Abstract
Textile materials from polyester fibres are sensitive to washing, especially at higher temperatures, due to their thermoplastic properties, hydrophobic nature and sensitivity to the alkaline medium. The issue of microplastic fibres’ (MFs’) release from polyester textiles is a topic that attracts the attention of researchers from different scientific fields, since microplastics are now among the serious environmental risks. In this study, two washing protocols, a standard and an innovative procedure, were presented, aiming to preserve the properties of polyester fabrics and reduce the pollution of washing effluents. The standard procedure followed HRN EN ISO 6330, while the innovative procedure was a modification of the standard that involved gradually cooling the bath before rinsing. The effects of these washing protocols were studied based on the physicochemical properties of the fabrics compared to the unwashed material, the composition of the effluents, and the filtrates after 10 cycles. The characterisation parameters of the fabrics, effluents and filtrates according to the standard and the innovative washing protocols showed differences in the observed parameters during the 10 washing cycles. The obtained results show the usefulness of the proposed concept of cooling the bath before rinsing in order to preserve the properties of polyester fabrics and reduce the load of washing effluents. Hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA) also confirmed differences in pH, conductivity and turbidity for effluents and filtrates from standard and innovative washing protocols.
1. Introduction
Within the synthetic fibre group, polyester is the most widely used in the world, with an estimated growth rate of 34% over the next decade [1,2].
Textiles made of polyester have certain advantages compared to other textiles, but also disadvantages that have been highlighted recently, especially due to their negative impact on the environment, which may be related in part to the effects of wearing them in dry and wet conditions, as well as alkalinity, mechanical stress and increased washing temperatures [3,4]. Alkaline hydrolysis of polyester by strong alkalis and high processing temperatures leads to irreversible changes in the polyester material and increases its reactivity and hydrophilic character [5,6,7].
A global problem in recent decades is the presence of microplastic particles in the environment (wastewater, air, soil and rocks). Microplastics are all plastic particles whose size/diameter is less than 5 mm and which can appear in various forms, such as spheres, fragments or fibres, and can be divided according to their origin into primary and secondary plastics [5,8,9].
Microplastic fibres (MFs) are released when synthetic fabrics are treated in horizontal and vertical household washing machines. According to the results of some studies, it is estimated that about 30% of these particles are released into the environment through the washing process of polyester textiles [10,11,12,13].
According to some estimates, 162 ± 52 MFs/g of clothing is released in one wash cycle, so about 6 million MFs are released annually from 5 kg of polyester clothing [9,13].
The release rate of these particles depends on the properties of the textiles and the stages of the technology and life cycle [14]. Quantification of released MF has been extensively studied, but the large number and variety of methods make it difficult to draw conclusions about the magnitude of the impact [9]. The estimation of MF loading during a washing cycle depends on the parameters of the washing process and on the structural parameters and properties of polyester textiles as a source of MF [15,16,17].
Preventive measures are needed to reduce the rate of released fibres, and one of the possible solutions to reducing the release of MFs from synthetic textiles is their structural properties’ functionalisation, e.g., with chitosan [18,19], and optimal conditions in the washing process according to the principles of Sinner’s cycle [20,21]. It is also possible to prevent MF emissions by implementing mitigation strategies in washing machines [22].
Shedding of MFs may be caused by temperature differences during washing and rinsing, which can sometimes exceed 30 °C, i.e., washing at 60 °C and rinsing with water at 14 ± 3 °C.
Thus, the study addresses the effects of two washing protocols for polyester fabrics, the standard and the innovative protocols. The standard washing protocol was performed according to HRN EN ISO 6330 [23], while the innovative washing protocol was the standard protocol modified by a cool-down concept.
The effects of these washing protocols were studied based on the physicochemical properties of the fabrics after 10 cycles compared to the unwashed material, the composition of the effluents and the filtrates after the first, second, third, fourth, fifth and sixth to tenth washing cycles.
Polyester fabrics before and after standard and innovative washing protocols were analysed based on surface characterisation (electrokinetic properties, SEM images, tendency of pilling and wrinkles) and tensile properties.
The physicochemical properties of the effluents and filtrates were monitored based on pH, conductivity, turbidity, total solids (TS), total dissolved solids (TDS) and total suspended solids (TSS) using standard analytical methods [24]. All effluent and filtrate characterisation data were used for hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA). After membrane filtration of the wastewater, the filter cake was examined by digital microscopy.
2. Materials and Methods
The study was performed using standard white polyester staple fibre fabric supplied by the Centre for Tesmaterials. B.V., The Netherlands, with a surface mass of 156 g/m2, density 27.7 threads/cm in the direction of the warp, and 20 thread/cm in the weft direction, with the fineness of the warp thread being 30.4 tex and the warp threads 31.9 tex.
The standard washing process was carried out with the reference detergent ECE A (non-phosphate detergent) at a concentration of 2.0 g/L at 60 °C and a bath ratio of 1:8 according to the standard method of HRN EN ISO 6330 in a laboratory washing equipment Linitest, Original Hanau. The washing protocol consists of 1 main wash and 4 rinses with water at 30 °C, followed by extraction and air drying.
The innovative washing protocol, designed as a standard protocol, was modified by cooling; fresh water was added at the end of the main wash cycle at 60 °C until the bath temperature was reduced to 30 °C by a temperature gradient of 4 °C/min. The effluents from the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th wash cycles according to the standard and innovative protocols were collected separately, while the effluents from the 6th to 10th were pooled for further analysis.
Polyester fabrics were designated as non-washed (N), polyester fabric washed 10 times with the standard protocol (N-St_10) and polyester fabric washed 10 times with the innovative protocol (N-In_10).
Surface characterisation of fabrics marked in this way was carried out using methods of streaming potential, scanning electron microscopy, propensity to pilling and smoothness appearance.
The streaming potential of polyester fabrics was measured using electrokinetic analyser SurPASS, A. Paar, Graz, Austria, depending on the pH 1 mmol/L KCl. Next, the equations H-S a zeta potential values were calculated [25].
The surface of the polyester fabrics was observed by means of a scanning electron microscope tt. Tescan, MIRA/LMU, Brno, Czech Republic, at a magnification of 3000×. Prepared samples for microscopy were previously coated with gold (Au) and palladium (Pd) over a period of 90 s.
The smoothness appearance of polyester fabrics after being subjected to repeated standard and innovative protocols was also assessed [26].
The propensity of polyester fabrics to surface fuzzing and to pilling was assessed by grades after 125, 500, 1000, 2000, 5000 and 7000 rubs [27].
Tensile properties of polyester fabrics through maximum force and elongation at a maximum force were determined using a Tensolab 3000 dynamometer, Mesdan s.p.A., Puegnago del Garda, Italy [28]. The change in breaking strength (ΔF) was calculated as a percentage of the difference between breaking force of fabrics before and after 10 washing cycles according to standard and innovative protocols.
For a complete evaluation of the innovative protocol in relation to the standard protocol of washing polyester fabrics, it is of particular importance to determine the physico-chemical parameters of the washing effluents using standard methods.
Physico-chemical characteristics of processing waters were monitored by determining the pH value, conductivity, turbidity, total solids (TS), total dissolved solids (TDS) and total suspended solids (TSS) using standard analytical methods. Characteristics TS, TSS and TDS were determined by implementation of in-house methods. Conductivity was measured using the conductivity meter CG 853 and pH using the pH meter CG 842, both supplied by Schott, Mainz, Germany [29,30]. Turbidity of effluents was determined by Turbidimeter, Hach TL2350, Manchester, UK [31].
After membrane filtration of effluents using a filter with 0.45 mm diameter and pore size of 0.7 μm, Ahlstrom-Munksj ö, Aalen, Germany, filtrates (f) of the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th and collected baths from the 6th to the 10th were analysed by measuring pH, conductivity and turbidity. All effluent and filtrate characterisation data were used for hierarchical cluster analysis. HCA is a set of methods for multidimensional classification with the aim of forming groups of similar objects, taking into account all grouping features simultaneously [32].
Filter cakes obtained from the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th and from the 6th to the 10th standard and innovative protocols were observed by digital microscopy, Dinolite AM7013MZT, type Premier, The Netherlands, and characterised by counting of MFs.
3. Results and Discussion
Studies on MF release during washing that examined fibre release as a function of material type, washing/drying method and variables tested [33] revealed the complexity, research priorities for improving MF monitoring and mitigation strategies [34], difficulties in comparison and the need for global standardisation protocols and methods.
This study focuses on standard and innovative washing polyester fabrics without impurities with reference detergents at 60 °C in 10 cycles. Results are presented for each observed system: polyester fabric, wash effluent, filtrate and filter cake.
3.1. Characterisation of Polyester Fabric
The effects of standard and innovative washing protocols on polyester fabric modification were evaluated by surface characterisation.
The analysis of the surface area of unwashed and washed standard fabrics based on zeta potential as a function of pH at 1 mmol/L KCl is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Zeta potential of fabrics in a variation of pH 1 mmol/L KCl.
The zeta potential of standard polyester fabric before and after standard and innovative washing protocols has positive and negative values. Unwashed fabric has the lowest negative zeta potential in the whole pH range, and the magnitude is similar to that of cellulose fabrics [35,36]. Such low negative values of zeta potential of standard polyester fabrics indicate a deviation in comparison with polyester textiles, which usually have a much more negative zeta potential [35]. This state of the surface may indicate the presence of preparations covering the surface and preventing the complete dissociation of the reactive groups of this polymer in an alkaline medium and adsorption in an acidic medium. Polyester fabrics washed according to standard and innovative protocols are more negative than unwashed ones in the whole pH range. The magnitude of the zeta potential values for these two samples shows that the effects of both protocols are similar. The difference in the size of the zeta potential of the washed samples according to the standard and innovative protocols is specific only for pH values below 3.5. The washed standard sample (N-St_10) has more positive values than the washed innovative sample (N-In_10). According to the results obtained, this is not due to the conductivity of an electrolyte solution in the titration process. Since the chemical structure of the polyester fabric is not changed during washing according to both protocols, this behaviour could be due to the release of the specific compounds from the surface. Similar isoelectric points of all fabrics prove that no chemical change occurred during the 10 cycles of washing.
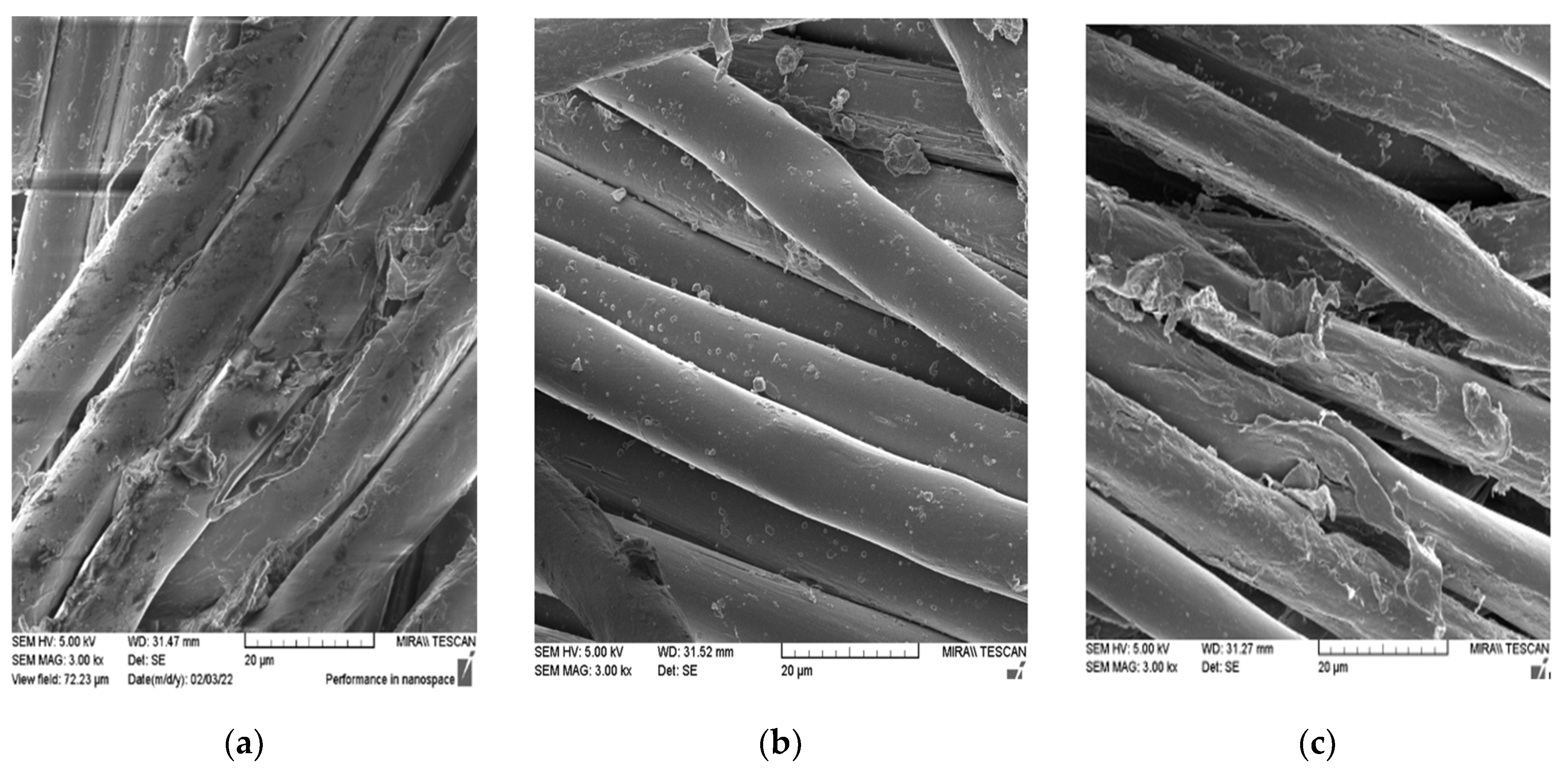
The characterisation of the fabric surface before (N) and after 10 cycles of standard (N-St_10) and 10 cycles of innovative (N-In_10) washing protocols was carried out using the scanning electron microscopy method with a magnification of 3000×; see Figure 1.
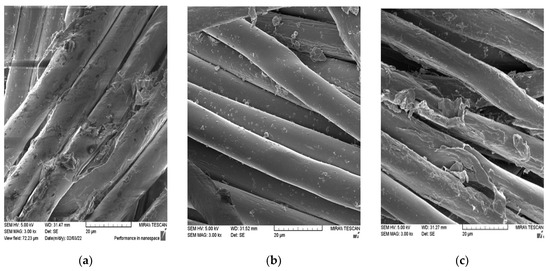
Figure 1.
SEM images of fabrics before and after 10 washing cycles. (a) N. (b) N-St_10. (c) N-In_10.
The alkali content of the detergent, temperature and mechanical agitation during several washing cycles resulted in slight surface changes in the polyester fabrics studied. The morphologies of samples N and N-In_10 are similar, while the surface of sample N-St_10 is smoother.
The panels evaluated the appearance of the washed fabrics primarily based on the presence of wrinkles over 10 wash cycles. The average test score is 5 for unwashed polyester fabric, 1 for fabric washed according to a standard protocol and 2 for fabric washed according to an innovative protocol. The results indicate that a standard washed fabric has more wrinkles than a fabric washed with an innovative protocol, which can be justified by a higher stabilisation rate due to a cooling concept of the innovative washing protocol.
Assessments of the appearance of the surface of unwashed and washed polyester fabrics after different numbers of cyclic rubbings are given in Table 2.

Table 2.
Grades of fabric propensity to surface pilling.
The evaluations presented in Table 2 show that cyclic rubbing has no effect on the surface change up to 2000 cycles. After 5000 cycles of cyclic rubbing, the surface appearance of the unwashed and washed fabric samples is unchanged. Increasing the cyclic rubbing to 7000 cycles further affected the appearance of all samples. Both the unwashed fabrics and the fabrics washed according to the standard protocol are rated 3–4, which corresponds to slight to moderate pill formation on a large part of the sample surface. The best behaviour is shown by the samples washed according to the innovative protocol, which were rated 4, corresponding to slight surface fluffing and/or partially formed pills. According to the obtained scores, the innovative protocol is more suitable for surface preservation when a tendency of pilling is observed. The results for polyester fabrics washed according to the standard protocol are consistent with previous results after 10 washing cycles [15], although there are differences in the selection of polyester fabrics and washing conditions.
The results of the reduction in the tensile strength of the fabric after 10 washing cycles with the standard (N-St_10) and innovative (N-In_10) protocols compared to the unwashed condition are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
The change in the reduction of the breaking force, ΔF and the breaking elongation, ε.
Polyester fabrics washed according to standard and innovative protocols have lower strength than unwashed standard polyester fabrics. The loss of strength properties or the reduction in breaking force is greater for fabrics washed according to the standard protocol. The integrity of a fabric washed according to the innovative protocol is better compared to the standard protocol. The obtained results in terms of surface are consistent with the morphological characteristics (SEM), which show that the fabric washed according to the standard protocol was more altered compared to the unwashed fabric and the fabric washed according to the innovative protocol Additionally, the scores for the fabric’s tendency of surface pilling agree well with ΔF and SEM. This proves that a cooling concept or gradual temperature stabilisation in the innovative protocol preserves the surface and integrity properties of the polyester fabric. It can be elaborated as an effect of less shock.
3.2. Characterisation of the Effluent and Filtrate
To assess the release of MFs, it is of particular importance to determine the physicochemical parameters of the wash effluent. The results for the individual wash cycles according to standard and innovative procedures (1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th and cumulative cycles from 6th to 10th) are presented in Table 4 and Table 5.

Table 4.
Physico-chemical parameters of effluents from washing of polyester fabrics by the standard protocol.

Table 5.
Physico-chemical parameters of effluents from washing of polyester fabrics by the innovative protocol.
The issue of MFs required control of parameters relating to solid and suspended substances (TS, TSS), turbidity and conductivity. The results obtained indicate that the effluent does not place a significant burden on the environment [37].
Comparing the results of the parameters of the effluents from the standard and innovative washing protocols, the turbidity values for the effluents from the standard washing are lower than those from the innovative washing protocol. The results for conductivity are lower for the standard wastewater than for the innovative wash protocol. No clear trends for solids and suspended solids were observed for the analysed wash cycles, confirming the dispersion of the system and the importance of sampling and analysis.
The wastewater characterisation parameters were used to verify the applicability of a particular method and its relevance to the characterisation of wastewater from washing processes according to standard and innovative protocols.
Membrane filtration was used to separate the effluents into a filtrate and a cake according previously described conditions [37]. Physico-chemical parameters for filtrates’ characterisation were pH, conductivity (κ) and turbidity; see Table 6.

Table 6.
Physico-chemical parameters of filtrates (f) from washing of polyester fabrics by the standard protocol.
The results obtained from these parameters for the individual washing cycles by the standard and innovative protocols are shown in Table 6 and Table 7.

Table 7.
Physico-chemical parameters of filtrates (f) from washing of polyester fabrics by the innovative protocol.
The conductivity of the innovative filtrate lowers the values compared to the standard filtrate, as previously observed on the effluent. Filtrates’ turbidities are significantly lower than those of the effluents, confirming the efficiency of filtration as well as retention of MFs from polyester fabrics.
The characterisation of the filter cake was analysed with a digital microscope with magnification of 50× by MFs number on the glass-fibre filter, Table 8.

Table 8.
Counted MFs on the filter.
The number of MFs on the filters decreased with an increasing number of cycles, which is consistent with the results of a previous study despite different washing protocols [38]. It was also found that the amount and length of released fibres were influenced by the structural polymer parameters but also by the number of washing cycles [39]. The number of MFs on the filter from the innovative protocol is higher than from the standard protocol. This can be associated with a decrease in tensile properties and smoothness of fabrics washed according to the standard protocol.
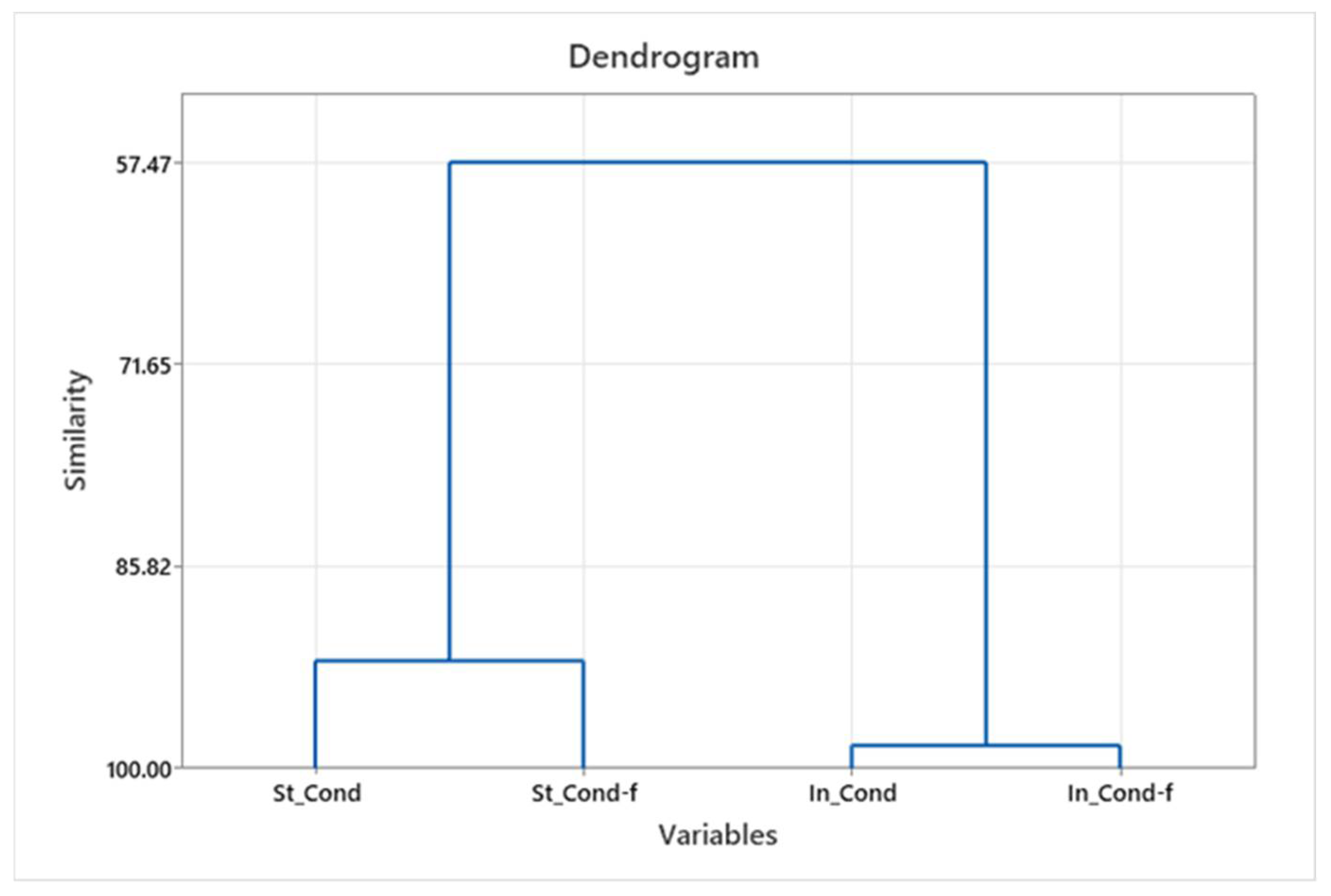
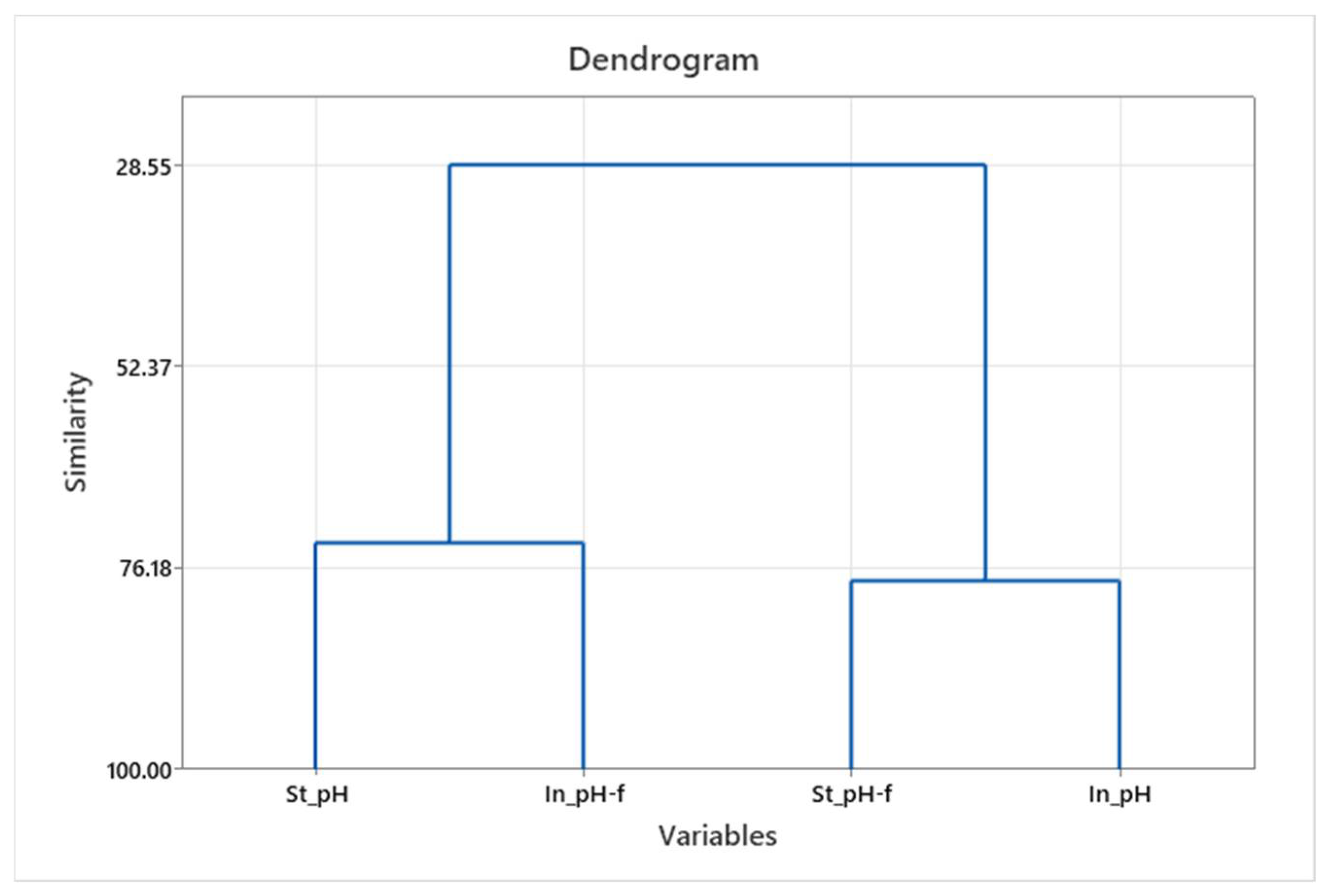
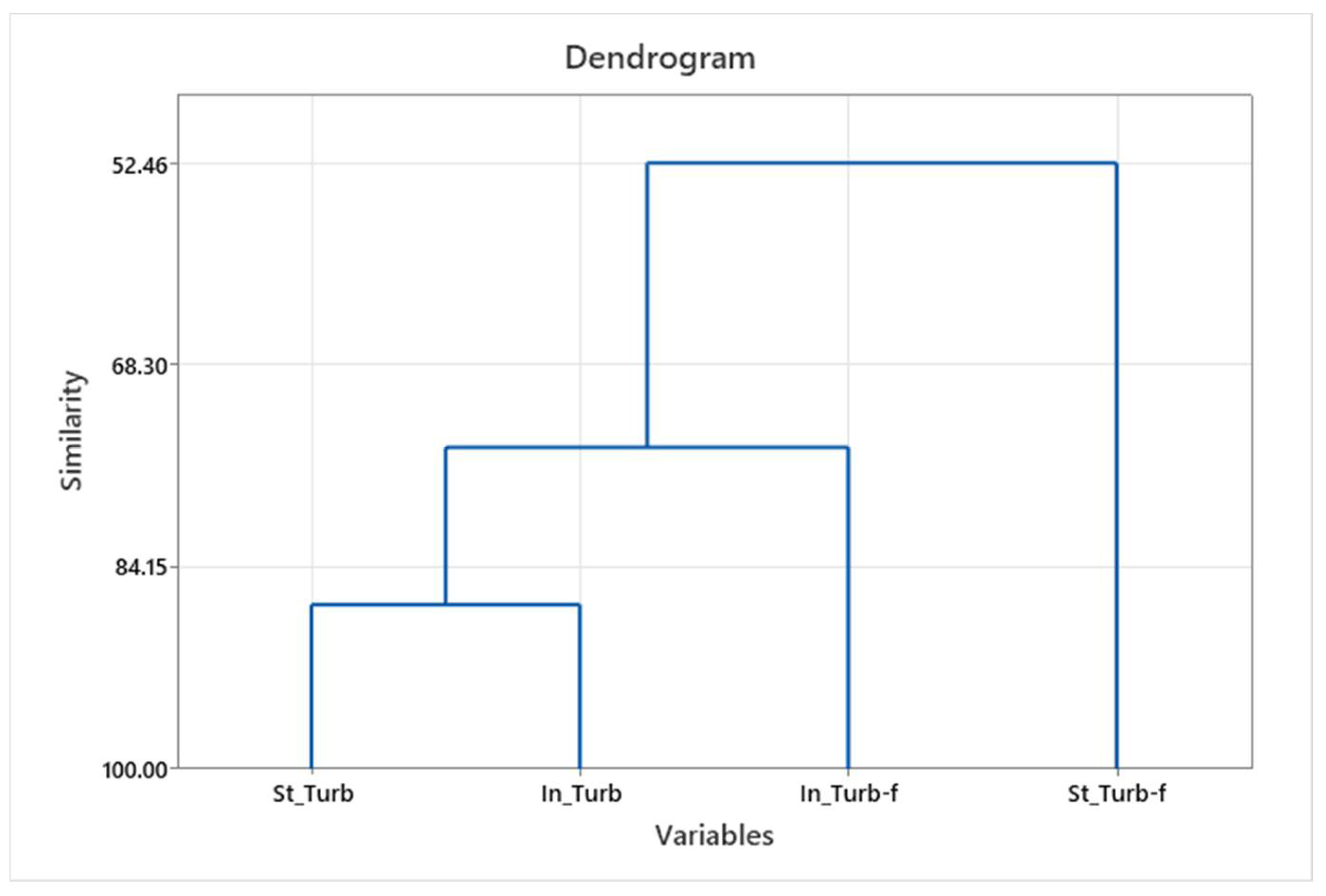
The similarity of individual parameters in effluents and filtrates across all washing cycles and the significance in the standard and innovative process were obtained by hierarchical cluster analysis (HCA). The results are shown with dendrograms showing the similarities of the parameters considered, as well as grouping them at the hierarchical level; see Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4.
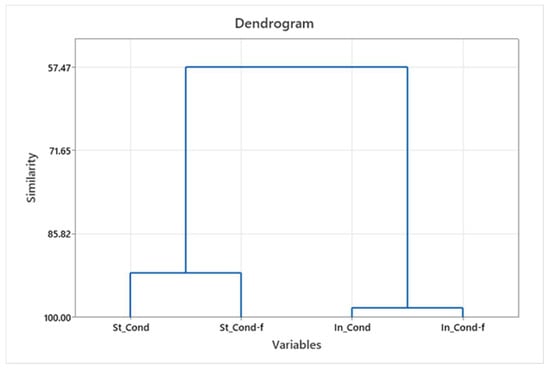
Figure 2.
Conductivity grouping dendrogram—effluent and filtrate for standard and innovative protocols.
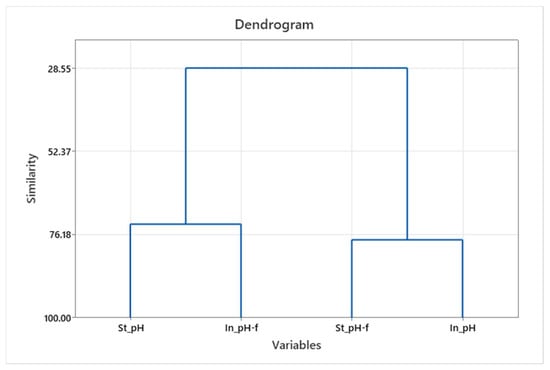
Figure 3.
Dendrogram of pH grouping—effluent and filtrate for standard and innovative protocols.
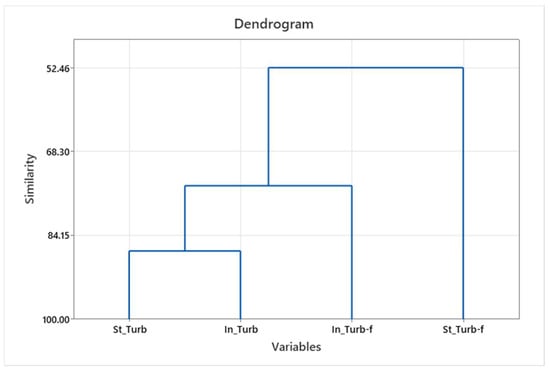
Figure 4.
Turbidity grouping dendrogram—effluent and filtrate for standard and innovative protocols.
Obtained groups for individual parameters (conductivity) were formed separately for the standard and innovative protocol, and for individual parameters (turbidity and pH), the grouping was obtained separately for effluent and filtrate.
4. Conclusions
Research has pointed out the usefulness of the proposed concept of cooling the bath before rinsing to preserve the properties of polyester fabrics and to reduce the load of washing wastewater.
Based on the results of the characterisation of fabrics, effluents and filtrates according to the standard and innovative washing protocols, differences in parameters were found.
The effects of the innovative process are more favourable for the tensile properties and appearance of the surface evaluated by both methods used. The SEM image of the surface favours the innovative protocol. The zeta potential results showed no differences between the fabrics washed with the standard process and the innovative process.
Wastewater analysis showed differences between the individual characterisation parameters. The turbidity of the effluent from the innovative process is higher than that from the standard process. TS, TDS and TSS are different, which did not harmonise the changes in the individual cycles (1–5) and the other cycles (6–10). The grouping of the parameters obtained by the hierarchical cluster analysis shows the differences between the standard protocol and the innovative protocol (conductivity) and the differences between effluent and filtrate (pH and turbidity). The characterisation of the filter cake by the number of MFs showed a higher number of MFs released in the innovative washing process.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, T.P., M.Č. and B.V.; Methodology, T.K, K.G. and Z.K., formal analysis, I.B., T.K. and K.Š.; writing and editing, T.P. and M.Č. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Croatian Science Foundation, grant number HRZZ-IP-2020-02-7575.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Available online: https://de.statista.com/statistik/daten/studie/176748/umfrage/weltproduktion-der-chemiefaser-industrie-nach-chemiefaserarten/ (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Available online: https://textileexchange.org/textile-exchange-preferred-fiber-and-materials-market-report-2021 (accessed on 17 June 2022).
- Carney Almroth, B.M.; Åström, L.; Roslund, S.; Petersson, H.; Johansson, M.; Persson, N.K. Quantifying Shedding of synthetic fibers from textiles; a source of microplastics released into the environment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 21191–21199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pribauer, B.; Laminger, T.; Ipsmiller, W.; Koch, D.; Bartl, A. Assessment of microplastics in the Environment—Fibres: The disgregarded twin? Detritus 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Čorak, I.; Tarbuk, A.; Đorđević, D.; Višić, K.; Botteri, L. Sustainable Alkaline Hydrolysis of Polyester Fabric at Low Temperature. Materials 2022, 15, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čorak, I.; Pušić, T.; Tarbuk, A. Enzimi za hidrolizu poliestera. Tekstil 2019, 68, 142–151. [Google Scholar]
- Ristić, N.; Jocić, D.; Ristić, I. Modifikovanje poliesterske tkanine obradom u alkalnom rastvoru. Tekst. Ind. 2019, 67, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Choobar, B.G.; Shahmirzadi, M.A.A.; Kargari, A.; Manouchehri, M. Fouling mechanism identification and analysis in microfiltration of Laundry wastewater. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiffin, L.; Hazlehurst, A.; Sumner, M.; Taylor, M. Reliable quantification of microplastic release from the domestic laundry of textile fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2021, 113, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, F.; Cocc, M.C.; Avella, M.; Thompson, R.C. Microfiber Release to Water, Via Laundering, and to Air, via Everyday Use: A Comparison between Polyester Clothing with Differing Textile Parameters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 3288–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napper, I.E.; Thompson, R.C. Release of synthetic microplastic plastic fibres from domestic washing machines: Effects of Fabric type and washing conditions. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 112, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirc, U.; Vidmar, M.; Mozer, A.; Kržan, A. Emissions of microplastic fibers from microfiber fleece during domestic washing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 22206–22211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Falco, F.; Gullo, M.P.; Gentile, G.; Di Pace, E.; Cocca, M.; Gelabert, L.; Brouta-Agnés, M.; Rovira, A.; Escudero, R.; Villalba, R.; et al. Evaluation of microplastic release caused by textile washing processes of synthetic fabrics. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šaravanja, A.; Pušić, T.; Dekanić, T. Microplastics in Wastewater by Washing Polyester Fabrics. Materials 2022, 15, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, E.; Nowack, B.; Mitrano, D.M. Synthetic Textiles as a Source of Microplastic from Households: A Mechanistic Study to Understand Microfiber Release During Washing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7036–7046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čurlin, M.; Pušić, T.; Vojnović, B.; Vinčić, A. STEM approach in assessment of microplastic particles in textile wastewater. Techical Gazzete 2022, 29, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Dris, R.; Gasperi, J.; Mirande, C.; Mandin, C.; Guerrouache, M.; Langlois, V.; Tassin, B. A first overview of textile fibres, including microplastics in indoor and outdoor environments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Park, S.; Lee, B.; Ahn, J.; Kim, S. Impact of Chitosan Pretreatment to Reduce Microfibers released from Synthetic Garments during Laundering. Water 2021, 13, 2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaurin, T.; Pušić, T.; Čurlin, M. Biopolymer Textile Structure of Chitosan with Polyester. Polymers 2022, 14, 3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijan, S.; Fijan, R.; Šostar Turk, S. Implementing sustainable laundering procedure for textile in a commercial laundry and thus decreasing wastewater burden. J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinner, H. Über das Waschen Mit Haushaltwaschmaschinen: In Welchem Umfange Erleichtern Haushaltwaschmaschinen und -Geräte das Wäschehaben Im Haushalt? Haus + Heim-Verl: Hamburg, Germany, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- McIlwraith, H.K.; Lin, J.; Erdle, L.M.; Mallos, N.; Diamond, M.L.; Rochman, C.M. Capturing microfibres-marketed technologies reduce microfiber emissions from washing machines. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 139, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HRN EN ISO 6330; Textiles—Domestic Washing and Drying Procedures for Textile Testing. Croatian Standard Institute: Zagreb, Croatia, 2021.
- HRN EN 872:2008; Water Quality—Determination of Suspended Solids—Method by Filtration through Glass Fibre Filters. Croatian Standard Institute: Zagreb, Croatia, 2008.
- Luxbacher, T.; Bukšek, H.; Petrinić, I.; Pušić, T. Mjerenje zeta potencijala ravnih čvrstih površina pomoću elektrokinetičkog analizatora SurPASS. Tekstil 2009, 58, 401–409. [Google Scholar]
- AATCC Test Method No. 124; Test Method for Smoothness Appearance of Fabrics after Home Laundering. American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC): Research Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2018.
- HRN EN ISO 12945-2:2003; Textiles—Determination of Fabric Propensity to Surface Fuzzing and to Pilling—Part 2: Modified Martindale Method. Croatian Standard Institute: Zagreb, Croatia, 2003.
- HRN EN ISO 13934-1:2013; Textiles—Tensile Properties of Fabrics—Part 1: Determination of Maximum Force and Elongation at Maximum Force Using the Strip Method. Croatian Standard Institute: Zagreb, Croatia, 2013.
- HRN EN 27888:2008; Water Quality—Determination of Electrical Conductivity. Croatian Standard Institute: Zagreb, Croatia, 2008.
- HRN EN ISO 10523:2012; Water Quality—Determination of pH. Croatian Standard Institute: Zagreb, Croatia, 2012.
- HRN EN ISO 7027-1: 2016; Water Quality—Determination of Turbidity—Part 1: Quantitative Methods. Croatian Standard Institute: Zagreb, Croatia, 2016.
- Miller, J.N.; Miller, J.C. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, 5th ed.; Pearson, Prentice Hall: London, UK, 2005; pp. 213–223. [Google Scholar]
- Gaylarde, C.; Baptista-Neto, J.A.; Da Fonseca, E.M. Plastic microfibre pollution: How important is clothes’ laundering? Heliyon 2021, 7, e07105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, B.; Laitala, K.; Klepp, I.G. Microfibres from apparel and home textiles: Prospects for including microplastics in environmental sustainability assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 652, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grancarić, A.M.; Tarbuk, A.; Pušić, T. Electrokinetic properties of textile fabrics. Coloration Technol. 2005, 121, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bišćan, J. Electrokinetic Data: Approaches, Interpretations and Applications. Croat. Chem. Acta 2007, 80, 357–365. [Google Scholar]
- Čurlin, M.; Pušić, T.; Vojnović, B.; Dimitrov, N. Particle Characterization of Washing Process Effluents by Laser Diffraction Technique. Materials 2021, 14, 7781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkan, I.; Gündoğdu, S. Investigation on the microfiber release under controlled washings from the knitted fabrics produced by recycled and virgin polyester yarns. J. Text. Inst. 2021, 112, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yang, T.; Mitrano, M.D.; Heuberger, M.; Hufenus, R.; Nowack, B. A systematic study of microplastic fiber release from 12 different polyester textiles during washing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4847–4855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).