Future Generation 5G Wireless Networks for Smart Grid: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Overview of Wireless Communications Technologies
3. 5G Networks―Outlook
3.1. Architecture of 5G Networks
3.2. Applications of 5G Networks in General
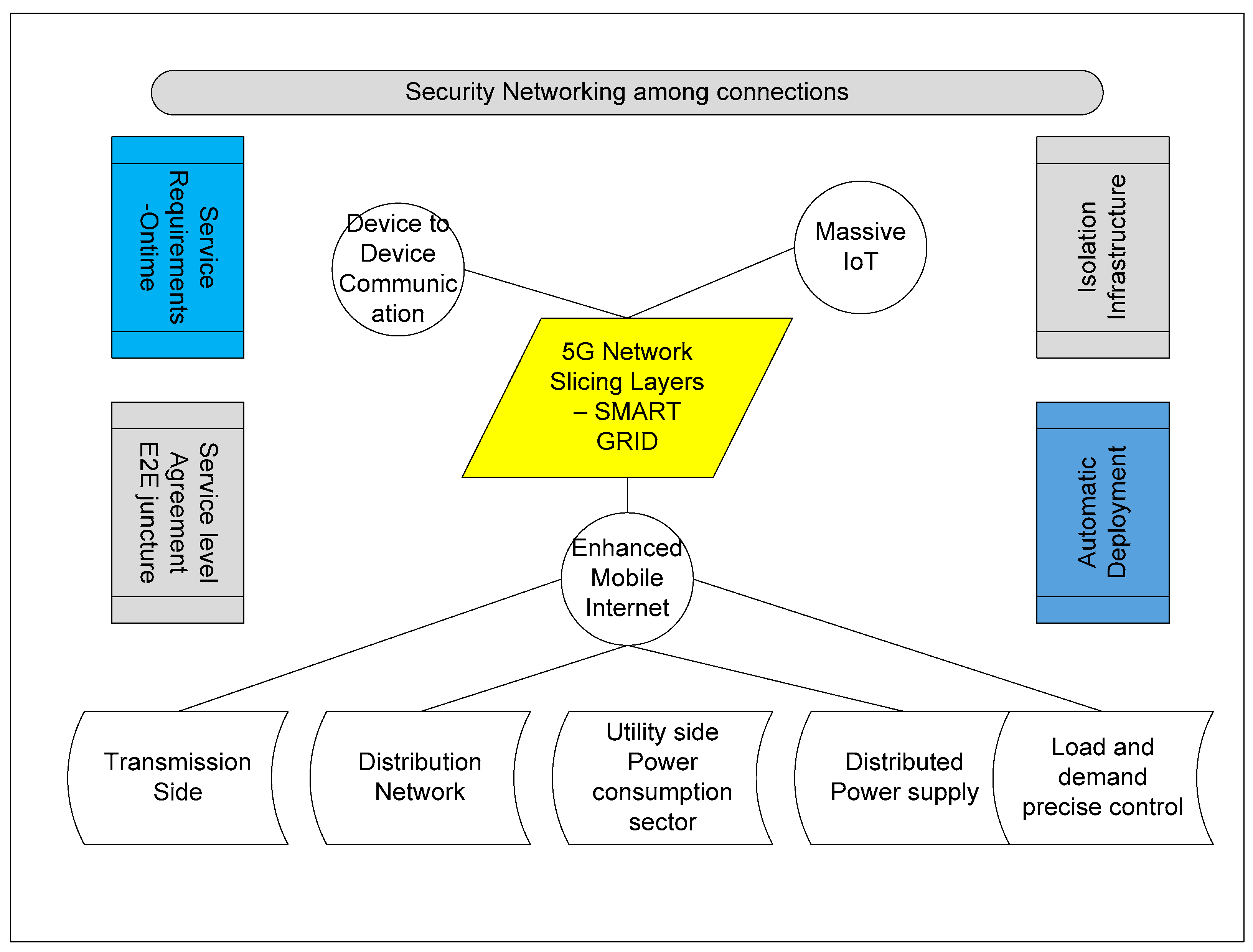
4. Smart Grid and 5G
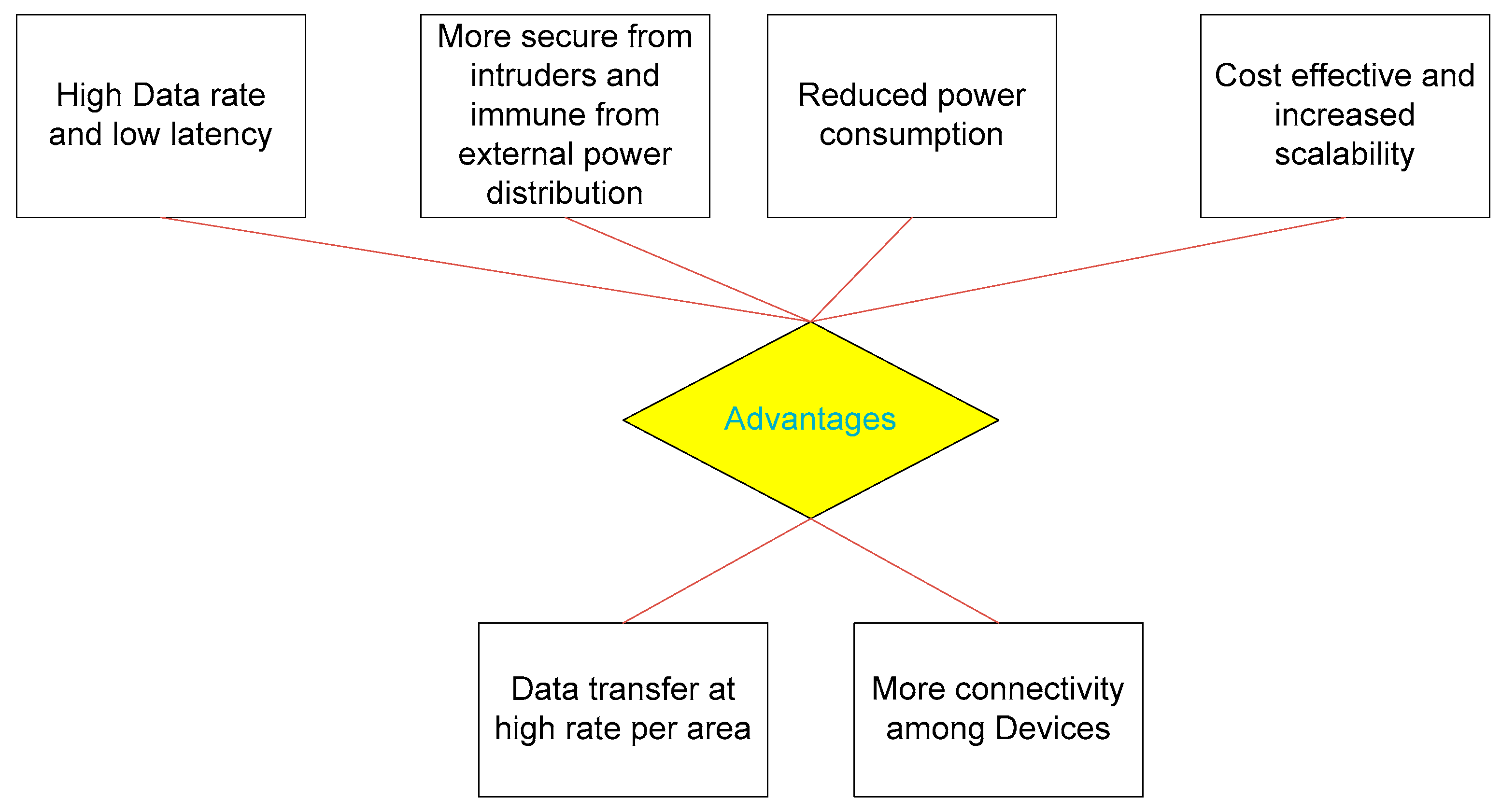
4.1. Advantages of 5G Networks in Smart Grid
4.2. Security in 5G Based Smart Grid Networks
4.3. Challenges of 5G Based Smart Grid Networks
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farhangi, H. The path of the smart grid. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2010, 8, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuballa, M.L.; Abundo, M.L. A review of the development of Smart Grid technologies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 710–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalci, Y. A survey on smart metering and smart grid communication. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 57, 302–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Chen, H.H.; Huang, Y.R.; Meng, W. Smart grid communication: Its challenges and opportunities. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, C.; Liang, H.; Guan, X. Cooperative Relaying Strategies for Smart Grid Communications: Bargaining Models and Solutions. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 2315–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Qian, Y.; Sharif, H.; Tipper, D. A survey on smart grid communication infrastructures: Motivations, requirements and challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, V.C.; Sahin, D.; Kocak, T.; Ergut, S.; Buccella, C.; Cecati, C.; Hancke, G.P. Smart grid technologies: Communication technologies and standards. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2011, 7, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xu, Y.; Khanna, M. A survey on the communication architectures in smart grid. Comput. Netw. 2011, 55, 3604–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuchtinger, U.; Eger, K.; Frank, R.; Riedl, J. Smart Grid Communication Architecture. MMB DFT 2014, 2014, 127. [Google Scholar]
- Zaballos, A.; Vallejo, A.; Selga, J.M. Heterogeneous communication architecture for the smart grid. IEEE Netw. 2011, 25, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werbos, P.J. Computational intelligence for the smart grid-history, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2011, 6, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, T.; Lobashov, M. End-to-end communication architecture for smart grids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osseiran, A.; Boccardi, F.; Braun, V.; Kusume, K.; Marsch, P.; Maternia, M.; Queseth, O.; Schellmann, M.; Schotten, H.; Taoka, H.; et al. Scenarios for 5G mobile and wireless communications: The vision of the METIS project. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaukat, N.; Ali, S.M.; Mehmood, C.A.; Khan, B.; Jawad, M.; Farid, U.; Ullah, Z.; Anwar, S.M.; Majid, M. A survey on consumers empowerment, communication technologies, and renewable generation penetration within Smart Grid. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 18, 1453–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, M.; Rayudu, R. Communication technologies for smart grid applications: A survey. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016, 74, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson. 5G Radio Access; White paper; Ericsson: Stockholm, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. Qualcomm’s 5G Vision; White paper; Qualcomm Technologies, Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Huawei. 5G a Technology Vision; White paper; Huawei: Shenzhen, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Olwal, T.O.; Djouani, K.; Kurien, A.M. A survey of resource management toward 5G radio access networks. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 1656–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 5G and the Internet of Energy. Available online: https://www.navigantresearch.com/reports/5g-and-the-internet-of-energy (accessed on 7 January 2019).
- Mishra, P.K.; Pandey, S.; Biswash, S.K. Efficient resource management by exploiting D2D communication for 5G networks. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 9910–9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Turjman, F. 5G-enabled devices and smart-spaces in social-IoT: An overview. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyapong, P.K.; Iwamura, M.; Staehle, D.; Kiess, W.; Benjebbour, A. Design considerations for a 5G network architecture. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 52, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, E.; Rasti, M.; Tabassum, H.; Abdelnasser, A. Evolution toward 5G multi-tier cellular wireless networks: An interference management perspective. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2014, 21, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Namboodiri, V.; Aravinthan, V.; Mohapatra, S.N.; Karimi, B.; Jewell, W. Toward a secure wireless-based home area network for metering in smart grids. IEEE Syst. J. 2014, 8, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol-Kantarci, M.; Mouftah, H.T. Energy-efficient information and communication infrastructures in the smart grid: A survey on interactions and open issues. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobaccaro, G.; Carlucci, S.; Löfström, E. A review of systems and technologies for smart homes and smart grids. Energies 2016, 9, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Molina, J.; Martínez-Núñez, M.; Martínez, J.F.; Pérez-Aguiar, W. Business models in the smart grid: Challenges, opportunities and proposals for prosumer profitability. Energies 2014, 7, 6142–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Filali, F.; Ko, Y.B. Trends and potentials of the smart grid infrastructure: From ICT sub-system to SDN-enabled smart grid architecture. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 706–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llaria, A.; Terrasson, G.; Curea, O.; Jiménez, J. Application of wireless sensor and actuator networks to achieve intelligent microgrids: A promising approach towards a global smart grid deployment. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Pérez, N.; Hernández, L.; de la Vega, D.; Angulo, I. State of the art and trends review of smart metering in electricity grids. Appl. Sci. 2016, 6, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Falahy, N.; Alani, O.Y. Technologies for 5G networks: Challenges and Opportunities. IT Prof. 2017, 9, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, A.; Masotti, D. Energizing 5G. IEEE Microw. Mag. 2017, 18, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agiwal, M.; Roy, A.; Saxena, N. Next Generation 5G wireless networks: A Comprehensive Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 1617–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, J.G.; Buzzi, S.; Choi, W.; Hanly, S.V.; Lozano, A.; Soong, A.C.; Zhang, J.C. What will 5G be? IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2014, 32, 1065–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappaport, T.S.; Sun, S.; Mayzus, R.; Zhao, H.; Azar, Y.; Wang, K.; Wong, G.N.; Schulz, J.K.; Samimi, M.; Gutierrez, F. Millimeter Wave Mobile Communications for 5G Cellular: It Will Work. IEEE Access 2013, 1, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levanen, T.; Pirskanen, J.; Valkama, M. Radio Interface Design for Ultra-Low Latency Millimeter-Wave Communications in 5G Era. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Austin, TX, USA, 8–12 December 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, N.; Cheng, N.; Gamage, A.P.; Zhang, K.; Mark, J.W.; Shen, X. Cloud Assisted Hetnets toward 5G wireless network. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, E.G.; Edfors, O.; Tufvesson, F.; Marzetta, T.L. Massive MIMO for next generation Wireless Systems. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2014, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wang, H.; Youn, C.H. Visible Light Communications for 5G Wireless Networking Systems: From Fixed to Mobile Communications. IEEE Netw. 2014, 28, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, P.; Kumar, L.; Kaur, J.; Mehandiratta, G.; Manu, R.K. Promising Technologies Intended for 5G Wireless Networks: A review. In Proceedings of the International Interdisciplinary Conference on Science Technology Engineering Management Pharmacy and Humanities, Singapore, Singapore, 22–23 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Wu, J.; Guo, L.; Li, J.; Wang, H. SDN based dynamic and autonomous bandwidth allocation as ACSI services of IEC61850 communications in smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Smart Energy Grid Engineering (SEGE) Conference, Oshawa, ON, Canada, 21–24 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, H.S.; Roy, R. Coverage Enhancement of Smart Grid Communication Systems with Binary Coding. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things (iThings), and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom), Taipei, Taiwan, 1–3 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ghebleh, R.; Ghaffari, A. A comprehensive survey on 5G: The prospect of future communication. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 94, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qian, Y.; Sharif, H. Multimedia communications over cognitive radio networks for smart grid applications. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2013, 20, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wu, D.; Chen, J.; Dong, Z. Greening the smart cities: Energy-efficient massive content delivery via D2D communications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, H.; Hadley, M.; Lu, N.; Frincke, D.A. Smart-grid security issues. IEEE Secur. Priv. 2010, 8, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ericsson, G.N. Cyber security and power system communication—Essential parts of a smart grid infrastructure. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2010, 25, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Lu, R.; Luo, J.; Lai, C.; Shen, X. Efficient self-healing group key management with dynamic revocation and collusion resistance for SCADA in smart grid. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2015, 8, 1026–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag, M.A.; Maglaras, L.A.; Janicke, H.; Jiang, J.; Shu, L. A systematic review of data protection and privacy preservation schemes for smart grid communications. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 806–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakran, S.; Chanana, S. Smart operations of smart grids integrated with distributed generation: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, K.; Gabbar, H.A. SCADA and smart energy grid control automation. In Smart Energy Grid Engineering; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 481–514. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Zheng, D.; Li, P.; Tian, Y. Privacy-preserving communication and power injection over vehicle networks and 5G smart grid slice. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2018, 122, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leligou, H.C.; Zahariadis, T.; Sarakis, L.; Tsampasis, E.; Voulkidis, A.; Velivassaki, T.E. Smart Grid: A demanding use case for 5G technologies. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and Communications Workshops (PerCom Workshops), Athens, Greece, 19–23 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Rehmani, M.H.; Tembine, H.; Mohammed, O.A.; Jamalipour, A. IEEE Access Special Section Editorial: Optimization for Emerging Wireless Networks: IoT, 5G, and Smart Grid Communication Networks. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 2096–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, N.; Sharma, S.; Singh, A.K. A survey on 5G: The next generation of mobile communication. Phys. Commun. 2016, 18, 64–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, W.; Wang, Y.; Lin, D.; Ge, N.; Lu, J.; Li, S. When mmWave communications meet network densification: A scalable interference coordination perspective. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2017, 35, 1459–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueguen, C.; Ezzaouia, M.; Yassin, M. Inter-cellular scheduler for 5G wireless networks. Phys. Commun. 2016, 18, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, B.; Ma, Y. Learning automata-based algorithms for solving the stochastic shortest path routing problems in 5G wireless communication. Phys. Commun. 2017, 25, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, K.J.; Hopkinson, K.M.; Pachter, M. Using a distributed agent-based communication enabled special protection system to enhance smart grid security. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 1216–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, W.; Zhitao, G.; Tingting, Y.; Yue, X. Top-k query framework in wireless sensor networks for smart grid. China Commun. 2014, 11, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalamifar, F.; Lampe, L. Optimized WiMAX profile configuration for smart grid communications. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 2723–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonov, M. Event-driven communication in smart grid. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2013, 17, 1061–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; Cheng, S.M.; Chen, K.C. Smart attacks in smart grid communication networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2012, 50, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, L.T.; Iniewski, K. (Eds.) Smart Grid: Applications, Communications, and Security; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Lu, N.; Cai, L. Reliable wireless communication networks for demand response control. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2013, 4, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horalek, J.; Holik, F.; Hurtova, V. Implementation and testing of Cisco IP SLA in smart grid environments. In Proceedings of the 2017 40th International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 22–26 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Desong, B.; Kuzlu, M.; Pipattanasomporn, M.; Rahman, S. Assessment of Communication Technology Alternatives for a Home Energy Management System in Premises Area Network. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Power & Energy Society Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT), Washington, DC, USA, 19–22 February 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Quang, D.N.; Hang See, O.; Jui, O.X. Smart Grid Ping–A Customized Ping Tool for a Heterogeneous and Hybrid Smart Grid Communication Network. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2014, 2, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, H.; Tonyali, S.; Rabieh, K.; Mahmoud, M.; Akkaya, K. Efficient privacy-preserving data collection scheme for smart grid AMI networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), Washington, DC, USA, 4–8 December 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kalalas, C.; Thrybom, L.; Alonso-Zarate, J. Cellular communications for smart grid neighborhood area networks: A survey. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 1469–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, S.; Scaglione, A.; Wang, Z. Power line communications and the smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2010 First IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications, Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 4–6 Octorber 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, L.; Hu, R.Q.; Qian, Y.; Wu, G. Key elements to enable millimeter wave communications for 5G wireless systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2014, 21, 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Doppler, K.; Rinne, M.; Wijting, C.; Ribeiro, C.B.; Hugl, K. Device-to-device communication as an underlay to LTE-advanced networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2009, 47, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag, M.A.; Maglaras, L.; Argyriou, A.; Kosmanos, D.; Janicke, H. Security for 4G and 5G cellular networks: A survey of existing authentication and privacy-preserving schemes. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 101, 55–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjioannou, V.; Mavromoustakis, C.X.; Mastorakis, G.; Batalla, J.M.; Kopanakis, I.; Perakakis, E.; Panagiotakis, S. Security in smart grids and smart spaces for smooth IoT deployment in 5G. In Internet of Things (IoT) in 5G Mobile Technologies; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 371–397. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Liu, G. An overview of 5G requirements. In 5G Mobile Communications; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 3–26. [Google Scholar]
- Trivisonno, R.; Guerzoni, R.; Vaishnavi, I.; Soldani, D. SDN-based 5G mobile networks: Architecture, functions, procedures and backward compatibility. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2015, 26, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalci, Y. 5G Mobile Communication Systems: Fundamentals, Challenges, and Key Technologies. In Smart Grids and Their Communication Systems; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 329–359. [Google Scholar]
- Valtanen, K.; Backman, J.; Yrjölä, S. Blockchain-Powered Value Creation in the 5G and Smart Grid Use Cases. IEEE Access 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, G.Y.; Chen, W.; Ng, D.W.K.; Schober, R. An overview of sustainable green 5G networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.C.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Guo, N.; Ranganathan, R.; Hou, S.; Zheng, G. Cognitive radio network for the smart grid: Experimental system architecture, control algorithms, security, and microgrid testbed. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2011, 2, 724–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metke, A.R.; Ekl, R.L. Security technology for smart grid networks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2010, 1, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K. Smart grid wide area monitoring, protection and control. Int. J. Comput. Eng. Res. 2012, 2, 553–584. [Google Scholar]
- Paulraj, A.J.; Gore, D.A.; Nabar, R.U.; Bolcskei, H. An overview of MIMO communications-a key to gigabit wireless. Proc. IEEE 2004, 92, 198–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Li, L. Integrated wireless communications and wireless power transfer: An overview. Phys. Commun. 2017, 25, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaddus, A.; Minhas, A.A. Wireless communication a sustainable solution for future smart grid networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Open Source Systems & Technologies (ICOSST), Lahore, Pakistan, 15–17 December 2016; pp. 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.A.; Rehmani, M.H.; Reisslein, M. Cognitive radio for smart grids: Survey of architectures, spectrum sensing mechanisms, and networking protocols. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 860–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, S. Aggregation points planning in smart grid communication system. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2015, 19, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 5G PPP. 5G Vision: The Next Generation of Communication Networks and Services. 2015. Available online: https://5g-ppp.eu/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/5G-Vision-Brochure-v1.pdf#page=8 (accessed on 11 February 2019).
- Cosovic, M.; Tsitsimelis, A.; Vukobratovic, D.; Matamoros, J.; Anton-Haro, C. 5G Mobile Cellular Networks: Enabling Distributed State Estimation for Smart Grid. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1703.00178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garau, M.; Anedda, M.; Desogus, C.; Ghiani, E.; Murroni, M.; Celli, G. A 5G cellular technology for distributed monitoring and control in smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Broadband Multimedia Systems and Broadcasting (BMSB), Cagliari, Italy, 7–9 June 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Erol-Kantarci, M.; Mouftah, H.T. Wireless sensor networks for cost-efficient residential energy management in the smart grid. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2011, 2, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, N.; Roy, A.; Kim, H. Efficient 5G Small Cell Planning With eMBMS for Optimal Demand Response in Smart Grids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ni, W.; Chen, T.; Collings, I.B.; Wang, X.; Guanacos, G.B. Real-time energy trading and future planning for fifth generation wireless communications. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Dong, Y.; Yu, M.; Steurer, M. A secure and distributed control network for the communications in smart grid. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Anchorage, AK, USA, 9–12 October 2011; pp. 2652–2657. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Z.; Kalogridis, G.; Efthymiou, C.; Sooriyabandara, M.; Serizawa, M.; McGeehan, J. The new frontier of communications research: Smart grid and smart metering. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Energy-Efficient Computing and Networking, Passau, Germany, 13–15 April 2010; pp. 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- Sechilariu, M.; Wang, B.; Locment, F. Building integrated photovoltaic system with energy storage and smart grid communication. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 1607–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghezchi, F.B.; Mantas, G.; Ribeiro, J.; Al-Rawi, M.; Mumtaz, S.; Rodriguez, J. Towards a secure network architecture for smart grids in 5G era. In Proceedings of the 2017 13th International Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Valencia, Spain, 26–30 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Misra, S.; Xue, G.; Yang, D. Smart grid—The new and improved power grid: A survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2012, 14, 944–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlullah, Z.M.; Fouda, M.M.; Kato, N.; Takeuchi, A.; Iwasaki, N.; Nozaki, Y. Toward intelligent machine-to-machine communications in smart grid. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2011, 49, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, W.; Han, Z.; Poor, H.V.; Basar, T. Game-theoretic methods for the smart grid: An overview of microgrid systems, demand-side management, and smart grid communications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, W.L.; Li, W.; Chen, H.H. Energy Big Data Security Threats in IoT-Based Smart Grid Communications. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputro, N.; Akkaya, K.; Uludag, S. A survey of routing protocols for smart grid communications. Comput. Netw. 2012, 56, 2742–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, W.; Chen, C.P. A survey of communication/networking in smart grids. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2012, 28, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Muljadi, E.; Gao, W. Security-oriented and load-balancing wireless data routing game in the integration of advanced metering infrastructure network in smart grid. In Proceedings of the North American Power Symposium (NAPS), Denver, CO, USA, 18–20 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Faheem, M.; Shah, S.B.H.; Butt, R.A.; Raza, B.; Anwar, M.; Ashraf, M.W.; Ngadi, M.A.; Gungor, V.C. Smart grid communication and information technologieserspective of Industry 4.0: Opportunities and challenges. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2018, 30, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, W.; Sharp, D.; Lancashire, S. Smart grid communication network capacity planning for power utilities. In Proceedings of the Transmission and Distribution Conference and Exposition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–22 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, W. Wireless mesh network in smart grid: Modeling and analysis for time critical communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2013, 12, 3360–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Shen, X.S.; Mark, J.W.; Shen, Q.; He, Y.; Lei, L. Enabling device-to-device communications in millimeter-wave 5G cellular networks. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowla, M.M.; Ahmad, I.; Habibi, D.; Phung, Q.V. A Green Communication Model for 5G Systems. IEEE Trans. Green Commun. Netw. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Qian, Y.; Sharif, H.; Tipper, D. A survey on cyber security for smart grid communications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2012, 14, 998–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, K.; Qiu, M.; Ming, Z.; Zhao, H.; Qiu, L. Spoofing-jamming attack strategy using optimal power distributions in wireless smart grid networks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reka, S.S.; Dragicevic, T. Future effectual role of energy delivery: A comprehensive review of Internet of Things and smart grid. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 91, 90–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmalifalak, M.; Liu, L.; Nguyen, N.; Zheng, R.; Han, Z. Detecting stealthy false data injection using machine learning in smart grid. IEEE Syst. J. 2017, 11, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaa, M.; Zaidan, A.A.; Zaidan, B.B.; Talal, M.; Kiah, M.L.M. A review of smart home applications based on Internet of Things. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2017, 97, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, D.; Su, L.; Vasilakos, A.V. A survey of millimeter wave communications (mmWave) for 5G: Opportunities and challenges. Wirel. Netw. 2015, 21, 2657–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Haines, R.; Kulkarni, P. M2M communications for E-health and smart grid: An industry and standard perspective. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2014, 21, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Features | 1G | 2G | 2.5G | 3G | 3.5G | 4G | 5G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Deployment | 1980 | 1990 | 2000 | 2001 | 2006 | 2010 | 2020 or later |
| Data | Analog | Digital narrow band data | Packet data | Digital broadband packet data | Packet data | Digital Broadband packet data. Very high throughput | Not yet defined |
| Frequency | 800 MHz | 850/ 900/ 1800/ 1900 MHz | 850/ 900/ 1800/ 1900 MHz | 800/ 850/ 900/ 1800/ 1900/ 2100 MHz | 800/ 850/ 900/ 1800/ 1900/ 2100 MHz | 2600 MHz | 3 to 90 GHz |
| Speed | 2.4 kbps | 64 kbps | 144 Kbps | 2Mbps | 5-30 Mbps | 100 Mbps | 10Gbps |
| Technology | AMPS, NMT TACS | GSM, CDMA, IS-95 | GPRS, EDGE, CDMA 2000 | WCDMA, UMTS, CDMA2000 | HSPA, EVDO [22,23,24] | Wi Max LTE Wi-Fi | Had to be defined |
| Multiple access [22] | Frequency division | Time division | Time division | Code division | Code division | Orthogonal Frequency division | Orthogonal Frequency division |
| Core network | Public switched telephone network | Public switched telephone network | Public Switched telephone network | Packet network | Packet network | Internet | Internet |
| Advantages | Mobility | Secure, Mass Adoption Longer lasting of battery [25,26,27]. | -- | Better Internet Experience [27,28,29,30] | -- | High data rate, wearable devices. | Coverage of data is better and no dropped calls, very low latency |
| Disadvantages | Very poor spectral efficiency and poor handoff | Data rates are very less and difficult to match the demand | -- | Failure of performance for internet [31,32] | -- | Usage of battery is more, so found to be expensive | -- |
| Architecture | Characteristics | Assets | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-tier architecture | A mm Wave Base station (MBS) is considered to be in a higher tier, and small base stations work under the control of MBS. The user equipment is connected between the networks. | The major advantages are better and higher data rates with considerable reduction of energy consumed. Among the MBS, less congestion is made and easy hand-off is attainable. | Some of the major disadvantages in this form of architecture are low reliability and comparatively very high operational cost between the MBS. |
| Cognitive Radio Network Architecture | These structures are analogous to multi-tier; as such, the base cell stations are more cognitive with cognitive radio nodes of secondary users. The main licensed users are in the primary nodes in functions. Majorly, the secondary users are easily operated at various frequencies, even though many primary users are not present in certain cases. | The major pros of this structure are minimum interference and improved network capacity with respect to higher bandwidth coverage and data rate perusal. | A few limitations exist, such as less energy efficiency and a major trade-off between the spatial frequency and the range of outage. |
| Device to Device Communication Architecture [44]. | With less involvement of MBS, this allows the user equipment to communicate efficiently. | There are reliable links that provide high data rate and instant communication with quick file sharing. | The major con in this structure is when there is need for relay nodes in networks, secure communication must be provided with proper links. |
| Cloud-based Architecture [44]. | There are various pools of resources that are easy to access on demand [44] and this also has the advantage of executing the function of base stations in the cloud. | The main advantage is resource sharing, which can be done easily by demand with easy traffic management. The other important aspect is that there is considerable reduction of cost with improved spectrum utilization. | The limitation of this architecture is that critical functioning of MBS at the cloud is very critical. Due to this, there are several security and privacy issues. |
| Parameter | Access Communication Network Domain | Backhaul Communication Network Domain | Backbone Communication Network Domain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diameter of region to be covered | <10 km | <100 km | <1000 km |
| Bandwidth | 1kbps | Several Mbps | Mbps to Gbps |
| End-to-end Latency | <1s | <50 ms | <5 ms |
| Packet loss | No specific requirements | <10−6 | <10−9 |
| Availability | 9 h downtime p.a | 50 min downtime p.a | 5 min downtime p.a |
| Failure convergence time | <1 s | <1 s | <several ms |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
S, S.R.; Dragičević, T.; Siano, P.; Prabaharan, S.R.S. Future Generation 5G Wireless Networks for Smart Grid: A Comprehensive Review. Energies 2019, 12, 2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12112140
S SR, Dragičević T, Siano P, Prabaharan SRS. Future Generation 5G Wireless Networks for Smart Grid: A Comprehensive Review. Energies. 2019; 12(11):2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12112140
Chicago/Turabian StyleS, Sofana Reka., Tomislav Dragičević, Pierluigi Siano, and S.R. Sahaya Prabaharan. 2019. "Future Generation 5G Wireless Networks for Smart Grid: A Comprehensive Review" Energies 12, no. 11: 2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12112140
APA StyleS, S. R., Dragičević, T., Siano, P., & Prabaharan, S. R. S. (2019). Future Generation 5G Wireless Networks for Smart Grid: A Comprehensive Review. Energies, 12(11), 2140. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12112140





