Assessment of the Physicochemical and Textural Properties of Food Hydrogels Obtained Using Pea Protein and Gellan Gum †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. Samples Preparation
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Volumetric Gelling Index
2.3.2. Microrheological Properties
2.3.3. Textural Properties
2.3.4. Physical Stability
2.3.5. Color Parameters
2.3.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hilal, A.; Florowska, A.; Florowski, T.; Wroniak, M. A Comparative Evaluation of the Structural and Biomechanical Properties of Food-Grade Biopolymers as Potential Hydrogel Building Blocks. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.C.; Chang, C.C.; Chan, H.P.; Chung, T.W.; Shu, C.W.; Chuang, K.P.; Duh, T.H.; Yang, M.H.; Tyan, Y.C. Hydrogels: Properties and Applications in Biomedicine. Molecules 2022, 27, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, F.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Plant-Based Food Hydrogels: Constitutive Characteristics, Formation, and Modulation. Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2021, 56, 101505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, D.; Meng, L.; Chen, Y.; Tang, X. Recent Applications of Hydrogels in Food Safety Sensing: Role of Hydrogels. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 129, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D. Recent Advances in Hydrogels. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 1987–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćorković, I.; Pichler, A.; Buljeta, I.; Šimunović, J.; Kopjar, M. Carboxymethylcellulose Hydrogels: Effect of Its Different Amount on Preservation of Tart Cherry Anthocyanins and Polyphenols. Curr. Plant Biol. 2021, 28, 100222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćorković, I.; Pichler, A.; Šimunović, J.; Kopjar, M. Hydrogels: Characteristics and Application as Delivery Systems of Phenolic and Aroma Compounds. Foods 2021, 10, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordbar-Khiabani, A.; Gasik, M. Smart Hydrogels for Advanced Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, T.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J.; Van der Meeren, P. Designing Delivery Systems for Functional Ingredients by Protein/Polysaccharide Interactions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, A.; Florowska, A.; Wroniak, M. Binary Hydrogels: Induction Methods and Recent Application Progress as Food Matrices for Bioactive Compounds Delivery—A Bibliometric Review. Gels 2023, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, A.; Li, D.; Guo, Y.; Sun, L. Applications of Mixed Polysaccharide-Protein Systems in Fabricating Multi-Structures of Binary Food Gels—A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klost, M.; Brzeski, C.; Drusch, S. Effect of Protein Aggregation on Rheological Properties of Pea Protein Gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Huang, W.; Guo, X.; Chen, L. Strong and Elastic Pea Protein Hydrogels Formed through PH-Shifting Method. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Giri, T.K. Hydrogels Based on Gellan Gum in Cell Delivery and Drug Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, M.; Ghosh, B.; Giri, T.K. Enhanced Intestinal Stability and PH Sensitive Release of Quercetin in GIT through Gellan Gum Hydrogels. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 196, 111341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilal, A. Hydrożele Białkowo-Polisacharydowe Jako Nośniki Substancji Bioaktywnych Na Przykładzie Kurkuminy. Przemysł Spożywczy 2022, 1, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Faqih, M.N.; Wang, S.S. Factors Affecting Gel Formation of Inulin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2001, 46, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobol, Z.; Jakubowski, T.; Nawara, P. Application of the CIE L*a*b* Method for the Evaluation of the Color of Fried Products from Potato Tubers Exposed to C Band Ultraviolet Light. Sustainability 2020, 12, 3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Zhang, W.; Zou, Y.; Xing, L.; Zheng, H.; Xu, X.; Zhou, G. Influence of RosA-Protein Adducts Formation on Myofibrillar Protein Gelation Properties under Oxidative Stress. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 67, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, A.; Florowska, A.; Wroniak, M. Evaluation of the Physicochemical and Textural Properties of Binary Protein-Polysaccharide Hydrogels. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2022, 18, 41. [Google Scholar]
| Samples Code | Pea Protein (PP) [%] | Gellan Gum (GG) [%] |
|---|---|---|
| C1 | 10 | 0 |
| C2 | 12.5 | 0 |
| C3 | 0 | 0.5 |
| C4 | 0 | 0.75 |
| H1 | 10 | 0.5 |
| H2 | 10 | 0.75 |
| H3 | 12.5 | 0.5 |
| H4 | 12.5 | 0.75 |
| Samples | VGI [%] | SLB [nm−2] | EI × 10−3 [nm−2] | MVI × 10−4 [nm−2·s] | Strength [N] | Spreadability [N·s] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 82 a ± 1.5 | 0.89 e ± 0.02 | 0.7 a ± 0.01 | 0.08 a ± 0.0 | 0.06 a ± 0.00 | 0.12 a ± 0.01 |
| C2 | 89 b ± 1.5 | 0.65 cd ± 0.01 | 1.3 a ± 0.01 | 16.4 ab ± 3.1 | 0.06 a ± 0.00 | 0.17 a ± 0.01 |
| C3 | 100 c ± 0.0 | 0.47 ab ± 0.04 | 1.5 a ± 3.8 | 30.2 b ± 8.1 | 0.73 b ± 0.03 | 2.54 d ± 0.04 |
| C4 | 100 c ± 0.0 | 0.43 a ± 0.04 | 2.1 a ± 4.4 | 39.4 b ± 3.5 | 1.14 c ± 0.01 | 3.89 e ± 0.09 |
| H1 | 100 c ± 0.0 | 0.68 d ± 0.04 | 1.7 a ± 0.2 | 0.58 a ± 0.2 | 0.07 a ± 0.00 | 0.78 b ± 0.11 |
| H2 | 100 c ± 0.0 | 0.60 cd ± 0.06 | 2.6 a ± 0.1 | 4.27 a ± 0.8 | 0.07 a ± 0.00 | 1.85 c ± 0.19 |
| H3 | 100 c ± 0.0 | 0.67 d ± 0.03 | 16 b ± 0.07 | 1.54 a ± 0.4 | 0.08 a ± 0.00 | 0.76 b ± 0.01 |
| H4 | 100 c ± 0.0 | 0.55 bc ± 0.03 | 20 b ± 0.2 | 18.5 ab ± 2.6 | 0.10 a ± 0.00 | 1.97 c ± 0.05 |
| Statistic ANOVA, η2 [-] | ||||||
| [PP] | 0.682 | 0.692 | ns | 0.297 | ns | ns |
| [GG] | ns | 0.587 | ns | 0.275 | 0.949 | 0.983 |
| [GG] | 0.811 | 0.716 | ns | ns | 0.969 | ns |
| Samples | Instability Index | Color Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WI | YI | |||||
| C1 | 0.18 e ± 0.00 | 73.5 bc ± 1.55 | −4.4 c ± 0.16 | 17.9 c ± 0.44 | 67.7 cd ± 1.02 | 34.9 cd ± 0.21 |
| C2 | 0.03 c ± 0.00 | 74.5 c ± 0.39 | −3.7 d ± 0.05 | 19.3 d ± 0.37 | 67.8 cd ± 0.29 | 37.0 de ± 0.65 |
| C3 | 0.01 a ± 0.00 | 16.5 a ± 0.23 | −0.19 e ± 0.01 | −0.90 a ± 0.12 | 16.5 a ± 0.23 | −8.0 a ± 1.15 |
| C4 | 0.00 a ± 0.00 | 17.7 a ± 0.48 | −0.07 e ± 0.02 | −0.10 a ± 0.13 | 17.6 a ± 0.48 | −7.9 a ± 1.27 |
| H1 | 0.09 d ± 0.00 | 72.5 bc ± 0.04 | −5.6 a ± 0.25 | 14.3 b ± 0.42 | 68.5 d ± 0.24 | 28.2 b ± 0.84 |
| H2 | 0.02 b ± 0.00 | 72.8 bc ± 0.53 | −4.8 b ± 0.11 | 17.3 c ± 0.71 | 67.4 cd ± 0.23 | 34.0 c ± 1.19 |
| H3 | 0.02 b ± 0.00 | 72.0 b ± 0.94 | −4.2 c ± 0.24 | 18.0 c ± 0.65 | 66.4 bc ± 0.64 | 35.7 cd ± 1.10 |
| H4 | 0.02 b ± 0.00 | 71.9 b ± 0.41 | −4.1 c ± 0.05 | 19.3 d ± 0.25 | 65.7 c ± 0.22 | 38.4 e ± 0.31 |
| Statistic ANOVA, η2 [-] | ||||||
| [PP] | 0.997 | ns | 0.924 | 0.891 | 0.644 | 0.891 |
| [GG] | 0.977 | ns | 0.581 | 0.756 | ns | 0.757 |
| [GG] | 0.996 | ns | 0.665 | 0.753 | 0.686 | 0.762 |
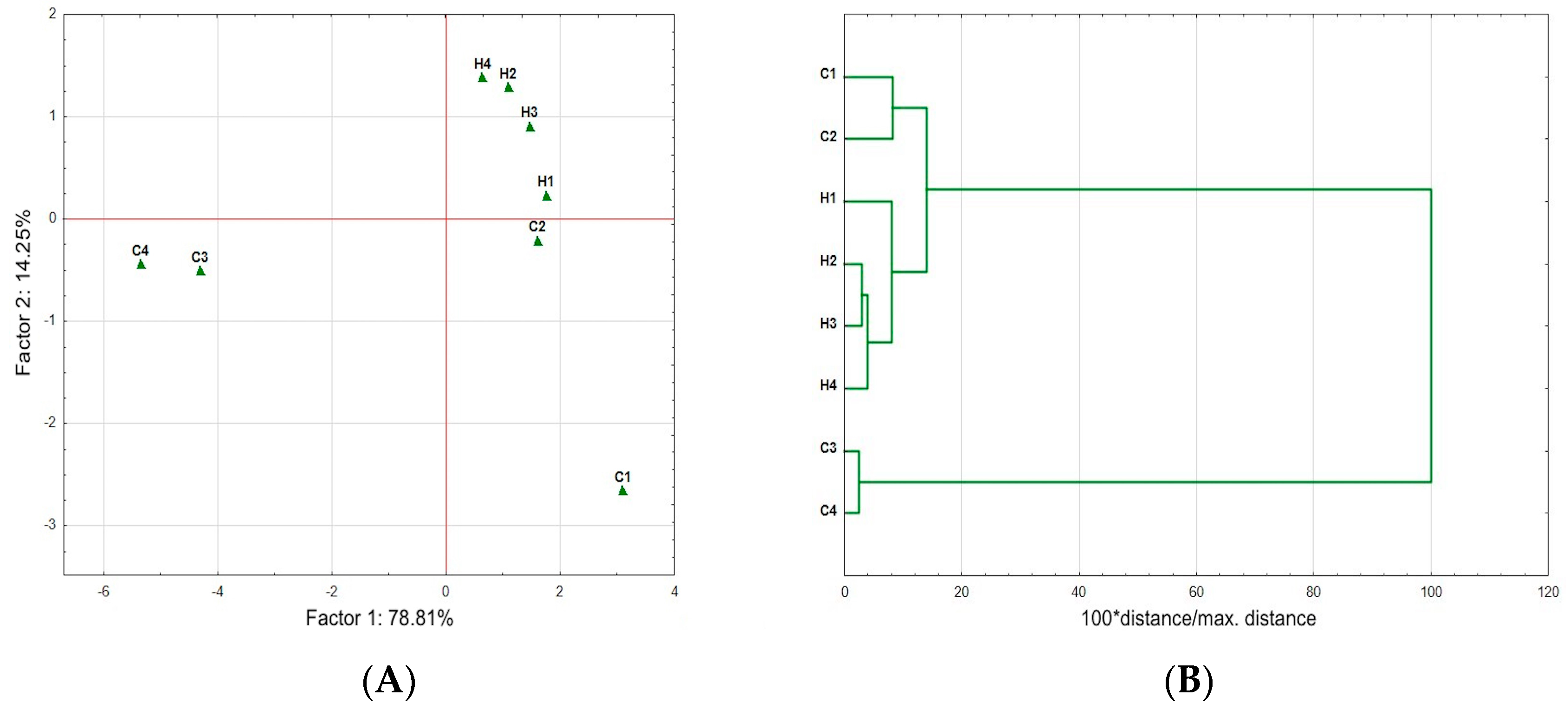
| Samples | H4 | H3 | H2 | H1 | C4 | C3 | C2 | C1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 2.13 | 1.57 | 1.06 | 3.98 | 59.14 | 60.18 | 1.81 | 0.00 |
| C2 | 2.58 | 2.88 | 2.85 | 5.73 | 60.44 | 61.47 | 0.00 | |
| C3 | 59.12 | 58.70 | 59.31 | 58.23 | 1.13 | 0.00 | ||
| C4 | 58.09 | 57.67 | 58.27 | 57.18 | 0.00 | |||
| H1 | 5.28 | 3.98 | 3.15 | 0.00 | ||||
| H2 | 2.28 | 1.22 | 0.00 | |||||
| H3 | 1.36 | 0.00 | ||||||
| H4 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hilal, A.; Florowska, A.; Florowski, T.; Wroniak, M. Assessment of the Physicochemical and Textural Properties of Food Hydrogels Obtained Using Pea Protein and Gellan Gum. Biol. Life Sci. Forum 2023, 26, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2023-15112
Hilal A, Florowska A, Florowski T, Wroniak M. Assessment of the Physicochemical and Textural Properties of Food Hydrogels Obtained Using Pea Protein and Gellan Gum. Biology and Life Sciences Forum. 2023; 26(1):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2023-15112
Chicago/Turabian StyleHilal, Adonis, Anna Florowska, Tomasz Florowski, and Małgorzata Wroniak. 2023. "Assessment of the Physicochemical and Textural Properties of Food Hydrogels Obtained Using Pea Protein and Gellan Gum" Biology and Life Sciences Forum 26, no. 1: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2023-15112
APA StyleHilal, A., Florowska, A., Florowski, T., & Wroniak, M. (2023). Assessment of the Physicochemical and Textural Properties of Food Hydrogels Obtained Using Pea Protein and Gellan Gum. Biology and Life Sciences Forum, 26(1), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2023-15112