100 | 12.9 | 2.00 | 1.50 | 1.43 | 10,000 | 9878 | 5001 | 657,580 | 1,072,315 | ||
| proC | 0.01 | 25.1 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 1.66 | 1.56 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.1 | 21.8 | 2.00 | 1.63 | 1.52 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 8 | 7 | ||
| 1 | 18.6 | 2.00 | 1.62 | 1.48 | 100 | 92 | 92 | 47 | 50 | ||
| 10 | 15.7 | 2.00 | 1.56 | 1.44 | 1000 | 666 | 666 | 336 | 222 | ||
| 100 | 12.7 | 2.00 | 1.36 | 1.30 | 10,000 | 5455 | 5455 | 7431 | 2449 | ||
| rpoD | 0.01 | 25.0 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.43 | 2.24 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 0.1 | 21.9 | 2.00 | 2.34 | 2.08 | 10 | 8 | 8 | 35 | 64 | ||
| 1 | 18.3 | 2.00 | 2.55 | 1.76 | 100 | 101 | 101 | 151 | 17,313 | ||
| 10 | 15.8 | 2.00 | 2.57 | 1.73 | 1000 | 556 | 556 | 1373 | 91,637 | ||
| 100 | 12.7 | 2.00 | 1.63 | 1.43 | 10,000 | 4916 | 4916 | 8,432,780 | 6,151,794 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Molina-Mora, J.A.; Sibaja-Amador, M.; Rivera-Montero, L.; Chacón-Arguedas, D.; Guzmán, C.; García, F. Assessment of Mathematical Approaches for the Estimation and Comparison of Efficiency in qPCR Assays for a Prokaryotic Model. DNA 2024, 4, 189-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna4030012
Molina-Mora JA, Sibaja-Amador M, Rivera-Montero L, Chacón-Arguedas D, Guzmán C, García F. Assessment of Mathematical Approaches for the Estimation and Comparison of Efficiency in qPCR Assays for a Prokaryotic Model. DNA. 2024; 4(3):189-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna4030012
Chicago/Turabian StyleMolina-Mora, Jose Arturo, Meriyeins Sibaja-Amador, Luis Rivera-Montero, Daniel Chacón-Arguedas, Caterina Guzmán, and Fernando García. 2024. "Assessment of Mathematical Approaches for the Estimation and Comparison of Efficiency in qPCR Assays for a Prokaryotic Model" DNA 4, no. 3: 189-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna4030012
APA StyleMolina-Mora, J. A., Sibaja-Amador, M., Rivera-Montero, L., Chacón-Arguedas, D., Guzmán, C., & García, F. (2024). Assessment of Mathematical Approaches for the Estimation and Comparison of Efficiency in qPCR Assays for a Prokaryotic Model. DNA, 4(3), 189-200. https://doi.org/10.3390/dna4030012






