Morphological, Phylogenetic and Toxinological Characterization of Potentially Harmful Algal Species from the Marine Coastal Waters of Buenos Aires Province (Argentina)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Established Cultures
2.2. Microscopy
2.3. Deposited Material
2.4. DNA Extraction, Amplification and Sequencing
2.5. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.6. Toxin Extraction and Analysis
2.6.1. Paralytic Shellfish Toxins (PSTs)
2.6.2. Yessotoxins (YTXs) and Isomers
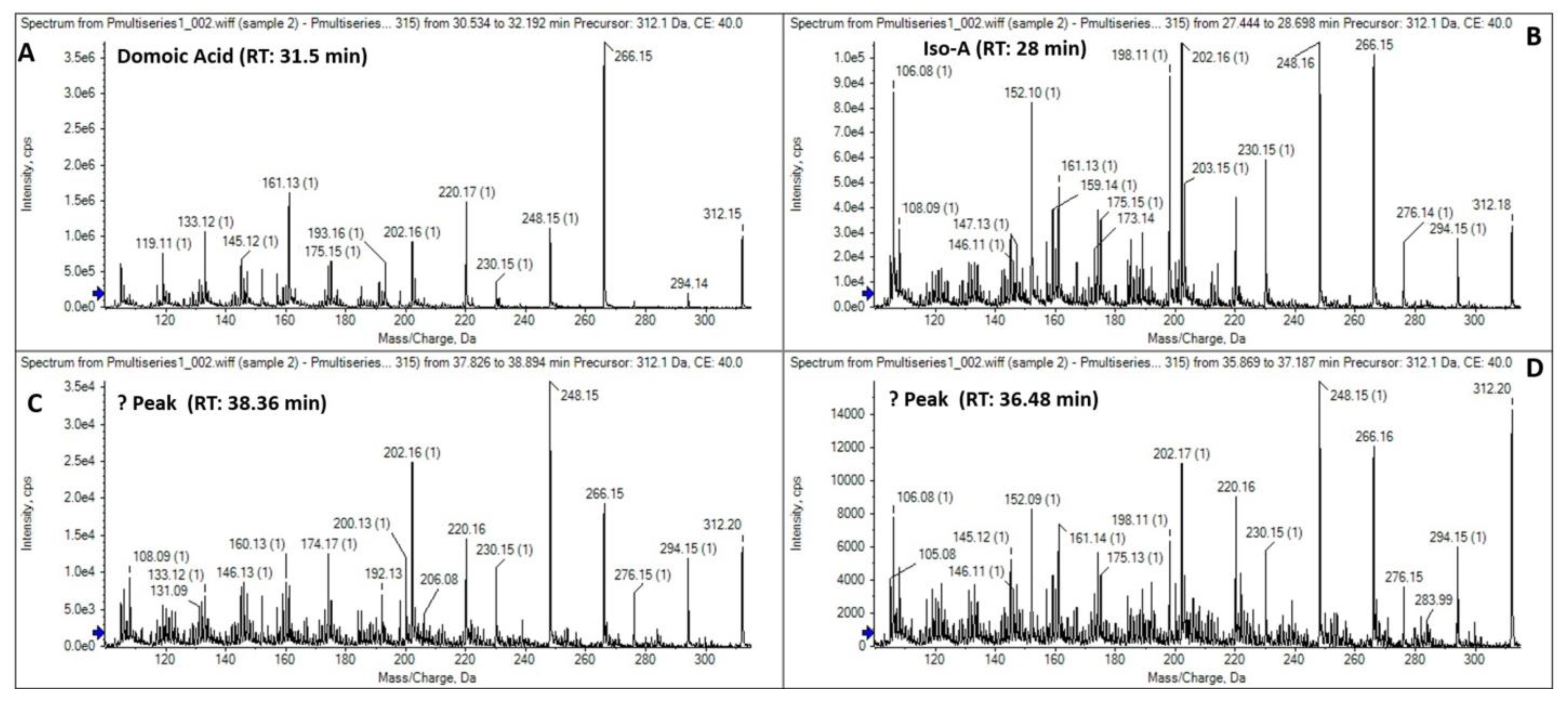
2.6.3. Domoic Acid (DA) and Isomers
3. Results
3.1. Morphological Analysis
3.1.1. Alexandrium catenella (Whedon and Kofoid) Balech (Figure 2A–N)
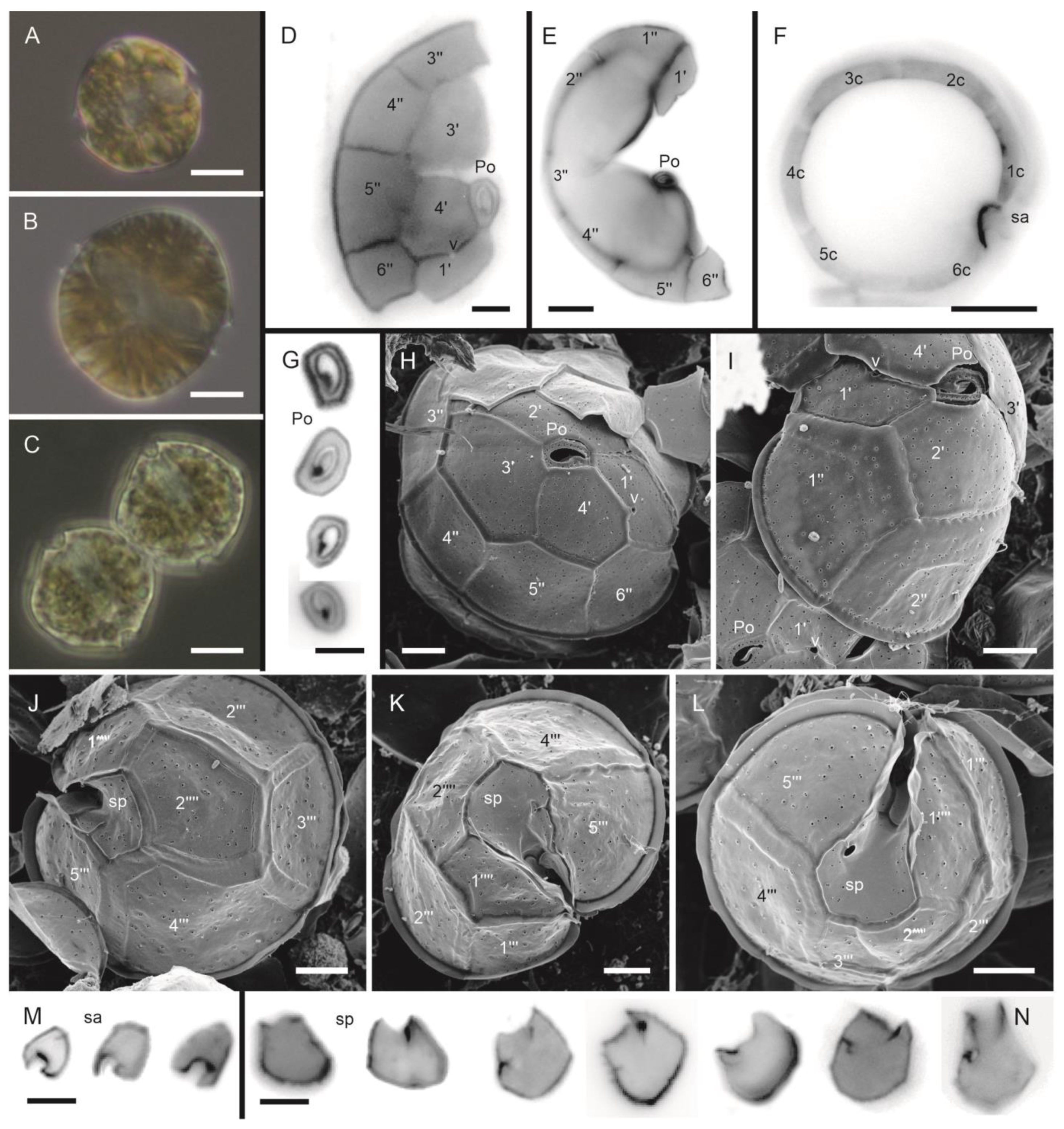
3.1.2. Protoceratium reticulatum (Claparède and Lachmann) Bütschli (Figure 3A–N)

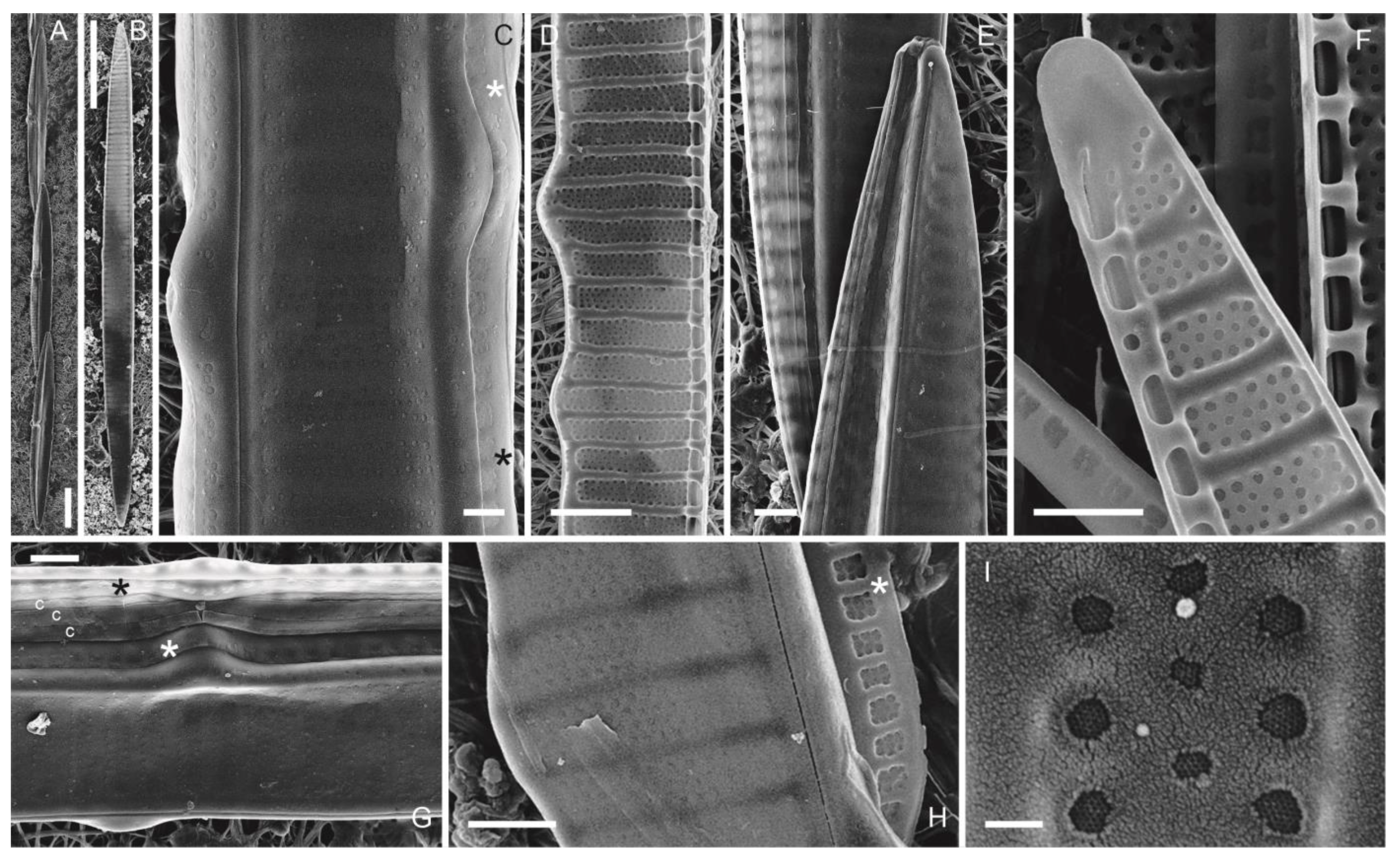
3.1.3. Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries (Hasle) Hasle (Figure 4A–I)
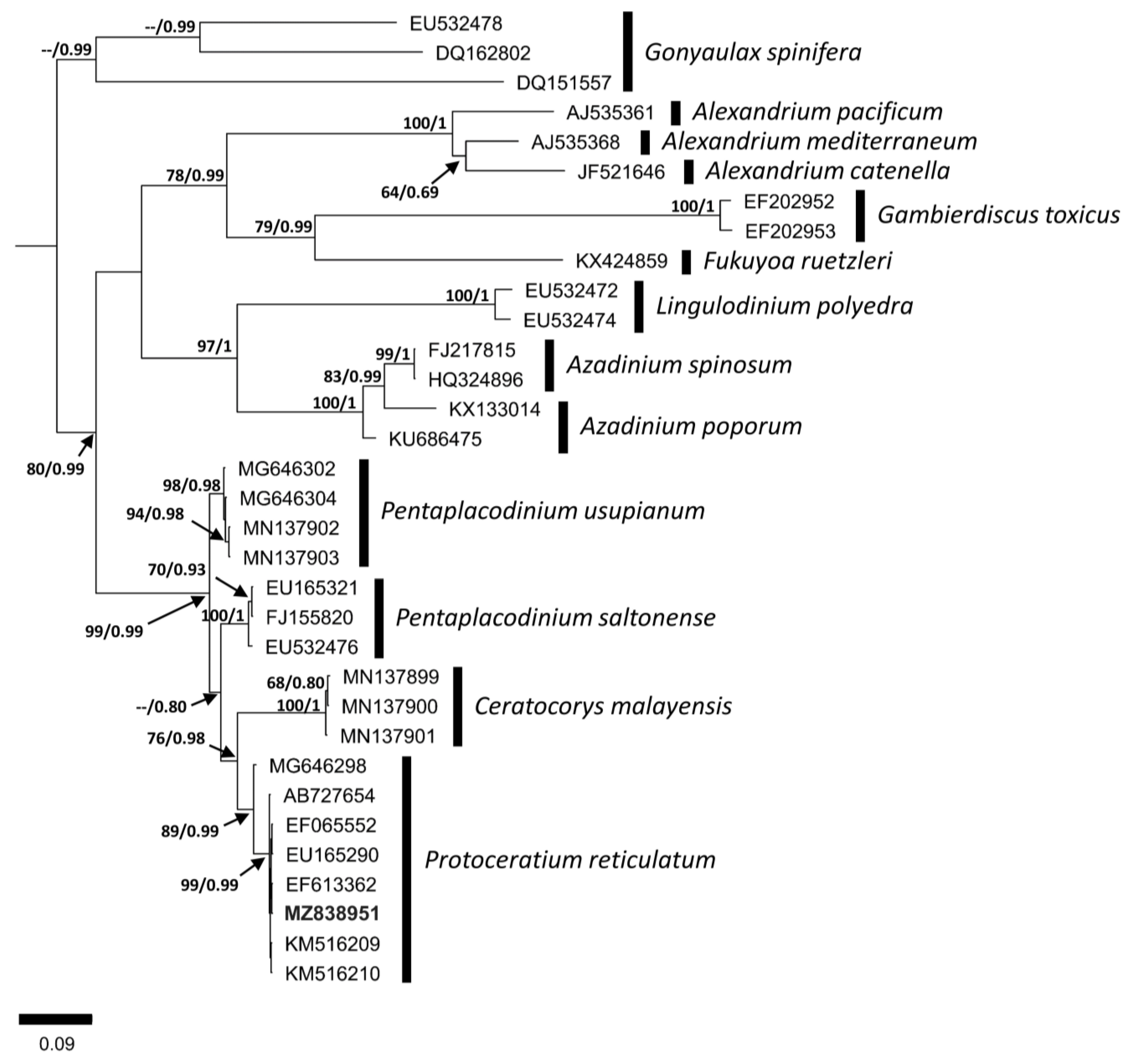
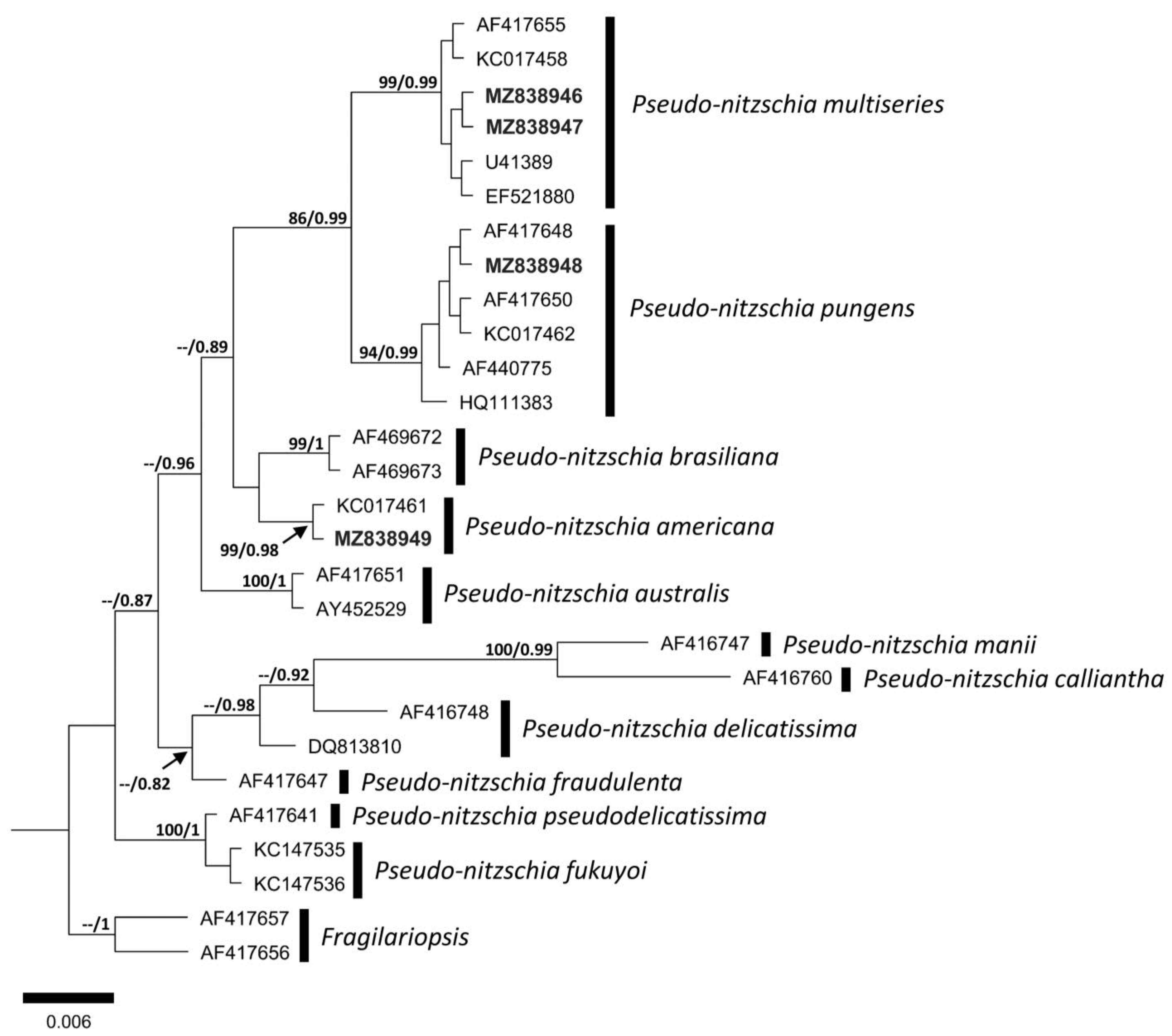
3.2. Molecular Analysis

3.3. Toxinological Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Morphometric and Morphological Features
4.2. Molecular Comparison
4.3. Toxinological Comparison
5. Final Considerations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sunesen, I.; Lavigne, A.S.; Goya, A.; Sar, E.A. Episodios de toxicidad en moluscos de aguas marinas costeras de la Provincia de Buenos Aires (Argentina) asociados a algas toxígenas (Marzo de 2008–Marzo de 2013). Bol. Soc. Argent. Bot. 2014, 49, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardivo Kubis, J.A.; Lavigne, A.S.; Aguiar Juárez, D.; Risso, A.; Sar, E.A.; Sunesen, I. Monitoreo de microalgas nocivas y monitoreo de ficotoxinas en moluscos en la costa bonaerense. In: Resúmenes extendidos de las II Jornadas Internacionales y IV Nacionales de Ambiente “Integrando Ambiente, Comunidad y Compromiso”, UNICEN, Tandil. Rev. Estud. Ambient. 2019, 6, 581–584. [Google Scholar]
- Krock, B.; Ferrario, M.E.; Akselman, R.; Montoya, N.G. Occurrence of marine biotoxins and shellfish poisoning events and their causative organisms in Argentine marine waters. Oceanography 2018, 31, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunesen, I.; Méndez, S.M.; Mancera–Pineda, J.E.; Dechraouie Bottein, M.-Y.; Enevoldsen, H. The Latin American and Caribbean status report based on OBIS and HAEDAT maps and databases. Harmful Algae 2021, 102, 101920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. AlgaeBase. World–Wide Electronic Publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. Available online: https://www.algaebase.org (accessed on 14 July 2022).
- Anderson, D.M.; Alpermann, T.J.; Cembella, A.D.; Collos, Y.; Masseret, E.; Montresor, M. The globally distributed genus Alexandrium: Multifaceted roles in marine ecosystems and impacts on human health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 10–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branco, S.; Oliveira, M.M.M.; Salguero, F.; Vilar, M.C.P.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Menezes, M. Morphology and molecular phylogeny of a new PST–producing dinoflagellate species: Alexandrium fragae sp. nov. (Gonyaulacales, Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2020, 95, 101793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbusto, C.A.; Ballabene de Rico, A.C.; Campero, C.M.; Ramírez, E.E.; Villanueva, C.R. Toxina paralizante de los moluscos del Mar Argentino. Acta Bioquim. Clin. Latinoam. 1981, 15, 447–456. [Google Scholar]
- Carreto, J.I.; Lasta, M.; Negri, R.M.; Benavides, H.R. Los fenómenos de marea roja y toxicidad de moluscos bivalvos en el Mar Argentino. Contrib. INIDEP 1981, 399, 1–55. [Google Scholar]
- Fabro, E.; Almandoz, G.O.; Ferrario, M.E.; John, U.; Tillmann, U.; Toebe, K.; Krock, B.; Cembella, A. Morphological, molecular and toxin analysis of field populations of Alexandrium genus from the Argentine Sea. J. Phycol. 2017, 53, 1206–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinder, V.A.; Tillmann, U.; Krock, B.; Delgado, A.L.; Krohn, T.; Garzón Cardona, J.E.; Metfies, K.; López Abbate, C.; Silva, R.; Lara, R. Plankton multiproxy analyses in the Northern Patagonian Shelf, Argentina: Community structure, phycotoxins, and characterization of toxic Alexandrium strains. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 75–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almandoz, G.O.; Montoya, N.G.; Hernando, M.P.; Benavides, H.R.; Carignan, M.O.; Ferrario, M.E. Toxic strains of the Alexandrium ostenfeldii complex in southern South America (Beagle Channel, Argentina). Harmful Algae 2014, 37, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; MacKenzie, L.; Yasumoto, T. Identification of Protoceratium reticulatum as the biogenetic origin of yessotoxin. Natural Toxins 1997, 5, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, B.; Daranas, A.H.; Norte, M.; Riobó, P.; Franco, J.M.; Fernández, J.J. Yessotoxins, a group of marine polyether toxins: An overview. Mar. Drugs 2008, 6, 73–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.D.; Goya, A.B. Occurrence and profiles of lipophilic toxins in shellfish harvested from Argentina. Toxicon 2015, 102, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akselman, R.; Krock, B.; Alpermann, T.J.; Tillmann, U.; Borel, C.M.; Almandoz, G.O.; Ferrario, M.E. Protoceratium reticulatum (Dinophyceae) in the austral Southwestern Atlantic and the first report on YTX–production in shelf waters of Argentina. Harmful Algae 2015, 45, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabro, E.; Krock, B.; Almandoz, G.O. Dinoflagelados productores de yessotoxinas en el Mar Argentino. Bol. Soc. Argent. Bot. 2018, 53, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelong, A.; Hégaret, H.; Soudant, P.; Bates, S.S. Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) species, domoic acid and amnesic shellfish poisoning: Revisiting previous paradigms. Phycologia 2012, 51, 168–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.S.; Hubbard, K.A.; Lundholm, N.; Montresor, M. Pseudo-nitzschia, Nitzschia, and domoic acid: New research since 2011. Harmful Algae 2018, 79, 3–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.T.; Abdullah, N.; Hanifah, A.H.; Tan, S.N.; Gao, C.; Law, I.K.; Leaw, C.P.; Lim, P.T. Toxic bloom of Pseudo-nitzschia cuspidata (Bacillariophyceae) and domoic acid contamination of bivalve molluscs in Malaysia Borneo. Toxicon 2021, 202, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.S.; Bird, C.J.; De Freitas, A.S.W.; Foxall, R.; Gilgan, M.; Hanic, L.A.; Johnson, G.R.; McCulloh, A.W.; Odense, P.; Pocklington, R.; et al. Pennate diatom Nitzschia pungens as the primary source of domoic acid, a toxin in shellfish from eastern Prince Edward Island, Canada. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1989, 46, 1203–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba Rao, D.V.; Quilliam, M.A.; Pocklington, R. Domoic acid –a neurotoxic amino acid produced by the marine diatom Nitzschia pungens in culture. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1988, 45, 2076–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, N.G.; Negri, R.M.; Carreto, J.I. Primera detección de toxina amnésica de moluscos en el Mar Argentino asociada a un florecimiento de la diatomea Pseudonitzschia australis en la Zona Común de Pesca Argentino–Uruguaya. In Proceedings of the Resúmenes del XV Simposio Científico–Tecnológico de la Comisión Técnica Mixta del Frente Marítimo, Mar del Plata, Argentina, 23 November 2000; p. 21. [Google Scholar]
- Negri, R.M.; Montoya, N.G.; Carreto, J.I.; Akselman, R.; Inza, D. Pseudo-nitzschia australis, Mytilus edulis, Engraulis anchoita, and domoic acid in the Argentine Sea. In Harmful Algae 2002; Steidinger, K.A., Landsberg, J.H., Tomas, C.R., Vargo, G.A., Eds.; Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission, Florida Institute of Oceanography, and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: St. Petersbourg, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 139–141. [Google Scholar]
- Sastre, A.V.; Santinelli, N.H.; Marino, G.; Solís, M.; Pujato, L.; Ferrario, M.E. First detection of domoic acid produced by Pseudo-nitzschia species, Chubut coastal waters, Patagonia, Argentina. Harmful Algae News 2007, 34, 12–14. [Google Scholar]
- Montoya, N.G.; Negri, R.M.; Carignan, M.O.; Carreto, J.I. Algunas características bioquímicas de la diatomea tóxica Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries aislada en el mar Argentino. In Aplicações da ficologia: Anais do XI Congresso Brasileiro de Ficología y Simposio Latino–Americano Sobre Algas Nocivas; Monné, M.A., Caramaschi, U., Eds.; Museu Nacional: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2008; pp. 259–266. [Google Scholar]
- Medina, D.; Méndez, S.; Inocente, G.; Ferrari, G.; Salhi, M.; Giudice, H.; Méndez, E.; Odizzio, M.; Otero, M.D. Shellfish monitoring programme in Uruguay. In Molluscan Shellfish Safety; Villalba, A., Reguera, B., Romalde, J.L., Beiras, R., Eds.; Consellería de Pesca e Asuntos Marítimos da Xunta de Galicia and Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Santiago de Compostela, Spain, 2003; pp. 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Fritz, L.; Triemer, R.E. A rapid simple technique utilizing Calcofluor White M2R for the visualization of dinoflagellate thecal plates. J. Phycol. 1985, 21, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prygiel, J.; Coste, M. Guide Méthodologique Pour la Mise en Oeuvre de l’Indice Biologique Diatomées NF T 90–354; Agences de l’Eau–Cemagref–Groupement de Bordeaux: Agences de l’eau, France, 2000; 133p. [Google Scholar]
- Utermöhl, H. Zur Vervollkommnung der quantitativen Phytoplankton–Methodik: Mit 1 Tabelle und 15 abbildungen im Text und auf 1 Tafel. SIL Communications, 1953–1996. Mitt. Int. Ver. Theor. Angew. Limnol. 1958, 9, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbeláez, M.N.; Mancera Pineda, J.E.; Reguera, B. Dinoflagelados epífitos de Thalassia testudinum en dos sistemas costeros del Caribe colombiano. Bol. Investig. Mar. Costeras 2017, 46, 9–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH image to image: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richlen, M.L.; Barber, P.H. A technique for the rapid extraction of microalgal DNA from single live and preserved cells. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2005, 5, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaers, G.; Maroteaux, L.; Michot, B.; Herzog, M. Dinoflagellates in evolution. A molecular phylogenetic analysis of large subunit ribosomal RNA. J. Mol. Evol. 1989, 29, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litaker, R.W.; Vandersea, M.W.; Kibler, S.R.; Reece, K.S.; Stokes, N.A.; Steidinger, K.A.; Millie, D.F.; Bendis, B.J.; Pigg, R.J.; Tester, P.A. Identification of Pfiesteria piscicida (Dinophyceae) and Pfiesteria–like organisms using internal transcribed spacer–specific PCR assays. J. Phycol. 2003, 39, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Nei, M. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1993, 10, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M.; Kumar, S. Molecular Evolution and Phylogenetics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2000; 333p. [Google Scholar]
- Rourke, W.A.; Murphy, C.J.; Pitcher, G.; van de Riet, J.M.; Burns, B.G.; Thomas, K.M.; Quilliam, M.A. Rapid postcolumn methodology for determination of paralytic shellfish toxins in shellfish tissue. J. AOAC Int. 2008, 91, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, P.; Riobó, P.; Rodríguez, F.; Franco, J.M.; Bravo, I. Differences in the toxin profiles of Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Dinophyceae) strains isolated from different geographic origins: Evidence of paralytic toxin, spirolide, and gymnodimine. Toxicon 2015, 103, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Marine biotoxins in shellfish–Saxitoxin group. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossignoli, A.E.; Mariño, C.; Martín, H.; Blanco, J. Development of a fast liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry method (LC–MS/MS) to determine fourteen lipophilic shellfish toxins based on fused–core technology: In house validation. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regueiro, J.; Martín–Morales, E.; Álvarez, G.; Blanco, J. Sensitive determination of domoic acid in shellfish by on–line coupling of weak anion exchange solid–phase extraction and liquid chromatography–diode array detection–tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2011, 129, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balech, E. The genus Alexandrium or Gonyaulax of the tamarensis group. In Toxic Dinoflagellates, Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Toxic Dinoflagellates, St. Andrews, NB, Canada, 8–12 June 1985; Anderson, D.M., White, A.W., Baden, D.G., Eds.; Elsevier North–Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1985; pp. 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Balech, E. The Genus Alexandrium Halim (Dinoflagellata); Sherkin Island Marine Station Publication: Co. Cork, Ireland, 1995; 151p. [Google Scholar]
- Krock, B.; Borel, C.M.; Barrera, F.; Tillmann, U.; Fabro, E.; Almandoz, G.O.; Ferrario, M.; Garzón Cardona, J.E.; Koch, B.P.; Alonso, C.; et al. Analysis of the hydrographic conditions and cyst beds in the San Jorge Gulf, Argentina, that favour dinoflagellate population development including toxigenic species and their toxins. J. Mar. Syst. 2015, 148, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balech, E.; Tangen, K. Morphology and taxonomy of toxic species in the tamarensis group (Dinophyceae): Alexandrium excavatum (Braarud) comb. nov. and Alexandrium ostenfeldii (Paulsen) comb. nov. Sarsia 1985, 70, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, U.; Fensome, R.A.; Medlin, L.K. The application of molecular clock based on molecular sequences and the fossil record to explain biogeographic distributions within the Alexandrium tamarense “species complex” (Dinophyceae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2003, 20, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilly, E.L.; Halanich, K.M.; Anderson, D.M. Species boundaries and global biogeography of the Alexandrium complex (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 2007, 43, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, U.; Litaker, R.W.; Montresor, M.; Murray, S.; Brosnahan, M.L.; Anderson, D.M. Formal revision of the Alexandrium tamarense species complex (Dinophyceae) taxonomy: The introduction of five species with emphasis on molecular based (rDNA) classification. Protist 2014, 165, 779–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, U.; Litaker, R.W.; Montresor, M.; Murray, S.; Brosnahan, M.L.; Anderson, D.M. (2302) Proposal to reject the name Gonyaulax catenella (Alexandrium catenella) (Dinophyceae). Taxon 2014, 63, 932–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraga, S.; Sampedro, N.; Larsen, J.; Moestrup, Ø.; Calado, A.J. Arguments against the proposal 2302 by John et al. to reject the name Gonyaulax catenella (Alexandrium catenella). Taxon 2015, 64, 634–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prud’homme van Reine, W. Report of the Nomenclature Committee for Algae: 15. Taxon 2017, 66, 191–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, N.G.; Fulco, V.K.; Carignan, M.O.; Carreto, J.I. Toxin variability in cultured and natural populations of Alexandrium tamarense from southern South America –evidences of diversity and environmental regulation. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1408–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, N.G.; Carignan, M.O.; Carreto, J.I. Alexandrium tamarense/catenella blooms in the Southwestern Atlantic: Paralytic Shellfish Toxin production and its trophic transference. In Plankton Ecology of the Southwestern Atlantic from the Subtropical to the Subantarctic Realm; Hoffmeyer, M.S., Sabatini, M.E., Brandini, F.P., Calliari, D.L., Santinelli, N.H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing A: Cham, Denmark, 2018; pp. 453–476. [Google Scholar]
- Penna, A.; Fraga, S.; Masó, M.; Giacobbe, M.G.; Bravo, I.; Garcés, E.; Vila, M.; Bertozzini, E.; Andreoni, F.; Lugliè, A.; et al. Phylogenetic relationships among the Mediterranean Alexandrium (Dinophyceae) species based on sequences of 5.8S gene and Internal Transcript Spacers of the rRNA operon. Eur. J. Phycol. 2008, 43, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balech, E. Los dinoflagelados del Atlántico Sudoccidental. Publicación Espec. Del Inst. Español De Oceanogr. 1988, 1, 1–310. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Mertens, K.N.; Krock, B.; Luo, Z.; Derrien, A.; Pospelova, V.; Liang, Y.; Bilien, G.; Smith, K.F.; de Schepper, S.; et al. Cryptic speciation in Protoceratium reticulatum (Dinophyceae): Evidence from morphological, molecular and ecophysiological data. Harmful Algae 2019, 88, 101610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasle, G.R. Pseudo-nitzschia pungens and P. multiseries (Bacillariophyceae): Nomenclatural history, morphology and distribution. J. Phycol. 1995, 31, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasle, G.R.; Lange, C.B.; Syvertsen, E.E. A review of Pseudo-nitzschia, with special reference to the Skagerrak, North Atlantic, and adjacent waters. Helgol. Meeresunters. 1996, 50, 131–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, M.E.; Sar, E.A.; Castaños, C.; Hinz, F. Potentially toxic species of the diatom genus Pseudo-nitzschia in Argentinian coastal waters. Nova Hedwigia 1999, 68, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, M.E.; Sar, E.A.; Sala, S.A. Diatomeas potencialmente toxígenas del cono sur Americano. In Floraciones Algales Nocivas en el cono sur Americano; Sar, E.A., Ferrario, M.E., Reguera, B., Eds.; Instituto Español de Oceanografía: Madrid, Spain, 2002; pp. 167–193. [Google Scholar]
- Larsen, J.; Nguyen, N.L. Potentially toxic microalgae of Vietnamese waters. Opera Bot. 2004, 140, 5–216. [Google Scholar]
- Hasle, G.R. Nomenclatural notes on marine planktonic diatoms. The family Bacillariaceae. Nova Hedwig. Beih. 1993, 106, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Hasle, G.R. Pseudo-nitzschia as a genus distinct from Nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae): Nomenclatural history, morphology and distribution. J. Phycol. 1994, 30, 1036–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, L.; de Salas, M.; Adamson, J.; Beuzenberg, V. The dinoflagellate genus Alexandrium (Halim) in New Zealand coastal waters: Comparative morphology, toxicity and molecular genetics. Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 71–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes–Mella, J.; Mardones, J.I.; Norambuena, L.; Fuenzalida, G.; Labra, G.; Espinoza–González, O.; Guzmán, L. Toxic Alexandrium catenella expanding northward along the Chilean coast: New risk of paralytic shellfish poisoning of the Bío–Bío region (36° S). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-Z.; Lin, L.; Gu, H.-F.; Chan, L.L.; Hong, H.-S. Comparative studies on morphology, ITS sequence and protein profile of Alexandrium tamarense and A. catenella isolated from the China Sea. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholin, C.A.; Herzog, M.; Sogin, M.; Anderson, D.M. Identification of group– and strain–specific genetic markers for globally distributed Alexandrium (Dinophyceae). II. Sequence analysis of a fragment of the LSU rRNA gene1. J. Phycol. 1994, 30, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilly, E.L. Phylogeny and Biogeography of the Toxic Dinoflagellate Alexandrium. Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. Ph.D Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, P.; Figueroa, R.I.; Ramilo, I.; Bravo, I. The life history of the toxic marine dinoflagellate Protoceratium reticulatum (Gonyaulacales) in culture. Harmful Algae 2017, 68, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, G.; Moestrup, Ø.; Roberts, K.R. Light and electron microscopical observations on Protoceratium reticulatum (Dinophyceae). Arch. Protistenkd. 1996, 147, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villac, M.C. Synecology of the Genus Pseudo-nitzschia H. Peragallo from Monterey Bay, California, USA. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A & M University, Department of Oceanography, College Station, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Orlova, T.Y.; Stonik, I.V.; Aizdaicher, N.A.; Bates, S.S.; Léger, C.; Fehling, J. Toxicity, morphology and distribution of Pseudo-nitzschia calliantha, P. multistriata and P. multiseries (Bacillariophyta) from the northwestern Sea of Japan. Bot. Mar. 2008, 51, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subba Rao, D.V.; Wohlgeschaffen, G. Morphological variants of Nitzschia pungens Grunow f. multiseries Hasle. Bot. Mar. 1990, 33, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blossom, H.E.; Markussen, B.; Daugbjerg, N.; Krock, B.; Norlin, A.; Hansen, P.J. The cost of toxicity in microalgae: Direct evidence from the Dinoflagellate Alexandrium. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebour, M.V. The Dinoflagellates of the Northern Seas; Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom: Plymouth, UK, 1925; pp. 1–250. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilera–Belmonte, A.; Inostroza, I.; Franco, J.M.; Riobó, P.; Gómez, P.I. The growth, toxicity and genetic characterization of seven strains of Alexandrium catenella (Whedon & Kofoid) Balech 1985 (Dinophyceae) isolated during the 2009 summer outbreak in southern Chile. Harmful Algae 2011, 12, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, D.; Paredes, J.; Alves–de–Souza, C.; Seguel, M.; Sfeir, A.; Frangópulos, M. Intraregional variation among Alexandrium catenella (Dinophyceae) strains from southern Chile: Morphological, toxicological and genetic diversity. Harmful Algae 2012, 15, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almandoz, G.O.; Cefarelli, A.O.; Diodato, S.; Montoya, N.; Benavides, H.R.; Carignan, M.; Hernando, M.; Fabro, E.; Metfies, K.; Lundholm, N.; et al. Harmful phytoplankton in the Beagle Channel (South America) as a potential threat to aquaculture activities. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 145, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persich, G.R.; Kulis, D.M.; Lilly, E.L.; Anderson, D.M.; Garcia, V.M.T. Probable origin and toxin profile of Alexandrium tamarense (Lebour) Balech from southern Brazil. Harmful Algae 2006, 5, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, M.; Branco, S.; Miotto, M.C.; Alves–de–Souza, C. The Genus Alexandrium (Dinophyceae, Dinophyta) in Brazilian coastal waters. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, M.D.A.; Smith, G.J.; Kudela, R.M. Phylogenetic relationships of yessotoxin–producing dinoflagellates, based on the large subunit and internal transcribed spacer ribosomal DNA domains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2009, 75, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Lim, Z.F.; Mertens, K.N.; Krock, B.; Teng, S.T.; Tan, T.H.; Leaw, C.P.; Lim, P.T.; Gu, H. Attributing Ceratocorys, Pentaplacodinium and Protoceratium to Protoceratiaceae (Dinophyceae), with descriptions of Ceratocorys malayensis sp. nov. and Pentaplacodinium usupianum sp. nov. Phycologia 2020, 59, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, P.; Fraga, S.; Rodríguez, F.; Riobó, P.; Bravo, I. Ceratocorys mariaovidiorum sp. nov. (Gonyaulacales), a new dinoflagellate species previously reported as Protoceratium reticulatum. J. Phycol. 2018, 54, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, K.N.; Carbonell–Moore, M.C.; Poslepova, V.; Head, M.J. Ceratocorys mariaovidiorum P.Salgado, S.Fraga, F.Rodríguez, P.Riobó, I.Bravo is a junior synonym of Pentaplacodinium saltonense K.N.Mertens, M.C.Carbonell–Moore, V.Pospelova, M.J.Head. Not. Algarum 2018, 45, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Mertens, K.N.; Carbonell–Moore, M.C.; Poslepova, V.; Head, M.J.; Highfield, A.; Schroeder, D.; Gu, H.; Andree, K.B.; Fernandez, M.; Yamaguchi, A.; et al. Pentaplacodinium saltonense gen. et sp. nov. (Dinophyceae) and its relationship to the cyst–defined genus Operculodinium and yessotoxin–producing Protoceratium reticulatum. Harmful Algae 2018, 71, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundholm, N.; Daugbjerg, N.; Moestrup, Ø. Phylogeny of the Bacillariaceae with emphasis on the genus Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyceae) based on partial LSU rDNA. Eur. J. Phycol. 2002, 37, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundholm, N.; Hasle, G.R.; Fryxell, G.A.; Hargraves, P.E. Morphology, phylogeny and taxonomy of species within the Pseudo-nitzschia americana complex (Bacillariophyceae) with descriptions of two new species, Pseudo-nitzschia brasiliana and Pseudo-nitzschia linea. Phycologia 2002, 41, 480–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.C.; Tan, S.N.; Teng, S.T.; Lundholm, N.; Orive, E.; David, H.; Quijano–Scheggia, S.; Leong, S.C.Y.; Wolf, M.; Bates, S.S.; et al. Phylogeny and species delineation in the marine diatom Pseudo-nitzschia (Bacillariophyta) using cox1, LSU, and ITS2 rRNA genes: A perspective in character evolution. J. Phycol. 2018, 54, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, T.; Murray, J.S.; Boundy, M.J.; Balci, M.; Bowers, H.A.; Smith, K.F.; Harwood, D.T.; Rhodes, L.L. Update of the planktonic diatom Genus Pseudo-nitzschia in Aotearoa New Zealand coastal waters: Genetic diversity and toxin production. Toxins 2021, 13, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreto, J.I.; Elbusto, C.; Sancho, H.; Carignan, M.; Yasumoto, T.; Oshima, Y. Comparative studies on paralytic shellfish toxin profiles of marine snails, mussels and an Alexandrium tamarense isolate from the Mar del Plata coast (Argentina). Rev. Investig. Desarr. Pesq. 1996, 10, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Carreto, J.I.; Carignan, M.O.; Montoya, N.G. Comparative studies on mycosporine–like amino acids, paralytic shellfish toxins and pigment profiles of the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense, A. catenella and A. minutum. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 223, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciminiello, P.; Dell’Aversano, C.; Fattorusso, E.; Forino, M.; Magno, S.; Guerrini, F.; Pistocchi, R.; Boni, L. Complex yessotoxins profile in Protoceratium reticulatum from north–western Adriatic Sea revealed by LC–MS analysis. Toxicon 2003, 42, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz, B.; Riobó, P.; Ramilo, I.; Franco, J.M. Yessotoxins profile in strains of Protoceratium reticulatum from Spain and USA. Toxicon 2007, 50, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Satake, M.; Yoshimatsu, S.; Oshima, Y.; Horie, Y.; Koike, K.; Iwataki, M. Yessotoxin analogues in several strains of Protoceratium reticulatum in Japan determined by liquid chromatography–hybrid triple quadrupole/linear ion trap mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1142, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, D.J.; Bates, S.S. Production of Domoic Acid, a neurotoxic amino acid, by an axenic culture of the marine diatom Nitzschia pungens f. multiseries Hasle. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1992, 49, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quilliam, M.A. Chemical methods for domoic acid, the amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP) toxin. In Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae; Hallegraeff, M., Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Eds.; Monographs on Oceanography Methodology 11; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, UNESCO: Paris, France, 2003; pp. 247–266. [Google Scholar]
- Trainer, V.L.; Bates, S.S.; Lundholm, N.; Thessen, A.E.; Cochlan, W.P.; Adams, N.G.; Trick, C.G. Pseudo-nitzschia physiological ecology, phylogeny, toxicity, monitoring and impacts on ecosystem health. Harmful Algae 2012, 14, 271–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitcher, G.C.; Cembella, A.D.; Krock, B.; Macey, B.M.; Mansfield, L.; Probyn, T.A. Identification of the marine diatom (Bacillariophyceae) as a source of the toxin domoic acid in Algoa Bay, South Africa Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries. Afr. J. Mar. Sci. 2014, 36, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, L.; Silva, A.; Castelo Branco, M.A.; Marques, A.; Costa, P.R. Evaluation of intracellular and extracellular domoic acid content in Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries cell cultures under different light regimes. Toxicon 2018, 155, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotaki, Y.; Furio, E.F.; Satake, M.; Lundholm, N.; Katayama, T.; Koike, K.; Fulgueras, V.P.; Bajarias, F.A.; Takata, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. Production of isodomoic acids A and B as major toxin components of a pennate diatom Nitzschia navis–varingica. Toxicon 2005, 46, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundholm, N.; Skov, J.; Pocklington, R.; Moestrup, Ø. Studies on the marine planktonic diatom Pseudo-nitzschia. 2. Autecology of P. pseudodelicatissima based on isolates from Danish coastal waters. Phycologia 1997, 36, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Subba Rao, D.; Mann, K.; Brown, R.; Pocklington, R. Effects of silicate limitation on production of domoic acid, a neurotoxin, by the diatom Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries. I. Batch culture studies. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1996, 131, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, S.S. Ecophysiology and metabolism of ASP toxin production. In Physiological Ecology of Harmful Algal Blooms; Anderson, D.M., Cembella, A.D., Hallegraeff, G.M., Eds.; NATO ASI Series; Serie G. Ecological Science 41; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 405–426. [Google Scholar]
- Kotaki, Y.; Koike, K.; Sato, S.; Ogata, T.; Fukuyo, Y.; Kodama, M. Confirmation of domoic acid production of Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries isolated from Ofunato Bay, Japan. Toxicon 1999, 37, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, S.S.; Gaudet, J.; Kaczmarska, I.; Ehrman, J.M. Interaction between bacteria and the domoic–acid–producing diatom Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries (Hasle) Hasle; can bacteria produce domoic acid autonomously? Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Código Alimentario Argentino (CAA). (Argentinean Food Code). Ley 18284. 1969. Available online: https://www.argentina.gob.ar/anmat/codigoalimentario (accessed on 4 August 2022).

| Toxin | ESI | Q1 | Q3 | CE (v) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YTX | NEG | 570.43 | 467.40 | −42 |
| YTX | NEG | 570.43 | 396.40 | −42 |
| Homo–YTX | NEG | 577.40 | 474.40 | −42 |
| Homo–YTX | NEG | 577.40 | 403.40 | −42 |
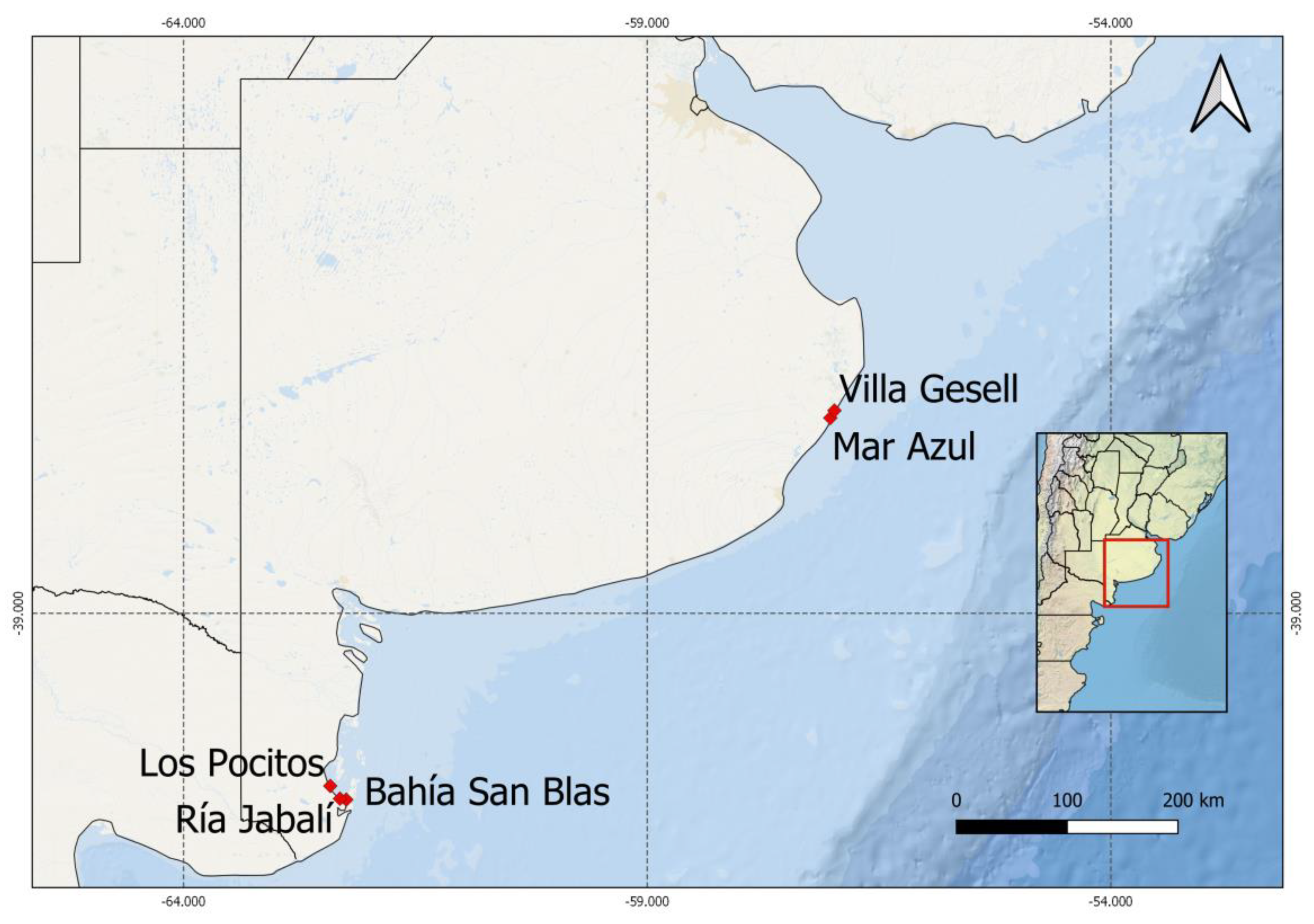
| Species | Strain Label | Collecting Site | Collecting Date | Gen Bank Acc. No |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alexandrium catenella | LPCc001 | Los Pocitos (40°25′53″ S; 62°25′5″ W) (LP) | 21 July 2015 | MZ838943 |
| Alexandrium catenella | LPCc002 | San Blas Bay (40°33′9″ S; 62°3′37″ W) (BSB) | 4 August 2016 | MZ838944 |
| Alexandrium catenella | LPCc004 | Los Pocitos | 27 September 2016 | not available |
| Alexandrium catenella | LPCc008 | Ria Jabalí (40°32′9″ S; 62°18′57″ W) (RJ) | 21 July 2015 | MZ838945 |
| Protoceratium reticulatum | LPCc021 | Villa Gesell (37°17′10″S; 56°59′12″ W) (VG) | 17 October 2017 | MZ838951 |
| Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries | LPCc036 | Mar Azul (37°20′38″ S; 57°1′31″ W) (MAZ) | 29 January 2019 | MZ838946 |
| Pseudo-nitzschia multiseries | LPCc037 | Mar Azul | 29 January 2019 | MZ838947 |
| Alexandrium affine * | LPCc012 | Mar Azul | 9 January 2017 | MZ838950 |
| Pseudo-nitzschia americana * | LPCc039 | Villa Gesell | 22 April 2019 | MZ838949 |
| Pseudo-nitzschia pungens * | LPCc038 | Villa Gesell | 22 April 2019 | MZ838948 |
| Mol % | Toxicity (pg STX eq. cell−1) | Toxin Content (fmol cell−1) | Toxin Content (pg cell−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. catenella Strains | GTX1,4 | GTX2,3 | dcGTX2,3 | C1,2 | |||
| LPCc001 | 25.9 (18.5 + 7.4) | 33.7 (22.2 + 11.5) | 14.9 (12.2 + 2.7) | 25.6 (18.0 + 7.6) | 12.38 | 67.41 | 27.65 |
| LPCc002 | 20.2 (15.6 + 4.6) | 15.3 (10.8 + 4.5) | 18.3 (14.0 + 4.3) | 46.3 (32.8 + 13.5) | 27.59 | 194.45 | 81.57 |
| LPCc004 | 33.8 (22.1 + 11.7) | 37.6 (21.5 + 16.1) | 11.9 (9.9 + 2.0) | 16.8 (15.3 + 1.5) | 46.40 | 216.96 | 88.04 |
| LPCc008 | 30.9 (21.8 + 9.1) | 20.3 (14.7 + 5.6) | 13.5 (10.3 + 3.2) | 35.4 (24.8 + 10.6) | 46.09 | 255.85 | 106.53 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tardivo Kubis, J.A.; Rodríguez, F.; Rossignoli, A.E.; Riobó, P.; Sar, E.A.; Sunesen, I. Morphological, Phylogenetic and Toxinological Characterization of Potentially Harmful Algal Species from the Marine Coastal Waters of Buenos Aires Province (Argentina). Phycology 2023, 3, 79-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3010006
Tardivo Kubis JA, Rodríguez F, Rossignoli AE, Riobó P, Sar EA, Sunesen I. Morphological, Phylogenetic and Toxinological Characterization of Potentially Harmful Algal Species from the Marine Coastal Waters of Buenos Aires Province (Argentina). Phycology. 2023; 3(1):79-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleTardivo Kubis, Jonás Adrián, Francisco Rodríguez, Araceli E. Rossignoli, Pilar Riobó, Eugenia A. Sar, and Inés Sunesen. 2023. "Morphological, Phylogenetic and Toxinological Characterization of Potentially Harmful Algal Species from the Marine Coastal Waters of Buenos Aires Province (Argentina)" Phycology 3, no. 1: 79-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3010006
APA StyleTardivo Kubis, J. A., Rodríguez, F., Rossignoli, A. E., Riobó, P., Sar, E. A., & Sunesen, I. (2023). Morphological, Phylogenetic and Toxinological Characterization of Potentially Harmful Algal Species from the Marine Coastal Waters of Buenos Aires Province (Argentina). Phycology, 3(1), 79-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/phycology3010006






