Impact of Incretin Mimetics on Thyroid Cancer Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Time-to-Event Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Study Cohort
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus diagnosis: Patients were included if they had a condition having SNOMED codes 201826 or 443732 for either “Type 2 diabetes mellitus” or “Disorder due to type 2 diabetes mellitus”, respectively. Any electronic health record codes derived from these codes were also considered indicative of a T2D diagnosis;
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c): Consistent with the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 2023 standards of care, patients with an A1c measure of 6.5% (48 mmol/mol) or greater were considered to have T2D [31]. Therefore, we considered a patient having at least two HbA1c measurements at or above 6.5% to have T2D;
- Plasma glucose: The ADA 2023 standard of care criteria permits a T2D diagnosis given an 8-h fasting plasma glucose of 126 mg/dL (7.0 mmol/L) or greater or a plasma glucose measure of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or greater using an anhydrous glucose load equivalent to 75 g [31]. In our study, patients who had two of either measurement beyond this threshold were considered to have T2D;
- Hyperglycemia: In line with the ADA 2023 standards, patients with a diagnosis of hyperglycemia or a symptom (excessive thirst, frequent urination, or blurred vision) and a random plasma glucose of at least 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) were included;
- Patients lacking a hyperglycemia diagnosis were required to have at least two elevated A1c or (fasting) plasma glucose test results.
2.3. Exposure Definition
2.4. Outcome Definition
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Covariates
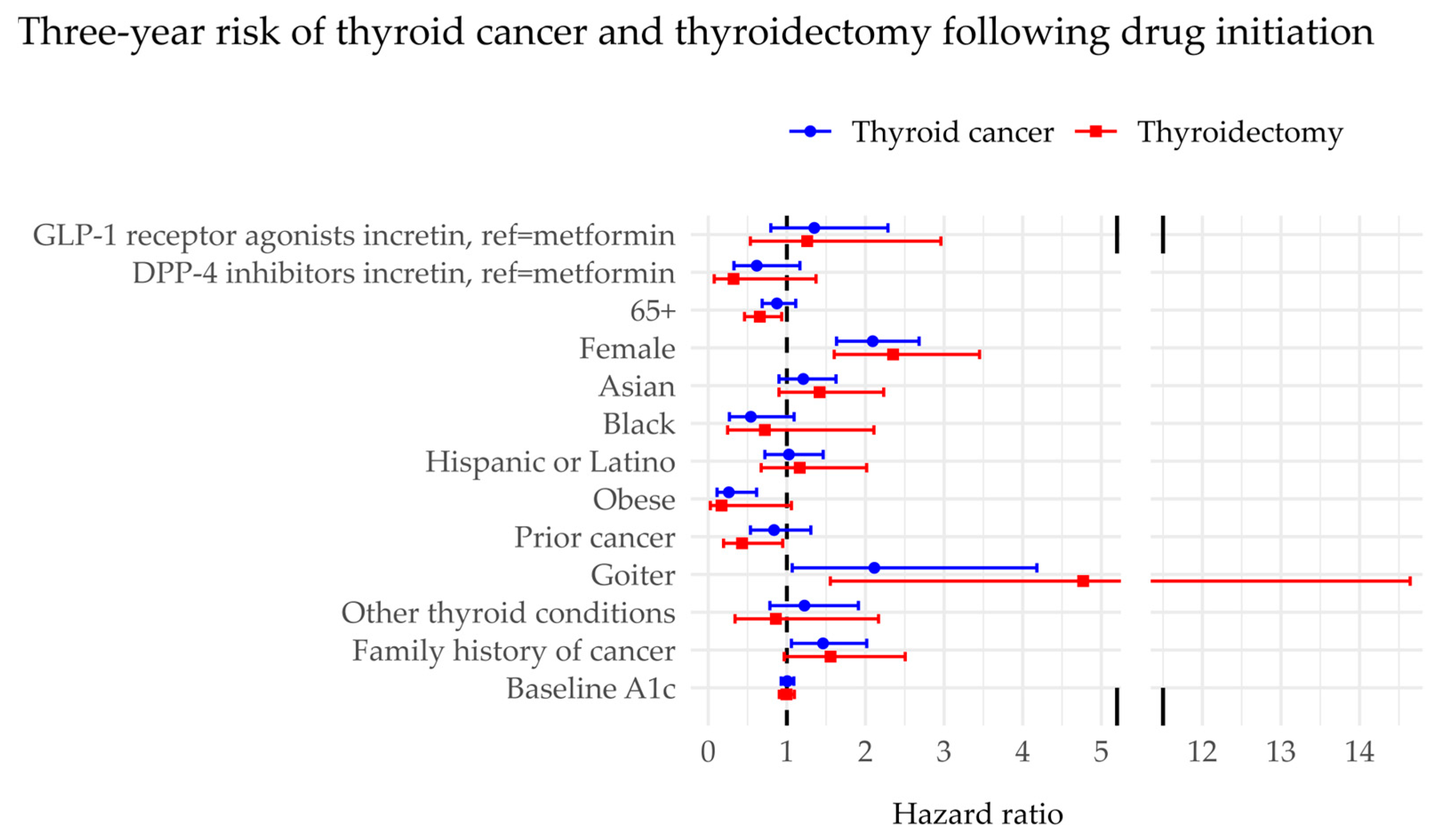
3. Results
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watanabe, J.H.; Kwon, J.; Nan, B.; Reikes, A. Trends in Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Use, 2014 to 2022. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2024, 64, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Market Size, Share & Analysis, 2023–2032. Available online: https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/glp-1-receptor-agonist-market (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Yao, H.; Zhang, A.; Li, D.; Wu, Y.; Wang, C.-Z.; Wan, J.-Y.; Yuan, C.-S. Comparative Effectiveness of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists on Glycaemic Control, Body Weight, and Lipid Profile for Type 2 Diabetes: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. BMJ 2024, 384, e076410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, I.; Giorgino, F. Renal Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Tirzepatide in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: Seeds of a Promising Future. Endocrine 2024, 84, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicker, D. DPP-4 Inhibitors: Impact on Glycemic Control and Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Diabetes Care 2011, 34 (Suppl. S2), S276–S278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; Lee, M.M.Y.; Kristensen, S.L.; Branch, K.R.H.; Del Prato, S.; Khurmi, N.S.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lopes, R.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pratley, R.E.; et al. Cardiovascular, Mortality, and Kidney Outcomes with GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.-H.; Lee, K.-Y.; Tseng, F.-H. An Updated Review on Cancer Risk Associated with Incretin Mimetics and Enhancers. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2015, 33, 67–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capuccio, S.; Scilletta, S.; La Rocca, F.; Miano, N.; Di Marco, M.; Bosco, G.; Di Giacomo Barbagallo, F.; Scicali, R.; Piro, S.; Di Pino, A. Implications of GLP-1 Receptor Agonist on Thyroid Function: A Literature Review of Its Effects on Thyroid Volume, Risk of Cancer, Functionality and TSH Levels. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverii, G.A.; Monami, M.; Gallo, M.; Ragni, A.; Prattichizzo, F.; Renzelli, V.; Ceriello, A.; Mannucci, E. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Risk of Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 891–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschebrook-Kilfoy, B.; Sabra, M.M.; Brenner, A.; Moore, S.C.; Ron, E.; Schatzkin, A.; Hollenbeck, A.; Ward, M.H. Diabetes and Thyroid Cancer Risk in the National Institutes of Health-AARP Diet and Health Study. Thyroid 2011, 21, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, S.-R.; Chiu, W.-Y.; Chang, T.-C.; Tseng, C.-H. Diabetes and Thyroid Cancer Risk: Literature Review. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2012, 2012, 578285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, Y.; Ma, S.-H.; Hwang, Y.; Horn-Ross, P.L.; Hsing, A.; Lee, K.-E.; Park, Y.J.; Park, D.-J.; Yoo, K.-Y.; Park, S.K. Diabetes Mellitus and Risk of Thyroid Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Phillips, L.; Liu, S.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; Margolis, K.L. Diabetes, Diabetes Treatment, and Risk of Thyroid Cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushchayeva, Y.; Kushchayev, S.; Jensen, K.; Brown, R.J. Impaired Glucose Metabolism, Anti-Diabetes Medications, and Risk of Thyroid Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenta, G.; Di Fermo, F. Thyroid Cancer and Insulin Resistance. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2024, 25, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Xu, S.; Renko, K.; Derwahl, M. Metformin Inhibits Growth of Thyroid Carcinoma Cells, Suppresses Self-Renewal of Derived Cancer Stem Cells, and Potentiates the Effect of Chemotherapeutic Agents. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E510–E520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-H. Metformin Reduces Thyroid Cancer Risk in Taiwanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, W.; Kaelber, D.C.; Xu, R.; Berger, N.A. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Colorectal Cancer Risk in Drug-Naive Patients with Type 2 Diabetes, with and Without Overweight/Obesity. JAMA Oncol. 2024, 10, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa De Ycaza, A.E.; Brito, J.P.; McCoy, R.G.; Shao, H.; Singh Ospina, N. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Thyroid Cancer: A Narrative Review. Thyroid 2024, 34, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisco, G.; De Tullio, A.; Disoteo, O.; Piazzolla, G.; Guastamacchia, E.; Sabbà, C.; De Geronimo, V.; Papini, E.; Triggiani, V. Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists and Thyroid Cancer: Is It the Time to Be Concerned? Endocr. Connect. 2023, 12, e230257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezin, J.; Gouverneur, A.; Pénichon, M.; Mathieu, C.; Garrel, R.; Hillaire-Buys, D.; Pariente, A.; Faillie, J.-L. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and the Risk of Thyroid Cancer. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bea, S.; Son, H.; Bae, J.H.; Cho, S.W.; Shin, J.; Cho, Y.M. Risk of Thyroid Cancer Associated with Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-based Cohort Study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Song, R.; Cheng, R.; Liu, C.; Guo, R.; Tang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Li, X.; Liu, J. Use of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Occurrence of Thyroid Disorders: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 927859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, D.; Elisei, R. Management of Medullary Thyroid Cancer. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PDQ Cancer Genetics Editorial Board. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2 (MEN2) (PDQ®): Health Professional Version. In PDQ Cancer Information Summaries; National Cancer Institute (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, H.; Schneeweiss, S.; Glynn, R.J.; Patorno, E. Trends in First-Line Glucose-Lowering Drug Use in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes in Light of Emerging Evidence for SGLT-2i and GLP-1RA. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matrone, A.; Ferrari, F.; Santini, F.; Elisei, R. Obesity as a Risk Factor for Thyroid Cancer. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2020, 27, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Xu, S.; Chen, G.; Derwahl, M.; Liu, C. Metformin and Thyroid Disease. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 233, R43–R51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, B.J.; Lenoir, K.M.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Lawrence, J.M.; Dabelea, D.; Pihoker, C.; Saydah, S.; Casanova, R.; Turley, C.; et al. Detection of Diabetes Status and Type in Youth Using Electronic Health Records: The SEARCH for Diabetes in Youth Study. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 2418–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudyakov, R.; Bowen, J.; Ewen, E.; West, S.L.; Daoud, Y.; Fleming, N.; Masica, A. Electronic Health Record Use to Classify Patients with Newly Diagnosed versus Preexisting Type 2 Diabetes: Infrastructure for Comparative Effectiveness Research and Population Health Management. Popul. Health Manag. 2012, 15, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Gaglia, J.L.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; et al. 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, S19–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.R. Regression Models and Life-Tables. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 1972, 34, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grambsch, P.M.; Therneau, T.M. Proportional Hazards Tests and Diagnostics Based on Weighted Residuals. Biometrika 1994, 81, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, A.L.; Hudgens, M.G.; Cole, S.R.; Lau, B.; Adimora, A.A.; for the Women’s Interagency HIV Study. Worth the Weight: Using Inverse Probability Weighted Cox Models in AIDS Research. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2014, 30, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, R.; Chiu, C.G.; Strugnell, S.S.; Gill, S.; Wiseman, S.M. Gender Differences in Thyroid Cancer: A Critical Review. Expert. Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 6, 215–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magreni, A.; Bann, D.V.; Schubart, J.R.; Goldenberg, D. The Effects of Race and Ethnicity on Thyroid Cancer Incidence. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 141, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keane, E.; Francis, E.C.; Catháin, É.Ó.; Rowley, H. The Role of Race in Thyroid Cancer: Systematic Review. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2017, 131, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fussey, J.M.; Beaumont, R.N.; Wood, A.R.; Vaidya, B.; Smith, J.; Tyrrell, J. Does Obesity Cause Thyroid Cancer? A Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e2398–e2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, N.; Medici, M.; Angell, T.E.; Liu, X.; Marqusee, E.; Cibas, E.S.; Krane, J.F.; Barletta, J.A.; Kim, M.I.; Larsen, P.R.; et al. The Influence of Patient Age on Thyroid Nodule Formation, Multinodularity, and Thyroid Cancer Risk. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 4434–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, F.; Dai, H.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; Chen, H.; Zhang, X. Association between Thyroid Dysfunction and Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Observational Studies. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gursoy, A. Rising Thyroid Cancer Incidence in the World Might Be Related to Insulin Resistance. Med. Hypotheses 2010, 74, 35–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-H. Rosiglitazone May Reduce Thyroid Cancer Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Ann. Med. 2013, 45, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C. Pioglitazone and Thyroid Cancer Risk in Taiwanese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Diabetes 2014, 6, 448–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.-H. Sitagliptin Use and Thyroid Cancer Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 24871–24879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, G.E.; Bindman, A.B.; Dreyer, N.A.; Platt, R.; Watanabe, J.H.; Horberg, M.; Hernandez, A.; Califf, R.M. When Can We Trust Real-World Data to Evaluate New Medical Treatments? Clin. Pharma. Ther. 2022, 111, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, A.; Tysinger, B.; Nguyen, P.; Goldman, D.; Lakdawalla, D. Benefits of Medicare Coverage for Weight Loss Drugs. 2023. Available online: https://doi.org/10.25549/4RF9-KH77 (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Ippolito, B.; Levy, J.F. Expanding Medicare Coverage of Anti-Obesity Medicines Could Increase Annual Spending by $3.1 Billion to $6.1 Billion: Article Examines Spending Implications If Medicare Were to Cover Antiobesity Medicines. Health Aff. 2024, 43, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.H.; Han, J.S.; Bae, W.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, K.; Lee, H.; Lee, K.H.; Jung, S.Y.; Lee, H.; Jeong, H.-Y.; et al. Changes in Diagnostic Performance of Thyroid Cancer Screening before and after the Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System Revision. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2022, 43, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaleontiou, M.; Haymart, M.R. Too Much of a Good Thing? A Cautionary Tale of Thyroid Cancer Overdiagnosis and Overtreatment. Thyroid 2020, 30, 651–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Metformin | Incretin Mimetic | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLP-1 Receptor Agonist | DPP-4 Inhibitor | |||
| N | 82,964 | 4912 | 3518 | |
| Age (avg, sd) | ||||
| At first prescription | 62.5 (13.8) | 58.0 (13.9) | 69.3 (12.5) | <0.01 |
| Gender (%) | ||||
| Female | 42,289 (51.0) | 3008 (61.2) | 1723 (49.0) | <0.01 |
| Race (%) | ||||
| Asian | 13,970 (16.8) | 341 (6.9) | 688 (19.6) | <0.01 |
| Black | 4970 (6.0) | 406 (8.3) | 210 (6.0) | <0.01 |
| White | 37,999 (45.8) | 2661 (54.2) | 1510 (42.9) | <0.01 |
| Ethnicity (%) | ||||
| Hispanic or Latino | 16,414 (19.8) | 1091 (22.2) | 739 (21.0) | <0.01 |
| Comorbidities (%) | ||||
| Obesity | 6743 (8.1) | 1304 (26.6) | 172 (4.9) | <0.01 |
| Thyroid issues | 8313 (10.0) | 895 (18.2) | 466 (13.3) | <0.01 |
| Goiter | 2286 (2.8) | 217 (4.4) | 73 (2.1) | <0.01 |
| Prior cancer | 8210 (9.9) | 589 (12.0) | 388 (11.0) | <0.01 |
| Family history of cancer | 9653 (11.6) | 664 (13.5) | 302 (8.6) | 0.63 |
| Measurements (avg, sd) | ||||
| A1c | 7.2 (2.0) | 6.7 (4.4) | 6.4 (1.3) | <0.01 |
| Outpatient visits | 1.0 (3.0) | 1.0 (2.6) | 2.6 (7.3) | <0.01 |
| Metformin | Incretin Mimetic | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLP-1 Receptor Agonist | DPP-4 Inhibitor | |||
| Outcome (%) | ||||
| Thyroid cancer | 289 (0.35) | 17 (0.35) | 11 (0.31) | 0.81 |
| Thyroidectomy | 126 (0.15) | 7 (0.14) | 2 (0.06) | 0.30 |
| MTC or MEN2 | 3 (0.00) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | NA |
| Thyroid Cancer | Thyroidectomy | |
|---|---|---|
| Metformin (%) | ||
| Metformin | 289 (0.35) | 126 (0.15) |
| DPP-4 inhibitor (%) | ||
| Alogliptin | 1 (1.61) | 0 (0) |
| Linagliptin | 3 (0.27) | 0 (0) |
| Saxagliptin | 1 (1.09) | 1 (1.09) |
| Sitagliptin | 6 (0.27) | 1 (0.04) |
| GLP-1 receptor agonist (%) | ||
| Dulaglutide | 2 (0.22) | 1 (0.11) |
| Liraglutide | 1 (0.18) | 1 (0.18) |
| Semaglutide | 11 (0.38) | 4 (0.14) |
| Tirzepatide | 3 (0.66) | 1 (0.22) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strand, M.W.; Chow, D.; Shen, W.; Watanabe, J.H. Impact of Incretin Mimetics on Thyroid Cancer Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Time-to-Event Analysis. Pharmacoepidemiology 2025, 4, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma4020009
Strand MW, Chow D, Shen W, Watanabe JH. Impact of Incretin Mimetics on Thyroid Cancer Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Time-to-Event Analysis. Pharmacoepidemiology. 2025; 4(2):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma4020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrand, Michael W., Daniel Chow, Weining Shen, and Jonathan H. Watanabe. 2025. "Impact of Incretin Mimetics on Thyroid Cancer Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Time-to-Event Analysis" Pharmacoepidemiology 4, no. 2: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma4020009
APA StyleStrand, M. W., Chow, D., Shen, W., & Watanabe, J. H. (2025). Impact of Incretin Mimetics on Thyroid Cancer Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Time-to-Event Analysis. Pharmacoepidemiology, 4(2), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharma4020009






