-
 Teacher Self-Efficacy in Asthma Management in Elementary and Middle Schools
Teacher Self-Efficacy in Asthma Management in Elementary and Middle Schools -
 Biologic Therapies and Janus Kinase Inhibitors for Medium and Variable Vessel Vasculitides: A Review of Clinical and Preclinical Evidence
Biologic Therapies and Janus Kinase Inhibitors for Medium and Variable Vessel Vasculitides: A Review of Clinical and Preclinical Evidence -
 Retrospective Study on Acute Effects of Mount Etna Volcanic Eruption in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis
Retrospective Study on Acute Effects of Mount Etna Volcanic Eruption in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis -
 Vitamins and Antioxidants in Plants: Are They Helpful in the Management of Allergies?
Vitamins and Antioxidants in Plants: Are They Helpful in the Management of Allergies?
Journal Description
Allergies
Allergies
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on allergy and immunology published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 34.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 5.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
Understanding Insect Bite Hypersensitivity in Horses: A Narrative Review for Clinical Practice
Allergies 2025, 5(3), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5030031 - 22 Sep 2025
Abstract
Insect bite hypersensitivity (IBH) is a seasonally recurrent allergic dermatitis representing one of the most prevalent dermatological conditions in horses worldwide. This condition, driven by hypersensitivity to salivary allergens of Culicoides spp., causes substantial discomfort, welfare impairment, and potentially economic loss in equine
[...] Read more.
Insect bite hypersensitivity (IBH) is a seasonally recurrent allergic dermatitis representing one of the most prevalent dermatological conditions in horses worldwide. This condition, driven by hypersensitivity to salivary allergens of Culicoides spp., causes substantial discomfort, welfare impairment, and potentially economic loss in equine populations. The pathogenesis of IBH is complex, involving genetic predisposition, epithelial barrier dysfunction, and a skewed T-helper 2 (Th2)-mediated immune response with elevated IgE production and eosinophilic inflammation. Advances in immunogenetics and molecular immunology have improved the understanding of the disease’s multifactorial nature. Research on immunotherapy and cytokine-targeted treatments is contributing to the development of more effective therapeutic options. This review synthesizes current knowledge on the immunopathogenesis and genetic determinants of IBH and discusses both conventional and emerging strategies for its clinical management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Veterinary Allergy)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Mast Cells in Tuberculosis: Immune Regulation, Allergic Environments, and Pathological Mechanisms
by
Seung Hoon Lee, Gunhyuk Park, Hye-Sun Lim, Yoonseo Hong and Huiyun Seo
Allergies 2025, 5(3), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5030030 - 4 Sep 2025
Abstract
Mast cells (MC) are key effector cells in allergic diseases and are increasingly recognized for their roles in the immunopathogenesis of tuberculosis (TB). In allergic conditions, MCs are hyperactivated, driving T-helper Type 2 (Th2)-skewed immune responses that may antagonize the T-helper Type 1
[...] Read more.
Mast cells (MC) are key effector cells in allergic diseases and are increasingly recognized for their roles in the immunopathogenesis of tuberculosis (TB). In allergic conditions, MCs are hyperactivated, driving T-helper Type 2 (Th2)-skewed immune responses that may antagonize the T-helper Type 1 (Th1)-mediated immunity essential for controlling Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infection. This immunological imbalance may contribute to increased TB susceptibility, altered granuloma dynamics, and accelerated fibrotic remodeling. Histopathological and in vivo studies have revealed that MCs are recruited to TB lesions, where they release a spectrum of mediators, including histamine, IL-17A, TNF-α, TGF-β, tryptase, and chymase. These mediators can either support initial immune defense or promote chronic inflammation and tissue damage, depending on context and regulation. Moreover, individuals with chronic allergic diseases such as asthma and allergic rhinitis may experience worse TB outcomes due to their baseline immune dysregulation. Environmental exposures (e.g., air pollution, smoking), genetic polymorphisms (e.g., IL-4 −589C/T, IL-13 R130Q), and gut-lung axis disturbances further modulate MC activity and TB pathogenesis. This review synthesizes current findings on MC involvement in TB, particularly in allergic settings, and highlights the need for epidemiological studies and mechanistic research. It also explores the promise of host-directed therapies (HDTs) that target MCs or their mediators, such as antihistamines, MC stabilizers, leukotriene inhibitors, and cytokine modulators, as novel adjuncts to standard TB treatment. Personalized approaches that consider immune profiles, genetic risk, and comorbid allergies may improve TB outcomes and inform future clinical guidelines.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physiopathology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Biologic Therapies and Janus Kinase Inhibitors for Medium and Variable Vessel Vasculitides: A Review of Clinical and Preclinical Evidence
by
Allison Bai, Rachel Granovsky, Courtney Chau and Gabriela Cobos
Allergies 2025, 5(3), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5030029 - 22 Aug 2025
Abstract
Medium and variable vessel vasculitides are a heterogeneous group of rare, immune-mediated vascular disorders that are associated with significant morbidity and mortality. The standard treatment approach involves glucocorticoids and immunosuppressive agents. However, many patients exhibit poor tolerance or respond inadequately to these medications.
[...] Read more.
Medium and variable vessel vasculitides are a heterogeneous group of rare, immune-mediated vascular disorders that are associated with significant morbidity and mortality. The standard treatment approach involves glucocorticoids and immunosuppressive agents. However, many patients exhibit poor tolerance or respond inadequately to these medications. Recent advances in biologic therapies and Janus Kinase inhibitors (JAKis) offer promising alternatives. This review consolidates current knowledge on the pathogenesis, immunology, and therapeutic efficacy of biologics and JAKis in the management of medium and variable vessel vasculitis. While further research is needed to establish long-term safety and optimize treatment protocols, biologics and JAKis represent emerging therapeutic strategies with the potential to improve outcomes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physiopathology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Food Allergy-Associated Cutaneous Manifestations in Children: A Narrative Review
by
Annabel Hou, Joyce J. Zhu, Pratiksha Patra and Sharon Albers
Allergies 2025, 5(3), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5030028 - 19 Aug 2025
Abstract
The rising prevalence of pediatric food allergies represents a growing public health concern, with hospitalizations for food-induced anaphylaxis on the rise. Early cutaneous manifestations, particularly in the setting of atopic dermatitis (AD), may indicate sensitization via the skin—a critical route for allergen exposure
[...] Read more.
The rising prevalence of pediatric food allergies represents a growing public health concern, with hospitalizations for food-induced anaphylaxis on the rise. Early cutaneous manifestations, particularly in the setting of atopic dermatitis (AD), may indicate sensitization via the skin—a critical route for allergen exposure in early life. Pediatric food allergies can be IgE-mediated, non-IgE-mediated, or mixed, with each type presenting distinct pathophysiological and clinical features. IgE-mediated reactions often involve acute urticaria and angioedema, while non-IgE forms, such as food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome (FPIES), manifest with delayed gastrointestinal symptoms and limited skin involvement. AD is closely linked with food allergies, both in pathogenesis and symptom exacerbation, with a high prevalence of co-occurrence. Diagnosis primarily relies on clinical evaluation, supported by testing such as skin prick testing, serum IgE, and oral food challenges, though limitations exist in sensitivity and specificity. Management emphasizes allergen avoidance, symptom control, and multidisciplinary care. While many pediatric food allergies resolve with age, others persist or present chronically, necessitating long-term strategies. Coordinated management between allergy and dermatology is key to minimizing complications and supporting better long-term outcomes for affected children.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Pediatric Allergy)
Open AccessArticle
Retrospective Study on Acute Effects of Mount Etna Volcanic Eruption in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis
by
Federica Trovato, Antonio Di Guardo, Alessandra Rallo, Annunziata Dattola, Elena Zappia, Steven Paul Nisticò and Giovanni Pellacani
Allergies 2025, 5(3), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5030027 - 8 Aug 2025
Abstract
Mount Etna, located on the eastern coast of Sicily, is Europe’s most active volcano. Over the past five years, it has experienced numerous significant eruptive episodes, with the most recent occurring in August 2024. During this event, substantial amounts of volcanic ash were
[...] Read more.
Mount Etna, located on the eastern coast of Sicily, is Europe’s most active volcano. Over the past five years, it has experienced numerous significant eruptive episodes, with the most recent occurring in August 2024. During this event, substantial amounts of volcanic ash were dispersed over densely populated areas, particularly in the province of Catania. Environmental factors, such as volcanic eruptions, are known to influence inflammatory skin conditions, including atopic dermatitis. We analyzed a cohort of patients with atopic dermatitis who were exposed to volcanic ash during the Mount Etna eruption in August 2024, aiming to evaluate the impact of the eruption on respiratory and cutaneous symptoms, treatment response, use of protective equipment, and changes in EASI scores over an eight-week period. A total of 67 Caucasian atopic dermatitis patients (mean age 41.2) were assessed after a volcanic eruption. Symptom worsening occurred in 58.9% (respiratory) and 26.9% (skin) of patients. EASI scores significantly increased (p < 0.05). No clinical difference was found between treatment types or mask use, which did not prevent symptom exacerbation. Volcanic ash exposure significantly worsened respiratory and skin symptoms in atopic dermatitis patients, underscoring the need for improved protective measures and further research on environmental triggers of chronic inflammatory conditions.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers 2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Intersections Between Allergic Diseases and Multiple Sclerosis: Mechanisms, Clinical Implications, and Hypersensitivity Reactions to Therapy
by
Guillermo Cervera-Ygual, Ana Delgado-Prada and Francisco Gascon-Gimenez
Allergies 2025, 5(3), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5030026 - 5 Aug 2025
Abstract
Multiple sclerosis (MS) and allergic diseases, traditionally considered immunologically opposing entities, may share pathogenic mechanisms rooted in immune dysregulation. While MS is predominantly mediated by Th1 and Th17 responses and allergies by Th2 responses, emerging evidence suggests overlapping immunological pathways, including the involvement
[...] Read more.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) and allergic diseases, traditionally considered immunologically opposing entities, may share pathogenic mechanisms rooted in immune dysregulation. While MS is predominantly mediated by Th1 and Th17 responses and allergies by Th2 responses, emerging evidence suggests overlapping immunological pathways, including the involvement of histamine, regulatory T cells, and innate lymphoid cells. This review synthesizes current knowledge on the epidemiological and immunopathological associations between MS and allergies. Epidemiological studies have yielded inconsistent results, with some suggesting a protective role for respiratory and food allergies against MS onset, while others find no significant correlation. Clinical studies indicate that food allergies in adults may be associated with increased MS inflammatory activity, whereas childhood atopy might exert a protective effect. In addition, we review hypersensitivity reactions to disease-modifying treatments for MS, detailing their immunological mechanisms, clinical presentation, and management, including desensitization protocols where applicable. Finally, we explore how treatments for allergic diseases—such as clemastine, allergen immunotherapy, montelukast, and omalizumab—may modulate MS pathophysiology, offering potential therapeutic synergies. Understanding the interplay between allergic and autoimmune processes is critical for optimizing care and developing innovative treatment approaches in MS.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Physiopathology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Teacher Self-Efficacy in Asthma Management in Elementary and Middle Schools
by
Ethan Schilling, Stacey Neuharth-Pritchett, Sofia H. Davie and Yvette Q. Getch
Allergies 2025, 5(3), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5030025 - 3 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: This study assessed teacher self-efficacy in school-based asthma management in two southern states in the United States. Current literature focuses primarily on supporting school-based asthma management, but few studies have focused on teacher self-efficacy in the asthma management process. Methods: With data
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: This study assessed teacher self-efficacy in school-based asthma management in two southern states in the United States. Current literature focuses primarily on supporting school-based asthma management, but few studies have focused on teacher self-efficacy in the asthma management process. Methods: With data collected from a two-state survey of a randomly selected group of teachers in grades kindergarten to grade eight (n = 379), teachers’ demographic variables, general opinions about asthma management practices, and their self-perceptions on the Teacher Asthma Management and Information Seeking Scale, which assesses self-efficacy, were examined. Results: Teachers’ self-efficacy in managing asthma and seeking information was significantly higher among teachers who had completed in-service professional learning sessions and those who had access to community resources or links to community agencies. Additionally, teachers with personal experience of chronic illness, asthma, or allergies and those who had students with chronic illnesses in their classrooms reported higher self-efficacy scores. Conclusions: Findings suggest that providing professional learning about asthma for teachers, offering access to asthma action plans and community resources, and increasing awareness of chronic conditions and training for handling medical emergencies can enhance teachers’ self-efficacy and improve outcomes for students with chronic illnesses.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Asthma/Respiratory)
Open AccessArticle
Toxocara spp. Infection Influences on Eosinophil Levels: An Immunological Indicator of Severe Asthma and Allergy
by
Raphael Chagas Silva, Márcia Barbosa da Silva, Alana Alcantara Galvão, Jamile Souza Fernandes, Gabriela Pimentel Pinheiro, Álvaro A. Cruz, Carina da Silva Pinheiro and Neuza Maria Alcântara-Neves
Allergies 2025, 5(3), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5030024 - 3 Jul 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Toxocara spp. infection has been associated with severe asthma and allergic manifestations due to the activation of eosinophils by the release of Th2 cell cytokines. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between Toxocara spp. infection and eosinophil levels
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Toxocara spp. infection has been associated with severe asthma and allergic manifestations due to the activation of eosinophils by the release of Th2 cell cytokines. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between Toxocara spp. infection and eosinophil levels in severe asthmatic patients. Methods: The socio-demographic, peripheral blood eosinophils counting total IgE, sIgE to aeroallergens and FEV1 results were acquired from the Program of Asthma and Rhinitis Control (ProAR) at the Salvador–Brazil databank; IgG anti-Toxocara spp. levels were measured in 176 severely asthmatic patients by indirect ELISA. Results: The Toxocara spp. seroprevalence was 50.6%. Eosinophilia was present in 54% of the population. The correlation between IgG anti-Toxocara spp. levels and eosinophils levels was positive. Eosinophilic individuals with SPT, sIgE for D. pteronyssinus, D. farinae and B. tropicalis showed positive results; IgE ≥ 160 UI/dL and uncontrolled asthma presented more positive results for IgG anti-Toxocara spp. Conclusions: Our findings suggest that eosinophil levels are influenced by the presence of IgG antibodies against Toxocara spp. Additionally, helminth infection may modulate immunological responses in allergies and uncontrolled asthma, which could help explain the exacerbation of asthma symptoms.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Asthma/Respiratory)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exploring Molecular Responses to Aeroallergens in Respiratory Allergy Across Six Locations in Peru
by
Oscar Manuel Calderón-Llosa, César Alberto Galván, María José Martínez, Ruperto González-Pérez, Eva Abel-Fernández and Fernando Pineda
Allergies 2025, 5(3), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5030023 - 3 Jul 2025
Abstract
Allergic diseases, particularly respiratory allergies like asthma and allergic rhinitis, are a growing public health concern influenced by environmental factors such as climate change and air pollution. The exposome framework enables a comprehensive assessment of how lifelong environmental exposures shape immune responses and
[...] Read more.
Allergic diseases, particularly respiratory allergies like asthma and allergic rhinitis, are a growing public health concern influenced by environmental factors such as climate change and air pollution. The exposome framework enables a comprehensive assessment of how lifelong environmental exposures shape immune responses and allergic sensitization. Peru’s diverse ecosystems and climates provide a unique setting to investigate regional variations in allergic sensitization. This study characterized these patterns in five Peruvian regions with distinct climatic, urbanization, and socioeconomic characteristics. A total of 268 individuals from Lima, Piura, Tarapoto, Arequipa, and Tacna were analysed for allergen-specific IgE responses using a multiplex IgE detection system. The results revealed significant geographical differences in sensitization frequencies and serodominance profiles, based on descriptive statistics and supported by Chi-square comparative analysis. House dust mites were predominant in humid regions, while Arequipa exhibited higher sensitization to cat allergens. In Tacna, olive pollen showed notable prevalence alongside house dust mites. Tarapoto’s high humidity correlated with increased fungal and cockroach allergen sensitization. Notably, some allergens traditionally considered minor, such as Der p 5 and Der p 21, reached sensitization prevalences close to or exceeding 50% in certain regions. These findings provide the most detailed molecular characterization of allergic sensitization in Peru to date, highlighting the importance of region-specific allergy management strategies. Understanding environmental influences on allergic diseases can support more effective diagnostic, therapeutic, and preventive approaches tailored to diverse geographical contexts.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Allergen/Pollen)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Vitamins and Antioxidants in Plants: Are They Helpful in the Management of Allergies?
by
Andreea D. Ona
Allergies 2025, 5(3), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5030022 - 2 Jul 2025
Abstract
Affecting around 30–40% of the population worldwide, allergic disorders including asthma, rhinitis, eczema, and food allergies, are relatively common. Environmental factors, such as air pollution and climate change, which aggravate allergic reactions, contribute to the growth of these diseases. Although conventional treatments such
[...] Read more.
Affecting around 30–40% of the population worldwide, allergic disorders including asthma, rhinitis, eczema, and food allergies, are relatively common. Environmental factors, such as air pollution and climate change, which aggravate allergic reactions, contribute to the growth of these diseases. Although conventional treatments such as antihistamines and immunotherapy remain the standard for symptom management, growing interest in natural remedies highlights the potential value of medicinal plants as complementary therapies. Commonly present in plants, vitamins and antioxidants have strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant actions that can control immune responses, lower oxidative stress, and thus reduce inflammation, which is the main element in allergic reactions. By focusing on the fundamental causes of inflammation and immunological dysregulation, phytochemicals have shown encouraging effects in reducing allergic symptoms. This review investigates the role of plant flavonoids, polyphenols, and vitamins in lowering allergic symptoms and inflammation, and suggests their potential in allergy management. It also aims to provide a short review of various plant species that are used in folk medicine for allergy treatment. The inclusion of plant-based compounds in allergy therapy could provide more complete and environmentally friendly remedies to enhance patients’ quality of life.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Diagnosis and Therapeutics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Pneumococcal Vaccine in Patients with Recurrent Infections
by
Mariana de Gouveia-Pereira Pimentel, Carolina Sanchez Aranda, Rafaela Rola Guimarães, Edson Kiyotaka Ishizuka, Dirceu Solé and Antônio Condino-Neto
Allergies 2025, 5(2), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020021 - 18 Jun 2025
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the immunological response to the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPV23) in patients investigated for immunodeficiencies due to recurrent infections at EPM-UNIFESP Clinical Immunology outpatient clinic. Methods: This is a longitudinal retrospective study. Data were collected from the
[...] Read more.
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the immunological response to the 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPV23) in patients investigated for immunodeficiencies due to recurrent infections at EPM-UNIFESP Clinical Immunology outpatient clinic. Methods: This is a longitudinal retrospective study. Data were collected from the medical records of patients between 2012 and 2020. The analyses were developed in two stages: before and after administration of the PPV23 vaccine. Results: A total of 390 patients who received the PPV23 vaccine were selected. Among those who demonstrated an adequate serological response (63.6%), there was a notable decrease in the risk of upper respiratory tract infections (URTI) by 66%, tonsillitis by 74%, otitis by 76%, sinusitis by 49%, and uncomplicated pneumonia (PNM) by 77%. For invasive infections, the risk reduction was 95% for pneumonia with parapneumonic effusion and 93% for meningitis. Conclusions: The study demonstrated a significant decrease in the risk of bacterial infections following the administration of the PPV23 vaccine in this population. Therefore, we recommend including PPV23 in the vaccination schedule following pneumococcal conjugated vaccines for patients with recurrent pneumococcal infections to enhance protection and avoid complications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers 2025)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Associations of Hidradenitis Suppurativa with Atopic Dermatitis: A Review of Shared Pathogenesis and Approach to Treatment of Concomitant Disease
by
Rayad B. Shams, Hiral S. Patel and Christopher J. Sayed
Allergies 2025, 5(2), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020020 - 13 Jun 2025
Abstract
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) and atopic dermatitis (AD) are both inflammatory dermatoses that can significantly impact patient quality of life, however, limited research exists regarding their association. The purpose of this comprehensive review is to compare the inflammatory pathogenesis of HS and AD, explore
[...] Read more.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) and atopic dermatitis (AD) are both inflammatory dermatoses that can significantly impact patient quality of life, however, limited research exists regarding their association. The purpose of this comprehensive review is to compare the inflammatory pathogenesis of HS and AD, explore the associations between these diseases, and discuss standalone and concomitant disease treatment options. Although HS and AD are understood to be primarily driven by the Th1 and Th2 inflammation pathways, respectively, these conditions both utilize the Janus Kinase/Signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK/STAT) pathway to promote inflammation. Newer research also suggests that IL-36 and IL-1 receptor-associated kinase 4 (IRAK4) may be two additional inflammatory signals shared between the HS and AD disease pathways. These shared mechanisms are reflected in patient presentations as HS and AD are often concomitantly present and demonstrate a bidirectional association in the current literature. Treatment options for concomitant disease are limited, but leverage the shared immune pathogenesis of both diseases. Dupilumab has been reported to improve both HS and AD symptoms in select patients. JAK inhibitors are currently FDA-approved for the treatment of AD, and early trials have suggested benefits from JAK inhibitors such as upadacitinib, povorcitinib, and topical ruxolitinib for HS. Possible future avenues for research on treating both HS and AD include IRAK-4 inhibitors such as zabedosertib and BAY1830839, and diet and gut microbiome modifications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Dermatology)
►▼
Show Figures
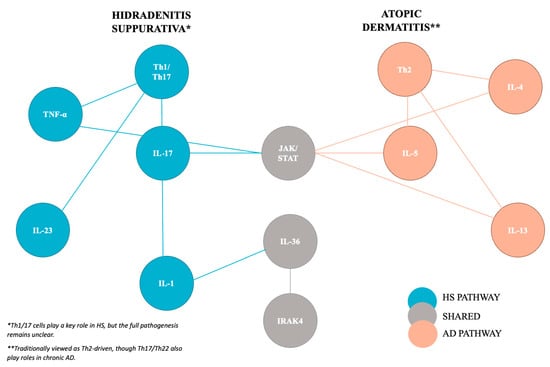
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
New Therapies in the Biological Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review
by
Mateusz Kamil Ożóg, Alicja Derkacz, Dawid Klimczak, Sara Winkler and Laura Wojciuch
Allergies 2025, 5(2), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020019 - 3 Jun 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease primarily affecting the skin and, in some cases, the joints, and is characterized by erythematous, scaling lesions. Building up the doses has been conventional, but many patients will not obtain good results and a new, more
[...] Read more.
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease primarily affecting the skin and, in some cases, the joints, and is characterized by erythematous, scaling lesions. Building up the doses has been conventional, but many patients will not obtain good results and a new, more targeted therapeutic strategy is desired. In the past few years, immune checkpoint inhibitors have revolutionized moderate to severe psoriasis management by blocking crucial pro-inflammatory cytokines, introducing new avenues for biological therapies. This review summarizes recent developments in biological therapies, including their mechanisms of action and clinical efficacy. While bimekizumab, an IL-17A and IL-17F inhibitor, strongly suppresses inflammation, selective inhibition of the IL-12/23 pathways is targeted with the small molecule TYK2 inhibitor deucravacitinib. For example, spesolimab, an inhibitor of IL-36 signaling, is being investigated for generalized pustular psoriasis. In this respect, new therapies provide better efficacy and quality of life, target specific psoriasis subtypes, and are safer and more effective than anti-inflammatory treatments. Such therapies could radically inform the standards of care, and the long-term safety and patient-centered outcomes of these innovative strategies will be the subject of continued research.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Dermatology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Exploring the Link Between Allergies and Neurological Diseases: Unveiling the Hidden Connections
by
Kamila Saramak
Allergies 2025, 5(2), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020018 - 3 Jun 2025
Abstract
The interplay between allergic diseases and neurological disorders has gained increasing attention over the past decades, highlighting potential shared pathophysiological pathways. Allergic diseases, including asthma, eczema, and allergic rhinitis, are characterized by chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation, which may impact the pathogenesis of
[...] Read more.
The interplay between allergic diseases and neurological disorders has gained increasing attention over the past decades, highlighting potential shared pathophysiological pathways. Allergic diseases, including asthma, eczema, and allergic rhinitis, are characterized by chronic inflammation and immune dysregulation, which may impact the pathogenesis of certain neurological conditions. Emerging evidence suggests that conditions such as multiple sclerosis (MS), migraine, epilepsy, neurodegenerative diseases, and neurodevelopmental disorders may be influenced by systemic inflammation and altered immune responses associated with allergies. The purpose of this paper is to provide an overview of current epidemiological evidence suggesting a relationship between allergic and neurological diseases. Understanding the complex interactions between allergic and neurological diseases could provide new insights into their aetiology and reveal novel therapeutic targets, paving the way for integrated approaches in managing comorbid allergic and neurological conditions, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers 2025)
Open AccessReview
Endoscopic Dilation for Fibrostenotic Complications in Eosinophilic Esophagitis—A Narrative Review
by
Marco Michelon, Edoardo Vincenzo Savarino, Michele Montori, Maria Eva Argenziano, Pieter Jan Poortmans, Pierfrancesco Visaggi, Roberto Penagini, David J. Tate, Marina Coletta and Andrea Sorge
Allergies 2025, 5(2), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020017 - 26 May 2025
Abstract
Esophageal fibrotic remodeling is a major complication of chronic inflammation in eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) and represents one of the main determinants of symptoms in adult patients with EoE, with a remarkable impact on patients’ quality of life and the healthcare system. Esophageal fibrotic
[...] Read more.
Esophageal fibrotic remodeling is a major complication of chronic inflammation in eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) and represents one of the main determinants of symptoms in adult patients with EoE, with a remarkable impact on patients’ quality of life and the healthcare system. Esophageal fibrotic remodeling is diagnosed through upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, radiological studies, and a functional luminal imaging probe. However, diagnostic underestimation of esophageal strictures and suboptimal adherence to EoE guidelines still represent limitations of current clinical practice. Combined with medical therapy and/or elimination diets, endoscopic dilation remains the cornerstone treatment for esophageal strictures and rings, offering a safe and effective option for managing obstructive symptoms. Different modalities are available for esophageal endoscopic dilation of EoE, including mechanical and balloon dilators. Mechanical dilators provide tactile feedback during the procedure and exert longitudinal and radial forces. In contrast, balloon dilators apply a purely radial force and enable direct visualization of the esophageal mucosa during the procedure. Both mechanical and balloon dilators are safe and effective, with no single modality demonstrating clear superiority. Consequently, the choice of dilation technique is guided by stricture characteristics, the expertise of the endoscopist, and considerations related to the financial and environmental sustainability of the devices. This review aims to summarize the most relevant evidence on the endoscopic evaluation and dilation of fibrostenotic complications in EoE, also providing practical guidance for clinicians to optimize the endoscopic management of these patients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Diagnosis and Therapeutics)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Diversity and Interactions of the Naso-Buccal Bacteriome in Individuals with Allergic Rhinitis, Asthma and Healthy Controls
by
Marcos Pérez-Losada
Allergies 2025, 5(2), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020016 - 12 May 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Allergic rhinitis and asthma are significant public health concerns worldwide. While previous studies have explored how nasal and buccal bacteriotas influence these conditions, few have directly compared their bacteriomes within the same cohort. To bridge this gap, I analyzed 16S rRNA next-generation sequencing
[...] Read more.
Allergic rhinitis and asthma are significant public health concerns worldwide. While previous studies have explored how nasal and buccal bacteriotas influence these conditions, few have directly compared their bacteriomes within the same cohort. To bridge this gap, I analyzed 16S rRNA next-generation sequencing data from 347 individuals, including participants with allergic rhinitis, asthma and healthy controls. The nasal and buccal bacteriomes shared all dominant bacterial taxa but differed significantly in their phylum- and genus-level relative abundances. Alpha-diversity was significantly higher in the buccal cavity, while beta-diversity varied significantly across all indices and clinical groups. Over 80% of the predicted metabolic pathways were differentially regulated between the two cavities, yet these functional differences remained fairly consistent across clinical groups. Naso-buccal bacterial networks exhibited striking differences in structure, complexity and hub nodes. Notably, the network of healthy controls showed a clear segregation between nasal and buccal bacteria, with 93.5% of the interactions occurring within each respective cavity, and contained few pathogenic keystone taxa. In contrast, bacterial networks from diseased individuals exhibited reduced ecological specialization and more pathogenic keystone taxa linked to airway disease. These findings, thus, demonstrate that the naso-buccal bacteriome plays distinct yet interconnected roles in allergic rhinitis and asthma.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Asthma/Respiratory)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Edible Insects and Allergy Risks: Implications for Children and the Elderly
by
Alessandra de Cássia Romero
Allergies 2025, 5(2), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020015 - 9 May 2025
Abstract
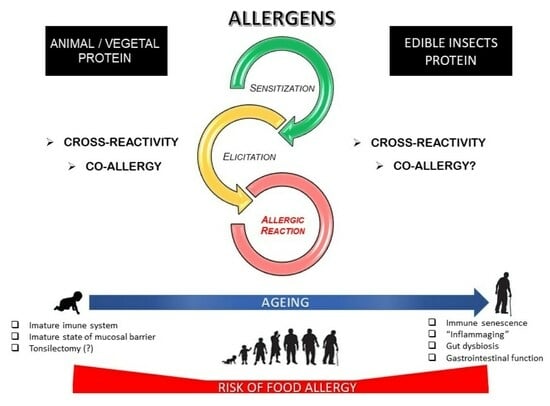
Population growth and the depletion of natural resources have driven the incorporation of edible insects into the human food matrix. Despite their high nutritional value and the environmental benefits of insect farming compared to conventional protein sources, their consumption poses potential risks, including
[...] Read more.
Population growth and the depletion of natural resources have driven the incorporation of edible insects into the human food matrix. Despite their high nutritional value and the environmental benefits of insect farming compared to conventional protein sources, their consumption poses potential risks, including food allergies. Sensitization to insect allergens can occur through various exposure routes, with cross-reactions involving other foods and environmental allergens being well-documented. Vulnerable groups such as children and the elderly may have increased susceptibility not only because of genetic predisposition but also because of age-related physiological factors. This review explores the emerging risks of edible insect consumption, with a focus on children and the elderly. Age-related alterations in the gut microbiota, digestion, immune function, and overall physiology can facilitate the absorption of intact allergenic proteins and impair immune responses. Furthermore, the allergenic potential of insect proteins and their associated microbiota remains poorly characterized. Limited research exists on the effects of processing methods on these proteins. Consequently, incorporating edible insects into food products could present an additional allergenic risk, particularly for these vulnerable populations. Understanding these risks is essential for ensuring the safety and acceptance of edible insects as sustainable food ingredients.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Food Allergy)
►▼
Show Figures
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Different Phenotypes of Pediatric Asthma Show Distinct Bacterial Functional Profiles and Network Relationships
by
Marcos Pérez-Losada
Allergies 2025, 5(2), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020014 - 6 May 2025
Abstract
Pediatric asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the US and a major public health concern. It is considered to comprise multiple clinical variants or phenotypes with different etiologies and pathophysiologies. Former research has shown that airway bacteriomes vary in composition
[...] Read more.
Pediatric asthma is the most common chronic childhood disease in the US and a major public health concern. It is considered to comprise multiple clinical variants or phenotypes with different etiologies and pathophysiologies. Former research has shown that airway bacteriomes vary in composition and structure across pediatric asthma phenotypes, but their functional diversity and bacterial interactions have hardly been investigated. A previous study of 163 children from Washington DC identified three statistically different asthma phenotypes, each with a unique nasopharyngeal bacterial composition and diversity. Here, I reanalyze 16S rRNA high-throughput sequences from the same cohort to characterize their bacterial metabolism and interactions. I detect 61 to 102 metabolic pathways (PICRUSt2; q ≤ 0.05) differentially expressed across the three asthma phenotypes. Most of those pathways are related to biosynthesis and degradation processes and statistically (p ≤ 0.0012) separated the three clinical groups. Co-occurrence networks also differ in connectivity across phenotypes, suggesting unique bacterial interactions in each group. Five to eight keystone taxa are detected across phenotypes. Insights from this and previous studies, hence, confirm the airway bacteriome heterogeneity across pediatric asthma, increasing our understanding of its etiology and pathophysiology, and provide new taxonomic and functional biomarkers of disease for targeted interventions and therapies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Asthma/Respiratory)
►▼
Show Figures
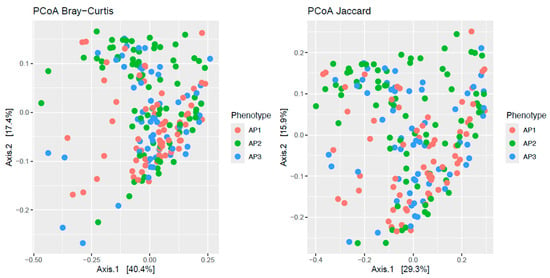
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
D-2-Hydroxyglutarate Attenuates Sinonasal Inflammation in Murine Allergic Rhinitis
by
Anuj Tharakan, Ankit Kumar, Carmen Camarena, Daniel H. Conrad and Rebecca K. Martin
Allergies 2025, 5(2), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020013 - 9 Apr 2025
Abstract
Introduction: Allergic rhinitis (AR) is largely driven by IgE-induced immune cell activation, which promotes allergen-induced upper airway inflammation. The regulatory mechanisms of IgE synthesis in AR are poorly understood. Several analyses associate single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) which reduce the expression of the D2HGDH
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Allergic rhinitis (AR) is largely driven by IgE-induced immune cell activation, which promotes allergen-induced upper airway inflammation. The regulatory mechanisms of IgE synthesis in AR are poorly understood. Several analyses associate single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) which reduce the expression of the D2HGDH gene with AR. D2HGDH encodes an enzyme that converts D-2-hydroxyglutarate (D2HG) to α-ketoglutarate (α-KG). This study aims to clarify the relationship between AR and SNPs in D2HGDH. Methods: Mice were treated with vehicle control or octyl-D2HG prior to intranasal exposure to Alternaria alternata. Draining lymph nodes (dLNs) were then evaluated for IgE-producing cells and T-cell polarization. Next, mice were exposed to intranasal Alternaria on days 0, 10, 20, and 27–30 and were treated intranasally with octyl-D2HG or vehicle control on days 20 and 27. Nasal inflammation was analyzed in nasal lavage fluid (NLF) cellularity and antigen-specific IgE production. Results: The administration of D2HG prior to Alternaria exposure suppressed IgE synthesis (p < 0.01) and Th2 cell polarization (p < 0.01) in dLNs. In a murine model of AR, D2HG administration reduced overall cellular infiltrates and eosinophils in NLF. Further, antigen-specific IgE in NLF was significantly reduced in mice treated with D2HG (p < 0.05). Conclusions: An analysis of the regulatory landscape surrounding the rs34290285 SNP demonstrates that the downregulation of D2HGDH expression reduces the risk of AR. Downregulation of D2HGDH likely results in accumulation of D2HG intracellularly, suggesting that D2HG is protective against allergic rhinitis. We show that the administration of D2HG impairs IgE production, leading to the amelioration of allergic sinonasal inflammation in a murine model of AR. These findings suggest a causal relationship between D2HGDH expression, D2HG levels, and allergic rhinitis risk.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Rhinology/Allergic Rhinitis)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Should the Cat Stay Home? A Guide to Managing Cat Allergies
by
Ramin Beheshti, Polly Huang, Megan Le, Rachel Peterson and Jody R. Tversky
Allergies 2025, 5(2), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/allergies5020012 - 8 Apr 2025
Abstract
Worldwide, cat allergies affect 15% of the population. Cat allergens are ubiquitous and challenging to eliminate from homes, making it difficult to implement effective allergen reduction strategies. Developing strategies to reduce cat allergens in homes could alleviate the burden of allergic diseases, enhance
[...] Read more.
Worldwide, cat allergies affect 15% of the population. Cat allergens are ubiquitous and challenging to eliminate from homes, making it difficult to implement effective allergen reduction strategies. Developing strategies to reduce cat allergens in homes could alleviate the burden of allergic diseases, enhance symptom management, lower healthcare expenses, and improve patients’ quality of life. Studies have produced varied results concerning the effectiveness of specific environmental control measures in lowering cat allergen levels and improving clinical outcomes for allergic diseases. This review evaluates the existing evidence on the effectiveness of environmental control measures in reducing cat allergens and their potential clinical impact.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Allergen/Pollen)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
19 September 2025
MDPI Webinar | The Science Behind the Prize: 2025 Nobel Physiology or Medicine Roundtable, 6 October 2025
MDPI Webinar | The Science Behind the Prize: 2025 Nobel Physiology or Medicine Roundtable, 6 October 2025

3 September 2025
Join Us at the MDPI at the University of Toronto Career Fair, 23 September 2025, Toronto, ON, Canada
Join Us at the MDPI at the University of Toronto Career Fair, 23 September 2025, Toronto, ON, Canada

Topics
Topic in
Cells, Immuno, IJMS, JCM, Allergies, Dermato
Skin Barrier Function and Immune Mediators as Key Therapeutic Targets of Main Inflammatory Diseases
Topic Editors: Marco Manfredini, Carlo PincelliDeadline: 31 August 2026
Topic in
Biomedicines, Cancers, Cells, JCM, Pharmaceutics, Reports, Allergies
The Tumor Microenvironment, Immuno-Oncology, and Immune Checkpoint: Implications for Current and Emergent Immunotherapies, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Joaquim Carreras, Luis J. Castro-VegaDeadline: 31 December 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Allergies
Future Directions of Specific Immunomodulatory Therapy in Children
Guest Editors: Francesco La Torre, Carla MastrorilliDeadline: 30 December 2025
Special Issue in
Allergies
Feature Papers 2025
Guest Editors: Pierre Rougé, Carmen CuadradoDeadline: 31 December 2025





