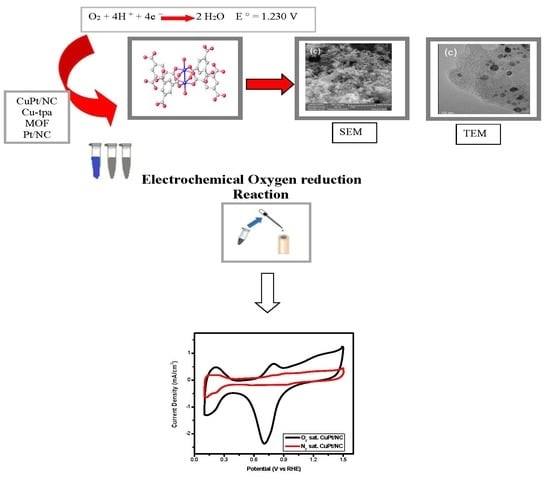
MOF-Derived CuPt/NC Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
Electrode Preparation and Electrochemical Evaluation
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
3.3. Synthesis of Cu-tpa MOF
3.4. Synthesis of CuPt/NC
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Chen, K.S.; Mishler, J.; Cho, S.C.; Adroher, X.C. A review of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells: Technology, applications, and needs on fundamental research. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 981–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, M.; Brodd, R.J. What Are Batteries, Fuel Cells, and Supercapacitors? ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Savinell, R.F.; Ota, K.-I.; Kreysa, G. Encyclopedia of Applied Electrochemistry; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Rizvi, S.A.M.; Iqbal, N.; Haider, M.D.; Noor, T.; Anwar, R.; Hanif, S. Synthesis and Characterization of Cu-MOF Derived Cu@ AC Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction in PEMFC. Catal. Lett. 2019, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Sumboja, A.; Wuu, D.; An, T.; Li, B.; Goh, F.T.; Hor, T.A.; Zong, Y.; Liu, Z. Oxygen reduction in alkaline media: From mechanisms to recent advances of catalysts. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 4643–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khotseng, L. Oxygen Reduction Reaction. In Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cells and Hydrogen Evolution—Theory to Design; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, B.Y.; Yan, Y.; Li, N.; Wu, H.B.; Lou, X.W.D.; Wang, X. A metal–organic framework-derived bifunctional oxygen electrocatalyst. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntivich, J.; Gasteiger, H.A.; Yabuuchi, N.; Nakanishi, H.; Goodenough, J.B.; Shao-Horn, Y. Design principles for oxygen-reduction activity on perovskite oxide catalysts for fuel cells and metal-air batteries. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daud, W.R.W.; Rosli, R.; Majlan, E.; Hamid, S.; Mohamed, R.; Husaini, T. PEM fuel cell system control: A review. Renew. Energy 2017, 113, 620–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wu, W.; Tang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Burns, R.; Tichnell, B.; Liu, Z.; Chen, S. Oxygen reduction reaction and hydrogen evolution reaction catalyzed by Pd–Ru nanoparticles encapsulated in porous carbon nanosheets. Catalysts 2018, 8, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xia, Z.; Dai, L. Carbon-based electrocatalysts for advanced energy conversion and storage. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, M.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, C.; Fan, J.; Wang, G.; Chen, J.; Wang, R. Recent developments in electrocatalysts and future prospects for oxygen reduction reaction in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J. Energy Chem. 2018, 27, 1124–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Ramírez, A.; Sánchez-Castro, M.; Alonso-Lemus, I.; Aruna, K.K.; Karthikeyan, P.; Manoharan, R.; Rodríguez-Varela, F. Evaluation of the nickel titanate-modified Pt nanostructured catalyst for the ORR in alkaline media. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, F16–F24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhavale, V.M.; Kurungot, S. Cu–Pt nanocage with 3-D electrocatalytic surface as an efficient oxygen reduction electrocatalyst for a primary Zn–Air battery. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, P.G.; Freunberger, S.A.; Hardwick, L.J.; Tarascon, J.-M. Li-O2 and Li-S batteries with high energy storage. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Pérez-Salcedo, K.; Hanif, S.; Anwar, R.; Cindrella, L.; Iqbal, N.; Jose, S.; Kannan, A. Progress on the Functionalization of Carbon Nanostructures for Fuel Cell Electrocatalysts. In Advanced Electrocatalysts for Low-Temperature Fuel Cells; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 215–234. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M. Novel Nanostructured Electrocatalysts for Fuel Cells. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wollongong, Wollongong, Australia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Mamtani, K.; Bruening, C.; Co, A. A Comparison of Oxygen Reduction Reaction (ORR) Performance for Iron-Nitrogen-Carbon (FeNC) Catalysts in Acidic and Alkaline Media. Res. Rev. Electrochem. 2017, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yaqoob, L.; Noor, T.; Iqbal, N.; Nasir, H.; Zaman, N. Development of Nickel-BTC-MOF-Derived Nanocomposites with rGO Towards Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Methanol and Its Product Analysis. Catalysts 2019, 9, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Iqbal, N.; Asghar, A.; Noor, T. Novel amine functionalized metal organic framework synthesis for enhanced carbon dioxide capture. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, T.; Ammad, M.; Zaman, N.; Iqbal, N.; Yaqoob, L.; Nasir, H. A Highly Efficient and Stable Copper BTC Metal Organic Framework Derived Electrocatalyst for Oxidation of Methanol in DMFC Application. Catal. Lett. 2019, 149, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noor, T.; Zaman, N.; Nasir, H.; Iqbal, N.; Hussain, Z. Electro catalytic study of NiO-MOF/rGO composites for methanol oxidation reaction. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 307, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-F.; Chen, L.; Pang, H.; Kaskel, S.; Xu, Q. MOF-derived electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction, oxygen evolution and hydrogen evolution reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1414–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Dong, X.Y.; Du, J.; Zhao, J.Y.; Zang, S.Q. MOF-Derived bifunctional Cu3P nanoparticles coated by a N, P-codoped carbon shell for hydrogen evolution and oxygen reduction. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1703711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, K.; Zack, J.W.; Richards, R.M.; Pivovar, B.S.; Kocha, S.S. Oxygen reduction reaction measurements on platinum electrocatalysts utilizing rotating disk electrode technique I. Impact of impurities, measurement protocols and applied corrections. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, F1144–F1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, I.B.; Schoonen, M.A.; Rickard, D.T. Removal of dissolved oxygen from water: A comparison of four common techniques. Talanta 1994, 41, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Gao, F.; Gao, F.; Yang, Y.; Guo, H. Highly dispersible and stable copper terephthalate metal–organic framework–graphene oxide nanocomposite for an electrochemical sensing application. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 11573–11580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M.; Jaroniec, M. Gas adsorption characterization of ordered organic–inorganic nanocomposite materials. Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3169–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Meng, S.; Wang, H.; He, Y. Metal organic frameworks enhanced graphene oxide electrode for humidity sensor. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 986, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, C.; Rao, K.V.; Chakra, C.S. Structural analysis of CuO nanomaterials prepared by novel microwave assisted method. J. Atoms Mol. 2014, 4, 803–806. [Google Scholar]
- Su, L.; Shrestha, S.; Zhang, Z.; Mustain, W.; Lei, Y. Platinum–copper nanotube electrocatalyst with enhanced activity and durability for oxygen reduction reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 12293–12301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Qi, W.; Wu, H.; He, J.; Li, Y.; Xie, H. One-pot synthesis of CuPt nanodendrites with enhanced activity towards methanol oxidation reaction. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 9293–9298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakisaka, M.; Mitsui, S.; Hirose, Y.; Kawashima, K.; Uchida, H.; Watanabe, M. Electronic structures of Pt–Co and Pt–Ru alloys for CO-tolerant anode catalysts in polymer electrolyte fuel cells studied by EC–XPS. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 23489–23496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, A.; Sharma, S.; Papakonstantinou, P.; Hamilton, J. Probing the thermal deoxygenation of graphene oxide using high-resolution in situ X-ray-based spectroscopies. J. Phy. Chem. C 2011, 115, 17009–17019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zheng, Y.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S.-Z. Determination of the electron transfer number for the oxygen reduction reaction: From theory to experiment. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 4720–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Zhao, J.; Liu, S.; Sun, W.; Li, H.; Hao, P.; Li, Z.; Ren, J. Nitrogen-doped graphene supported copper catalysts for methanol oxidative carbonylation: Enhancement of catalytic activity and stability by nitrogen species. Carbon 2018, 130, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sa, Y.J.; Seo, D.-J.; Woo, J.; Lim, J.T.; Cheon, J.Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Kang, D.; Shin, T.J.; Shin, H.S. A general approach to preferential formation of active Fe–N x sites in Fe–N/C electrocatalysts for efficient oxygen reduction reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 15046–15056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.; Rocha, I.M.; Fernandes, D.M.; Mestre, A.S.; Moura, C.N.; Carvalho, A.P.; Pereira, M.F.; Freire, C. Sucrose-derived activated carbons: Electron transfer properties and application as oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 102919–102931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiwata, M.; Kakinuma, K.; Wakisaka, M.; Uchida, M.; Deki, S.; Watanabe, M.; Uchida, H. Oxygen reduction reaction activity and durability of Pt catalysts supported on titanium carbide. Catalysts 2015, 5, 966–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinagawa, T.; Garcia-Esparza, A.T.; Takanabe, K. Insight on Tafel slopes from a microkinetic analysis of aqueous electrocatalysis for energy conversion. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehek, R.; Iqbal, N.; Noor, T.; Nasir, H.; Mehmood, Y.; Ahmed, S. Novel Co-MOF/graphene oxide electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 255, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanif, S.; Shi, X.; Iqbal, N.; Noor, T.; Anwar, R.; Kannan, A. ZIF derived PtNiCo/NC cathode catalyst for proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 258, 117947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Elements | Cu-tpa MOF | Cu/NC | CuPt/NC |
|---|---|---|---|
| C wt % | 71.46 | 66.88 | 51.01 |
| O wt % | 9.52 | 9.60 | 8.01 |
| Cu wt % | 19.01 | 23.51 | 39.95 |
| Pt wt % | - | - | 1.03 |
| Electrochemical Properties | CuPt/NC | Pt/C |
|---|---|---|
| Onset potential | 0.9 V (vs. RHE) | 0.85 V (vs. RHE) |
| Peak current density | 4.2 mA cm−2 | 4.32 mA cm−2 |
| Tafel slope | 213 mV dec−1 | 190 mV dec−1 |
| Electron transfer number | ~4 | 4 |
| Charge transfer coefficient | 0.035 | 0.027 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anwar, R.; Iqbal, N.; Hanif, S.; Noor, T.; Shi, X.; Zaman, N.; Haider, D.; M. Rizvi, S.A.; Kannan, A.M. MOF-Derived CuPt/NC Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Catalysts 2020, 10, 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10070799
Anwar R, Iqbal N, Hanif S, Noor T, Shi X, Zaman N, Haider D, M. Rizvi SA, Kannan AM. MOF-Derived CuPt/NC Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Catalysts. 2020; 10(7):799. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10070799
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnwar, Rehan, Naseem Iqbal, Saadia Hanif, Tayyaba Noor, Xuan Shi, Neelam Zaman, Daarain Haider, Syed Aun M. Rizvi, and A. M. Kannan. 2020. "MOF-Derived CuPt/NC Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction" Catalysts 10, no. 7: 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10070799
APA StyleAnwar, R., Iqbal, N., Hanif, S., Noor, T., Shi, X., Zaman, N., Haider, D., M. Rizvi, S. A., & Kannan, A. M. (2020). MOF-Derived CuPt/NC Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Catalysts, 10(7), 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10070799