Biomass Carbon Sequestration Potential by Riparian Forest in the Tarim River Watershed, Northwest China: Implication for the Mitigation of Climate Change Impact
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
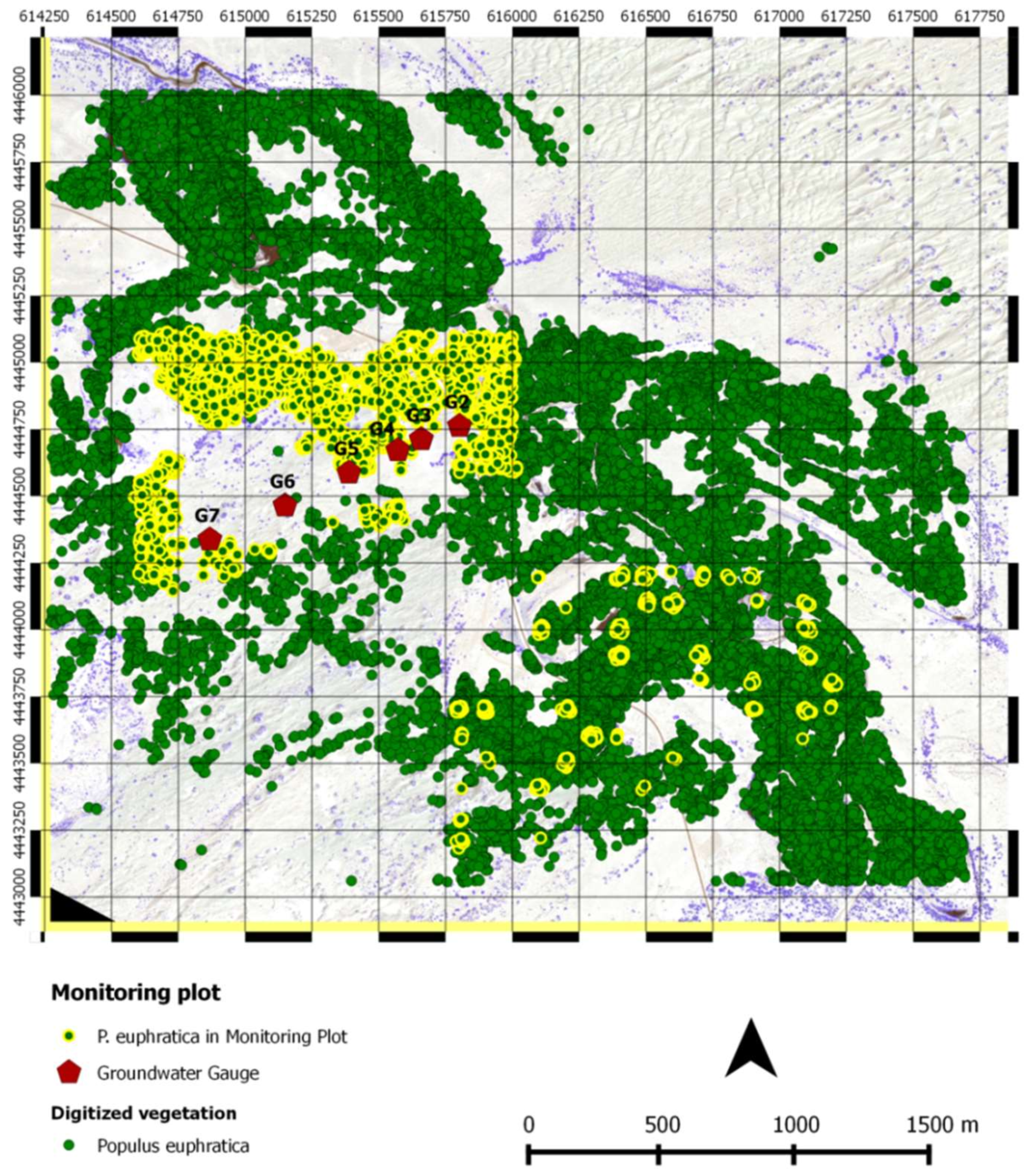
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Data Collection and Processing
3. Results and Discussions
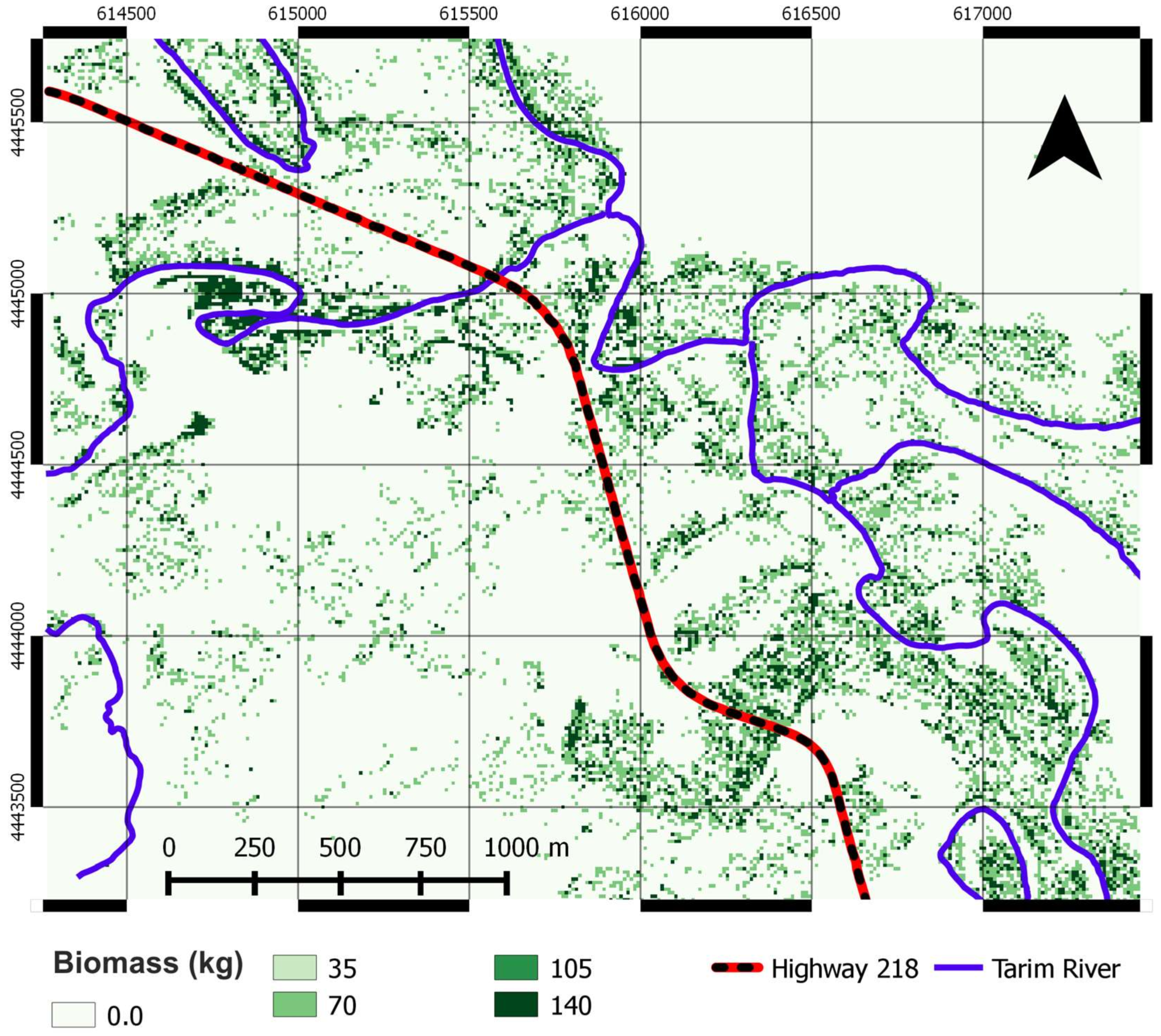
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Biomass, Carbon Storage, and Ecosystem Service Value
3.2. Dependency of Tree Biomass Production and Carbon Storage on Water Availability
3.3. Potential Effect of Water Diversion Project in Relation to Forest Carbon Storage
3.4. Implications of the Results for Climate Change Mitigation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories, Prepared by the National Greenhouse Gas Inventories Programme; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006; Volume 4, ISBN 4-88788-032-4. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, J.Y.; Chen, A.P.; Peng, C.H.; Zhao, S.Q.; Ci, L.J. Changes in forest biomass carbon storage in China between 1949 and 1998. Science 2001, 292, 2320–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, S.L.; Fang, J.Y.; Ciais, P.; Peylin, P.; Huang, Y.; Sitch, S.; Wang, T. The carbon balance of terrestrial ecosystems in China. Nature 2009, 458, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.G.; Houghton, R.A.; Tang, L.S. Hidden carbon sink beneath desert. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 5880–5887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, T.J.; Woodburry, P.B.; Battles, J.J.; Goodale, J.C.L.; Hamburg, S.P.; Ollinger, S.V.; Wodall, C.W. Forest Carbon Storage: Ecology, Management and Policy. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2010, 8, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Birdsey, R.S.; Fang, J.; Houghton, R.; Kauppi, P.E.; Kurz, W.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Shvidenko, A.; Lewis, S.L.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. A large and persistent Carbon Sink in the World’s Forests. Science 2011, 333, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerbe, S.; Thevs, N. Restoring Central Asian Floodplain Ecosystems as Natural Capital and Cultural Heritage in a continental Desert Environment. In Landscape Ecology in Asian Cultures; Hong, S.K., Kim, J.E., Wu, J., Nakagoshi, N., Eds.; Ecological Research Monographs; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2011; pp. 277–297. ISBN 978-4-431-87798-1. [Google Scholar]
- Grünzweig, J.M.; Lin, T.; Rotenberg, E.; Schwartz, A.; Yakir, D. Carbon sequestration in arid-land forest. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2010, 9, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Luo, G.P.; Maisupova, B.; Chen, X.; Mukanov, B.M.; Wu, M.; Mambetov, B.T.; Huang, J.F.; Li, C.F. Carbon budget from forest land use and management in Central Asia during 1961–2010. Agr. For. Meteorol. 2016, 221, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevs, N.; Buras, A.; Zerbe, S.; Kühnel, E.; Abdusalih, N.; Ovezberdiyeva, A. Structure and wood biomass of near-natural floodplain forests along the Central Asian Rivers Tarim and Amu Darya. Forestry 2012, 85, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buras, A.; Thevs, N.; Zerbe, S.; Wilmking, M. Productivity and carbon sequestration of Populus euphratica at the Amu River, Turkmenistan. Forestry 2013, 86, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuba, M.; Aishan, T.; Cyffka, B.; Halik, Ü. Analysis of connections between soil moisture, groundwater level and vegetation vitality along two transects at the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River, Northwest China. Geo-Öko 2013, 34, 103–127. [Google Scholar]
- Hai, Y.; Wai, L.; Hoppe, T.; Thevs, N. Half a Century of Environmental Change in the Tarim River Valley—An Outline of Cause and Remedies. In Watershed and Floodplain Management along the Tarim River in China’s Arid Northwest; Hoppe, T., Kleinschmit, B., Roberts, B., Thevs, N., Halik, U., Eds.; Shaker Press: Aachen, Germany, 2006; pp. 39–76. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.D.; Fan, Z.L.; Lei, Z.D. Research on Water Resources and Ecology of the Tarim River, China; Peoples Press: Urumqi, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P. Irrigation-Free Vegetation and It’s Recovery in Arid Region; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002; pp. 15–50. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Chen, Y.N.; Ma, J.X.; Chen, Y.P. Study on change in value of ecosystem service function of Tarim River. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyffka, B.; Rumbaur, C.; Kuba, M.; Disse, M. Sustainable Management of River Oases along the Tarim River, P.R. China (SuMaRiO) and the Ecosystem Services Approach. Geogr. Soc. Environ. 2013, 6, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giese, E.; Mamatkanov, D.M.; Wang, R. Wasserressourcen und deren Nutzung im Flussbecken des Tarim (Autonome Region Xinjiang/VR China); Discussion Papers 25.; Zentrum für Internationale Entwicklungs- und Umweltforschung: Justus Liebig University Giessen, Germany, 2006; Volume 20, p. 63. Available online: http://geb.uni-giessen.de/geb/volltexte/2006/2661 (accessed on 13 January 2018).
- Tao, H.; Gemmer, M.; Bai, Y.; Su, B.; Mao, W. Trends of stream flow in the Tarim River Basin through the past 50 years: Human Impact or Climate Change? J. Hydrol. 2011, 400, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishan, T.; Halik, Ü.; Cyffka, B.; Kuba, M.; Abliz, A.; Baidourela, A. Monitoring the hydrological and ecological response to water diversion in the lower reaches of the Tarim River, northwest China. Quat. Int. 2013, 311, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halik, U.; Kurban, A.; Mijit, M.; Schulz, J.; Paproth, F.; Coenradie, B. The Potential Influence of Embankment Engineering and Ecological Water Transfer on the Riparian Vegetation along the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Tarim River. In Watershed and Floodplain Management along the Tarim River in China’s Arid Northwest; Hoppe, T., Kleinschmit, B., Roberts, B., Thevs, N., Halik, U., Eds.; Shaker Press: Aachen, Germany, 2006; pp. 221–236. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.N.; Chen, Y.P.; Xu, C.C.; Ye, Z.X.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhu, C.G.; Ma, X.D. Effects of ecological water conveyance on groundwater dynamics and riparian vegetation in the lower reaches of Tarim River, China. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, F.; Halik, Ü.; Kuba, M.; Aishan, T.; Cyffka, B. Controls on aeolian sediment dynamics by natural riparian vegetation in the Eastern Tarim Basin, NW China. Aeolian Res. 2015, 18, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, T.; Kleinschmit, B.; Roberts, B.; Thevs, N.; Halik, Ü. Watershed and Floodplain Management along the Tarim River in China’s Arid Northwest; Shaker Press: Aachen, Germany, 2006; ISBN 978-3-8322-5662-3. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.L.; Ye, M.; Li, J.M. The ecological characteristics of the riparian vegetation affected by river overflowing disturbance in the lower Tarim River. Environ. Geol. 2009, 58, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.N.; Ye, Z.X.; Shen, Y.J. Desiccation of the Tarim River, Xinjiang, China, and mitigation strategy. Quat. Int. 2011, 244, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.L.; Ye, M.; Li, J.M. Changes in groundwater levels and the response of natural vegetation to transfer of water to the lower reaches of the Tarim River. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halik, Ü.; Chai, Z.; Kurban, A.; Cyffka, B. The positive response of some ecological indices of Populus euphratica to the emergency water transfer in the lower reaches of the Tarim River. Resour. Sci. 2009, 31, 1309–1314. [Google Scholar]
- Halik, Ü.; Aishan, T.; Kurban, A.; Cyffka, B.; Opp, C. Response of Crown Diameter of Populus euphratica to Ecological Water Transfer in the Lower Reaches of Tarim River. J. Northeast For. Univ. 2011, 39, 82–84. [Google Scholar]
- Aishan, T.; Halik, Ü.; Kurban, A.; Cyffka, B.; Kuba, M.; Betz, F.; Keyimu, M. Eco-morphological response of floodplain forests (Populus euphratica Oliv.) to water diversion in the lower Tarim River, northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tang, D.S. The influence of water conveyances on restoration of vegetation to the lower reaches of Tarim River. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 59, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aishan, T. Degraded Tugai Forests under Rehabilitation in the Tarim Riparian Ecosystem, Northwest China: Monitoring, Assessing and Modelling. Ph.D. Thesis, Katholische Universität Eichstätt-Ingolstadt, Eichstätt, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.H.; Li, H.Q. Study on Biomass of natural Diversifolious Poplar Plantations in River Talimu, Xinjiang, Western China. For. Sci. Technol. Xinjiang 1984, 3, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, F.M.; Jeschke, M.; Zhang, X.; Lang, P. Stand structure and productivity of Populus euphratica along a gradient of groundwater distances at the Tarim River (NW China). J. Plant Ecol. 2016, 10, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, R.A.; Schafer, S.E. Forest Carbon Sequestration and Storage of the Kargasoksky Leshoz of the Tomsk Oblast, Russia—Current Status and the Investment Potential. In Climate Change and Terrestrial Carbon Sequestration in Central Asia; Lal, R., Suleimenov, M., Stewart, B.A., Hansen, D.O., Doraiswamy, P., Eds.; CRC Press: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 363–370. ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, N.H.; Peters, S.; Bakhski, V.; Bowen, A.; Cameron, C.; Catovsky, S.; Crane, D.; Cruickshank, S.; Dietz, S.; Edmondson, N.; et al. Stern Review: The Economics of Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Tol, R.S.J. The Economic Effects of Climate Change. J. Econ. Perspect. 2009, 23, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natural Capital Project. Available online: https://www.naturalcapitalproject.org/invest/ (accessed on 20 March 2018).
- Nordhaus, W.D. A Review of the Stern Review on the Economics of Climate Change. J. Econ. Lit. 2007, 45, 686–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzman, M.L. A Review of the Stern Review on the Economics of Climate Change. J. Econ. Lit. 2007, 45, 703–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzek, V.; Puleston, C.; Gunn, J. Can carbon credits fund riparian forest restoration? Restor. Ecol. 2015, 23, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.H.; Chen, X.; Qian, J.; Liu, S.G. Spatial Pattern of Populus euphratica Forest Change as Affected by Water Conveyance in the Lower Tarim River. Forests 2014, 5, 134–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.J.; Wang, X.K.; Zhang, X.Q.; Lu, F. Biomass and Its Allocation of Forest Ecosystems in China; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2013; pp. 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger, W.H.; Belnap, J.; Marion, G. On carbon sequestration in desert ecosystems. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 1488–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huxman, T.E.; Snyder, K.A.; Tissue, D.; Leffler, A.J.; Ogle, K.; Pockman, W.T.; Sandquist, D.R.; Potts, D.L.; Schwinning, S. Precipitation pulses and carbon fluxes in semiarid and arid ecosystems. Oecologia 2004, 141, 254–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyimu, M.; Halik, Ü.; Rouzi, A. Relating Water Use to Tree Vitality of Populus euphratica Oliv. in the Lower Tarim River, NW China. Water 2017, 9, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyimu, M.; Halik, Ü.; Kurban, A. Estimation of water consumption of riparian forest in the lower reaches of Tarim River, northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.M. Ecology of Phreatophytes. In Progress in Botany; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; Volume 75, pp. 335–375. ISBN 978-3-642-38796-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.; Li, W. Impacts of ecological water conveyance on groundwater dynamics and vegetation recovery in the lower reaches of the Tarim River in northwest China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 7605–7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumbaur, C.; Thevs, N.; Disse, M.; Ahlheim, M.; Brieden, A.; Cyffka, B.; Duethmann, D.; Feike, T.; Frör, O.; Gärtner, P.; et al. Sustainable management of river oases along the Tarim River (SuMaRiO) in Northwest China under conditions of climate change. Earth Syst. Dyn. 2015, 6, 83–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamat, Z.; Halik, Ü.; Keyimu, M.; Keram, A.; Nurmamat, K. Variation of the Floodplain Forest Ecosystem Service Value in the Lower Reaches of Tarim River, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Feng, Q.; Yu, T.; Su, Y.; Deo, R.C. Carbon dioxide fluxes and their environmental controls in a riparian forest within the hyper-arid region of Northwest China. Forests 2017, 8, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.J.; Yang, P.N.; Zhou, H.Y.; Xu, H.L. Water Conversion and Strategy of Ecological Water Conveyance in the Lower Reaches of the Tarim River. Arid Zone Res. 2017, 34, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyer, C.; Guericke, M.; Ibisch, P.L. Climate change mitigation via afforestation, reforestation and deforestation avoidance: And what about adaptation to environmental change? New For. 2009, 38, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, M.R.; Barros, V.R.; Broome, J.; Cramer, W.; Christ, R.; Church, J.A.; Clarke, L.; Dahe, Q.; Dasgupta, P.; Dubash, N.K.; et al. IPCC Fifth Assessment Synthesis Report—Climate Change 2014 Synthesis Report; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; 167p. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, A.Y.; Cong, R. After CDM: Domestic carbon offsetting in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Biomass Fraction | Formula | Correlation Coefficient R |
|---|---|---|
| Trunk biomass (BT) | LogBT = log0.0382 + 0.8837 × logDBH2H | 0.99 |
| Branch and twig biomass (BB) | LogBB = log0.1072 + 0.6350 × logDBH2H | 0.89 |
| Leaf biomass (BL) | LogBL = log(1.41 × 10−3) + 0.8134 × logDBH2H | 0.71 |
| Root Biomass(BR) | LogBR = log0.1059 + 0.6185 × logDBH2H | 0.94 |
| Total Biomass (B) | B = BT + BB + BL + BR |
| Lower Boundary of CI | Median | Upper Boundary of CI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biomass | 26,737.29 kg | 1,581,166 kg | 12,416,286 kg |
| Carbon Storage | 13,368.64 kg | 790,583.20 kg | 6,208,143 kg |
| Value | 1163.072 $ | 68,780.74 $ | 540,108.4 $ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aishan, T.; Betz, F.; Halik, Ü.; Cyffka, B.; Rouzi, A. Biomass Carbon Sequestration Potential by Riparian Forest in the Tarim River Watershed, Northwest China: Implication for the Mitigation of Climate Change Impact. Forests 2018, 9, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9040196
Aishan T, Betz F, Halik Ü, Cyffka B, Rouzi A. Biomass Carbon Sequestration Potential by Riparian Forest in the Tarim River Watershed, Northwest China: Implication for the Mitigation of Climate Change Impact. Forests. 2018; 9(4):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9040196
Chicago/Turabian StyleAishan, Tayierjiang, Florian Betz, Ümüt Halik, Bernd Cyffka, and Aihemaitijiang Rouzi. 2018. "Biomass Carbon Sequestration Potential by Riparian Forest in the Tarim River Watershed, Northwest China: Implication for the Mitigation of Climate Change Impact" Forests 9, no. 4: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9040196
APA StyleAishan, T., Betz, F., Halik, Ü., Cyffka, B., & Rouzi, A. (2018). Biomass Carbon Sequestration Potential by Riparian Forest in the Tarim River Watershed, Northwest China: Implication for the Mitigation of Climate Change Impact. Forests, 9(4), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/f9040196







