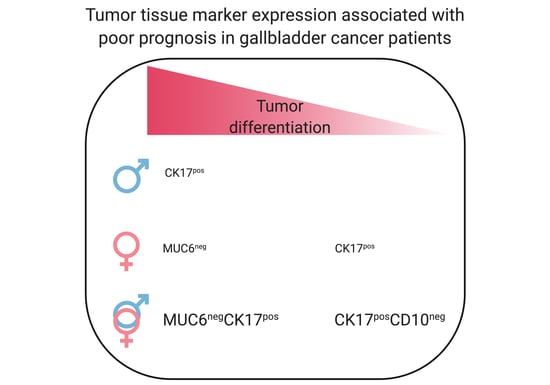
The Evaluation of 17 Gastrointestinal Tumor Markers Reveals Prognosis Value for MUC6, CK17, and CD10 in Gallbladder-Cancer Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Tumor Samples
2.2. Tissue Microarray
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinicopathological Characteristics of GBC Patients
3.2. Immunohistochemistry Analysis of Broad Panel of Tumor-Associated Markers in Primary GBC Samples
3.3. Association of Tumor-Associated Markers with GBC Patient Prognosis
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hundal, R.; Shaffer, E.A. Gallbladder cancer: Epidemiology and outcome. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 6, 99–109. [Google Scholar]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roa, I.; Ibacache, G.; Muñoz, S.; de Aretxabala, X. Gallbladder cancer in Chile: Pathologic characteristics of survival and prognostic factors: Analysis of 1366 cases. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2014, 141, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Randi, G.; Franceschi, S.; La Vecchia, C. Gallbladder cancer worldwide: Geographical distribution and risk factors. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldin, R.D.; Roa, J.C. Gallbladder cancer: A morphological and molecular update. Histopathology 2009, 55, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roa, I.; de Aretxabala, X. Gallbladder cancer in Chile: What have we learned? Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 31, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.A.; Marcano-Bonilla, L.; Roberts, L.R. Gallbladder cancer: Epidemiology and genetic risk associations. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinton, L.M.; Shaffer, E.A. Epidemiology of gallbladder disease: Cholelithiasis and cancer. Gut Liver 2012, 6, 72–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lorenzo Bermejo, J.; Boekstegers, F.; González Silos, R.; Marcelain, K.; Baez Benavides, P.; Barahona Ponce, C.; Müller, B.; Ferreccio, C.; Koshiol, J.; Fischer, C.; et al. Subtypes of Native American ancestry and leading causes of death: Mapuche ancestry-specific associations with gallbladder cancer risk in Chile. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Talwar, R.; Kannan, N.; Tyagi, A.K.; Jaiswal, P.; Kumar, A. Chemotherapy compared with best supportive care for metastatic/unresectable gallbladder cancer: A non-randomized prospective cohort study. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 7, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pollom, E.L.; Alagappan, M.; Park, L.S.; Whittemore, A.S.; Koong, A.C.; Chang, D.T. Does radiotherapy still have a role in unresected biliary tract cancer? Cancer Med. 2016, 6, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Feng, F.L.; Zhao, X.H.; Ye, Z.X.; Zeng, H.P.; Li, Z.; Jiang, X.Q.; Peng, Z.H. Combined detection tumor markers for diagnosis and prognosis of gallbladder cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 4085–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, J.V.; Savas, L.; Banner, B.F. Expression of cytokeratins 7 and 20 in carcinomas of the extrahepatic biliary tract, pancreas, and gallbladder. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2000, 124, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, K.S.; Choi, H.S.; Jun, D.W.; Lee, H.L.; Lee, O.Y.; Yoon, B.C.; Lee, K.G.; Paik, S.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J. MUC Expression in Gallbladder Epithelial Tissues in Cholesterol-Associated Gallbladder Disease. Gut Liver 2016, 10, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hiraki, T.; Yamada, S.; Higashi, M.; Hatanaka, K.; Yokoyama, S.; Kitazono, I.; Goto, Y.; Kirishima, M.; Batra, S.; Yonezawa, S.; et al. Immunohistochemical expression of mucin antigens in gallbladder adenocarcinoma: MUC1-positive and MUC2-negative expression is associated with vessel invasion and shortened survival. Histol. Histopathol. 2017, 32, 585–596. [Google Scholar]
- Varona, A.; Blanco, L.; Perez, I.; Gil, J.; Irazusta, J.; López, J.I.; Candenas, M.L.; Pinto, F.M.; Larrinaga, G. Expression and activity profiles of DPP IV/CD26 and NEP/CD10 glycoproteins in the human renal cancer are tumor type dependent. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Patwa, T.H.; Lubman, D.M.; Simeone, D.M. Protein biomarkers in cancer: Natural glycoprotein microarray approaches. Curr. Opin. Mol. Ther. 2008, 10, 602–610. [Google Scholar]
- Moll, R.; Robine, S.; Dudouet, B.; Louvard, D. Villin: A cytoskeletal protein and a differentiation marker expressed in some human adenocarcinomas. Virchows Arch. B Cell Pathol. Incl. Mol. Pathol. 1987, 54, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Xu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wu, L.; Song, H.; Zhou, L. Expression of vimentin and Oct-4 in gallbladder adenocarcinoma and their relationship with vasculogenic mimicry and their clinical significance. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 3618–3627. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.L.; Yang, Z.L.; Liu, J.Q.; Miao, X.Y. Expression of CDX2 and hepatocyte antigen in benign and malignant lesions of gallbladder and its correlation with histopathologic type and clinical outcome. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2011, 17, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amin, M.B.; Edge, S.; Greene, F.; Byrd, D.R.; Brookland, R.K.; Washington, M.K.; Gershenwald, J.E.; Compton, C.C.; Hess, K.R.; Sullivan, D.C.; et al. (Eds.) AJCC Cancer Staging Manual, 8th ed.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA; American Joint Commission on Cancer: Chicago, IL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, J.; Upadhye, S.; Worster, A. Understanding receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. CJEM 2006, 8, 19–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everson, G.T.; McKinley, C.; Kern, F., Jr. Mechanisms of gallstone formation in women. Effects of exogenous estrogen (Premarin) and dietary cholesterol on hepatic lipid metabolism. J. Clin. Investig. 1991, 87, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridgewater, J.; Lopes, A.; Wasan, H.; Malka, D.; Jensen, L.; Okusaka, T.; Knox, J.; Wagner, D.; Cunningham, D.; Shannon, J.; et al. Prognostic factors for progression-free and overall survival in advanced biliary tract cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, R.; Simoes, E.J.; Schmaltz, C.; Jackson, C.S.; Ibdah, J.A. Trend analysis and survival of primary gallbladder cancer in the United States: A 1973–2009 population-based study. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.J.; Hyung, J.; Yoo, C.; Kim, K.P.; Park, S.J.; Lee, S.S.; Park, D.H.; Song, T.J.; Seo, D.W.; Lee, S.K.; et al. Prognostic factors in patients with advanced biliary tract cancer treated with first-line gemcitabine plus cisplatin: Retrospective analysis of 740 patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cao, J.; Zhang, B.; Pan, L.; Cai, X. A Nomogram for Prediction of Overall Survival in Patients with Node-negative Gallbladder Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 3246–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gnerlich, J.L.; Deshpande, A.D.; Jeffe, D.B.; Seelam, S.; Kimbuende, E.; Margenthaler, J.A. Poorer survival outcomes for male breast cancer compared with female breast cancer may be attributable to in-stage migration. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldus, S.E.; Engelmann, K.; Hanisch, F.G. MUC1 and the MUCs: A family of human mucins with impact in cancer biology. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2004, 41, 189–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukita, S.; Nomoto, M.; Kitajima, S.; Tanaka, S.; Goto, M.; Irimura, T.; Kim, Y.S.; Sato, E.; Yonezawa, S. Expression of mucins (MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6) in mucinous carcinoma of the breast: Comparison with invasive ductal carcinoma. Histopathology 2003, 42, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norum, L.F.; Erikstein, B.; Nustad, K. Elevated CA125 in breast cancer—A sign of advanced disease. Tumour. Biol. 2001, 22, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Miao, R.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, R.; Pang, Q.; Xu, X.; Liu, C. Exploring the diagnosis markers for gallbladder cancer based on clinical data. Front. Med. 2015, 9, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.S.; Shi, L.B.; Li, M.L.; Ding, Q.; Weng, H.; Wu, W.G.; Cao, Y.; Bao, R.F.; Shu, Y.J.; Ding, Q.C.; et al. Evaluation of two inflammation-based prognostic scores in patients with resectable gallbladder carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiumi, N.; Abe, Y.; Inoue, Y.; Hatanaka, H.; Inada, K.I.; Kijima, H.; Yamazaki, H.; Tatematsu, M.; Ueyama, Y.; Iwasaki, M.; et al. Use of 11p15 mucins as prognostic factors in small adenocarcinoma of the lung. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 5616–5619. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thuwajit, P.; Chawengrattanachot, W.; Thuwajit, C.; Sripa, B.; Paupairoj, A.; Chau-In, S. Enhanced expression of mucin 6 glycoprotein in cholangiocarcinoma tissue from patients in Thailand as a prognostic marker for survival. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aishima, S.; Kuroda, Y.; Nishihara, Y.; Taguchi, K.; Taketomi, A.; Maehara, Y.; Tsuneyoshi, M. Gastric mucin phenotype defines tumour progression and prognosis of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: Gastric foveolar type is associated with aggressive tumour behaviour. Histopathology 2006, 49, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Roh, S.J.; Kim, Y.N.; Kim, S.Z.; Park, H.S.; Jang, K.Y.; Chung, M.J.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, D.G.; Moon, W.S.; et al. Expression of MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6 in cholangiocarcinoma: Prognostic impact. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 22, 649–657. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein, N.S.; Bassi, D. Cytokeratins 7, 17, and 20 reactivity in pancreatic and ampulla of vater adenocarcinomas. Percentage of positivity and distribution is affected by the cut-point threshold. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 115, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ide, M.; Kato, T.; Ogata, K.; Mochiki, E.; Kuwano, H.; Oyama, T. Keratin 17 expression correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in gastric adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 3506–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Lang, H.Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, T.; Li, Y.R.; Liu, J.Y.; et al. Overexpression of keratin 17 is associated with poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Tumour. Biol. 2013, 34, 1685–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Lee, H.W.; Chae, S.W.; Kim, D.H.; Do, I.G.; Lee, H.J.; Do, S.I.; Min, K.W.; Pyo, J.S.; Shin, J.H.; et al. Cytokeratin 17 Expression is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Gallbladder Adenocarcinoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2017, 25, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, A.; Schlomm, T.; Huland, H.; Köllermann, J.; Simon, P.; Mirlacher, M.; Salomon, G.; Chun, F.H.K.; Steuber, T.; Simon, R.; et al. Distinct subcellular expression patterns of neutral endopeptidase (CD10) in prostate cancer predict diverging clinical courses in surgically treated patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 7838–7842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oba, J.; Nakahara, T.; Hayashida, S.; Kido, M.; Xie, L.; Takahara, M.; Uchi, H.; Miyazaki, S.; Abe, T.; Hagihara, A.; et al. Expression of CD10 predicts tumor progression and unfavorable prognosis in malignant melanoma. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 65, 1152–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.W.; Sung, C.O.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, M.; Yoo, H.Y.; Kim, H.H.; Um, S.H.; Kim, S.H. CD10 expression is enhanced by Twist1 and associated with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma with facilitating tumorigenicity in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hainsworth, J.D.; Greco, F.A. Adenocarcinoma of Unknown Primary Site. In Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine, 6th ed.; Kufe, D.W., Pollock, R.E., Weichselbaumm, R.R., Bast, R.C., Gansler, T.S., Holland, J.F., Frei, E., Eds.; BC Decker: Hamilton, ON, Canada, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kamel, H.F.M.; Al-Amodi, H.S.A.B. Exploitation of Gene Expression and Cancer Biomarkers in Paving the Path to Era of Personalized Medicine. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 15, 220–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| CHARACTERISTICS | ||
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 77.8% (n = 140) |
| Male | 22.2% (n = 40) | |
| Median age (SD) | All | 67.5 (±12.3) |
| Female | 66.5 (±12.6) | |
| Male | 70 (±11.5) | |
| Tumor differentiation | Poor | 32.8% (59 cases) 79.7% female; 20.3% male Median age: 67 (±13.1) Tumor staging: Early (TIS–T1): 0% Advanced (T2–T4): 100% |
| Moderate | 58.3% (105 cases) 75.2% female; 24.8% male Median age: 69 (±11.5) Tumor staging: Early (TIS–T1): 13% Advanced (T2–T4): 87% | |
| Well | 8.9% (16 cases) 87.5% female; 12.5% male Median age: 60 (±14.8) Tumor staging: Early (TIS–T1): 45% Advanced (T2–T4): 55% |
| Marker | Total Positive | Tumor Differentiation, # Cases + (%) | Tumor Staging, # Cases + (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Good/Moderate | Poor | Statistics a | Early b | Advanced c | Statistics a | ||
| CK7 | 164 (97.6%) | 112 (99.1%) | 52 (94.5%) | NS | 16 (100%) | 131 (98.5%) | NS |
| CK20 | 26 (15.4%) | 21 (18.3%) | 5 (9.3%) | NS | 5 (29.4%) | 20 (15.1%) | NS |
| CK17 | 118 (72.8%) | 81 (74.3%) | 37 (69.8%) | NS | 8 (53.3%) | 97 (75.8%) | NS |
| CK19 | 166 (98.2%) | 112 (97.4%) | 54 (100%) | NS | 16 (94.1%) | 132 (98.5%) | NS |
| CKLMW | 169 (100%) | 114 (100%) | 54 (100%) | NS | 16 (100%) | 132 (100%) | NS |
| CKHMW | 153 (91.6%) | 104 (92%) | 49 (90.7%) | NS | 13 (92.9%) | 123 (92.5%) | NS |
| VIMENTIN | 7 (3.9%) | 1 (0.8%) | 6 (10.7%) | p = 0.0014 | 0 | 7 (5%) | NS |
| MUC1 | 165 (97.1%) | 113 (97.4%) | 52 (96.3%) | NS | 15 (100%) | 130 (97%) | NS |
| MUC2 | 5 (3.1%) | 2 (1.9%) | 3 (5.8%) | NS | 0 | 4 (3.2%) | NS |
| MUC5AC | 135 (81.8%) | 93 (83%) | 42 (79.2%) | NS | 15 (88.2%) | 107 (82.3%) | NS |
| MUC6 | 68 (41%) | 52 (45.6%) | 16 (30.8%) | NS | 11 (64.7%) | 50 (38.7%) | p = 0.04 |
| CDX2 | 120 (72.7%) | 86 (76.8%) | 34 (64.1%) | NS | 12 (85.7%) | 92 (70.8%) | NS |
| CEA | 99 (57.9%) | 64 (55.2%) | 35 (63.6%) | NS | 8 (47.1%) | 82 (61.2%) | NS |
| CA125 | 51 (30%) | 31 (26%) | 20 (39.2%) | NS | 0 | 46 (34.8%) | p = 0.009 |
| CD10 | 73 (44.2%) | 50 (45.4%) | 23 (41.8%) | NS | 10 (62.5%) | 53 (40.4%) | NS |
| CLAUDIN4 | 132 (81%) | 90 (80.4%) | 42 (80.8%) | NS | 12 (85.7%) | 106 (81.5%) | NS |
| VILLIN | 81 (46.8%) | 62 (51.2%) | 19 (36.5%) | NS | 11 (61.1%) | 61 (45.9%) | NS |
| Patients with poorly differentiated tumors (n = 58). | |||||||||||
| Variable | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||||||
| HR | 95% CI | p value | HR | 95% CI | p value | ||||||
| MUC1 | 1.37 | 0.54–3.52 | 0.509 | 0.76 | 0.05–10.89 | 0.843 | |||||
| MUC2 | 1.48 | 0.98–2.23 | 0.061 | 1.78 | 0.83–3.83 | 0.138 | |||||
| MUC5AC | 0.81 | 0.48–1.36 | 0.421 | 0.74 | 0.29–1.89 | 0.532 | |||||
| MUC6 | 0.9 | 0.6–1.36 | 0.631 | 0.62 | 0.3–1.31 | 0.212 | |||||
| CK7 | 1.66 | 0.64–4.3 | 0.292 | 0.68 | 0.11–4.23 | 0.678 | |||||
| CK20 | 1.29 | 0.77–2.16 | 0.338 | 1.27 | 0.53–3.03 | 0.586 | |||||
| CK17 | 2 | 1.26–3.19 | 0.003 | 2.46 | 1.06–5.74 | 0.037 | |||||
| CK19 | 1.76 | 0.62–4.94 | 0.285 | 0.63 | 0.01–38.41 | 0.824 | |||||
| CKHMW | 1.7 | 0.8–3.59 | 0.166 | 2.87 | 0.96–8.54 | 0.058 | |||||
| CKLMW | 1.85 | 0.56–6.03 | 0.31 | 0.1 | 0.005–1.85 | 0.121 | |||||
| CDX2 | 0.88 | 0.52–1.47 | 0.616 | 0.55 | 0.24–1.28 | 0.17 | |||||
| CD10 | 1.7 | 1.08–2.69 | 0.023 | 3.76 | 1.65–8.56 | 0.002 | |||||
| CEA | 1.12 | 0.67–1.89 | 0.664 | 1.03 | 0.45–2.35 | 0.95 | |||||
| CA125 | 1.52 | 1.02–2.25 | 0.038 | 1.99 | 0.98–4.07 | 0.058 | |||||
| Vimentin | 1.49 | 0.94–2.36 | 0.09 | 0.74 | 0.32–1.75 | 0.5 | |||||
| Villin | 0.79 | 0.52–1.22 | 0.289 | 0.95 | 0.45–2.03 | 0.903 | |||||
| Claudin 4 | 1.21 | 0.63–2.32 | 0.571 | 0.96 | 0.4–2.34 | 0.931 | |||||
| Age | 0.75 | 0.44–1.28 | 0.289 | 1.71 | 0.82–3.57 | 0.152 | |||||
| Gender | 1.16 | 0.6–2.24 | 0.649 | 0.97 | 0.42–2.26 | 0.954 | |||||
| Patients with well- to moderately differentiated tumors (n = 118). | |||||||||||
| Variable | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||||||
| HR | 95% CI | p Value | HR | 95% CI | p Value | ||||||
| MUC1 | 0.68 | 0.38–1.21 | 0.194 | 0.91 | 0.38–2.14 | 0.825 | |||||
| MUC2 | 0.8 | 0.59–1.09 | 0.154 | 0.96 | 0.61–1.53 | 0.878 | |||||
| MUC5AC | 0.87 | 0.58–1.3 | 0.507 | 1.13 | 0.66–1.92 | 0.665 | |||||
| MUC6 | 0.69 | 0.5–0.96 | 0.029 | 0.46 | 0.24–0.86 | 0.015 | |||||
| CK7 | 0.57 | 0.27–1.2 | 0.143 | 0.71 | 0.46–1.28 | 0.138 | |||||
| CK20 | 0.8 | 0.57–1.11 | 0.182 | 0.89 | 0.58–1.37 | 0.614 | |||||
| CK17 | 1.01 | 0.72–1.4 | 0.966 | 1.21 | 0.78–1.87 | 0.384 | |||||
| CK19 | 1.08 | 0.59–1.98 | 0.792 | 1.48 | 0.66–3.35 | 0.342 | |||||
| CKHMW | 0.74 | 0.48–1.14 | 0.17 | 0.82 | 0.43–1.56 | 0.543 | |||||
| CKLMW | 1.08 | 0.56–2.08 | 0.823 | 1.72 | 0.67–4.42 | 0.259 | |||||
| CDX2 | 0.72 | 0.5–1.01 | 0.06 | 0.6 | 0.39–0.93 | 0.023 | |||||
| CD10 | 0.95 | 0.71–1.26 | 0.706 | 1.23 | 0.82–1.84 | 0.309 | |||||
| CEA | 1.03 | 0.74–1.44 | 0.846 | 0.96 | 0.63–1.46 | 0.859 | |||||
| CA125 | 1.18 | 0.84–1.65 | 0.335 | 1.35 | 0.86–2–1 | 0.188 | |||||
| Vimentin | 1 | 0.53–1.88 | 0.996 | 1.32 | 0.56–3.11 | 0.524 | |||||
| Villin | 0.86 | 0.62–1.21 | 0.396 | 0.85 | 0.55–1.32 | 0.48 | |||||
| Claudin 4 | 0.77 | 0.54–1.11 | 0.169 | 0.7 | 0.42–1.14 | 0.152 | |||||
| Age | 1.86 | 1.24–2.81 | 0.003 | 2.28 | 1.43–3.64 | 0.001 | |||||
| Gender | 1.63 | 1.02–2.6 | 0.041 | 1.16 | 0.67–2.02 | 0.598 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carrasco, C.; Tittarelli, A.; Paillaleve, N.; Pozo, M.D.; Rojas-Sepúlveda, D.; Barría, O.; Fluxá, P.; Hott, M.; Martin, C.; Quezada, C.; et al. The Evaluation of 17 Gastrointestinal Tumor Markers Reveals Prognosis Value for MUC6, CK17, and CD10 in Gallbladder-Cancer Patients. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020153
Carrasco C, Tittarelli A, Paillaleve N, Pozo MD, Rojas-Sepúlveda D, Barría O, Fluxá P, Hott M, Martin C, Quezada C, et al. The Evaluation of 17 Gastrointestinal Tumor Markers Reveals Prognosis Value for MUC6, CK17, and CD10 in Gallbladder-Cancer Patients. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(2):153. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020153
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarrasco, Cristian, Andrés Tittarelli, Natalia Paillaleve, Maeva Del Pozo, Daniel Rojas-Sepúlveda, Omar Barría, Paula Fluxá, Melissa Hott, Carolina Martin, Claudia Quezada, and et al. 2021. "The Evaluation of 17 Gastrointestinal Tumor Markers Reveals Prognosis Value for MUC6, CK17, and CD10 in Gallbladder-Cancer Patients" Diagnostics 11, no. 2: 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020153
APA StyleCarrasco, C., Tittarelli, A., Paillaleve, N., Pozo, M. D., Rojas-Sepúlveda, D., Barría, O., Fluxá, P., Hott, M., Martin, C., Quezada, C., & Salazar-Onfray, F. (2021). The Evaluation of 17 Gastrointestinal Tumor Markers Reveals Prognosis Value for MUC6, CK17, and CD10 in Gallbladder-Cancer Patients. Diagnostics, 11(2), 153. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11020153