Old and New Concepts in Ubiquitin and NEDD8 Recognition
Abstract
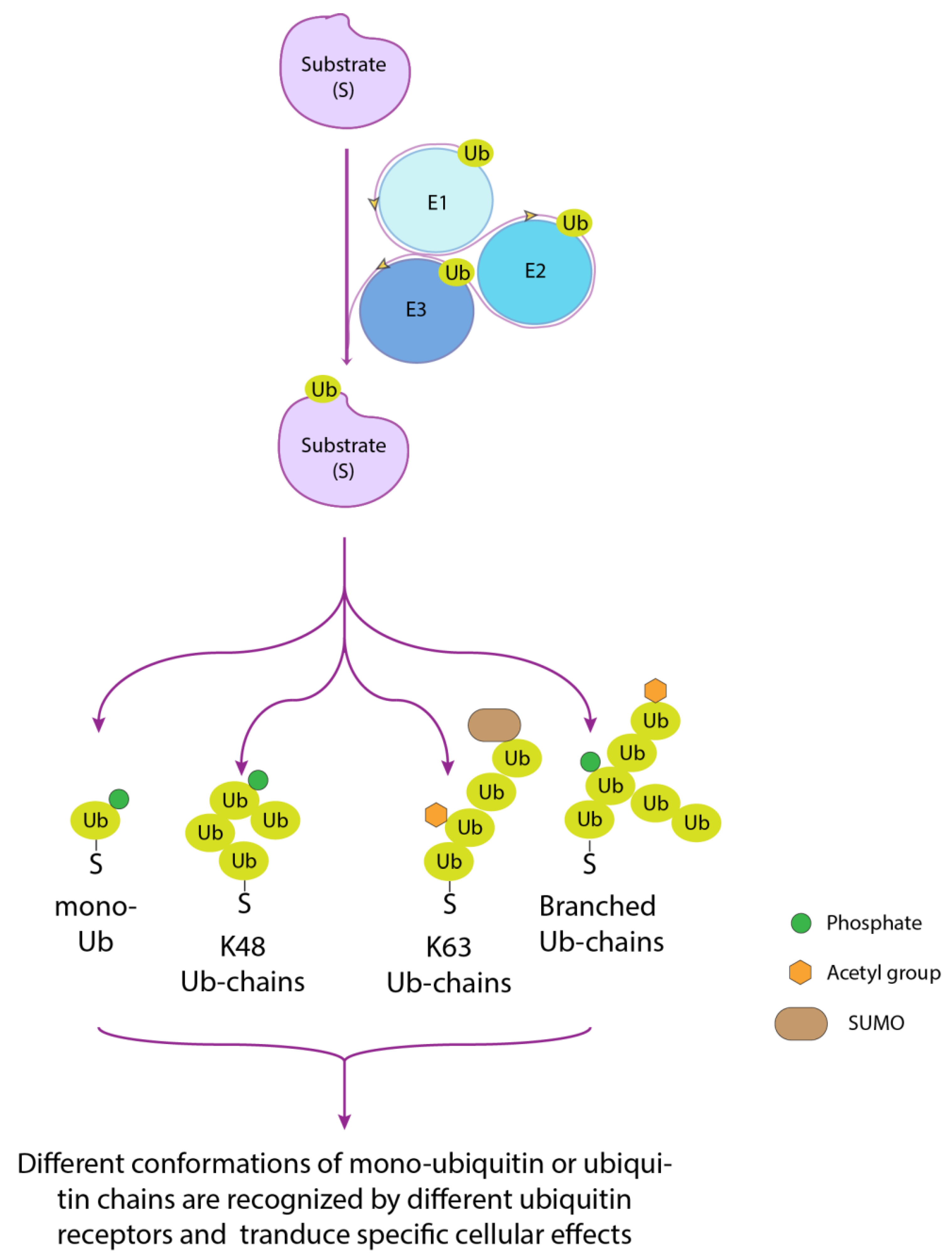
:1. Ubiquitination and Ubiquitin-Binding Domains: A General Overview
2. Ubiquitin-Like Proteins
2.1. The NEDD8 “Enigma”
2.2. CUBAN and CoCUN: Similar but Different
3. The PRORP Family Members
4. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hershko, A.; Ciechanover, A. The ubiquitin system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 425–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burroughs, A.M.; Balaji, S.; Iyer, L.M.; Aravind, L. Small but versatile: The extraordinary functional and structural diversity of the β-grasp fold. Biol. Direct 2007, 2, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, N. Ubiquitin Ligases: Structure, Function, and Regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 129–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciechanover, A.; Ben-Saadon, R. N-terminal ubiquitination: More protein substrates join in. Trends Cell Biology 2004, 14, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadwell, K.; Coscoy, L. Ubiquitination on Nonlysine Residues by a Viral E3 Ubiquitin Ligase. Science 2005, 309, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDowell, G.S.; Philpott, A. New insights into the role of ubiquitylation (Chapter two). Int. Rev. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2016, 325, 35–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, R.; Rape, M. The increasing complexity of the ubiquitin code. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulathu, Y.; Komander, D. Atypical ubiquitylation—The unexplored world of polyubiquitin beyond Lys48 and Lys63 linkages. Nat. Publ. Group 2012, 13, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghames, C.M.; Lobato-Gil, S.; Perrin, A.; Trauchessec, H.; Rodriguez, M.S.; Urbach, S.; Marin, P.; Xirodimas, D.P. NEDDylation promotes nuclear protein aggregation and protects the Ubiquitin Proteasome System upon proteotoxic stress. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, a004374-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez Berrocal, D.A.; Witting, K.F.; Ovaa, H.; Mulder, M.P.C. Hybrid Chains: A Collaboration of Ubiquitin and Ubiquitin-Like Modifiers Introducing Cross-Functionality to the Ubiquitin Code. Front. Chem. 2020, 7, e51672-9. [Google Scholar]
- Santonico, E. New Insights into the Mechanisms Underlying NEDD8 Structural and Functional Specificity. IntechOpen 2019, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swatek, K.N.; Komander, D. Ubiquitin modifications. Nat. Publ. Group 2016, 26, 399–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kliza, K.; Husnjak, K. Resolving the Complexity of Ubiquitin Networks. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahighi, S.; Dikic, I. Selectivity of the ubiquitin-binding modules. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 2705–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Husnjak, K.; Dikic, I. Ubiquitin-Binding Proteins: Decoders of Ubiquitin-Mediated Cellular Functions. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 291–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikic, I.; Wakatsuki, S.; Walters, K.J. Ubiquitin-binding domains—From structures to functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.H.; Lee, S.; Prag, G. Ubiquitin-binding domains. Biochem. J. 2006, 399, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randles, L.; Walters, K.J. Ubiquitin and its binding domains. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed) 2012, 17, 2140–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, F.; Dikic, I. Atypical ubiquitin chains: New molecular signals. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hofmann, K.; Falquet, L. A ubiquitin-interacting motif conserved in components of the proteasomal and lysosomal protein degradation systems. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 26, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo, S.; Sigismund, S.; Faretta, M.; Guidi, M.; Capua, R.M.; Bossi, G.; Chen, H.; De Camilli, P.; Di Fiore, P.P. A single motif responsible for ubiquitin recognition and monoubiquitination in endocytic proteins. Lett. Nat. 2002, 416, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raasi, S.; Pickart, C.M. Rad23 ubiquitin-associated domains (UBA) inhibit 26 S proteasome-catalyzed proteolysis by sequestering lysine 48-linked polyubiquitin chains. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 8951–8959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Opipari, A.W.; Dixit, V.M. The A20 cDNA induced by tumor necrosis factor alpha encodes a novel type of zinc finger protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 14705–14708. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Hurley, J.H. VHS domains of ESCRT-0 cooperate in high-avidity binding to polyubiquitinated cargo. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, E.; Kawahata, K.; Kato, M.; Kitamura, N.; Komada, M. STAM Proteins Bind Ubiquitinated Proteins on the Early Endosome via the VHS Domain and Ubiquitin- interacting Motif. Moi. Biol. Cell. 2003, 14, 3675–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laplantine, E.; Fontan, E.; Chiaravalli, J.; Lopez, T.; Lakisic, G.; Véron, M.; Agou, F.; Israël, A. NEMO specifically recognizes K63-linked poly-ubiquitin chains through a new bipartite ubiquitin-binding domain. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 2885–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, J.D.; Hicke, L. Non-traditional Functions of Ubiquitin and Ubiquitin-binding Proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 35857–35860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winget, J.M.; Mayor, T. The Diversity of Ubiquitin Recognition: Hot Spots and Varied Specificity. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicke, L.; Schubert, H.L.; Hill, C.P. Ubiquitin-binding domains. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radley, E.H.; Long, J.; Gough, K.C.; Layfield, R. The “dark matter” of ubiquitin-mediated processes: Opportunities and challenges in the identification of ubiquitin-binding domains. Biochm. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 1949–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabbe, C.; Husnjak, K.; Dikic, I. The spatial and temporal organization of ubiquitin networks. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deveraux, Q.; Pickart, C.; Rechsteiner, M. A 26 S Protease Subunit That Binds Ubiquitin Conjugates. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 7059–7061. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Oania, R.; Graumann, J.; Deshaies, R.J. Multiubiquitin Chain Receptors Define a Layer of Substrate Selectivity in the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System. Cell 2004, 118, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Young, P.; Walters, K.J. Structure of S5a Bound to Monoubiquitin Provides a Model for Polyubiquitin Recognition. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 348, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, R.M.; Pickart, C.M. In vitro assembly and recognition of Lys-63 polyubiquitin chains. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 27936–27943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polo, S.; Confalonieri, S.; Salcini, A.E.; Di Fiore, P.P. EH and UIM: Endocytosis and More. Sci. STKE 2003, 2003, re17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Kim, Y.-S.; Yang, X.-P.; Li, L.-P.; Liao, G.; Xia, F.; Jetten, A.M. The ubiquitin-interacting motif containing protein RAP80 interacts with BRCA1 and functions in DNA damage repair response. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6647–6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobhian, B.; Shao, G.; Lilli, D.R.; Culhane, A.C.; Moreau, L.A.; Xia, B.; Livingston, D.M.; Greenberg, R.A. RAP80 targets BRCA1 to specific ubiquitin structures at DNA damage sites. Science 2007, 316, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rahighi, S.; Ikeda, F.; Kawasaki, M.; Akutsu, M.; Suzuki, N.; Kato, R.; Kensche, T.; Uejima, T.; Bloor, S.; Komander, D.; et al. Specific Recognition of Linear Ubiquitin Chains by NEMO Is Important for NF-κB Activation. Cell 2009, 136, 1098–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshikawa, A.; Sato, Y.; Yamashita, M.; Mimura, H.; Yamagata, A.; Fukai, S. Crystal structure of the NEMO ubiquitin-binding domain in complex with Lys 63-linked di-ubiquitin. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 3317–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, F.; Xu, D.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.; Hu, S.; Gong, Y.; Yuan, J.; Pan, L. Structural insights into the ubiquitin recognition by OPTN (optineurin) and its regulation by TBK1- mediated phosphorylation. Autophagy 2018, 14, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, F.; Deribe, Y.L.; Skånland, S.S.; Stieglitz, B.; Grabbe, C.; Franz-Wachtel, M.; van Wijk, S.J.L.; Goswami, P.; Nagy, V.; Terzic, J.; et al. SHARPIN forms a linear ubiquitin ligase complex regulating NF-κB activity and apoptosis. Nature 2011, 471, 637–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared Principles in NF-κB Signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; Dass, J.F.P. Study of pathway cross-talk interactions with NF-κB leading to its activation via ubiquitination or phosphorylation: A brief review. Gene 2016, 584, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, C.; Pacifico, F.; Lavorgna, A.; Mellone, S.; Iannetti, A.; Acquaviva, R.; Formisano, S.; Vito, P.; Leonardi, A. ABIN-1 Binds to NEMO/IKK and Co-operates with A20 in Inhibiting NF-kB. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 18482–18488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ryan, T.A.; Tumbarello, D.A. Optineurin: A Coordinator of Membrane-Associated Cargo Trafficking and Autophagy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1601–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.; Sliter, D.A.; Herhaus, L.; Stolz, A.; Wang, C.; Beli, P.; Zaffagnini, G.; Wild, P.; Martens, S.; Wagner, S.A.; et al. Phosphorylation of OPTN by TBK1 enhances its binding to Ub chains and promotes selective autophagy of damaged mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4039–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ying, H.; Yue, B.Y.J.T. Optineurin: The autophagy connection. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 144, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herhaus, L.; Dikic, I. Expanding the ubiquitin code through post-translational modification. EMBO Rep. 2015, 16, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herhaus, L.; van den Bedem, H.; Tang, S.; Maslennikov, I.; Wakatsuki, S.; Dikic, I.; Rahighi, S. Molecular Recognition of M1-Linked Ubiquitin Chains by Native and Phosphorylated UBAN Domains. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3146–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heo, J.-M.; Ordureau, A.; Paulo, J.A.; Rinehart, J.; Harper, J.W. The PINK1-PARKIN Mitochondrial Ubiquitylation Pathway Drives a Program of OPTN/NDP52 Recruitment and TBK1 Activation to Promote Mitophagy. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tu, D.; Zhu, Z.; Zhou, A.Y.; Yun, C.-H.; Lee, K.-E.; Toms, A.V.; Li, Y.; Dunn, G.P.; Chan, E.; Thai, T.; et al. Structure and Ubiquitination-Dependent Activation of TANK-Binding Kinase 1. Cell Rep. 2013, 3, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pilli, M.; Arko-Mensah, J.; Ponpuak, M.; Roberts, E.; Master, S.; Mandell, M.A.; Dupont, N.; Ornatowski, W.; Jiang, S.; Bradfute, S.B.; et al. TBK-1 Promotes Autophagy-Mediated Antimicrobial Defense by Controlling Autophagosome Maturation. Immunity 2012, 37, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lim, J.; Lachenmayer, L.M.; Wu, S.; Liu, W.; Kundu, M.; Wang, R.; Komatsu, M.; Oh, Y.J.; Zhao, Y.; Yue, Z. Proteotoxic Stress Induces Phosphorylation of p62/SQSTM1 by ULK1 to Regulate Selective Autophagic Clearance of Protein Aggregates. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, G.; Wada, K.; Okuno, M.; Kurosawa, M.; Nukina, N. Serine 403 Phosphorylation of p62/SQSTM1 Regulates Selective Autophagic Clearance of Ubiquitinated Proteins. Mol. Cell 2011, 44, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappadocia, L.; Lima, C.D. Ubiquitin-like Protein Conjugation: Structures, Chemistry, and Mechanism. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 889–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veen, A.G.; Ploegh, H.L. Ubiquitin-Like Proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 323–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welchman, R.L.; Gordon, C.; Mayer, R.J. Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins as multifunctional signals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerscher, O.; Felberbaum, R.; Hochstrasser, M. Modification of Proteins by Ubiquitin and Ubiquitin-Like Proteins. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006, 22, 159–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hochstrasser, M. Origin and function of ubiquitin-like proteins. Nature 2009, 458, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kito, K.; Yeh, E.T.H.; Kamitani, T. NUB1, a NEDD8-interacting protein, is induced by interferon and down-regulates the NEDD8 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 20603–20609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, T.; Kawashima, H.; Yeh, E.T.H.; Kamitani, T. Regulation of the NEDD8 Conjugation System by a Splicing Variant, NUB1L. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 32905–32913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandau, S.; Knebel, A.; Gage, Z.O.; Wood, N.T.; Alexandru, G. UBXN7 docks on neddylated cullin complexes using its UIM motif and causes HIF1α accumulation. BMC Biol. 2012, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castagnoli, L.; Mandaliti, W.; Nepravishta, R.; Valentini, E.; Mattioni, A.; Procopio, R.; Iannuccelli, M.; Polo, S.; Paci, M.; Cesareni, G.; et al. Selectivity of the CUBAN domain in the recognition of ubiquitin and NEDD8. FEBS J. 2018, 286, 653–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hipp, M.S.; Raasi, S.; Groettrup, M.; Schmidtke, G. NEDD8 ultimate buster-1L interacts with the ubiquitin-like protein FAT10 and accelerates its degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 16503–16510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.; Durrin, L.K.; Wilkinson, T.A.; Krontiris, T.G.; Chen, Y. Identification of a SUMO-binding motif that recognizes SUMO-modified proteins. PNAS 2004, 101, 14373–14378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noda, N.N.; Ohsumi, Y.; Inagaki, F. Atg8-family interacting motif crucial for selective autophagy. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radoshevich, L.; Murrow, L.; Chen, N.; Fernandez, E.; Roy, S.; Fung, C.; Debnath, J. ATG12 Conjugation to ATG3 Regulates Mitochondrial Homeostasis and Cell Death. Cell 2010, 142, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanada, T.; Noda, N.N.; Satomi, Y.; Ichimura, Y.; Fujioka, Y.; Takao, T.; Inagaki, F.; Ohsumi, Y. The Atg12-Atg5 conjugate has a novel E3-like activity for protein lipidation in autophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 37298–37302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pankiv, S.; Clausen, H.T.; Lamark, T.; Brech, A.; Bruun, J.A.; Outzen, H.; Øvervatn, A.; BjØrkØy, G.; Johansen, T. p62/SQSTM1 Binds Directly to Atg8/LC3 to Facilitate Degradation of Ubiquitinated Protein Aggregates by Autophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukhopadhyay, D.; Dasso, M. Modification in reverse: The SUMO proteases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.; Müller, S. SUMO-specific proteases/isopeptidases: SENPs and beyond. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, E.S. Protein Modification by SUMO. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 355–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minty, A.; Dumont, X.; Kaghad, M.; Caput, D. Covalent modification of p73alpha by SUMO-1. Two-hybrid screening with p73 identifies novel SUMO-1-interacting proteins and a SUMO-1 interaction motif. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 36316–36323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hannich, J.T.; Lewis, A.; Kroetz, M.B.; Li, S.-J.; Heide, H.; Emili, A.; Hochstrasser, M. Defining the SUMO-modified Proteome by Multiple Approaches in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 4102–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, W.; Chen, Y. Small Ubiquitin-like Modifier (SUMO) Recognition of a SUMO Binding Motif. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 40122–40129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perry, J.J.P.; Tainer, J.A.; Boddy, M.N. A SIM-ultaneous role for SUMO and ubiquitin. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2008, 33, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.; Wu, K.; Yang, Y.; Guerrero, C.; Nillegoda, N.; Pan, Z.-Q.; Huang, L. A Targeted Proteomic Analysis of the Ubiquitin-Like Modifier Nedd8 and Associated Proteins. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 1274–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enchev, R.I.; Schulman, B.A.; Peter, M. Protein neddylation: Beyond cullin–RING ligases. Nature Publ. Group 2015, 16, 30–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami, T.; Chiba, T.; Suzuki, T.; Iwai, K.; Yamanaka, K.; Minato, N.; Suzuki, H.; Shimbara, N.; Hidaka, Y.; Osaka, F.; et al. NEDD8 recruits E2-ubiquitin to SCF E3 ligase. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 4003–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Z.-Q.; Kentsis, A.; Dias, D.C.; Yamoah, K.; Wu, K. Nedd8 on cullin: Building an expressway to protein destruction. Oncogene 2004, 23, 1985–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sakata, E.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Miyauchi, Y.; Iwai, K.; Chiba, T.; Saeki, Y.; Matsuda, N.; Tanaka, K.; Kato, K. Direct interactions between NEDD8 and ubiquitin E2 conjugating enzymes upregulate cullin-based E3 ligase activity. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 167–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.C.; Sviderskiy, V.O.; Monda, J.K.; Lydeard, J.R.; Cho, S.E.; Harper, J.W.; Schulman, B.A. Structure of a RING E3 Trapped in Action Reveals Ligation Mechanism for the Ubiquitin-like Protein NEDD8. Cell 2014, 157, 1671–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohki, Y.; Funatsu, N.; Konishi, N.; Chiba, T. The mechanism of poly-NEDD8 chain formation in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 381, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, A.P.; Perrin, A.; Serrano-Macia, M.; Maghames, C.; Leidecker, O.; Trauchessec, H.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Gartner, A.; Xirodimas, D.P. The Balance between Mono- and NEDD8-Chains Controlled by NEDP1 upon DNA Damage Is a Regulatory Module of the HSP70 ATPase Activity. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xirodimas, D.P. Novel substrates and functions for the ubiquitin-like molecule NEDD8. Biochm. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 802–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leidecker, O.; Matic, I.; Mahata, B.; Pion, E.; Xirodimas, D.P. The ubiquitin E1 enzyme Ube1 mediates NEDD8 activation under diverse stress conditions. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarikas, A.; Hartmann, T.; Pan, Z.-Q. The cullin protein family. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hjerpe, R.; Thomas, Y.; Chen, J.; Zemla, A.; Curran, S.; Shpiro, N.; Dick, L.R.; Kurz, T. Changes in the ratio of free NEDD8 to ubiquitin triggers NEDDylation by ubiquitin enzymes. Biochem. J. 2012, 441, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamitani, T.; Kito, K.; Fukuda-Kamitani, T.; Yeh, E.T.H. Targeting of NEDD8 and its conjugates for proteasomal degradation by NUB1. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 46655–46660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanji, K.; Tanaka, T.; Kamitani, T. Interaction of NUB1 with the proteasome subunit S5a. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 337, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidtke, G.; Kalveram, B.; Weber, E.; Bochtler, P.; Lukasiak, S.; Hipp, M.S.; Groettrup, M. The UBA domains of NUB1L are required for binding but not for accelerated degradation of the ubiquitin-like modifier FAT10. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 20045–20054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Den Besten, W.; Verma, R.; Kleiger, G.; Oania, R.S.; Deshaies, R.J. NEDD8 links cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase function to the p97 pathway. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oved, S.; Mosesson, Y.; Zwang, Y.; Santonico, E.; Shtiegman, K.; Marmor, M.D.; Kochupurakkal, B.S.; Katz, M.; Lavi, S.; Cesareni, G.; et al. Conjugation to Nedd8 Instigates Ubiquitylation and Down-regulation of Activated Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 21640–21651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.K.; Zerath, S.; Kleifeld, O.; Scheffner, M.; Glickman, M.H.; Fushman, D. Recognition and cleavage of related to ubiquitin 1 (Rub1) and Rub1-ubiquitin chains by components of the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2012, 11, 1595–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, T.; Guan, J.; Huang, Z.; Hu, X.; Zheng, X. RNF168-mediated H2A neddylation antagonizes ubiquitylation of H2A and regulates DNA damage repair. J. Cell. Sci. 2014, 127, 2238–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kelsall, I.R.; Duda, D.M.; Olszewski, J.L.; Hofmann, K.; Knebel, A.; Langevin, F.E.D.E.R.; Wood, N.; Wightman, M.; Schulman, B.A.; Alpi, A.F. TRIAD1 and HHARI bind to and are activated by distinct neddylated Cullin-RING ligase complexes. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 2848–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santonico, E.; Nepravishta, R.; Mandaliti, W.; Castagnoli, L.; Cesareni, G.; Paci, M. CUBAN, a Case Study of Selective Binding: Structural Details of the Discrimination between Ubiquitin and NEDD8. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nepravishta, R.; Ferrentino, F.; Mandaliti, W.; Mattioni, A.; Weber, J.; Polo, S.; Castagnoli, L.; Cesareni, G.; Paci, M.; Santonico, E. CoCUN, a Novel Ubiquitin Binding Domain Identified in N4BP1. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shih, S.C.; Hurley, J.H.; Hicke, L. A ubiquitin-binding motif required for intramolecular monoubiquitylation, the CUE domain. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walden, H.; Huang, D.T.; Schulman, B.A. The Structure of the APPBP1-UBA3-NEDD8-ATP Complex Reveals the Basis for Selective Ubiquitin-like Protein Activation by an E1. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.T.; Hunt, H.W.; Zhuang, M.; Ohi, M.D.; Holton, J.M.; Schulman, B.A. Basis for a ubiquitin-like protein thioester switch toggling E1–E2 affinity. Nature 2007, 445, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.T.; Zhuang, M.; Ayrault, O.; Schulman, B.A. Identification of conjugation specificity determinants unmasks vestigial preference for ubiquitin within the NEDD8 E2. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 280–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souphron, J.; Waddell, M.B.; Paydar, A.; Tokgöz-Gromley, Z.; Roussel, M.F.; Schulman, B.A. Structural dissection of a gating mechanism preventing misactivation of ubiquitin by NEDD8’s E1. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 8961–8969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kamadurai, H.B.; Souphron, J.; Scott, D.C.; Duda, D.M.; Miller, D.J.; Stringer, D.; Piper, R.C.; Schulman, B.A. Insights into ubiquitin transfer cascades from a structure of a UbcH5B approximately ubiquitin-HECT(NEDD4L) complex. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woelk, T.; Oldrini, B.; Maspero, E.; Confalonieri, S.; Cavallaro, E.; Di Fiore, P.P.; Polo, S. Molecular mechanisms of coupled monoubiquitination. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haglund, K.; Stenmark, H. Working out coupled monoubiquitination. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1218–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mayoral, M.F.; Hollingworth, D.; Masino, L.; Díaz-Moreno, I.; Kelly, G.; Gherzi, R.; Chou, C.-F.; Chen, C.-Y.; Ramos, A. The Structure of the C-Terminal KH Domains of KSRP Reveals a Noncanonical Motif Important for mRNA Degradation. Structure 2007, 15, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valverde, R.; Edwards, L.; Regan, L. Structure and function of KH domains. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 2712–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grishin, N. KH domain: One motif, two folds. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matelska, D.; Steczkiewicz, K.; Ginalski, K. Comprehensive classification of the PIN domain-like superfamily. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 6995–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jura, J.; Skalniak, L.; Koj, A. Monocyte chemotactic protein-1-induced protein-1 (MCPIP1) is a novel multifunctional modulator of inflammatory reactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Res. 2012, 1823, 1905–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matsushita, K.; Takeuchi, O.; Standley, D.M.; Kumagai, Y.; Kawagoe, T.; Miyake, T.; Satoh, T.; Kato, H.; Tsujimura, T.; Nakamura, H.; et al. Zc3h12a is an RNase essential for controlling immune responses by regulating mRNA decay. Nature 2009, 458, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.-J.; Chien, H.-L.; Lin, S.-Y.; Chang, B.-L.; Yu, H.-P.; Tang, W.-C.; Lin, Y.-L. MCPIP1 ribonuclease exhibits broad-spectrum antiviral effects through viral RNA binding and degradation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 3314–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, H.I.; Arase, M.; Matsuyama, H.; Choi, Y.L.; Ueno, T.; Mano, H.; Sugimoto, K.; Miyazono, K. MCPIP1 Ribonuclease Antagonizes Dicer and Terminates MicroRNA Biogenesis through Precursor MicroRNA Degradation. Mol. Cell 2011, 44, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillas, R.; Simms, K.S.; Hatakeyama, S.; Weissman, A.M.; Kuehn, M.R. Identification of Developmentally Expressed Proteins That Functionally Interact with Nedd4 Ubiquitin Ligase. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 2897–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oberst, A.; Malatesta, M.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Rossi, M.; Salomoni, P.; Murillas, R.; Sharma, P.; Kuehn, M.R.; Oren, M.; Croce, C.M.; et al. The Nedd4-binding partner 1 (N4BP1) protein is an inhibitor of the E3 ligase Itch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11280–11285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; Murillas, R.; Zhang, H.; Kuehn, M.R. N4BP1 is a newly identified nucleolar protein that undergoes SUMO-regulated polyubiquitylation and proteasomal turnover at promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies. J. Cell. Sci. 2010, 123, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ficarelli, M.; Wilson, H.; Galão, R.P.; Mazzon, M.; Antzin-Anduetza, I.; Marsh, M.; Neil, S.J.; Swanson, C.M. KHNYN is essential for the zinc finger antiviral protein (ZAP) to restrict HIV-1 containing clustered CpG dinucleotides. eLife 2019, 8, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharaman, V.; Aravind, L. The NYN domains: Novel predicted RNAses with a PIN domain-like fold. RNA. Biol. 2006, 3, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gobert, A.; Bruggeman, M.; Giegé, P. Involvement of PIN-like domain nucleases in tRNA processing and translation regulation. IUBMB Life 2019, 24, 1832–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Saad, Y.; Lei, T.; Wang, J.; Qi, D.; Yang, Q.; Kolattukudy, P.E.; Fu, M. MCP-induced protein 1 deubiquitinates TRAF proteins and negatively regulates JNK and NF-κB signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2959–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spel, L.; Nieuwenhuis, J.; Haarsma, R.; Stickel, E.; Bleijerveld, O.B.; Altelaar, M.; Boelens, J.J.; Brummelkamp, T.R.; Nierkens, S.; Boes, M. Nedd4 Binding Protein 1 (N4BP1) and TNFAIP3 Interacting Protein 1 (TNIP1) control MHC-1 display in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6621–6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirza, S.P.; Halligan, B.D.; Greene, A.S.; Olivier, M. Improved method for the analysis of membrane proteins by mass spectrometry. Physiol. Genom. 2007, 30, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, A.; Marín, I. CGIN1: A retroviral contribution to mammalian genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 2167–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucy, T.A.; Smith, P.G.; Rolfe, M. Targeting NEDD8-activated cullin-RING ligases for the treatment of cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3912–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swords, R.; Kelly, K.; Smith, P.G.; Gamsey, J.J.; Mahalingam, D.; Medina, E.; Oberheu, K.; Padmanabhan, S.; ODwyer, M.; Nawrocki, S.T.; et al. Inhibition of NEDD8-activating enzyme: A novel approach for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2010, 115, 3796–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Jia, L. Protein neddylation and its alterations in human cancers for targeted therapy. Cell. Signal. 2018, 44, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucy, T.A.; Smith, P.G.; Milhollen, M.A.; Berger, A.J.; Gavin, J.M.; Adhikari, S.; Brownell, J.E.; Burke, K.E.; Cardin, D.P.; Critchley, S.; et al. An inhibitor of NEDD8-activating enzyme as a new approach to treat cancer. Nature 2009, 458, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milhollen, M.A.; Traore, T.; Adams-Duffy, J.; Thomas, M.P.; Berger, A.J.; Dang, L.; Dick, L.R.; Garnsey, J.J.; Koenig, E.; Langston, S.P.; et al. MLN4924, a NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor, is active in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma models: Rationale for treatment of NF-κB–dependent lymphoma. Blood 2010, 116, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xirodimas, D.P.; Saville, M.K.; Bourdon, J.-C.; Hay, R.T.; Lane, D.P. Mdm2-Mediated NEDD8 Conjugation of p53 Inhibits Its Transcriptional Activity. Cell 2004, 118, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shu, J.; Liu, C.; Wei, R.; Xie, P.; He, S.; Zhang, L. Nedd8 targets ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 for neddylation and promote its degradation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 474, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Cao, Y.; Xie, P.; Dong, G.; Zhang, L. The Nedd8 Non-covalent Binding Region in the Smurf HECT Domain is Critical to its Ubiquitn Ligase Function. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loftus, S.J.; Liu, G.; Carr, S.M.; Munro, S.; La Thangue, N.B. NEDDylation regulates E2F-1-dependent transcription. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Yang, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Song, A.-X.; Hu, H.-Y. NEDD8 ultimate buster-1 long (NUB1L) protein promotes transfer of NEDD8 to proteasome for degradation through the P97UFD1/NPL4 complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 31339–31349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rotin, D.; Kumar, S. Physiological functions of the HECT family of ubiquitin ligases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Matesic, L.E. The Nedd4-like family of E3 ubiquitin ligases and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007, 26, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernassola, F.; Karin, M.; Ciechanover, A.; Melino, G. The HECT Family of E3 Ubiquitin Ligases: Multiple Players in Cancer Development. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluimer, J. Ben Distel Regulating the human HECT E3 ligases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 3121–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Type-I UBL | Protein Name | Binding Domain | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| UBQ | Ubiquitin | UBDs | [15] |
| NEDD8 | Neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated 8 | CUBAN, UIM, UBA | [61,62,63,64] |
| FAT10 | Human Leukocyte Antigen F Locus Adjacent Transcript 10 | UBA | [65] |
| ISG15 | Interferon-stimulated gene 15 | Specific ISG15-interacting motifs have not been identified | |
| SUMOs | Small ubiquitin-like modifiers | SIM (SUMO-interacting motif) | [66] |
| Atg8 | Autophagy-related protein 8 | AIM (ATG8-family interacting motif) | [67] |
| Atg12 | Autophagy-related protein 12 | Specific Atg12-interacting motifs have not been identified | |
| URM1 | Ubiquitin-related modifier-1 | Specific URM1-interacting motifs have not been identified | |
| UFM1 | Ubiquitin-fold modifier 1 | Specific UFM1-interacting motifs have not been identified |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santonico, E. Old and New Concepts in Ubiquitin and NEDD8 Recognition. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040566
Santonico E. Old and New Concepts in Ubiquitin and NEDD8 Recognition. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(4):566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040566
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantonico, Elena. 2020. "Old and New Concepts in Ubiquitin and NEDD8 Recognition" Biomolecules 10, no. 4: 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040566
APA StyleSantonico, E. (2020). Old and New Concepts in Ubiquitin and NEDD8 Recognition. Biomolecules, 10(4), 566. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10040566




