Evaluation of MMP Inhibitors Isolated from Ligustrum japonicum Fructus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
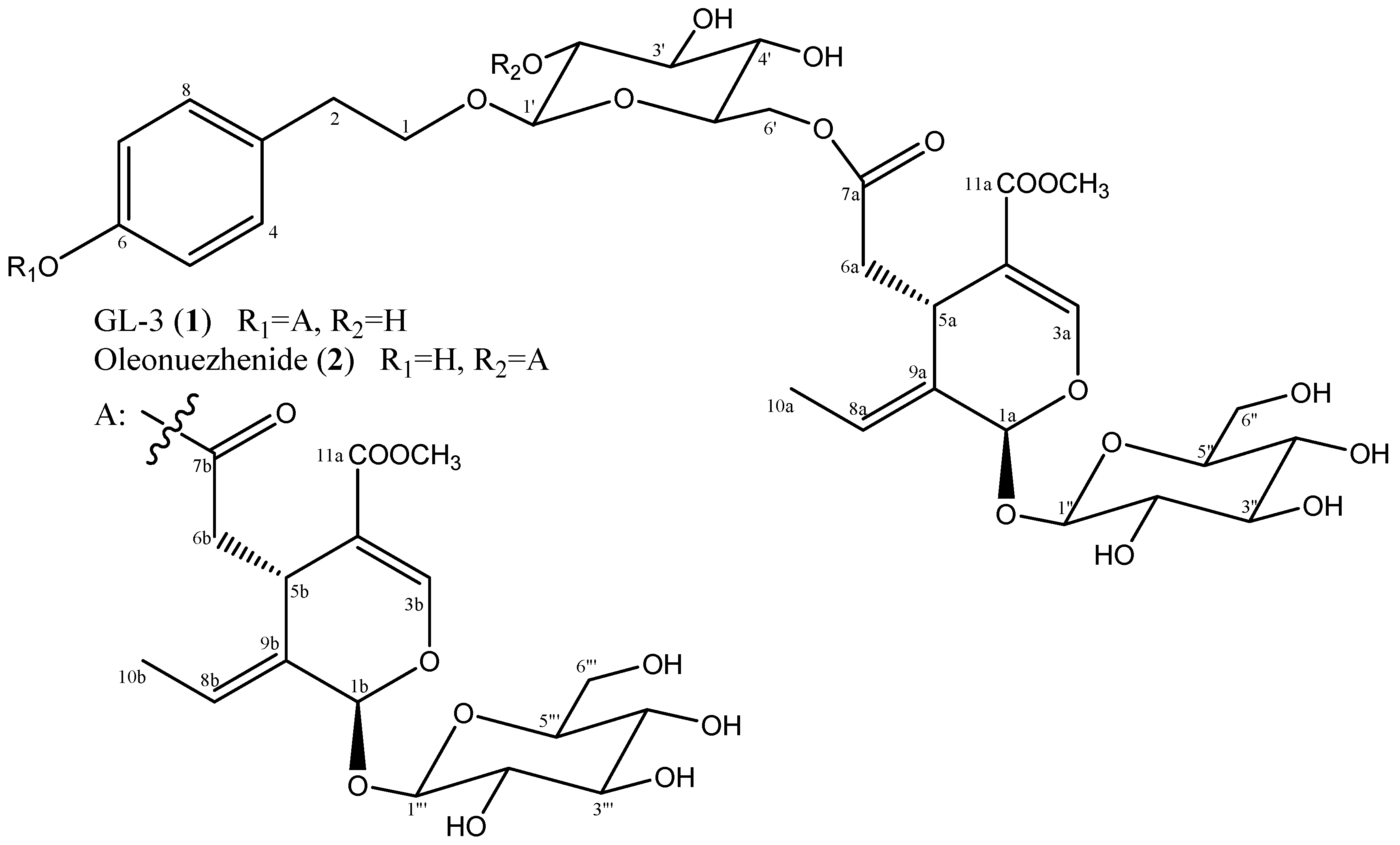
2.1. Structure Identification
2.2. Inhibition of MMP-2 and MMP-9 Enzymatic Activity
2.3. Inhibition of MMP-2 and MMP-9 mRNA and Protein Expression
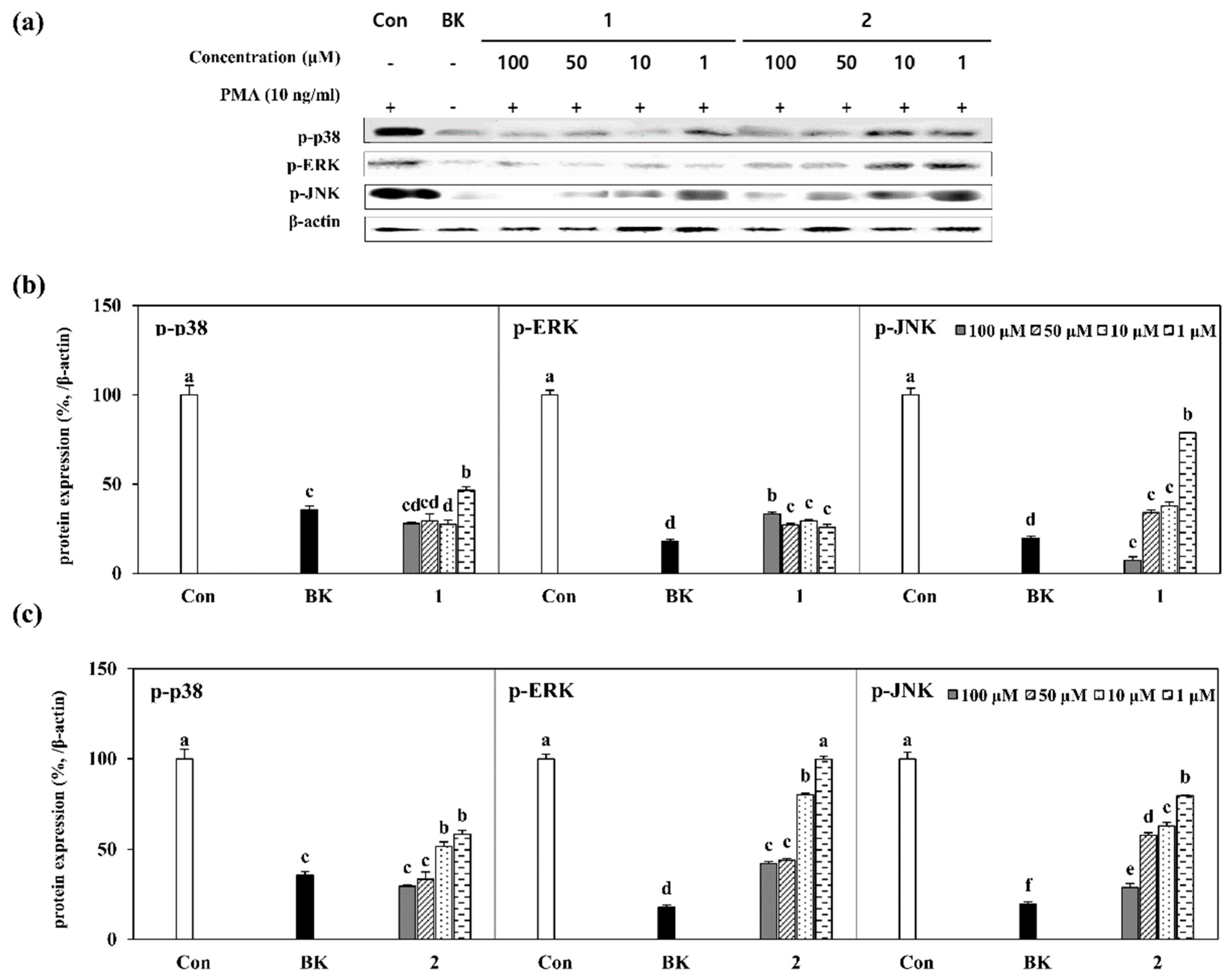
2.4. Inhibition of MAPK Pathway by Isolated Compounds
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Apparatus and Reagents
3.2. Materials and Isolation
3.2.1. GL-3 (1)
3.2.2. Oleonuezhenide (2)
3.3. Cell Culture and Cytotoxicity Determination
3.4. Determination of MMP Activity by Gelatin Zymography
3.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
3.6. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction Analysis
3.7. Western Blot Analysis
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malemud, C.J. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in health and disease: An overview. Front. Biosci. 2006, 11, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarti, S.; Patel, K.D. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9 in pulmonary pathology. Exp. Lung Res. 2005, 31, 599–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birkedal-Hansen, H.; Moore, W.G.I.; Bodden, M.K.; Windsor, L.J.; Birkedal-Hansen, B.; DeCarlo, A.; Engler, J.A. Matrix metalloproteinases: A review. Crit. Rev. Oral Biol. Med. 1993, 4, 197–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, P.; Wolf, K. Tube travel: The role of proteases in individual and collective cancer cell invasion. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7247–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourboulia, D.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs): Positive and negative regulators in tumor cell adhesion. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2010, 20, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, T.; Qin, Z.; Xia, W.; Shao, Y.; Voorhees, J.J.; Fisher, G.J. Matrix-degrading metalloproteinases in photoaging. In Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 14, pp. 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, G.J.; Kang, S.; Varani, J.; Bata-Csorgo, Z.; Wan, Y.; Datta, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Mechanisms of photoaging and chronological skin aging. Arch. Dermatol. 2002, 138, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Plaks, V.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2010, 141, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryugina, E.I.; Quigley, J.P. Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 9–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Takahashi, H.; Murai, Y.; Cui, Z.; Nomoto, K.; Niwa, H.; Tsuneyama, K.; Takano, Y. Expressions of MMP-2, MMP-9 and VEGF are closely linked to growth, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis of gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2006, 26, 3579–3583. [Google Scholar]
- Daniele, A.; Zito, A.F.; Giannelli, G.; Divella, R.; Asselti, M.; Mazzocca, A.; Paradiso, A.; Quaranta, M. Expression of metalloproteinases MMP-2 and MMP-9 in sentinel lymph node and serum of patients with metastatic and non-metastatic breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 3521–3527. [Google Scholar]
- Drummond, A.H.; Beckett, P.; Brown, P.D.; Bone, E.A.; Davidson, A.H.; Galloway, W.A.; Gearing, A.J.H.; Huxley, P.; Laber, D.; McCourt, M.; et al. Preclinical and clinical studies of MMP inhibitors in cancer. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 878, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucker, S.; Cao, J. Selective matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitors in cancer therapy: Ready for prime time? Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 2371–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gialeli, C.; Theocharis, A.D.; Karamanos, N.K. Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.H. Metalloproteinase inhibitors: Biological actions and therapeutic opportunities. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 3719–3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, O.; Oswald, M.; Tretzel, L.; Herres, E.; Arend, J.; Efferth, T. Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis by antibodies, synthetic small molecules and natural products. Curr. Med. Chem. 2011, 18, 3136–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.; Lu, J.; Huang, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, G.; Gong, J.; Zhong, Z.; Xu, Z.; Dang, Y.; et al. Anti-cancer natural products isolated from Chinese medicinal herbs. Chin. Med. 2011, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.O.; Kim, H.; Jeong, H.; Ju, E.; Kong, C.-S.; Seo, Y. Antioxidant activity of the halophyte Ligustrum japonicum. KSBB J. 2015, 30, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kong, C.-S.; Seo, Y. Inhibitory activity of Ligustrum japonicum fructus on MMP-2 and MMP-9. KSBB J. 2017, 32, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Lee, Y.R.; Lee, H.S.; Cheon, J.W. Anti-aging effect of Ligustrum japonicum extract in the human fibroblast cells. J. Soc. Cosmet. Sci. Korea 2010, 36, 295–301. [Google Scholar]
- Ngo, Q.-M.T.; Cao, T.Q.; Woo, M.H.; Min, B.S.; Weon, K.-Y. Cytotoxic triterpenoids from the fruits of Ligustrum japonicum. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2018, 24, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaLonde, R.T.; Wong, C.; Tsai, A.I.-M. Polyglucosidic metabolites of Oleaceae. The chain sequence of oleoside aglucon, tyrosol, and glucose units in three metabolites from Fraxinus Americana. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1976, 98, 3007–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, Y.; Koshino, K.; Hasegawa, T.; Yamada, T.; Nakagawa, K. New secoiridoid glucosides from Ligustrum japonicum. Planta Med. 1987, 53, 427–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, S.; Honda, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Miura, T.; Sugawara, R.; Yaoita, Y.; Kikuchi, M.; Machida, K. Six new secoiridoids from the dried fruits of Ligustrum lucidum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, M.-J.; Karadeniz, F.; Lee, S.-G.; Seo, Y.; Kong, C.-S. Inhibition of MMP-2 and MMP-9 activities by Limonium tetragonum extract. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 21, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Wang, Z. Evaluation of matrix metalloproteinase inhibition by peptide microarray-based fluorescence assay on polymer brush substrate and in vivo assessment. Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 44241–44250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, B.; Givant-Horwitz, V.; Lazarovici, P.; Risberg, B.; Nesland, J.M.; Trope, C.G.; Schaefer, E.; Reich, R. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP), EMMPRIN (extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK): Co-expression in metastatic serous ovarian carcinoma. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2003, 20, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.B.; Krueger, J.S.; Kondapaka, S.B.; Diglio, C.A. Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) regulates the expression of progelatinase B (MMP-9) in breast epithelial cells. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 82, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarasamy, Y.; Nahar, L.; Cox, P.J.; Jaspars, M.; Sarker, S.D. Bioactivity of secoiridoid glycosides from Centaurium erythraea. Phytomedicine 2003, 10, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisalberti, E.L. Biological and pharmacological activity of naturally occurring iridoids and secoiridoids. Phytomedicine 1998, 5, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, B.; Chowdhury, D.R.; Mohanta, B.C. Naturally occurring iridoids, secoiridoids and their bioactivity. An updated review, part 3. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2009, 57, 765–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, R. Anti-cancer properties of olive oil secoiridoid phenols: A systematic review of in vivo studies. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 4145–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, H.B.; Giri, S.; Jain, M.; Goyal, R.K. Decrease in serum matrix metalloproteinase-9 and matrix metalloproteinase-3 levels in Zucker fa/fa obese rats after treatment with swertiamarin. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2012, 17, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bulotta, S.; Oliverio, M.; Russo, D.; Procopio, A. Biological activity of oleuropein and its derivatives. In Natural Products: Phytochemistry, Botany and Metabolism of Alkaloids, Phenolics and Terpenes; Ramawat, K.G., Merillon, J.-M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 3605–3638. [Google Scholar]
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds GL-3 and oleonuezhenide are available from corresponding author upon reasonable request. |



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.; Karadeniz, F.; Kong, C.-S.; Seo, Y. Evaluation of MMP Inhibitors Isolated from Ligustrum japonicum Fructus. Molecules 2019, 24, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030604
Kim H, Karadeniz F, Kong C-S, Seo Y. Evaluation of MMP Inhibitors Isolated from Ligustrum japonicum Fructus. Molecules. 2019; 24(3):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030604
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hojun, Fatih Karadeniz, Chang-Suk Kong, and Youngwan Seo. 2019. "Evaluation of MMP Inhibitors Isolated from Ligustrum japonicum Fructus" Molecules 24, no. 3: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030604
APA StyleKim, H., Karadeniz, F., Kong, C.-S., & Seo, Y. (2019). Evaluation of MMP Inhibitors Isolated from Ligustrum japonicum Fructus. Molecules, 24(3), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24030604




