Plant PP2A: A Versatile Enzyme with Key Physiological Functions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structure of Plant PP2A: The Basis of Versatility
2.1. PP2A Subunits
2.2. Number and Subcellular Localization of PP2A Subunits
| Arabidopsis | Potato | Rubber Tree | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WoLF PSORT | SUBA | WoLF PSORT | WoLF PSORT | ||||
| C | C1 | cyt | PM | C1 | cyt | C1-1 | cyt |
| C2 | cyt | PM | C2a | cyt | C1-2 | cyt | |
| C3 | cyt | cyt | C2b | cyt | C2-1 | cyt | |
| C4 | cyt | cyt | C3 | cyt | C2-2 | cyt | |
| C5 | cyt | cyt | C4 | cyt | C4-1 | cyt/nu | |
| C5 | cyt | C4-2 | nu | ||||
| C4-3 | cyt | ||||||
| C6 | cyt | ||||||
| A | A1 | cyt/chl | PM | A1 | PM | A1-1 | cyt |
| A2 | chl | golgi | A2 | cyt | A1-2 | ER | |
| A3 | chl | cyt | A3 | cyt | A2 | chl | |
| A3 | cyt | ||||||
| B | Bα | nu | nu | Bα | nu | Bα-1 | nu |
| Bβ | cysk | nu | Bβ | nu | Bα-2 | cyt | |
| Bγ | cyt | Bα-3 | ER | ||||
| Bδ | nu | Bβ | cysk | ||||
| B′ | B′α | mito | nu | B′α | mito | B′α | cyt |
| B′β | mito | nu | B′β | mito | B′β | cyt | |
| B′γ | mito | plastid | B′γ | mito | B′γ | mito | |
| B′δ | cyt | golgi | B′δ | mito | B′ζ | nu | |
| B′ε | cyt | nu | B′ε | mito | B′η-1 | mito | |
| B′ζ | mito | mito | B′ζ | cyt | B′η-2 | mito | |
| B′η | cyt | nu/cyt | B′η | mito | B′η-3 | mito | |
| B′θ | mito | mito | B′θ | cyt | B′η-4 | mito | |
| B′κ | mito | plastid | B′ι | mito | B′η-5 | chl | |
| B′κ | nu | B′θ-1 | mito | ||||
| B′λ | mito | B′θ-2 | mito | ||||
| B′κ-1 | mito | ||||||
| B′κ-2 | chl | ||||||
| B′μ | nu/mito | ||||||
| B″ | B″α | nu | cyt | B″α | nu | B″α | nu |
| B″β | nu | nu | B″β | cyt | B″β | nu | |
| B″γ | nu | cyt | B″γ | nu/cyt | B″δ | cyt | |
| B″δ | nu | cyt | B″ε | nu/cyt/chl | |||
| B″ε | nu | cyt | T2/F1-1 | nu | |||
| T2/F1 | nu | cyt | T2/F1-2 | nu/cyt | |||
2.3. Regulation of PP2A Activity
3. Physiological Roles of Plant PP2A
3.1. Abiotic Stress
3.2. Biotic Stress
3.3. Developmental Programs
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PP2A | Protein phosphatase 2A |
| PPP | Phosphoprotein phosphatase |
| PPM | Mg2+- or Mn2+-dependent protein phosphatase |
| PP2C | Protein phosphatase 2C |
| PTP | Phosphotyrosine phosphatase |
| PP1 | Protein phosphatase 1 |
| PP4 | Protein phosphatase 4 |
| PP5 | Protein phosphatase 5 |
| PP6 | Protein phosphatase 6 |
| PP7 | Protein phosphatase 7 |
| SLP | Shewanella-like protein phosphatase |
| PPKL | Protein phosphatase with Kelch-like repeat domains |
| T2/F1 | TON2/FASS1 |
| Cyt | Cytosol |
| PM | Plasma membrane |
| Nu | Nucleus |
| Chl | Chloroplast |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| Cysk | Cytoskeleton |
| Mito | Mitochondria |
| SBI1 | SUPPRESSOR OF BRI1 |
| LCMT1 | Leucine Carboxyl Methyltransferase 1 |
| PTPA | PHOSPHOTYROSYL PHOSPHATASE ACTIVATOR |
| PGPR | Plant-growth-promoting rhizobacteria |
References
- Uhrig, R.G.; Labandera, A.M.; Moorhead, G.B. Arabidopsis PPP family of serine/threonine protein phosphatases: Many targets but few engines. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, H.T.; Nimick, M.; Uhrig, R.G.; Templeton, G.; Morrice, N.; Gourlay, R.; DeLong, A.; Moorhead, G.B. Arabidopsis thaliana histone deacetylase 14 (HDA14) is an α-tubulin deacetylase that associates with PP2A and enriches in the microtubule fraction with the putative histone acetyltransferase ELP3. Plant J. 2012, 71, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillo, C.; Kataya, A.R.; Heidari, B.; Creighton, M.T.; Nemie-Feyissa, D.; Ginbot, Z.; Jonassen, E.M. Protein phosphatases PP2A, PP4 and PP6: Mediators and regulators in development and responses to environmental cues. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 2631–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bheri, M.; Mahiwal, S.; Sanyal, S.K.; Pandey, G.K. Plant protein phosphatases: What do we know about their mechanism of action? FEBS J. 2021, 288, 756–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubillaga, M.; Yaconis, I.; Cortelezzi, J.I.; Capiati, D.A.; Muñiz García, M.N. Identification of PP2A B subunits potentially involved in modulating salt and osmotic stress responses in Solanum tuberosum. Theor. Exp. Plant Physiol. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, I.; Dombrádi, V.; Miskei, M.; Szabados, L.; Koncz, C. Arabidopsis PPP family of serine/threonine phosphatases. Trends Plant Sci. 2007, 12, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Chao, Y.; Lin, Z.; Li, Z.; Strack, S.; Stock, J.B.; Shi, Y. Structure of protein phosphatase 2A core enzyme bound to tumor-inducing toxins. Cell 2006, 127, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, I.; Domínguez, T.; Sauer, M.; Paredes, P.; Duprat, A.; Rojo, E.; Sanmartín, M.; Sánchez-Serrano, J.J. Specialized functions of the PP2A subfamily II catalytic subunits PP2A-C3 and PP2A-C4 in the distribution of auxin fluxes and development in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2013, 73, 862–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Stanevich, V.; Wlodarchak, N.; Sengupta, R.; Jiang, L.; Satyshur, K.A.; Xing, Y. Structural basis of PP2A activation by PTPA, an ATP-dependent activation chaperone. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstykh, T.; Lee, J.; Vafai, S.; Stock, J.B. Carboxyl methylation regulates phosphoprotein phosphatase 2A by controlling the association of regulatory B subunits. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 5682–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groves, M.R.; Hanlon, N.; Turowski, P.; Hemmings, B.A.; Barford, D. The structure of the protein phosphatase 2A PR65/A subunit reveals the conformation of its 15 tandemly repeated HEAT motifs. Cell 1999, 96, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Xing, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chao, Y.; Lin, Z.; Fan, E.; Yu, J.W.; Strack, S.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Shi, Y. Structure of the protein phosphatase 2A holoenzyme. Cell 2006, 127, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Virshup, D.M. Two conserved domains in regulatory B subunits mediate binding to the A subunit of protein phosphatase 2A. Eur. J. Biochem. 2002, 269, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Lottes, E.N.; Nanda, S.; Golshir, A.; Patel, A.A.; Ascoli, G.A.; Cox, D.N. PP2A phosphatase regulates cell-type specific cytoskeletal organization to drive dendrite diversity. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 926567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, B.; Nemie-Feyissa, D.; Lillo, C. Distinct Clades of Protein Phosphatase 2A Regulatory B’/B56 Subunits Engage in Different Physiological Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máthé, C.; Freytag, C.; Kelemen, A.; Hamvas, M.M.; Garda, T. “B” Regulatory Subunits of PP2A: Their Roles in Plant Development and Stress Reactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, J.; Huang, Z.; Yang, S.; Deng, X.; Tian, W. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the phosphatase 2A family in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Kamiya, Y.; Otegui, M.S.; Chory, J. Methylation of a phosphatase specifies dephosphorylation and degradation of activated brassinosteroid receptors. Sci. Signal 2011, 4, ra29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Hu, R.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, G.; Zhang, H. Arabidopsis PHOSPHOTYROSYL PHOSPHATASE ACTIVATOR is essential for PROTEIN PHOSPHATASE 2A holoenzyme assembly and plays important roles in hormone signaling, salt stress response, and plant development. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 1519–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.S.; Han, J.A.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, S.; Pai, H.S. The PP2A regulatory subunit Tap46, a component of the TOR signaling pathway, modulates growth and metabolism in plants. Plant Cell 2011, 23, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Geng, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, S.; Hao, C.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, W.; et al. TaTIP41 and TaTAP46 positively regulate drought tolerance in wheat by inhibiting PP2A activity. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 2056–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, J.; Chen, J.; Shi, H.; Shen, G.; Zhang, H. Overexpression of PP2A-C5 that encodes the catalytic subunit 5 of protein phosphatase 2A in Arabidopsis confers better root and shoot development under salt conditions. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Jing, R.; Mao, X.; Jia, X.; Chang, X. A wheat (Triticum aestivum) protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit gene provides enhanced drought tolerance in tobacco. Ann. Bot. 2007, 99, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- País, S.M.; González, M.A.; Téllez-Iñón, M.T.; Capiati, D.A. Characterization of potato (Solanum tuberosum) and tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) protein phosphatases type 2A catalytic subunits and their involvement in stress responses. Planta 2009, 230, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz García, M.N.; Baroli, I.; Cortelezzi, J.I.; Zubillaga, M.; Capiati, D.A. Genetic manipulation of protein phosphatase 2A affects multiple agronomic traits and physiological parameters in potato. Funct. Plant Biol. 2023, 50, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakeslee, J.J.; Zhou, H.W.; Heath, J.T.; Skottke, K.R.; Barrios, J.A.; Liu, S.Y.; DeLong, A. Specificity of RCN1-mediated protein phosphatase 2A regulation in meristem organization and stress response in roots. Plant Physiol. 2008, 146, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, A.; Mao, X.; Jing, R. Cloning and characterization of TaPP2AbB”-α, a member of the PP2A regulatory subunit in wheat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Li, B.; Feng, G.; Mao, X.; Li, A.; Chang, X.; Jing, R. TaPP2AbBʺ-γ, a Wheat regulatory subunit of PP2A enhanced abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 9, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Fan, X.H.; Wang, Q.; Yin, Z.G.; Sheng, X.W.; Chen, J.; Zhou, Y.B.; Chen, M.; Ma, Y.Z.; Ma, J.; et al. Genomic analysis of soybean PP2A-B″ family and its effects on drought and salt tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 784038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Anderson, J.C.; del Pozo, O.; Gu, Y.Q.; Tang, X.; Martin, G.B. Silencing of subfamily I of protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunits results in activation of plant defense responses and localized cell death. Plant J. 2004, 38, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Su, Z.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Z. Silencing of the Wheat Protein Phosphatase 2A Catalytic Subunit TaPP2Ac Enhances Host Resistance to the Necrotrophic Pathogen Rhizoctonia cerealis. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Q.J.; Chu, J.; Kumar, V.; Yuan, P.; Li, Z.M.; Mei, Q.; Xuan, Y.H. Protein Phosphatase 2A Catalytic Subunit PP2A-1 Enhances Rice Resistance to Sheath Blight Disease. Front. Genome Ed. 2021, 3, 632136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz García, M.N.; Grossi, C.; Ulloa, R.M.; Capiati, D.A. The protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit StPP2Ac2b enhances susceptibility to Phytophthora infestans and senescence in potato. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Sheng, G.L.; Li, Y.P.; Xing, Y.P.; Huang, S.X.; Tao, H.; Kuan, T.; et al. The RXLR Effector PcAvh1 Is Required for Full Virulence of Phytophthora capsici. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2019, 2, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trotta, A.; Wrzaczek, M.; Scharte, J.; Tikkanen, M.; Konert, G.; Rahikainen, M.; Holmström, M.; Hiltunen, H.M.; Rips, S.; Sipari, N.; et al. Regulatory subunit B’gamma of protein phosphatase 2A prevents unnecessary defense reactions under low light in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 1464–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz García, M.N.; Muro, M.C.; Mazzocchi, L.C.; País, S.M.; Stritzler, M.; Schlesinger, M.; Capiati, D.A. The protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit StPP2Ac2b acts as a positive regulator of tuberization induction in Solanum tuberosum L. Plant Mol. Biol. 2017, 93, 227–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñiz García, M.N.; Cortelezzi, J.I.; Capiati, D.A. The protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit StPP2Ac2b is involved in the control of potato tuber sprouting and source-sink balance in tubers and sprouts. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 6784–6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durian, G.; Jeschke, V.; Rahikainen, M.; Vuorinen, K.; Gollan, P.J.; Brosché, M.; Salojärvi, J.; Glawischnig, E.; Winter, Z.; Li, S.; et al. Protein Phosphatase 2A-B’γ Controls Botrytis cinerea Resistance and Developmental Leaf Senescence. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 1161–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, C.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, T.; DeLong, A.; Dong, J. Protein phosphatase 2A promotes stomatal development by stabilizing SPEECHLESS in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13127–13137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averkina, I.O.; Harris, M.; Asare, E.O.; Hourdin, B.; Paponov, I.A.; Lillo, C. Pinpointing regulatory protein phosphatase 2A subunits involved in beneficial symbiosis between plants and microbes. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averkina, I.O.; Paponov, I.A.; Sánchez-Serrano, J.J.; Lillo, C. Specific PP2A Catalytic Subunits Are a Prerequisite for Positive Growth Effects in Arabidopsis Co-Cultivated with Azospirillum brasilense and Pseudomonas simiae. Plants 2020, 10, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segonzac, C.; Macho, A.P.; Sanmartín, M.; Ntoukakis, V.; Sánchez-Serrano, J.J.; Zipfel, C. Negative control of BAK1 by protein phosphatase 2A during plant innate immunity. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Li, L. Dephosphorylation of bZIP59 by PP2A ensures appropriate shade avoidance response in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2024, 60, 551–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Zhang, C.; Jin, P.; Tetteh, C.; Dong, X.; Luo, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H. The cell-type specific role of Arabidopsis bZIP59 transcription factor in plant immunity. Plant Cell Environ. 2022, 45, 1843–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Máthé, C.; Garda, T.; Freytag, C.; Hamvas, M.M. The Role of Serine-Threonine Protein Phosphatase PP2A in Plant Oxidative Stress Signaling-Facts and Hypotheses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- País, S.M.; García, M.N.; Téllez-Iñón, M.T.; Capiati, D.A. Protein phosphatases type 2A mediate tuberization signaling in Solanum tuberosum L. leaves. Planta 2010, 232, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinner, L.; Gadeyne, A.; Belcram, K.; Goussot, M.; Moison, M.; Duroc, Y.; Eeckhout, D.; De Winne, N.; Schaefer, E.; Van De Slijke, E.; et al. A protein phosphatase 2A complex spatially controls plant cell division. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Sandal, P.; Williams, E.L.; Murphy, E.; Stes, E.; Nikonorova, N.; Ramakrishna, P.; Czyzewicz, N.; Montero-Morales, L.; Kumpf, R.; et al. PP2A-3 interacts with ACR4 and regulates formative cell division in the Arabidopsis root. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Ahootapeh, B.H.; Komaki, S.; Schnittger, A.; Lillo, C.; De Storme, N.; Geelen, D. Protein Phoshatase 2A B’α and β Maintain Centromeric Sister Chromatid Cohesion during Meiosis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
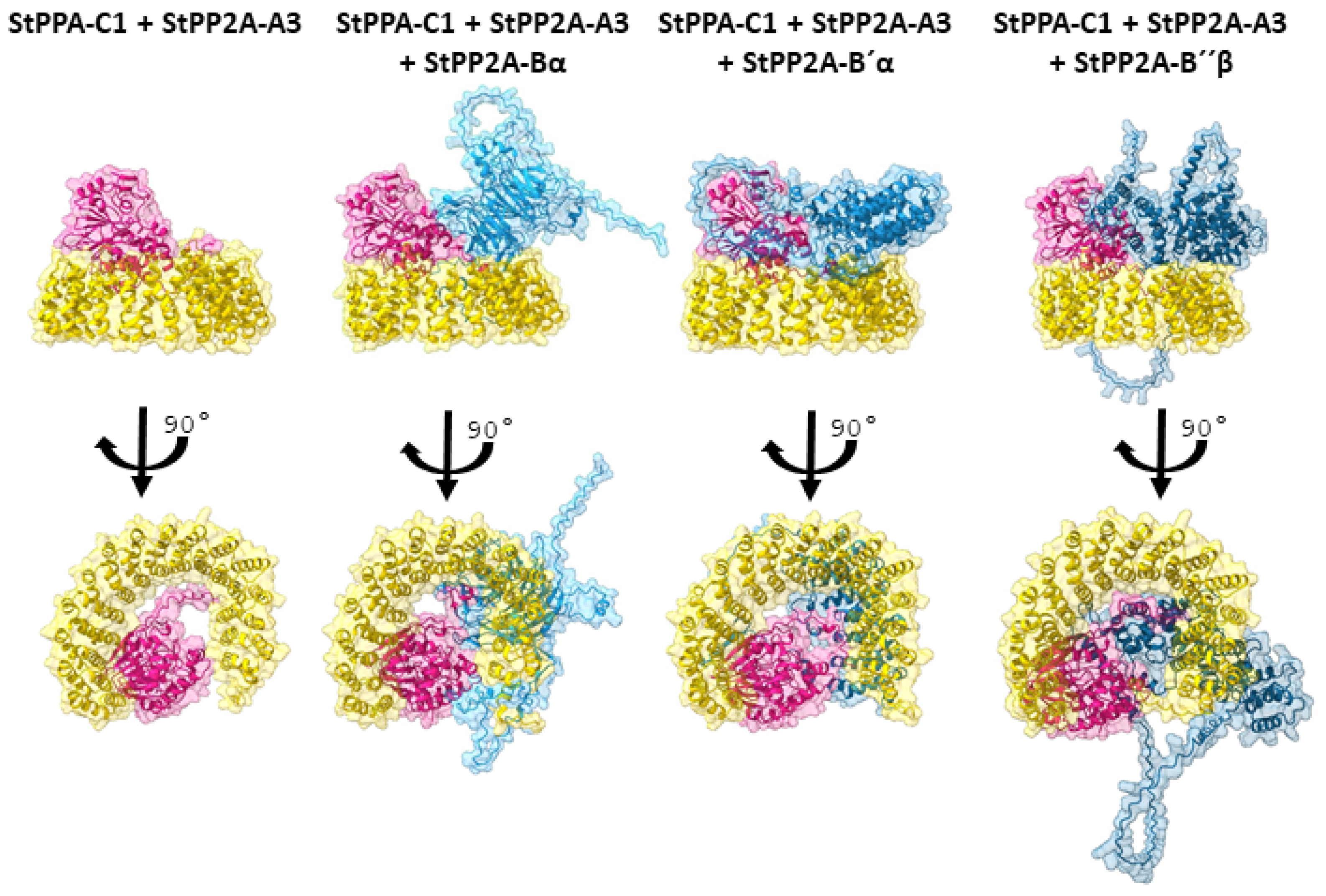
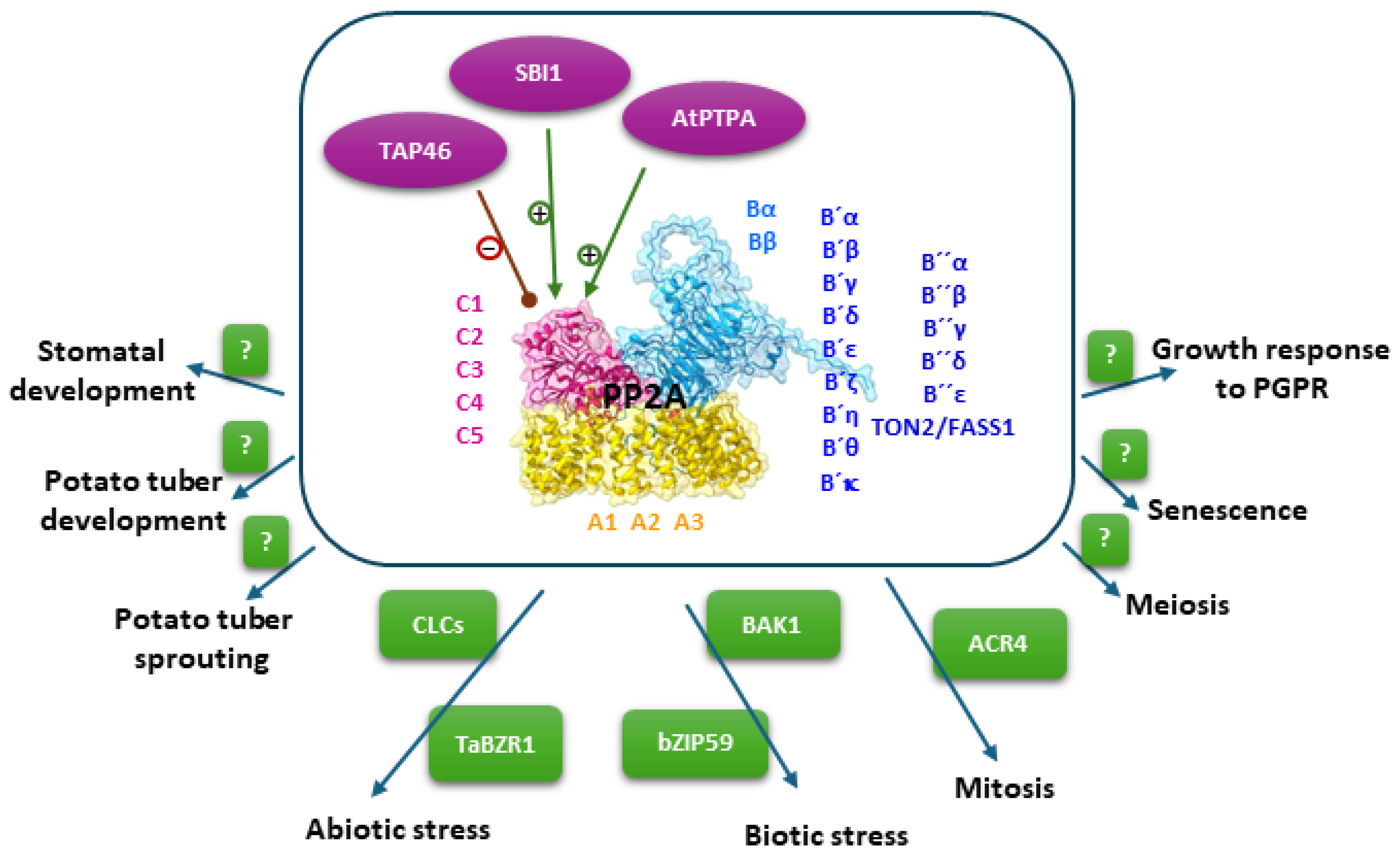
| Species | Subunit | Effect | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abiotic stress | A. thaliana | PP2AC-5 (C) overexpression | Increased salt-stress tolerance | [22] |
| Triticum aestivum | TaPP2Ac-1 (C) overexpression | Increased drought tolerance | [23] | |
| T. aestivum | TaPP2A-2 (C) silencing | Increased drought tolerance | [21] | |
| S. tuberosum | StPP2A-C2b (C) overexpression | Enhanced molecular response to abiotic stress | [5] | |
| A. thaliana | RCN1/A1 (A) mutation | Increased sensitivity to drought and salt stress | [26] | |
| T. aestivum | TaPP2AbB″-α (B) overexpression | Increased drought and osmotic stress tolerance | [27] | |
| T. aestivum | TaPP2AbB″-γ (B) overexpression | Increased drought and osmotic stress tolerance | [28] | |
| Glycine max | GmPP2A-B″71 (B) overexpression | Increased drought and salt-stress tolerance | [29] | |
| Biotic stress | Nicotiana benthamiana | C subfamily I silencing | Enhanced hypersensitive response | [30] |
| T. aestivum | TaPP2Ac-4D (C) silencing | Increased pathogen resistance | [31] | |
| Oryza sativa | OsPP2A-1 (C) knockout | Increased pathogen susceptibility | [32] | |
| S. tuberosum | StPP2A-C2b (C) overexpression | Increased pathogen susceptibility | [33] | |
| N. benthamiana | PP2Aa (A) silencing | Increased pathogen susceptibility | [34] | |
| A. thaliana | PP2A-B′γ (B) mutation | Increased pathogen resistance | [35] | |
| Development | S. tuberosum | StPP2A-C2b (C) overexpression | Enhanced tuber development | [36] |
| S. tuberosum | StPP2A-C2b (C) overexpression | Delayed tuber sprouting | [37] | |
| A. thaliana | PP2A-B′γ (B) mutation | Delayed senescence | [38] | |
| S. tuberosum | StPP2A-C2b (C) overexpression | Accelerated senescence | [33] | |
| A. thaliana | PP2A-A1 (A) PP2A-A1/A2 (A) PP2A-A1/A3 (A) mutation | Reduced stomatal production | [39] | |
| S. tuberosum | StPP2A-C2b (C) overexpression | Reduced stomatal density and increased stomatal size | [25] | |
| Solanum lycoperiscum | PP2A B′θ (B) overexpression | Decreased growth in response to PGPR | [40] | |
| A. thaliana | PP2A-C2/C5 (C) mutation | Enhanced growth in response to PGPR | [41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cortelezzi, J.I.; Zubillaga, M.; Scardino, V.R.; Muñiz García, M.N.; Capiati, D.A. Plant PP2A: A Versatile Enzyme with Key Physiological Functions. Kinases Phosphatases 2025, 3, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3010005
Cortelezzi JI, Zubillaga M, Scardino VR, Muñiz García MN, Capiati DA. Plant PP2A: A Versatile Enzyme with Key Physiological Functions. Kinases and Phosphatases. 2025; 3(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleCortelezzi, Juan I., Martina Zubillaga, Victoria R. Scardino, María N. Muñiz García, and Daniela A. Capiati. 2025. "Plant PP2A: A Versatile Enzyme with Key Physiological Functions" Kinases and Phosphatases 3, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3010005
APA StyleCortelezzi, J. I., Zubillaga, M., Scardino, V. R., Muñiz García, M. N., & Capiati, D. A. (2025). Plant PP2A: A Versatile Enzyme with Key Physiological Functions. Kinases and Phosphatases, 3(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/kinasesphosphatases3010005







