Neuroinflammatory Mechanisms in Ischemic Stroke: Focus on Cardioembolic Stroke, Background, and Therapeutic Approaches
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Neuroinflammation in Ischemic Stroke
3. Roles of Cytokines in Cerebral Ischemia
3.1. TNF-α
3.2. IL-1β
3.3. IL-6
3.4. IFN-γ
4. Role of Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines
5. Pro and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokine Interplay in Ischemic Stroke
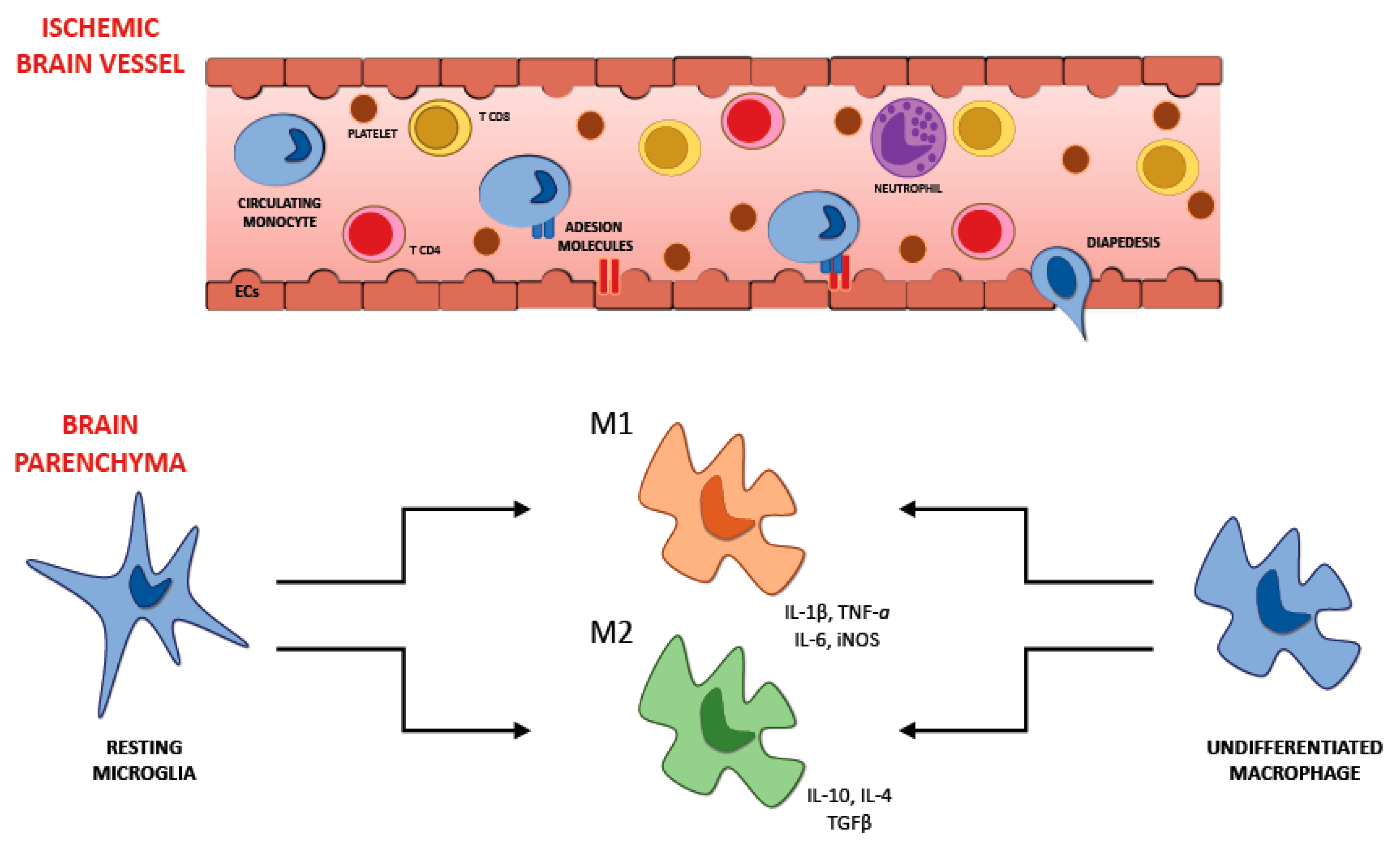
6. Recruitment of Inflammatory Cells in Ischemic Brain Injury
6.1. Microglia
6.2. Astrocytes
6.3. Neutrophils
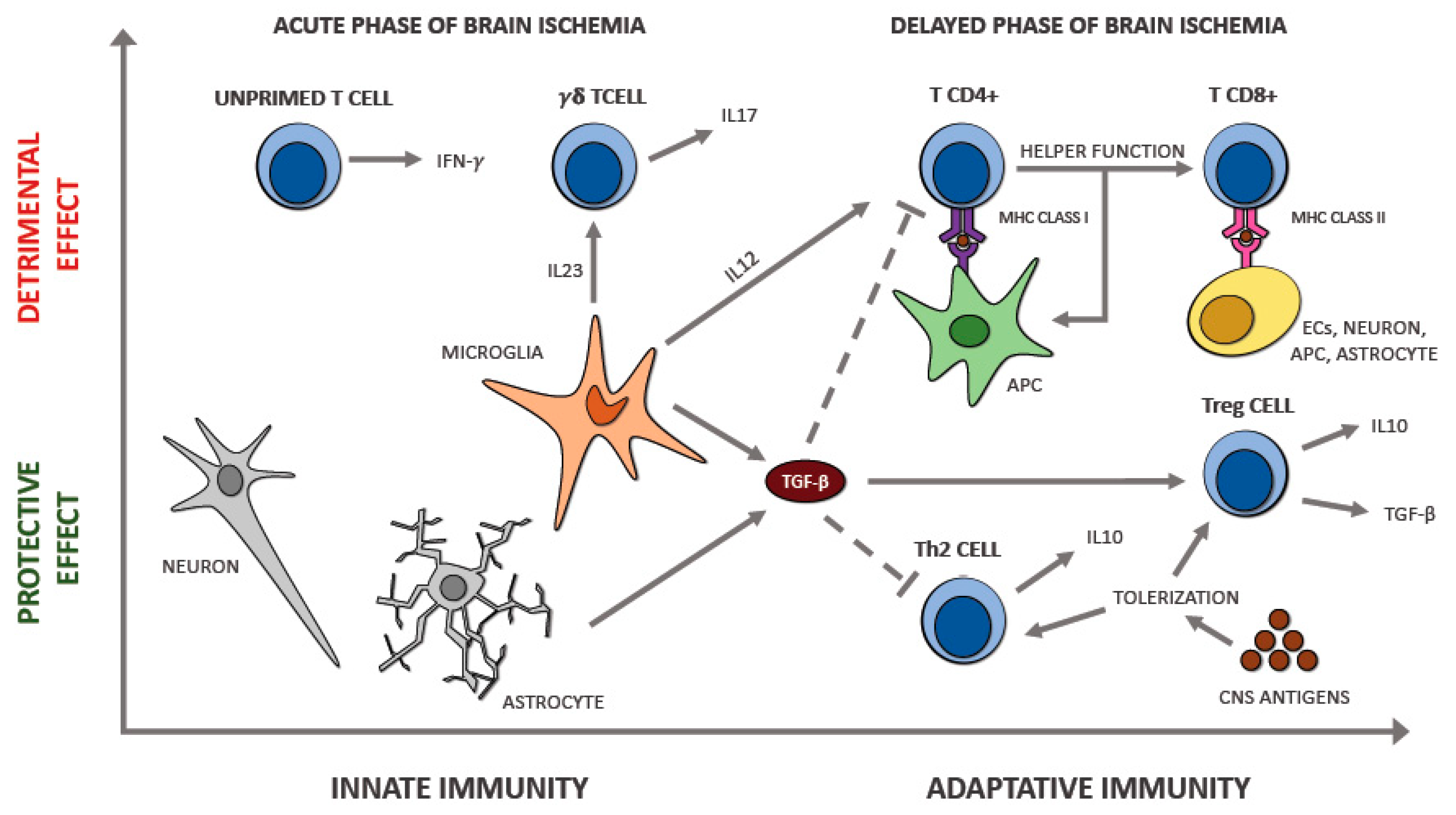
6.4. T Lymphocytes
7. The Interplay between Immune Cell Populations in Ischemic Stroke
8. The Interaction between Brain and Heart: Cardiac Complications after Stroke
8.1. Myocardial Injury as a Consequence of Brain Damage
8.2. Ischemic Stroke Caused Cardiac Injury
8.3. Mechanisms Underlying Brain–Heart Interaction
9. Cardioembolic Stroke
9.1. Risk Factors for Cardioembolic Stroke
9.1.1. Atrial Fibrillation
9.1.2. Heart Failure
9.1.3. Patent Foramen Ovale
9.1.4. Myocardial Infarction
9.1.5. Prosthetic Heart Valves
9.1.6. Infective Endocarditis
9.1.7. Other Causes
10. Diagnostic Criteria for Cardioembolic Stroke
11. Inflammation Background in Cardioembolic Stroke
12. Therapeutic Strategy for Cardioembolic Stroke
13. Potential Treatment Strategies in Neuroinflammation after Ischemic Stroke
14. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McKay, J.; Mensah, G.A.; Mendis, S.; Greenlund, K.; World Health Organization. The Atlas of Heart Disease and Stroke; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Go, A.S.; Arnett, D.K.; Blaha, M.J.; Cushman, M.; Das, S.R.; De Ferranti, S.; Després, J.-P.; Fullerton, H.J.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2016 Update. Circulation 2016, 133, E38–E360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthi, R.V.; Feigin, V.L.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Mensah, G.A.; Connor, M.; Bennett, D.A.; Moran, A.E.; Sacco, R.L.; Anderson, L.M.; Truelsen, T.; et al. Global and regional burden of first-ever ischaemic and haemorrhagic stroke during 1990–2010: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet Glob. Health 2013, 1, e259–e281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynch, J.R.; Blessing, R.; White, W.D.; Grocott, H.P.; Newman, M.F.; Laskowitz, D.T. Novel Diagnostic Test for Acute Stroke. Stroke 2004, 35, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bogousslavsky, J.; Van Melle, G.; Regli, F. The Lausanne Stroke Registry: Analysis of 1000 consecutive patients with first stroke. Stroke 1988, 19, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Passero, S.; Rossi, G.; Nardini, M.; Bonelli, G.; D’Ettorre, M.; Martini, A.; Battistini, N.; Albanese, V.; Bono, G.; Brambilla, G.L. Italian multicenter study of reversible cerebral ischemic attacks. Part 5. Risk factors and cerebral atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 1987, 63, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, J.M. Cardioembolic stroke: An update. Lancet Neurol. 2003, 2, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoo, C.W.; Lip, G.Y.H. Clinical outcomes of acute stroke patients with atrial fibrillation. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. 2009, 7, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, S.; Marini, C.; Totaro, R.; Russo, T.; Cerone, D.; Carolei, A. A population-based study of the incidence and prognosis of lacunar stroke. Neurology 2006, 66, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, G.W.; Brown, R.D.; Whisnant, J.P.; Sicks, J.D.; O’Fallon, W.M.; O Wiebers, D. Ischemic stroke subtypes: A population-based study of incidence and risk factors. Stroke 1999, 30, 2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.-J.; Wolf, P.A.; Kelly-Hayes, M.; Beiser, A.; Kase, C.S.; Benjamin, E.J.; D’Agostino, S.R.B. Stroke Severity in Atrial Fibrillation. Stroke 1996, 27, 1760–1764. [Google Scholar]
- Bogiatzi, C.; Hackam, D.G.; McLeod, A.I.; Spence, J.D. Secular Trends in Ischemic Stroke Subtypes and Stroke Risk Factors. Stroke 2014, 45, 3208–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moskowitz, M.A.; Lo, E.H.; Iadecola, C. The science of stroke: Mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 2010, 67, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucas, D.R.; Newhouse, J.P. The Toxic Effect of Sodium L-Glutamate on the Inner Layers of the Retina. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1957, 58, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrenius, S.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Nicotera, P. Regulation of cell death: The calcium–apoptosis link. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 4, 552–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.J.; Kim, J.-E.; Cittolin-Santos, G.F.; Swanson, R.A. Assessment at the Single-Cell Level Identifies Neuronal Glutathione Depletion as Both a Cause and Effect of Ischemia-Reperfusion Oxidative Stress. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 7143–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mishra, M.; Hedna, V.S. Neuroinflammation after acute ischemic stroke: A volcano hard to contain. Chin. J. Contemp. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2013, 13, 964. [Google Scholar]
- Iadecola, C.; Anrather, J. The immunology of stroke: From mechanisms to translation. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, H.L.; Selkoe, D.J. Inflammation and therapeutic vaccination in CNS diseases. Nature 2002, 420, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Maida, C.; Pinto, A. Inflammation and Inflammatory Cell Recruitment in Acute Cerebrovascular Diseases. Curr. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 11, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davalos, D.; Grutzendler, J.; Yang, G.; Kim, J.V.; Zuo, Y.; Jung, S.; Littman, D.R.; Dustin, M.L.; Gan, W.-B. ATP mediates rapid microglial response to local brain injury in vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissmann, F.; Gordon, S.; Hume, D.A.; Mowat, A.; Randolph, G.J. Unravelling mononuclear phagocyte heterogeneity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayer, A.; Clifford, J.A.; Aldulescu, M.; Frenkel, J.A.; Holland, M.A.; Hall, M.L.; Glaser, K.B.; Berry, J. Cyanobacterial Microcystis aeruginosa Lipopolysaccharide Elicits Release of Superoxide Anion, Thromboxane B2, Cytokines, Chemokines, and Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 by Rat Microglia. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 121, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Na, K.-S.; Jung, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.-K. The role of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the neuroinflammation and neurogenesis of schizophrenia. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 48, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ip, C.W.; Kroner, A.; Groh, J.; Huber, M.; Klein, D.; Spahn, I.; Diem, R.; Williams, S.K.; Nave, K.-A.; Edgar, J.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation by Cytotoxic T-Lymphocytes Impairs Retrograde Axonal Transport in an Oligodendrocyte Mutant Mouse. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Di Raimondo, D.; Di Sciacca, R.; Pinto, A.; Licata, G. Inflammatory cytokines in acute ischemic stroke. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 3574–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, K.; Lee, F.; Miyajima, A.; Miyatake, S.; Arai, N.; Yokota, T. Cytokines: Coordinators of immune and inflammatory responses. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 1990, 59, 783–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, F.C.; Arvin, B.; White, R.F.; Miller, A.; Webb, C.L.; Willette, R.N.; Lysko, P.G.; Feuerstein, G.Z. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha. A mediator of focal ischemic brain injury. Stroke 1997, 28, 1233–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, G.; Arumugam, T.V.; Stokes, K.Y.; Granger, D.N. Role of T lymphocytes and interferon-g in ischemic stroke. Circulation 2006, 113, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lambertsen, K.L.; Gregersen, R.; Meldgaard, M.; Clausen, B.H.; Heibøl, E.K.; Ladeby, R.; Knudsen, J.; Frandsen, A.; Owens, T.; Finsen, B. A role for interferon-g in focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 63, 942–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stone, M.J.; Hayward, J.A.; Huang, C.; Huma, Z.E.; Sanchez, J. Mechanisms of Regulation of the Chemokine-Receptor Network. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Clark, R.K.; McDonnell, P.C.; Young, P.R.; White, R.F.; Barone, F.C.; Feuerstein, G.Z. Tumor necrosis factor-α expression in ischemic neurons. Stroke 1994, 5, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yue, T.-L.; Barone, F.C.; White, R.F.; Gagnon, R.C.; Feuerstein, G.Z. Concomitant cortical expression of TNF-α and IL-1β mRNAs follows early response gene expression in transient focal ischemia. Mol. Chem. Neuropathol. 1994, 23, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Saito, K.; Hara, A.; Zhu, Y.; Sudo, K.; Niwa, M.; Fujii, H.; Wada, H.; Ishiguro, H.; Mori, H.; et al. Increases in tumor necrosis factor-α following transient global cerebral ischemia do not contribute to neuron death in mouse hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Offner, H.; Subramanian, S.; Parker, S.M.; Afentoulis, E.M.; Vandenbark, A.A.; Hurn, P.D. Experimental Stroke Induces Massive, Rapid Activation of the Peripheral Immune System. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 26, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huțanu, A.; Iancu, M.; Bălaşa, R.; Maier, S.; Dobreanu, M. Predicting functional outcome of ischemic stroke patients in Romania based on plasma CRP, sTNFR-1, D-Dimers, NGAL and NSE measured using a biochip array. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sotgiu, S.; Zanda, B.; Marchetti, B.; Fois, M.L.; Arru, G.; Pes, G.M.; Salaris, F.S.; Arru, A.; Pirisi, A.; Rosati, G. Inflammatory biomarkers in blood of patients with acute brain ischemia. Eur. J. Neurol. 2006, 13, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, R.S.; Purohit, H.J.; Daginawala, H.F.; Nayak, A.R.; Kabra, D.; Taori, G.M. Time course of inflammatory cytokines in acute ischemic stroke patients and their relation to inter-alfa trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 4 and outcome. Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol. 2012, 15, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barger, S.W.; Horster, D.; Furukawa, K.; Goodman, Y.; Krieglstein, J.; Mattson, M.P. Tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta protect neurons against amyloid beta-peptide toxicity: Evidence for involvement of a kappa B-binding factor and attenuation of peroxide and Ca2+ accumulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 9328–9332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Satoh, T.; Otsuka, A.; Contassot, E.; French, L.E. The inflammasome and IL-1beta: Implications for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Immunotherapy 2015, 7, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Xiao, H.-T.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, R.-S.; Zhang, L.-J.; Bian, Y.; He, X. IL-1?: A key modulator in asthmatic airway smooth muscle hyper-reactivity. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2015, 9, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Zoppo, G.J. Inflammation and the neurovascular unit in the setting of focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 2009, 158, 972–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ohtaki, H.; Takaki, A.; Yin, L.; Dohi, K.; Nakamachi, T.; Matsunaga, M.; Horai, R.; Asano, M.; Iwakura, Y.; Shioda, S. Suppression of oxidative stress after transient focal ischemia in interleukin-1 knock out mice. Acta Neurosirurgica. Suppl. 2003, 86, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Matsuura, N.; Shozuhara, H.; Onodera, H.; Itoyama, Y.; Kogure, K. Interleukin-1 as a Pathogenetic Mediator of Ischemic Brain Damage in Rats. Stroke 1995, 26, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Lazovic, J.; Krady, J.K.; Mauger, D.T.; Rothstein, R.P.; Smith, M.B.; Levison, S.W. Interleukin-1 and the Interleukin-1 Type 1 Receptor are Essential for the Progressive Neurodegeneration that Ensues Subsequent to a Mild Hypoxic/Ischemic Injury. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 25, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothwell, N.J. Interleukin-1 and neuronal injury: Mechanisms, modification, and therapeutic potential. Brain Behav. Immun. 2003, 17, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protopsaltis, J.; Kokkoris, S.; Korantzopoulos, P.; Milionis, H.J.; Karzi, E.; Anastasopoulou, A.; Filioti, K.; Antonopoulos, S.; Melidonis, A.; Giannoulis, G. Prediction of long-term functional outcome in patients with acute ischemic non-embolic stroke. Atherosclerosis 2009, 203, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzi, P.; Cain, K.; Kalil, A.; Zierath, D.; Savos, A.; Gee, J.M.; Shibata, D.; Hadwin, J.; Carter, K.; Becker, K.J. Post-stroke infection: A role for IL-1ra? Neurocrit. Care 2011, 14, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erta, M.; Quintana, A.; Hidalgo, J. Interleukin-6, a Major Cytokine in the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1254–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, S.; Tanaka, K.; Suzuki, N. Ambivalent aspects of interleukin-6 in cerebral ischemia: Inflammatory versus neurotrophic aspects. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2009, 29, 464–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrmann, O.; Tarabin, V.; Suzuki, S.; Attigah, N.; Coserea, I.; Schneider, A.; Vogel, J.; Prinz, S.; Scwab, S.; Monyer, H.; et al. Regulation of body temperature and neuroprotection by endogenous interleukin-6 in cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2003, 23, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loddick, S.A.; Turnbull, A.V.; Rothwell, N.J. Cerebral Interleukin-6 is Neuroprotective during Permanent Focal Cerebral Ischemia in the Rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 18, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.-H.; Jiang, N.; Zheng, X.-L.; Cayabyab, F.S.; Tang, Z.-B.; Tang, C.-K. Interleukin-17A in lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 431, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, W.M.; Chevillotte, M.D.; Rice, C.M. Interferon-stimulated genes: A complex web of host defenses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 513–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Folsom, A.R.; Gottesman, R.F.; Appiah, D.; Shahar, E.; Mosley, T.H. Plasma d-Dimer and Incident Ischemic Stroke and Coronary Heart Disease: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Stroke 2015, 47, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schroeter, M.; Jander, S.; Witte, O.; Stoll, G. Local immune responses in the rat cerebral cortex after middle cerebral artery occlusion. J. Neuroimmunol. 1994, 55, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T.R.; Sad, S. The expanding universe of T-cell subsets: Th1, Th2 and more. Immunol. Today 1996, 17, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Garra, A.; Vieira, P.L.; Vieira, P.; Goldfeld, A.E. IL-10–producing and naturally occurring CD4+ Tregs: Limiting collateral damage. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 1372–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grilli, M.; Barbieri, I.; Basudev, H.; Brusa, R.; Casati, C.; Lozza, G.; Ongini, E. Interleukin-10 modulates neuronal threshold of vulnerability to ischaemic damage. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 2265–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, C.E.; Bednar, M.M.; Howard, D.B.; Sporn, M.B. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 reduces infarct size after experimental cerebral ischemia in a rabbit model. Stroke 1993, 24, 558–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nair, M.G.; Guild, K.J.; Artis, D. Novel Effector Molecules in Type 2 Inflammation: Lessons Drawn from Helminth Infection and Allergy1. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cekanaviciute, E.; Buckwalter, M.S. Astrocytes: Integrative Regulators of Neuroinflammation in Stroke and Other Neurological Diseases. Neurotherapeuthics 2016, 13, 685–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Kakkar, V.; Lu, X. Essential Roles of Toll-Like Receptors in Atherosclerosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2016, 23, 431–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietdijk, C.D.; Van Wezel, R.J.A.; Garssen, J.; Kraneveld, A.D. Neuronal toll-like receptors and neuro-immunity in Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease and stroke. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fassbender, K.; Rossol, S.; Kammer, T.; Daffertshofer, M.; Wirth, S.; Dollman, M.; Hennerici, M. Proinflammatory cytokines in serum of patients with acute cerebral ischemia: Kinetics of secretion and relation to the extent of brain damage and outcome of disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 1994, 122, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beamer, N.B.; Coull, B.M.; Clark, W.M.; Briley, D.P.; Wynn, M.; Sexton, G. Persistent inflammatory response in stroke survivors. Neurology 1998, 50, 1722–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beridze, M.; Sanikidze, T.; Shakarishvili, R.; Intskirveli, N.; Bornstein, N.M. Selected acute phase CSF factors in ischemic stroke: Findings and prognostic value. BMC Neurol. 2011, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mazzotta, G.; Sarchielli, P.; Caso, V.; Paciaroni, M.; Floridi, A.; Gallai, V. Different cytokine levels in thrombolysis patients as predictors for clinical outcome. Eur. J. Neurol. 2004, 11, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kes, V.B.; Simundic, A.-M.; Nikolac, N.; Topić, E.; Demarin, V. Pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines in acute ischemic stroke and their relation to early neurological deficit and stroke outcome. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 41, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruswamy, R.; ElAli, A. Complex Roles of Microglial Cells in Ischemic Stroke Pathobiology: New Insights and Future Directions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schilling, M.; Besselmann, M.; Müller, M.; Strecker, J.K.; Ringelstein, E.B.; Kiefer, R. Predominant phagocytic activity of resident microglia over hematogenous macrophages following transient focal cerebral ischemia: An investigation using green fluorescent protein transgenic bone marrow chimeric mice. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 196, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, P.; Guo, Y.; Wang, H.; Leak, R.K.; Chen, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J. Microglia/Macrophage Polarization Dynamics Reveal Novel Mechanism of Injury Expansion After Focal Cerebral Ischemia. Stroke 2012, 43, 3063–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ransohoff, R.M. A polarizing question: Do M1 and M2 microglia exist? Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 987–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, I.M.; Morimoto, E.T.; Goodarzi, H.; Liao, J.T.; O’Keeffe, S.; Phatnani, H.P.; Muratet, M.; Carroll, M.C.; Levy, S.; Tavazoie, S.; et al. A Neurodegeneration-Specific Gene-Expression Signature of Acutely Isolated Microglia from an Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Mouse Model. Cell Rep. 2013, 4, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamasaki, R.; Lu, H.; Butovsky, O.; Ohno, N.; Rietsch, A.M.; Cialic, R.; Wu, P.M.; Doykan, C.E.; Lin, J.; Cotleur, A.C.; et al. Differential roles of microglia and monocytes in the inflamed central nervous system. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 1533–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, J.; Schmidt, S.V.; Sander, J.; Draffehn, A.; Krebs, W.; Quester, I.; De Nardo, D.; Gohel, T.D.; Emde, M.; Schmidleithner, L.; et al. Transcriptome-based network analysis reveals a spectrum model of human macrophage activation. Immunity 2014, 40, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bylicky, M.; Mueller, G.P.; Day, R.M. Mechanisms of Endogenous Neuroprotective Effects of Astrocytes in Brain Injury. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, E.; Griffin, E.W.; Cunningham, C. Astrocytes Are Primed by Chronic Neurodegeneration to Produce Exaggerated Chemokine and Cell Infiltration Responses to Acute Stimulation with the Cytokines IL-1β and TNF-α. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 8411–8422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Song, G.; Chuang, H.; Chiu, C.; Abdelmaksoud, A.; Ye, Y.; Zhao, L. Portrait of glial scar in neurological diseases. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2018, 31, 2058738418801406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Syková, E. Glial diffusion barriers during aging and pathological states. Prog. Brain Res. 2001, 132, 339–363. [Google Scholar]
- Rempe, R.G.; Hartz, A.M.; Bauer, B. Matrix metalloproteinases in the brain and blood–brain barrier: Versatile breakers and makers. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 36, 1481–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Overman, J.J.; Clarkson, A.N.; Wanner, I.B.; Overman, W.T.; Eckstein, I.; Maguire, J.L.; Dinov, I.D.; Toga, A.W.; Carmichael, S.T. A role for ephrin-A5 in axonal sprouting, recovery, and activity-dependent plasticity after stroke. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E2230–E2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jickling, G.C.; Liu, D.; Ander, B.P.; Stamova, B.; Zhan, X.; Sharp, F.R. Targeting Neutrophils in Ischemic Stroke: Translational Insights from Experimental Studies. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 35, 888–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weston, R.M.; Jones, N.M.; Jarrott, B.; Callaway, J.K. Inflammatory Cell Infiltration after Endothelin-1-Induced Cerebral Ischemia: Histochemical and Myeloperoxidase Correlation with Temporal Changes in Brain Injury. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 27, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Watcharotayangul, J.; Mao, L.; Xu, H.; Vetri, F.; Baughman, V.L.; Paisansathan, C.; Pelligrino, D.A. Post-ischemic vascular adhesion protein-1 inhibition provides neuroprotection in a rat temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion model. J. Neurochem. 2012, 123, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-De-Puig, I.; Miró, F.; Ferrer-Ferrer, M.; Gelpi, E.; Pedragosa, J.; Justicia, C.; Urra, X.; Chamorro, Á.; Planas, A.M. Neutrophil recruitment to the brain in mouse and human ischemic stroke. Acta Neuropathol. 2014, 129, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Connolly, E.S.; Winfree, C.J.; Springer, T.A.; Naka, Y.; Liao, H.; Yan, S.D.; Stern, D.M.; Solomon, R.A.; Gutierrez-Ramos, J.C.; Pinsky, D.J. Cerebral protection in homozygous null ICAM-1 mice after middle cerebral artery occlusion. Role of neutrophil adhesion in the pathogenesis of stroke. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, M.; Leira, R.; Serena, J.; Pumar, J.M.; Lizasoain, I.; Castillo, J.; Dávalos, A. Plasma Metalloproteinase-9 Concentration Predicts Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2003, 34, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gökhan, S.; Ozhasenekler, A.; Durgun, H.M.; Akil, E.; Ustündag, M.; Orak, M. Neutrophil lymphocyte ratios in stroke subtypes and transient ischemic attack. Eur. Rev. Med Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 653–657. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Liao, S.; Wei, C.; Jia, D.; Wood, K.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Shi, F.-D.; Jin, W.-N. Infiltration and persistence of lymphocytes during late-stage cerebral ischemia in middle cerebral artery occlusion and photothrombotic stroke models. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Ono, M.; Setoguchi, R.; Yagi, H.; Hori, S.; Fehervari, Z.; Shimizu, J.; Takahashi, T.; Nomura, T. Foxp3+CD25+CD4+ natural regulatory T cells in dominant self-tolerance and autoimmune disease. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 212, 8–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesz, A.; Suri-Payer, E.; Veltkamp, C. Regulatory T cells are key cerebroprotective immunomodulators in acute experimental stroke. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelderblom, M.; Arunachalam, P.; Magnus, T. γδ T cells as early sensors of tissue damage and mediators of secondary neurodegeneration. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, M.R.; Nakajima, T.; Leibson, P.J.; Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J. Stimulatory killer Ig-like receptors modulate T cell activation through DAP12-dependent and DAP12-independent mechanisms. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 3725–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zal, B.; Kaski, J.C.; Arno, G.; Akiyu, J.P.; Xu, Q.; Cole, D.; Whelan, M.; Russell, N.; Madrigal, A.; Dodi, I.A.; et al. Heat-Shock Protein 60-Reactive CD4 + CD28 null T Cells in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndromes. Circulation 2004, 109, 1230–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weyand, C.M.; Brandes, J.C.; Schmidt, D.; Fulbright, J.W.; Goronzy, J.J. Functional properties of CD4þ CD28- T cells in the ageing immune system. Mech. Ageing Dev. 1998, 102, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowik, M.; Nowacki, P.; Grabarek, J.; Drechsler, H.; Białecka, M.; Widecka, K.; Stankiewicz, J.; Safranow, K. Can We Talk about CD4+CD28– Lymphocytes as a Risk Factor for Ischemic Stroke? Eur. Neurol. 2007, 58, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadareishvili, Z.G.; Li, H.; Wright, V.; Maric, D.; Warach, S.; Hallenbeck, J.M.; Dambrosia, J.; Barker, J.L.; Vaird, A.E. Elevated proinflammatory CD4+CD28– lymphocytes and stroke recurrence and death. Neurology 2004, 63, 1446–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Pecoraro, R.; Casuccio, A.; Di Raimondo, D.; Buttá, C.; Clemente, G.; Della Corte, V.; Guggino, G.; Arnao, V.; Maida, C.; et al. Peripheral Frequency of CD4+ CD28− Cells in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Medicine 2015, 94, e813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakajima, T.; Goek, O.; Zhang, X.; Kopecky, S.L.; Frye, R.L.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. De Novo Expression of Killer Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors and Signaling Proteins Regulates the Cytotoxic Function of CD4 T Cells in Acute Coronary Syndromes. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Di Raimondo, D.; Pecoraro, R.; Casuccio, A.; Di Bona, D.; Aiello, A.; Accardi, G.; Arnao, V.; Clemente, G.; On behalf of KIRIIND (KIR Infectious and Inflammatory Diseases) Collaborative Group. HLA and killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIRs) genotyping in patients with acute ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buck, B.H.; Liebeskind, D.S.; Saver, J.L.; Bang, O.Y.; Yun, S.W.; Starkman, S.; Ali, L.K.; Kim, O.; Villablanca, J.P.; Salamon, N.; et al. Early Neutrophilia Is Associated with Volume of Ischemic Tissue in Acute Stroke. Stroke 2008, 39, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gelderblom, M.; Gallizioli, M.; Ludewig, P.; Thom, V.; Arunachalam, P.; Rissiek, B.; Bernreuther, C.; Glatzel, M.; Korn, T.; Arumugam, T.V.; et al. IL-23 (Interleukin-23)–Producing Conventional Dendritic Cells Control the Detrimental IL-17 (Interleukin-17) Response in Stroke. Stroke 2018, 49, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ay, H.; Koroshetz, W.J.; Benner, T.; Vangel, M.G.; Melinosky, C.; Arsava, E.M.; Ayata, C.; Zhu, M.; Schwamm, L.; Sorensen, A.G. Neuroanatomic correlates of stroke-related myocardial injury. Neurology 2006, 66, 1325–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tranmer, B.I.; Keller, T.S.; Kindt, G.W.; Archer, D. Loss of cerebral regulation during cardiac output variations in focal cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosurg. 1992, 77, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Bilt, I.A.; Hasan, D.; Vandertop, W.P.; Wilde, A.A.; Algra, A.; Visser, F.C.; Rinkel, G.J. Impact of cardiac complications on outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: A meta-analysis. Neurology 2009, 72, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, S.; Toyoda, K.; Ohara, T.; Nagasawa, H.; Ohtani, N.; Kuwashiro, T.; Naritomi, H.; Minematsu, K. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy in acute ischemic stroke. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bilt, I.A.; Hasan, D.; Brink, R.B.V.D.; Cramer, M.J.; Van Der Jagt, M.; Van Kooten, F.; Regtien, J.G.; Berg, M.P.V.D.; Groen, R.J.; Cate, F.J.T.; et al. Time Course and Risk Factors for Myocardial Dysfunction After Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 2015, 76, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milionis, H.; Faouzi, M.; Cordier, M.; D’Ambrogio-Remillard, S.; Eskandari, A.; Michel, P. Characteristics and early and long-term outcome in patients with acute ischemic stroke and low ejection fraction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolín, A.; Norris, J.W. Myocardial damage from acute cerebral lesions. Stroke 1984, 15, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prosser, J.; MacGregor, L.; Lees, K.R.; Diener, H.-C.; Hacke, W.; Davis, S.M.; on behalf of the VISTA Investigators. Predictors of Early Cardiac Morbidity and Mortality After Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2007, 38, 2295–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavy, S.; Yaar, I.; Melamed, E.; Stern, S. The Effect of Acute Stroke on Cardiac Functions as Observed in an Intensive Stroke Care Unit. Stroke 1974, 5, 775–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rauh, G.; Fischereder, M.; Spengel, F.A. Transesophageal Echocardiography in Patients with Focal Cerebral Ischemia of Unknown Cause. Stroke 1996, 27, 691–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schömig, A. Catecholamines in myocardial ischemia. Systemic and cardiac release. Circulation 1990, 82, 13–22. [Google Scholar]
- Mertes, P.M.; Carteaux, J.P.; Jaboin, Y.; Pinelli, G.; El Abassi, K.; Dopff, C.; Atkinson, J.; Villemot, J.P.; Burlet, C.; Boulange, M. Estimation of myocardial interstitial norepinephrine release after brain death using cardiac microdialysis. Transplantation 1994, 57, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, W.; Van Bogaert, A.; De Groodt-Lasseel, M. Myocardial ultrastructure and haemodynamic reactions during experimental subarachnoid haemorrhage. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 1972, 4, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachinski, V.C.; Smith, K.E.; Silver, M.D.; Gibson, C.J.; Ciriello, J. Acute myocardial and plasma catecholamine changes in experimental stroke. Stroke 1986, 17, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nef, H.M.; Möllmann, H.; Hilpert, P.; Troidl, C.; Voss, S.; Rolf, A.; Behrens, C.B.; Weber, M.; Hamm, C.W.; Elsässer, A. Activated cell survival cascade protects cardiomyocytes from cell death in Tako-Tsubo cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Hear. Fail. 2009, 11, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, S.J.; Fuster, J.M. Electrocardiographic changes produced by localized hypothalamic stimulations. Ann. Intern. Med. 1960, 53, 332–341. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, R.E.; Livingston, R.B.; Bloor, C.M. Orbital cortical influences on cardiovascular dynamics and myocardial structure in conscious monkeys. J. Neurosurg. 1977, 46, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Özdemir, Ö.; Hachinski, V.C. Brain lateralization and sudden death: Its role in the neurogenic heart syndrome. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 268, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Farooq, M.U.; Greenberg, E.; Aloka, F.; Bhatt, A.; Kassab, M.; Morgan, J.P.; Majid, A. Cardiac dysfunction after left permanent cerebral focal ischemia: The brain and heart connection. Stroke 2009, 40, 2560–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sörös, P.; Hachinski, V.C. Cardiovascular and neurological causes of sudden death after ischaemic stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algra, A.; Gates, P.C.; Fox, A.J.; Hachinski, V.; Barnett, H.J. Side of Brain Infarction and Long-Term Risk of Sudden Death in Patients with Symptomatic Carotid Disease. Stroke 2003, 34, 2871–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, T.; Sato, K.; Yamamoto, S.; Matsuyama, N.; Shimohama, T.; Matsunaga, A.; Obuchi, S.; Shiba, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Izumi, T. Sympathetic nervous activity and myocardial damage immediately after subarachnoid hemorrhage in a unique animal model. Stroke 2002, 33, 1671–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winklewski, P.J.; Radkowski, M.; Demkow, U. Cross-Talk between the inflammatory response, sympathetic activation and pulmonary infection in the ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.D.; Campisi, J.; Sharkey, C.; Kennedy, S.; Nickerson, M.; Greenwood, B.; Fleshner, M. Catecholamines mediate stress-induced increases in peripheral and central inflammatory cytokines. Neuroscience 2005, 135, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bilt, I.A.; Vendeville, J.-P.; Van De Hoef, T.P.; Begieneman, M.P.; Lagrand, W.K.; Kros, J.M.; Wilde, A.A.; Rinkel, G.J.; Niessen, H.W. Myocarditis in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: A histopathologic study. J. Crit. Care 2016, 32, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, P.A.; Abbott, R.D.; Kannel, W.B. Atrial fibrillation as an independent risk factor for stroke: The Framingham Study. Stroke 1991, 22, 983–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Go, A.S.; Hylek, E.M.; Phillips, K.A.; Chang, Y.; Henault, L.E.; Selby, J.V.; Singer, D.E. Prevalence of Diagnosed Atrial Fibrillation in Adults. JAMA 2001, 285, 2370–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Anker, S.D.; Bueno, H.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Coats, A.J.S.; Falk, V.; González-Juanatey, J.R.; Harjola, V.-P.; Jankowska, E.A.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Hear. J. 2016, 37, 2129–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lip, G.Y.; Gibbs, C.R. Does heart failure confer a hypercoagulable state? Virchow’s triad revisited. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1999, 33, 1424–1426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hara, H.; Virmani, R.; Ladich, E.; Mackey-Bojack, S.; Titus, J.; Reisman, M.; Gray, W.; Nakamura, M.; Mooney, M.; Poulose, A.; et al. Patent Foramen Ovale: Current Pathology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Status. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Handke, M.; Harloff, A.; Olschewski, M.; Hetzel, A.; Geibel, A. Patent Foramen Ovale and Cryptogenic Stroke in Older Patients. New Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 2262–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koton, S.; Schneider, A.L.C.; Rosamond, W.D.; Shahar, E.; Sang, Y.; Gottesman, R.F.; Coresh, J. Stroke Incidence and Mortality Trends in US Communities, 1987 to 2011. JAMA 2014, 312, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Myint, P.K.; Kwok, C.S.; Roffe, C.; Kontopantelis, E.; Zaman, A.; Berry, C.; Ludman, P.F.; de Belder, M.A.; Mamas, M.A.; British Cardiovascular Intervention Society and the National Institute for Cardiovascular Outcomes Research. Determinants and outcomes of stroke following percutaneous coronary intervention by indication. Stroke 2016, 47, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lichtman, J.H.; Dharmarajan, K.; Masoudi, F.A.; Ross, J.S.; Dodson, J.A.; Chen, J.; Spertus, J.A.; Chaudhry, S.I.; Nallamothu, B.K.; et al. National trends in stroke after acute myocardial infarction among Medicare patients in the United States: 1999 to 2010. Am. Hear. J. 2014, 169, 78–85.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, R.A.; Otto, C.M.; Bonow, R.O.; Carabello, B.A.; Erwin, J.P., 3rd; Guyton, R.A.; O’Gara, P.T.; Ruiz, C.E.; Skubas, N.J.; Sorajja, P.; et al. 2014 AHA/ACC guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2438–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cannegieter, S.C.; Rosendaal, F.R.; Briët, E. Thromboembolic and bleed- ing complications in patients with mechanical heart valve prostheses. Circulation 1994, 89, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brennan, J.M.; Edwards, F.H.; Zhao, Y.; O’Brien, S.; Booth, M.E.; Dokholyan, R.S.; Douglas, P.S.; Peterson, E.D. Long-Term Safety and Effectiveness of Mechanical Versus Biologic Aortic Valve Prostheses in Older Patients. Circulation 2013, 127, 1647–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Idrees, J.J.; Schiltz, N.K.; Johnston, D.R.; Mick, S.; Smedira, N.G.; Sabik, J.F.; Blackstone, E.H.; Svensson, L.G.; Soltesz, E.G. Trends, Predictors, and Outcomes of Stroke After Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement in the United States. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2016, 101, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kondur, A.; Briasoulis, A.; Palla, M.; Penumetcha, A.; Mallikethi-Reddy, S.; Badheka, A.; Schreiber, T.; Information P.E.K.F.C. Meta-Analysis of Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement Versus Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement in Patients With Severe Aortic Valve Stenosis. Am. J. Cardiol. 2016, 117, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baddour, L.M.; Wilson, W.R.; Bayer, A.S.; Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Tleyjeh, I.M.; Rybak, M.J.; Barsic, B.; Lockhart, P.B.; Gewitz, M.H.; Levison, M.E.; et al. Infective Endocarditis in Adults: Diagnosis, Antimicrobial Therapy, and Management of Complications: A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2015, 132, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkler, A.E.; Chu, S.Y.; Lerario, M.P.; Navi, B.B.; Kamel, H. Temporal relationship between infective endocarditis and stroke. Neurology 2015, 85, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hart, R.G.; Diener, H.-C.; Coutts, S.B.; Easton, J.D.; Granger, C.B.; O’Donnell, M.; Sacco, R.L.; Connolly, S.J. Embolic strokes of undetermined source: The case for a new clinical construct. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplan, L.R. (Ed.) Basic Pathology, Anatomy, and Pathophysiology of Stroke. In Caplan’s Stroke; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 22–63. [Google Scholar]
- Nah, H.-W.; Lee, J.-W.; Chung, C.-H.; Choo, S.J.; Kwon, S.U.; Kim, J.S.; Warach, S.; Kang, D.-W. New brain infarcts on magnetic resonance imaging after coronary artery bypass graft surgery: Lesion patterns, mechanism, and predictors. Ann. Neurol. 2014, 76, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboix, A.; Oliveres, M.; Massons, J.; Pujades, R.; Garcia-Eroles, L. Early differentiation of cardioembolic from atherothrombotic cerebral infarction: A multivariate analysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 1999, 6, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timsit, S.; Sacco, R.L.; Mohr, J.P.; Foulkes, M.A.; Tatemichi, T.K.; Wolf, P.A.; Price, T.R.; Hier, D.B. Early clinical differentiation of cerebral infarction from severe atherosclerotic stenosis and cardioembolism. Stroke 1992, 23, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Di Raimondo, D.; Pecoraro, R.; Arnao, V.; Pinto, A.; Licata, G. Inflammation in ischemic stroke subtypes. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 4289–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licata, G.; Tuttolomondo, A.; Di Raimondo, D.; Corrao, S.; Di Sciacca, R.; Pinto, A. Immuno-inflammatory activation in acute cardio-embolic strokes in comparison with other subtypes of ischaemic stroke. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 101, 929–937. [Google Scholar]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Di Sciacca, R.; Di Raimondo, D.; Serio, A.; D’Aguanno, G.; La Placa, S.; Pecoraro, R.; Arnao, V.; Marino, L.; Monaco, S. Plasma levels of inflammatory and thrombotic/fibrinolytic markers in acute ischemic strokes: Relationship with TOAST subtype, outcome and infarct site. J. Neuroimmunol. 2009, 215, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakase, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Ogura, N.; Suzuki, A.; Nagata, K. The impact of inflammation on the pathogenesis and prognosis of ischemic stroke. J. Neurol. Sci. 2008, 271, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.; Kappelle, L.; Eliasziw, M.; Babikian, V.; Pearce, L.; Barnett, H. Occurrence of Hemispheric and Retinal Ischemia in Atrial Fibrillation Compared with Carotid Stenosis. Stroke 2002, 33, 1963–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jørgensen, H.S.; Nakayama, H.; Reith, J.; Raaschou, H.O.; Olsen, T.S. Acute Stroke with Atrial Fibrillation. Stroke 1996, 27, 1765–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Easton, J.D.; Saver, J.L.; Albers, G.W.; Alberts, M.J.; Chaturvedi, S.; Feldmann, E.; Hatsukami, T.S.; Higashida, R.T.; Johnston, S.C.; Kidwell, C.S.; et al. Definition and Evaluation of Transient Ischemic Attack. Stroke 2009, 40, 2276–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Lip, G.Y.; Apostolakis, S. Inflammation in Atrial Fibrillation. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 2263–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prage, P.; Hisham, D.; Peter, T.; Nasser, L. Update on the association of inflammation and atrial fibrillation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2010, 21, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, A.; Tuttolomondo, A.; Casuccio, A.; Di Raimondo, D.; Di Sciacca, R.; Arnao, V.; Licata, G. Immuno-inflammatory predictors of stroke at follow-up in patients with chronic non-valvular atrial fibrillation (NVAF). Clin. Sci. 2009, 116, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maida, C.D.; Vasto, S.; Di Raimondo, D.; Casuccio, A.; Vassallo, V.; Daidone, M.; Del Cuore, A.; Pacinella, G.; Cirrincione, A.; Simonetta, I.; et al. Inflammatory activation and endothelial dysfunction markers in patients with permanent atrial fibrillation: A cross-sectional study. Aging 2020, 12, 8423–8433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, C.T.; Giugliano, R.P.; Braunwald, E.; Hoffman, E.B.; Deenadayalu, N.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Camm, A.J.; Weitz, J.I.; Lewis, B.S.; Parkhomenko, A.; et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: A meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 2014, 383, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhof, P.; Benussi, S.; Kotecha, D.; Ahlsson, A.; Atar, D.; Casadei, B.; Castellà, M.; Diener, H.-C.; Heidbuchel, H.; Hendriks, J.M.H.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur. Hear. J. 2016, 37, 2893–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arima, H.; Hart, R.G.; Colman, S.; Chalmers, J.P.; Anderson, C.S.; Rodgers, A.; Woodward, M.; MacMahon, S.; Neal, B.; for the PROGRESS Collaborative Group. Perindopril-Based Blood Pressure-Lowering Reduces Major Vascular Events in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Prior Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack. Stroke 2005, 36, 2164–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flint, A.C.; Conell, C.; Ren, X.; Kamel, H.; Chan, S.L.; Rao, V.A.; Johnston, S.C. Statin Adherence Is Associated with Reduced Recurrent Stroke Risk in Patients with or Without Atrial Fibrillation. Stroke 2017, 48, 1788–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, H.; LeFeuvre, R.A.; Horai, R.A.; Asano, M.; Iwakura, Y.; Rothwell, N.J. Role of IL-1α and IL-1β in ischemic brain damage. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 5528–5534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, D.; Chinookoswong, N.; Miller, G. The Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist (rhIL-1ra) Protects against Cerebral Infarction in a Rat Model of Hypoxia-Ischemia. Exp. Neurol. 1994, 130, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, N.J.; Ross, J.; Rothwell, N.J.; Loddick, S.A. Delayed administration of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protects against transient cerebral ischaemia in the rat. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 140, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LaVine, S.D.; Hofman, F.M.; Zlokovic, B.V. Circulating Antibody against Tumor Necrosis Factor–Alpha Protects Rat Brain from Reperfusion Injury. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 18, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Bilbao, F.; Arsenijevic, D.; Moll, T.; Gracia-Gabay, I.; Vallet, P.; Langhans, W.; Giannakopoulos, P. In vivo overexpression of interleukin-10 increases resistance to focal brain ischemia in mice. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Geyter, D.; Stoop, W.; Sarre, S.; De Keyser, J.; Kooijman, R. Neuroprotective efficacy of subcutaneous insulin-like growth factor-I administration in normotensive and hypertensive rats with an ischemic stroke. Neuroscience 2013, 250, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.A.; Sansing, L. Microglial Responses after Ischemic Stroke and Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2013, 2013, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Ritzel, R.; McCullough, L.D.; Liu, F. Microglia and ischemic stroke: A double-edged sword. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 5, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hyakkoku, K.; Hamanaka, J.; Tsuruma, K.; Shimazawa, M.; Tanaka, H.; Uematsu, S.; Akira, S.; Inagaki, N.; Nagai, H.; Hara, H. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), but not TLR3 or TLR9, knock-out mice have neuroprotective effects against focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 2010, 171, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohacek, I.; Cordeau, P.; Lalancette–Hébert, M.; Gorup, D.; Weng, Y.-C.; Gajovic, S.; Kriz, J. Toll-like receptor 2 deficiency leads to delayed exacerbation of ischemic injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hum, P.D.; Subramanian, S.; Parker, S.M.; Afentoulis, M.E.; Kaler, L.J.; Vandenbark, A.A.; Offner, H. T- and B-Cell-Deficient Mice with Experimental Stroke have Reduced Lesion Size and Inflammation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 27, 1798–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liesz, A.; Zhou, W.; Mracskó, É.; Karcher, S.; Bauer, H.; Schwarting, S.; Sun, L.; Bruder, D.; Stegemann, S.; Cerwenka, A. Inhibition of lymphocyte trafficking shields the brain against deleterious neuroinflammation after stroke. Brain 2011, 134, 704–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, H. Hypoxia inducible factor 1 as a therapeutic target in ischemic stroke. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 4593–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Miyake, M.; Liu, K.J.; Shi, H. Specific inhibition of hypoxia inducible factor 1 exaggerates cell injury induced by in vitro ischemia through deteriorating cellular redox environment. J. Neurochem. 2009, 108, 1309–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; Hu, Q.; Yan, J.; Lei, J.; Qin, L.; Shi, X.; Luan, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, K.; Han, J.; et al. Multiple effects of 2ME2 and D609 on the cortical expression of HIF-1α and apoptotic genes in a middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced focal ischemia rat model. J. Neurochem. 2007, 102, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, O.; Miranda, L.F.; Pichiule, P.; Dragatsis, I.; Johnson, R.S.; Chavez, J.C. Neuron-Specific Inactivation of the Hypoxia Inducible Factor 1α Increases Brain Injury in a Mouse Model of Transient Focal Cerebral Ischemia. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 6320–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helton, R.; Cui, J.; Scheel, J.R.; Ellison, J.A.; Ames, C.; Gibson, C.; Blouw, B.; Ouyang, L.; Dragatsis, I.; Zeitlin, S.; et al. Brain-Specific Knock-Out of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Reduces Rather Than Increases Hypoxic-Ischemic Damage. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 4099–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereczki, D.; Balla, J. Heme Oxygenase-1: Clinical Relevance in Ischemic Stroke. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 2229–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balla, G.; Jacob, H.S.; Balla, J.; Rosenberg, M.; Nath, K.; Apple, F.; Eaton, J.W.; Vercellotti, G.M. Ferritin: A cytoprotective antioxidant strategem of endothelium. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 18148–18153. [Google Scholar]
- Balla, J.; Vercellotti, G.M.; Jeney, V.; Yachie, A.; Varga, Z.; Jacob, H.S.; Eaton, J.W.; Balla, G. Heme, Heme Oxygenase, and Ferritin: How the Vascular Endothelium Survives (and Dies) in an Iron-Rich Environment. Antioxid. Redox Signal 2007, 9, 2119–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredenburgh, L.E.; Merz, A.A.; Cheng, S. Haeme oxygenase signalling pathway: Implications for cardiovascular disease. Eur. Hear. J. 2015, 36, 1512–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Motterlini, R.; Otterbein, L.E. The therapeutic potential of carbon monoxide. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 728–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolisetty, S.; Zarjou, A.; Hull, T.D.; Traylor, A.M.; Perianayagam, A.; Joseph, R.; Kamal, A.I.; Arosio, P.; Soares, M.P.; Jeney, V.; et al. Macrophage and epithelial cell H-ferritin expression regulates renal inflammation. Kidney Int. 2015, 88, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chao, X.D.; Ma, Y.H.; Luo, P.; Cao, L.; Lau, W.B.; Zhao, B.C.; Han, F.; Liu, W.; Ning, W.D.; Su, N.; et al. Up-regulation of Heme oxygenase-1 attenuates brain damage after cerebral ischemia via simultaneous inhibition of superoxide production and preservation of NO bioavailability. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 239, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panahian, N.; Yoshiura, M.; Maines, M.D. Overexpression of Heme Oxygenase-1 Is Neuroprotective in a Model of Permanent Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Transgenic Mice. J. Neurochem. 2008, 72, 1187–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, Z.A.; Nada, S.E.; Doré, S. Heme oxygenase 1, beneficial role in permanent ischemic stroke and in Gingko biloba (EGb 761) neuroprotection. Neuroscience 2011, 180, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Powers, W.J.; Rabinstein, A.A.; Ackerson, T.; Adeoye, O.M.; Bambakidis, N.C.; Becker, K.; Biller, J.; Brown, M.; Demaerschalk, B.M.; Hoh, B.; et al. Guidelines for the Early Management of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke: 2019 Update to the 2018 Guidelines for the Early Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Guideline for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2019, 50, e344–e418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.M. Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Bayl. Univ. Med Cent. Proc. 2011, 24, 257–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Target | Subjects | Result | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Interleukin (IL)-1 | IL-1a and IL-1b deficient mice | Subjects showed a reduction of the ischemic area compared to wild-type mice | H. Boutin, R.A. LeFeuvre, R. Horai, M. Asano, Y. Iwakura, and N.J. Rothwell, “Role of IL-1α and IL-1β in ischemic brain damage,” The Journal of Neuroscience, vol. 21, no. 15, pp. 5528–5534, 2001. |
| IL-1 | Mice treated with rhIL-1ra after the ligation of a carotid artery | Subjects showed a reduction of neurological deficit | Martin D, Chinookoswong N, Miller G. The interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (rhIL-1ra) protects against cerebral infarction in a rat model of hypoxia-ischemia. Exp Neurol 1994; 130(2): 362–367. |
| Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α | Mice treated with antibodies anti-TNF-α after reversible temporary occlusion of the middle cerebral artery (MCAO) | Subjects showed a better neurological outcome | Lavine SD, Hofman FM, Zlokovic BV. Circulating antibody against tumor necrosis factor-alpha protects rat brain from reperfusion injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1998; 18(1): 52–58. |
| IL-10 | IL-1T mice after permanent MCAO | Subjects showed a 40% reduction of the area involved in ischemia | F. de Bilbao, D. Arsenijevic, T. Moll et al., “In vivo overexpression of interleukin-10 increases resistance to focal brain ischemia in mice,” Journal of Neurochemistry, vol. 110, no. 1, pp. 12–22, 2009 |
| Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) | Mice treated with IGF-1 subcutaneously after permanent MCAO | Subjects showed a reduction of the ischemic area with an improvement of sensibility and mobility | D. de Geyter, W. Stoop, S. Sarre, J. de Keyser, and R. Kooijman, “Neuroprotective efficacy of subcutaneous insulin-like growth factor-I administration in normotensive and hypertensive rats with an ischemic stroke,” Neuroscience, vol. 250, pp. 253–262, 2013. |
| TLR4 | Knock out mice for TLR4 24 h after induced cerebral ischemia and successive reperfusion | Subjects showed a reduction of the ischemic area compared to wild-type mice | K. Hyakkoku, J. Hamanaka, K. Tsuruma et al., “Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), but not TLR3 or TLR9, knock-out mice have neuroprotective effects against focal cerebral ischemia,” Neuroscience, vol. 171, no. 1, pp. 258–267, 2010. |
| T cells | Mice deficient in T cell subsets | Subjects showed a smaller ischemic area compared to wild-type mice | Hurn PD, Subramanian S, Parker SM, et al. T- and B- cell-deficient mice with experimental stroke have reduced lesion size and inflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2007; 27: 1798–1805. |
| Leukocyte very late antigen-4 and endothelial vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 | Mice affected by cerebral ischemia | The inhibition of these molecules resulted in a reduction of the leukocytes’ recruitment in ischemic parenchyma with consequent decreased neuronal damage | Liesz A1, Zhou W, Mracskó É, Karcher S, Bauer H, Schwarting S, Sun L, Bruder D, Stegemann S, Cerwenka A, Sommer C, Dalpke AH, Veltkamp R. Inhibition of lymphocyte trafficking shields the brain against deleterious neuroinflammation after stroke. Brain. 2011 Mar;134(Pt 3):704–20. DOI: 10.1093/brain/awr008. |
| Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α | Ischemic cerebral tissue in vitro | The stimulation of HIF-1α resulted in a reduced neuronal death, on the other hand, its suppression by small interfering RNA (siRNA) was associated with increased production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) | Guo S, Miyake M, Liu KJ, Shi H. Specific inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor exaggerates cell injury induced by in vitro ischemia through deteriorating cellular redox environment. J Neurochem 2009; 5:1309–1321. |
| HIF-1α | Mice after induced MCAO | The inhibition of HIF-1α was associated with a better neurological outcome by the suppression of BNIP3 (BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3) which is responsible for mitochondrial dysfunction | Chen C, Hu Q, Yan J, Lei J, Qin L, Shi X, Luan L, Yang L, Wang K, Han J, Nanda A, Zhou C., Multiple effects of 2ME2 and D609 on the cortical expression of HIF-1α and apoptotic genes in a middle cerebral artery occlusion-induced focal ischemia rat model. J Neurochem. 2007 |
| HIF-1α | Mice after 30-min MCAO | The inhibition of HIF-1α was associated with a worse neurological outcome | Baranova O, Miranda LF, Pichiule P, Dragatsis I, Johnson RS, Chavez JC. Neuron-specific inactivation of the hypoxia-inducible factor 1α increases brain injury in a mouse model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 2007; 23:6320–6332. |
| HIF-1α | Mice after 75-min bilateral occlusion of carotid arteries | The stimulation of HIF-1α was associated with a worse neurological outcome | Helton R, Cui J, Scheel JR, Ellison JA, Ames C, Gibson C, Blouw B, Ouyang L, Dragatsis I, Zeitlin S, Johnson RS, Lipton SA, Barlow C. Brain-specific knock-out of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α reduces rather than increases hypoxic-ischemic damage. J Neurosci 2005;16: 4099–4107. |
| Heme oxygenase (HO)-1 | Rats treated with viral carries expressing HO-1 after MCAO | Subjects showed a reduction of the ischemic area and an improvement of the neurological symptomatology | Chao XD, Ma YH, Luo P, et al. Up-regulation of heme oxygenase-1 attenuates brain damage after cerebral ischemia via simultaneous inhibition of superoxide production and preservation of NO bioavailability. Exp Neurol 2013; 239: 163–9. |
| HO-1 | Transgenic mice expressing HO-1 after permanent MCAO | Subjects showed a reduction of the ischemic area and an improvement of the neurological symptomatology | Panahian N, Yoshiura M, Maines MD. Overexpression of heme oxygenase-1 is neuroprotective in a model of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in transgenic mice. J Neurochem 1999; 72: 1187–203. |
| HO-1 | HO-1 knockout mice affected by cerebral ischemia | Subjects showed an increased ischemic area compared to wild-type mice | Shah ZA, Nada SE, Dore S. Heme oxygenase 1, beneficial role in permanent ischemic stroke and in Gingko biloba (EGb 761) neuroprotection. Neuroscience 2011; 180: 248–55. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maida, C.D.; Norrito, R.L.; Daidone, M.; Tuttolomondo, A.; Pinto, A. Neuroinflammatory Mechanisms in Ischemic Stroke: Focus on Cardioembolic Stroke, Background, and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186454
Maida CD, Norrito RL, Daidone M, Tuttolomondo A, Pinto A. Neuroinflammatory Mechanisms in Ischemic Stroke: Focus on Cardioembolic Stroke, Background, and Therapeutic Approaches. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(18):6454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186454
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaida, Carlo Domenico, Rosario Luca Norrito, Mario Daidone, Antonino Tuttolomondo, and Antonio Pinto. 2020. "Neuroinflammatory Mechanisms in Ischemic Stroke: Focus on Cardioembolic Stroke, Background, and Therapeutic Approaches" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 18: 6454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186454
APA StyleMaida, C. D., Norrito, R. L., Daidone, M., Tuttolomondo, A., & Pinto, A. (2020). Neuroinflammatory Mechanisms in Ischemic Stroke: Focus on Cardioembolic Stroke, Background, and Therapeutic Approaches. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(18), 6454. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186454






