Epoprostenol Delivered via High Flow Nasal Cannula for ICU Subjects with Severe Hypoxemia Comorbid with Pulmonary Hypertension or Right Heart Dysfunction
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
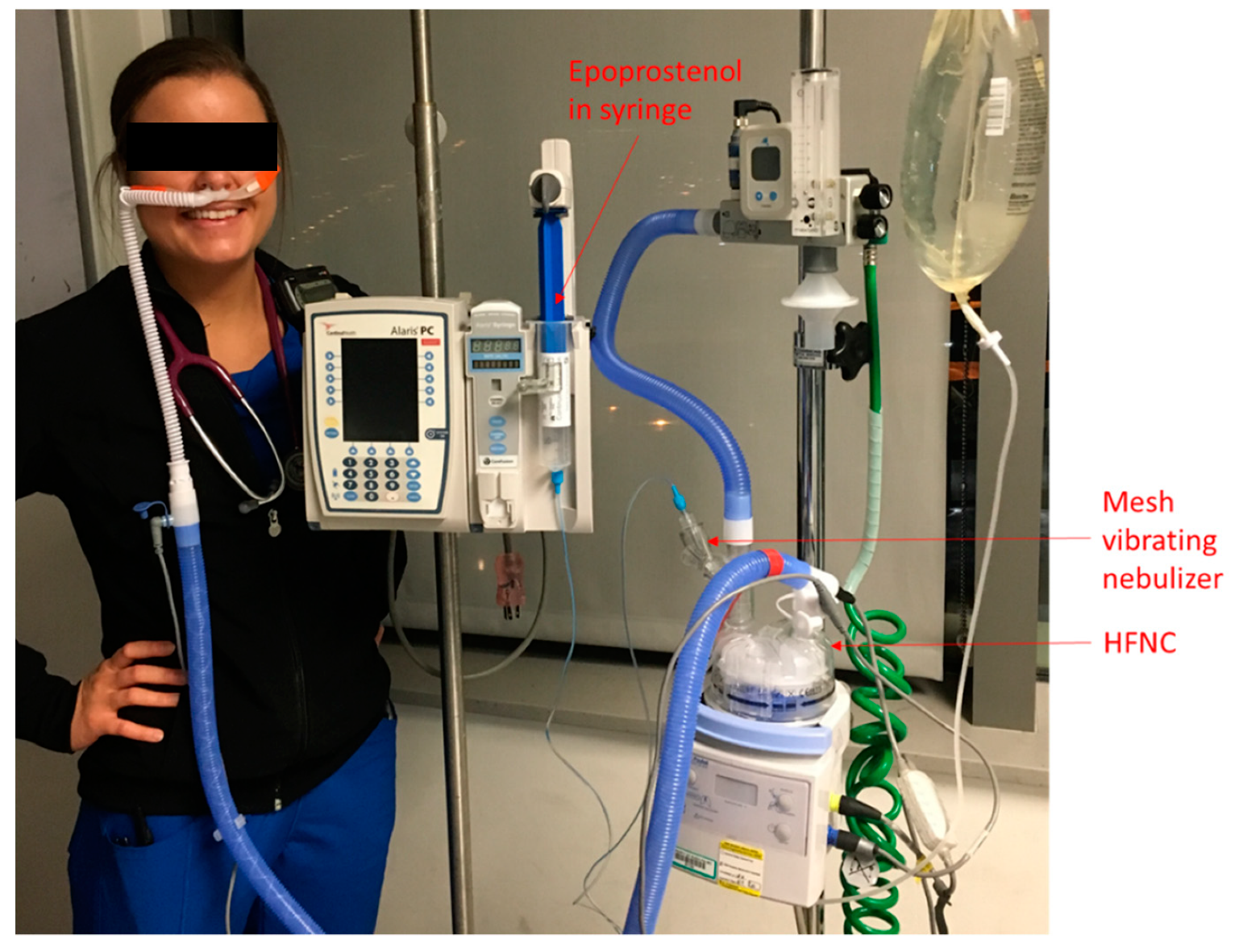
2.2. iEPO Use via HFNC
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Information
3.2. Oxygenation Effects and Safety
3.3. Outcome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elmi-Sarab, M.; Deschamps, A.; Delisle, S.; Ased, H.; Haddad, F.; Lamarche, Y.; Perrault, L.P.; Lambert, J.; Turgeon, A.F.; Denault, A.Y. Aerosolized vasodilators for the treatment of pulmonary hypertension in cardiac surgical patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesth. Analg. 2017, 125, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, S.; Ishida, K.; Masuda, M.; Ueda, H.; Kohno, H.; Matsuura, K.; Tamura, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Matsumiya, G. A prospective; randomized study of inhaled prostacyclin versus nitric oxide in patients with residual pulmonary hypertension after pulmonary endarterectomy. Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2017, 65, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinn, K.; Reichert, M.A. Comparison of inhaled nitric oxide versus inhaled epoprostenol for acute pulmonary hypertension following cardiac surgery. Ann. Pharmacother. 2016, 50, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preston, I.R.; Sagliani, K.D.; Roberts, K.E.; Shah, A.M.; DeSouza, S.A.; Howard, W.; Brennan, J.; Hill, N.S. Comparison of acute hemodynamic effects of inhaled nitric oxide and inhaled epoprostenol in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Pulm. Circ. 2013, 3, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, B.M.; Mohr, N.M.; Skrupky, L.; Shah, A.M.; Desouza, S.A.; Howard, W.; Brennan, J.; Hill, N.S. The use of inhaled prostaglandins in patients with ARDS: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest 2015, 147, 1510–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, M.A.; Bauer, S.R.; Bass, S.N.; Sasidhar, M.; Mullin, R.; Lam, S.W. Noninferiority of Inhaled Epoprostenol to Inhaled Nitric Oxide for the Treatment of ARDS. Ann. Pharmacother. 2015, 49, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torbic, H.; Szumita, P.M.; Anger, K.E.; Nuccio, P.; LaGambina, S.; Weinhouse, G. Inhaled epoprostenol vs inhaled nitric oxide for refractory hypoxemia in critically ill patients. J. Crit. Care 2013, 28, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Yin, H.; Zhang, R.; Wei, J. High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy versus conventional oxygen therapy in patients with acute respiratory failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.-N.; Luo, J.; Yu, H.; Liu, D.; Liang, B.-M.; Yao, R.; Liang, Z.-A. Can high-flow nasal cannula reduce the rate of reintubation in adult patients after extubation? A meta-analysis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2017, 17, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ari, A. Aerosol drug delivery through high flow nasal cannula. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2017, 18, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réminiac, F.; Vecellio, L.; Heuze-Vourc, N.; Petitcollin, A.; Respaud, R.; Cabrera, M.; Le Pennec, D.; Diot, P.; Ehrmann, S. Aerosol Therapy in Adults Receiving High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy. J. Aerosol Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2016, 29, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dailey, P.; Harwood, R.; Walsh, K.; Fink, J.B.; Thayer, T.; Gagnon, G.; Ari, A. Aerosol Delivery Through Adult High Flow Nasal Cannula with Heliox and Oxygen. Respir. Care 2017, 62, 1186–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gong, L.; Ari, A.; Fink, J.B. Decrease the flow setting to improve trans-nasal pulmonary aerosol delivery via “high-flow nasal cannula” to infants and toddlers. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2019, 54, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcoforado, L.; Ari, A.; Barcelar, J.M.; Brandão, C.S.S.; Fink, J.B.; Dornelas de Andrade, A. Deposition of aerosol via high flow nasal cannula is impacted by gas flow and heated humidity in vivo and in vitro. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 195, A3683. [Google Scholar]
- Dugernier, J.; Hesse, M.; Jumetz, T.; Bialais, E.; Roeseler, J.; Depoortere, V.; Michotte, J.B.; Wittebole, X.; Ehrmann, S.; Laterre, P.F.; et al. Aerosol delivery with two nebulizers through high-flow nasal cannula: A randomized cross-over single-photon emission computed tomography-computed tomography study. J. Aerosol. Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2017, 30, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, S.E.; Mosakowski, S.; Solano, P.; Hall, J.B.; Tung, A. High-flow nasal cannula and aerosolized β agonists for rescue therapy in children with bronchiolitis: A case series. Respir. Care 2015, 60, e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudin, F.; Buisson, A.; Vanel, B.; Massenavette, B.; Pouyau, R.; Javouhey, E. Nasal high flow in management of children with status asthmaticus: a retrospective observational study. Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräunlich, J.; Wirtz, H. Oral versus nasal high-flow bronchodilator inhalation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J. Aerosol. Med. Pulm. Drug Deliv. 2018, 31, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reminiac, F.; Vecellio, L.; Bodet-Contentin, L.; Gissot, V.; Le Pennec, D.; Gandonnière, C.S.; Cabrera, M.; Dequin, P.-F.; Plantier, L.; Ehrmann, S. Nasal high-flow bronchodilator nebulization: A randomized cross-over study. Ann. Intensive Care 2018, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madney, Y.M.; Fathy, M.; Elberry, A.A.; Rabea, H.; Abdelrahim, M.E. Aerosol delivery through an adult high-flow nasal cannula circuit using low-flow oxygen. Respir. Care 2019, 64, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, T.W.; Wheeler, A.P.; Bernard, G.R.; Hayden, D.L.; Schoenfeld, D.A.; Ware, L.B. National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute ARDS Network. Comparison of the SpO2/FIO2 ratio and the PaO2/FIO2 ratio in patients with acute lung injury or ARDS. Chest 2007, 132, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Janz, D.R.; Shaver, C.M.; Bernard, G.R.; Bastarache, J.A.; Ware, L.B. Clinical characteristics and outcomes are similar in ARDS diagnosed by oxygen saturation/Fio2 ratio compared with Pao2/Fio2 ratio. Chest 2015, 148, 1477–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, L.; Roozeman, J.-P.; Simonis, F.D.; Giangregorio, A.; Van Der Hoeven, S.M.; Schouten, L.R.; Horn, J.; Neto, A.S.; Festic, E.; Dondorp, A.M.; et al. Risk stratification using SpO2/FiO2 and PEEP at initial ARDS diagnosis and after 24 h in patients with moderate or severe ARDS. Ann. Intensive Care 2017, 7, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammar, M.A.; Sasidhar, M.; Lam, S.W. Inhaled Epoprostenol Through Noninvasive Routes of Ventilator Support Systems. Ann. Pharmacother. 2018, 52, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhong, M. Comment: Inhaled epoprostenol through noninvasive routes of ventilator support systems. Ann. Pharmacother 2019, 53, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attaway, A.H.; Myers, C.; Velani, S.; Schilz, R. Inhaled prostacyclin as salvage therapy for ARDS: Can we find the right patient? Respir. Care 2017, 62, 1113–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallet, R.H.; Burns, G.; Zhuo, H.; Ho, K.; Phillips, J.S.; Pangilinan, L.P.; Yip, V.; Gomez, A.; Lipnick, M.S. Severity of hypoxemia and other factors that influence the response to aerosolized prostacyclin in ARDS. Respir. Care 2017, 62, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gong, L.; Fink, J.B. The ratio of nasal cannula gas flow to patient inspiratory flow on trans-nasal pulmonary aerosol delivery for adults: An in vitro study. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcoforado, L.; Brandão, S.; Rattes, C.; Brandão, D.; Lima, V.; Ferreira Lima, G.; Fink, J.B.; Dornelas de Andrade, A. Evaluation of lung function and deposition of aerosolized bronchodilators carried by heliox associated with positive expiratory pressure in stable asthmatics: A randomized clinical trial. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, J.C.; Lu, M.S.; Zhao, Z.H.; Jiang, W.; Xu, B.; Weng, L.; Li, T.; Du, B. Positive end-expiratory pressure effect of 3 high-flow nasal cannula devices. Respir. Care 2017, 62, 888–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, J.; Arnold, H.; Skrupky, L.; Watts, P.; Micek, S.T.; Kollef, M.H. Predictors of outcome in 216 subjects with ARDS treated with inhaled epoprostenol. Respir. Care 2014, 59, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| ID | Gender | Race* | Age | APACHE II | Diagnosis # | Home O2 | HFNC Hours Pre- iEPO | Pre- iEPO SpO2 | Pre- iEPO FiO2 | Pre- iEPO Flow | Post- iEPO SpO2 | Post- iEPO FiO2 | Post- iEPO Flow | iEPO Duration (Mins) | Respond & | Intubation | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | M | 2 | 85 | 26 | HTN, HFpEF, PH, COPD, CVA, PVD, CKD, BPH s/p TURP | Yes | 11.5 | 92 | 6 | 40 | 94 | 6 | 40 | 176 | No | No | Died in hospice |
| 2 | F | 1 | 69 | 18 | DLBCL s/p chemo, acute respiratory failure with hypoxia, sepsis; PAH | No | 44 | 96 | 1.0 | 50 | 95 | 1.0 | 40 | 1135 | No | Yes | Alive |
| 3 | F | 3 | 23 | 7 | Myocarditis due to influenza A virus, PH | No | 28 | 80 | 1.0 | 50 | 98 | 1.0 | 50 | 6276 | Yes | No | Alive |
| 4 | F | 1 | 72 | 22 | HTN, breast cancer, and IIIA non-small cell lung cancer s/p lobectomy; septic shock; RHF | No | 82 | 98 | 1.0 | 45 | 98 | 8 | 45 | 13662 | Yes | Yes | Alive. VV-ECMO with iEPO |
| 5 | M | 1 | 51 | 27 | CAD, COPD, stage III squamous cell carcinoma of lung; RHF from PE | No | 21 | 90 | 9 | 40 | 91 | 9 | 40 | 1400 | No | No | Died. VV-ECMO with iEPO, |
| 6 | F | 2 | 42 | 14 | SLE, HTN, CHF, CAD, CKD, ILD, PH | Yes | 0 | 90 | 6 | / | 92 | 6 | 30 | 1298 | No | No | Alive |
| 7 | F | 1 | 61 | 16 | group 1 PAH with connective tissue disease | Yes | 1 | 91 | 8 | 35 | 94 | 1.0 | 35 | 4104 | No | No | Alive. |
| 8 | F | 2 | 23 | 14 | ASD; biventricular systolic dysfunction; PH (WHO group 1 2/2 ASD with Eisenmenger’s), chronic hypoxemia | Yes | 30.5 | 69 | 1.0 | 20 | 93 | 7 | 20 | 2089 | Yes | No | Alive |
| 9 | M | 1 | 78 | 19 | CHF, PAH (group 1 functional class 3), ASD. | Yes | 2 | 93 | 1.0 | 50 | 97 | 8 | 45 | 3184 | Yes | No | Alive |
| 10 | M | 2 | 71 | 21 | PH (moderate R to L shunt), HFrEF (EF 35–40%) c/b VF s/p ICD, hypertension, CKD stage IV, DM c/b retinopathy, glaucoma, HLD | Yes | 1 | 98 | 8 | 30 | 97 | 5 | 30 | 944 | Yes | Yes | Died, withdrew therapy |
| 11 | F | 2 | 63 | 19 | PH (chronic), chronic hypoxemic respiratory failure, atypical carcinoid lung tumor, DM II, CKD, CAD, asthma | Yes | 54 | 85 | 8 | 30 | 89 | 8 | 30 | 9921 | No | Yes | Died |
| Items | Responders | Non-Responders | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects | 5 | 6 | |
| Pulmonary hypertension | 4 | 5 | / |
| Right heart failure | 3 | 2 | 0.567 |
| Pre respiratory rate | 25.8 ± 9.4 | 25.8 ± 7.8 | 0.931 |
| Pre FIO2 | 96 ± 8.9 | 78.3± 16.0 | 0.082 |
| Pre flow | 39 ± 13.4 | 35.8 ± 4.9 | 0.456 |
| Pre SpO2 | 87.6 ± 12.7 | 90.7 ± 3.6 | 0.792 |
| Pre SpO2/FIO2 | 92.5 ± 20.2 | 120 ± 25.3 | 0.082 |
| Post respiratory rate | 26.4 ± 4.9 | 26.3 ± 8.8 | 0.931 |
| Post FIO2 | 76 ± 18.2 | 81.7 ± 18.3 | 0.662 |
| Post flow | 38 ± 12.6 | 35.8 ± 4.9 | 0.537 |
| Post SpO2 | 96.6 ± 2.1 | 92.5 ± 2.3 | 0.03 |
| Post SpO2/FIO2 | 133.7 ± 36 | 118.6 ± 28.9 | 0.429 |
| Intubation | 2 | 3 | / |
| ICU stay | 12 (7, 24) | 14 (10, 21) | 0.931 |
| Hospital stay | 12 (7, 24) | 16 (11, 21) | 0.792 |
| Hospital survival | 4 | 3 | / |
| Items | Pre iEpo | Post iEpo | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| HR (beats/min) | 108.1 ± 31.1 | 101.1 ± 20.4 | 0.284 |
| mBP (mmHg) | 87.7 ± 15.8 | 89.4 ± 16.2 | 0.824 |
| RR (breaths/min) | 25.8 ± 8.1 | 26.4 ± 7.0 | 0.681 |
| SpO2 /FIO2 | 107.5 ± 26.3 | 125.5 ± 31.6 | 0.026 |
| FIO2 | 0.9 (0.8, 1.0) | 0.8 (0.65, 0.95) | 0.129 |
| SpO2 (%) | 91.5 (90, 96) | 94.4 ± 3.0 | 0.016 |
| Flow (L/min) | 40 (30, 50) | 40 (30,45) | 0.066 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Harnois, L.J.; Markos, B.; Roberts, K.M.; Homoud, S.A.; Liu, J.; Mirza, S.; Vines, D. Epoprostenol Delivered via High Flow Nasal Cannula for ICU Subjects with Severe Hypoxemia Comorbid with Pulmonary Hypertension or Right Heart Dysfunction. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11060281
Li J, Harnois LJ, Markos B, Roberts KM, Homoud SA, Liu J, Mirza S, Vines D. Epoprostenol Delivered via High Flow Nasal Cannula for ICU Subjects with Severe Hypoxemia Comorbid with Pulmonary Hypertension or Right Heart Dysfunction. Pharmaceutics. 2019; 11(6):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11060281
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jie, Lauren J. Harnois, Bethelhem Markos, Keith M. Roberts, Salma Al Homoud, Jing Liu, Sara Mirza, and David Vines. 2019. "Epoprostenol Delivered via High Flow Nasal Cannula for ICU Subjects with Severe Hypoxemia Comorbid with Pulmonary Hypertension or Right Heart Dysfunction" Pharmaceutics 11, no. 6: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11060281
APA StyleLi, J., Harnois, L. J., Markos, B., Roberts, K. M., Homoud, S. A., Liu, J., Mirza, S., & Vines, D. (2019). Epoprostenol Delivered via High Flow Nasal Cannula for ICU Subjects with Severe Hypoxemia Comorbid with Pulmonary Hypertension or Right Heart Dysfunction. Pharmaceutics, 11(6), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics11060281





