Pathophysiological Implication of Fetuin-A Glycoprotein in the Development of Metabolic Disorders: A Concise Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Role of Fetuin-A in Physiological Processes
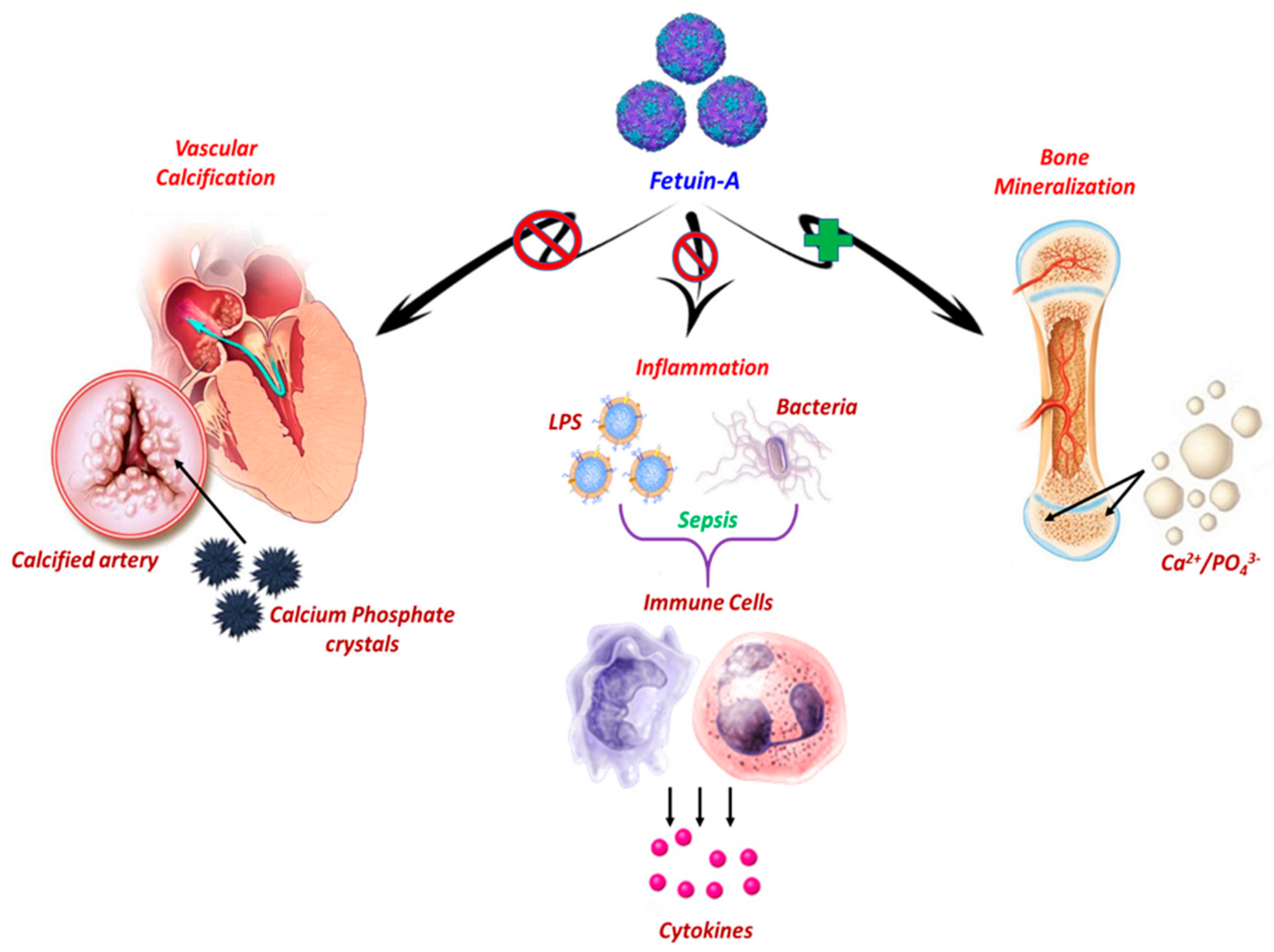
2.1. Fetuin-A and Bone Metabolism
2.2. Fetuin-A and Vascular Calcification
2.3. Fetuin-A and Inflammatory Response
3. Fetuin-A in Metabolic and Cardiovascular Disorders
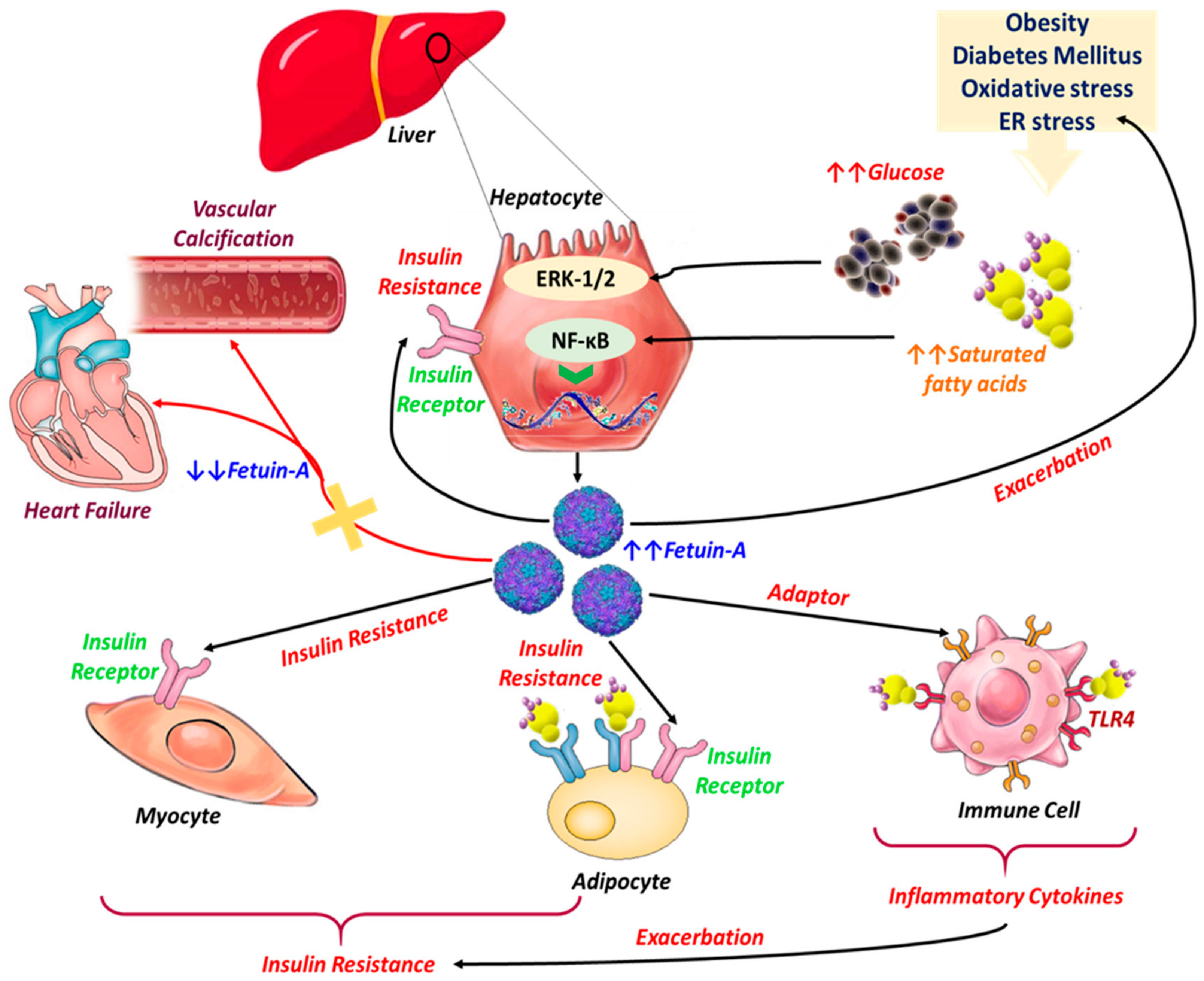
3.1. Fetuin-A, Insulin Resistance, and Diabetes Mellitus
3.2. Fetuin-A in the Course of Obesity
3.3. Fetuin-A and Its Relation to NAFLD
3.4. Fetuin-A in Cardiovascular Diseases
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.T.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the international diabetes federation task force on epidemiology and prevention; National heart, lung, and blood institute; American heart association; World heart federation; international atherosclerosis society; and international association for the study of obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Golden, S.H.; Robinson, K.A.; Saldanha, I.; Anton, B.; Ladenson, P.W. Prevalence and incidence of endocrine and metabolic disorders in the united states: A comprehensive review. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 1853–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aganović, I.; Dušek, T. Pathophysiology of Metabolic Syndrome. EJIFCC 2007, 18, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rochlani, Y.; Pothineni, N.V.; Kovelamudi, S.; Mehta, J.L. Metabolic syndrome: Pathophysiology, management, and modulation by natural compounds. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 11, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendrick, D.L.; Diehl, A.M.; Topor, L.S.; Dietert, R.R.; Will, Y.; La Merrill, M.A.; Bouret, S.; Varma, V.; Hastings, K.L.; Schug, T.T.; et al. Metabolic Syndrome and Associated Diseases: From the Bench to the Clinic. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 162, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, H.; Nayudu, S.; Akella, S.; Glandt, M.; Chilimuri, S. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Pancreatic Disease: A Review of Literature. Gastroenterol. Res. 2016, 9, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. The pathogenesis of insulin resistance: Integrating signaling pathways and substrate flux. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaribeygi, H.; Farrokhi, F.R.; Butler, A.E.; Sahebkar, A. Insulin resistance: Review of the underlying molecular mechanisms. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 8152–8161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, F. Metabolic Syndrome: Cluster of Diseases. 2019. 1–9. Available online: https://www.jsmcentral.org/Nutrition/jsmhnfs835760.pdf (accessed on 25 September 2019).
- Kahn, B.B.; Flier, J.S. Flier Obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 106, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandona, P.; Aljada, A.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Inflammation the link between insulin resistance. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, S.; Matsuda, M.; Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome Find the latest version: Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, L.M.; Somwar, R.; Sweeney, G.; Niu, W.; Klip, A. Activation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 by insulin. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 80, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Li, X.; Adams, H.; Kubena, K.; Guo, S. Etiology of metabolic syndrome and dietary intervention. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komsa-Penkova, R.S.; Golemanov, G.M.; Radionova, Z.V.; Tonchev, P.T.; Iliev, S.D.; Penkov, V.V. Fetuin-A—Alpha2-Heremans-Schmid Glycoprotein: From Structure to a Novel Marker of Chronic Diseases Part 1. Fetuin-A as a Calcium Chaperone and Inflammatory Marker. J. Biomed. Clin. Res. 2018, 10, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinehr, T.; Roth, C.L. Fetuin-A and its relation to metabolic syndrome and fatty liver disease in obese children before and after weight loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 4479–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Emoto, M.; Inaba, M. Fetuin-A: A Multifunctional Protein. Recent Pat. Endocr. Metab. Immune Drug Discov. 2012, 5, 124–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.O. Fetuin, a new globulin isolated from serum. Nature 1944, 154, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brylka, L.; Jahnen-Dechent, W. The role of fetuin-A in physiological and pathological mineralization. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2013, 93, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultze, H.E.; Heide, K.; Haupt, H. Characterization of a Low Molecular 2-Mucoid from Human Serum. Naturwissenschaften 1962, 49, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.C.; Bowman, B.H.; Yang, F. Human α2-HS-glycoprotein: The A and B chains with a connecting sequence are encoded by a single mRNA transcript. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 4403–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, Y.; Gejyo, F.; Marti, T.; Rickli, E.E.; Bürgi, W.; Offner, G.D.; Troxler, R.F.; Schmid, K. The complete amino acid sequence of the A-chain of human plasma α2HS-glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nie, Z. Fetuin: Its enigmatic property of growth promotion. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 1992, 263, C551–C562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, C.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Brandenburg, V. Klinische Relevanz des Serumproteins Fetuin A—Einem Regulator der Kalzifizierung. Laborwelt 2005, 6, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Termine, J. Non-collagen proteins in bone. Ciba Found. Symp. 1988, 136, 178–202. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, S. Molecular recognition in biomineralization. Nature 1988, 332, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonucci, E. Bone mineralization. Front. Biosci. 2012, 17, 100–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giachelli, C.M. Ectopic calcification: Gathering hard facts about soft tissue mineralization. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshed, M. Mechanism of Bone Mineralization. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a031229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, S.M.; Reslerova, M.; Ketteler, M.; O’Neill, K.; Duan, D.; Koczman, J.; Westenfeld, R.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Chen, N.X. Role of calcification inhibitors in the pathogenesis of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2295–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emoto, M.; Mori, K.; Lee, E.; Kawano, N.; Yamazaki, Y.; Tsuchikura, S.; Morioka, T.; Koyama, H.; Shoji, T.; Inaba, M.; et al. Fetuin-A and atherosclerotic calcified plaque in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2010, 59, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkertt, C.; Demetriou, M.; Sukhu, B.; Szweras, M.; Tenenbaum, H.C.; Dennis, J.W. Regulation of osteogenesis by fetuin. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 28514–28520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundberg, C.M.; Lian, J.B.; Booth, S.L. Vitamin K-Dependent Carboxylation of Osteocalcin: Friend or Foe? Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetriou, M.; Binkert, C.; Sukhu, B.; Tenenbaum, H.C.; Dennis, J.W. Fetuin/α2-HS glycoprotein is a transforming growth factor-β type II receptor mimic and cytokine antagonist. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 12755–12761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinke, T.; Amendt, C.; Trindl, A.; Pöschke, O.; Müller-Esterl, W.; Jahnen-Dechent, W. The serum protein α2-HS glycoprotein/fetuin inhibits apatite formation in vitro and in mineralizing calvaria cells. A possible role in mineralization and calcium homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 20789–20796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.L.; Joannides, A.J.; Skepper, J.N.; Mcnair, R.; Schurgers, L.J.; Proudfoot, D.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Weissberg, P.L.; Shanahan, C.M. Human vascular smooth muscle cells undergo vesicle-mediated calcification in response to changes in extracellular calcium and phosphate concentrations: A potential mechanism for accelerated vascular calcification in ESRD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 2857–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westenfeld, R.; Schäfer, C.; Krüger, T.; Haarmann, C.; Schurgers, L.J.; Reutelingsperger, C.; Ivanovski, O.; Drueke, T.; Massy, Z.A.; Ketteler, M.; et al. Fetuin-A protects against atherosclerotic calcification in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guttman, M.; Weinkam, P.; Sali, A.; Lee, K.K. All-atom ensemble modeling to analyze small angle X-ray scattering of glycosylated proteins. Structure 2013, 21, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, P.A.; Thomas, G.R.; Pardini, A.W.; Figueira, W.F.; Caputo, J.M.; Williamson, M.K. Discovery of a high molecular weight complex of calcium, phosphate, fetuin, and matrix γ-carboxyglutamic acid protein in the serum of etidronate-treated rats. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 3926–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holt, S.G.; Smith, E.R. Fetuin-A-containing calciprotein particles in mineral trafficking and vascular disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 1583–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heiss, A.; DuChesne, A.; Denecke, B.; Grötzinger, J.; Yamamoto, K.; Renneé, T.; Jahnen-Dechent, W. Structural basis of calcification inhibition by α2-HS glycoprotein/fetuin-A: Formation of colloidal calciprotein particles. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 13333–13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dey, S.; Das, M.; Balla, V.K. Effect of hydroxyapatite particle size, morphology and crystallinity on proliferation of colon cancer HCT116 cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 39, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merx, M.W.; Schäfer, C.; Westenfeld, R.; Brandenburg, V.; Hidajat, S.; Weber, C.; Ketteler, M.; Jahnen-Dechent, W. Myocardial stiffness, cardiac remodeling, and diastolic dysfunction in calcification-prone fetuin-A-deficient mice. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, J.L.; Skepper, J.N.; McNair, R.; Kasama, T.; Gupta, K.; Weissberg, P.L.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Shanahan, C.M. Multifunctional roles for serum protein fetuin-A in inhibition of human vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 2920–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ketteler, M.; Bongartz, P.; Westenfeld, R.; Wildberger, J.E.; Mahnken, A.H.; Böhm, R.; Metzger, T.; Wanner, C.; Jahnen-dechent, W.; Floege, J. Association of low fetuin-A (AHSG) concentrations in serum with cardiovascular mortality in patients on dialysis: A cross-sectional study. Mech. Dis. 2003, 361, 827–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, M.L.; Tomlinson, L.A.; Smith, E.R.; Rajkumar, C.; Holt, S.G. Fetuin-A is an independent determinant of change of aortic stiffness over 1 year in non-diabetic patients with CKD stages 3 and 4. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scialla, J.J.; Linda Kao, W.H.; Crainiceanu, C.; Sozio, S.M.; Oberai, P.C.; Shafi, T.; Coresh, J.; Powe, N.R.; Plantinga, L.C.; Jaar, B.G.; et al. Biomarkers of vascular calcification and mortality in patients with ESRD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, W.; Zhu, S.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Fan, X.; Yang, H.; Gong, X.; Eissa, N.T.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; et al. A hepatic protein, fetuin-A, occupies a protective role in lethal systemic inflammation. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.E.; Sama, A. Anti-Inflammatory Role of Fetuin-A in Injury and Infection. Curr. Mol. Med. 2012, 12, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Tracey, K.J. Fetuin Opsonizes Macrophage-Deactivating Cations. In Immune Response in the Critically Ill; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2002; pp. 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Caragine, T.; Wang, H.; Cohen, P.S.; Botchkina, G.; Soda, K.; Bianchi, M.; Ulrich, P.; Cerami, A.; Sherry, B.; et al. Spermine inhibits proinflammatory cytokine synthesis in human mononuclear cells: A counterregulatory mechanism that restrains the immune response. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1759–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Soda, K.; Sama, A.; Tracey, K.J. Fetuin protects the fetus from TNF. Lancet 1997, 350, 861–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, M.; Bianchi, M.; Sherry, B.; Sama, A.; Tracey, K.J. Fetuin (α2-HS-glycoprotein) opsonizes cationic macrophage-deactivating molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14429–14434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dziegielewska, K.M.; Andersen, N.A.; Saunders, N.R. Modification of macrophage response to lipopolysaccharide by fetuin. Immunol. Lett. 1998, 60, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terkeltaub, R.A.; Santoro, D.A.; Mandel, G.; Mandel, N. Serum and plasma inhibit neutrophil. Arthritis Rheum. 1988, 31, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.S.; Lee, H.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Choi, J.-H.; Yoo, H.J.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, N.H.; Choi, D.S.; Baik, S.H.; et al. Relationship of Circulating Fetuin-A Levels with Body Size and Metabolic Phenotypes. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Després, J.-P.; Lemieux, I. Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature 2006, 444, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Day, C.P. Progression of NAFLD to diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease or cirrhosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease—A global public health perspective. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stefan, N.; Häring, H.-U. The role of hepatokines in metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iroz, A.; Couty, J.-P.; Postic, C. Hepatokines: Unlocking the multi-organ network in metabolic diseases. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennequin, G.; Sirvent, P.; Whitham, M. Role of exercise-induced hepatokines in metabolic disorders. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2019, 317, E11–E24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.-L.; Xie, Q.-Y.; Guo, G.-L.; Ma, K.; Huang, Y.-Y. Serum Fetuin-A Levels in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Ling, W. Lower Plasma Fetuin-A Levels Are Associated with a Higher Mortality Risk in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 2213–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, K.M. The Impact of Organokines on Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 31, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auberger, P.; Falquerho, L.; Contreres, J.O.; Pages, G.; Le Cam, G.; Rossi, B.; Cam, A. Le Characterization of a natural inhibitor of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase: cDNA cloning, purification, and anti-mitogenic activity. Cell 1989, 58, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauth, G.; Poschke, O.; Fink, E.; Eulitz, M.; Tippmer, S.; Kellerer, M.; Haring, H.-U.; Nawratil, P.; Haasemann, M.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; et al. The nucleotide and partial amino acid sequences of rat fetuin. Identity with the natural tyrosine kinase inhibitor of the rat insulin receptor. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 204, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srinivas, P.R.; Wagner, A.S.; Reddy, L.V.; Deutsch, D.D.; Leon, M.A.; Goustin, A.S.; Grunberger, G. Serum alpha 2-HS-glycoprotein is an inhibitor of the human insulin receptor at the tyrosine kinase level. Mol. Endocrinol. 1993, 7, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar]
- Mathews, S.T.; Srinivas, P.R.; Leon, M.A.; Grunberger, G. Bovine fetuin is an inhibitor of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. Life Sci. 1997, 61, 1583–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Srinivas, P.R.; Cong, L.-N.; Li, Y.; Grunberger, G.; Quon, M.J. α2-Heremans Schmid Glycoprotein Inhibits Insulin-Stimulated Elk-1 Phosphorylation, But Not Glucose Transport, in Rat Adipose Cells 1. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 4147–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, S. α2-HSG, a specific inhibitor of insulin receptor autophosphorylation, interacts with the insulin receptor. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2000, 164, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goustin, A.-S.; Abou-Samra, A.B. The “thrifty” gene encoding Ahsg/Fetuin-A meets the insulin receptor: Insights into the mechanism of insulin resistance. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.E. The relative contributions of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction to the pathophysiology of Type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mori, K.; Emoto, M.; Yokoyama, H.; Araki, T.; Teramura, M.; Koyama, H.; Shoji, T.; Inaba, M.; Nishizawa, Y. Association of Serum Fetuin-A with Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetic and Nondiabetic Subjects. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stefan, N.; Hennige, A.M.; Staiger, H.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Krober, S.M.; Machicao, F.; Fritsche, A.; Haring, H.-U. 2-Heremans-Schmid Glycoprotein/ Fetuin-A Is Associated with Insulin Resistance and Fat Accumulation in the Liver in Humans. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stefan, N.; Fritsche, A.; Weikert, C.; Boeing, H.; Joost, H.-G.; Haring, H.-U.; Schulze, M.B. Plasma Fetuin-A Levels and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2762–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ix, J.H. Fetuin-A and Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Older Persons. JAMA 2008, 300, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roshanzamir, F.; Miraghajani, M.; Rouhani, M.H.; Mansourian, M.; Ghiasvand, R.; Safavi, S.M. The association between circulating fetuin-A levels and type 2 diabetes mellitus risk: Systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2018, 41, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brix, J.M.; Stingl, H.; Höllerl, F.; Schernthaner, G.H.; Kopp, H.-P.; Schernthaner, G. Elevated Fetuin-A Concentrations in Morbid Obesity Decrease after Dramatic Weight Loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4877–4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pal, D.; Dasgupta, S.; Kundu, R.; Maitra, S.; Das, G.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Ray, S.; Majumdar, S.S.; Bhattacharya, S. Fetuin-A acts as an endogenous ligand of TLR4 to promote lipid-induced insulin resistance. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennige, A.M.; Staiger, H.; Wicke, C.; Machicao, F.; Fritsche, A.; Häring, H.-U.; Stefan, N. Fetuin-A Induces Cytokine Expression and Suppresses Adiponectin Production. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, S.; Chattopadhyay, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Dasgupta, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Bhattacharya, S. Fetuin-A downregulates adiponectin through Wnt-PPARγ pathway in lipid induced inflamed adipocyte. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ix, J.H.; Sharma, K. Mechanisms Linking Obesity, Chronic Kidney Disease, and Fatty Liver Disease: The Roles of Fetuin-A, Adiponectin, and AMPK. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, P.; Seal, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Kundu, R.; Mukherjee, S.; Ray, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Majumdar, S.S.; Bhattacharya, S. Adipocyte Fetuin-A Contributes to Macrophage Migration into Adipose Tissue and Polarization of Macrophages. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 28324–28330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Sotelo, D.; Roca-Rivada, A.; Larrosa-García, M.; Castelao, C.; Baamonde, I.; Baltar, J.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Seoane, L.M.; Casanueva, F.F.; Pardo, M. Visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue express and secrete functional alpha2hsglycoprotein (fetuin a) especially in obesity. Endocrine 2017, 55, 435–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Norheim, F.; Gulseth, H.L.; Langleite, T.M.; Kolnes, K.J.; Tangen, D.S.; Stadheim, H.K.; Gilfillan, G.D.; Holen, T.; Birkeland, K.I.; et al. Interaction between plasma fetuin-A and free fatty acids predicts changes in insulin sensitivity in response to long-term exercise. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Hermoso, A.; Ceballos-Ceballos, R.J.M.; Poblete-Aro, C.E.; Hackney, A.C.; Mota, J.; Ramírez-Vélez, R. Exercise, adipokines and pediatric obesity: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramírez-Vélez, R.; García-Hermoso, A.; Hackney, A.C.; Izquierdo, M. Effects of exercise training on Fetuin-a in obese, type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease in adults and elderly: A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, K.M.; Han, K.A.; Ahn, H.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, B.-H.; Hong, H.C.; Choi, H.Y.; Yang, S.J.; Yoo, H.J.; et al. The effects of caloric restriction on Fetuin-A and cardiovascular risk factors in rats and humans: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Endocrinol. 2013, 79, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Lee, W.-J.; Asakawa, A.; Fujitsuka, N.; Chong, K.; Chen, S.-C.; Lee, S.-D.; Inui, A. Insulin Secretion and Interleukin-1β Dependent Mechanisms in Human Diabetes Remission After Metabolic Surgery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 2374–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schauer, P.R.; Bhatt, D.L.; Kirwan, J.P.; Wolski, K.; Brethauer, S.A.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Aminian, A.; Pothier, C.E.; Kim, E.S.H.; Nissen, S.E.; et al. Bariatric Surgery versus Intensive Medical Therapy for Diabetes—3-Year Outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2002–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeh, C.; Huang, H.-H.; Chen, S.-C.; Chen, T.-F.; Ser, K.-H.; Chen, C.-Y. Comparison of consumption behavior and appetite sensations among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus after bariatric surgery. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kahraman, A.; Sowa, J.-P.; Schlattjan, M.; Sydor, S.; Pronadl, M.; Wree, A.; Beilfuss, A.; Kilicarslan, A.; Altinbaş, A.; Bechmann, L.P.; et al. Fetuin-A mRNA expression is elevated in NASH compared with NAFL patients. Clin. Sci. 2013, 125, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.-J.; Ser, K.-H.; Lin, M.-T.; Nien, H.-C.; Chen, C.-N.; Yang, W.-S.; Lee, W.-J. Diabetes Associated Markers After Bariatric Surgery: Fetuin-A, but Not Matrix Metalloproteinase-7, Is Reduced. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 2328–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.-H.; Yeh, C.; Chen, J.-C.; Lee, T.-H.; Chen, S.-C.; Lee, W.-J.; Chen, C.-Y. Does bariatric surgery influence plasma levels of fetuin-A and leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-2 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus? PeerJ 2018, 6, e4884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verras, C.G.; Christou, G.A.; Simos, Y.V.; Ayiomamitis, G.D.; Melidonis, A.J.; Kiortsis, D.N. Serum fetuin-A levels are associated with serum triglycerides before and 6 months after bariatric surgery. Hormones 2017, 16, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roden, M. Mechanisms of Disease: Hepatic steatosis in type 2 diabetes—Pathogenesis and clinical relevance. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 2, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Braymer, H.D.; Bray, G.A.; York, D.A. Differential expression of insulin receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (fetuin) gene in a model of diet-induced obesity. Life Sci. 1998, 63, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Biswas, A.; Majumdar, S.S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Ray, S.; Bhattacharya, S. NF-κB mediates lipid-induced fetuin-A expression in hepatocytes that impairs adipocyte function effecting insulin resistance. Biochem. J. 2010, 429, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takata, H.; Ikeda, Y.; Suehiro, T.; Ishibashi, A.; Inoue, M.; Kumon, Y.; Terada, Y. High Glucose Induces Transactivation of the ALPHA.2-HS Glycoprotein Gene Through the ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2009, 16, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haukeland, J.W.; Dahl, T.B.; Yndestad, A.; Gladhaug, I.P.; Løberg, E.M.; Haaland, T.; Konopski, Z.; Wium, C.; Aasheim, E.T.; Johansen, O.E.; et al. Fetuin A in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: In vivo and in vitro studies. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 166, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.W.; Youn, B.-S.; Choi, H.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Hong, H.C.; Yang, S.J.; Yoo, H.J.; Kim, B.-H.; Baik, S.H.; Choi, K.M. Salsalate and adiponectin ameliorate hepatic steatosis by inhibition of the hepatokine fetuin-A. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 86, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haukeland, J.W.; Konopski, Z.; Eggesbø, H.B.; von Volkmann, H.L.; Raschpichler, G.; Bjøro, K.; Haaland, T.; Løberg, E.M.; Birkeland, K. Metformin in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized, controlled trial. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malin, S.K.; Mulya, A.; Fealy, C.E.; Haus, J.M.; Pagadala, M.R.; Scelsi, A.R.; Huang, H.; Flask, C.A.; McCullough, A.J.; Kirwan, J.P. Fetuin-A is linked to improved glucose tolerance after short-term exercise training in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 115, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foley, R.; Parfrey, P.; Sarnak, M. Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1998, 32, S112–S119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvinkel, P. Coronary Artery Disease in End-Stage Renal Disease: No Longer a Simple Plumbing Problem. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003, 14, 1927–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nascimbeni, F.; Romagnoli, D.; Ballestri, S.; Baldelli, E.; Lugari, S.; Sirotti, V.; Giampaoli, V.; Lonardo, A. Do Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Fetuin-A Play Different Roles in Symptomatic Coronary Artery Disease and Peripheral Arterial Disease? Diseases 2018, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eleftheriadou, I.; Grigoropoulou, P.; Kokkinos, A.; Mourouzis, I.; Perrea, D.; Katsilambros, N.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Tentolouris, N. Association of plasma fetuin-a levels with peripheral arterial disease and lower extremity arterial calcification in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroner, S.A.; St-Jules, D.E.; Mukamal, K.J.; Katz, R.; Shlipak, M.G.; Criqui, M.H.; Kestenbaum, B.; Siscovick, D.S.; de Boer, I.H.; Jenny, N.S.; et al. Fetuin-A, glycemic status, and risk of cardiovascular disease: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2016, 248, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akyuz, A.; Oran, M.; Alpsoy, S.; Mutlu, L.C.; Akkoyun, D.C.; Guzel, S.; Alp, R. Association Between Serum Fetuin-A levels, Carotid Artery Stiffness, and Intima–Media Thickness in Patients with Normotensive Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Angiology 2014, 65, 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenvinkel, P.; Wang, K.; Qureshi, A.R.; Axelsson, J.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Gao, P.; Barany, P.; Lindholm, B.; Jogestrand, T.; Heimberger, O.; et al. Low fetuin-A levels are associated with cardiovascular death: Impact of variations in the gene encoding fetuin. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 2383–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lebreton, J.P.; Joisel, F.; Raoult, J.P.; Lannuzel, B.; Rogez, J.P.; Humbert, G. Serum concentration of human alpha 2 HS glycoprotein during the inflammatory process: Evidence that alpha 2 HS glycoprotein is a negative acute-phase reactant. J. Clin. Investig. 1979, 64, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laughlin, G.A.; Cummins, K.M.; Wassel, C.L.; Daniels, L.B.; Ix, J.H. The Association of Fetuin-A with Cardiovascular Disease Mortality in Older Community-Dwelling Adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 59, 1688–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bourebaba, L.; Marycz, K. Pathophysiological Implication of Fetuin-A Glycoprotein in the Development of Metabolic Disorders: A Concise Review. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122033
Bourebaba L, Marycz K. Pathophysiological Implication of Fetuin-A Glycoprotein in the Development of Metabolic Disorders: A Concise Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2019; 8(12):2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122033
Chicago/Turabian StyleBourebaba, Lynda, and Krzysztof Marycz. 2019. "Pathophysiological Implication of Fetuin-A Glycoprotein in the Development of Metabolic Disorders: A Concise Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 8, no. 12: 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122033
APA StyleBourebaba, L., & Marycz, K. (2019). Pathophysiological Implication of Fetuin-A Glycoprotein in the Development of Metabolic Disorders: A Concise Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(12), 2033. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8122033



