Preparation of Polypropylene Micro and Nanofibers by Electrostatic-Assisted Melt Blown and Their Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrostatic-Assisted Melt-Blown Setup
2.3. Preparation of PP Nonwoven Fabrics
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
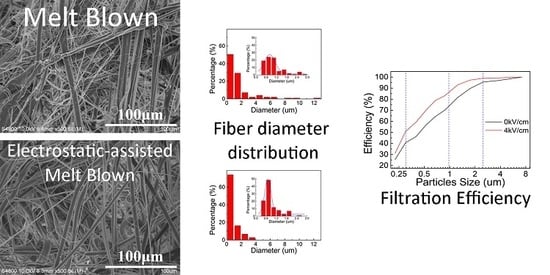
3.1. Morphology and Structure
3.2. Stress and Strain
3.3. Pore Size Distribution and Air Permeability
3.4. Filtration Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ellison, C.J.; Phatak, A.; Giles, D.W.; Macosko, C.W.; Bates, F.S. Melt blown nanofibers: Fiber diameter distributions and onset of fiber breakup. Polymer 2007, 48, 3306–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J. Preparation and properties of poly(lactic acid) fiber melt blown non-woven disordered mats. Mater. Lett. 2017, 189, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Truong, Y.B.; Padhye, R.; Arnold, L.; Peeters, G.; Nichols, L.; O’Shea, M. Fabrication and characterisation of nanofibres by meltblowing and melt electrospinning. In Advanced Materials Research; Chen, W.Z., Xu, X.P., Dai, P.Q., Chen, Y.L., Eds.; Trans Tech Publications: Zurich, Switzerland, 2012; Volume 472–475, pp. 1294–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Han, S.W.; Joshi, M.K.; Kim, C.S. Fabrication and characterization of silver nanoparticle-incorporated bilayer electrospun-melt-blown micro/nanofibrous membrane. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomat. 2017, 66, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; He, W.; Qin, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, H. Melt electro-blowing spinning for preparation of nanofibers. Plastics 2017, 46, 121–124. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, K. Investigation on compound field of electrospinning and melt blowing for producing nanofibers. Int. J. Numer. Methods Heat Fluid Flow 2017, 27, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yao, J.; Pan, X. Fiber splitting of bicomponent meltblown nonwovens by ultrasonic wave. Int. J. Chem. 2009, 1, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, K.C. Overview and analysis of the meltblown process and parameters. J. Text. Appar. Technol. Manag. 2008, 6, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.A.; Yeom, B.Y.; Wilkie, A.; Pourdeyhimi, B.; Khan, S.A. Fabrication of nanofiber meltblown membranes and their filtration properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 427, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majchrzycka, K.; Okrasa, M.; Brochocka, A.; Urbaniak-Domagala, W. Influence of low-temperature plasma treatment on the liquid filtration efficiency of melt-blown pp nonwovens in the conditions of simulated use of respiratory protective equipment. Chem. Process Eng. 2017, 38, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Song, Y.; Chen, G. Correlation between charge decay and solvent effect for melt-blown polypropylene electret filter fabrics. J. Electrost. 2014, 72, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Han, W.; Jiang, G.; Chen, C. Turbulent air flow field in slot-die melt blowing for manufacturing microfibrous nonwoven materials. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 6991–7003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, C.; Jin, X. Design of electret polypropylene melt blown air filtration material containing nucleating agent for effective pm2.5 capture. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7932–7941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.W.; Song, J.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.H. Numerical modelling of microfibers formation and motion during melt blowing. J. Text. Inst. 2018, 109, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, W. Investigation on producing micro-nano fibers by melt electrospinning. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2010, 18, 425–433. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Wu, W.; Bubakir, M.M.; Chen, H.; Zhong, X.; Liu, Z.; Ding, Y.; Yang, W. Polypropylene fibers fabricated via a needleless melt-electrospinning device for marine oil-spill cleanup. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosmayer, P.; Budliger, J.P.; Zurcher, E.; Wadsworth, L.C. Apparatus for Electrically Charging Meltblown Webs (b-001). U.S. Patent 4,904,174, 27 February 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, B.; Hsiao, B.S.; Fang, D.; Okamoto, A. Electro-Blowing Technology for Fabrication of Fibrous Articles and its Applications of Hyaluronan. U.S. Patent 7,662,332, 16 February 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.J.; Stoyanov, S.D.; Stride, E.; Pelan, E.; Edirisinghe, M. Electrospinning versus fiber production methods: From specifics to technological convergence. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4708–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, K.; Lee, Y.J.; Nakamura, T.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, I.S. Development of melt blown electrospinning apparatus of isotactic polyproylene. NSTI-Nanotech 2009, 1, 826–829. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Lee, C.; Kim, I.W.; Kim, J. Performance modification of a melt-blown filter medium via an additional nano-web layer prepared by electrospinning. Fibers Polym. 2009, 10, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppal, R.; Bhat, G.; Eash, C.; Akato, K. Meltblown nanofiber media for enhanced quality factor. Fibers Polym. 2013, 14, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, D.; Skrybeck, D.; Misslitz, H.; Nardini, D.; Kern, A.; Kreger, K.; Schmidt, H.-W. Tailoring supramolecular nanofibers for air filtration applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14885–14892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misslitz, H.; Kreger, K.; Schmidt, H.-W. Supramolecular nanofiber webs in nonwoven scaffolds as potential filter media. Small 2013, 9, 2053–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Shen, Z.; Hong, J. Preparation and properties of electrospun composite material for high-efficiency ash filtration. J. Text. Res. 2015, 36, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Huang, C.; Jin, X. Online prediction of the filtration performance of polypropylene melt blown nonwovens by blue-colored glow. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Gui, J.; Chen, G.; Xiao, C. Study on correlation of filtration performance and charge behavior and crystalline structure for melt-blown polypropylene electret fabrics. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaojun, B.X. Disussion of electret air filtration material utilizing electrostatic electret. Contam. Control Air-cond. Technol. 2005, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 3682-2000, Determination of the Melt Mass-Flow Rate (MFR) and the Melt Volume-Flow Rate (MVR) of Thermoplastics; Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2001.
- GB/T 9345.1-2008, Plastics—Determination of Ash—Part 1: Generalmethods; Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Fridrikh, S.V.; Yu, J.H.; Brenner, M.P.; Rutledge, G.C. Controlling the fiber diameter during electrospinning. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 144502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, R.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Xie, P.; Luo, L.; Yang, W. Melt electrospinning of low-density polyethylene having a low-melt flow index. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 114, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detta, N.; Brown, T.D.; Edin, F.K.; Albrecht, K.; Chiellini, F.; Chiellini, E.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Melt electrospinning of polycaprolactone and its blends with poly(ethylene glycol). Polym. Int. 2010, 59, 1558–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhmayev, E.; Cho, D.; Joo, Y.L. Modeling of melt electrospinning for semi-crystalline polymers. Polymer 2010, 51, 274–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-F.; Huang, Z.-M. Melt-electrospinning of pmma. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2010, 28, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.C.; Kothari, V.K. Relationship between tensile properties of fibres and nonwoven fabrics. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2001, 26, 398–402. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.; Gamcsik, M.P.; King, M.W. Novel scaffold design with multi-grooved pla fibers. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 6, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ya, L.I.U.; Bowen, C.; Zhe, Z.; Guoxiang, C. Study on pla meltblowns. J. Text. Res. 2007, 28, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Cheng, B.W.; Wang, N.; Kang, W.M.; Zhang, W.L.; Xing, K.Q.; Yang, W.J. Development and performance study of polypropylene/polyester bicomponent melt-blowns for filtration. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimin, K.; Bowen, C.; Xupin, Z.; Changkun, D. Electrospun nano-fiber composite membrane and its filtration properties. J. Text. Res. 2006, 27, 6. [Google Scholar]







| Particle Size | 0.3 μm | 1 μm | 2.5 μm |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melt-blown | 40.651% | 73.986% | 95.353% |
| Electrostatic-assisted Melt-blown | 50.826% | 86.442% | 98.969% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Chen, F.; Long, Y.; Wu, H.; Li, Q.; Yu, S.; Wang, X.; Ning, X. Preparation of Polypropylene Micro and Nanofibers by Electrostatic-Assisted Melt Blown and Their Application. Polymers 2018, 10, 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10090959
Pu Y, Zheng J, Chen F, Long Y, Wu H, Li Q, Yu S, Wang X, Ning X. Preparation of Polypropylene Micro and Nanofibers by Electrostatic-Assisted Melt Blown and Their Application. Polymers. 2018; 10(9):959. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10090959
Chicago/Turabian StylePu, Yi, Jie Zheng, Fuxing Chen, Yunze Long, Han Wu, Qiusheng Li, Shuxin Yu, Xiaoxiong Wang, and Xin Ning. 2018. "Preparation of Polypropylene Micro and Nanofibers by Electrostatic-Assisted Melt Blown and Their Application" Polymers 10, no. 9: 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10090959
APA StylePu, Y., Zheng, J., Chen, F., Long, Y., Wu, H., Li, Q., Yu, S., Wang, X., & Ning, X. (2018). Preparation of Polypropylene Micro and Nanofibers by Electrostatic-Assisted Melt Blown and Their Application. Polymers, 10(9), 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10090959