Implementation of High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) in Aptamer Selection Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
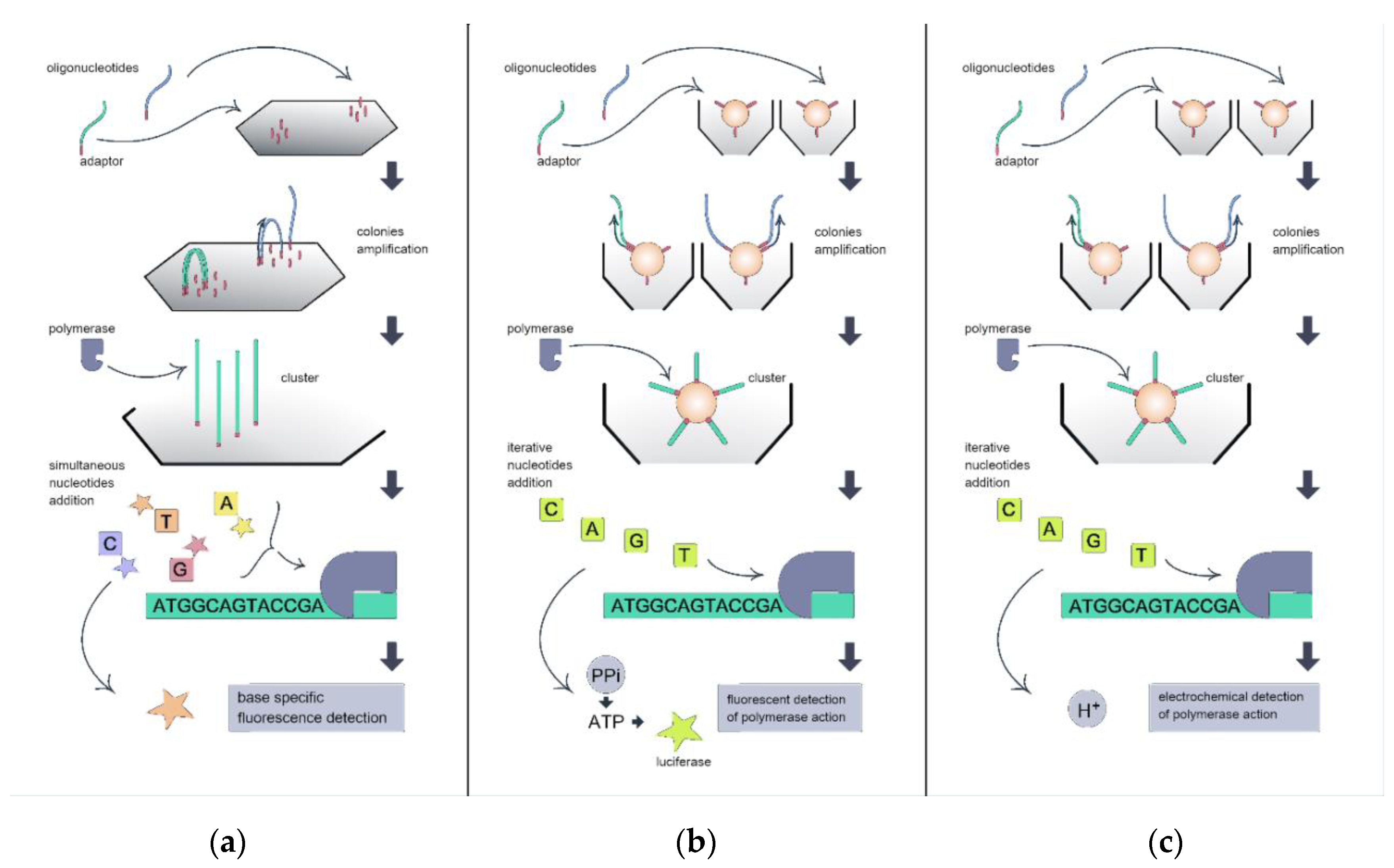
2. Sequencing Platforms
3. Sample Preparation for High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS)
4. Processing of HTS Data
5. Insights to Aptamer Selection Process Derived from HTS Data
5.1. Identification of the Most Prominent Candidate Aptamer Sequences
5.2. Decreasing the Number of Selection Cycles
5.3. Validation of the Starting SELEX Libraries
5.4. Study of Sequence and Nucleotide Bias in the Selection Process
5.5. Comparison and Validation of SELEX Strategies
5.6. Assisting Novel SELEX Strategies
5.7. Deeper Analysis of Aptamer Structure and Function
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HTS | High-throughput sequencing |
| SELEX | Systematic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential enrichment |
| ISFET | Ion-sensitive field effect transistor |
| NGS | Next generation sequencing |
| GUI | Graphical user interface |
| IT | Information technology |
| CE | Capillary electrophoresis |
| TBA | Thrombin-binding aptamer (TBA) |
| ctITP | Capillary transient isotachophoresis (ctITP) |
| MACE | Microbead-assisted capillary electrophoresis (MACE) |
| PAI-1 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) |
References
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellington, A.D.; Szostak, J.W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 1990, 346, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komarova, N.; Kuznetsov, A. Inside the Black Box: What Makes SELEX Better? Molecules 2019, 24, 3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, C.; Yang, G.; Ghulam, M.; Li, L.; Qu, F. Evolution of multi-functional capillary electrophoresis for high-efficiency selection of aptamers. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 107432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, S.; McPherson, J.D.; McCombie, W.R. Coming of age: Ten years of next-generation sequencing technologies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 333–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.K.; Bruno, J.G.; Dhiman, A. ABCs of DNA aptamer and related assay development. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 275–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, B.; Bilusic, I.; Lorenz, C.; Schroeder, R. Genomic SELEX: A discovery tool for genomic aptamers. Methods 2010, 52, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dijk, E.L.; Jaszczyszyn, Y.; Thermes, C. Library preparation methods for next-generation sequencing: Tone down the bias. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 322, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawluczyk, M.; Weiss, J.; Links, M.G.; Egaña Aranguren, M.; Wilkinson, M.D.; Egea-Cortines, M. Quantitative evaluation of bias in PCR amplification and next-generation sequencing derived from metabarcoding samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolle, F.; Mayer, G. Preparation of SELEX Samples for Next-Generation Sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Aptamers. Methods in Molecular Biology; Mayer, G., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1380, pp. 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Riley, K.R.; Gagliano, J.; Xiao, J.; Libby, K.; Saito, S.; Yu, G.; Cubicciotti, R.; Macosko, J.; Colyer, C.L.; Guthold, M.; et al. Combining capillary electrophoresis and next-generation sequencing for aptamer selection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valenzano, S.; De Girolamo, A.; DeRosa, M.C.; McKeague, M.; Schena, R.; Catucci, L.; Pascale, M. Screening and Identification of DNA Aptamers to Tyramine Using in Vitro Selection and High-Throughput Sequencing. ACS Comb. Sci. 2016, 18, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quang, N.N.; Miodek, A.; Cibiel, A.; Ducongé, F. Selection of Aptamers Against Whole Living Cells: From Cell-SELEX to Identification of Biomarkers. In Synthetic Antibodies; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 253–272. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, J.A.; Parekh, P.; Kim, Y.; Morey, T.E.; Sefah, K.; Gravenstein, N.; Dennis, D.M.; Tan, W. Selection of an Aptamer Antidote to the Anticoagulant Drug Bivalirudin. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Teng, I.-T.; Zhang, L.; Delgado, S.; Champanhac, C.; Cansiz, S.; Wu, C.; Shan, H.; Tan, W. Molecular Recognition of Human Liver Cancer Cells Using DNA Aptamers Generated via Cell-SELEX. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimoto, M.; Matsunaga, K.; Hirao, I. DNA Aptamer Generation by Genetic Alphabet Expansion SELEX (ExSELEX) Using an Unnatural Base Pair System. In Nucleic Acid Aptamers; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 47–60. [Google Scholar]
- Spiga, F.M.; Maietta, P.; Guiducci, C. More DNA–Aptamers for Small Drugs: A Capture–SELEX Coupled with Surface Plasmon Resonance and High-Throughput Sequencing. ACS Comb. Sci. 2015, 17, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoon, S.; Zhou, B.; Janda, K.; Brenner, S.; Scolnick, J. Aptamer selection by high-throughput sequencing and informatic analysis. Biotechniques 2011, 51, 413–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, M.; Xiao, Y.; Nie, J.; Stewart, R.; Csordas, A.T.; Oh, S.S.; Thomson, J.A.; Soh, H.T. Quantitative selection of DNA aptamers through microfluidic selection and high-throughput sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 15373–15378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kupakuwana, G.V.; Crill, J.E.; McPike, M.P.; Borer, P.N. Acyclic Identification of Aptamers for Human alpha-Thrombin Using Over-Represented Libraries and Deep Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beier, R.; Boschke, E.; Labudde, D. New Strategies for Evaluation and Analysis of SELEX Experiments. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoinka, J.; Berezhnoy, A.; Dao, P.; Sauna, Z.E.; Gilboa, E.; Przytycka, T.M. Large scale analysis of the mutational landscape in HT-SELEX improves aptamer discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 5699–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroli, J.; Taccioli, C.; De La Fuente, A.; Serafini, P.; Bicciato, S. APTANI: A computational tool to select aptamers through sequence-structure motif analysis of HT-SELEX data. Bioinformatics 2015, 32, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Meyer, S.; Hou, Z.; Propson, N.E.; Soh, H.T.; Thomson, J.A.; Stewart, R. MPBind: A Meta-motif-based statistical framework and pipeline to Predict Binding potential of SELEX-derived aptamers. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2665–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jing, M.; Bowser, M.T. Tracking the Emergence of High Affinity Aptamers for rhVEGF 165 During Capillary Electrophoresis-Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment Using High Throughput Sequencing. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10761–10770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kurtz, S.; Narechania, A.; Stein, J.C.; Ware, D. A new method to compute K-mer frequencies and its application to annotate large repetitive plant genomes. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stoltenburg, R.; Nikolaus, N.; Strehlitz, B. Capture-SELEX: Selection of DNA Aptamers for Aminoglycoside Antibiotics. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2012, 2012, 415697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiel, W.H.; Giangrande, P.H. Analyzing HT-SELEX data with the Galaxy Project tools—A web based bioinformatics platform for biomedical research. Methods 2016, 97, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiel, W.H. Galaxy Workflows for Web-based Bioinformatics Analysis of Aptamer High-throughput Sequencing Data. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoinka, J.; Przytycka, T. AptaPLEX—A dedicated, multithreaded demultiplexer for HT-SELEX data. Methods 2016, 106, 82–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütze, T.; Wilhelm, B.; Greiner, N.; Braun, H.; Peter, F.; Mörl, M.; Erdmann, V.A.; Lehrach, H.; Konthur, Z.; Menger, M.; et al. Probing the SELEX Process with Next-Generation Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e29604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alam, K.K.; Chang, J.L.; Burke, D.H. FASTAptamer: A Bioinformatic Toolkit for High-throughput Sequence Analysis of Combinatorial Selections. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2015, 4, e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulmé, J.-J.; Azéma, L.; Darfeuille, F.; Dausse, E.; Durand, G.; Paurelle, O. Aptamers in Bordeaux 2017: An exceptional “millésime”. Biochimie 2018, 145, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhler, J. Efficient large-scale sequence comparison by locality-sensitive hashing. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoinka, J.; Berezhnoy, A.; Sauna, Z.E.; Gilboa, E.; Przytycka, T.M. AptaCluster—A Method to Cluster HT-SELEX Aptamer Pools and Lessons from Its Application. In International Conference on Research in Computational Molecular Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 115–128. [Google Scholar]
- Pitt, J.N.; Rajapakse, I.; Ferre-D’Amare, A.R. SEWAL: An open-source platform for next-generation sequence analysis and visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 7908–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozupone, C.; Changayil, S.; Majerfeld, I.; Yarus, M. Selection of the simplest RNA that binds isoleucine. RNA 2003, 9, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cowperthwaite, M.C.; Ellington, A.D. Bioinformatic Analysis of the Contribution of Primer Sequences to Aptamer Structures. J. Mol. Evol. 2008, 67, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoinka, J.; Zotenko, E.; Friedman, A.; Sauna, Z.E.; Przytycka, T.M. Identification of sequence-structure RNA binding motifs for SELEX-derived aptamers. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, i215–i223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Höner zu Siederdissen, C.; Tafer, H.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.F.; Hofacker, I.L. ViennaRNA Package 2.0. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2011, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroli, J.; Forcato, M.; Bicciato, S. APTANI2: Update of aptamer selection through sequence-structure analysis. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2266–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shieh, K.R.; Kratschmer, C.; Maier, K.E.; Greally, J.M.; Levy, M.; Golden, A. AptCompare: Optimized de novo motif discovery of RNA aptamers via HTS-SELEX. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2905–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditzler, M.A.; Lange, M.J.; Bose, D.; Bottoms, C.A.; Virkler, K.F.; Sawyer, A.W.; Whatley, A.S.; Spollen, W.; Givan, S.A.; Burke, D.H. High-throughput sequence analysis reveals structural diversity and improved potency among RNA inhibitors of HIV reverse transcriptase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 1873–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, M. Next-Generation Analysis of Deep Sequencing Data: Bringing Light into the Black Box of SELEX Experiments. In Nucleic Acid Aptamers. Selection, Characterization, and Application; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ishida, R.; Adachi, T.; Yokota, A.; Yoshihara, H.; Aoki, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Hamada, M. RaptRanker: In silico RNA aptamer selection from HT-SELEX experiment based on local sequence and structure information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, T.; Ozaki, H.; Terai, G.; Asai, K.; Iwasaki, W.; Kiryu, H. CapR: Revealing structural specificities of RNA-binding protein target recognition using CLIP-seq data. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoinka, J.; Backofen, R.; Przytycka, T.M. AptaSUITE: A Full-Featured Bioinformatics Framework for the Comprehensive Analysis of Aptamers from HT-SELEX Experiments. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 11, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoltenburg, R.; Strehlitz, B. Refining the Results of a Classical SELEX Experiment by Expanding the Sequence Data Set of an Aptamer Pool Selected for Protein A. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Civit, L.; Taghdisi, S.M.; Jonczyk, A.; Haßel, S.K.; Gröber, C.; Blank, M.; Stunden, H.J.; Beyer, M.; Schultze, J.; Latz, E.; et al. Systematic evaluation of cell-SELEX enriched aptamers binding to breast cancer cells. Biochimie 2018, 145, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Simaeys, D.; López-Colón, D.; Sefah, K.; Sutphen, R.; Jimenez, E.; Tan, W. Study of the Molecular Recognition of Aptamers Selected through Ovarian Cancer Cell-SELEX. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezhnoy, A.; Stewart, C.A.; Mcnamara, J.O., II; Thiel, W.; Giangrande, P.; Trinchieri, G.; Gilboa, E. Isolation and Optimization of Murine IL-10 Receptor Blocking Oligonucleotide Aptamers Using High-throughput Sequencing. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 1242–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.-W.; Lee, S.J.; Ren, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Laurell, T. Acousto-microfluidics for screening of ssDNA aptamer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stuart, C.H.; Riley, K.R.; Boyacioglu, O.; Herpai, D.M.; Debinski, W.; Qasem, S.; Marini, F.C.; Colyer, C.L.; Gmeiner, W.H. Selection of a Novel Aptamer Against Vitronectin Using Capillary Electrophoresis and Next Generation Sequencing. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, B.; Gesell, T.; Chen, D.; Lorenz, C.; Schroeder, R. Monitoring Genomic Sequences during SELEX Using High-Throughput Sequencing: Neutral SELEX. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soldevilla, M.M.; Hervas, S.; Villanueva, H.; Lozano, T.; Rabal, O.; Oyarzabal, J.; Lasarte, J.J.; Bendandi, M.; Inoges, S.; López-Díaz de Cerio, A.; et al. Identification of LAG3 high affinity aptamers by HT-SELEX and Conserved Motif Accumulation (CMA). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jayasena, S.D. Aptamers: An emerging class of molecules that rival antibodies in diagnostics. Clin. Chem. 1999, 45, 1628–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roth, F.; De La Fuente, A.C.; Vella, J.L.; Zoso, A.; Inverardi, L.; Serafini, P. Aptamer-Mediated Blockade of IL4R Triggers Apoptosis of MDSCs and Limits Tumor Progression. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1373–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, R.; Bourne, C.; Chaudhuri, R.R.; Gregory, R.; Kenny, J.; Cossins, A. Single-Step Selection of Bivalent Aptamers Validated by Comparison with SELEX Using High-Throughput Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lisi, S.; Fiore, E.; Scarano, S.; Pascale, E.; Boehman, Y.; Ducongé, F.; Chierici, S.; Minunni, M.; Peyrin, E.; Ravelet, C. Non-SELEX isolation of DNA aptamers for the homogeneous-phase fluorescence anisotropy sensing of tau Proteins. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1038, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, K.; Latulippe, D.R.; Ozer, A.; Pagano, J.M.; White, B.S.; Shalloway, D.; Lis, J.T.; Craighead, H.G. RAPID-SELEX for RNA Aptamers. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vorobyeva, M.; Davydova, A.; Vorobjev, P.; Pyshnyi, D.; Venyaminova, A. Key Aspects of Nucleic Acid Library Design for in Vitro Selection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, M.; Wu, X.; Ho, M.; Chomchan, P.; Rossi, J.J.; Burnett, J.C.; Zhou, J. High throughput sequencing analysis of RNA libraries reveals the influences of initial library and PCR methods on SELEX efficiency. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall, B.; Micheletti, J.M.; Satya, P.; Ogle, K.; Pollard, J.; Ellington, A.D. Design, Synthesis, and Amplification of DNA Pools for In Vitro Selection. In Current Protocols in Nucleic Acid Chemistry; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 9.2.1–9.2.28. [Google Scholar]
- Scoville, D.J.; Uhm, T.K.B.; Shallcross, J.A.; Whelan, R.J. Selection of DNA Aptamers for Ovarian Cancer Biomarker CA125 Using One-Pot SELEX and High-Throughput Sequencing. J. Nucleic Acids 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terekhov, S.S.; Eliseev, I.E.; Ovchinnikova, L.A.; Kabilov, M.R.; Prjibelski, A.D.; Tupikin, A.E.; Smirnov, I.V.; Belogurov, A.A.; Severinov, K.V.; Lomakin, Y.A.; et al. Liquid drop of DNA libraries reveals total genome information. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 27300–27306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skouridou, V.; Jauset-Rubio, M.; Ballester, P.; Bashammakh, A.S.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Alyoubi, A.O.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Selection and characterization of DNA aptamers against the steroid testosterone. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, H.; Ren, S.; Kang, J.; Kim, M.; Jiang, Y.; Jin, M.M.; Min, I.M.; Kim, S. Sol-Gel SELEX Circumventing Chemical Conjugation of Low Molecular Weight Metabolites Discovers Aptamers Selective to Xanthine. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2013, 23, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakui, K.; Yoshitomi, T.; Yamaguchi, A.; Tsuchida, M.; Saito, S.; Shibukawa, M.; Furusho, H.; Yoshimoto, K. Rapidly Neutralizable and Highly Anticoagulant Thrombin-Binding DNA Aptamer Discovered by MACE SELEX. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lorenz, C.; von Pelchrzim, F.; Schroeder, R. Genomic systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (Genomic SELEX) for the identification of protein-binding RNAs independent of their expression levels. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2204–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, C.; Gesell, T.; Zimmermann, B.; Schoeberl, U.; Bilusic, I.; Rajkowitsch, L.; Waldsich, C.; von Haeseler, A.; Schroeder, R. Genomic SELEX for Hfq-binding RNAs identifies genomic aptamers predominantly in antisense transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 3794–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiss, D.J.; Mobley, H.L.T. Determination of Target Sequence Bound by PapX, Repressor of Bacterial Motility, in flhD Promoter Using Systematic Evolution of Ligands by Exponential Enrichment (SELEX) and High Throughput Sequencing. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 44726–44738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiss, D.J.; Howard, F.M.; Mobley, H.L.T. A Novel Approach for Transcription Factor Analysis Using SELEX with High-Throughput Sequencing (TFAST). PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitta, K.R.; Vincentelli, R.; Jacox, E.; Cimino, A.; Ohtsuka, Y.; Sobral, D.; Satou, Y.; Cambillau, C.; Lemaire, P. High-Throughput Protein Production Combined with High-Throughput SELEX Identifies an Extensive Atlas of Ciona robusta Transcription Factor DNA-Binding Specificities. In High-Throughput Protein Production and Purification; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 487–517. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelsayed, M.M.; Ho, B.T.; Vu, M.M.K.; Polanco, J.; Spitale, R.C.; Lupták, A. Multiplex Aptamer Discovery through Apta-Seq and Its Application to ATP Aptamers Derived from Human-Genomic SELEX. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 2149–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, D.M.; Larsen, N.; Jensen, J.K.; Andreasen, P.A.; Kjems, J. Characterisation of aptamer–target interactions by branched selection and high-throughput sequencing of SELEX pools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madsen, J.B.; Dupont, D.M.; Andersen, T.B.; Nielsen, A.F.; Sang, L.; Brix, D.M.; Jensen, J.K.; Broos, T.; Hendrickx, M.L.V.; Christensen, A.; et al. RNA Aptamers as Conformational Probes and Regulatory Agents for Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 4103–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauset-Rubio, M.; Botero, M.L.; Skouridou, V.; Aktas, G.B.; Svobodova, M.; Bashammakh, A.S.; El-Shahawi, M.S.; Alyoubi, A.O.; O’Sullivan, C.K. One-Pot SELEX: Identification of Specific Aptamers against Diverse Steroid Targets in One Selection. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 20188–20196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.; Maufort, J.P.; Nie, J.; Stewart, R.; McIntosh, B.E.; Conti, L.R.; Ahmad, K.M.; Soh, H.T.; Thomson, J.A. Development of an Efficient Targeted Cell-SELEX Procedure for DNA Aptamer Reagents. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pleiko, K.; Saulite, L.; Parfejevs, V.; Miculis, K.; Vjaters, E.; Riekstina, U. Differential binding cell-SELEX method to identify cell-specific aptamers using high-throughput sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levay, A.; Brenneman, R.; Hoinka, J.; Sant, D.; Cardone, M.; Trinchieri, G.; Przytycka, T.M.; Berezhnoy, A. Identifying high-affinity aptamer ligands with defined cross-reactivity using high-throughput guided systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen Quang, N.; Perret, G.; Ducongé, F. Applications of High-Throughput Sequencing for In Vitro Selection and Characterization of Aptamers. Pharmaceuticals 2016, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozer, A.; Pagano, J.M.; Lis, J.T. New Technologies Provide Quantum Changes in the Scale, Speed, and Success of SELEX Methods and Aptamer Characterization. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dausse, E.; Taouji, S.; Evadé, L.; Di Primo, C.; Chevet, E.; Toulmé, J.-J. HAPIscreen, a method for high-throughput aptamer identification. J. Nanobiotechnology 2011, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cho, M.; Soo Oh, S.; Nie, J.; Stewart, R.; Eisenstein, M.; Chambers, J.; Marth, J.D.; Walker, F.; Thomson, J.A.; Soh, H.T. Quantitative selection and parallel characterization of aptamers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18460–18465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Software | Analysis Stages | Platforms | GUI | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Galaxy [28,29] | Data preprocessing | Web/Linux/Mac OS | Yes | https://usegalaxy.org/ |
| Enrichment counting | ||||
| FastAptamer [32] | Enrichment counting | Linux/Mac OS/Windows/Galaxy | No | https://github.com/FASTAptamer/FASTAptamer |
| Sequence based clustering | ||||
| Searching known motifs | ||||
| PATTERNITY-seq [33] | Sequence based clustering | Linux/Mac OS/Windows | No | https://github.com/AptaFred/EGE_tree |
| MEME/GLAM [37] | Sequence motif searching | Linux/Mac OS/Web | Yes (Web) | http://meme-suite.org |
| MPBind [24] | Data preprocessing | Linux/Mac OS | No | https://morgridge.org/research/regenerative-biology/software-resources/mpbind/ |
| Sequence motif searching | ||||
| Aptamotif [40] | Structure motif searching | Linux/Mac OS | No | By request |
| APTANI [23] | Enrichment counting | Linux/Mac OS | No | http://aptani.unimore.it/ |
| Structure motif searching | ||||
| APTANI2 [42] | Enrichment counting | Linux/Mac OS | Yes | http://aptani.unimore.it/ |
| Structure motif searching | ||||
| AptCompare [43] | Data preprocessing | Linux/Mac OS/Windows | Yes | https://bitbucket.org/shiehk/aptcompare/src/master/ |
| Enrichment counting | ||||
| Sequence based clustering | ||||
| Sequence motif searching | ||||
| Structure motif searching | ||||
| COMPAS [45] | Data preprocessing | Unknown | Yes | Unknown |
| Enrichment counting | ||||
| Sequence based clustering | ||||
| Structure motif searching | ||||
| RaptRanker [46] | Data preprocessing | Linux/Mac OS | No | https://github.com/hmdlab/RaptRanker |
| Enrichment counting | ||||
| Structure motif searching | ||||
| AptaSUITE [48] | Data preprocessing | Linux/Mac OS/Windows | Yes | https://github.com/drivenbyentropy/aptasuite |
| Enrichment counting | ||||
| Sequence based clustering | ||||
| Structure motif searching | ||||
| SELEX simulation |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Komarova, N.; Barkova, D.; Kuznetsov, A. Implementation of High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) in Aptamer Selection Technology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228774
Komarova N, Barkova D, Kuznetsov A. Implementation of High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) in Aptamer Selection Technology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(22):8774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228774
Chicago/Turabian StyleKomarova, Natalia, Daria Barkova, and Alexander Kuznetsov. 2020. "Implementation of High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) in Aptamer Selection Technology" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 22: 8774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228774
APA StyleKomarova, N., Barkova, D., & Kuznetsov, A. (2020). Implementation of High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) in Aptamer Selection Technology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(22), 8774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228774





