Treatment Strategy of Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Hemodynamics in the Liver and HCC
2.1. Microvasculature of the Normal Liver
2.2. Hemodynamics in Hypervascular HCC
3. Limitation of TACE and Necessity of Curative TACE
3.1. Limitation of TACE
3.2. Necessity of Curative TACE
4. Rationale for Each TACE Technique
4.1. Rationale for Bland Embolization and DEB-TACE
4.2. Rationale for cTACE
4.3. Therapeutic Effects of Bland Embolization with Particles
4.4. Proper Use of Chemotherapeutics in TACE
4.5. Comparison of Therapeutic Effects between DEB-TACE and cTACE
4.6. Technical Advantages of Selective cTACE Compared with Non-Selective cTACE
5. Technical Tips for Performing Effective Superselective cTACE
5.1. Achievement of Marked Portal Vein Visualization with Iodized Oil During cTACE
5.2. Importance of the Order of Embolization of Each Tumor Feeder
5.3. Usefulness of Stepwise cTACE for Large HCCS
5.4. Usefulness of CT/CBCT and TACE Guidance Software
6. Concept of TACE Unsuitability
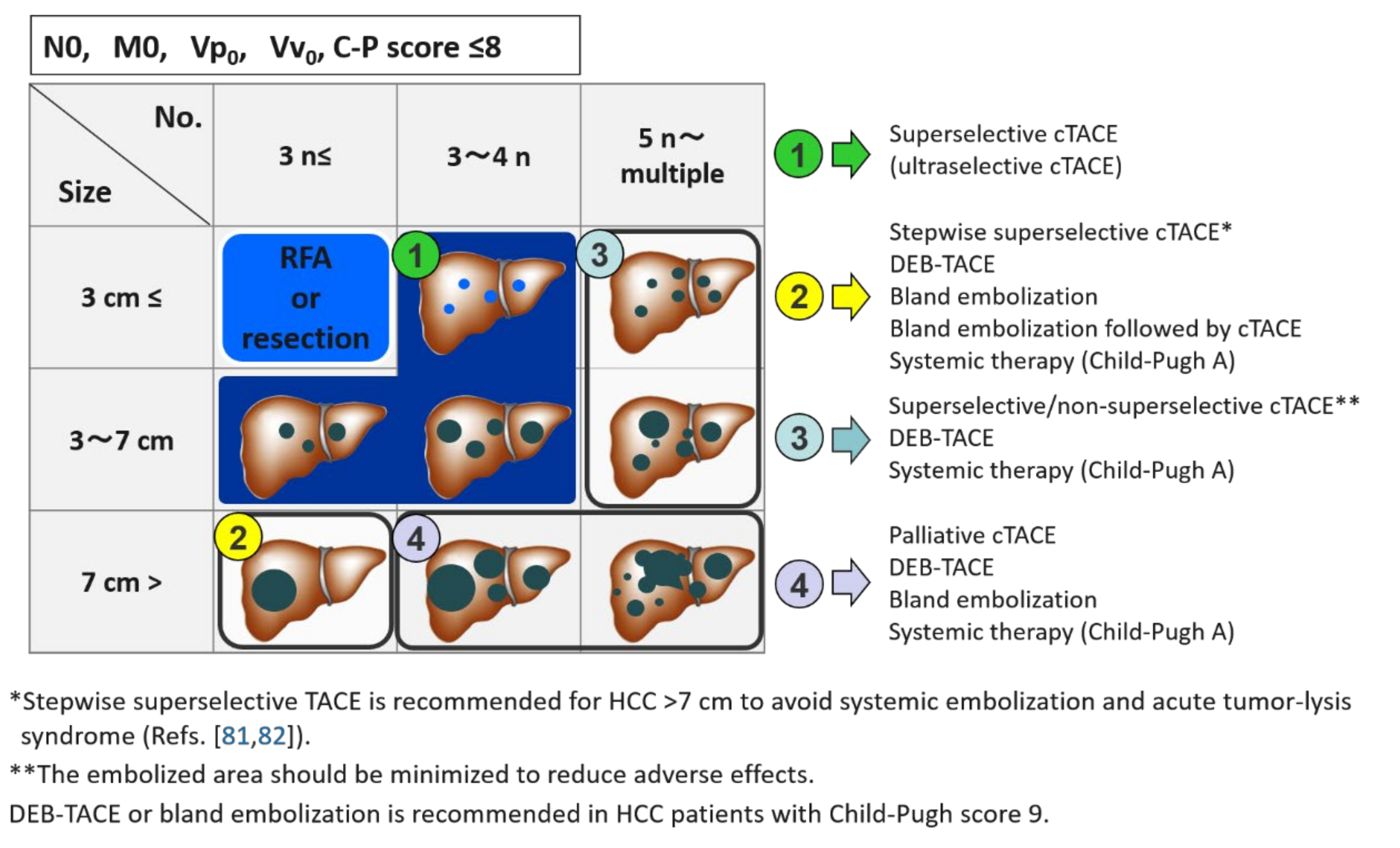
7. TACE Strategy According to the Number and Size of HCC
8. Further Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamada, R.; Sato, M.; Kawabata, M.; Nakatsuka, H.; Nakamura, K.; Takashima, S. Hepatic artery embolization in 120 patients with unresectable hepatoma. Radiology 1983, 148, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.M.; Ngan, H.; Tso, W.K.; Liu, C.L.; Lam, C.M.; Poon, R.T.; Fan, S.T.; Wong, J. Randomized controlled trial of transarterial lipiodol chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2002, 35, 1164–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Real, M.I.; Montaña, X.; Planas, R.; Coll, S.; Aponte, J.; Ayuso, C.; Sala, M.; Muchart, J.; Solà, R.; et al. Arterial embolisation or chemoembolisation versus symptomatic treatment in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 1734–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammà, C.; Schepis, F.; Orlando, A.; Albanese, M.; Shahied, L.; Trevisani, F.; Andreone, P.; Craxì, A.; Cottone, M. Transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Radiology 2002, 224, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marelli, L.; Stigliano, R.; Triantos, C.; Senzolo, M.; Cholongitas, E.; Davies, N.; Tibballs, J.; Meyer, T.; Patch, T.M.; Burroughs, A.K. Transarterial therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Which technique is more effective? A systematic review of cohort and randomized studies. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2007, 30, 6–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ekataksin, W. The isolated artery: An intrahepatic arterial pathway that can bypass the lobular parenchyma in mammalian livers. Hepatology 2000, 31, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.; Nakanuma, Y.; Terada, T.; Matsui, O. Postmortem survey of bile duct necrosis and biloma in hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization therapy: Relevance to microvascular damages of peribiliary capillary plexus. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1993, 88, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, S.; Nakamuma, Y.; Matsui, O. Histopathology of portal tracts in livers after transcatheter arterial chemo-embolization therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1994, 9, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, K.; Matsui, O.; Miyayama, S.; Ibukuro, K.; Yoneda, N.; Inoue, D.; Kozaka, K.; Minami, T.; Koda, W.; Gabata, T. Isolated arteries originating from the intrahepatic arteries: Anatomy, function, and importance in intervention. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 531–537.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, N.; Uchida, H.; Nishimine, K.; Soda, S.; Oshima, M.; Nakano, H.; Nagano, N.; Nishimura, Y.; Yoshioka, T.; Guo, Q.; et al. Segmental transcatheter hepatic artery chemoembolization with iodized oil for hepatocellular carcinoma: Antitumor effect and influence on normal tissue. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 1993, 4, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyayama, S.; Mitsui, T.; Zen, Y.; Sudo, Y.; Yamashiro, M.; Okuda, M.; Yoshie, Y.; Sanada, T.; Notsumata, K.; Tanaka, N.; et al. Histopathological findings after ultraselective transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2009, 39, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyayama, S.; Matsui, O. Superselective conventional transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: Rationale, technique, and outcome. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2016, 27, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, M.; Matsui, O.; Ueda, K.; Kawamori, Y.; Kadoya, M.; Yoshikawa, J.; Gabata, T.; Takashima, T.; Nonomua, A.; Nakanuma, Y. Correlation between the blood supply and grade of malignancy of hepatocellular nodules associated with liver cirrhosis: Evaluation by CT during intraarterial injection of contrast medium. AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1999, 172, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuroda, C.; Sakurai, M.; Monden, M.; Marukawa, T.; Hosoki, T.; Tokunaga, K.; Wakasa, K.; Okamura, J.; Kozuka, T. Limitation of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization using iodized oil for small hepatocellular carcinoma. A study in resected cases. Cancer 1991, 67, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitao, A.; Zen, Y.; Matsui, O.; Gabata, T.; Nakanuma, Y. Hepatocarcinogenesis: Multistep changes of drainage vessels at CT during arterial portography and hepatic arteriography–radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiology 2009, 252, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, K.; Matsui, O.; Kawamori, Y.; Nakamuma, Y.; Kadoya, M.; Yoshikawa, J.; Gabata, T.; Nonomura, A.; Takashima, T. Hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma: Evaluation of hemodynamics with dynamic CT during hepatic arteriography. Radiology 1998, 206, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goseki, N.; Nosaka, T.; Endo, M.; Koike, M. Nourishment of hepatocellular carcinoma cells through the portal blood flow with and without transcatheter arterial embolization. Cancer 1995, 76, 736–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekelund, L.; Lin, G.; Jeppsson, B. Blood supply of experimental liver tumors after intraarterial embolization with Gelfoam powder and absolute ethanol. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 1984, 7, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.K.; Kim, S.U.; Kim, K.A.; Chung, Y.E.; Kim, M.J.; Park, M.S.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, D.Y.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, M.D.; et al. Complete response at first chemoembolization is still the most robust predictor for favorable outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1304–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojiro, M.; Sugihara, S.; Kakizoe, S.; Nakashima, O.; Kiyomatsu, K. Hepatocellular carcinoma with sarcomatous change: A special reference to the relationship with anticancer therapy. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1989, 23, S4–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zen, C.; Zen, Y.; Mitry, R.R.; Corbeil, D.; Karbanová, J.; O’Gray, J.; Karani, J.; Kane, P.; Heaton, N.; Portmann, B.C.; et al. Mixed phenotype hepatocellular carcinoma after transarterial chemoembolization and liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2011, 17, 943–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergio, A.; Cristofori, C.; Cardin, R.; Pivetta, G.; Ragazzi, R.; Baldan, A.; Girardi, L.; Cillio, U.; Burra, P.; Giacomin, A.; et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): The role of angiogenesis and invasiveness. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 103, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Xu, H.; Gao, Z.Q.; Ning, H.F.; Sun, Y.Q.; Cao, G.W. Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Acta. Radiol. 2008, 49, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyayama, S.; Matsui, O.; Zen, Y.; Yamashiro, M.; Hattori, Y.; Orito, N.; Matsui, K.; Tsuji, K.; Yoshida, M.; Sudo, Y. Portal blood supply to locally progressed hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization: Observation on CT during arterial portography. Hepatol. Res. 2011, 41, 853–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyayama, S.; Yamashiro, M.; Sugimori, N.; Ikeda, R.; Okimura, K.; Sakuragawa, N. Outcomes of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with conventional transarterial chemoembolization using guidance software. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2019, 30, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arizumi, T.; Minami, T.; Chishina, H.; Kono, M.; Takita, M.; Yada, N.; Hagiwara, S.; Minami, Y.; Ida, H.; Ueshima, K.; et al. Time to transcatheter arterial chemoembolization refractoriness in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in Kinki Criteria stages B1 and B2. Dig. Dis. 2017, 35, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monier, A.; Guiu, B.; Duran, R.; Aho, S.; Bize, P.; Deltenre, P.; Dunet, V.; Denys, A. Liver and biliary damages following transarterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison between drug-eluting beads and lipiodol emulsion. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namur, J.; Wassef, M.; Millot, J.M.; Lewis, A.L.; Manfait, M.; Laurent, A. Drug-eluting beads for liver embolization: Concentration of doxorubicin in tissue and in beads in a pig model. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padia, S.A.; Shivaram, G.; Bastawrous, S.; Bhargava, P.; Vo, N.J.; Vaidya, S.; Valji, K.; Harris, W.P.; Hippe, D.S.; Kogut, M.J. Safety and Efficacy of drug-eluting bead chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison of small-versus medium-size particles. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, K.T. Fatal pulmonary complications after arterial embolization with 40-120- micro m tris-acryl gelatin microspheres. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2004, 15 Pt 1, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maluccio, M.A.; Covey, A.M.; Porat, L.B.; Schubert, J.; Brody, L.A.; Sofocleoud, C.T.; Getrajdman, G.I.; Jarnagin, W.; Dematteo, R.; Blumgart, L.H.; et al. Transcatheter arterial embolization with only particles for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2008, 19, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyayma, S.; Matsui, O. Applying superselective conventional TACE. Endovasc. Today 2017, 16, 52–56. [Google Scholar]
- Minamiguchi, K.; Tanaka, T.; Nishiofuku, H.; Fukuoka, Y.; Taiji, R.; Matsumoto, T.; Saito, N.; Taguchi, H.; Marugami, N.; Hirai, T.; et al. Comparison of embolic effect between water-in-oil emulsion and microspheres in transarterial embolization for rat hepatocellular carcinoma model. Hepatol. Res. 2020. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32822527/ (accessed on 21 August 2020). [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, M.D.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, S.U.; Won, J.Y. Hepatic arterial damage after transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison of drug-eluting bead and conventional chemoembolization in a retrospective controlled study. Acta. Radiol. 2017, 58, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimose, S.; Iwamoto, H.; Tanaka, M.; Niizeki, T.; Shirono, T.; Nakano, M.; Okumura, S.; Noda, Y.; Kamachi, N.; Sakai, M.; et al. Increased arterio-portal shunt formation after drug-eluting beads TACE for hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 2020, 98, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Baere, T.; Zhang, X.; Aubert, B.; Harry, G.; Lagrange, C.; Ropers, J.; Dufaux, J.; Lumbroso, J.; Rougier, P.; Ducreux, M.; et al. Quantification of tumor uptake of iodized oils and emulsions of iodized oils: Experimental study. Radiology 1996, 201, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demachi, H.; Matsui, O.; Abo, H.; Tatsu, H. Simulation model based on non-Newtonian fluid mechanics applied to the evaluation of the embolic effect of emulsions of iodized oil and anticancer drug. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2000, 23, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terayama, N.; Matsui, O.; Gabata, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Sanada, J.; Ueda, K.; Kadoya, M.; Kawamori, Y. Accumulation of iodized oil within the nonneoplastic liver adjacent to hepatocellular carcinoma via the drainage routes of the tumor after transcatheter arterial embolization. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2001, 24, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyayama, S.; Matsui, O.; Yamashiro, M.; Ryu, Y.; Kaito, K.; Ozaki, K.; Takeda, T.; Yoneda, N.; Notsumata, K.; Toya, D.; et al. Ultraselective transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with a 2-F tip microcatheter for small hepatocellular carcinomas: Relationship between local tumor recurrence and visualization of the portal vein with iodized oil. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2007, 18, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyayama, S.; Yamashiro, M.; Okuda, M.; Abrano, H.; Shigenari, N.; Morinaga, K.; Matsui, O. Anastomosis between the hepatic artery and the extrahepatic collateral or between extrahepatic collaterals: Observation on angiography. J. Med. Imag. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 53, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irie, T.; Kuramochi, M.; Takahashi, N. Diameter of main tumor feeding artery of a hepatocellular carcinoma: Measurement at the entry site into the nodule. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, E100–E104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iwamoto, S.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hongo, O.; Iwamoto, H.; Sanefuji, H. Excellent outcomes with angiographic subsegmentectomy in the treatment of typical hepatocellular carcinoma. A retrospective study of local recurrence and long-term survival rates in 120 patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2010, 116, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Baere, T.; Arai, Y.; Lencioni, R.; Geschwind, J.F.; Rilling, W.; Salem, R.; Matsui, O.; Soulen, M.C. Treatment of liver tumors with Lipiodol TACE: Technical recommendations from experts opinion. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2016, 239, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malagari, K.; Pomoni, M.; Kelekis, A.; Pomoni, A.; Dourakis, S.; Spyridopoulos, T.; Moschouris, H.; Emmanouil, E.; Rizos, S.; Kelekis, D. Prospective randomized comparison of chemoembolization with doxorubicin-eluting beads and bland embolization with BeadBlock for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2010, 33, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.T.; Do, R.K.; Gonen, M.; Covey, A.M.; Getrajdman, G.I.; Sofocleous, C.T.; Jarnagin, W.R.; D’Angelica, M.I.; Allen, P.J.; Erinjeri, J.P.; et al. Randomized trial of hepatic artery embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma using doxorubicin-eluting microspheres compared with embolization with microspheres alone. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2046–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osuga, K.; Khankan, A.A.; Hori, S.; Okada, A.; Sugiura, T.; Maeda, M.; Nagano, H.; Yamada, A.; Murakami, T.; Nakamura, H. Transarterial embolization for large hepatocellular carcinoma with use of superabsorbent polymer microspheres: Initial experience. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2002, 13 Pt 1, 929–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osuga, K.; Hori, S.; Hiraishi, K.; Sugiura, T.; Hata, Y.; Higashihara, H.; Maeda, N.; Tomoda, K.; Nakamura, N. Bland embolization of hepatocellular carcinoma using superabsorbent polymer microspheres. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2008, 31, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanza, E.; Muglia, R.; Bolengo, I.; Poretti, D.; D’Antuono, F.; Ceriani, R.; Torzilli, G.; Pedicini, V. Survival analysis of 230 patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma treated with bland transarterial embolization. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, C.T.; Liu, B.M.; Ng, S.H.; Lee, T.Y.; Cheng, Y.F.; Chen, M.C.; Ko, S.F. Transcatheter arterial embolization in the emergency department for hemodynamic instability due to ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma: Analysis of 167 cases. AJR. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 191, W231–W239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamada, K.; Nakanishi, T.; Kitamoto, M.; Aikata, H.; Kawakami, Y.; Ito, K.; Kajiyama, G. Long-term prognosis of patients undergoing transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison of cisplatin lipiodol suspension and doxorubicin hydrochloride emulsion. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2001, 12, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yodono, H.; Matsuo, K.; Shinohara, A. A retrospective comparative study of epirubicin-lipiodol emulsion and cisplatin-lipiodol suspension for use with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Anticancer Drugs 2011, 22, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasai, K.; Ushio, A.; Sawara, K.; Miyamoto, Y.; Kasai, Y.; Oikawa, K.; Kuroda, H.; Takikawa, Y.; Suzuki, K. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with a fine-powder formulation of cisplatin for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 3437–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahara, S.; Kawai, N.; Sato, M.; Minamiguchi, H.; Nakai, M.; Takasaka, I.; Nakata, K.; Ikoma, A.; Sawa, N.; Sonomura, T.; et al. Prospective comparison of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization with Lipiodol-epirubicin and Lipiodol-cisplatin for treatment of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2010, 28, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaoka, T.; Aikata, H.; Katamura, Y.; Takaki, S.; Waki, K.; Hiramatsu, A.; Takahashi, S.; Hieda, M.; Kakizawa, H.; Chayama, K. Hypersensitivity reactions to transcatheter chemoembolization with cisplatin and Lipiodol suspension for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, N.; Osuga, K.; Higashihara, H.; Tomoda, K.; Mikami, K.; Nakazawa, T.; Nakamura, H.; Tomiyama, N. Transarterial chemoembolization with cisplatin as second-line treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma unresponsive to chemoembolization with epirubicin-Lipiodol emulsion. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2012, 35, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, M.; Kudo, M.; Aikata, H.; Nagamatsu, H.; Ishii, H.; Yokosuka, O.; Torimura, T.; Morimoto, M.; Ikeda, K.; Kumada, H.; et al. Transarterial chemoembolization with miriplatin vs. epirubicin for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomized trial. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyayama, S.; Yamashiro, M.; Shibata, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Yoshida, M.; Tsuji, K.; Toshima, F.; Matsui, O. Comparison of local control effects of superselective transcatheter arterial chemoembolization using epirubicin plus mitomycin C and miriplatin for hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2012, 30, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwazawa, J.; Ohue, S.; Hashimoto, N.; Mitani, T. Local tumor progression following lipiodol-based targeted chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective comparison of miriplatin and epirubicin. Cancer Manag. Res. 2012, 4, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irie, T.; Kuramochi, M.; Takahashi, N. Dense accumulation of Lipiodol emulsion in hepatocellular carcinoma nodule during selective balloon-occluded transarterial chemoembolization: Measurement of balloon occluded arterial stump pressure. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2013, 36, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, N.; Osuga, K.; Higashihara, H.; Mikami, K.; Tomoda, K.; Hori, S.; Nakazawa, T.; Nakamura, H. In vitro characterization of cisplatin-loaded superabsorbent polymer microspheres designed for chemoembolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammer, J.; Malagari, K.; Vogl, T.; Pilleul, F.; Denys, A.; Watkinson, A.; Pitton, M.; Sergent, G.; Pfammatter, T.; Terraz, S.; et al. Prospective randomized study of doxorubicin-eluting-bead embolization in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: Results of the PRECISION V study. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2010, 33, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sacco, R.; Bargellini, I.; Bertini, M.; Bozzi, E.; Romano, A.; Petruzzi, P.; Tumino, E.; Gianni, B.; Federici, G.; Cioni, R.; et al. Conventional versus doxorubicin-eluting bead transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 22, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golifieri, R.; Giampalma, E.; Renzulli, M.; Cioni, R.; Bargellini, I.; Bartolozzi, C.; Breatta, A.D.; Gandini, G.; Nani, R.; Gasparini, D.; et al. Randomised controlled trial of doxorubicin-eluting beads vs conventional chemoembolisation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, M.; Inaba, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Sugawara, S.; Kodama, Y.; Aramaki, T.; Anai, H.; Morita, S.; Tsukahara, Y.; Seki, H.; et al. A prospective, randomized, controlled trial of selective DEB-TACE vs. selective cTACE with epirubicinfor hepatocellular carcinoma: JIVROSG-1302 PRESIDENT study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38. (suppl; abstr 4518). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikura, H.; Sotozaki, Y.; Adachi, H.; Sato, M.; Yoshiki, T. Granulomatous arteritis with massive eosinophilic leukocyte infiltration and transient peripheral eosinophilia subsequent to transarterial embolization therapy with a gelatin sponge. Acta. Pathol. Jpn. 1991, 41, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyayama, S.; Yanakado, K.; Anai, H.; Abo, D.; Minami, T.; Takaki, H.; Kodama, T.; Yamanaka, T.; Nishiofuku, H.; Morimoto, K.; et al. Guidelines on the use of gelatin sponge particles in embolotherapy. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2014, 32, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.C.; Chung, J.W.; Lee, W.; Jae, H.J.; Park, J.H. Recognizing extrahepatic collateral vessels that supply hepatocellular carcinoma to avoid complications of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Radiographics 2005, 25 (Suppl. S1), S25–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyayama, S.; Matsui, O.; Taki, K.; Minami, T.; Ryu, Y.; Ito, C.; Nakamura, K.; Inoue, D.; Notsumata, K.; Toya, D.; et al. Extrahepatic blood supply to hepatocellular carcinoma: Angiographic demonstration and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2006, 29, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakon, M.; Nagano, H.; Nakamori, S.; Dono, K.; Ueshita, K.; Murakami, T.; Nakamura, H.; Monden, M. Intrahepatic recurrences of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: Analysis based on tumor hemodynamics. Arch. Surg. 2002, 137, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyayama, S.; Yamashiro, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Hashimoto, N.; Ikuno, M.; Okumura, K.; Yoshida, M.; Matsui, O. Comparison of local control in transcatheter arterial chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma ≤6 cm with or without intraprocedural monitoring of the embolized area using cone-beam computed tomography. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2014, 37, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyayama, S.; Yamashiro, M.; Ikuno, M.; Okumura, K.; Yoshida, M. Ultraselective transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for small hepatocellular carcinoma guided by automated tumor-feeders detection software: Technical success and short-term tumor response. Abdom. Imaging 2014, 39, 645–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, A.; Kai, S.; Iwashita, Y.; Hirano, S.; Ohta, M.; Kitano, S. Microsatellite distribution and indication for locoregional therapy in small hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2005, 103, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyayama, S. Ultraselective conventional transarterial chemoembolization: When and how? Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2019, 25, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeuchi, Y.; Arai, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Ohno, K.; Maeda, T.; Itai, Y. Extrahepatic arterial supply to the liver: Observation with a unified CT and angiography system during temporary balloon occlusion of the proper hepatic artery. Radiology 1998, 209, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, K.T.; Wang, B.W.; Lo, G.H.; Liang, H.L.; Liu, S.I.; Chou, N.H.; Tsai, C.C.; Chen, I.S.; Yeh, M.H.; Chen, Y.C. Multimodality management of hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 10 cm. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2003, 197, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.H.; Wu, J.C.; Chen, S.C.; Chen, C.H.; Chiang, J.H.; Huo, T.I.; Lee, P.C.; Chang, F.Y.; Lee, S.D. Survival benefit of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma larger than 10 cm in diameter. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 23, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.W.; Park, J.H.; Im, J.G.; Han, J.K.; Han, M.C. Pulmonary oil embolism after transcatheter oily chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 1993, 187, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ni, R.F.; Busireddy, K.K.; Jin, Y.H.; Zhao, X.; Li, M.M.; Yang, C. Cerebral lipiodol embolism following transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A report of two cases and literature review. Chin. Med. J. 2011, 124, 4355–4358. [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto, N.; Monzawa, S.; Nagano, H.; Nishizaki, H.; Arai, Y.; Sugimura, K. Acute tumor lysis syndrome caused by transcatheter oily chemoembolization in a patient with a large hepatocellular carcinoma. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2007, 30, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyayama, S.; Yamashiro, M.; Okuda, M.; Yoshie, Y.; Sugimori, N.; Igarashi, S.; Nakashima, Y.; Notsumata, K.; Toya, D.; Tanaka, N.; et al. Chemoembolization for the treatment of large hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, 1226–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyayama, S.; Kikuchi, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Yamashiro, M.; Sugimori, N.; Ikeda, R.; Okimura, K.; Sakuragawa, N.; Ueda, T.; Sanada, T.; et al. Outcomes of conventional transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma ≥10 cm. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidaka, T.; Anai, H.; Sakaguchi, H.; Sueyoshi, S.; Tanaka, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Morimoto, K.; Nishiofuku, H.; Maeda, S.; Nagata, T.; et al. Efficacy of combined bland embolization and chemoembolization for huge (≥10 cm) hepatocellular carcinoma. Minim. Invasive Ther. Allied. Technol. 2020. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32031474/ (accessed on 7 February 2020). [CrossRef]
- Takayasu, K.; Muramatsu, Y.; Maeda, T.; Iwata, R.; Furukawa, H.; Muramatsu, Y.; Moriyama, N.; Okusaka, T.; Okada, S.; Ueno, H. Targeted transarterial oily chemoembolization for small foci of hepatocellular carcinoma using a unified helical CT and angiography system: Analysis of factors affecting local recurrence and survival rates. AJR. Am. J. Roentogenol. 2001, 176, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwazawa, J.; Ohue, S.; Hashimoto, N.; Muramoto, O.; Mitani, T. Survival after C-arm CT-assisted chemoembolization of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur. J. Radiol. 2012, 81, 3985–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschamps, F.; Solomon, S.B.; Thornton, R.H.; Rao, P.; Hakime, A.; Kuoch, V.; De Baere, T. Computed analysis of three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography angiography for determination of tumor-feeding vessels during chemoembolization of liver tumor: A pilot study. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2010, 33, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwazawa, J.; Ohue, S.; Hashimoto, N.; Muramoto, O.; Mitani, T. Clinical utility and limitations of tumor-feeder detection software for liver cancer embolization. Eur. J. Radiol. 2013, 82, 1665–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyayama, S.; Yamashiro, M.; Hashimoto, M.; Hashimoto, N.; Ikuno, M.; Okumura, K.; Yoshida, M.; Matsui, O. Identification of small hepatocellular carcinoma and tumor-feeding branches with cone-beam CT guidance technology during transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2013, 24, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, Y.; Yagyu, Y.; Murakami, T.; Kudo, M. Tracking navigation imaging of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma using three-dimensional cone-beam CT angiography. Liver Cancer 2014, 3, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyayama, S.; Yamashiro, M.; Nagai, K.; Tohyama, J.; Kawamura, K. Efficacy of automated tumor-feeder detection software using cone-beam computed tomography technology in transarterial targeted therapy. Intervent. Radiol. 2016, 1, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyayama, S.; Yamashiro, M.; Nagai, K.; Tohyama, J.; Kawamura, K.; Yoshida, M.; Sakuragawa, N. Efficacy of automated tumor-feeder detection software using cone-beamcomputed tomography technology in transarterial embolization through extrahepatic collateral vessels for malignant hepatic tumors. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Han, K.H.; Ye, S.L.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Y.H.; Lin, S.M.; Wang, C.K.; Ikeda, M.; Chan, S.T.; Choo, S.P.; et al. A changing paradigm for the treatment of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: Asia-Pacific Primary Liver Cancer Expert Consensus Statements. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, N.; Tanaka, T.; Nishiofuku, H.; Sato, T.; Masada, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Anai, H.; Sakaguchi, H.; Sueyoshi, S.; Marugami, N.; et al. Transarterial chemoembolization remains an effective therapy for intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma with preserved liver function. Hepatol. Res. 2020. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32721060/ (accessed on 28 July 2020). [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K. Normalization of tumor vasculature: An emerging concept in antiangiogenic treatment. Science 2005, 307, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, M.R.; Komuta, Y.; Iwata, C.; Oka, M.; Shirai, Y.; Morishita, Y.; Ouchi, Y.; Kataoka, K.; Miyazono, K. Comparison of the effects of the kinase inhibitors imatinib, sorafenib, and transforming growth factor-beta receptor inhibitor on extravasation of nanoparticles from neovasculature. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakado, K.; Miyayama, S.; Hirota, S.; Mizunuma, K.; Nakamura, K.; Inaba, Y.; Maeda, H.; Matsuo, K.; Nishida, N.; Aramaki, T.; et al. Subgrouping of intermediate-stage (BCLC stage B) hepatocellular carcinoma based on tumor number and size and Child-Pugh grade correlated with prognosis after transarterial chemoembolization. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2014, 32, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakado, K.; Miyayama, S.; Hirota, S.; Mizunuma, K.; Nakamura, K.; Inaba, Y.; Maeda, H.; Matsuo, K.; Nishida, N.; Aramaki, T.; et al. Prognosis of patients with intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinomas based on the Child-Pugh score: Subclassifying the intermediate stage (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Stage B). Jpn. J. Radiol. 2014, 32, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakado, K.; Miyayama, S.; Hirota, S.; Mizunuma, K.; Nakamura, K.; Inaba, Y.; Maeda, H.; Matsuo, K.; Nishida, N.; Aramaki, T.; et al. Hepatic arterial embolization for unresectable hepatocellular carcinomas: Do technical factors affect prognosis? Jpn. J. Radiol. 2012, 30, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, A.; Wilkerson, J.; Greten, T.F. Hemorrhagic events in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with antiangiogenic therapies. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyayama, S.; Matsui, O.; Yamashiro, M.; Ryu, Y.; Takata, H.; Takeda, T.; Aburano, H.; Shigenari, N. Iodized oil accumulation in the hypovascular tumor portion of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma after ultraselective transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Hepatol. Int. 2007, 1, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ESMO Guidelines Committee. eUpdate Hepatocellular Carcinoma Algorithm. Available online: https://www.esmo.org/guidelines/gastrointestinal-cancers/hepatocellular-carcinoma/eupdate-hepatocellular-carcinoma-algorithm (accessed on 19 June 2020).
- Sato, Y.; Nishiofuku, H.; Yasumoto, T.; Nakatsuka, A.; Matsuo, K.; Kodama, Y.; Okubo, H.; Abo, D.; Takaki, H.; Inaba, Y.; et al. Multicenter phase II clinical trial of sorafenib with transarterial chemoembolization for advanced stage hepatocellular carcinomas (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage C): STAB Study. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2018, 29, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokudo, N.; Takemura, N.; Hasegawa, K.; Takayama, T.; Kubo, S.; Shimada, M.; Nagano, H.; Hatano, E.; Izumi, N.; Kaneko, S.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for hepatocellular carcinoma: The Japan Society of Hepatology 2017 (4th JSH-HCC guidelines) 2019 update. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 49, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Author | Group/ | TACE | N | Bead | CR | PR | OR | P-Value | OS (%) | P-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Year) | Subgroup | Technique | Size (μm) | (%) | (%) | (%) | 1 y | 2 y | |||
| Lammer Ref. [62] (2010) | Advanced disease * | DEB | 93 | mainly, 300–500 | 26.9 | 24.7 | 51.6 | 0.11 | |||
| cTACE | 108 | 22.2 | 21.3 | 43.5 | |||||||
| DEB | 63 | 52.4 | 0.038 | ||||||||
| cTACE | 72 | 34.7 | |||||||||
| Sacco Ref. [63] (2011) | DEB | 33 | 100–300 | 51.5 | 48.5 | 100 | 0.1 | 90 | 87 | 0.96 | |
| cTACE | 34 | 70.6 | 29.4 | 100 | 90 | 84 | |||||
| Golfieri Ref. [64] (2014) | DEB | 89 | 100–300 | 52.2 | 7.5 | 59.7 | 0.217 | 86 | 57 | 0.949 | |
| cTACE | 88 | 58.1 | 12.2 | 70.3 | 84 | 55 | |||||
| Ikeda Ref. [65] (2020) | DEB | 99 | 100–300 | 35.7 at 1 month | <0.0001 | ||||||
| 27.6 at 3 months | |||||||||||
| cTACE | 101 | 84.2 at 1 month | <0.0001 | ||||||||
| 75.2 at 3 months | |||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyayama, S. Treatment Strategy of Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7337. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207337
Miyayama S. Treatment Strategy of Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(20):7337. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207337
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyayama, Shiro. 2020. "Treatment Strategy of Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Applied Sciences 10, no. 20: 7337. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207337
APA StyleMiyayama, S. (2020). Treatment Strategy of Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Applied Sciences, 10(20), 7337. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10207337





