Long-Term Orbit Prediction and Deorbit Disposal Investigation of MEO Navigation Satellites
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Long-Term Evolution Modeling and Safety Analysis for MEO Region
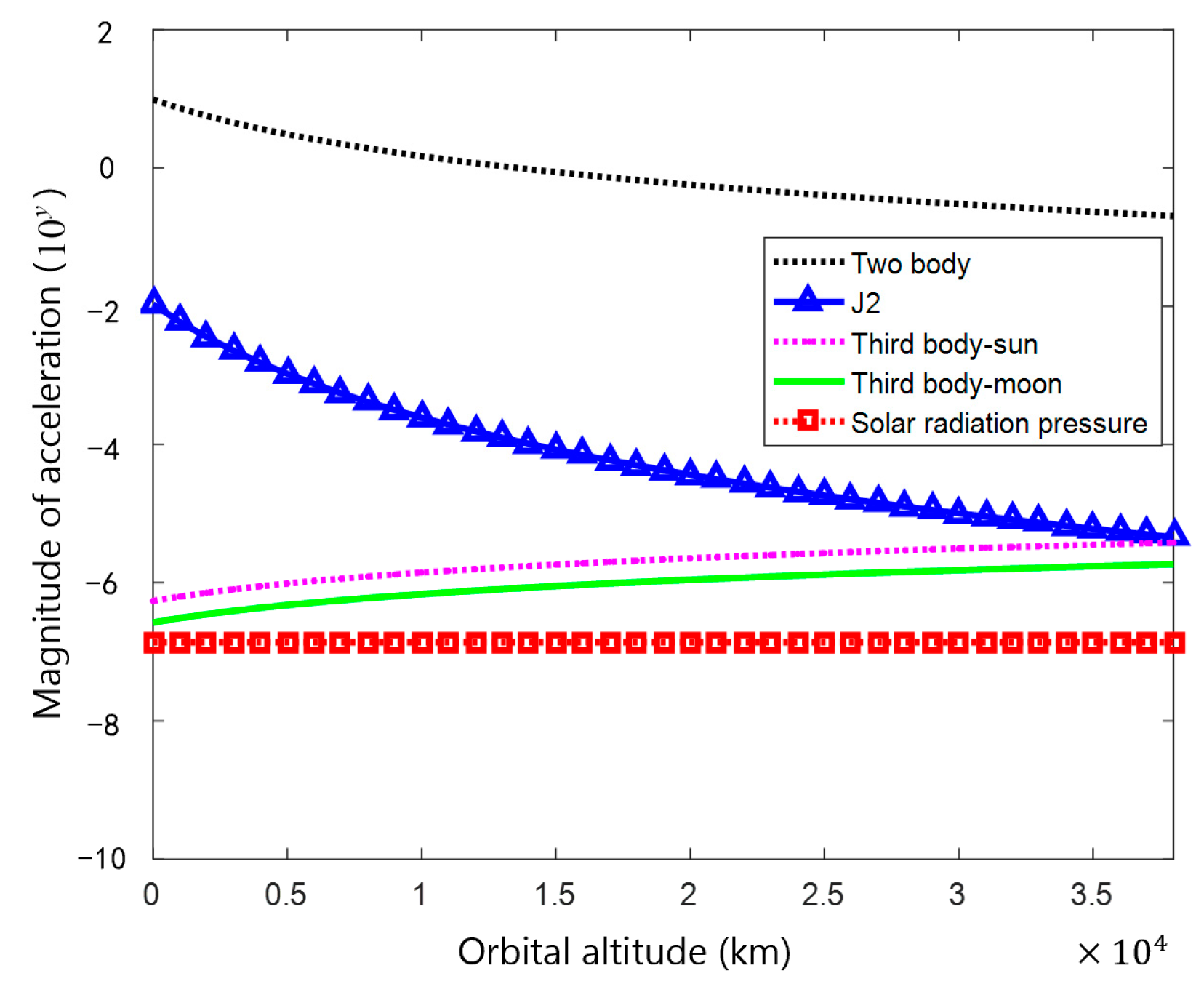
2.1. Perturbations Analysis
2.1.1. Analysis of the Earth Nonspherical Perturbations
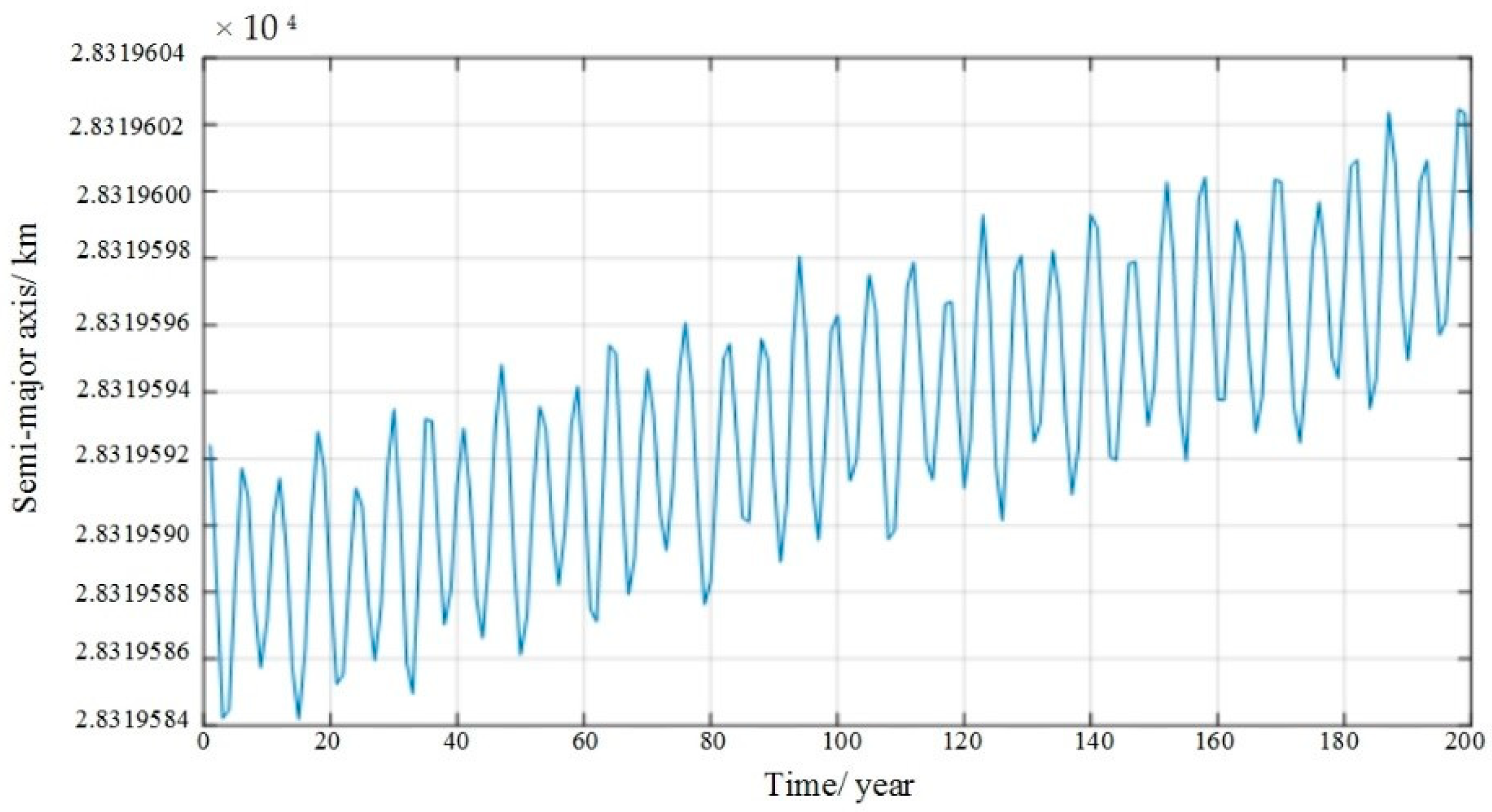
2.1.2. Analysis of the Luni-Solar Perturbations
2.1.3. Analysis of the Solar Radiation Pressure Perturbations
- (1)
- Earth’s gravitational field model: EGM-96 (70 × 70).
- (2)
- The positions of the Sun and the Moon are obtained using the ephemeris data released by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
- (3)
- The calculation of light pressure perturbation needs to judge whether the satellite is outside the shadow of the Earth and the Moon; use the conical shadow; perform boundary mitigation when the satellite enters and exits the shadow.
- (4)
- Numerical integration model: RKF 7 (8).
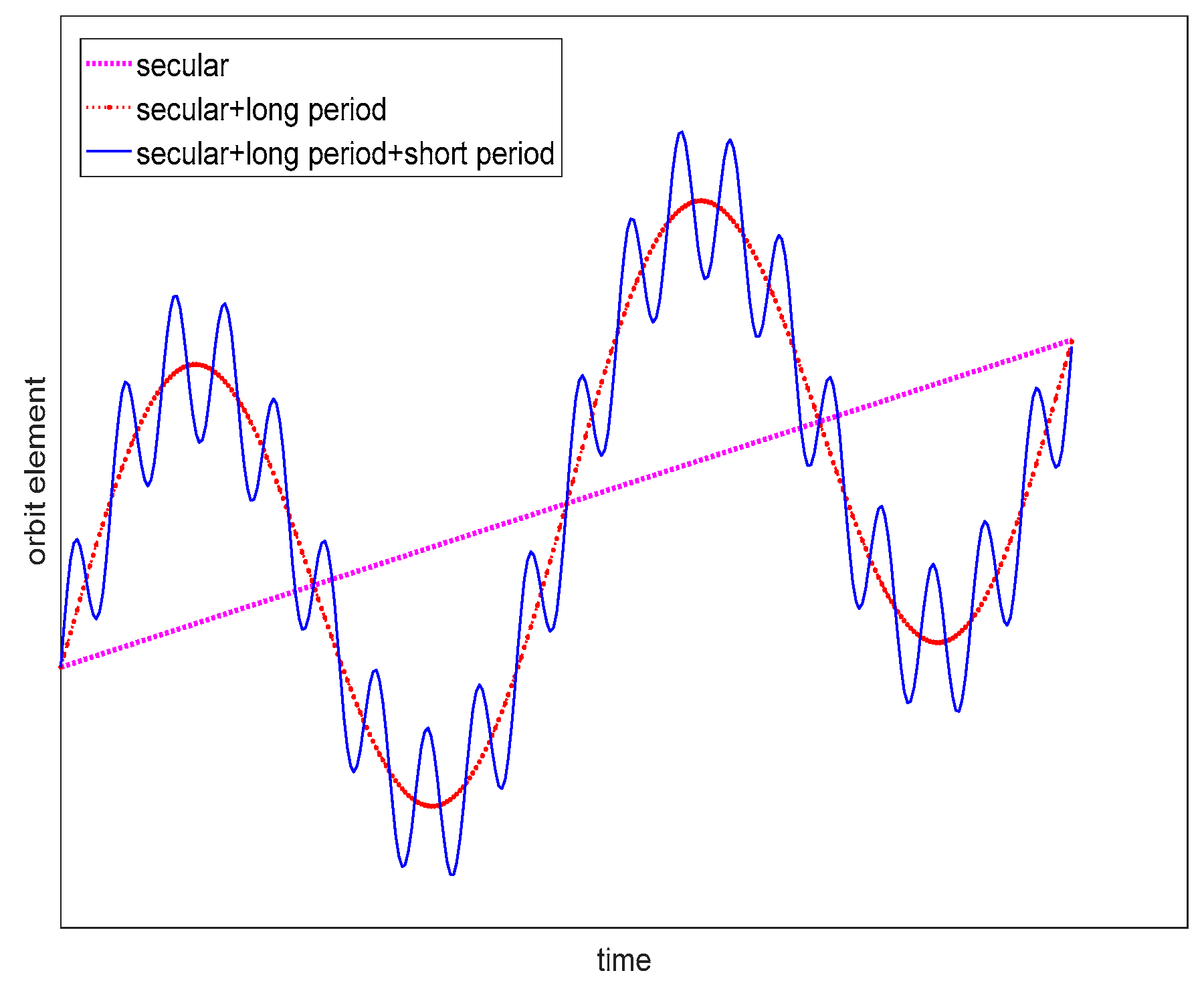
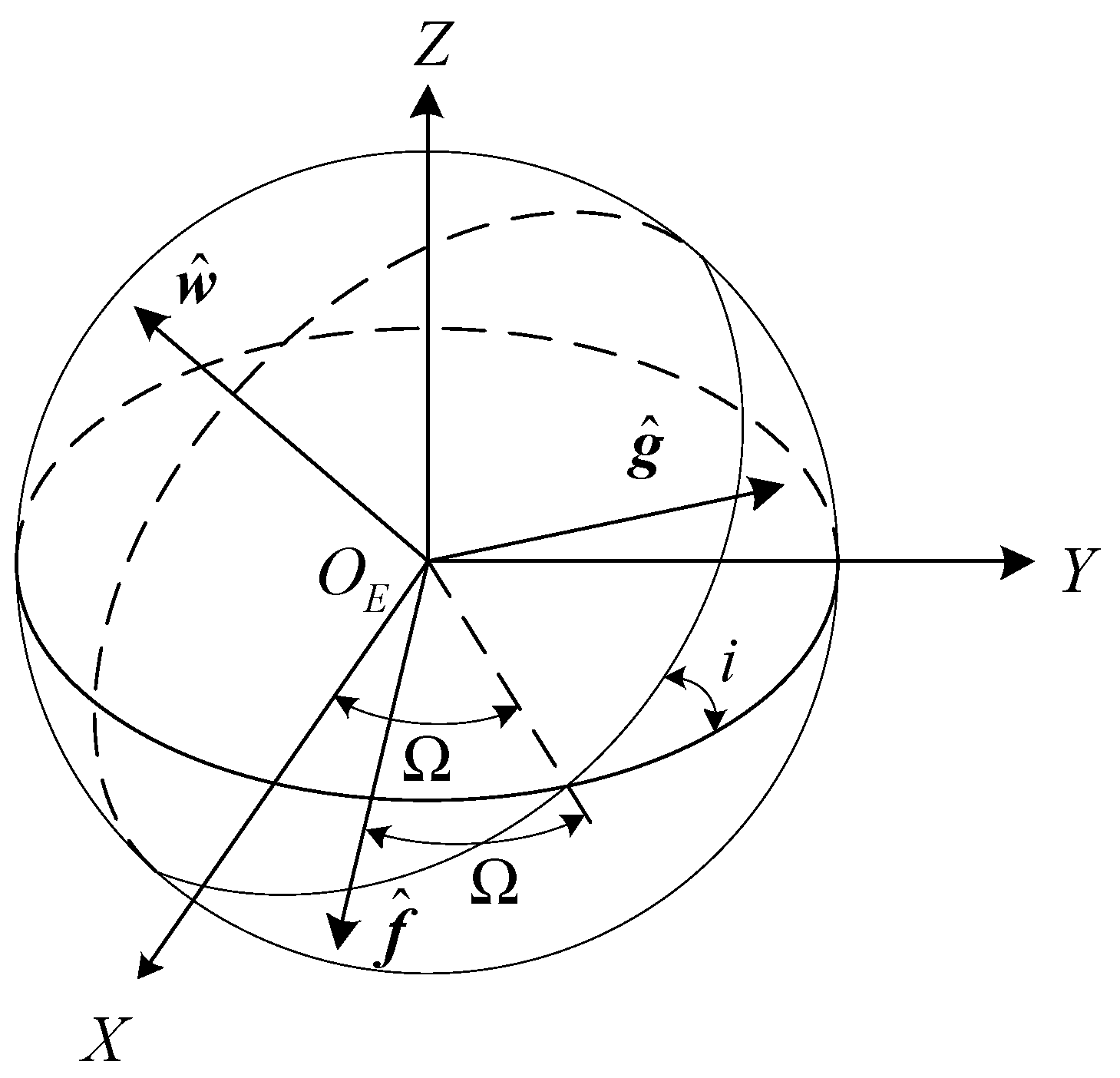
2.2. Perturbations Models
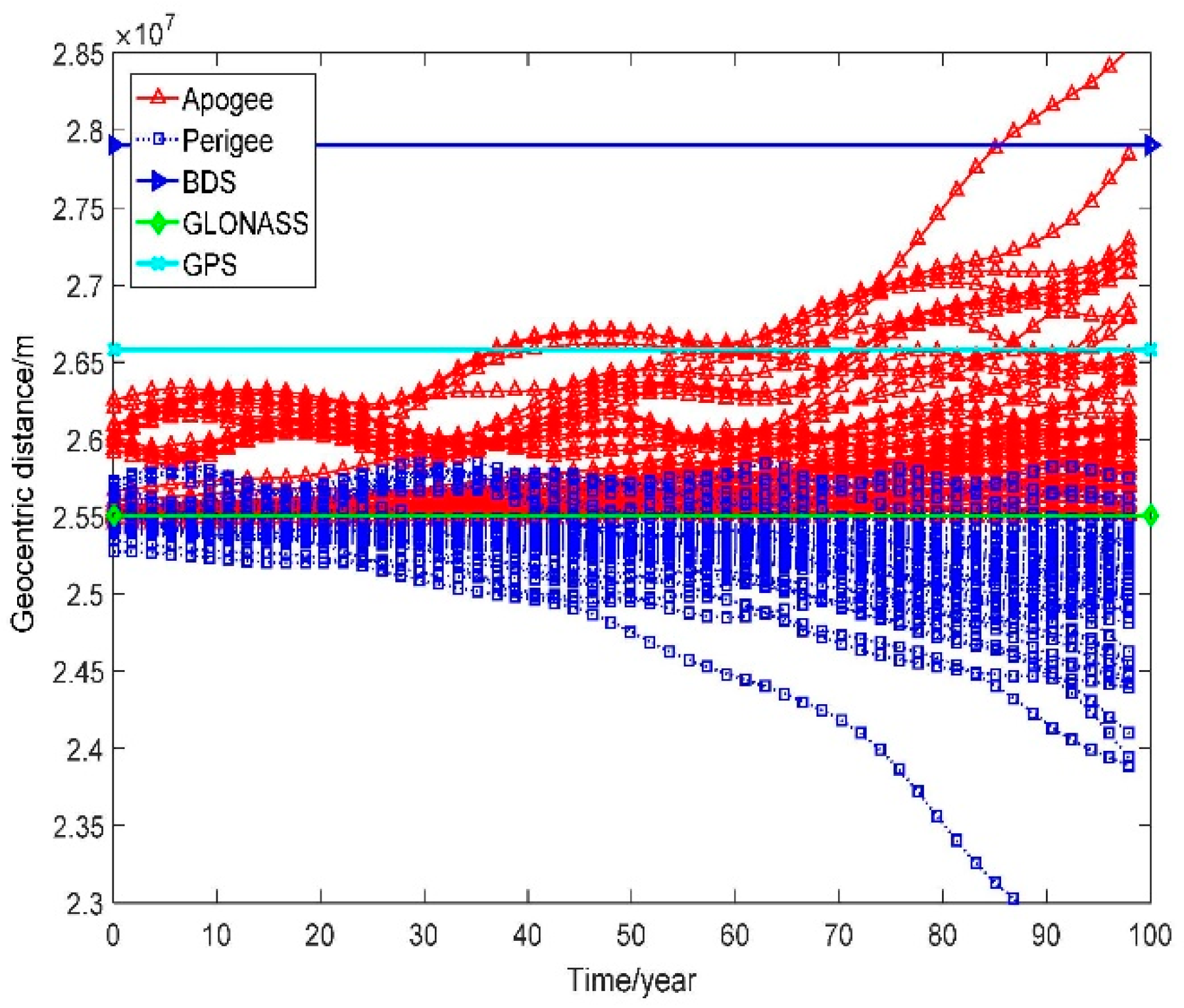
2.3. Safety Analysis for MEO Region
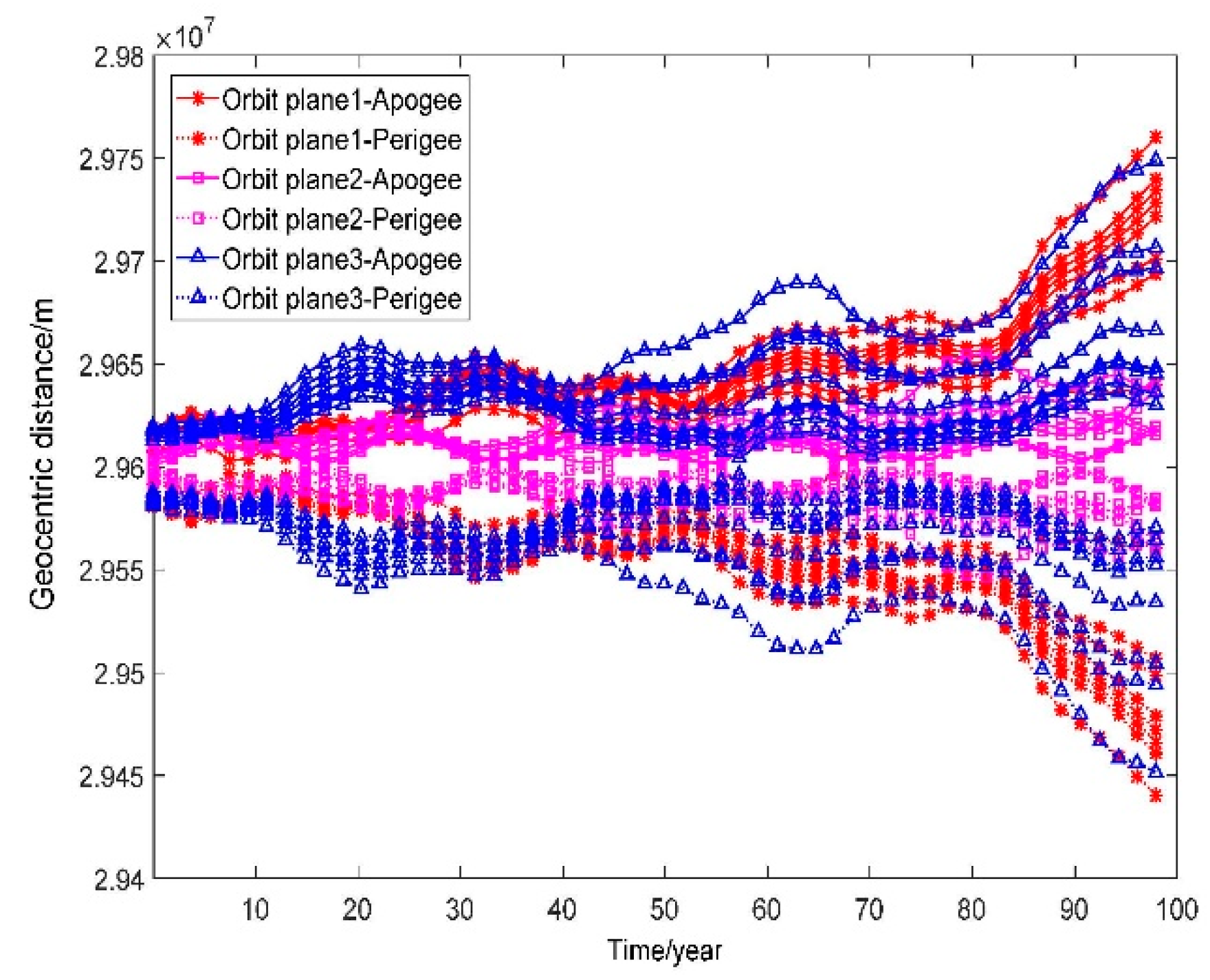
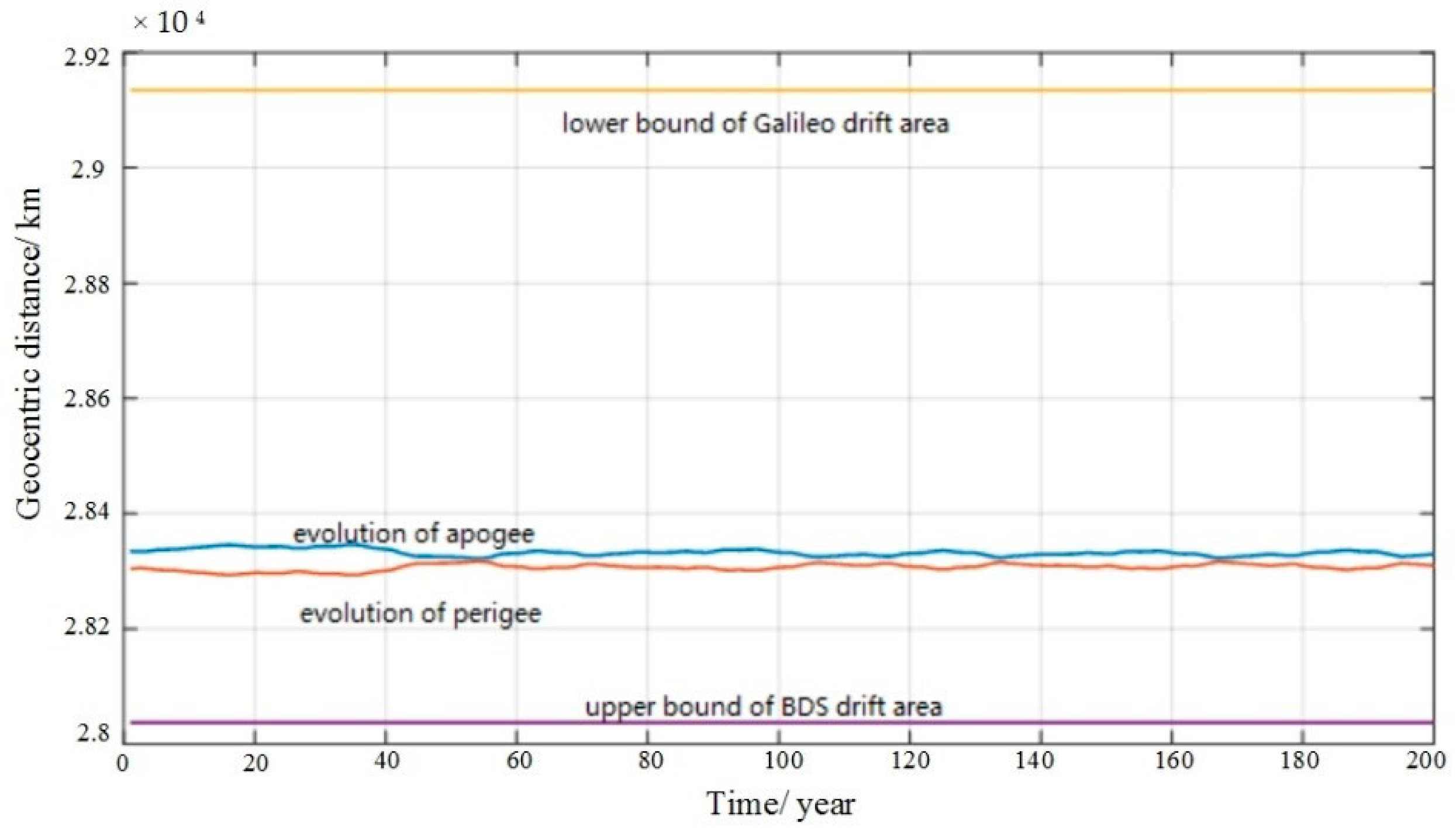
2.3.1. Galileo Constellation
2.3.2. BDS Constellation
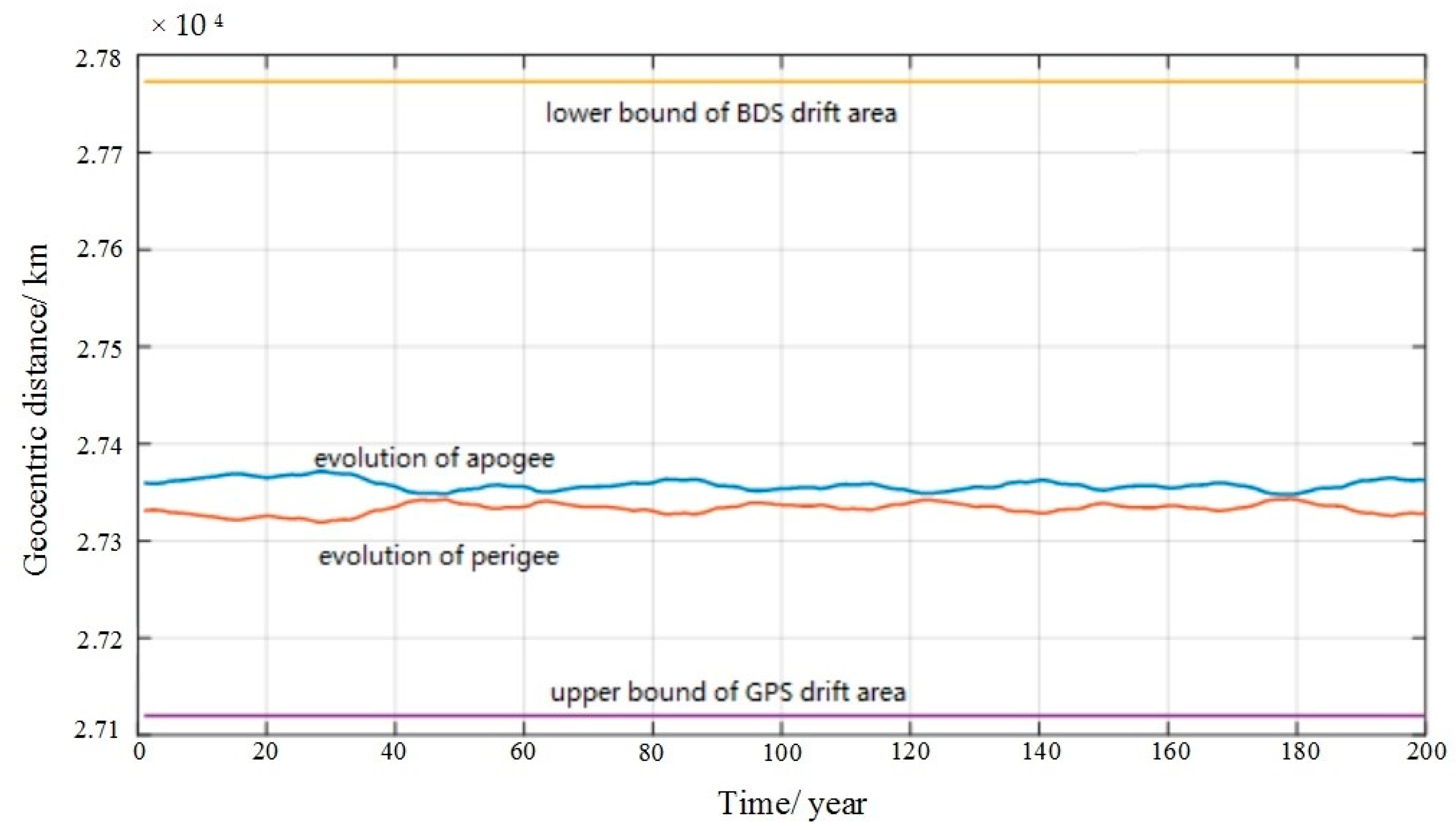
2.3.3. GPS Constellation
2.3.4. GLONASS Constellation
3. End-of-Life Disposal Analysis for BDS MEO Satellites
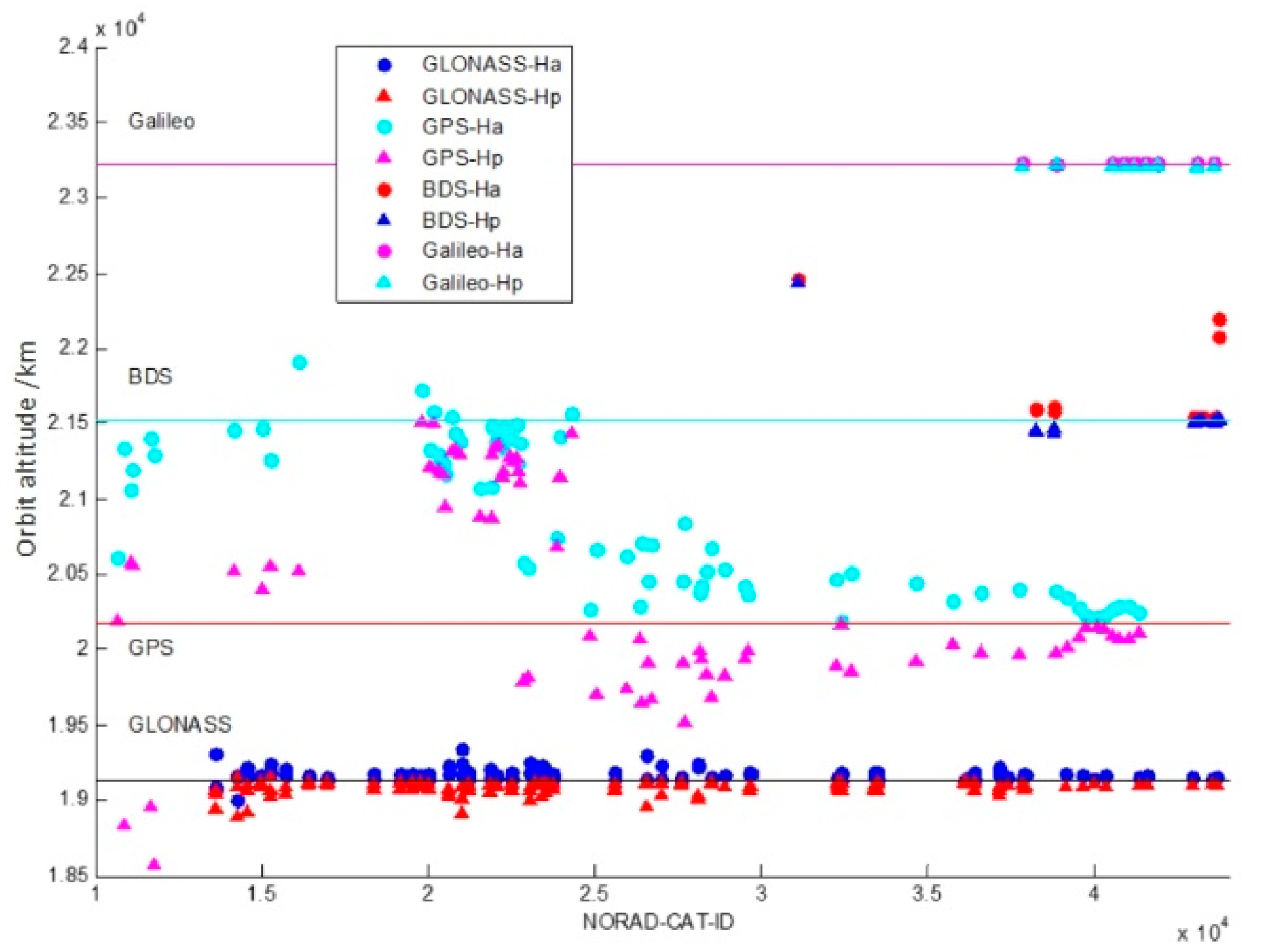
3.1. Distribution Status of the Space Objects in MEO Region
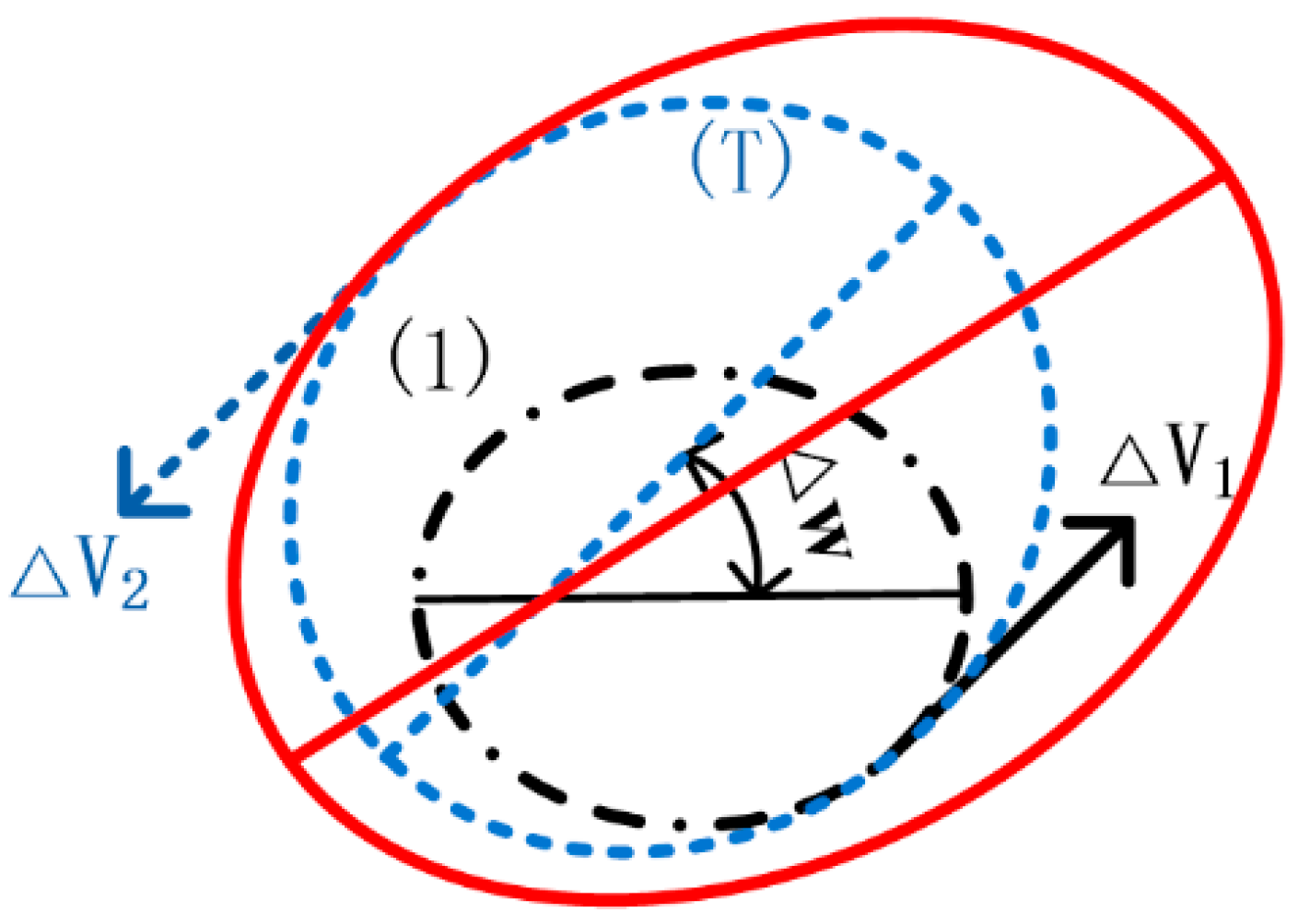
3.2. Orbit Manoeuvre Model
3.3. Disposal Orbit Optimization Models
3.3.1. Object Function
3.3.2. Bounds for Disposal Region of BDS MEO Satellites
3.4. Simulations
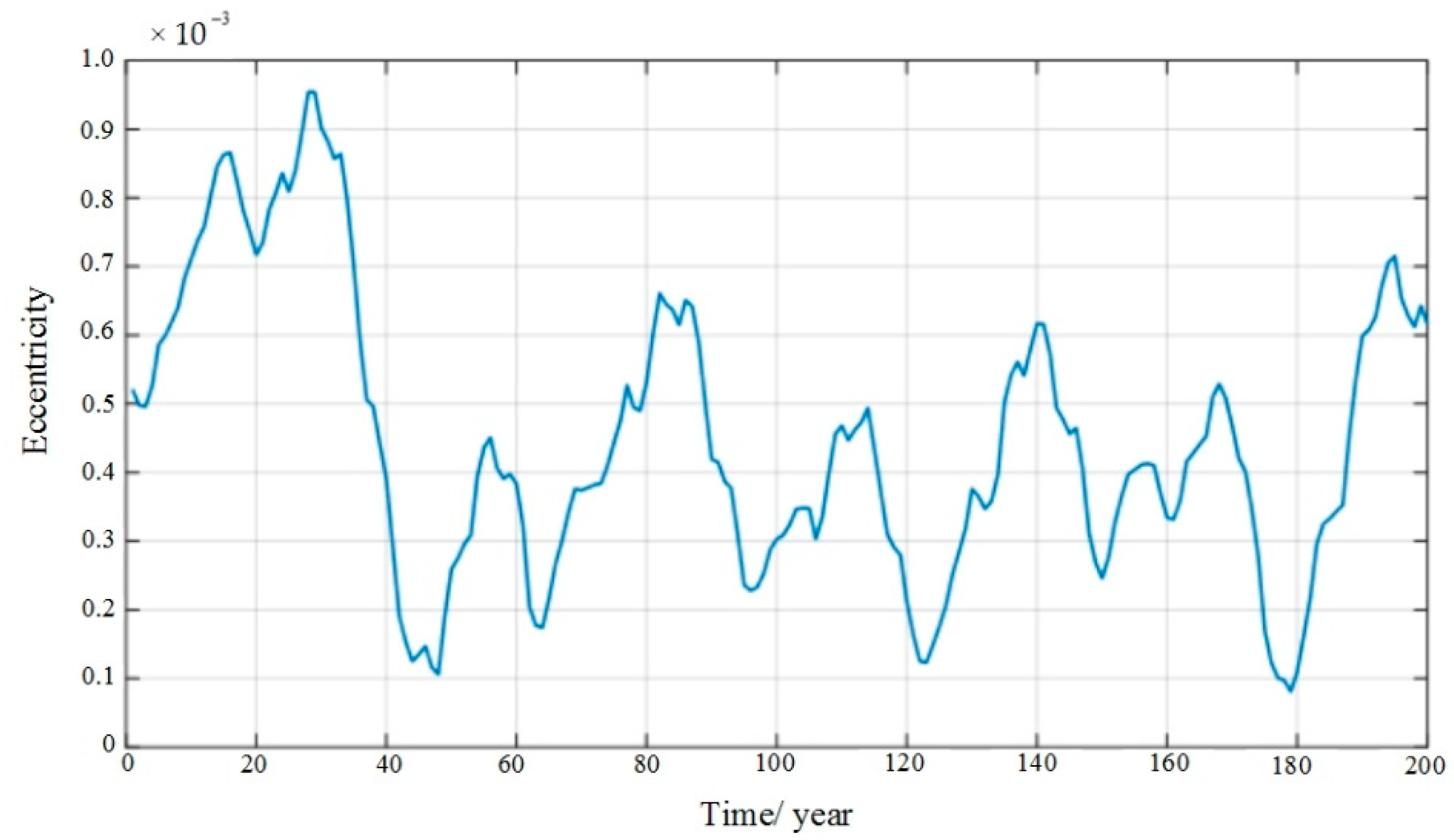
3.4.1. Raising Orbit Scenario
3.4.2. Reducing Orbit Scenario
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Navigation Satellite Systems. Available online: https://www.glonass-iac.ru/index.php (accessed on 9 March 2022).
- Scala, F.; Colombo, C.; Gkolias, I. Design of disposal orbits for high altitude spacecraft with a semi-analytical model. In Proceedings of the 18th Australian Aerospace Congress, Melbourne, Australia, 24–28 February 2019; pp. 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B. Research on Space Debris Environment Long-Term Evolution Modeling and Its Safety Problem. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Métris, G.; Exertier, P. Semi-analytical theory of the mean orbital motion. Astron. Astrophys. 1995, 294, 278–286. [Google Scholar]
- Valk, S.; Lemaître, A.; Deleflie, F. Semi-analytical theory of mean orbital motion for geosynchronous space debris under gravitational influence. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 43, 1070–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, M.; San-Juan, J.F.; López-Ochoa, L.M.; Cefola, P. Long-term evolution of Galileo operational orbits by canonical perturbation theory. Acta Astronaut. 2014, 94, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valk, S.; Lemaître, A.; Anselmo, L. Analytical and semi-analytical investigations of geosynchronous space debris with high area-to-mass ratios. Adv. Space Res. 2008, 41, 1077–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, G.; Steindorfer, M.; Wang, P.; Koidl, F.; Kucharski, D.; Silha, J.; Schildknecht, T.; Krag, H.; Flohrer, T. Determination of attitude and attitude motion of space debris, using laser ranging and single-photon light curve data. In Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Space Debris, Darmstadt, Germany, 18–21 April 2017; pp. 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kucharski, D.; Kirchner, G.; Bennett, J.; Lachut, M.; Sośnica, K.; Koshkin, N.; Shakun, L.; Koidl, F.; Steindorfer, M.; Wang, P. Photon pressure force on space debris TOPEX/Poseidon measured by satellite laser ranging. Earth Space Sci. 2017, 4, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovlev, M. The “IADC Space Debris Mitigation Guidelines” and supporting documents. In Proceedings of the 4th European Conference on Space Debris, Darmstadt, Germany, 18–20 April 2005; pp. 591–597. [Google Scholar]
- Chobotov, V. Disposal of spacecraft at end of life in geosynchronous orbit. J. Spacecr. Rockets 1990, 27, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C. MEO disposal orbit stability and direct reentry strategy. In Proceedings of the AAS/AIAA Spaceflight Mechanics Meeting, Clearwater, FL, USA, 23–26 January 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, A. Resonant dynamics of Medium Earth Orbits: Space debris issues. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 2008, 100, 267–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Gick, R.A. Long-term evolution of navigation satellite orbits: GPS/GLONASS/GALILEO. Adv. Space Res. 2004, 34, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domınguez-González, R.; Sánchez-Ortiz, N.; Cacciatore, F.; Radtke, J.; Flegel, S. Disposal strategies analysis for MEO orbits. In Proceedings of the 64th International Astronautical Congress, Beijing, China, 23–27 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Alessi, E.M.; Rossi, A.; Valsecchi, G.; Anselmo, L.; Pardini, C.; Colombo, C.; Lewis, H.; Daquin, J.; Deleflie, F.; Vasile, M. Effectiveness of GNSS disposal strategies. Acta Astronaut. 2014, 99, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radtke, J.; Domínguez-González, R.; Flegel, S.K.; Sánchez-Ortiz, N.; Merz, K. Impact of eccentricity build-up and graveyard disposal strategies on MEO navigation constellations. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 56, 2626–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armellin, R.; San-Juan, J.F. Optimal Earth’s reentry disposal of the Galileo constellation. Adv. Space Res. 2018, 61, 1097–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armellin, R.; San-Juan, J.F.; Lara, M. End-of-life disposal of high elliptical orbit missions: The case of INTEGRAL. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 56, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mistry, D.; Armellin, R. The design and optimisation of end-of-life disposal manoeuvres for GNSS spacecraft: The case of Galileo. In Proceedings of the 66th International Astronautical Congress, Jerusalem International Convention Cente, Jerusalem, Israel, 12–16 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Fan, L.; Yang, M. Optimal disposal orbit design for MEO navigation constellations. In Proceedings of the 67th International Astronautical Congress, Guadalajara, Mexico, 26–30 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, M.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Long-term evolution safety analysis and disposal orbit design method of BDS MEO satellite orbits. In Proceedings of the 69th International Astronautical Congress, Bremen, Germany, 1–5 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Skoulidou, D.K.; Rosengren, A.J.; Tsiganis, K.; Voyatzis, G. Medium Earth Orbit dynamical survey and its use in passive debris removal. Adv. Space Res. 2019, 63, 3646–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dominguez-Gonzalez, R. Long-Term Implications of GNSS Disposal Strategies for the Space Debris Environment. In Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Space Debris, Darmstadt, Germany, 18–21 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gondelach, D.J.; Armellin, R.; Wittig, A. On the predictability and robustness of Galileo disposal orbits. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 2019, 131, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H. The Analytical Theory of Space-Based Gravity Measurements and Its Realization Method by Satellite Formation. Ph.D. Thesis, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkin, A.B.; McVey, J.P.; Sorgeb, M.E. Assessment of time spent in the LEO, GEO, and semi-synchronous zones by spacecraft on long-term reentering disposal orbits. Acta Astronaut. 2021, 193, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordovitsyna, T.; Tomilova, I.; Chuvashov, I. The effect of secular resonances on the long-term orbital evolution of uncontrollable objects on satellite radio navigation systems in the MEO region. Sol. Syst. Res. 2012, 46, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cefola, P.; Folcik, Z.; Di-Costanzo, R.; Bernard, N.; Setty, S.; Juan, J. Revisiting the DSST standalone orbit propagator. In Proceedings of the 24th AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 26–30 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- MEO tle. Available online: http://www.space-track.org (accessed on 10 December 2021).
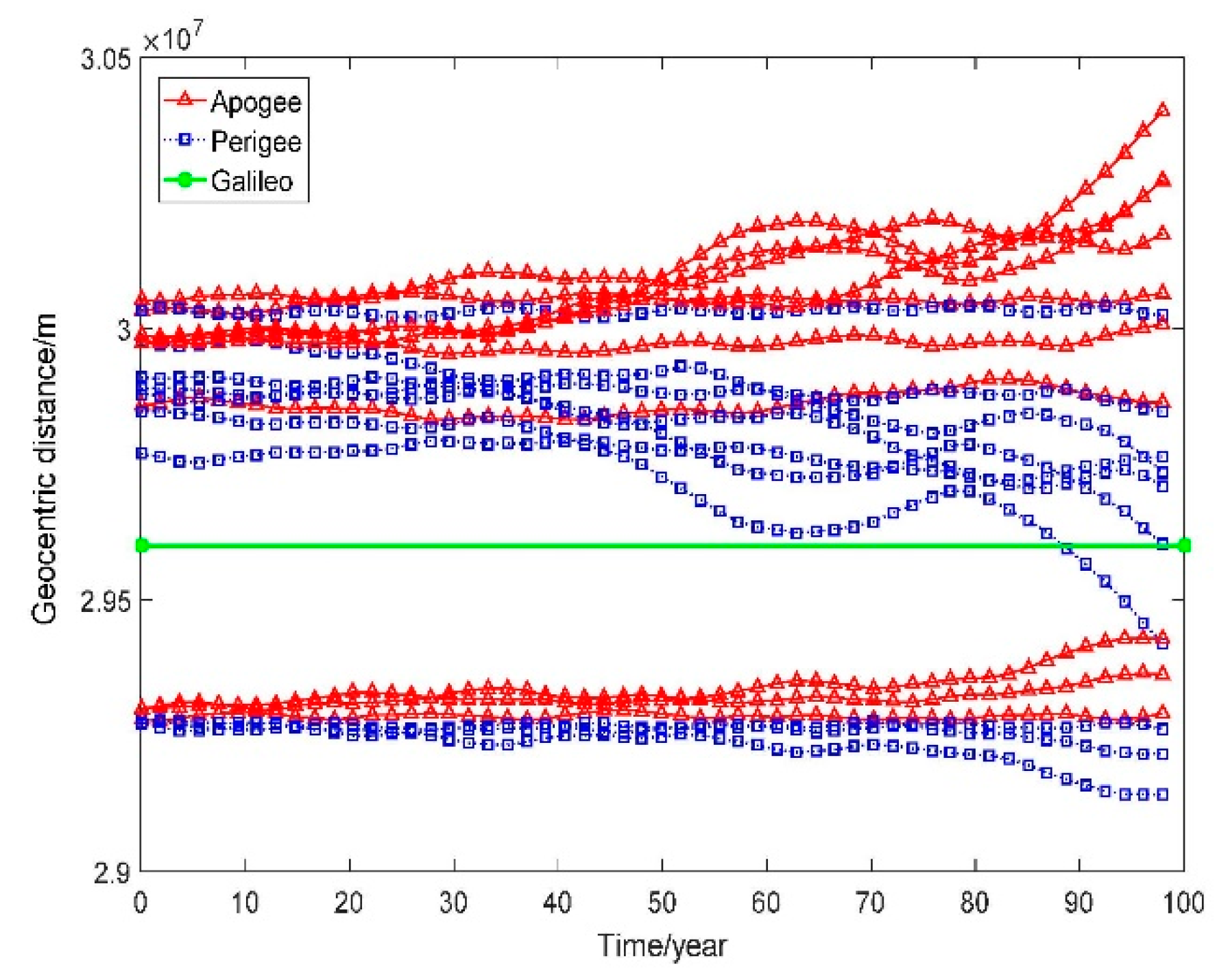

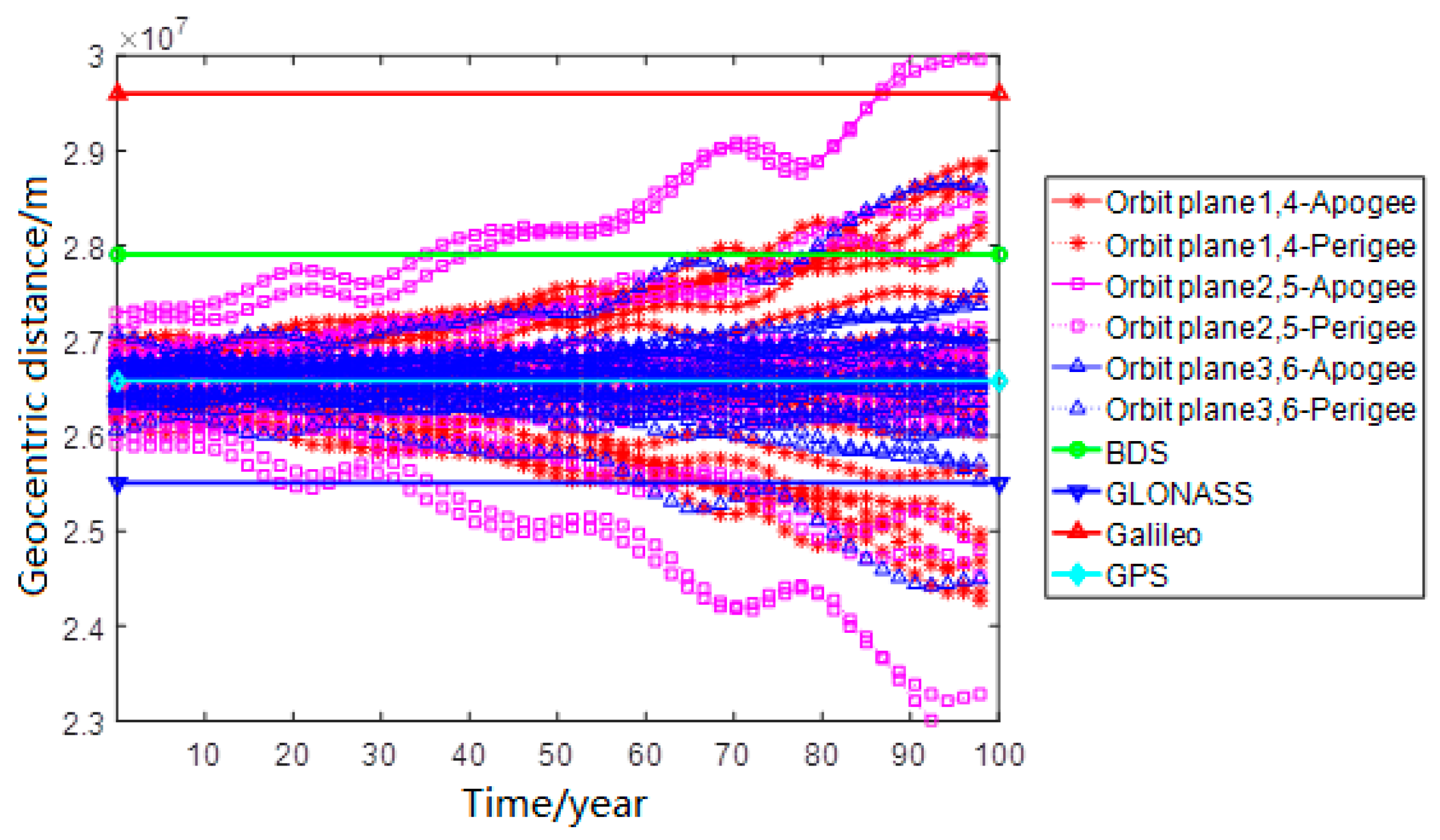

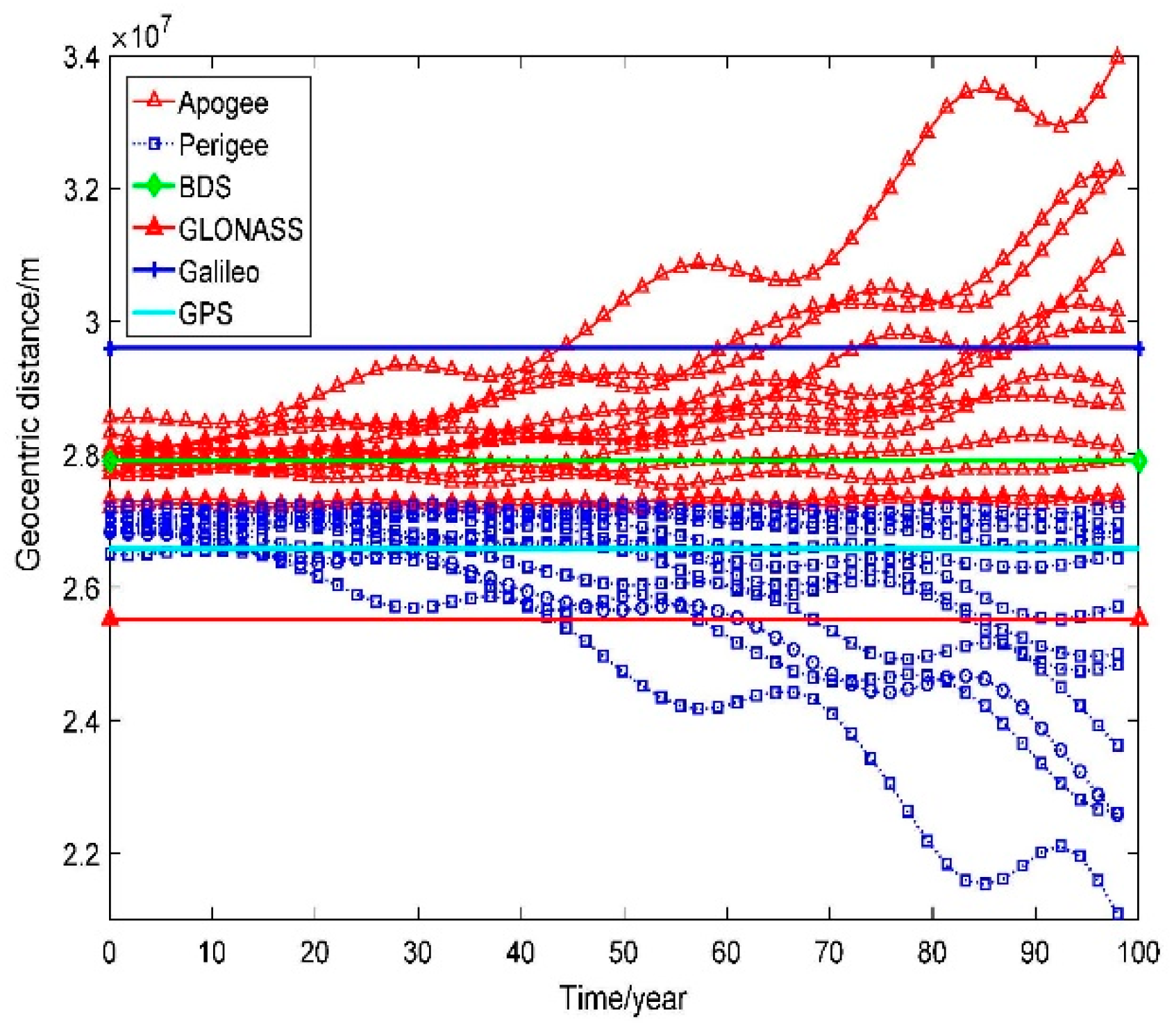
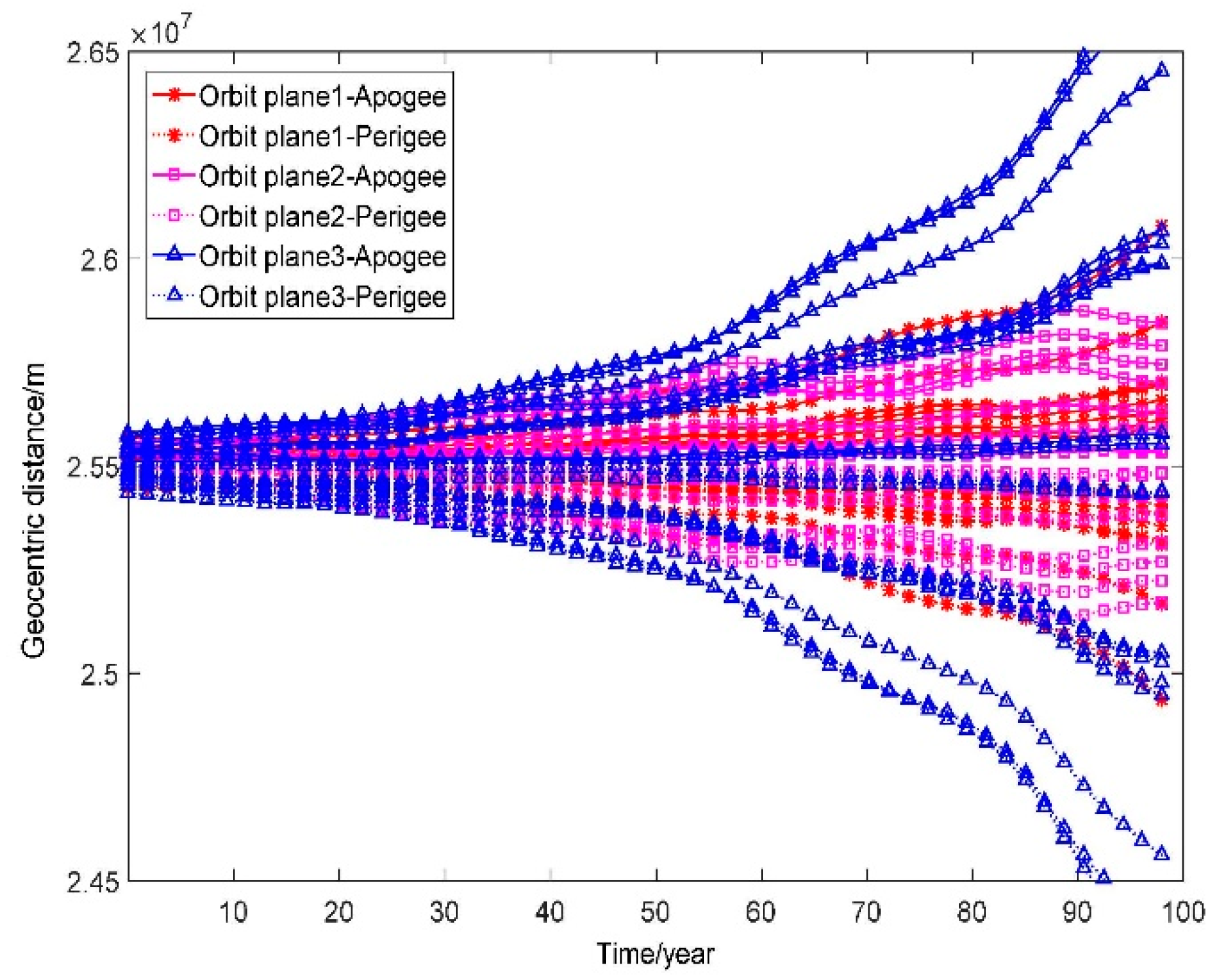





| NOARD | Apogee Altitude/km | Perigee Altitude/km |
|---|---|---|
| 40128 | 26,255 | 16,944 |
| 40129 | 26,251 | 16,947 |
| NOARD | Apogee Altitude/km | Perigee Altitude/km |
|---|---|---|
| 40130 | 26,090 | 13,500 |
| Constellation | Deorbit Navigation | Deorbit Upper Stages | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Apogee/km | Number | Apogee/km | |
| GPS | >30 | +350~1700 | 12 | +600~1900 |
| GLONASS | — | — | 20 | 0~+00 |
| Galileo | 2 | +120~+600 | 8 | +350~+2900 |
| BDS | 1 | +300 | 7 | +200~+6000 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, M.; Ruan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xu, J.; Xue, W. Long-Term Orbit Prediction and Deorbit Disposal Investigation of MEO Navigation Satellites. Aerospace 2022, 9, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9050266
Hu M, Ruan Y, Zhou H, Xu J, Xue W. Long-Term Orbit Prediction and Deorbit Disposal Investigation of MEO Navigation Satellites. Aerospace. 2022; 9(5):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9050266
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Min, Yongjing Ruan, Huifeng Zhou, Jiahui Xu, and Wen Xue. 2022. "Long-Term Orbit Prediction and Deorbit Disposal Investigation of MEO Navigation Satellites" Aerospace 9, no. 5: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9050266
APA StyleHu, M., Ruan, Y., Zhou, H., Xu, J., & Xue, W. (2022). Long-Term Orbit Prediction and Deorbit Disposal Investigation of MEO Navigation Satellites. Aerospace, 9(5), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/aerospace9050266






