A Sediment Supply Assessment in a Touristic Zone: A Case Study of West Cyprus †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
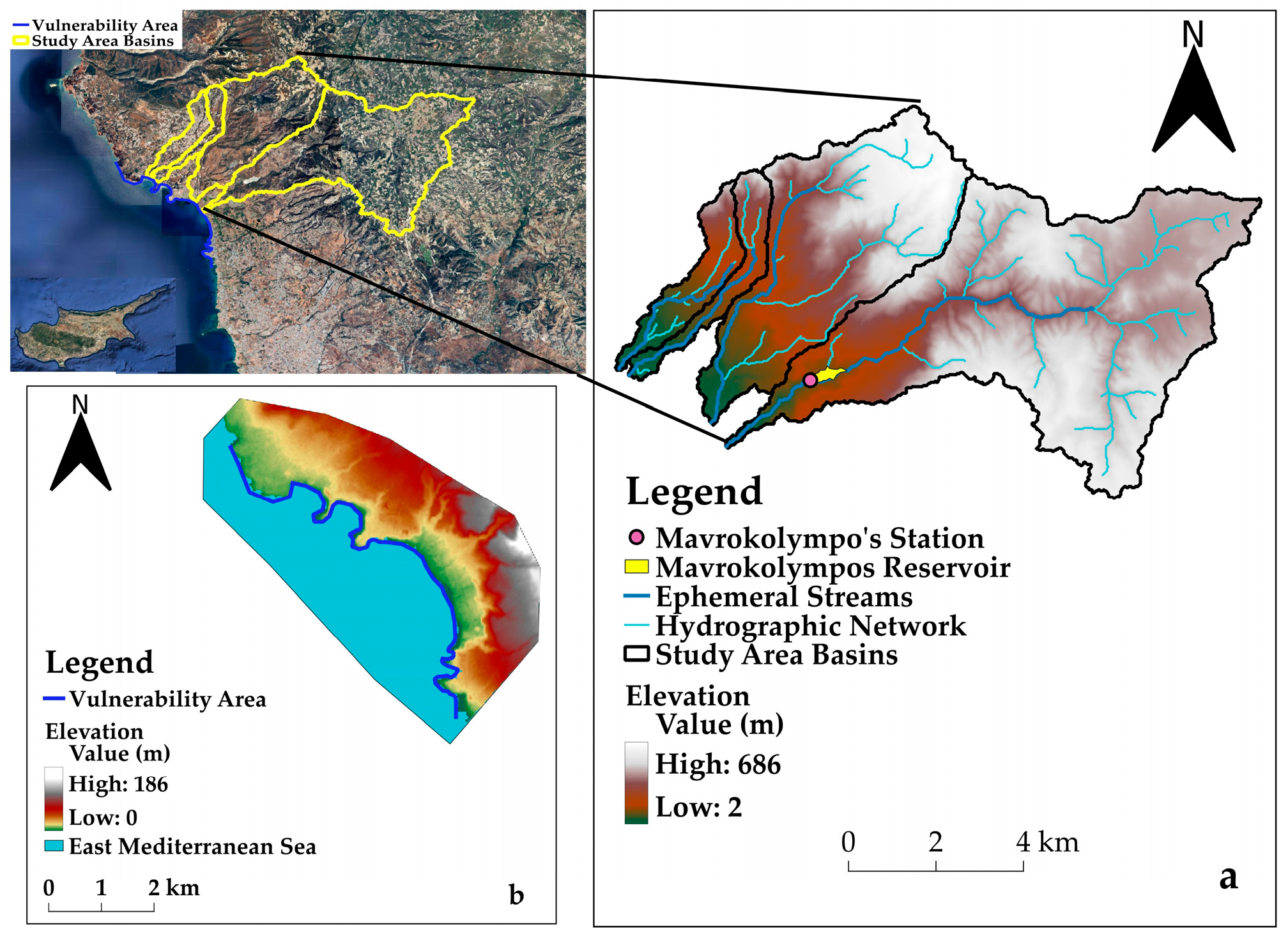
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Available Data
2.3. Sediment Yield Trends and Influencing Factors
2.3.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor R
2.3.2. Soil Erodibility Factor K
2.3.3. Topographic Factor LS
2.3.4. Cover and Management Factor C
2.3.5. Conservation Practice Factor P
2.3.6. Sediment Delivery Ratio
3. Results
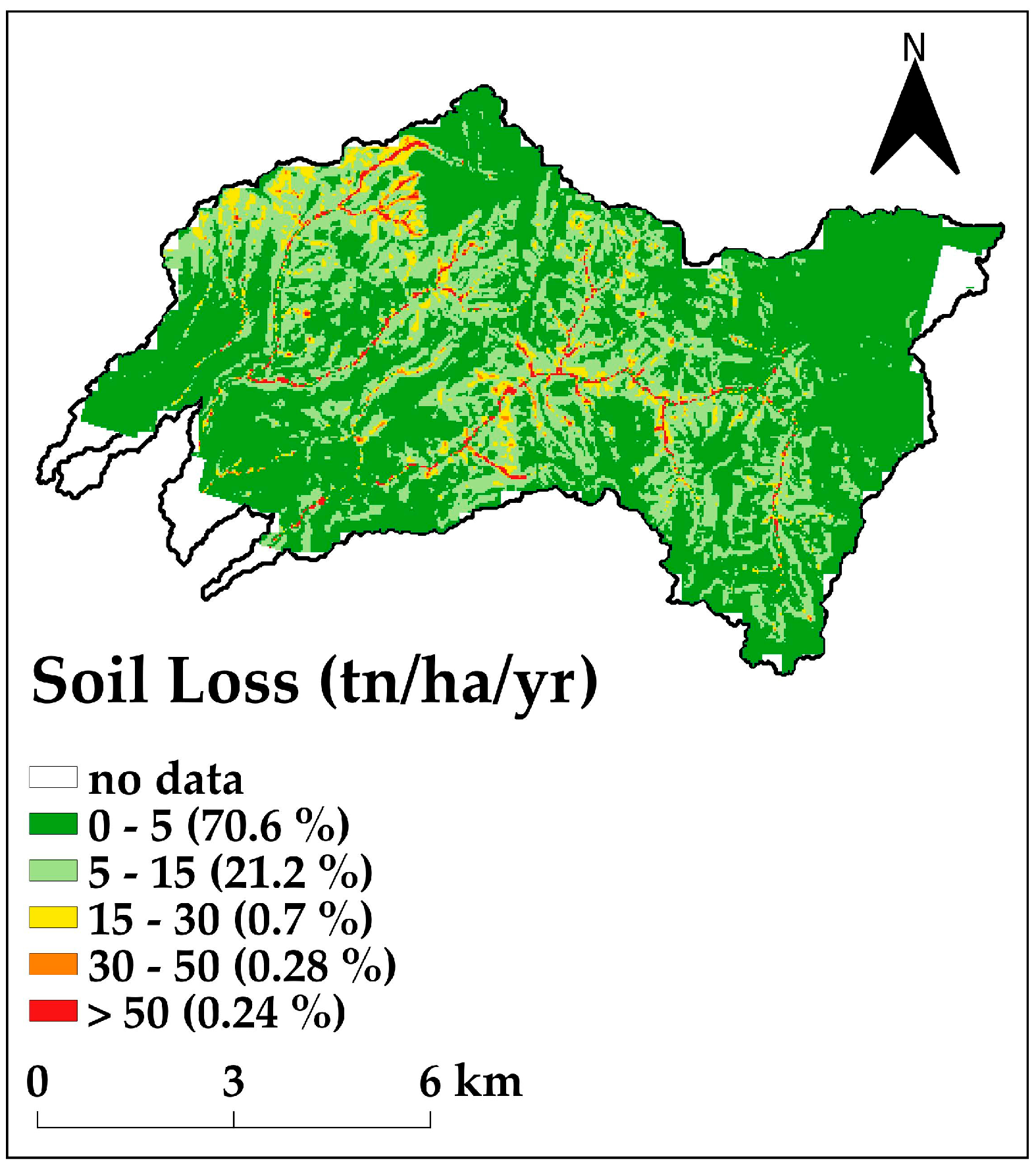
3.1. Soil Loss Assessment
3.2. Sediment Yield Analysis
4. Discussion and Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Posada, P.B.O.; Henao, P.W. Diagnóstico de La Erosión En La Zona Costera Del Caribe Colombiano; Serie Publicaciones Especiales No. 13; INVEMAR: Santa Marta, Colombia, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Malara, G.; Zema, D.A.; Arena, F.; Bombino, G.; Zimbone, S.M. Coupling watershed-coast systems to study evolutionary trends: A review. Earth Sci. Rev. 2020, 201, 103040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anfuso, G.; Postacchini, M.; Di Luccio, D.; Benassai, G. Coastal Sensitivity/Vulnerability Characterization and Adaptation Strategies: A Review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monioudi, I.N.; Velegrakis, A.F.; Chatzipavlis, A.E.; Rigos, A.; Karambas, T.; Vousdoukas, M.I.; Hasiotis, T.; Koukourouvli, N.; Peduzzi, P.; Manoutsoglou, E.; et al. Assessment of island beach erosion due to sea level rise: The case of the Aegean archipelago (Eastern Mediterranean). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 17, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papasarafianou, S.; Siarkos, I.; Gkaifyllia, A.; Sahtouris, S.; Varra, G.; Chatzipavlis, A.; Hasiotis, T.; Tzoraki, O. A Holistic Approach for Coastal-Watershed Management on Tourist Islands: A Case Study from Petra Molyvos Coast, Lesvos Island (Greece). Geosciences 2024, 14, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monioudi, I.N.; Velegrakis, A.F.; Chatzistratis, D.; Vousdoukas, M.I.; Savva, C.; Wang, D.; Bove, G.; Mentaschi, L.; Paprotny, D.; Morales-Nápoles, O.; et al. Climate change-induced hazards on touristic island beaches: Cyprus, Eastern Mediterranean. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1188896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syvitski, J.P.M.; Peckham, S.D.; Hilberman, R.; Mulder, T. Predicting the terrestrial flux of sediment to the global ocean: A planetary perspective. Sediment. Geol. 2003, 162, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaras, A.G.; Koutitas, C.G. Modelling the impact on coastal morphology of the water management in transboundary river basins: The case of River Nestos. Manag. Env. Qual. Inter. J. 2008, 19, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safakli, O.V.; Kutlay, K. Potential multiplier effect of tourism sector in northern Cyprus. Int. J. Acad. Res. Accounting Financ. Manag. Sci. 2016, 6, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Development Department (WDD), Ministry of Agriculture, Rural Development and Environment. 2017. Available online: https://www.moa.gov.cy/moa/wdd/wdd.nsf/index_en/index_en?opendocument (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Gkaifyllia, A.; Sahtouris, S.; Ðorđević, N.; Papasarafianou, S.; Monioudi, I.; Tzoraki, O.; Hasiotis, T. Coastal Zone Vulnerability Analysis in East Mediterranean Basin: Greece, Cyprus and Montenegro; CEST: Athens, Greece, 2023; pp. 2944–9820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camera, C.; Zomeni, Z.; Noller, J.S.; Zissimos, A.M.; Christoforou, I.C.; Bruggeman, A. A high-resolution map of soil types and physical properties for Cyprus: A digital soil mapping optimization. Geoderma 2017, 285, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmi, A.M. Quantifying catchments sediment release in arid regions using GIS-based Universal soil loss equation (USLE). Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14, 102038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todisco, F.; Vergni, L.; Ortenzi, S.; Di Matteo, L. Soil Loss Estimation Coupling a Modified USLE Model with a Runoff Correction Factor Based on Rainfall and Satellite Soil Moisture Data. Water 2022, 14, 2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michas, S.; Nikolaou, K.; Koukouvinos, A.; Mamassis, N. Estimation of Sediment Yield with MUSLE and Monitoring. A Case Study for Tsiknias Dam at Lesvos Island in Greece; IWA Balkan Young Water Professionals: Thessaloniki, Greece, 2015; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Papageorgiou, N.; Hadjimitsis, D.G. Evaluation of Soil Loss by Water in Archaeological Landscapes by Using the (R)USLE Model and GIS. The Case Study of Paphos District, Cyprus. In Digital Heritage. Progress in Cultural Heritage: Documentation, Preservation, and Protection; Ioannides, M., Fink, E., Cantoni, L., Champion, E., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Meusburger, K.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Alewell, C. Soil erodibility in Europe: A high-resolution dataset based on LUCAS. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479–480, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagos, P.; Meusburger, K.; Alewell, C.; Montanarella, L. Soil erodibility estimation using LUCAS point survey data of Europe. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 30, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Knijff, J.M.; Jones, R.J.A.; Montanarella, L. Soil Erosion Risk Assessment in Europe, JRC Scientific and Technical Report-EUR 19022 EN; European Soil Bureau, European Commission: Brussel, Belgium, 2000.
- Van der Knijff, J.M.; Jones, R.J.A.; Montanarella, L. Soil Erosion Risk Assessment in Italy, JRC Scientific and Technical Report-848 EUR 19044 EN; European Soil Bureau, European Commission: Brussel, Belgium, 2000.
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, C.; Alewell, C.; Lugato, E.; Montanarella, L. Estimating the soil erosion cover-management factor at European scale. Land Use Policy 2015, 48, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, G. Comment on Modelling Topographic Potential for Erosion and Deposition Using GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 1997, 11, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. A New European Slope Length and Steepness Factor (LS-Factor) for Modeling Soil Erosion by Water. Geosciences 2015, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karydas, C.G.; Panagos, P. Modelling monthly soil losses and sediment yields in Cyprus. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2016, 9, 766–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vente, J.; Poesen, J. Predicting Soil Erosion and Sediment Yield at the Basin Scale: Scale Issues and Semi Quantitative Models. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2005, 71, 95–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombino, G.; Barbaro, G.; D’Agostino, D.; Denisi, P.; Foti, G.; Labate, A.; Zimbone, S.M. Shoreline change and coastal erosion: The role of check dams. First indications from a case study in Calabria, southern Italy. Catena 2022, 217, 106494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velegrakis, A.F.; Vousdoukas, M.; Andreadis, E.P.; Adamakis, G.; Meligonitis, R. Impacts of dams on their downstream beaches: A case study from Eresos coastal basin, island of Lesvos, Greece. Mar. Geores. Geotechnol. 2008, 24, 350–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
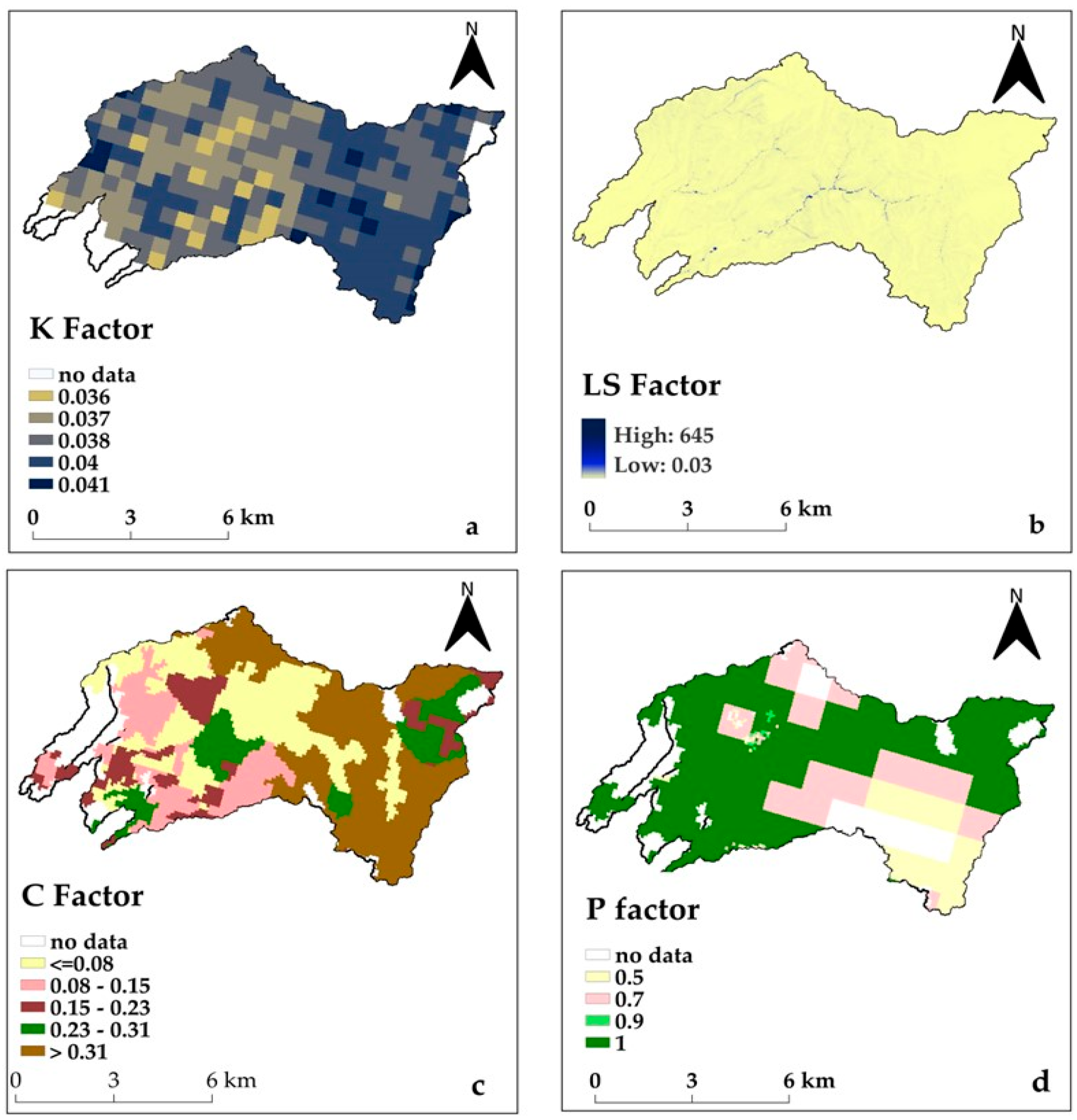
| ID | Soil Texture | K-Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Bc | Calcaric Cambisols | 0.036 |
| Bv | Vertic Cambisols | 0.036 |
| Eo | Ochric Rendzinas | 0.038 |
| Ic | Calcaric Lithosols | 0.041 |
| Ie | Eutric Lithosols | 0.036 |
| Rc | Calcaric Regosols | 0.038 |
| Xv | Vertic Xerosols | 0.036 |
| CORINE Code | Land Cover in Study Area | C | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| 112 | Discontinuous urban fabric | 0.10 | 1.00 |
| 131 | Mineral extraction sites | 0.15 | 1.00 |
| 142 | Sport and leisure facilities | 0.20 | 1.00 |
| 211 | Non-irrigated arable land | 0.10 | 0.70 |
| 221 | Vineyards | 0.35 | 0.50 |
| 222 | Fruit trees and berry plantations | 0.10 | 0.50 |
| 231 | Pastures | 0.12 | 0.90 |
| 241 | Annual crops associated with permanent crops | 0.23 | 0.90 |
| 242 | Complex cultivation patterns | 0.16 | 0.50 |
| 243 | Land principally occupied by agriculture | 0.13 | 0.70 |
| 323 | Sclerophyllous vegetation | 0.06 | 1.00 |
| 324 | Transitional woodland-shrub | 0.03 | 1.00 |
| Parameters | Units | Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Soil loss | Mean annual soil loss (per ha) | t ha−1 yr−1 | 20.1 |
| Mean annual soil loss (per km2) | t km−2 yr−1 | 2010 | |
| Catchment area | km2 | 66.5 | |
| Total annual soil loss | t yr−1 | 133,665 | |
| Sediment yield | Reduction sediment yield factor (De Vente and Poesen [25]) | - | 0.44 |
| Annual sediment yield (per km2) | t km−2 yr−1 | 888 | |
| Total annual sediment yield | t yr−1 | 59.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papasarafianou, S.; Varra, G.; Cozzolino, L.; Tzoraki, O. A Sediment Supply Assessment in a Touristic Zone: A Case Study of West Cyprus. Environ. Earth Sci. Proc. 2025, 32, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025032016
Papasarafianou S, Varra G, Cozzolino L, Tzoraki O. A Sediment Supply Assessment in a Touristic Zone: A Case Study of West Cyprus. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings. 2025; 32(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025032016
Chicago/Turabian StylePapasarafianou, Stamatia, Giada Varra, Luca Cozzolino, and Ourania Tzoraki. 2025. "A Sediment Supply Assessment in a Touristic Zone: A Case Study of West Cyprus" Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings 32, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025032016
APA StylePapasarafianou, S., Varra, G., Cozzolino, L., & Tzoraki, O. (2025). A Sediment Supply Assessment in a Touristic Zone: A Case Study of West Cyprus. Environmental and Earth Sciences Proceedings, 32(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/eesp2025032016








