Phylogenetic Analysis of HIV-1 Genomes Based on the Position-Weighted K-mers Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Complete Genome Datasets
2.2. The Measure of Position-Weighted K-mers
2.3. Distance Calculations
2.4. Selection of the k Value
2.5. Accuracy Test of the Phylogenetic Tree Based on the Robinson–Foulds Distance and Robustness Test Using the Modified Bootstrap Method
3. Results
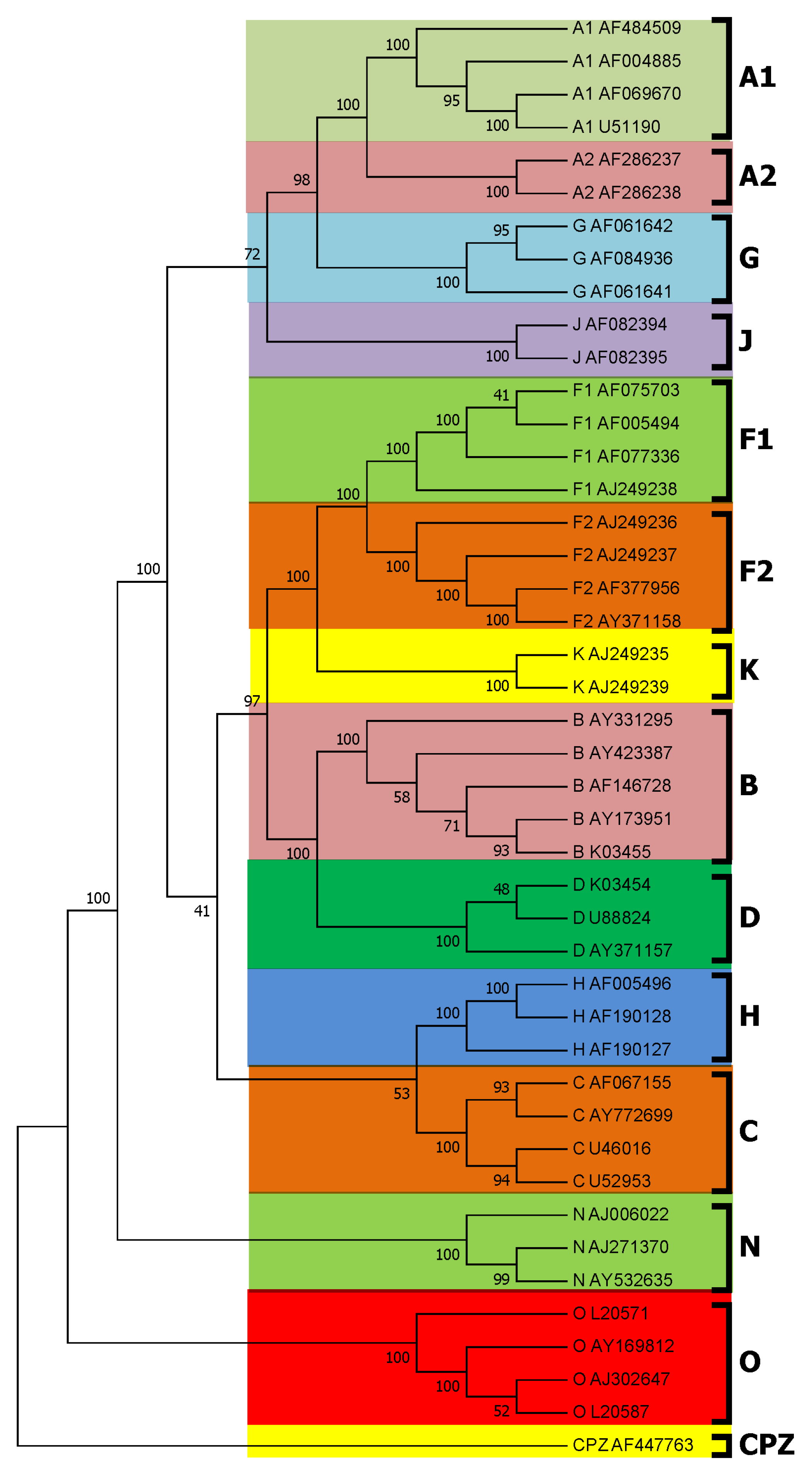
3.1. Subtyping of HIV-1 Based on PWkmer Feature for Complete Genome Sequences
3.2. Application of Our Method on Other Datasets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zachary, T.; Aboulafia, D.M. Review of screening guidelines for non-AIDS-defining malignancies: Evolving issues in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Aids Rev. 2012, 14, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Lemey, P.; Pybus, O.G.; Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Robertson, D.L.; Roques, P.; Worobey, M.; Vandamme, A.M. The molecular population genetics of HIV-1 group O. Genetics 2004, 167, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tebit, D.M.; Nankya, I.; Arts, E.J.; Gao, Y. HIV diversity, recombination and disease progression: How does fitness “fit” into the puzzle? Aids Rev. 2015, 9, 75–87. [Google Scholar]
- Herniou, E.A.; Luque, T.; Chen, X.; Vlak, J.M.; Winstanley, D.; Cory, J.S.; O’reilly, D.R. Use of whole genome sequence data to infer baculovirus phylogeny. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 8117–8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Cai, Z.; Wan, X.F.; Hoang, T.; Goebel, R.; Lin, G. Nucleotide composition string selection in HIV-1 subtyping using whole genomes. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1744–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.G.; Chu, K.H.; Li, C.P.; Vo, A.; Zhou, L.Q.; Wang, R.W. Whole-proteome phylogeny of large dsDNA viruses and parvoviruses through a composition vector method related to dynamical language model. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Wang, T. A novel statistical measure for sequence comparison on the basis of k-word counts. J. Theor. Biol. 2013, 318, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, G.; Wang, H.; Zhang, T. A novel alignment-free method for whole genome analysis: Application to HIV-1 subtyping and HEV genotyping. Inf. Sci. 2014, 279, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leimeister, C.A.; Boden, M.; Horwege, S.; Lindner, S.; Morgenstern, B. Fast alignment-free sequence comparison using spaced-word frequencies. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1991–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, X.H.; Yu, Z.G.; Han, G.S.; Yang, W.F.; Anh, V. Whole-proteome based phylogenetic tree construction with inter-amino-acid distances and the conditional geometric distribution profiles. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 89, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.F.; Yu, Z.G.; Anh, V. Whole genome/proteome based phylogeny reconstruction for prokaryotes using higher order Markov model and chaos game representation. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 96, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Yu, Z.G.; Yang, J. Dltree: Efficient and accurate phylogeny reconstruction using the dynamical language method. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2214–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Freudenberg, J. Alignment-free approaches for predicting novel Nuclear Mitochondrial Segments (NUMTs) in the human genome. Gene. 2019, 691, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielezinski, A.; Vinga, S.; Almeida, J.; Karlowski, W.M. Alignment-free sequence comparison: Benefits, applications, and tools. Genome Biol. 2017, 18, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hao, B.; Qi, J. Prokaryote phylogeny without sequence alignment: From avoidance signature to composition distance. J. Bioinf. Comput. Biol. 2004, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, A.; Dasanna, A.K.; Sinha, S. Multifractal analysis of HIV-1 genomes. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 62, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaisdell, B.E. A measure of the similarity of sets of sequences not requiring sequence alignment. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 5155–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snel, B.; Bork, P.; Huynen, M.A. Genomes in flux: The evolution of archaeal and proteobacterial gene content. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, K.; Ren, J.; Reinert, G.; Deng, M.; Waterman, M.S.; Sun, F. New developments of alignment-free sequence comparison: Measures, statistics and next-generation sequencing. Brief. Bioinf. 2014, 15, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.G.; Anh, V.; Lau, K.S. Multifractal and correlation analyses of protein sequences from complete genomes. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 68, 021913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuo, G.; Hao, B. CVTree3 web server for whole-genome-based and alignment-free prokaryotic phylogeny and taxonomy. Genom. Proteom. Bioinf. 2015, 13, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, G.-B.; Cho, D.-H. Genome classification improvements based on k-mer intervals in sequences. Genomics 2019, 111, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.G.; Zhou, L.Q.; Anh, V.V.; Chu, K.H.; Long, S.C.; Deng, J.Q. Phylogeny of prokaryotes and chloroplasts revealed by a simple composition approach on all protein sequences from complete genomes without sequence alignment. J. Mol. Evol. 2005, 60, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krause, E.F. Taxicab geometry: Adventure in non-euclidean geometry. Mathematical Gazette 1988, 72, 255. [Google Scholar]
- Solis-Reyes, S.; Avino, M.; Poon, A.; Kari, L. An open-source k-mer based machine learning tool for fast and accurate subtyping of HIV-I genomes. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Han, G.S.; Yu, Z.G.; Li, J. Laplacian normalization and random walk on heterogeneous networks for disease-gene prioritization. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2015, 57, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robinson, D.F.; Foulds, L.R. Comparison of phylogenetic trees. Math. Biosci. 1981, 53, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Mathematics vs. evolution: Mathematical evolutionary theory. Science 1989, 246, 941–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, B.T.; Korber, B.T.M.; Leitner, T.K.; Apetrei, C.; Hahn, B.; Mizrachi, I.; Mullins, J.; Rambaut, A.; Wolinsky, S. HIV Sequence Compendium 2018. Available online: https://www.osti.gov/biblio/1458915 (accessed on 22 February 2020).
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; Mcgettigan, P.A.; Mcwilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manns, M.P.; Lohse, A.W.; Vergani, D. Autoimmune hepatitis-Update 2015. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, S100–S111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Z.; Meng, J.; Sun, X. A novel feature-based method for whole genome phylogenetic analysis without alignment: Application to HEV genotyping and subtyping. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 368, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, L.; Li, C.; Hagedorn, C.H. Phylogenetic analysis of global hepatitis E virus sequences: Genetic diversity, subtypes and zoonosis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2006, 16, 5–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, T. A simple k-word interval method for phylogenetic analysis of DNA sequences. J. Theor. Biol. 2013, 317, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Hua, K.; Chen, M.; Zhang, R.; Xie, X. A novel k-word relative measure for sequence comparison. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2014, 53, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| No. | Accession | Subtype | Length (bp) | Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | U51190 | A1 | 8999 | Uganda |
| 2 | AF004885 | A1 | 9160 | Kenya |
| 3 | AF069670 | A1 | 8813 | Somalia |
| 4 | AF484509 | A1 | 8807 | Uganda |
| 5 | AF286237 | A2 | 9060 | Cyprus |
| 6 | AF286238 | A2 | 8972 | DRC |
| 7 | AY173951 | B | 8996 | Thailand |
| 8 | AY331295 | B | 8834 | USA |
| 9 | AY423387 | B | 9359 | Netherlands |
| 10 | K03455 | B | 9719 | France |
| 11 | AF146728 | B | 8887 | Australia |
| 12 | AF067155 | C | 9002 | India |
| 13 | AY772699 | C | 9011 | South Africa |
| 14 | U46016 | C | 9031 | Ethopia |
| 15 | U52953 | C | 8959 | Brazil |
| 16 | AY371157 | D | 8379 | Cameroon |
| 17 | K03454 | D | 9176 | DRC |
| 18 | U88824 | D | 8952 | Uganda |
| 19 | AF005494 | F1 | 8968 | Brazil |
| 20 | AF075703 | F1 | 8925 | Finland |
| 21 | AF077336 | F1 | 8903 | Belgium (DRC) |
| 22 | AJ249238 | F1 | 8614 | France |
| 23 | AF377956 | F2 | 8782 | Cameroon |
| 24 | AJ249236 | F2 | 8555 | Cameroon |
| 25 | AJ249237 | F2 | 8589 | Cameroon |
| 26 | AY371158 | F2 | 8349 | Cameroon |
| 27 | AF061641 | G | 9047 | Finland(Kenya) |
| 28 | AF061642 | G | 9074 | Sweden (DRC) |
| 29 | AF084936 | G | 9707 | Belgium (DRC) |
| 30 | AF005496 | H | 8953 | Cent.Afr. Rep |
| 31 | AF190127 | H | 9056 | Belgium |
| 32 | AF190128 | H | 9707 | Belgium |
| 33 | AF082394 | J | 8943 | Sweden |
| 34 | AF082395 | J | 8953 | Sweden |
| 35 | AJ249235 | K | 8600 | DRC |
| 36 | AJ249239 | K | 8604 | Cameroon |
| 37 | AJ006022 | N | 9182 | Cameroon |
| 38 | AJ271370 | N | 9045 | Cameroon |
| 39 | AY532635 | N | 8938 | Cameroon |
| 40 | AJ302647 | O | 9829 | Senegal |
| 41 | AY169812 | O | 9110 | Cameroon |
| 42 | L20571 | O | 9793 | Cameroon |
| 43 | L20587 | O | 9754 | Cameroon |
| 44 | AF447763 | CPZ | 9326 | Tanzania |
| Species | k = 2 | k = 3 | k = 4 | k = 5 | k = 6 | k = 7 | k = 8 | k = 9 | k = 10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIV | 74 | 54 | 38 | 26 | 20 | 14 | 10 | 12 | 14 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Y.; Yu, Z.; Tang, R.; Xie, X.; Han, G.; Anh, V.V. Phylogenetic Analysis of HIV-1 Genomes Based on the Position-Weighted K-mers Method. Entropy 2020, 22, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020255
Ma Y, Yu Z, Tang R, Xie X, Han G, Anh VV. Phylogenetic Analysis of HIV-1 Genomes Based on the Position-Weighted K-mers Method. Entropy. 2020; 22(2):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020255
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Yuanlin, Zuguo Yu, Runbin Tang, Xianhua Xie, Guosheng Han, and Vo V. Anh. 2020. "Phylogenetic Analysis of HIV-1 Genomes Based on the Position-Weighted K-mers Method" Entropy 22, no. 2: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020255
APA StyleMa, Y., Yu, Z., Tang, R., Xie, X., Han, G., & Anh, V. V. (2020). Phylogenetic Analysis of HIV-1 Genomes Based on the Position-Weighted K-mers Method. Entropy, 22(2), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/e22020255





