Expanding the Clinical and Mutational Spectrum of the PLP1-Related Hypomyelination of Early Myelinated Structures (HEMS)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Histories
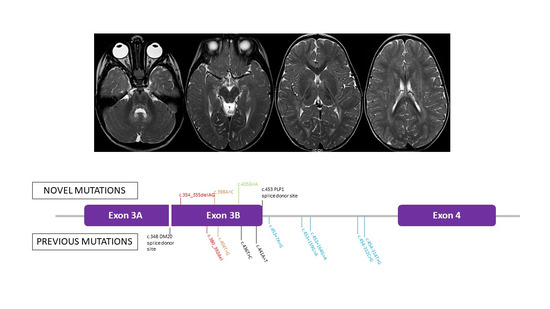
3.2. Genetic Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yool, D.A.; Edgar, J.M.; Montague, P.; Malcolm, S. The proteolipid protein gene and myelin disorders in man and animal models. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2000, 9, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kevelam, S.H.; Taube, J.R.; van Spaendonk, R.M.L.; Bertini, E.; Sperle, K.; Tarnopolsky, M.; Tonduti, D.; Valente, E.M.; Travaglini, L.; Sistermans, E.A.; et al. Altered PLP1 splicing causes hypomyelination of early myelinating structures. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2015, 2, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenweg, M.E.; Wolf, N.I.; Schieving, J.H.; Elsaid, M.F.; Friederich, R.L.; Østergaard, J.R.; Barkhof, F.; Pouwels, P.J.W.; van der Knaap, M.S. Novel hypomyelinating leukoencephalopathy affecting early myelinating structures. Arch. Neurol. 2012, 69, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichiecchio, A.; Wolf, N.I.; Ariaudo, G.; van der Knaap, M.S.; Bastianello, S.; Balottin, U.; Orcesi, S.; Tonduti, D. Novel hypomyelinating leukoencephalopathy affecting early myelinating structures: Clinical course in two brothers. Neuropediatrics 2013, 44, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saugier-Veber, P.; Munnich, A.; Bonneau, D.; Rozet, J.-M.; Le Merrer, M.; Gil, R.; Boespflug-Tanguy, O. X-linked spastic paraplegia and Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease are allelic disorders at the proteolipid protein locus. Nat. Genet. 1994, 6, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, K.; Sambuughin, N.; Selenge, B.; Nagle, J.W.; Baasanjav, D.; Hudson, L.D.; Goldfarb, L.G. Novel exon 3B proteolipid protein gene mutation causing late-onset spastic paraplegia type 2 with variable penetrance in female family members. Ann. Neurol. 1999, 45, 680–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cailloux, F.; Gauthier-Barichard, F.; Mimault, C.; Isabelle, V.; Courtois, V.; Giraud, G.; Dastugue, B.; Boespflug-Tanguy, O. Clinical European Network on Brain Dysmyelinating Disease. Genotype-phenotype correlation in inherited brain myelination defects due to proteolipid protein gene mutations. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2000, 8, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shy, M.E.; Hobson, G.; Jain, M.; Boespflug-Tanguy, O.; Garbern, J.; Sperle, K.; Li, W.; Gow, A.; Rodriguez, D.; Bertini, E.; et al. Schwann cell expression of PLP1 but not DM20 is necessary to prevent neuropathy. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 53, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hübner, C.; Senning, A.; Orth, U.; Zerres, K.; Urbach, H.; Gal, A.; Rudnik-Schöneborn, M.S. Mild Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease caused by a point mutation affecting correct splicing of PLP1 mRNA. Neuroscience 2005, 132, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, M.P.; Golomb, M.R.; Walsh, L.E.; Hobson, G.M.; Garbern, J.Y.; Kinkel, R.P.; Darras, B.T.; Urion, D.K.; Eksioglu, Y.Z. Steroid-responsive neurologic relapses in a child with a proteolipid protein-1 mutation. Neurology 2007, 68, 1305–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osaka, H.; Koizume, S.; Aoyama, H.; Iwamoto, H.; Kimura, S.; Nagai, J.-I.; Kurosawa, K.; Yamashita, S. Mild phenotype in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease caused by a PLP1-specific mutation. Brain Dev. 2010, 32, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laukka, J.J.; Stanley, J.A.; Garbern, J.Y.; Trepanier, A.; Hobson, G.; LaFleur, T.; Gow, A.; Kamholz, J. Neuroradiologic correlates of clinical disability and progression in the X-linked leukodystrophy Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2013, 335, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, H.; Feng, H.; Ji, J.; Wu, Y.; Kou, L.; Li, N.; Ji, H.; Wu, X.; Niu, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Identification and functional study of novel PLP1 mutations in Chinese patients with Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Brain Dev. 2015, 37, 797–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omata, T.; Nagai, J.-I.; Shimbo, H.; Koizume, S.; Miyagi, Y.; Kurosawa, K.; Yamashita, S.; Osaka, H.; Inoue, K. A splicing mutation of proteolipid protein 1 in Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease. Brain Dev. 2016, 38, 581–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Patient | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General data | ||||
| PLP1 mutation | c.354_355delAG; p.(G120PfsTer83) | c.398A>C; p.(H133P) | c.435G>A; p.(W145Ter) | c.435G>A; p.(W145Ter) |
| Male/Female | M | M | M | M |
| Ethnicity | Georgian | Italian | Italian | Italian |
| Current age | 6 years 4 months | 3 years 4 months | 8 years | 46 years |
| Familial/Isolated | I | I | F | F |
| Presentation | ||||
| Age at onset | 8 months | 6 months | 9 months | 6 months |
| Signs at onset | Psychomotor delay | Nystagmus | Psychomotor delay | Psychomotor delay |
| First examination | ||||
| Age | 4 years 5 months | 2 years | 1 year | 40 years |
| Eye movements | No | Nystagmus | Strabismus, nystagmus | No |
| Muscle tone | Mild axial and lower limbs hypotonia | Mild hypertonia | Axial hypotonia, limbs hypertonia | Limbs hypertonia |
| Pyramidal signs | Yes (mildly increased OTR) | Yes (increased OTR) | Yes (Babinski, clonus, increased OTR) | Yes (Babinski, clonus, increased OTR) |
| Extrapyramidal signs | No | No | Yes (orofacial dyskinesia) | No |
| Bulbar signs | No | No | Yes (dysphagia) | No |
| Cerebellar signs | Yes (ataxia, upper limbs tremor, dysarthria) | Yes (ataxia, mild dysmetria, and dysarthria) | Yes (head and trunk titubation, upper limbs tremor, dysarthria) | Yes (ataxia, upper limbs tremor, dysarthria) |
| Sensory function | Normal | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Gait | Supported | Unsupported | Supported | Lost |
| Clinical course | ||||
| Age at last evaluation | 5 years 6 months | 3 years 1 month | 8 years | 46 years |
| Functional | Ataxic syndrome | Ataxic-spastic syndrome | Ataxic-spastic syndrome | Ataxic-spastic syndrome |
| Motor outcome | Sitting position 2 years; able to walk with light support from age of 4 years | Sitting position 1 year; autonomous walking from age of 2 years; running possible | Sitting position 3 years; able to walk with stroller from age of 6.5 years | Able to walk from 2.5 to 20 years |
| Cognitive outcome | Speak with simple sentences from age of 3 years | First words from 2 years; speak with complex sentences from age of 3 years | Limited speech, only few words easy to understand) | Unintelligible speech |
| Regression | No | No | No | Loss of ambulation |
| Other features | No | No | No | No |
| GMFCS | III | I | III | NA |
| EDACS | I | I | III | NA |
| MACS/Mini-MACS | II | II | III | NA |
| CFCS | II | I | III | NA |
| VSS | II | I | III | IV |
| Patient | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age at first MRI | 4 years 4 months | 2 years 1 months | 1 years 9 months |
| Increased T2 signal | |||
| Medulla | − | + | + |
| Pons | + (mild, posterior) | + (peripheral) | + (posterior) |
| Midbrain | − | + | − |
| Dentate nuclei | − | + | + |
| Hilus of dentate nuclei | − | + | + |
| Cerebellar WM | − | − | − |
| Optic radiations | + | + | + |
| Periventricular WM | + (very mild) | + | + |
| IC, anterior limb | − | − | − |
| IC, posteriori limb | + (poor definition, stripes) | + (tram track) | + (tram track) |
| Corpus callosum | − | − | − |
| Subcortical WM | + (very mild) | + | + |
| Basal ganglia | − | − | − |
| Thalami | − | + (dorsomedial) | + (dorsomedial) |
| Cerebral cortex | − | − | − |
| Age at last MRI | 5 years 5 months | NP | 7 years 8 months |
| Variations | No | NA | Yes |
| Improvement | − | NA | Medulla, DN, pons |
| Unchanged | − | NA | Optic radiations, PLIC, thalami |
| Worsening | − | NA | Periventricular and subcortical WM |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nicita, F.; Aiello, C.; Vasco, G.; Valeriani, M.; Stregapede, F.; Sancesario, A.; Armando, M.; Bertini, E. Expanding the Clinical and Mutational Spectrum of the PLP1-Related Hypomyelination of Early Myelinated Structures (HEMS). Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11010093
Nicita F, Aiello C, Vasco G, Valeriani M, Stregapede F, Sancesario A, Armando M, Bertini E. Expanding the Clinical and Mutational Spectrum of the PLP1-Related Hypomyelination of Early Myelinated Structures (HEMS). Brain Sciences. 2021; 11(1):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11010093
Chicago/Turabian StyleNicita, Francesco, Chiara Aiello, Gessica Vasco, Massimiliano Valeriani, Fabrizia Stregapede, Andrea Sancesario, Michela Armando, and Enrico Bertini. 2021. "Expanding the Clinical and Mutational Spectrum of the PLP1-Related Hypomyelination of Early Myelinated Structures (HEMS)" Brain Sciences 11, no. 1: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11010093
APA StyleNicita, F., Aiello, C., Vasco, G., Valeriani, M., Stregapede, F., Sancesario, A., Armando, M., & Bertini, E. (2021). Expanding the Clinical and Mutational Spectrum of the PLP1-Related Hypomyelination of Early Myelinated Structures (HEMS). Brain Sciences, 11(1), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11010093