Capsule Endoscopy: Pitfalls and Approaches to Overcome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Maneuverability
2.1. Magnetic Navigation System
2.1.1. Magnetic Maneuverable Capsule
2.1.2. Magnetically Guided Capsule Endoscopy
2.1.3. Magnetically Controlled Capsule Endoscopy System
2.1.4. MiroCam Navi
2.2. Internal Locomotion System
2.2.1. Inchworm-Like Capsule Endoscope
2.2.2. Paddle/Legged-Based Capsule Endoscope
2.2.3. Hydrodynamic Force-Based Capsule Endoscope
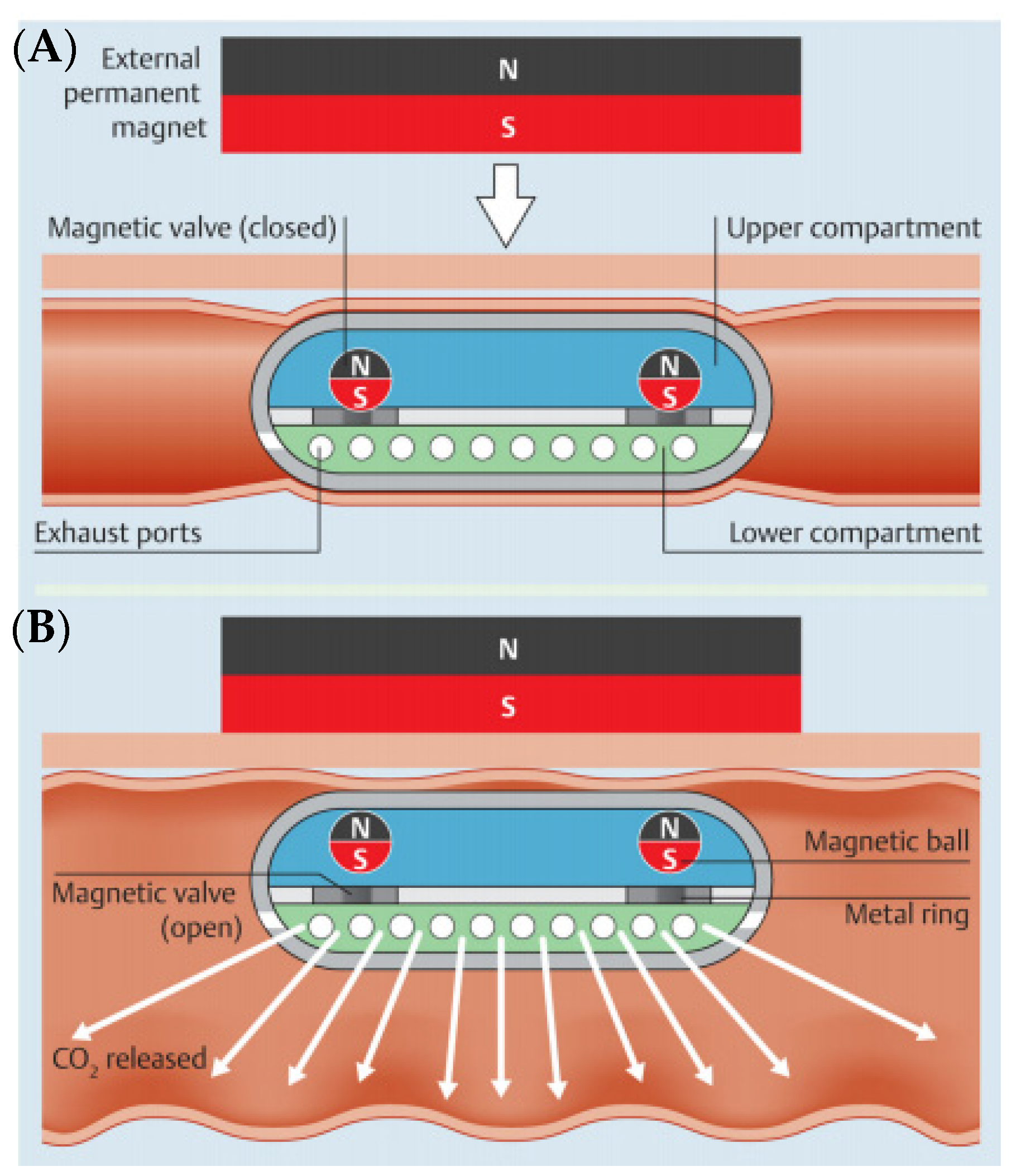
3. Air Insufflation
4. Visibility for the Diagnostic Ability
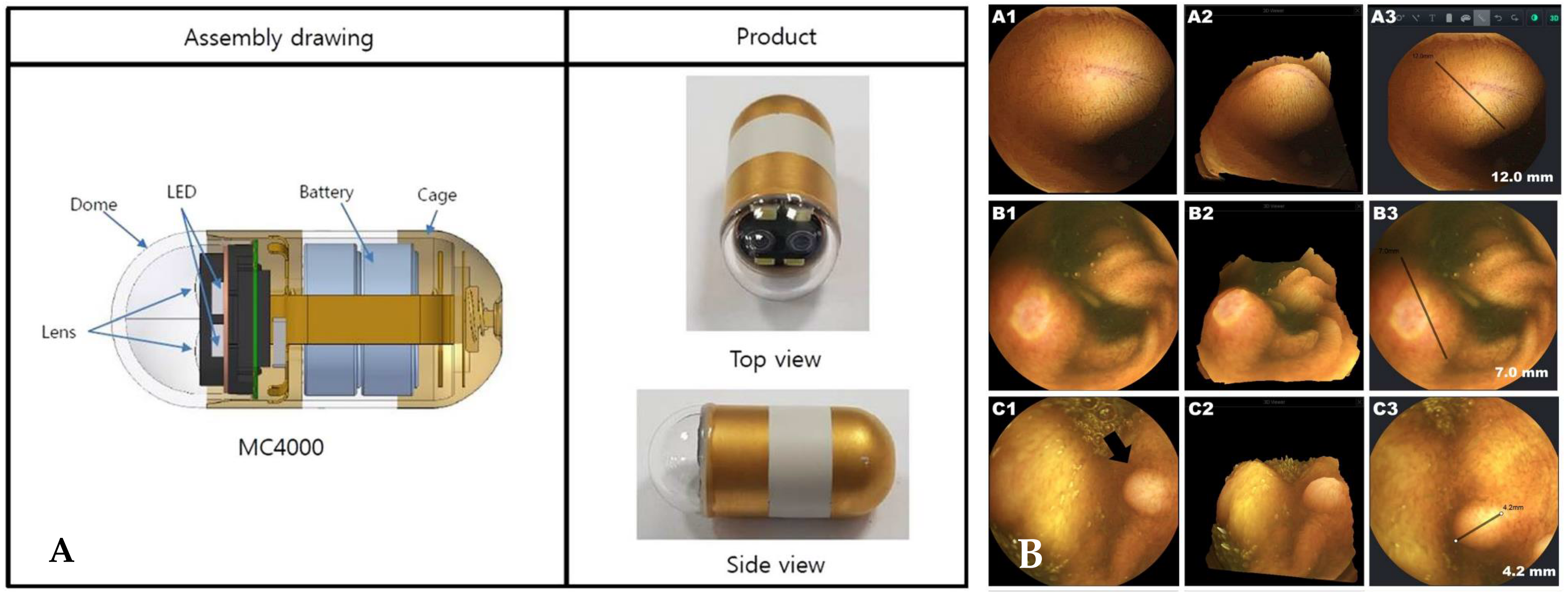
4.1. Upgrade of a Capsule Endoscope Device
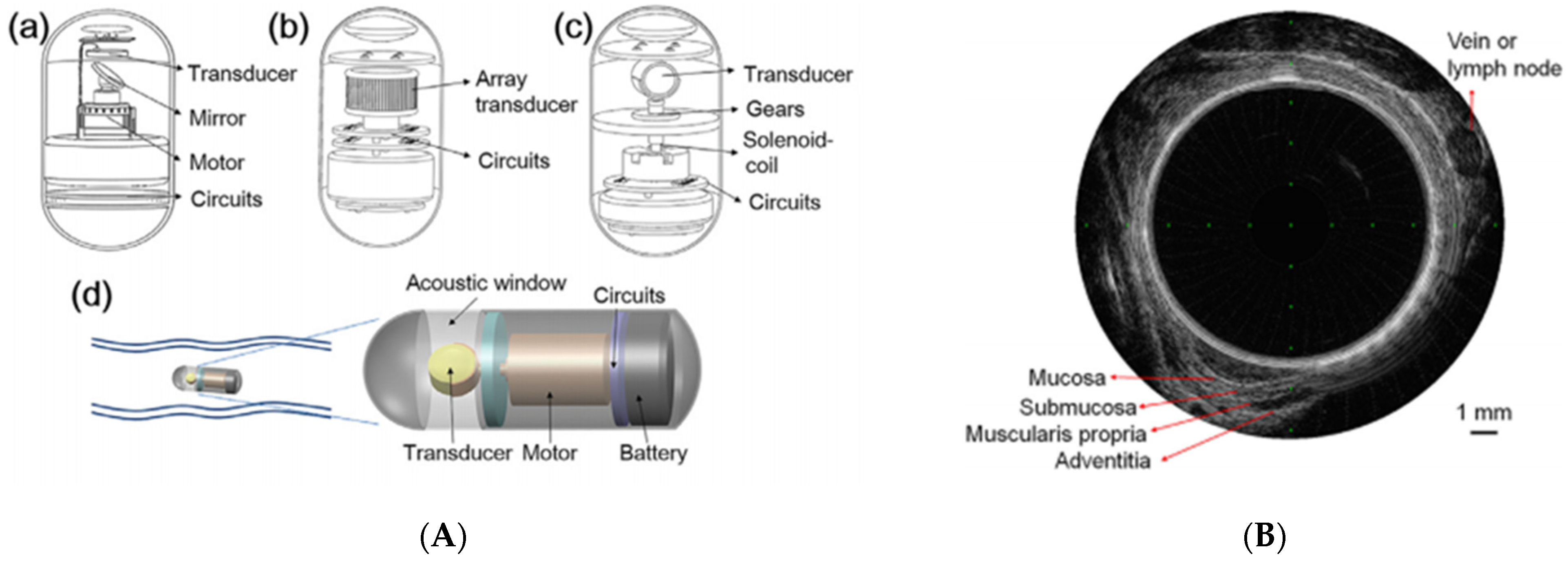
4.2. Non-White Light Imaging
4.3. 3D Reconstruction
5. Bowel Preparation
6. Abilities of Procedure
6.1. Biopsy
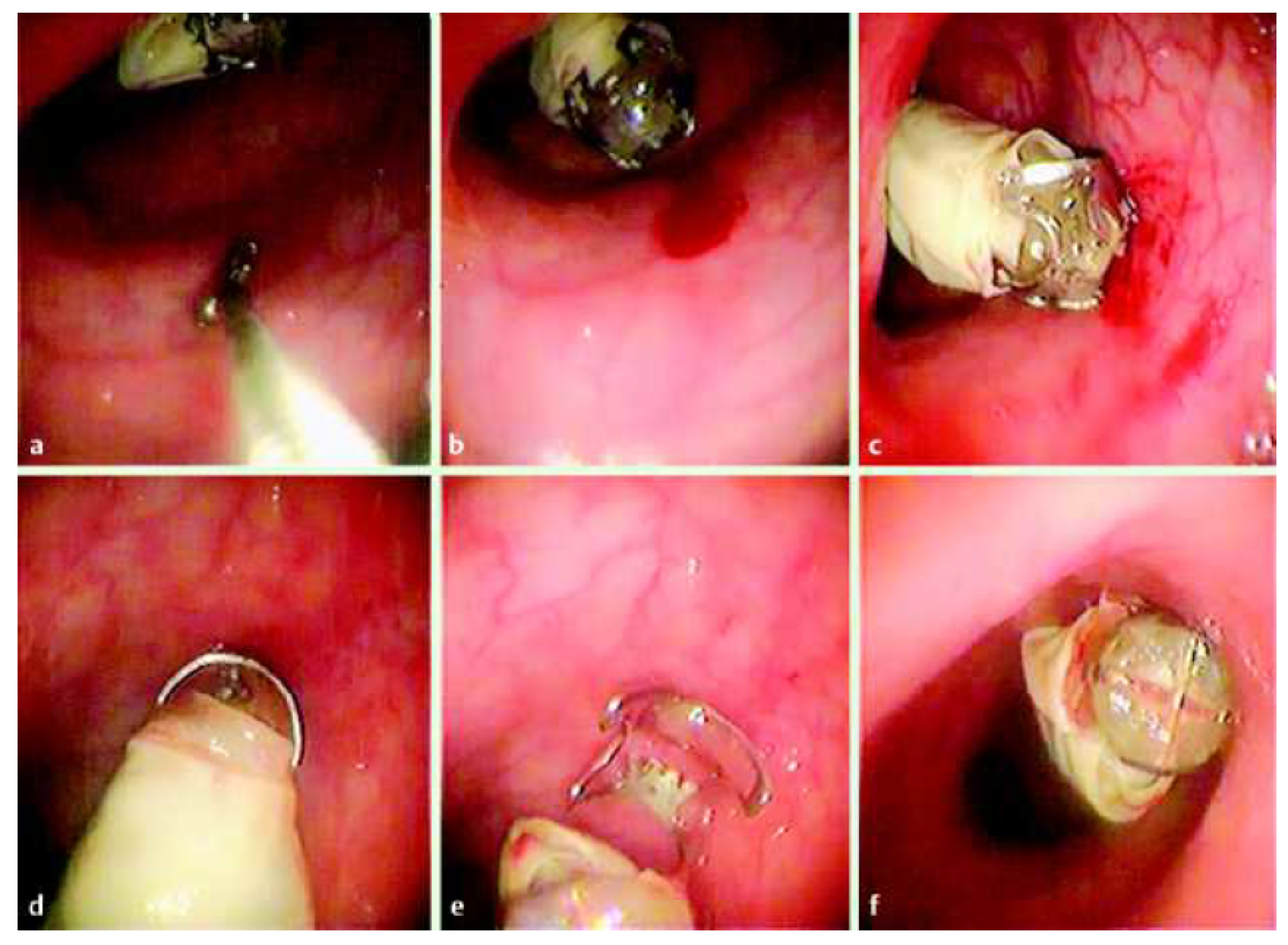
6.2. Hemostasis
7. Retention
8. Interpretation
8.1. Software Upgrade
8.2. Artificial Intelligence
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iddan, G.; Meron, G.; Glukhovsky, A.; Swain, P. Wireless capsule endoscopy. Nature 2000, 405, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soncini, M.; Girelli, C.M.; de Franchis, R.; Rondonotti, E. Small-Bowel Capsule Endoscopy in Clinical Practice: Has Anything Changed Over 13 Years? Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 2244–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharazmi, A.A.; Aslani, S.; Kristiansen, M.F.; Dahl, E.E.; Berner-Hansen, M. Indications and diagnostic yield of small-bowel capsule endoscopy in a real-world setting. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020, 20, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Z.; Gao, R.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.S. Indications and detection, completion, and retention rates of small-bowel capsule endoscopy: A systematic review. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 71, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chetcuti Zammit, S.; Sidhu, R. Capsule endoscopy—Recent developments and future directions. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enns, R.A.; Hookey, L.; Armstrong, D.; Bernstein, C.N.; Heitman, S.J.; Teshima, C.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Tse, F.; Sadowski, D. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Use of Video Capsule Endoscopy. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hale, M.F.; Sidhu, R.; McAlindon, M.E. Capsule endoscopy: Current practice and future directions. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7752–7759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, H.; Fry, L.C.; Neurath, M.F. Review article on current applications and future concepts of capsule endoscopy. Digestion 2013, 87, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goenka, M.K.; Majumder, S.; Goenka, U. Capsule endoscopy: Present status and future expectation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 10024–10037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, G. Posture Dynamic Modeling and Stability Analysis of a Magnetic Driven Dual-Spin Spherical Capsule Robot. Micromachines 2021, 12, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.S.; Eisen, G.M.; Friedman, S. A pooled analysis to evaluate results of capsule endoscopy trials. Endoscopy 2005, 37, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grady, M.S.; Howard, M.A., III; Dacey, R.G., Jr.; Blume, W.; Lawson, M.; Werp, P.; Ritter, R.C. Experimental study of the magnetic stereotaxis system for catheter manipulation within the brain. J. Neurol. Surg. 2000, 93, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filgueiras-Rama, D.; Estrada, A.; Shachar, J.; Castrejón, S.; Doiny, D.; Ortega, M.; Gang, E.; Merino, J.L. Remote magnetic navigation for accurate, real-time catheter positioning and ablation in cardiac electrophysiology procedures. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 74, 3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsudhin, N.; Zverev, V.I.; Keller, H.; Pane, S.; Egolf, P.W.; Nelson, B.J.; Tishin, A.M. Magnetically guided capsule endoscopy. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, e91–e111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swain, P.; Toor, A.; Volke, F.; Keller, J.; Gerber, J.; Rabinovitz, E.; Rothstein, R.I. Remote magnetic manipulation of a wireless capsule endoscope in the esophagus and stomach of humans (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 71, 1290–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.; Afzal, N.A.; Patel, P. The role of magnetic assisted capsule endoscopy (MACE) to aid visualisation in the upper GI tract. Comput. Biol. Med. 2015, 65, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Hou, X.; Lin-Hu, E.Q.; Sheng, J.Q.; Ge, Z.Z.; Jiang, B.; Hou, X.H.; Liu, J.Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, Q.Y.; et al. Accuracy of Magnetically Controlled Capsule Endoscopy, Compared With Conventional Gastroscopy, in Detection of Gastric Diseases. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 14, 1266–1273.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ching, H.L.; Hale, M.F.; Sidhu, R.; Beg, S.; Ragunath, K.; McAlindon, M.E. Magnetically assisted capsule endoscopy in suspected acute upper GI bleeding versus esophagogastroduodenoscopy in detecting focal lesions. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 90, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, I.; Pioche, M.; Shim, C.S.; Lee, S.P.; Sung, I.K.; Saurin, J.C.; Patel, P. Magnetic-assisted capsule endoscopy in the upper GI tract by using a novel navigation system (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016, 83, 889–895.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Galbiati, S.; Carpi, A. Controlled navigation of endoscopic capsules: Concept and preliminary experimental investigations. IEEE Trans. BioMed. Eng. 2007, 54, 2028–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, P.; Cheung, E.; Sitti, M. A legged anchoring mechanism for capsule endoscopes using micropatterned adhesives. IEEE Trans. BioMed. Eng. 2008, 55, 2759–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.M.; Yang, S.; Kim, J.; Park, S.; Cho, J.H.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, T.S.; Yoon, E.S.; Song, S.Y.; Bang, S. Active locomotion of a paddling-based capsule endoscope in an in vitro and in vivo experiment (with videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2010, 72, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, H.; Park, S.; Jee, C.; Kim, J.; Kim, B. Capsular locomotive microrobot for gastrointestinal tract. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, New York, NY, USA, 30 August–3 September 2006; pp. 2211–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Park, K.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.S.; Cho, I.J.; Yoon, E.S. Autonomous locomotion of capsule endoscope in gastrointestinal tract. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 6659–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Towfighian, S.; Hila, A. A Review of Locomotion Systems for Capsule Endoscopy. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 8, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheung, E.; Karagozler, M.E.; Park, S.; Kim, B.; Sitti, M. A New Endoscopic Microcapsule Robot using Beetle Inspired Microfibrillar Adhesives. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, Monterey, CA, USA, 24–28 July 2005; pp. 551–557. [Google Scholar]
- Karagozler, M.E.; Cheung, E.; Jiwoon, K.; Sitti, M. Miniature Endoscopic Capsule Robot using Biomimetic Micro-Patterned Adhesives. In Proceedings of the First IEEE/RAS-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Pisa, Italy, 20–22 February 2006; Volume 2006, pp. 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, S.-J.; Lee, H.S.; Lim, Y.J. Evaluation of Gastric Disease with Capsule Endoscopy. Clin. Endosc. 2018, 51, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gorlewicz, J.L.; Battaglia, S.; Smith, B.F.; Ciuti, G.; Gerding, J.; Menciassi, A.; Obstein, K.L.; Valdastri, P.; Webster, R.J., III. Wireless insufflation of the gastrointestinal tract. IEEE Trans. BioMed. Eng. 2013, 60, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasricha, T.; Smith, B.F.; Mitchell, V.R.; Fang, B.; Brooks, E.R.; Gerding, J.S.; Washington, M.K.; Valdastri, P.; Obstein, K.L. Controlled colonic insufflation by a remotely triggered capsule for improved mucosal visualization. Endoscopy 2014, 46, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoe, N.; Takabayashi, K.; Ogata, H.; Kanai, T. Capsule endoscopy for small-intestinal disorders: Current status. Dig. Endosc. 2019, 31, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, T.; Hara, T.; Sakasai, S.; Kambayashi, H.; Murasugi, S.; Ito, A.; Nakamura, S.; Tokushige, K. Does the PillCam SB3 capsule endoscopy system improve image reading efficiency irrespective of experience? A pilot study. Endosc. Int. Open 2018, 6, E669–E675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Har-Noy, O.; Katz, L.; Avni, T.; Battat, R.; Bessissow, T.; Yung, D.E.; Engel, T.; Koulaouzidis, A.; Eliakim, R.; Ben-Horin, S.; et al. Chromoendoscopy, Narrow-Band Imaging or White Light Endoscopy for Neoplasia Detection in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 2982–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, A.; Manner, H.; Rey, J.W.; Kiesslich, R. A guide to multimodal endoscopy imaging for gastrointestinal malignancy—An early indicator. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gono, K. Narrow Band Imaging: Technology Basis and Research and Development History. Clin. Endosc. 2015, 48, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, C.-T.; Lai, Z.-W.; Lin, Y.-T.; Cheng, H.-C. Optical Design with Narrow-Band Imaging for a Capsule Endoscope. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 5830759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, T.H.; Wahid, K.A. White and narrow band image compressor based on a new color space for capsule endoscopy. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2014, 29, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Memon, F.; Touma, G.; Baltsavias, S.; Jang, J.H.; Chang, C.; Rasmussen, M.F.; Olcott, E.; Jeffrey, R.B.; Arbabian, A.; et al. Capsule ultrasound device: Characterization and testing results. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Washington, DC, USA, 6–9 September 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Seetohul, V.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, M.; Shi, Z.; Yang, G.; Mu, P.; Wang, C.; Huang, Z.; et al. Development of a Mechanical Scanning Device With High-Frequency Ultrasound Transducer for Ultrasonic Capsule Endoscopy. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 1922–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, B.F.; Stewart, F.; Lay, H.; Cummins, G.; Newton, I.P.; Desmulliez, M.P.Y.; Steele, R.J.C.; Näthke, I.; Cochran, S. Ultrasound capsule endoscopy: Sounding out the future. Ann. Transl. Med. 2017, 5, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cox, B.F.; Liu, R.; Hong, J.; Mu, P.; Lay, H.S.; Cummins, G.; Desmulliez, M.P.Y.; et al. Ultrasound Capsule Endoscopy With a Mechanically Scanning Micro-ultrasound: A Porcine Study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Rawhani, M.A.; Beeley, J.; Cumming, D.R. Wireless fluorescence capsule for endoscopy using single photon-based detection. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demosthenous, P.; Pitris, C.; Georgiou, J. Infrared Fluorescence-Based Cancer Screening Capsule for the Small Intestine. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2016, 10, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemiroski, A.; Ryou, M.; Thompson, C.C.; Westervelt, R.M. Swallowable fluorometric capsule for wireless triage of gastrointestinal bleeding. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 4479–4487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gora, M.J.; Sauk, J.S.; Carruth, R.W.; Gallagher, K.A.; Suter, M.J.; Nishioka, N.S.; Kava, L.E.; Rosenberg, M.; Bouma, B.E.; Tearney, G.J. Tethered capsule endomicroscopy enables less invasive imaging of gastrointestinal tract microstructure. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, K.; Traverso, G.; Lee, H.C.; Ahsen, O.O.; Wang, Z.; Potsaid, B.; Giacomelli, M.; Jayaraman, V.; Barman, R.; Cable, A.; et al. Ultrahigh speed en face OCT capsule for endoscopic imaging. Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 1146–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stewart, I.B.; Stewart, K.L.; Worringham, C.J.; Costello, J.T. Physiological tolerance times while wearing explosive ordnance disposal protective clothing in simulated environmental extremes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e83740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niedermann, R.; Wyss, E.; Annaheim, S.; Psikuta, A.; Davey, S.; Rossi, R.M. Prediction of human core body temperature using non-invasive measurement methods. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2014, 58, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stein, E.; Berger, Z.; Hutfless, S.; Shah, L.; Wilson, L.M.; Haberl, E.B.; Bass, E.B.; Clarke, J.O. AHRQ Comparative Effectiveness Reviews. Wireless Motility Capsule Versus Other Diagnostic Technologies for Evaluating Gastroparesis and Constipation: A Comparative Effectiveness Review; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality: Rockville, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Kreikemeier-Bower, C.; Xie, W.; Kothari, V.; Terry, B.S. Design of a Wireless Medical Capsule for Measuring the Contact Pressure Between a Capsule and the Small Intestine. J. Biomech. Eng. 2017, 139, 051003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, R.J. The Wireless Motility Capsule: A One-Stop Shop for the Evaluation of GI Motility Disorders. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2016, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.H.; Cho, J.H. Telemetry system for slow wave measurement from the small bowel. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2010, 48, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochman, J.A.; Favaloro-Sabatier, J. Tolerance and reliability of wireless pH monitoring in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2005, 41, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziolek, M.; Grimm, M.; Becker, D.; Iordanov, V.; Zou, H.; Shimizu, J.; Wanke, C.; Garbacz, G.; Weitschies, W. Investigation of pH and Temperature Profiles in the GI Tract of Fasted Human Subjects Using the Intellicap® System. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 104, 2855–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulaouzidis, A.; Karargyris, A.; Rondonotti, E.; Noble, C.L.; Douglas, S.; Alexandridis, E.; Zahid, A.M.; Bathgate, A.J.; Trimble, K.C.; Plevris, J.N. Three-dimensional representation software as image enhancement tool in small-bowel capsule endoscopy: A feasibility study. Dig. Liver Dis. 2013, 45, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondonotti, E.; Koulaouzidis, A.; Karargyris, A.; Giannakou, A.; Fini, L.; Soncini, M.; Pennazio, M.; Douglas, S.; Shams, A.; Lachlan, N.; et al. Utility of 3-dimensional image reconstruction in the diagnosis of small-bowel masses in capsule endoscopy (with video). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2014, 80, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turan, M.; Pilavci, Y.; Jamiruddin, R.; Araujo, H.; Konukoglu, E.; Sitti, M. A Fully Dense and Globally Consistent 3D Map Reconstruction Approach for GI Tract to Enhance Therapeutic Relevance of the Endoscopic Capsule Robot. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.06524. [Google Scholar]
- Prasath, V.B.S.; Figueiredo, I.N.; Figueiredo, P.N.; Palaniappan, K. Mucosal region detection and 3D reconstruction in wireless capsule endoscopy videos using active contours. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 4014–4017. [Google Scholar]
- Koulaouzidis, A.; Karargyris, A. Three-dimensional image reconstruction in capsule endoscopy. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 4086–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karargyris, A.; Rondonotti, E.; Mandelli, G.; Koulaouzidis, A. Evaluation of 4 three-dimensional representation algorithms in capsule endoscopy images. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 8028–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.J.; Lim, Y.J.; Nam, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Hwang, Y.; Park, J.; Chun, H.J. 3D reconstruction of small bowel lesions using stereo camera-based capsule endoscopy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Sun, X.; Zhou, M.; Jiao, S.; Wang, H.; Xiaopeng, Z. On building an accurate stereo matching system on graphics hardware. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCV Workshops), Barcelona, Spain, 6–13 November 2011; pp. 467–474. [Google Scholar]
- Viazis, N.; Sgouros, S.; Papaxoinis, K.; Vlachogiannakos, J.; Bergele, C.; Sklavos, P.; Panani, A.; Avgerinos, A. Bowel preparation increases the diagnostic yield of capsule endoscopy: A prospective, randomized, controlled study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2004, 60, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladas, S.D.; Triantafyllou, K.; Spada, C.; Riccioni, M.E.; Rey, J.F.; Niv, Y.; Delvaux, M.; de Franchis, R.; Costamagna, G. European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE): Recommendations (2009) on clinical use of video capsule endoscopy to investigate small-bowel, esophageal and colonic diseases. Endoscopy 2010, 42, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rokkas, T.; Papaxoinis, K.; Triantafyllou, K.; Pistiolas, D.; Ladas, S.D. Does purgative preparation influence the diagnostic yield of small bowel video capsule endoscopy?: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Cao, Y.; Liao, C.; Huang, J.; Gao, F. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of Simethicone for gastrointestinal endoscopic visibility. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondonotti, E.; Spada, C.; Adler, S.; May, A.; Despott, E.J.; Koulaouzidis, A.; Panter, S.; Domagk, D.; Fernandez-Urien, I.; Rahmi, G.; et al. Small-bowel capsule endoscopy and device-assisted enteroscopy for diagnosis and treatment of small-bowel disorders: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Technical Review. Endoscopy 2018, 50, 423–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koulaouzidis, A.; Giannakou, A.; Yung, D.E.; Dabos, K.J.; Plevris, J.N. Do prokinetics influence the completion rate in small-bowel capsule endoscopy? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2013, 29, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simi, M.; Gerboni, G.; Menciassi, A.; Valdastri, P. Magnetic Torsion Spring Mechanism for a Wireless Biopsy Capsule. J. Med. Devices 2013, 7, 041009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyoung-chul, K.; Jinhoon, C.; Doyoung, J.; Dong-il Dan, C. A rotational micro biopsy device for the capsule endoscope. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2–6 August 2005; pp. 1839–1843. [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski, R. Overview of technical solutions and assessment of clinical usefulness of capsule endoscopy. Biomed. Eng. OnLine 2015, 14, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valdastri, P.; Quaglia, C.; Susilo, E.; Menciassi, A.; Dario, P.; Ho, C.N.; Anhoeck, G.; Schurr, M.O. Wireless therapeutic endoscopic capsule: In vivo experiment. Endoscopy 2008, 40, 979–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leung, B.H.K.; Poon, C.C.Y.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, Y.; Chan, C.K.W.; Chiu, P.W.Y.; Lau, J.Y.W.; Sung, J.J.Y. A Therapeutic Wireless Capsule for Treatment of Gastrointestinal Haemorrhage by Balloon Tamponade Effect. IEEE Trans. BioMed. Eng. 2017, 64, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Römmele, C.; Brueckner, J.; Messmann, H.; Gölder, S.K. Clinical Experience with the PillCam Patency Capsule prior to Video Capsule Endoscopy: A Real-World Experience. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 9657053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chao, W.L.; Manickavasagan, H.; Krishna, S.G. Application of Artificial Intelligence in the Detection and Differentiation of Colon Polyps: A Technical Review for Physicians. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.J. The Future of Capsule Endoscopy: The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Other Technical Advancements. Clin. Endosc. 2020, 53, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, T.; Yamada, A.; Aoyama, K.; Saito, H.; Tsuboi, A.; Nakada, A.; Niikura, R.; Fujishiro, M.; Oka, S.; Ishihara, S.; et al. Automatic detection of erosions and ulcerations in wireless capsule endoscopy images based on a deep convolutional neural network. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 89, 357–363.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klang, E.; Barash, Y.; Margalit, R.Y.; Soffer, S.; Shimon, O.; Albshesh, A.; Ben-Horin, S.; Amitai, M.M.; Eliakim, R.; Kopylov, U. Deep learning algorithms for automated detection of Crohn’s disease ulcers by video capsule endoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 91, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Aoki, T.; Aoyama, K.; Kato, Y.; Tsuboi, A.; Yamada, A.; Fujishiro, M.; Oka, S.; Ishihara, S.; Matsuda, T.; et al. Automatic detection and classification of protruding lesions in wireless capsule endoscopy images based on a deep convolutional neural network. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 144–151.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| MiroCam Navi | Navicam™ Stomach Capsule System | Magnetic Maneuverable Capsule | Magnetically Guided Capsule Endoscopy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company | Intromedic, Seoul, South Korea | Ankon Technologies, Wuhan, China | Given Imaging, Yoqneam, Israel | Siemens Healthcare, Erlangen, Germany and Olympus Medical Corp, Tokyo, Japan |
| Type | Hand-held magnetic field generators | Robotic magnetic capsule guidance system | Hand-held magnetic field generators | Multicoil guidance system |
| Human application | Yes | Yes | Yes | N/A |
| Year | 2013 | 2012 | 2010 | 2010 |
| Commercially available | Yes | Yes | N/A | N/A |
| FDA approval | N/A | Yes | N/A | N/A |
| Capsule Endoscopy | PillCam SB3 | MiroCam | CapsoCam SV-1 | Endocapsule 10 | OMOM Capsule2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company | Medtronic | IntroMedic | CapsoVision | Olympus | Jinshan Science and Technology |
| Size (mm) | 11 × 26 | 11 × 25 | 11 × 31 | 11 × 26 | 11 × 25 |
| Weight (g) | 3.0 | 3.25–4.70 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 4.5 |
| Camera lens (n) | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | |
| Data transmission | Radiofrequency communication | Human body communication | N/A | Radiofrequency communication | Radiofrequency communication |
| Battery life (h) | 11 | 12 | 15 | 12 | 10 |
| Frame rate (frames/s) | 2–6 | 3–6 | 12–20 | 2 | 2–6 |
| Field of view (degree) | 156 | 170 | 360 | 160 | 165 |
| US FDA approval | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Rapid V 8.0 | MiroView 4.0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Software mode | Suspected blood indicator | Video function for a quick review of suspected hemorrhagic lesions | Express view | A function that helps the reading by filtering out overlapping images and images of less importance among recorded images |
| QuickView | Ability to play clinically important images to provide quick preview and location | SGIB | A function to help the reading of suspected bleeding lesions | |
| Complementary QuickView | A mode that plays back videos not provided in QuickView mode. | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.H.; Chun, H.J. Capsule Endoscopy: Pitfalls and Approaches to Overcome. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101765
Kim SH, Chun HJ. Capsule Endoscopy: Pitfalls and Approaches to Overcome. Diagnostics. 2021; 11(10):1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101765
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seung Han, and Hoon Jai Chun. 2021. "Capsule Endoscopy: Pitfalls and Approaches to Overcome" Diagnostics 11, no. 10: 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101765
APA StyleKim, S. H., & Chun, H. J. (2021). Capsule Endoscopy: Pitfalls and Approaches to Overcome. Diagnostics, 11(10), 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics11101765






