The Dark Side of Cardiac and Aortic Interventions: Unveiling Cerebral Microbleeds with Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Rationale
1.2. Objectives
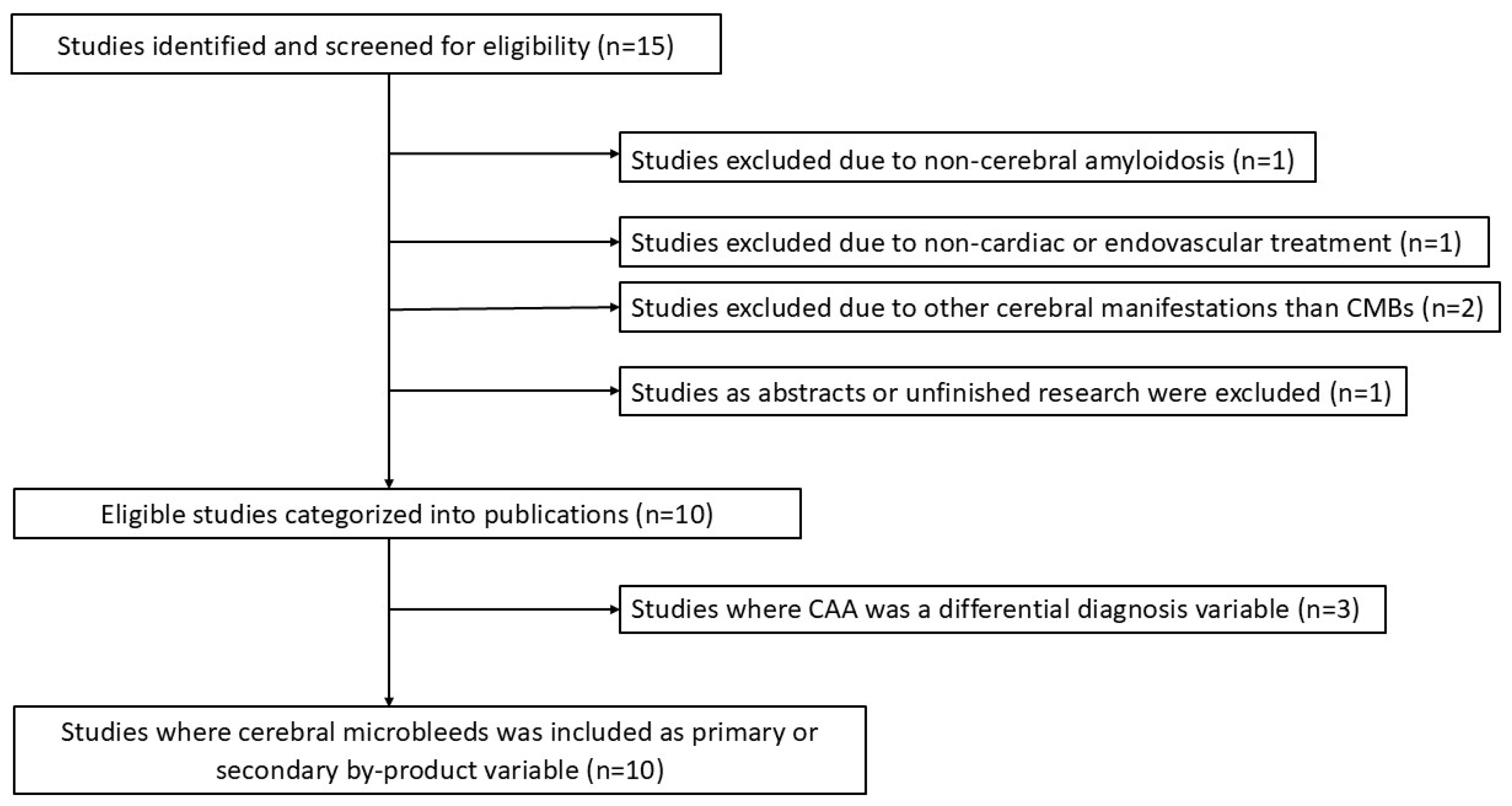
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria and Data Items
- Participants were identified with heart or aortic disease requiring mandatory surgery;
- Studies had to investigate specific surgical and/or endovascular procedures, such as cardiac surgery, TEVAR, and TAVR;
- Post-surgery MRI was performed using a 1.5 or 3 Tesla scanner with a protocol including at least one sequence between T2*-GRE or SWI; pre-surgery MRI was not mandatory;
- “Cerebral microbleeds” was either a primary or secondary outcome variable;
- The paper was the result of primary research;
- The paper had to be written in English.
2.2. Selection of Sources of Evidence, Data Charting and Synthesis of Results
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Evidence
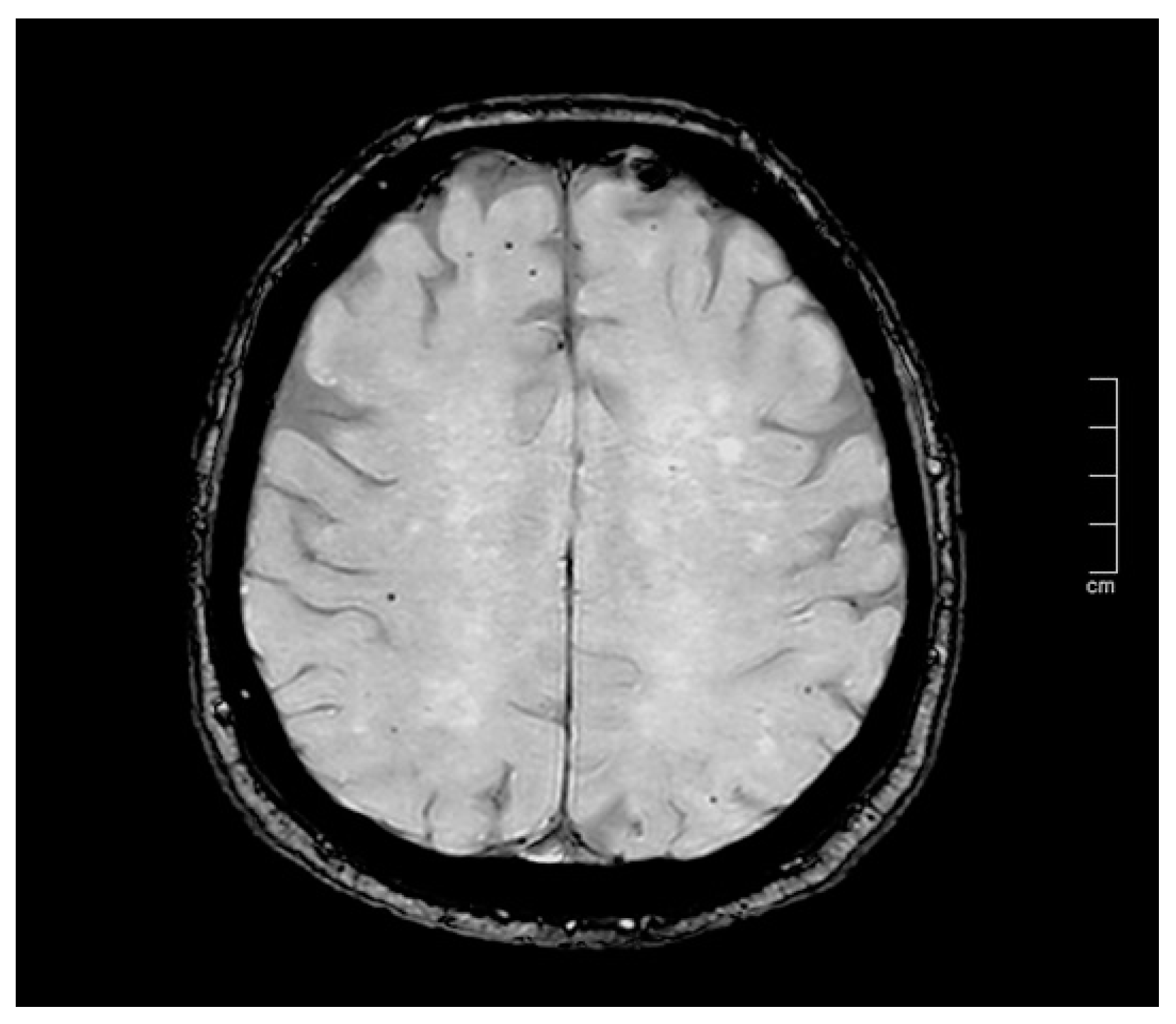
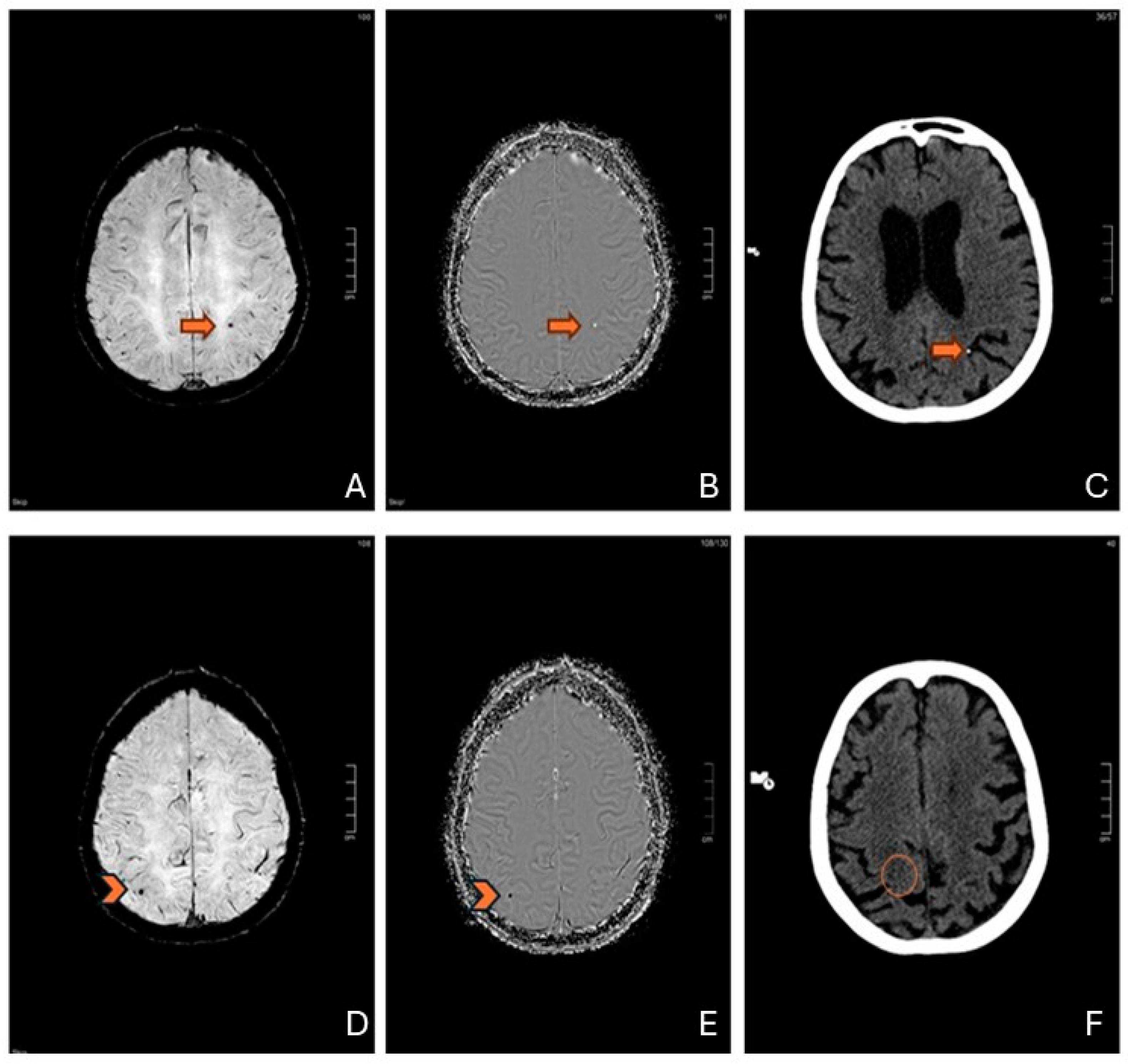
4.2. The Accuracy of MR Imaging—A SWI Technical Note
4.3. “Probable” or “Possible” CAA—Differential Diagnosis and Clinical Implications
4.4. Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Insights
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SWI | susceptibility-weighted imaging |
| GRE | gradient-echo |
| MR | magnetic resonance |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| CMBs | cerebral microbleeds |
| CPB | cardiopulmonary bypass |
| CABG | coronary artery bypass grafting |
| TEVAR | thoracic endovascular aortic repair |
| TAVI | transcatheter aortic valve implantation |
| CAA | cerebral amyloid angiopathy |
| TAVR | Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement |
| SWM | subcortical white matter |
| SIRS | systemic inflammatory response syndrome |
| MOF | Multiorgan Failure |
| DWI | diffusion-weighted imaging |
| FGF | fibroblast growth factor |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| vWF | Von Willebrand Factor |
References
- Greenberg, S.M.; Vernooij, M.W.; Cordonnier, C.; Viswanathan, A.; Al-Shahi Salman, R.; Warach, S.; Launer, L.J.; Van Buchem, M.A.; Breteler, M.M. Cerebral Microbleeds: A Guide to Detection and Interpretation. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akoudad, S.; Wolters, F.J.; Viswanathan, A.; de Bruijn, R.F.; van der Lugt, A.; Hofman, A.; Koudstaal, P.J.; Ikram, M.A.; Vernooij, M.W. Association of Cerebral Microbleeds With Cognitive Decline and Dementia. JAMA Neurol. 2016, 73, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, A.; Ajmera, P.; Sharma, P.; Kanekar, S. Cerebral Microbleeds: Causes, Clinical Relevance, and Imaging Approach—A Narrative Review. J. Neurosci. Rural Pract. 2024, 15, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Tozer, D.J.; Markus, H.S. Cerebral Microbleeds and Their Association With Inflammation and Blood-Brain Barrier Leakage in Small Vessel Disease. Stroke 2025, 56, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kou, Z.; Tian, Y. Diffuse Axonal Injury after Traumatic Cerebral Microbleeds: An Evaluation of Imaging Techniques. Neural Regen. Res. 2014, 9, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Zhai, F.F.; Han, F.; Zhou, L.X.; Ni, J.; Yao, M.; Zhang, S.; Jin, Z.; Cui, L.; et al. Cerebral Microbleeds Are Associated with Loss of White Matter Integrity. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, C.; Wen, H.; Wang, S.; Feng, M.; Xin, H.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, L.; Liang, C. Characterization of White Matter Microstructural Abnormalities Associated with Cognitive Dysfunction in Cerebral Small Vessel Disease with Cerebral Microbleeds. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 324, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studerus-Germann, A.M.; Gautschi, O.P.; Bontempi, P.; Thiran, J.-P.; Daducci, A.; Romascano, D.; von Ow, D.; Hildebrandt, G.; von Hessling, A.; Engel, D.C. Central Nervous System Microbleeds in the Acute Phase Are Associated with Structural Integrity by DTI One Year after Mild Traumatic Brain Injury: A Longitudinal Study. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2018, 52, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, J.; Tenovuo, O.; Posti, J.P.; Hirvonen, J.; Katila, A.J.; Frantzén, J.; Maanpää, H.-R.; Takala, R.; Löyttyniemi, E.; Tallus, J.; et al. Cerebral Microbleeds and Structural White Matter Integrity in Patients With Traumatic Brain Injury—A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 888815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, S.M.; Charidimou, A. Diagnosis of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Evolution of the Boston Criteria. Stroke 2018, 49, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.P.C.; Nasman, B.W.; Kinne, E.L.; Oyoyo, U.E.; Kido, D.K.; Jacobson, J.P. Cerebral Microhemorrhage: A Frequent Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding in Pediatric Patients after Cardiopulmonary Bypass. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2017, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eilenberg, W.; Bechstein, M.; Charbonneau, P.; Rohlffs, F.; Eleshra, A.; Panuccio, G.; Bhangu, J.S.; Fiehler, J.; Greenhalgh, R.M.; Haulon, S.; et al. Cerebral Microbleeds Following Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair. Br. J. Surg. 2022, 109, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sciscio, M.; De Sciscio, P.; Vallat, W.; Kleinig, T. Cerebral Microbleed Distribution Following Cardiac Surgery Can Mimic Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy. BMJ Neurol. Open 2021, 3, e000166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.; Banahan, C.; Janus, J.; Horsfield, M.A.; Cox, A.; Li, X.; Cappellugola, L.; Colman, J.; Egan, V.; Garrard, P.; et al. Perioperative Cerebral Microbleeds after Adult Cardiac Surgery. Stroke 2019, 50, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braemswig, T.B.; Kusserow, M.; Bellmann, B.; Beckhoff, F.; Reinthaler, M.; von Rennenberg, R.; Erdur, H.; Scheitz, J.F.; Galinovic, I.; Villringer, K.; et al. New Cerebral Microbleeds After Catheter-Based Structural Heart Interventions: An Exploratory Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.Y.; Luo, C.Y.; Tang, H.H.; Søndergaard, L.; Prendergast, B.; Lui, S.; Chen, M. Novel Neuroimaging Evidence of Brain Lesions Following Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e023395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiding, P.S.; Duerrenmatt, J.T.; Meinel, F.G.; Carrel, T.; Schönhoff, F.; Zibold, F.; Kaesmacher, J.; Gralla, J.; Pilgrim, T.; Jung, S.; et al. Prevalence and Evolution of Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging Lesions in Patients With Artificial Heart Valves. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Belle, E.; Debry, N.; Vincent, F.; Kuchcinski, G.; Cordonnier, C.; Rauch, A.; Robin, E.; Lassalle, F.; Pontana, F.; Delhaye, C.; et al. Cerebral Microbleeds during Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement: A Prospective Magnetic Resonance Imaging Cohort. Circulation 2022, 146, 383–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.B.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, S.J.; Chung, C.H.; Kwon, S.U.; Choi, C.G.; Choo, S.J.; Nah, H.W.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, D.W. New Cerebral Lesions on T2*-Weighted Gradient-Echo Imaging after Cardiac Valve Surgery. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2010, 30, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michałowska, I.; Furmanek, M.I.; Smaga, E.; Juraszyński, Z.; Zieliński, T.; Chełstowska, S.; Kuśmierczyk, M.; Szpakowski, E.; Mierzyńska, A.; Walecki, J.M. Evaluation of Brain Lesions in Patients after Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Using MRI with the Emphasis on Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging. Kardiochirurgia I Torakochirurgia Pol. 2015, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Feng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, A.P.; Fang, M.; Liu, X. A Meta-Analysis of Association between Cerebral Microbleeds and Cognitive Impairment. Med. Sci. Monit. 2014, 20, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhao, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, R.; Hu, M.; He, X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, H. Risk Factor Analysis in Patients Exhibiting Cerebral Microbleeds and the Correlation with Cognitive Impairment. Gerontol. Geriatr. Med. 2024, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.P.; Chou, K.H.; Chen, W.T.; Liu, L.K.; Lee, W.J.; Chen, L.K.; Lin, C.P.; Wang, P.N. Strictly Lobar Cerebral Microbleeds Are Associated with Cognitive Impairment. Stroke 2016, 47, 2497–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haller, S.; Haacke, E.M.; Thurnher, M.M.; Barkhof, F. Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging: Technical Essentials and Clinical Neurologic Applications. Radiology 2021, 299, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, S.; Martola, J.; Cavallin, L.; Granberg, T.; Shams, M.; Aspelin, P.; Wahlund, L.O.; Kristoffersen-Wiberg, M. SWI or T2*: Which MRI Sequence to Use in the Detection of Cerebral Microbleeds? The Karolinska Imaging Dementia Study. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 36, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, A.; Waszczuk, Ł.; Trybek, G.; Kapetanakis, S.; Bladowska, J. Application of Susceptibility Weighted Imaging (SWI) in Diagnostic Imaging of Brain Pathologies—A Practical Approach. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2022, 221, 107368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halefoglu, A.M.; Yousem, D.M. Susceptibility Weighted Imaging: Clinical Applications and Future Directions. World J. Radiol. 2018, 10, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen-Kondering, U.; Heß, K.; Neumann, A.; Margraf, N.G. Neuroradiological Findings in Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy with a Particular Consideration of the Boston Criteria 2.0: An Imaging Review. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, K.A.; Rosand, J.; Karluk, D.; Greenberg, S.M. Clinical Diagnosis of Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy: Validation of the Boston Criteria. Neurology 2001, 56, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rooden, S.; van der Grond, J.; van den Boom, R.; Haan, J.; Linn, J.; Greenberg, S.M.; van Buchem, M.A. Descriptive Analysis of the Boston Criteria Applied to a Dutch-Type Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Population. Stroke 2009, 40, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linn, J.; Halpin, A.; Demaerel, P.; Ruhland, J.; Giese, A.D.; Dichgans, M.; van Buchem, M.A.; Bruckmann, H.; Greenberg, S.M. Prevalence of Superficial Siderosis in Patients with Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy. Neurology 2010, 74, 1346–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogue, C.W.; Gottesman, R.F.; Stearns, J. Mechanisms of Cerebral Injury from Cardiac Surgery. Crit. Care Clin. 2008, 24, 83–98, viii–ix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paparella, D.; Yau, T.M.; Young, E. Cardiopulmonary Bypass Induced Inflammation: Pathophysiology and Treatment. An Update. Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2002, 21, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohn, A.; Malewicz-Oeck, N.M.; Buchwald, D.; Annecke, T.; Zahn, P.K.; Baumann, A. REmoval of Cytokines during CArdiac Surgery (RECCAS): A Randomised Controlled Trial. Crit. Care 2024, 28, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Ueno, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Iguro, Y.; Yamada, K.; Sakata, R. Relationship between Cerebral Injury and Inflammatory Responses in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery with Cardiopulmonary Bypass. Cytokine 2005, 29, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Han, W. Circulating Inflammatory Cytokines and the Risk of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Analysis. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2025, 34, 108163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudilosso, S.; Stringer, M.S.; Thrippleton, M.; Chappell, F.; Blair, G.W.; Jaime Garcia, D.; Doubal, F.; Hamilton, I.; Janssen, E.; Kopczak, A.; et al. Blood-Brain Barrier Leakage Hotspots Collocating with Brain Lesions Due to Sporadic and Monogenic Small Vessel Disease. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2023, 43, 1490–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Key Points | |
|---|---|
| Neuroimaging technique for CMBs | Imaging sensitivity is crucial: SWI is more sensitive than T2*-weighted gradient echo for CMB detection. |
| Differential Diagnosis | The distribution of CMBs after cardiac surgery can mimic CAA, highlighting the importance of considering this condition in the differential diagnosis. |
| Pathophysiological analysis | The mechanisms remain partially understood, with potential contributors including the application of CPB, embolization, issues in anticoagulation management, and inflammatory processes associated with surgery. |
| Future directions | Research priorities include assessing the long-term impact of CMBs, as well as the development of targeted interventions to minimize neurological complications in the post-surgical cohort. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Casseri, T.; Maccaglia, M.G.; Lombardo, I.; Bianchi, A.; Tartarone, R.; Busto, G.; Ginestroni, A.; Speziali, S.; Dorigo, W.; Fainardi, E. The Dark Side of Cardiac and Aortic Interventions: Unveiling Cerebral Microbleeds with Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging. J. Vasc. Dis. 2025, 4, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4020016
Casseri T, Maccaglia MG, Lombardo I, Bianchi A, Tartarone R, Busto G, Ginestroni A, Speziali S, Dorigo W, Fainardi E. The Dark Side of Cardiac and Aortic Interventions: Unveiling Cerebral Microbleeds with Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging. Journal of Vascular Diseases. 2025; 4(2):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleCasseri, Tommaso, Maria Giulia Maccaglia, Ivano Lombardo, Andrea Bianchi, Rosaria Tartarone, Giorgio Busto, Andrea Ginestroni, Sara Speziali, Walter Dorigo, and Enrico Fainardi. 2025. "The Dark Side of Cardiac and Aortic Interventions: Unveiling Cerebral Microbleeds with Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging" Journal of Vascular Diseases 4, no. 2: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4020016
APA StyleCasseri, T., Maccaglia, M. G., Lombardo, I., Bianchi, A., Tartarone, R., Busto, G., Ginestroni, A., Speziali, S., Dorigo, W., & Fainardi, E. (2025). The Dark Side of Cardiac and Aortic Interventions: Unveiling Cerebral Microbleeds with Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging. Journal of Vascular Diseases, 4(2), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/jvd4020016