Regulatory Mechanism of Insulin Signaling in Diseases
A special issue of Cells (ISSN 2073-4409). This special issue belongs to the section "Cellular Metabolism".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: closed (10 October 2022) | Viewed by 1577
Special Issue Editors
Interests: mitochondria; mitochondria endoplasmic reticulum contact sites; insulin; skeletal muscle; diabetes; hypertension; obesity; cardiovascular disease
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
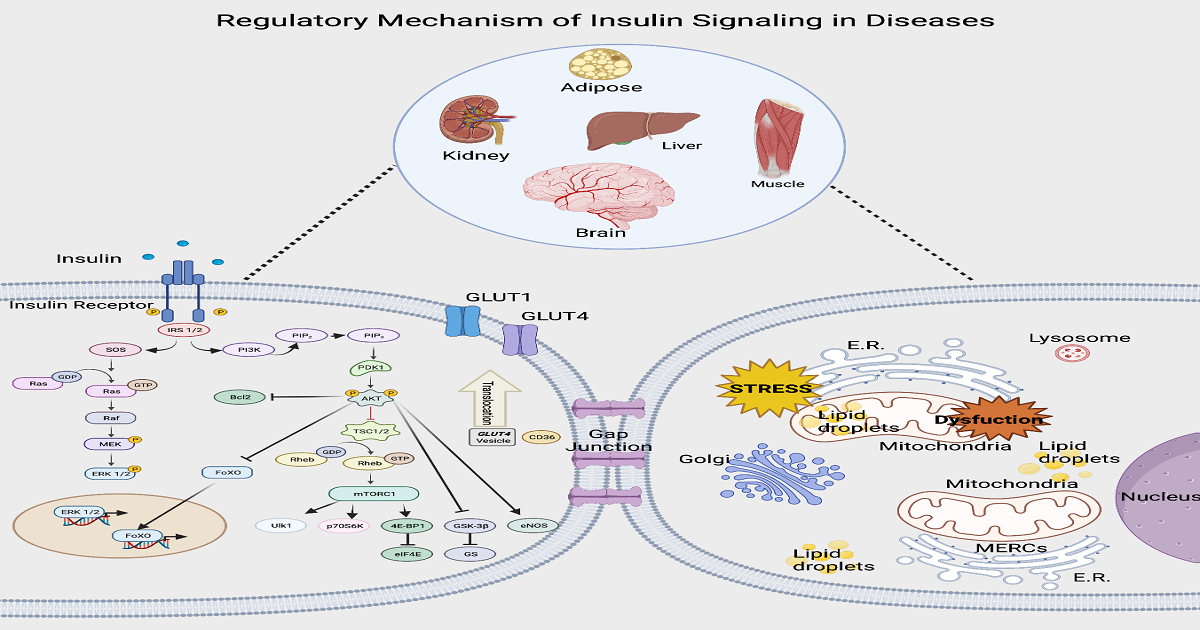
This Special Issue on the regulatory mechanism of insulin signaling in diseases captures the ongoing challenges of insulin resistance. The Special Issue seeks to examine and identify novel biological processes that regulate insulin resistance in multiple tissues (e.g., adipose, pancreas, skeletal muscle, brain, cardiac muscle, and liver tissue). With this Special Issue, we aim to develop an integrative physiological perspective with a special focus on intricate signaling effectors that regulate cell-cell communication during insulin signaling and connectors that coordinate tissue specific responses. We will try to better understand insulin resistance, which in turn requires knowledge of normal insulin function and the pathophysiological effects of insulin resistance.
Insulin’s discovery has ignited interest in the study of the molecular mechanisms of cellular insulin action. Many fundamental cellular processes, including mitochondrial morphology, transfer of molecules across the mitochondrial endoplasmic reticulum contact space, trafficking of vesicles, regulation of gap junctions, mediating metabolic enzymes, activation of transcriptional factors, and auto degradation, are controlled by insulin. Importantly, insulin coordinates these complex processes to ensure glucose homeostasis in the body. More than that, recent literature has suggested that insulin also plays a role in maintaining mitochondrial function and regulating cell-cell communication. Insulin maintains homeostasis by regulating heart metabolism through the stimulation of glucose uptake.
Dr. Antentor Hinton
Prof. Dr. Sandra A. Murray
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 100 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for announcement on this website.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Cells is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2700 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- insulin resistance
- insulin signaling
- gap junction
- cell-cell communication
- mitochondria
- mitochondria endoplasmic reticulum contacts
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- e-Book format: Special Issues with more than 10 articles can be published as dedicated e-books, ensuring wide and rapid dissemination.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.







