Journal Description
Acta Microbiologica Hellenica
Acta Microbiologica Hellenica
(AMH) is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on medical microbiology. The journal is owned by the Hellenic Society for Microbiology and is published quarterly online by MDPI (since Volume 69, Issue 1 - 2024). HMS members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, Biological Abstracts and BIOSIS Previews (Web of Science), and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 24.1 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 9.3 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
COVID-19: What We Have Learnt and Where Are We Going?
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(4), 42; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70040042 (registering DOI) - 6 Nov 2025
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in high morbidity and mortality, as well as severe social and economic disruption globally. Since the pandemic began in 2019, the severe acute respiratory syndrome, coronavirus 2, has undergone numerous changes, resulting in the emergence of new variants and
[...] Read more.
The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in high morbidity and mortality, as well as severe social and economic disruption globally. Since the pandemic began in 2019, the severe acute respiratory syndrome, coronavirus 2, has undergone numerous changes, resulting in the emergence of new variants and subvariants. The emergence of new variants of the virus poses a challenge to scientists. There is currently no SARS-CoV-2 variant meeting the criteria of variants of concern, whereas the only variant of interest is JN.1, and there are six variants under monitoring: LP8.1, NP1.8.1, XEC, KP.3, KP.3.1.1 and the latest, XFG (Stratus). Although the latter appears to be more transmissible than the others, genomic evidence indicates that it is less aggressive than some recent variants. Nevertheless, continuous genomic surveillance of COVID-19 is still important to detect any new variants that could threaten public health. Numerous therapeutic strategies, such as drugs, vaccines, and nutritional supplements, are being used to treat COVID-19. This narrative review is an overview of COVID-19 and its various facets, from the number of cases to the therapies used, the current variants, and the ongoing clinical trials, specifically focusing on the most recent studies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Research in the Mediterranean and Neighboring Regions for COVID-19: Facts Scenarios and Growing Awareness)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Genome Editing Against HPV-Driven Cancers: From Bench to Clinic
by
Muharrem Okan Cakir, Melis Selek, Betul Yilmaz, Mustafa Ozdogan and Gholam Hossein Ashrafi
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(4), 41; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70040041 - 31 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Genome editing technologies, including CRISPR/Cas9, TALENs, and ZFNs, offer promising approaches to disrupt HPV oncogenes E6 and E7, thereby restoring tumor-suppressor pathways. In this review, we summarize recent preclinical findings demonstrating selective apoptosis and tumor regression in HPV-positive cell and animal models, as
[...] Read more.
Genome editing technologies, including CRISPR/Cas9, TALENs, and ZFNs, offer promising approaches to disrupt HPV oncogenes E6 and E7, thereby restoring tumor-suppressor pathways. In this review, we summarize recent preclinical findings demonstrating selective apoptosis and tumor regression in HPV-positive cell and animal models, as well as early-phase clinical studies exploring local CRISPR-based therapies. We also compare the relative strengths and limitations of major editing platforms, discuss delivery strategies, and highlight their potential integration with immunotherapy and conventional treatments. While preclinical studies show encouraging efficacy (e.g., up to 60% tumor regression in xenograft models and marked reactivation of p53/pRb pathways), translation into routine practice remains limited by challenges such as efficient delivery, minimizing off-target effects, long-term safety, cost, and ethical considerations. Continued optimization of high-fidelity nucleases, tissue-specific delivery systems, and genotype-tailored guide RNAs will be essential. Genome editing therefore represents a potential future addition to the therapeutic landscape of HPV-related diseases, but substantial barriers must be addressed before clinical implementation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Dermatophilosis: Current Advances and Future Directions
by
Olamilekan Gabriel Banwo, Olalekan Chris Akinsulie, Ridwan Olamilekan Adesola and Olalekan Taiwo Jeremiah
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(4), 40; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70040040 - 17 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Dermatophilosis, caused by the Gram-positive, filamentous bacterium Dermatophilus congolensis, is an important skin disease that adversely affects cattle health and productivity. It also affects other domestic and wild animals and occasionally humans. This review provides a detailed overview of the molecular characteristics
[...] Read more.
Dermatophilosis, caused by the Gram-positive, filamentous bacterium Dermatophilus congolensis, is an important skin disease that adversely affects cattle health and productivity. It also affects other domestic and wild animals and occasionally humans. This review provides a detailed overview of the molecular characteristics and resistome profile of D. congolensis, highlighting recent advances in genomic research. We examine the bacterium’s genome architecture, including its genome size, GC content, gene composition, and phylogenetic placement within the Actinomycetales. Key virulence factors are discussed, including proteolytic enzymes, hyphal invasion, zoospore motility, and the gene products of nasp and agac, emphasizing their roles in tissue invasion, pathogenesis, and diagnostic detection. Furthermore, we analyze resistome, focusing on identified antibiotic resistance genes, diverse resistance mechanisms such as efflux pumps and beta-lactamases, and the contribution of mobile genetic elements to horizontal gene transfer. The implications of these molecular insights for accurate diagnosis, effective treatment, and antibiotic stewardship in cattle production are critically evaluated. Finally, we highlight future research priorities aimed at deepening our understanding of D. congolensis biology and improving strategies for disease control. This review underscores the importance of integrating molecular surveillance with antimicrobial monitoring to safeguard cattle health and promote sustainable livestock management.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Polymicrobial Infections: A Comprehensive Review on Current Context, Diagnostic Bottlenecks and Future Directions
by
Amit Patnaik, Titirsha Kayal and Soumya Basu
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(4), 39; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70040039 - 14 Oct 2025
Abstract
Worldwide, polymicrobial infections (PMIs) account for an estimated 20–50% of severe clinical infection cases, with biofilm-associated and device-related infections reaching 60–80% in hospitalized patients. This review discusses the clinical burden of major infections in which PMIs are almost inevitable, such as diabetic foot
[...] Read more.
Worldwide, polymicrobial infections (PMIs) account for an estimated 20–50% of severe clinical infection cases, with biofilm-associated and device-related infections reaching 60–80% in hospitalized patients. This review discusses the clinical burden of major infections in which PMIs are almost inevitable, such as diabetic foot infections, intra-abdominal infections, pneumonia, and biofilm-associated device infections. Globally, the PMI landscape is diverse; however, the Indian subcontinent is a PMI hotspot where high comorbidities, endemic antimicrobial resistance, and underdeveloped diagnostic capacity elevate the risks of poor outcomes. Existing diagnostic like culture-based methods, PCR panels, sequencing, and biomarker-based assays are constrained by sensitivity, turnaround times (TATs), and high costs. Vulnerable populations, particularly neonates, the elderly, immunocompromised patients, and socioeconomically marginalized groups, show case-fatality rates 2-fold higher than monomicrobial infections in similar settings. Emerging diagnostic solutions include CRISPR-based multiplex assays, artificial intelligence-based metagenomic platforms, and sensitive biosensors with point-of-care applicability. These technologies show potential in reducing the TAT (<2 h) with high accuracy (>95%). However, their translation to real-world settings depends critically on affordability, integration into healthcare pathways, and supportive policy. This will provide equitable diagnostic access, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Androgen Receptor Blockade Induces the Phagocytosis of MRSA and Pseudomonas aeruginosa by Monocyte-Derived Macrophages In Vitro
by
Amina Belboul, Mohamed El Mohtadi, Abdulmannan Fadel, Jessica Mcloughlin, Ayman Mahmoud, Caitlin O’Malley and Jason Ashworth
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(4), 38; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70040038 - 26 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Age-related impaired wounds often become infected with bacteria, leading to substantial mortality and morbidity in the elderly. The decline in androgen levels with increasing age is believed to exacerbate inflammation during wound infections. Despite its well-documented anti-inflammatory activities in wound repair, little is
[...] Read more.
Age-related impaired wounds often become infected with bacteria, leading to substantial mortality and morbidity in the elderly. The decline in androgen levels with increasing age is believed to exacerbate inflammation during wound infections. Despite its well-documented anti-inflammatory activities in wound repair, little is known about the effect of age-related androgen deprivation on bacterial phagocytosis in impaired chronic wounds. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of age-related testosterone deprivation on the phagocytic functions of THP-1 monocyte-derived macrophages to eliminate Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria in vitro. Host–pathogen interaction experiments were conducted to quantify the macrophage-mediated clearance of two common wound-associated bacteria, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, under in vitro environments that model testosterone levels representative of those found in elderly males, healthy young adults and testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). Testosterone and its metabolite 5α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT) significantly dampened the macrophage-mediated phagocytosis of both MRSA and P. aeruginosa in a dose-dependent manner (p < 0.05). Blockade of the androgen receptor (AR) using enzalutamide confirmed that testosterone mediates bacterial clearance through binding to the AR. Blocking the conversion of testosterone to DHT through stimulation of macrophages with the 5-α-reductase inhibitor finasteride reversed the testosterone-mediated effects on bacterial clearance, which confirmed that testosterone could potentially dampen the innate phagocytic responses in macrophages through conversion to DHT. Novel findings in this study suggest that the selective manipulation of the AR and/or blockade of testosterone–DHT conversion may provide effective therapeutic treatments to combat wound infections in the elderly.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
In Vitro Synergy Evaluation of Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole Combined with Levofloxacin and Ceftazidime Against Stenotrophomonas maltophilia: A Comparative Study Using Checkerboard and Gradient Diffusion Methods
by
Melda Payaslioğlu, Reyhan Başkiliç, Esra Kazak and Halis Akalin
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(3), 37; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030037 - 22 Sep 2025
Abstract
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is a nosocomial pathogen that is resistant to many broad-spectrum antibiotics. This study aimed to evaluate the in vitro synergy of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (SXT) combined with levofloxacin (LEV) or ceftazidime (CAZ) using checkerboard and gradient diffusion methods. Between 2016 and 2021, 20
[...] Read more.
Stenotrophomonas maltophilia is a nosocomial pathogen that is resistant to many broad-spectrum antibiotics. This study aimed to evaluate the in vitro synergy of trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole (SXT) combined with levofloxacin (LEV) or ceftazidime (CAZ) using checkerboard and gradient diffusion methods. Between 2016 and 2021, 20 S. maltophilia strains (five SXT-resistant and 15 SXT-susceptible strains) were collected from various clinical settings. Their susceptibility to SXT, LEV, and CAZ was assessed using both checkerboard and gradient diffusion synergy tests. The gradient diffusion method was performed using commercial strip-based tests (Liofilchem®). It should be noted that the gradient diffusion method has not been standardized by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) for synergy testing and is considered for research purposes only. In the checkerboard method, the SXT + LEV combination showed synergy in one strain and an additive effect in 19 strains; the SXT + CAZ combination exhibited synergy in eight strains and an additive effect in 12 strains. In the gradient diffusion method, the SXT + LEV combination showed synergy in one strain and an additive effect in 19 strains; the SXT + CAZ combination exhibited synergy in five strains, an additive effect in 14 strains, and antagonism in one strain. A correlation between the two methods was observed in 90% of SXT + LEV combinations and 65% of SXT + CAZ combinations. Both checkerboard and gradient diffusion methods yielded similar results, indicating their reliability in determining antibiotic combinations. Given the observed synergy, CAZ combinations may be effective for treating SXT-resistant strains.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Microbiome-Targeted Therapies in Gastrointestinal Diseases: Clinical Evidence and Emerging Innovations
by
Enoch Chi Ngai Lim and Chi Eung Danforn Lim
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(3), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030036 - 13 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Microbiome-targeted therapies are redefining gastroenterology by delivering precision interventions that align with the body’s natural microbial ecosystem. This narrative review evaluates evidence for established approaches, probiotics, prebiotics, fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), and postbiotics, and examines emerging innovations such as engineered probiotics, bacteriophage therapy,
[...] Read more.
Microbiome-targeted therapies are redefining gastroenterology by delivering precision interventions that align with the body’s natural microbial ecosystem. This narrative review evaluates evidence for established approaches, probiotics, prebiotics, fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), and postbiotics, and examines emerging innovations such as engineered probiotics, bacteriophage therapy, and metabolite-based interventions. Cure rates for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection in randomized trials range from 67% to 94%, depending on route and donor protocol, while multi-strain probiotics provide moderate benefits in inflammatory bowel disease. New modalities, including engineered bacteria and defined bacterial consortia, have progressed to Phase 3 trials, with several granted FDA breakthrough therapy designation. Approvals of Rebyota and Vowst mark a pivotal milestone, creating validated regulatory pathways for microbiome therapeutics. Despite progress, challenges remain in protocol standardisation, patient selection, cost-effectiveness, and clinical integration. Over 200 active trials and growing pharmaceutical investment signal a robust pipeline, with applications expanding to oncology, metabolic disorders, and immune modulation. Continued progress depends on validated biomarkers and personalized strategies guided by microbiome profiling. International regulatory harmonization will also be required to ensure safe and equitable adoption. The field is shifting toward working with, rather than against, the body’s microbial ecosystem, offering substantial potential for personalized gastrointestinal disease management.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Pancreatic Stone Protein: A Multifaceted Biomarker—A Comprehensive Review
by
Nika Vlahović Vlašić, Lada Zibar, Petra Smajić, Luka Švitek and Domagoj Drenjančević
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(3), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030035 - 9 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Pancreatic stone protein (PSP) has emerged as a promising biomarker for the early diagnosis of sepsis, infectious diseases, and chronic inflammatory conditions, including cancer, diabetes, and inflammatory bowel disease. This review evaluates the role of PSP as a biomarker and functional protein,
[...] Read more.
Background: Pancreatic stone protein (PSP) has emerged as a promising biomarker for the early diagnosis of sepsis, infectious diseases, and chronic inflammatory conditions, including cancer, diabetes, and inflammatory bowel disease. This review evaluates the role of PSP as a biomarker and functional protein, emphasizing its diagnostic and prognostic value. Methods: This review was conducted through a comprehensive literature search using the PubMed database, covering publications from the discovery of PSP in the 1980s up to 2025. The information was gathered into thematic sections to provide a comprehensive and structured review of PSP as a biomarker and functional protein in health and disease. Results: A total of 256 articles were reviewed and critically assessed, with 80 meeting the inclusion criteria and forming the basis of this review. The reviewed literature underscores PSP as a multifaceted protein involved in inflammation, immune modulation, tissue regeneration, and systemic infection. PSP shows promise as an early biomarker in critically ill patients. Conclusions: PSP is a clinically promising but not yet fully validated biomarker. To enable its routine clinical application, standardized diagnostic cutoffs, validation through multicenter trials, and integration with existing biomarker panels are required. Further research is warranted to fully establish its diagnostic and prognostic potential across diverse clinical settings.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Identification and Genomic Characterization of Aeromonas dhakensis from a Human Sample
by
David Badenas-Alzugaray, Alexander Tristancho-Baró, Juan Manuel García-Lechuz, Natalia Burillo-Navarrete, Sara Sanz-Sanz, Ana María Milagro-Beamonte, Ana Isabel López-Calleja and Antonio Rezusta-López
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(3), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030034 - 15 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Aeromonas is a genus of Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic bacteria commonly found in aquatic environments and increasingly recognized as opportunistic pathogens. Among them, Aeromonas dhakensis stands out for its high virulence and antimicrobial resistance, but it is often misidentified due to its phenotypic similarity
[...] Read more.
Aeromonas is a genus of Gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic bacteria commonly found in aquatic environments and increasingly recognized as opportunistic pathogens. Among them, Aeromonas dhakensis stands out for its high virulence and antimicrobial resistance, but it is often misidentified due to its phenotypic similarity with A. hydrophila and A. caviae. In this study, a microorganism was isolated from the peritoneal fluid of a patient with signs of intra-abdominal infection. MALDI-TOF MS initially suggested A. hydrophila or A. caviae, but the identification was confirmed with high confidence only after further molecular analyses and the use of genome-based tools, which identified the organism as A. dhakensis. This was further supported by phylogenomic and ANI analysis. Resistome analysis revealed intrinsic resistance genes, including a chromosomal class C β-lactamase and an imiH-type carbapenemase, consistent with the observed carbapenem resistance. No plasmid-mediated carbapenemases were found. These findings underscore the limitations of MALDI-TOF in identifying Aeromonas species in certain cases and highlight the value of genomic approaches for accurate species determination and resistance profiling, especially for isolates from sterile body fluids.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
The Impact of Genital Infections on Women’s Fertility
by
Sara Occhipinti, Carla Ettore, Giosuè Giordano Incognito, Chiara Gullotta, Dalila Incognito, Roberta Foti, Giuseppe Nunnari and Giuseppe Ettore
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(3), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030033 - 7 Aug 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are a significant global health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide, particularly sexually active adolescents and young adults. These infections, caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi, can have profound implications for women’s reproductive health and
[...] Read more.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are a significant global health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide, particularly sexually active adolescents and young adults. These infections, caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi, can have profound implications for women’s reproductive health and fertility. This review explores the role of vaginal and uterine infections in women’s infertility, focusing on the most common pathogens and their impact on reproductive outcomes. Bacterial infections, such as those caused by intracellular bacteria (Mycoplasma, Ureaplasma, and Chlamydia), Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and bacterial vaginosis, are among the most prevalent causes of infertility in women. Studies have shown that these infections can lead to pelvic inflammatory disease, tubal occlusion, and endometrial damage, all of which can impair fertility. Mycobacterium tuberculosis, in particular, is a significant cause of genital tuberculosis and infertility in high-incidence countries. Viral infections, such as Human papillomavirus (HPV) and Herpes simplex virus (HSV), can also affect women’s fertility. While the exact role of HPV in female infertility remains unclear, studies suggest that it may increase the risk of endometrial implantation issues and miscarriage. HSV may be associated with unexplained infertility. Parasitic infections, such as trichomoniasis and schistosomiasis, can directly impact the female reproductive system, leading to infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and other complications. Fungal infections, such as candidiasis, are common but rarely have serious outcomes related to fertility. The vaginal microbiome plays a crucial role in maintaining reproductive health, and alterations in the microbial balance can increase susceptibility to STIs and infertility. Probiotics have been proposed as a potential therapeutic strategy to restore the vaginal ecosystem and improve fertility outcomes, although further research is needed to establish their efficacy. In conclusion, vaginal and uterine infections contribute significantly to women’s infertility, with various pathogens affecting the reproductive system through different mechanisms. Early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and preventive measures are essential to mitigate the impact of these infections on women’s reproductive health and fertility.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Assessment of Bacterial Contamination and Biofilm Formation in Popular Street Foods of Biskra, Algeria
by
Sara Boulmaiz, Ammar Ayachi and Widad Bouguenoun
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(3), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030032 - 28 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This study assessed microbiological contamination in street-sold meat products, focusing on Enterobacterales and coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) species and their antibiotic resistance. Chicken and mutton street foods like shawarma and brochettes were tested for bacterial load, species distribution. and resistance profiles. The results showed
[...] Read more.
This study assessed microbiological contamination in street-sold meat products, focusing on Enterobacterales and coagulase-negative staphylococci (CoNS) species and their antibiotic resistance. Chicken and mutton street foods like shawarma and brochettes were tested for bacterial load, species distribution. and resistance profiles. The results showed significant contamination, with Enterobacter cloacae (5.38 Log 10 CFU/g). Staphylococcus lentus and Staphylococcus xylosus were also common, reaching 6.23 Log 10 CFU/g in some samples. Contamination levels varied significantly by food type, with chicken shawarma showing the highest risk. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing revealed high multidrug resistance, particularly among E. cloacae and Staphylococcus species. Biofilm formation an indicator of resistance was observed mainly in staphylococci and enhanced under fed-batch culture. These findings highlight public health concerns tied to poor hygiene and undercooking in street food environments. The study emphasizes the need for improved hygiene practices, standardized cooking methods, and systematic food safety monitoring to reduce contamination and antibiotic resistance risks.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Exposure to Treponema pallidum Alters Villous Histomorphology of Human Placentae
by
Patience B. Tetteh-Quarcoo, Joana Twasam, John Ahenkorah, Bismarck Afedo Hottor, Nicholas T. K. D. Dayie, Stephen Opoku-Nyarko, Peter Ofori Appiah, Emmanuel Afutu, Fleischer C. N. Kotey, Eric S. Donkor, Emilia Asuquo Udofia, Nii Koney-Kwaku Koney, Benjamin Arko-Boham and Kevin Kofi Adutwum-Ofosu
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(3), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030031 - 23 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Syphilis, which is caused by Treponema pallidum, remains one of the most common congenital infection worldwide and has tremendous consequences for the mother and her developing foetus if left untreated. The complexity of the exposure to this pathogen extends beyond the well-established
[...] Read more.
Syphilis, which is caused by Treponema pallidum, remains one of the most common congenital infection worldwide and has tremendous consequences for the mother and her developing foetus if left untreated. The complexity of the exposure to this pathogen extends beyond the well-established clinical manifestations, as it can profoundly affect placental histomorphology. This study aimed to compare T. pallidum-exposed placental villi structures with healthy placentae at term to evaluate the histomorphological differences using stereology. In this case-control study conducted at term (38 weeks ± 2 weeks), 78 placentae were collected from the hospital delivery suites, comprising 39 cases (T. pallidum-exposed) and 39 controls (non-exposed), who were gestational age-matched with other potential confounders excluded. Blood samples from the umbilical vein and placental basal plate were tested for syphilis, using rapid diagnostic test (RDT) kits for T. pallidum (TP) antibodies (IgG and IgM) to classify placentae as exposed to T. pallidum (cases) and non-exposed (controls). Tissue sections were prepared and stained with haematoxylin and eosin, and the mean volume densities of syncytial knots, foetal capillaries, syncytial denuded areas, and intervillous spaces were estimated using stereological methods. Statistical analysis was performed to compare the mean values between the case and control groups. Stereological assessment revealed significant differences between the T. pallidum-exposed and non-exposed groups with regard to syncytial knots (p < 0.0001), syncytial denudation (p < 0.0001), and foetal capillaries (p < 0.0001), but no significant difference in the intervillous space was found (p = 0.1592). Therefore, our study shows, for the first time, that the histomorphology of human placental villi appears to be altered by exposure to T. pallidum. It will, therefore, be interesting to determine whether these changes in the placental villi translate into long-term effects on the baby.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Genetic Diversity and Phylogenetic Analysis Among Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas spp. Isolated from Solid Waste Dump Sites and Dairy Farms
by
Tuhina Das, Arkaprava Das, Neha Das, Rittika Mukherjee, Mousumi Saha, Dipanwita Das and Agniswar Sarkar
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(3), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030030 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The excessive use of antimicrobials drives the emergence of multidrug resistance (MDR) in bacterial strains, which harbor resistance genes to survive under diverse drug pressures. Such resistance can result in life-threatening infections. The predominance of MDR Pseudomonas spp. poses significant challenges to public
[...] Read more.
The excessive use of antimicrobials drives the emergence of multidrug resistance (MDR) in bacterial strains, which harbor resistance genes to survive under diverse drug pressures. Such resistance can result in life-threatening infections. The predominance of MDR Pseudomonas spp. poses significant challenges to public health and environmental sustainability, particularly in ecosystems affected by human activities. Characterizing MDR Pseudomonas spp. is crucial for developing effective diagnostic tools and biosecurity protocols, with broader implications for managing other pathogenic bacteria. Strains were diagnosed through 16S rRNA PCR and sequencing, complemented by phylogenetic analysis to evaluate local and global evolutionary connections. Antibiotic susceptibility tests revealed extensive resistance across multiple classes, with MIC values surpassing clinical breakpoints. This study examined the genetic diversity, resistance potential, and phylogenetic relationships among Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain DG2 and Pseudomonas fluorescens strain FM3, which were isolated from solid waste dump sites (n = 30) and dairy farms (n = 22) in West Bengal, India. Phylogenetic analysis reveals distinct clusters that highlight significant geographic linkages and genetic variability among the strains. Significant biofilm production under antibiotic exposure markedly increased resistance levels. RAPD-PCR profiling revealed substantial genetic diversity among the isolates, indicating variations in their genetic makeup. In contrast, SDS-PAGE analysis provided insights into the protein expression patterns that are activated by stress, which are closely linked to MDR. This dual approach offers a clearer perspective on their adaptive responses to environmental stressors. This study underscores the need for vigilant monitoring of MDR Pseudomonas spp. in anthropogenically impacted environments to mitigate risks to human and animal health. Surveillance strategies combining phenotypic and molecular approaches are essential to assess the risks posed by resilient pathogens. Solid waste and dairy farm ecosystems emerge as critical reservoirs for the evolution and dissemination of MDR Pseudomonas spp.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Trichomonas vaginalis in Vaginal Samples from Symptomatic Women in Greece: Assessment of Test Performance and Prevalence Rate, and Comparison with European Prevalence Estimates
by
Lazaros Tsoukalas, Constantine M. Vassalos, Nikos Gkitsakis, Panagiota Gkotzamani, Eleni Gkoumalatsou, Konstantia Bakalianou, Eleftheria Palla, Stavroula Baka, Constantina Skanavis and Evdokia Vassalou
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(3), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030029 - 11 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Trichomonas vaginalis infection (TVI) is the most common curable sexually transmitted infection (STI). In this study, we aimed to assess the performances of different tests for TVI diagnosis in symptomatic Greek women, evaluating the TVI prevalence rate (PR) in Greece and comparing the
[...] Read more.
Trichomonas vaginalis infection (TVI) is the most common curable sexually transmitted infection (STI). In this study, we aimed to assess the performances of different tests for TVI diagnosis in symptomatic Greek women, evaluating the TVI prevalence rate (PR) in Greece and comparing the latter with TVI-PR estimates from Europe. A laboratory-based cross-sectional analysis and a meta-analysis were conducted. Of 399 symptomatic Greek women, 17 had TVI, corresponding to a TVI-PR of 4.3%. The commercial nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) achieved a sensitivity of 94.1%, which was 6% higher than the sensitivity of the culture method, 35% higher than that of the wet mount test, and 59% higher than that of the Giemsa stain test. The wet mount test achieved the lowest positive predictive value of 76.9%. All the tests had high specificity levels and negative predictive values. Data from 34 European TVI-PR studies in symptomatic women were pooled. The TVI-PR established in our study was similar to the TVI-PR estimates of 4.8% in Europe and 4.5% in Greece, with the second being higher than those of 2.1% in Northwestern Europe and 1.5% in Southern Europe but closer to that of 6.7% in Türkiye. In Greece, a European country with a relatively high TVI-PR among symptomatic women, the highly sensitive and specific, automated, point-of-care NAAT would facilitate rapid, accurate TVI diagnosis and the treatment of this target population to meet the WHO’s goal of ending STI epidemics by 2030.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Oral Microbiome Diversity in Transfusion-Dependent Thalassemia Using a Metagenomic Approach in Indonesian Communities
by
Wahyu Siswandari, Dyahayu Nisa Arini, Ali Taqwim, Shinta Prima Ardinas, Dwi Utami Anjarwati and Lantip Rujito
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(3), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030028 - 3 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Beta-thalassemia major is an inherited disorder that requires lifelong blood transfusions, with the risk of complications including poor oral health and dental caries. The objective of this study was to compare the oral microbiome diversity and composition in transfusion-dependent thalassemia patients and relate
[...] Read more.
Beta-thalassemia major is an inherited disorder that requires lifelong blood transfusions, with the risk of complications including poor oral health and dental caries. The objective of this study was to compare the oral microbiome diversity and composition in transfusion-dependent thalassemia patients and relate it to oral hygiene and dental caries. A cross-sectional analysis of 35 patients of beta-thalassemia major aged 6–18 years was performed. The status of oral hygiene was examined through the Oral Hygiene Index—Simplified (OHI-S) and Decayed, Missing, and Filled Teeth (DMFT) index. Saliva was taken for DNA extraction, followed by the 16S rRNA sequencing of V3-V4 hypervariable regions. The bioinformatics pipeline in QIIME2 was utilized for analyzing the comparison of microbial composition and diversity in groups of varying oral hygiene status and severity of caries. Metagenomic analysis revealed 3334 Amplicon Sequence Variants (ASVs), of which the most prevalent genera were Streptococcus, Haemophilus, Veillonella, Rothia, and Prevotella. High-oral-hygiene groups presented increased levels of cariogenic bacteria, while moderate-oral-hygiene groups presented an equilibrated microbiome. No statistically significant differences in microbial diversity were found between the study groups (p > 0.05). This study sheds light on the critical importance of oral hygiene in microbiome diversity in patients with beta-thalassemia major.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Risk Factors for Dengue Virus Infection Among Hospitalized Patients in Bangladesh
by
Shirajum Monira, K. A. N. K. Karunarathna, Mohammad Ezazul Hoque Iqubal, Md Abu Sayeed, Tazrina Rahman, Md Kaisar Rahman, Shahneaz Ali Khan, Philip P. Mshelbwala, John I. Alawneh and Mohammad Mahmudul Hassan
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(3), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030027 - 3 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Dengue virus infection (DVI), a mosquito-borne arboviral infection, is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, including Bangladesh, where incidence has surged over the past three decades—particularly in urban and peri-urban areas. This study investigates the factors influencing DVI seropositivity among clinically suspected patients
[...] Read more.
Dengue virus infection (DVI), a mosquito-borne arboviral infection, is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, including Bangladesh, where incidence has surged over the past three decades—particularly in urban and peri-urban areas. This study investigates the factors influencing DVI seropositivity among clinically suspected patients admitted to the selected hospitals of Savar, Dhaka, and Chattogram. Data were collected from 850 clinically suspected patients admitted to two hospitals in Savar, Dhaka, and two in Chattogram during 2019. Questionnaire responses and laboratory test results (NS1, IgM, and IgG) were analyzed using descriptive statistics, chi-square tests, and logistic regression. Out of 450 admissions in Savar, 330 tested positive, while Chattogram reported 145 positives from 400 cases. No significant differences were observed between regions in relation to hospital type, season, gender, or household preventive measures. In Savar, DVI status was significantly associated with season, mosquito net use, and patient contact. In Chattogram, household repellent use and patient contact were key factors. Diagnostic tests varied in detection capability. These findings can inform targeted intervention strategies and public health messaging, such as promoting personal protection measures and community awareness campaigns, particularly in high-incidence urban settings. However, further research across diverse geographic and socio-ecological contexts is needed to enhance the generalizability and policy relevance of these results.
Full article
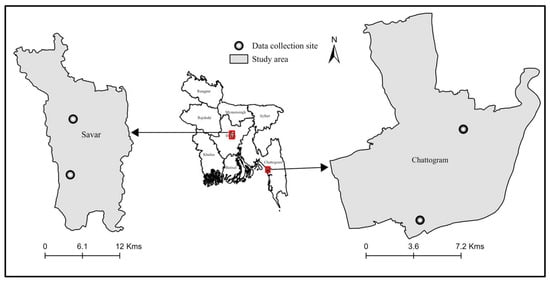
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
High Prevalence of Vaginal Candidiasis and Absence of Trichomonas vaginalis Among Female Patients in Da Nang, Vietnam
by
Vinh Xuan Le, Kieu Thi Nguyen, Minh Van Nguyen, Tram ThiHoang Ho, Tuyen ThiThanh Tran, Cong Phi Dang, Van Cao and Thuy Thi Le
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(3), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70030026 - 24 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Vaginitis is a major health concern among women, with inadequate treatment potentially leading to reproductive complications. This study aimed to assess vaginitis prevalence, identify predominant pathogens, and evaluate associated risk factors among female patients at Da Nang Dermato-Venereology Hospital. A prospective study of
[...] Read more.
Vaginitis is a major health concern among women, with inadequate treatment potentially leading to reproductive complications. This study aimed to assess vaginitis prevalence, identify predominant pathogens, and evaluate associated risk factors among female patients at Da Nang Dermato-Venereology Hospital. A prospective study of 796 female patients undergoing physical examinations was conducted, with demographic, clinical, and microbiological data collected. Vaginitis was diagnosed in 180 (22.6%) of 796 female patients, predominantly caused by Candida spp. (66.1%) and bacterial pathogens (31.7%), with no Trichomonas vaginalis detected, and was most prevalent in women aged 20–30 years. Poor hygiene practices, including infrequent sanitary pad changes (OR = 5.01, p < 0.001) and routine vaginal douching (OR = 6.77, p < 0.001), were significantly associated with vaginitis. The Amsel criteria showed high specificity (99.1%) for bacterial vaginosis diagnosis. The absence of T. vaginalis suggests a potential shift in the epidemiology of vaginal infections. The Amsel criteria are a practical diagnostic tool in resource-limited settings. Our findings highlight the need for targeted hygiene education to reduce vaginitis prevalence in Vietnam.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Talaromyces marneffei Outside Endemic Regions: An Overlooked Mycosis Under a One-Health Lens
by
Paulo Afonso, Luís Cardoso, Ana Sofia Soares, Manuela Matos, Hélder Quintas and Ana Cláudia Coelho
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(2), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70020025 - 16 Jun 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Talaromyces marneffei is a zoonotic dimorphic pathogen endemic to Southeast Asia and reported in 33 countries, with an estimated 17,300 human cases and 4900 deaths annually. We aimed to identify the best available evidence regarding the epidemiological and clinical features and the prevalence
[...] Read more.
Talaromyces marneffei is a zoonotic dimorphic pathogen endemic to Southeast Asia and reported in 33 countries, with an estimated 17,300 human cases and 4900 deaths annually. We aimed to identify the best available evidence regarding the epidemiological and clinical features and the prevalence of T. marneffei reported in companion animals, wildlife, and humans in Europe. A systematic literature review was conducted by searching three databases under PRISMA guidelines for “Talaromyces marneffei” or “talaromycosis” in Europe or the equivalent. References from the obtained publications were also checked to identify additional papers that met the inclusion criteria. The search was not limited by language or year. Studies published until 30 April 2025 were included. Due to the limited number of publications on animals, the geographic scope was expanded to a global level. Of the 915 studies identified, 33 were eligible and categorised according to the subject they addressed: talaromycosis in humans (n = 26), talaromycosis in companion animals (n = 4), and talaromycosis in wildlife (n = 3). Talaromycosis has been reported 28 times in 11 different European countries among humans. Additionally, one case of T. marneffei in wildlife has been documented in Europe. There is a potential liaison host between bamboo rats and humans. Talaromycosis is an emerging planetary neglected disease. Confusion with other diseases and potential misdiagnosis leads to delayed diagnosis and unnecessary risk to lives. Immunocompromised and HIV-positive patients should be screened for talaromycosis. The unexplained worldwide reports in atypical species and locations prompt a call to action for a more proactive search for T. marneffei in other domestic and wild animals, as well as in soil, to fully understand its hosts and transmission, which must incorporate the Stockholm Paradigm and Planetary Health perspectives.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Antibiotic Resistance Profiles of Diarrhoeagenic Enterobacterales in Bioko Island, Equatorial Guinea
by
Úrsula-Eva Eñeso Efuá, Silvia Herrera-León, Fátima Patabobe, Pascual Erasmo Owono and Agustín Benito
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(2), 24; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70020024 - 10 Jun 2025
Abstract
Acute diarrhoeal disease caused by antibiotic-resistant diarrhoeagenic bacteria is a significant global public health issue, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. This study provides the first molecular characterisation of antimicrobial resistance profiles, including the detection of CTX-M-15 and CTX-M-55 extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs), among
[...] Read more.
Acute diarrhoeal disease caused by antibiotic-resistant diarrhoeagenic bacteria is a significant global public health issue, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. This study provides the first molecular characterisation of antimicrobial resistance profiles, including the detection of CTX-M-15 and CTX-M-55 extended-spectrum beta-lactamases (ESBLs), among diarrhoeagenic Enterobacterales in Bioko Island, Equatorial Guinea, offering novel epidemiological insights into an understudied region. This study investigated the antibiotic resistance profiles of pathogenic bacteria isolated from diarrhoeal samples on Bioko Island. A total of 153 clinical isolates were collected between 1 February and 30 May 2014, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing was performed at Loeri Comba Polyclinic (Malabo) using the Kirby–Bauer method. The molecular characterisation of β-lactamase-associated genes was performed on different isolates of diarrhoeagenic pathotypes—144 Escherichia coli, 7 Salmonella enterica, and 2 Shigella flexneri—at the National Centre for Microbiology (Majadahonda, Spain). High resistance rates were detected against ampicillin (98%), tetracycline (93.5%), sulfonamides (94.8%), sulfamethoxazole–trimethoprim (88.2%), and cefotaxime (78.8%), while moderate rates of resistance were noted for ciprofloxacin (26.7%), and all isolates remained susceptible to imipenem. Of the isolates, 107 (69.9%) produced either single or multiple β-lactamases. Among these, 73 (68.2%) harbored classical β-lactamases, specifically TEM and OXA-1 types, representing 47.7% of the total sample. Additionally, 34 (31.8%) of the isolates were identified as producers of extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs), specifically CTX-M enzymes. Sequencing identified CTX-M-15 and CTX-M-55 variants. The predominant ESBL-producing bacteria were enteroaggregative Escherichia coli (56.2%), followed by enteropathogenic and enterotoxigenic E. coli. These findings confirm the circulation of multidrug-resistant diarrhoeagenic Enterobacterales in Equatorial Guinea, raising concerns about limited treatment options due to widespread resistance to multiple antibiotic classes, including third-generation cephalosporins and quinolones. The most important conclusion drawn from this study is that a high percentage of diarrhoeagenic bacteria have an antibiotic resistance and multi-resistance profile, especially to beta-lactams and other groups of antibiotics such as tetracyclines and sulphonamides. There is also a moderate prevalence of isolates carrying ESBLs on Bioko Island, Equatorial Guinea, which could indicate the inappropriate use of antimicrobials.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Sexually Transmitted Diseases and Their Associated Factors in a Cohort in Da Nang City: An Alarming Trend in Syphilis Rates and Infection at Young Ages
by
Thuy Thi Le, Trinh ThiDoan Nguyen, Ngan DangThu Nguyen, Hoang Huy Nguyen, Hoa ThiMinh Hoang, Lam ThiKieu Bui, Minh Van Nguyen, Cong Phi Dang and Van Cao
Acta Microbiol. Hell. 2025, 70(2), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/amh70020023 - 5 Jun 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) remain a global issue, causing health problems and financial burdens. This study aimed to provide an update on the invasive pathogens and analyze any associated factors in patients visiting Da Nang Dermato-Venereology Hospital who were diagnosed with genital tract
[...] Read more.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) remain a global issue, causing health problems and financial burdens. This study aimed to provide an update on the invasive pathogens and analyze any associated factors in patients visiting Da Nang Dermato-Venereology Hospital who were diagnosed with genital tract infections in males and lower genital tract infections in females; 535 participants underwent clinical examinations and microbiological tests to identify the invasive microorganisms, before we analyzed previously gathered laboratory results and associated risk factors. The rate of infection was 37.6% amongst 535 participants. Treponema pallidum infection accounted for the highest rate of 21.3%, followed by HSV, standing at 6%. The prevalence of syphilis infection was highest in the 20–29 age group, standing at 51.7%. There was a positive correlation between age under 20 and infected conditions (OR = 3.78, 95% CI: 1.41–10.11, p = 0.008). Having multiple sexual partners was identified as a risk factor for infection, as those with three or more sexual partners showed a high correlation (OR = 3.19, 95% CI: 1.44–7.05, p = 0.004). The high syphilis prevalence among young adults and teenagers underscores the need for improved STI education and screening programs in Vietnam.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
AMH
Research in the Mediterranean and Neighboring Regions for COVID-19: Facts Scenarios and Growing Awareness
Guest Editors: Ekatherina Charvalos, Eugenia Bezirtzoglou, Anastasia BarbouniDeadline: 31 December 2025