Solar Particle Acceleration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Magnetic Reconnection
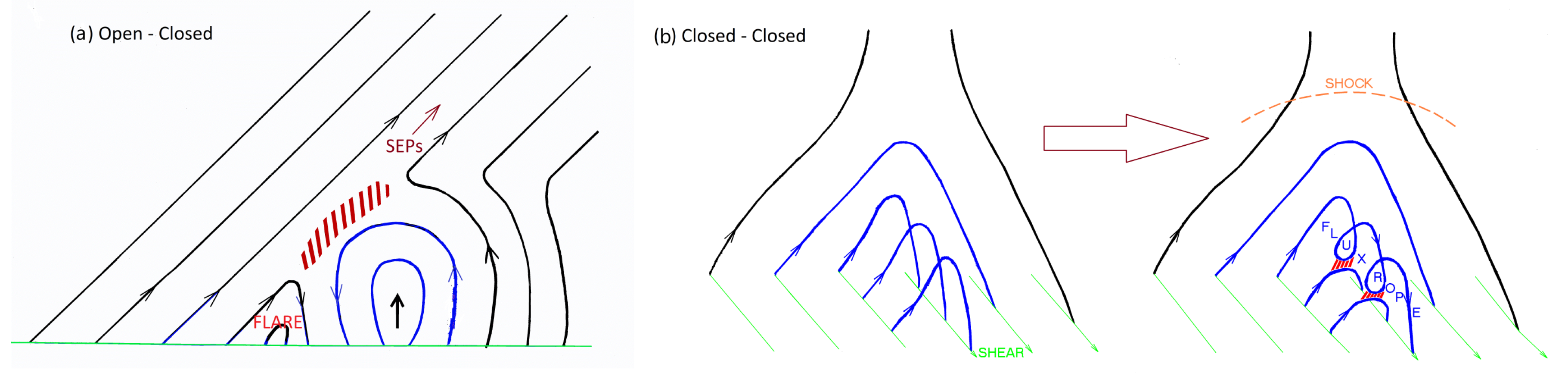
3. Impulsive Events
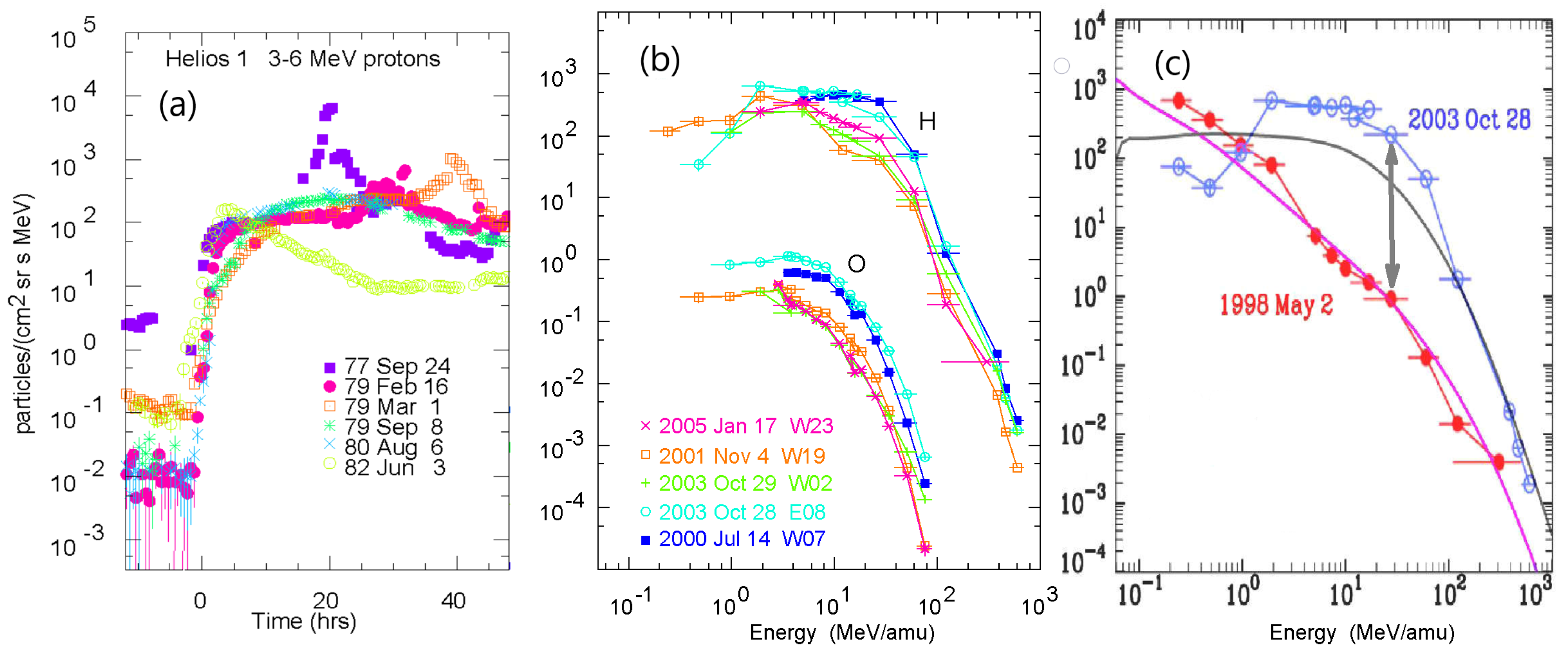
4. Shock Acceleration
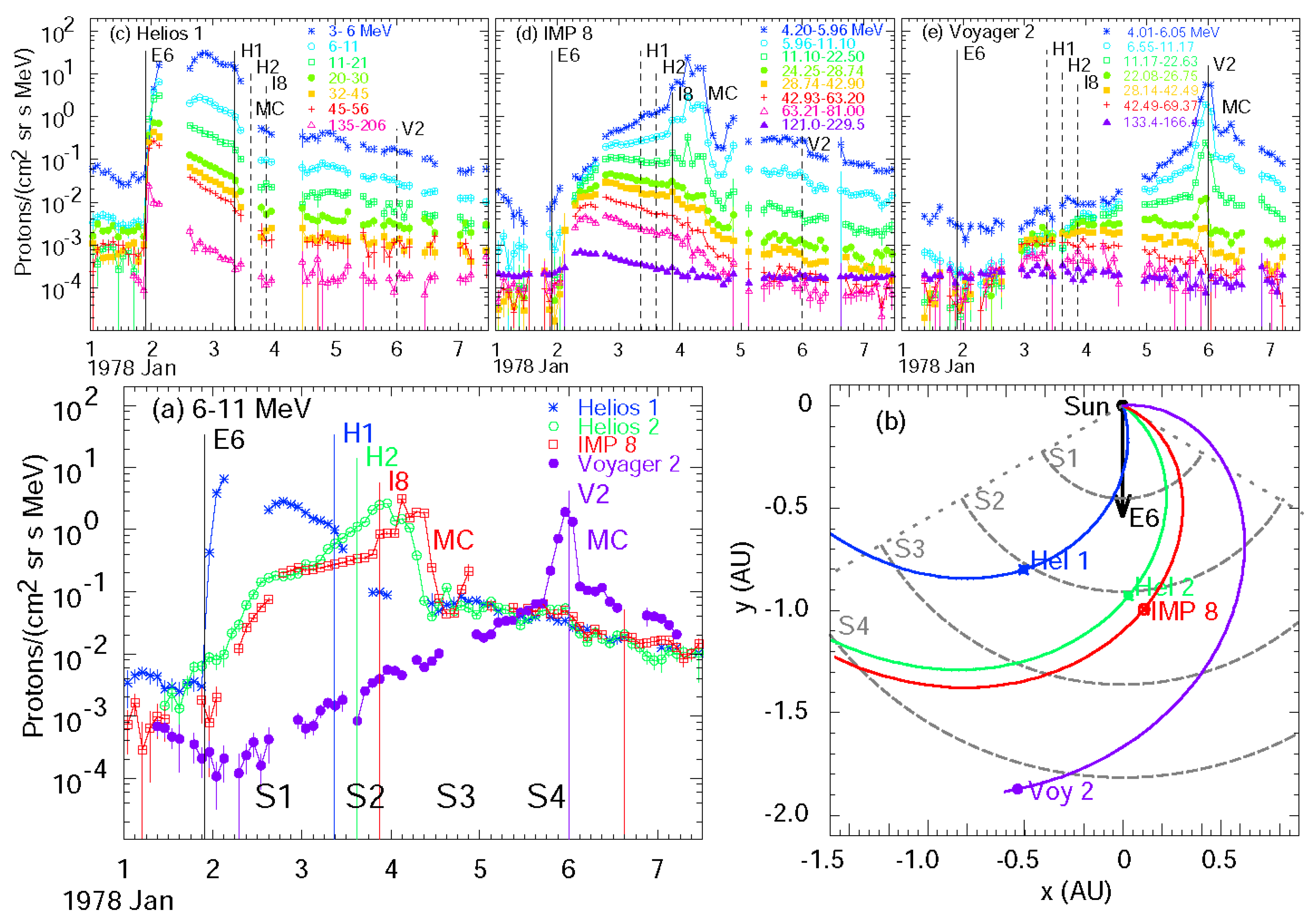
4.1. Spatial Distributions
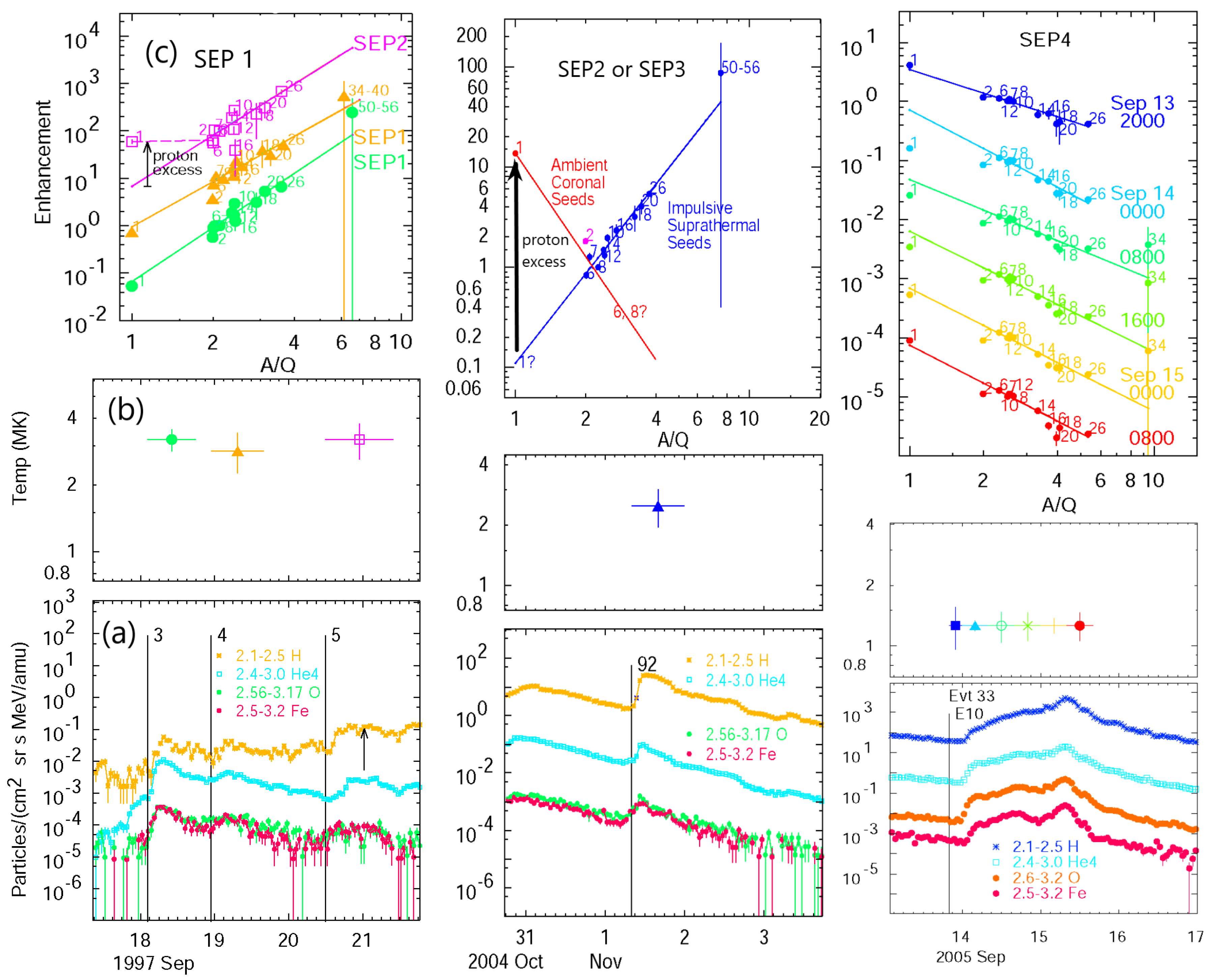
4.2. Element Abundances and Seed Particles
- SEP1: “Pure” impulsive SEPs with enhanced heavy elements from reconnections in solar jets, but no fast shocks.
- SEP3: Enhanced abundances accelerated by a fast CME-driven shock traversing an active region with residual seed ions from many small impulsive events that will dominate high Z.
- SEP4: Particles accelerated by a fast, wide, CME-driven shock with only ambient coronal abundances available as the dominant seed particles.
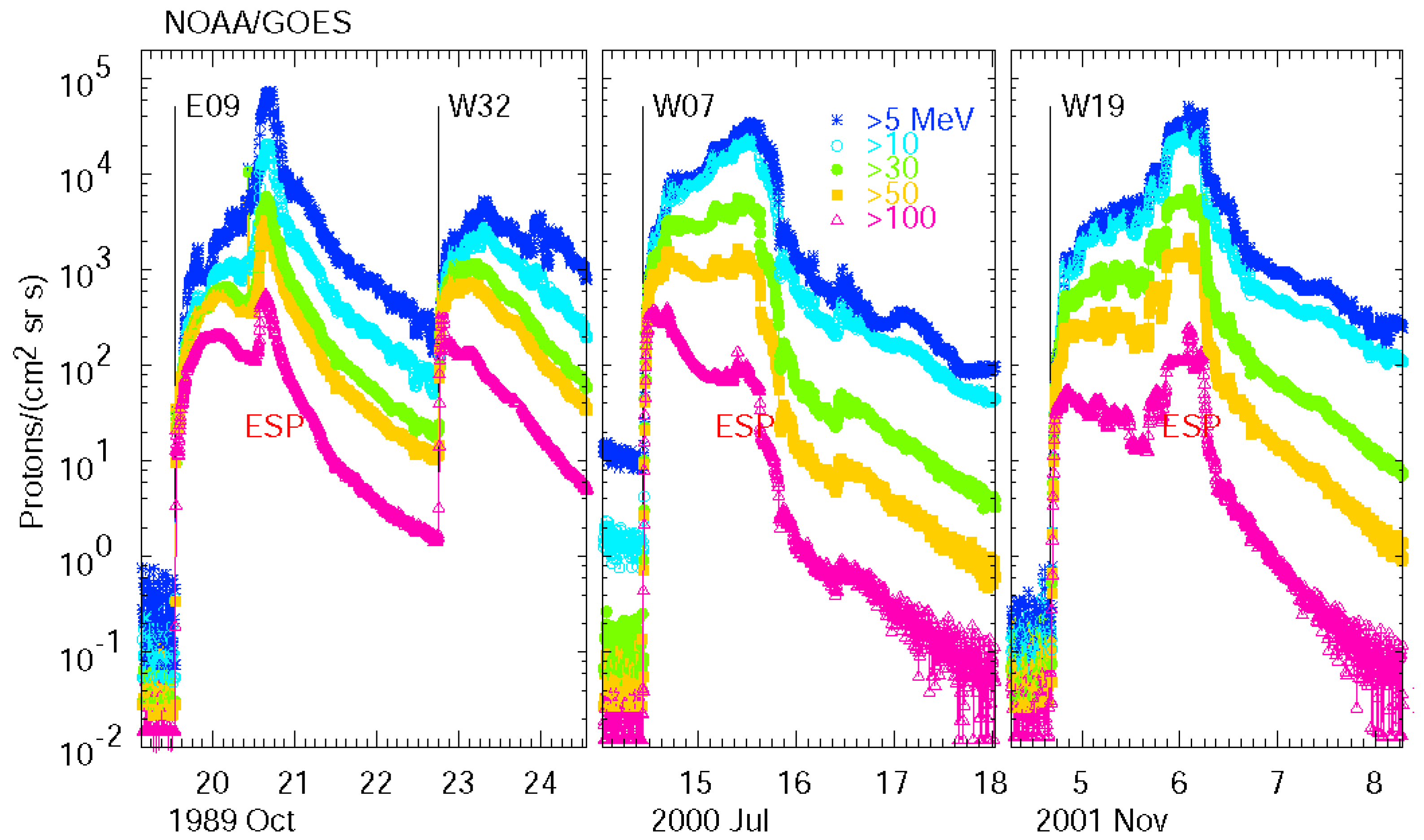
4.3. Energetic Storm Particle (ESP) Events
5. Discussion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kahler, S.W.; Sheeley, N.R., Jr.; Howard, R.A.; Koomen, M.J.; Michels, D.J.; McGuire, R.E.; von Rosenvinge, T.T.; Reames, D.V. Associations between coronal mass ejections and solar energetic proton events. J. Geophys. Res. 1984, 89, 9683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Solar Energetic Particles, 2nd ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Bimodal abundances in the energetic particles of solar and interplanetary origin. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1988, 330, L71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Abundances of trans-iron elements in solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2000, 540, L111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. The two sources of solar energetic particles. Space Sci. Rev. 2013, 175, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Abundances, ionization states, temperatures, and FIP in solar energetic particles. Space Sci. Rev. 2018, 214, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Element abundances and the physics of solar energetic particles. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2024, 11, 1368043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V.; Meyer, J.P.; von Rosenvinge, T.T. Energetic-particle abundances in impulsive solar flare events. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1994, 90, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V.; Cliver, E.W.; Kahler, S.W. Abundance enhancements in impulsive solar energetic-particle events with associated coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys. 2014, 289, 3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, G.M.; Reames, D.V.; Klecker, B.; Hovestadt, D.; von Rosenvinge, T.T. The heavy-ion compositional signature in He-3-rich solar particle events. Astrophys. J. 1986, 303, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, G.M.; Mazur, J.E.; Dwyer, J.R.; Jokippi, J.R.; Gold, R.E.; Krimigis, S.M. Abundances of heavy and ultraheavy ions in 3He-rich solar flares. Astrophys. J. 2004, 606, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V.; Ng, C.K. Heavy-element abundances in solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. 2004, 610, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, G.M. 3He-rich solar energetic particle events. Space Sci. Rev. 2007, 130, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bučík, R. 3He-rich solar energetic particles: Solar sources. Space Sci. Rev. 2020, 216, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.A. Coupled hydromagnetic wave excitation and ion acceleration at interplanetary traveling shocks. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.A. Coupled hydromagnetic wave excitation and ion acceleration at an evolving coronal/interplanetary shock. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 2005, 158, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Particle acceleration at the Sun and in the heliosphere. Space Sci. Rev. 1999, 90, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. How do shock waves define the space-time structure of gradual solar energetic-particle events? Space Sci. Rev. 2023, 219, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zank, G.P.; Rice, W.K.M.; Wu, C.C. Particle acceleration and coronal mass ejection driven shocks: A theoretical model. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 25079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.I.; Giacalone, J. Large gradual solar energetic particle events. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2016, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, E.N. The formation of sunspots from the solar toroidal field. Astrophys. J. 1955, 121, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.F.; Cassak, P.A.; Shay, M.A.; Swisdak, M.; Quataert, E. A magnetic reconnection mechanism for ion acceleration and abundance enhancements in impulsive flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2009, 700, L16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramoliš, D.; Bárta, M.; Varady, M.; Bučík, R. Preferential acceleration of heavy ions in a spontaneously fragmenting flare current sheet. Astrophys. J. 2022, 927, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzmaurice, A.; Drake, J.F.; Swisdak, M. Wave generation by flare-accelerated ions and implications for 3He acceleration. Astrophys. J. 2024, 964, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V.; Dennis, B.R.; Stone, R.G.; Lin, R.P. X-ray and radio properties of solar 3He-rich events. Astrophys. J. 1988, 327, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Temperature dependence of the abundances of elements in solar 3He-rich events. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1988, 325, L53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, R.A.; Pneuman, G.W. Magnetic reconnection in the corona and the loop prominence phenomena. Sol. Phys. 1976, 50, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Magnetic topology of impulsive and gradual solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2002, 571, L63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archontis, V.; Hood, A.W. A numerical model of standard to blowout jets. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2013, 769, L21, Erratum in: Astrophys. J. Lett. 2013, 770, L41.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Archontis, V.; Hood, A.W. Plasma jets and eruptions in solar coronal holes: A three-dimensional flux emergence experiment. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2015, 798, L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariat, E.; Dalmasse, K.; DeVore, C.R.; Antiochos, S.K.; Karpen, J.T. Model for straight helical solar jets. I. Parametric studies of the magnetic field geometry. Astron. Astrophys. 2015, 573, A130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, J.P.; Smerd, S.F.; Weiss, A.A. Solar Bursts. Annu. Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 1963, 1, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.P. The emission and propagation of 40 keV solar flare electrons. I: The relationship of 40 keV electron to energetic proton and relativistic electron emission by the sun. Sol. Phys. 1970, 12, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serlemitsos, A.T.; Balasubrahmanyan, V.K. Solar particle events with anomalously large relative abundance of 3He. Astrophys. J. 1975, 198, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V.; von Rosenvinge, T.T.; Lin, R.P. Solar 3He-rich events and nonrelativistic electron events—A new association. Astrophys. J. 1985, 292, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V.; Stone, R.G. The identification of solar 3He-rich events and the study of particle acceleration at the sun. Astrophys. J. 1986, 308, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibragimov, I.A.; Kocharov, G.E. Possible mechanism for enrichment of solar cosmic rays by helium—Three and heavy nuclei. In Proceedings of the 15th International Cosmic Ray Conference, Plovdiv, Bulgaria, 13–26 August 1977; Volume 11, p. 340. [Google Scholar]
- Kocharov, G.E.; Kocharov, L.G. Present state of experimental and theoretical investigations of solar events enriched by helium-3. In Proceedings of the 10th Symposium on Cosmic Rays, Aligarh, India, 12–16 December 1967; p. 37. [Google Scholar]
- Fisk, L.A. 3He-rich flares—A possible explanation. Astrophys. J. 1978, 224, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvoglis, H.; Papadopoulis, K. Selective nonresonant acceleration of He-3(2+) and heavy ions by H(+) cyclotron waves. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1983, 270, L95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocharov, G.E.; Kocharov, L.G. 3He-rich solar flares. Space Sci. Rev. 1984, 38, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherall, J. Turbulent heating in solar cosmic-ray theory. Astrophys. J. 1984, 281, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winglee, R.M. Heating and acceleration of heavy ions during solar flares. Astrophys. J. 1989, 343, 511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyopoulos, S. Subthreshold stochastic diffusion with application to selective acceleration of 3He in solar flares. Astrophys. J. 1991, 381, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temerin, M.; Roth, I. The production of 3He and heavy ion enrichment in 3He-rich flares by electromagnetic hydrogen cyclotron waves. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1992, 391, L105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, G.C.; Roelof, E.C.; Mason, G.M. The upper limit on 3He fluence in solar energetic particle events. Atrophys. J. Lett. 2005, 621, L141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Petrosian, V.; Mason, G.M. Stochastic acceleration of 3He and 4He in solar flares by parallel-propagating plasma waves. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2004, 613, L13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Petrosian, V.; Mason, G.M. Stochastic acceleration of 3He and 4He in solar flares by parallel-propagating plasma waves: General results. Astrophys. J. 2006, 636, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosian, V.; Jiang, Y.W.; Liu, S.; Ho, G.C.; Mason, G.M. Relative distributions of fluences of 3He and 4He in solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J. 2009, 701, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogro-Campero, A.; Simpson, J.A. Enrichment of very heavy nuclei in the composition of solar accelerated particles. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1972, 171, L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, D. Particle acceleration in solar flares by cyclotron damping of cascading turbulence. Astrophys. J. 1979, 229, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.A.; Reames, D.V. Heavy ion acceleration by cascading Alfvén waves in impulsive solar flares. AIP Conf. Proc. 1996, 374, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, D. Ultraheavy element enrichment in impulsive solar flares. Astrophys. J. 2014, 794, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, F.C.; Ellison, D.E. The plasma physics of shock acceleration. Space Sci. Rev. 1991, 58, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.R. The acceleration of cosmic rays in shock fronts—I. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 1978, 182, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.R. The acceleration of cosmic rays in shock fronts—II. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 1978, 182, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.K.; Reames, D.V. Shock acceleration of solar energetic protons: The first 10 minutes. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2008, 686, L123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stix, T.H. Waves in Plasmas; AIP: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Melrose, D.B. Plasma Astrophysics; Gordon & Breach: New York, NY, USA; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Decker, R.B. Formation of shock-spike events at quasi-perpendicular shocks. J. Geophys. Res. 1983, 88, 9959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Solar release times of energetic particles in ground-level events. Astrophys. J. 2009, 693, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Solar energetic-particle release times in historic ground-level events. Astrophys. J. 2009, 706, 844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cliver, E.W.; Kahler, S.W.; Reames, D.V. Coronal shocks and solar energetic proton events. Astrophys. J. 2004, 605, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J.P. The baseline composition of solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J. Suppl. 1985, 57, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laming, J.M. The FIP and inverse FIP effects in solar and stellar coronae. Living Rev. Sol. Phys. 2015, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Coronal Abundances determined from energetic particles. Adv. Space Res. 1995, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Element abundances in solar energetic particles and the solar corona. Sol. Phys. 2014, 289, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V.; Richardson, I.G.; Barbier, L.M. On the differences in element abundances of energetic ions from corotating events and from large solar events. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1991, 382, L43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mewaldt, R.A.; Cohen, C.M.S.; Leske, R.A.; Christian, E.R.; Cummings, A.C.; Stone, E.C.; von Rosenvinge, T.T.; Wiedenbeck, M.E. Fractionation of solar energetic particles and solar wind according to first ionization potential. Adv. Space Res. 2002, 30, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. The “FIP effect” and the origins of solar energetic particles and of the solar wind. Sol. Phys. 2018, 293, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laming, J.M.; Vourlidas, A.; Korendyke, C.; Chua, D.; Cranmer, S.R.; Ko, Y.-K.; Kuroda, N.; Provornikova, E.; Raymond, J.C.; Raouafi, N.-E.; et al. Element abundances: A new diagnostic for the solar wind. Astrophys. J. 2019, 879, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, G.M.; Ng, C.K.; Klecker, B.; Green, G. Impulsive acceleration and scatter-free transport of about 1 MeV per nucleon ions in 3He-rich solar particle events. Astrophys. J. 1989, 339, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breneman, H.H.; Stone, E.C. Solar coronal and photospheric abundances from solar energetic particle measurements. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1985, 299, L57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Acceleration of energetic particles by shock waves from large solar flares. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1990, 358, L63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V.; Ng, C.K. Streaming-limited intensities of solar energetic particles. Astrophys. J. 1998, 504, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V.; Ng, C.K. Streaming-limited intensities of solar energetic particles on the intensity plateau. Astrophys. J. 2010, 723, 1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacalone, J.; Cohen, C.M.S.; McComas, D.J.; Chen, X.; Dayeh, M.A.; Matthaeus, W.H.; Klein, K.G.; Bale, S.D.; Christian, E.R.; Desai, M.I.; et al. Analyses of ~0.05–2 MeV ions associated with the 2022 February 16 energetic storm particle event observed by Parker Solar Probe. Astrophys. J. 2023, 958, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.K.; Reames, D.V.; Tylka, A.J. Solar energetic particles: Shock acceleration and transport through self-amplified waves. AIP Conf. Proc. 2012, 1436, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.K.; Reames, D.V.; Tylka, A.J. Modeling shock-accelerated solar energetic particles coupled to interplanetary Alfvén waves. Astrophys. J. 2003, 591, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V.; Ng, C.K. The streaming limit of solar energetic-particle intensities. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.K. Effect of solar-wind velocity, magnetic field and density on solar energetic particle transport. ASP Conf. Ser. 2014, 484, 156. [Google Scholar]
- Vainio, R.; Pönni, A.; Battarbee, M.; Koskinen, H.E.J.; Afanasiev, A.; Laitinen, T. A semi-analytical foreshock model for energetic storm particle events inside 1 AU. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2014, 4, A08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Review and outlook of solar-energetic-particle measurements on multispacecraft missions. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2023, 10, 1254266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, G.M.; Mazur, J.E.; Dwyer, J.R. 3He enhancements in large solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. Lett. 1999, 525, L133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.I.; Mason, G.M.; Dwyer, J.R.; Mazur, J.E.; Gold, R.E.; Krimigis, S.M.; Smith, C.W.; Skoug, R.M. Evidence for a suprathermal seed population of heavy ions accelerated by interplanetary shocks near 1 AU. Astrophys. J. 2003, 588, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylka, A.J.; Cohen, C.M.S.; Dietrich, W.F.; Lee, M.A.; Maclennan, C.G.; Mewaldt, R.A.; Ng, C.K.; Reames, D.V. Shock geometry, seed populations, and the origin of variable elemental composition at high energies in large gradual solar particle events. Astrophys. J. 2005, 625, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylka, A.J.; Lee, M.A. Spectral and compositional characteristics of gradual and impulsive solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. 2006, 646, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandroos, A.; Vainio, R. Simulation results for heavy ion spectral variability in large gradual solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. 2007, 662, L127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Four distinct pathways to the element abundances in solar energetic particles. Space Sci. Rev. 2020, 216, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahler, S.W.; Reames, D.V.; Sheeley, N.R., Jr. Coronal mass ejections associated with impulsive solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. 2001, 562, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, N.V.; Reames, D.V.; DeRosa, M.L.; Yashiro, S.; Gopalswamy, N. Solar sources of impulsive solar energetic particle events and their magnetic field connection to the earth. Astrophys. J. 2006, 650, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-M.; Pick, M.; Mason, G.M. Coronal holes, jets, and the origin of 3He-rich particle events. Astrophys. J. 2006, 639, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, P.; Mazzitelli, G.; Colafrancesco, S.; Vittorio, N. Ionization balance for optically thin plasmas: Rate coefficients for all atoms and ions of the elements H to Ni. Astron. Astrophys. Suppl. 1988, 133, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, D.E.; Jensen, R.V.; Tarter, C.B.; Grasberger, W.H.; Lokke, W.A. Steady-state radiative cooling rates for low-density, high temperature plasmas. At. Data Nucl. Data Tables 1977, 20, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V.; Cliver, E.W.; Kahler, S.W. Variations in abundance enhancements in impulsive solar energetic-particle events and related CMEs and flares. Solar Phys. 2014, 289, 4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Temperature of the source plasma in gradual solar energetic particle events. Solar Phys. 2016, 291, 911–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reames, D.V. Seeds and sequences of element abundances in solar energetic particle events. Eur. Phys. J. Plus 2024, 139, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bučík, R.; Mulay, S.M.; Mason, G.M.; Nitta, N.V.; Desai, M.I.; Dayeh, M.A. Temperature in solar sources of 3He-rich solar energetic particles and relation to ion abundances. Astrophys. J. 2021, 908, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Kahler, S.; Raymond, J.C.; Ko, Y.K. Solar energetic particle charge states and abundances with nonthermal electrons. Astrophys. J. 2024, 963, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiFabio, R.; Guo, Z.; Möbius, E.; Klecker, B.; Kucharek, H.; Mason, G.M.; Popecki, M. Energy-dependent charge states and their connection with ion abundances in impulsive solar energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. 2008, 687, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AKouloumvakos, A.; Wijsen, N.; Jebaraj, C.; Afanasiev, A.; Lario, D.; Cohen, C.M.S.; Riley, P.; Mitchell, D.G.; Ding, Z.; Vourlidas, A.; et al. Shock and SEP modeling study for the 2022 September 5 SEP event. Astrophys. J. 2025, 797, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, G.M.; Roth, I.; Nitta, N.V.; Bučík, R.; Lario, D.; Ho, G.C.; Allen, R.C.; Kouloumvakos, A.; Wimmer-Schweingruber, R.F.; Rodriguez-Pacheco, J. Heavy-ion acceleration in 3He-rich solar energetic particle events: New insights from Solar Orbiter. Astrophys. J. 2023, 957, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, G.M.; Nitta, N.V.; Wiedenbeck, M.E.; Innes, D.E. Evidence for a common acceleration mechanism for enrichments of 3He and heavy ions in impulsive EP events. Astrophys. J. 2016, 823, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, I.; Temerin, M. Enrichment of 3He and heavy ions in impulsive solar flares. Astrophys. J. 1997, 477, 940–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, J.T. The solar flare myth. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 18937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, J.T. Corrections to “The solar flare myth”. J. Geophys. Res. 1994, 99, 4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandzhavidze, N.; Ramaty, R.; Kozlovsky, B. Determination of the abundances of subcoronal 4He and of solar flare-accelerated 3He and 4He from gamma-ray spectroscopy. Astrophys. J. 1999, 518, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.J.; Kozlovsky, B.; Share, G.H. Evidence for enhanced 3He in flare-accelerated particles based on new calculations of the gamma-ray line spectrum. Astrophys. J. 2016, 833, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.J.; Ramaty, R.; Kozlovsky, B.; Reames, D.V. Solar abundances from gamma-ray spectroscopy: Comparisons with energetic particle, photospheric, and coronal abundances. Astrophys. J. 1991, 371, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen CM, S.; Mason, G.M.; Mewaldt, R.A. Characteristics of solar energetic ions as a function of longitude. Astrophys. J. 2017, 843, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.G.; Cohen, C.M.S.; Leske, R.A.; Muro, G.D.; Cummings, A.C.; McComas, D.J.; Schwadron, N.A.; Christian, E.R.; Wiedenbeck, M.E.; McNutt, R.L.; et al. Composition variation of the May 16 2023 Solar Energetic Particle Event observed by SolO and PSP. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2024, 976, L3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.K.; Reames, D.V. Focused interplanetary transport of approximately 1 MeV solar energetic protons through self-generated Alfven waves. Astrophys. J. 1994, 424, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.K.; Reames, D.V.; Tylka, A.J. Effect of proton-amplified waves on the evolution of solar energetic particle composition in gradual events. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, E.N. Nanoflares and the solar X-ray corona. Astrophys. J. 1988, 330, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahler, S.W. The role of the big flare syndrome in correlations of solar energetic proton fluxes and associated microwave burst parameters. J. Geophys. Res. 1982, 87, 3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahler, S.W.; Ling, A.G. Forecasting solar energetic particle (SEP) events with flare X-ray peak ratios. J. Space Weather Space Clim. 2018, 8, A47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Airapetian, V.; Li, G.; Zank, G.; Jin, M. Extreme energetic particle events by superflare-asssociated CMEs from solar-like stars. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabi9743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Airapetian, V.; Hu, J.; Li, G.; Zank, G. Effect of star rotation rates on the characteristics of energetic particle events. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2019, 878, L36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Mondal, S.; Wedemeyer, S.; Gopalswamy, N. Energetic particle activity in AD Leo: Detection of a solar-like type-IV burst. Astron. Astrophys. 2024, 686, A51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Gopalswamy, N.; Mondal, S.; Kumari, A.; Sindhuja, G. CME-associated type-IV radio bursts: The solar paradigm and the unique case of AD Leo. In Solar and Stellar Coronal Mass Ejections, Proceedings of the IAU Symposium No. 388, Krakow, Poland, 5–10 May 2024; Gopalswamy, N., Malandraki, O., Vidotto, A., Manchester, W., Eds.; IAU: Paris, France, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, A.; Gopalswamy, N.; Kumari, A.; Akiyama, S.; Sindhuja, G. Interplanetary Type IV Solar Radio Bursts: A Comprehensive Catalog and Statistical Results. Astrophys. J. 2024, 971, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reames, D.V. Solar Particle Acceleration. Astronomy 2025, 4, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/astronomy4010005
Reames DV. Solar Particle Acceleration. Astronomy. 2025; 4(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/astronomy4010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleReames, Donald V. 2025. "Solar Particle Acceleration" Astronomy 4, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/astronomy4010005
APA StyleReames, D. V. (2025). Solar Particle Acceleration. Astronomy, 4(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/astronomy4010005





