The Effectiveness of Benzalkonium Chloride as an Active Compound on Selected Foodborne Pathogens Biofilm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents and Bacterial Strains
2.2. Preparation of Ceramic Tiles
2.3. Determining Total Bacteria Number
2.4. Determining RLU Values by ATP Bioluminescence
2.5. Determining Biomass Reduction by Crystal-Violet Staining
2.6. Statistical Analysis and Graphing
3. Results
3.1. Reduction of the Number of Cultivable Bacteria Caused by 5% and 20% BDA
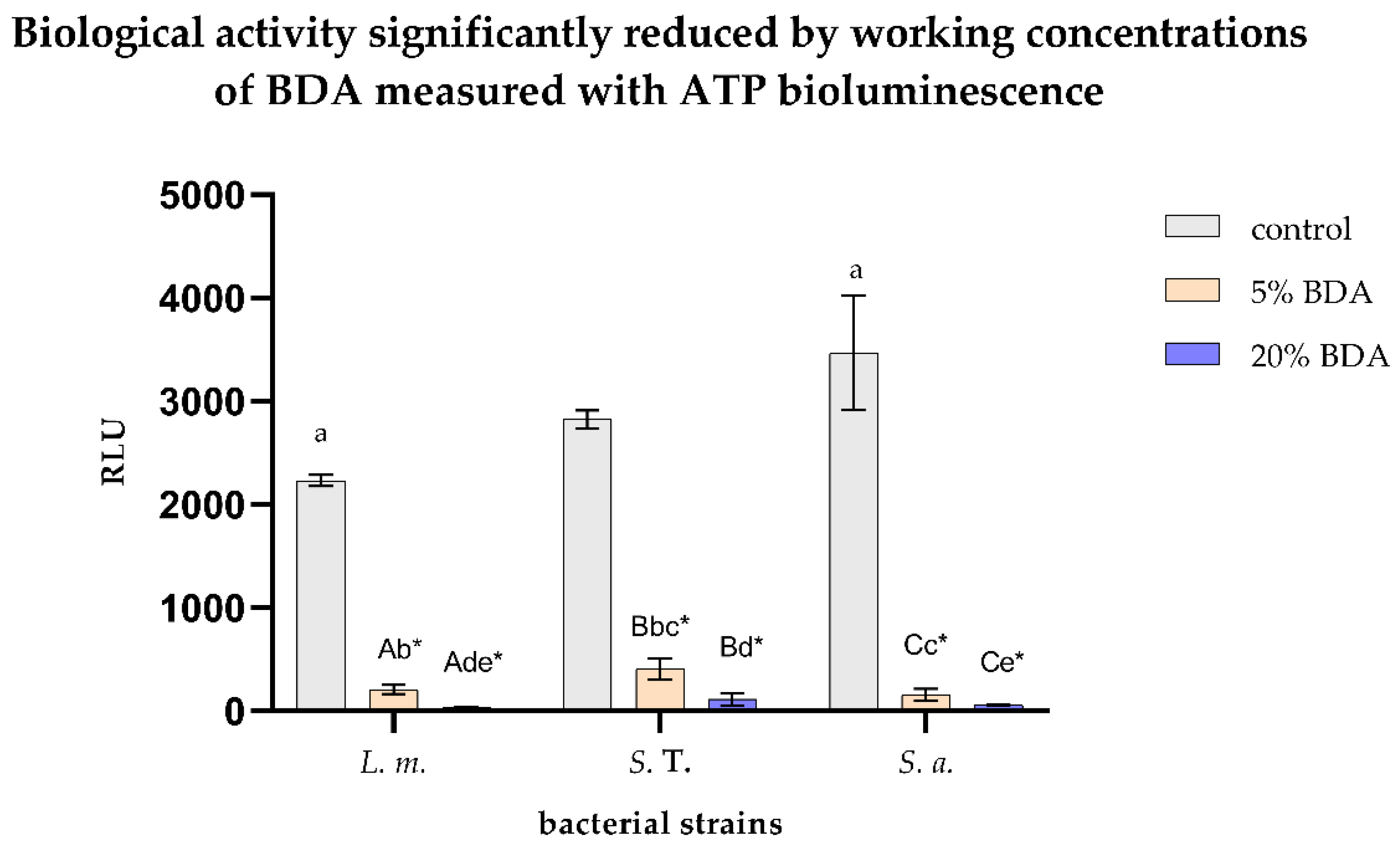
3.2. Biological Activity Significantly Reduced by Working Concentrations of BDA Measured with ATP Bioluminescence
3.3. Biomass Reduction by Working Concentrations of BAC Measured with Crystal Violet Staining
3.4. Biofilm Inhibition Rates Varied Using Different Detection Methods
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BAC | benzalkonium chloride |
| BDA | Bis duo Active |
| ca. | circa |
| CFU/cm2 | colony forming unit per square centimeter |
| CV | crystal violet |
| EPS | exopolysaccharide |
| L. m. | Listeria monocytogenes |
| OD | optical density |
| RLU | relative light units |
| S. T. | Salmonella Typhimurium |
| S. a. | Staphylococcus aureus |
| VBNC | viable but not cultivable state of bacteria |
References
- Merchel Piovesan Pereira, B.; Tagkopoulos, I. Benzalkonium Chlorides: Uses, Regulatory Status, and Microbial Resistance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, e00377-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, R.C.; Sheskey, P.J.; Quinn, M.E. Handbook of Pharmaceutical Excipients, 6th ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-0-85369-792-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kuca, K.; Marek, J.; Stodulka, P.; Musilek, K.; Hanusova, P.; Hrabinova, M.; Jun, D. Preparation of Benzalkonium Salts Differing in the Length of a Side Alkyl Chain. Molecules 2007, 12, 2341–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackner, M.; Guggenbichler, J.P. Antimicrobial Surfaces. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–13. ISBN 978-3-527-30673-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lavorgna, M.; Russo, C.; D’Abrosca, B.; Parrella, A.; Isidori, M. Toxicity and Genotoxicity of the Quaternary Ammonium Compound Benzalkonium Chloride (BAC) Using Daphnia Magna and Ceriodaphnia Dubia as Model Systems. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Chemicals Agency. Guidance on the Biocidal Products Regulation. Volume IV, Environment. Part A: Information Requirements; European Chemicals Agency: Helsinki, Finland, 2018.
- Choi, H.-Y.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lim, C.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Lee, I.-S.; Jo, J.-M.; Lee, H.-Y.; Cha, H.-G.; Woo, H.J.; Seo, D.-S. Assessment of Respiratory and Systemic Toxicity of Benzalkonium Chloride Following a 14-Day Inhalation Study in Rats. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakaran, S.; Abu-Hasan, M.; Hendeles, L. Benzalkonium Chloride: A Bronchoconstricting Preservative in Continuous Albuterol Nebulizer Solutions. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2017, 37, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Benzalkonium Chloride Used as an Excipient; Comittee for Human Medicinal Products (CHMP): Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; p. 14.
- Marple, B.; Roland, P.; Benninger, M. Safety Review of Benzalkonium Chloride Used as a Preservative in Intranasal Solutions: An Overview of Conflicting Data and Opinions. Otolaryngol. Neck Surg. 2004, 130, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeen, L. Introduction to Food Irradiation and Medical Sterilization. In The Effect of Sterilization on Plastics and Elastomers; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 1–40. ISBN 978-1-4557-2598-4. [Google Scholar]
- Vickery, K. Special Issue: Microbial Biofilms in Healthcare: Formation, Prevention and Treatment. Materials 2019, 12, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galié, S.; García-Gutiérrez, C.; Miguélez, E.M.; Villar, C.J.; Lombó, F. Biofilms in the Food Industry: Health Aspects and Control Methods. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizan, M.F.R.; Jahid, I.K.; Ha, S.-D. Microbial Biofilms in Seafood: A Food-Hygiene Challenge. Food Microbiol. 2015, 49, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, A.C.; Woodward, J.J.; Call, D.R.; Nero, L.A. Listeria monocytogenes in Food-Processing Facilities, Food Contamination, and Human Listeriosis: The Brazilian Scenario. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestby, L.K.; Grønseth, T.; Simm, R.; Nesse, L.L. Bacterial Biofilm and Its Role in the Pathogenesis of Disease. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkemngong, C.A.; Voorn, M.G.; Li, X.; Teska, P.J.; Oliver, H.F. A Rapid Model for Developing Dry Surface Biofilms of Staphylococcus Aureus and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa for in Vitro Disinfectant Efficacy Testing. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2020, 9, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, E.T.; Wilkinson, M.; Bradley, T. Chemical Disinfectants: Controversies Regarding Their Use in Low Risk Healthcare Environments (Part 1). J. Infect. Prev. 2019, 20, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Ma, M.; Sun, Y.; Xu, X.; Qiu, S.; Yin, J.; Chen, L. The Effect of Sublethal Concentrations of Benzalkonium Chloride on the LuxS/AI-2 Quorum Sensing System, Biofilm Formation and Motility of Escherichia coli. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 353, 109313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, P.S.; William Costerton, J. Antibiotic Resistance of Bacteria in Biofilms. Lancet 2001, 358, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridier, A.; Briandet, R.; Thomas, V.; Dubois-Brissonnet, F. Resistance of Bacterial Biofilms to Disinfectants: A Review. Biofouling 2011, 27, 1017–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, M.W.; Bell, R.; Ferreira, C.M.; Gonzalez-Escalona, N.; Hoffmann, M.; Muruvanda, T.; Ottesen, A.; Ramachandran, P.; Reed, E.; Sharma, S.; et al. Genomics of Foodborne Pathogens for Microbial Food Safety. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2018, 49, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanković, T.; Goić-Barišić, I.; Hrenović, J. Reduced Susceptibility to Disinfectants of Acinetobacter Baumannii Biofilms on Glass and Ceramic. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2017, 68, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletić, K.; Kovač, B.; Perčić, M.; Žigon, J.; Broznić, D.; Karleuša, L.; Lučić Blagojević, S.; Oder, M.; Gobin, I. Disinfecting Action of Gaseous Ozone on OXA-48-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae Biofilm In Vitro. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Bawazir, M.; Dhall, A.; Kim, H.-E.; He, L.; Heo, J.; Hwang, G. Implication of Surface Properties, Bacterial Motility, and Hydrodynamic Conditions on Bacterial Surface Sensing and Their Initial Adhesion. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 643722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piletić, K.; Kovač, B.; Planinić, M.; Vasiljev, V.; Karačonji, I.B.; Žigon, J.; Gobin, I.; Oder, M. Combined Biocidal Effect of Gaseous Ozone and Citric Acid on Acinetobacter Baumannii Biofilm Formed on Ceramic Tiles and Polystyrene as a Novel Approach for Infection Prevention and Control. Processes 2022, 10, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador, C.I.; Stannius, R.O.; Røder, H.L.; Burmølle, M. High-Throughput Screening Alternative to Crystal Violet Biofilm Assay Combining Fluorescence Quantification and Imaging. J. Microbiol. Methods 2021, 190, 106343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazan, R.; Que, Y.-A.; Maura, D.; Rahme, L.G. A Method for High Throughput Determination of Viable Bacteria Cell Counts in 96-Well Plates. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroyo, M.G.; Ferreira, A.M.; Frota, O.P.; Rigotti, M.A.; de Andrade, D.; Brizzotti, N.S.; Peresi, J.T.M.; Castilho, E.M.; de Almeida, M.T.G. Effectiveness of ATP Bioluminescence Assay for Presumptive Identification of Microorganisms in Hospital Water Sources. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monica, S.; Bancalari, E.; Castellone, V.; Rijkx, J.; Wirth, S.; Jahns, A.; Bottari, B. ATP Bioluminescence for Rapid and Selective Detection of Bacteria and Yeasts in Wine. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, C. Surface Sampling and the Detection of Contamination. In Handbook of Hygiene Control in the Food Industry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 673–696. ISBN 978-0-08-100155-4. [Google Scholar]



| L. monocytogenes | S. Typhimurium | S. aureus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5% BDA | 20% BDA | 5% BDA | 20% BDA | 5% BDA | 20% BDA | |
| CFU/cm2 | 99 | 99 | 98 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| RLU | 91 | 98 | 86 | 96 | 95 | 98 |
| CV | 52 | 57 | 58 | 64 | 28 | 43 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kovač, B.; Piletić, K.; Kovačević Ganić, N.; Gobin, I. The Effectiveness of Benzalkonium Chloride as an Active Compound on Selected Foodborne Pathogens Biofilm. Hygiene 2022, 2, 226-235. https://doi.org/10.3390/hygiene2040020
Kovač B, Piletić K, Kovačević Ganić N, Gobin I. The Effectiveness of Benzalkonium Chloride as an Active Compound on Selected Foodborne Pathogens Biofilm. Hygiene. 2022; 2(4):226-235. https://doi.org/10.3390/hygiene2040020
Chicago/Turabian StyleKovač, Bruno, Kaća Piletić, Nikolina Kovačević Ganić, and Ivana Gobin. 2022. "The Effectiveness of Benzalkonium Chloride as an Active Compound on Selected Foodborne Pathogens Biofilm" Hygiene 2, no. 4: 226-235. https://doi.org/10.3390/hygiene2040020
APA StyleKovač, B., Piletić, K., Kovačević Ganić, N., & Gobin, I. (2022). The Effectiveness of Benzalkonium Chloride as an Active Compound on Selected Foodborne Pathogens Biofilm. Hygiene, 2(4), 226-235. https://doi.org/10.3390/hygiene2040020







