Journal Description
Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction
Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction
(CMTR) is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal that covers all types of research in surgery of the head, face and jaw. The journal is owned by AO CMF and is published quarterly online by MDPI (since Volume 18, Issue 1, March 2025). Craniomaxillofacial Trauma and Reconstruction is a member of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE).
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, Embase, and other databases.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 23.6 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 6.1 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Impact Factor:
0.4 (2024);
5-Year Impact Factor:
1.2 (2024)
subject
Imprint Information
Open Access
ISSN: 1943-3883
Latest Articles
Postoperative Complications Following Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Mandibular Condylar Fractures Using the High Perimandibular Approach: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(4), 47; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18040047 - 25 Oct 2025
Abstract
Background: The high perimandibular approach (HPA) is a feasible surgical technique for open reduction and internal fixation (OR-IF) of mandibular condylar fractures, offering reduced complication rates. In this study, we retrospectively evaluated the treatment outcomes and complications associated with HPA use. Patients and
[...] Read more.
Background: The high perimandibular approach (HPA) is a feasible surgical technique for open reduction and internal fixation (OR-IF) of mandibular condylar fractures, offering reduced complication rates. In this study, we retrospectively evaluated the treatment outcomes and complications associated with HPA use. Patients and Methods: Patients who underwent OR-IF for mandibular condylar fractures using the HPA at three hospitals in Shimane between June 2019 and March 2024 were included. Data collected included the mechanism of injury, AO classification of the fracture site, fracture type and mode, surgical duration, mouth-opening range at 6 months post-operatively, and peri- and post-operative complications. Results: A total of 42 patients (46 condylar fractures; 18 males and 24 females; mean age, 63.0 years) were included. The fracture pattern included dislocations in 18 cases (42.8%). The mean surgical duration was 75.0 min. Post-operative trismus occurred in 16 patients (38.1%) at 6 months. Longer surgical duration and dislocated fractures were significantly associated with post-operative trismus (p < 0.05). Conclusions: The HPA is safe and effective for managing mandibular condylar fractures. However, post-operative trismus may be influenced by longer surgical duration and fracture types, warranting further investigation and potential post-surgical management.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Advances in Facial Trauma Surgery)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Development of an Automatic Computer Program to Determine the Optimal Dental Implant Size and Position for Fibula Free Flap Surgery
by
Ming Yan Cheung, Ankit Nayak, Xing-Na Yu, Kar Yan Li, Yu-Xiong Su and Jingya Jane Pu
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(4), 46; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18040046 - 25 Oct 2025
Abstract
Computer-assisted surgery (CAS) and virtual surgical planning (VSP) have transformed jaw reconstruction, allowing immediate insertion of dental implants during surgery for better rehabilitation of occlusal function. However, traditional planning for optimal location and angulation of dental implants and fibula relies on experience and
[...] Read more.
Computer-assisted surgery (CAS) and virtual surgical planning (VSP) have transformed jaw reconstruction, allowing immediate insertion of dental implants during surgery for better rehabilitation of occlusal function. However, traditional planning for optimal location and angulation of dental implants and fibula relies on experience and can be time-consuming. This study aimed to propose a function-driven workflow and develop an automatic computer program for optimal positioning of simultaneous dental implants and fibula segments. A customized computer program was developed using MATLAB. Computed tomography (CT) of the lower limbs of ninety-one Southern Chinese individuals was retrieved and cross-sections of three-dimensional (3D) fibula models were comprehensively investigated for implant installation. Our research proves that the accuracy of the program in identifying the anatomical orientation of the fibula was 92%. The ideal location, angulation and length of implant could be automatically generated based on any selected implant diameter, with a surgical feasibility of 94%. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to develop and validate a customized automatic computer program for osseointegrated implant design in fibula flap surgery. This program can be incorporated into the current workflow of CAS to further the development of reliable and efficient surgical planning for function-driven jaw reconstruction.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovation in Oral- and Cranio-Maxillofacial Reconstruction)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Optimizing Maxillomandibular Position in Orthognathic Surgery: Introducing the T Concept in Treatment Planning
by
Abdulmalik Alyahya and Saud Bin Jasser
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(4), 45; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18040045 - 25 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Orthognathic surgery aims to align the jaws with the facial skeleton and correct dental occlusion. This paper introduces the concept of planning the maxillomandibular complex (MMC) as a whole, utilizing a t-forming set of landmarks: the maxillary central incisor, the chin,
[...] Read more.
Background: Orthognathic surgery aims to align the jaws with the facial skeleton and correct dental occlusion. This paper introduces the concept of planning the maxillomandibular complex (MMC) as a whole, utilizing a t-forming set of landmarks: the maxillary central incisor, the chin, and the occlusal plane. Methods: The background, hypothesis, and rationale of the new T concept are explained. A case of a 28-year-old male with skeletal class III malocclusion and an open bite was used to illustrate the application of the T concept in step-by-step surgical planning. The planning encompasses four phases: Phase One involves correcting frontal deformity and various asymmetries, Phase Two involves correcting chin anterior–posterior deformity, Phase Three involves correcting anterior–posterior and vertical MMC position, and Phase Four involves correcting MMC rotation. Results: The T concept provided a structured approach to plan MMC as a whole and integrate all structures into harmony. Conclusions: The T concept provides a logical approach to MMC positioning in orthognathic surgery, addressing functional and aesthetic concerns. It acts as a checkpoint to verify MMC position, helping surgeons achieve better results and avoid compensatory procedures.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Globe Intussusception Following Orbital Trauma: Case Series and Review of Literature
by
Akruti Desai, Gautam Dendukuri and Milind Naik
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(4), 44; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18040044 - 20 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The aim of this paper is to report “Globe Intussusception” as an extreme form of globe dislocation outside the orbital pyramid, and provide a literature review. A single-center, retrospective, interventional case series of three patients is presented. A review of the English-language literature
[...] Read more.
The aim of this paper is to report “Globe Intussusception” as an extreme form of globe dislocation outside the orbital pyramid, and provide a literature review. A single-center, retrospective, interventional case series of three patients is presented. A review of the English-language literature from the years 1971 to 2024 was performed using the search terms “traumatic globe dislocation”, “maxillary sinus” and “ethmoid sinus”. Three cases of globe intussusception are reported. Computed tomography imaging revealed orbital fracture, and globe prolapse into the maxillary sinus with or without involvement of ethmoid sinus. This was associated with complete intussusception of the globe through the conjunctiva, giving an “empty socket” appearance. In all three cases, fracture repair along with retrieval of the eyeball from the sinus was carried out surgically. Reduction of the intussusception, and bringing the eyeball out of the conjunctival pouch was a special additional challenge in these cases. The review of 35 cases reported in world literature till date is presented. We suggest retrieval of the intussuscepted eyeball via a 360° peritomy and suture tagging of extraocular muscles to ensure safe repositioning of globe with intact extraocular muscles.
Full article
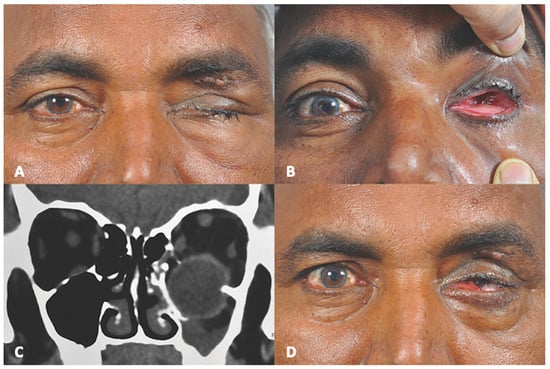
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Chronic Osteomyelitis of the Jaws: Management and Outcomes in a Tertiary Maxillofacial Surgery Unit
by
Patrícia Santos, Carolina Moreira, Nuno Gião and Paulo Valejo Coelho
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(4), 43; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18040043 - 15 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the management and outcomes over 14 years at a tertiary maxillofacial surgery unit. Methods: Retrospective cohort study of patients from a Portuguese tertiary center of maxillofacial surgery with histopathologically confirmed diagnoses of chronic osteomyelitis of the jaws
[...] Read more.
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the management and outcomes over 14 years at a tertiary maxillofacial surgery unit. Methods: Retrospective cohort study of patients from a Portuguese tertiary center of maxillofacial surgery with histopathologically confirmed diagnoses of chronic osteomyelitis of the jaws between January 2010 and December 2023. Demographic and clinical characteristics, treatment, and progression of the disease were evaluated. Results: Fifty-three patients were included—28 women (52.8%), mean age 55 (95% CI 5–90) years. The mandible was affected in 84.9% (n = 45) of cases. Secondary chronic osteomyelitis was diagnosed in 88.7% (n = 47), with medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) being the most common etiology (38.3%). Bacteriological samples were contributory in 52% (n = 13) and 46.1% (n = 6) were resistant to amoxicillin. All received antibiotics for a median time of 27.3 days. Surgical treatment included sequestrectomy (n = 40, 75.5%), marginal (n = 5, 9.4%), and segmental mandibulectomy (n = 8, 15.1%). Clinical remission was achieved in 77.4% (n = 41) of cases with higher success in MRONJ (n = 15, 83.3%) than ORN (n = 4, 57.1%). Conclusions: Almost half of the isolates were amoxicillin-resistant, reinforcing the need for susceptibility testing. Surgical management guided by etiology and disease stage remains essential, with more extensive resection needed in MRONJ and ORN.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrative Innovation in Genioplasty: Advanced 3D Plate Design: Promoting Stability, Aesthetics, and Harmony Excellence
by
Bruno Nifossi Prado, Lucas Cavalieri Pereira, Bianca Pulino and Raphael Capelli Guerra
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(3), 42; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18030042 - 22 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background: Genioplasty is a well-established surgical technique for reshaping the chin and enhancing facial harmony. However, conventional fixation methods may present biomechanical and aesthetic limitations. Objective: This study introduces and evaluates a novel Anatomical Chin Plate (ACP), designed to enhance mechanical performance and
[...] Read more.
Background: Genioplasty is a well-established surgical technique for reshaping the chin and enhancing facial harmony. However, conventional fixation methods may present biomechanical and aesthetic limitations. Objective: This study introduces and evaluates a novel Anatomical Chin Plate (ACP), designed to enhance mechanical performance and facial aesthetics compared to the conventional chin plate (CP). Methods: A three-dimensional finite element analysis (FEA) was conducted to compare stress distribution in ACP and CP models under a standardized oblique load of 60 N, simulating muscle forces from the mentalis and digastric muscles. Plates were modeled using Blender and analyzed using ANSYS software 2025 r2. Mechanical behavior was assessed based on von Mises stress, concentration sites, and potential for plastic deformation or fatigue failure. Results: The ACP demonstrated a significantly lower maximum von Mises stress (77.19 MPa) compared to the CP (398.48 MPa). Stress distribution in the ACP was homogeneous, particularly around the lateral fixation holes, while the CP exhibited concentrated stress between central screw holes. These findings indicate that the anatomical geometry of the ACP enhances load dispersion, reduces critical stress concentrations, and minimizes fatigue risk. Conclusions: The ACP design offers superior biomechanical behavior and improved aesthetic potential for genioplasty procedures. Its optimized shape allows for better integration with facial anatomy while providing stable fixation. Further studies are recommended to validate in vitro performance and explore clinical applicability in advanced genioplasty and complex osteotomies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovation in Oral- and Cranio-Maxillofacial Reconstruction)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Minimally Invasive Endoscopic Transorbital Approach for Frontal Sinus Fractures: A Comparative Study
by
Laurence Verstraete, Paulien Schillemans, Jan Meeus, Philippe Vuylsteke and Robin Willaert
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(3), 41; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18030041 - 22 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: This study aims to evaluate the use of the endoscopic transorbital approach for reducing frontal sinus fractures and compare its outcomes with the traditional bicoronal approach. Methods: A retrospective comparative analysis of case studies including all patients with frontal sinus fractures treated
[...] Read more.
Background: This study aims to evaluate the use of the endoscopic transorbital approach for reducing frontal sinus fractures and compare its outcomes with the traditional bicoronal approach. Methods: A retrospective comparative analysis of case studies including all patients with frontal sinus fractures treated at our institution between January 2013 and December 2023 was conducted. Patients were categorized based on treatment approach (through traumatic laceration, bicoronal, or endoscopic transorbital). For the comparative analysis, cases with associated maxillofacial fractures or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leakage were excluded. Results: Out of 133 patients, 35 underwent surgery, with 6 patients treated using the endoscopic transorbital approach. This group of patients treated with the transorbital endoscopic approach demonstrated significantly shorter operative times compared to the bicoronal approach (mean 102 vs. 168 min, p = 0.021). They also had only minor complications, including temporary hypoesthesia and one transient ptosis. One patient had a minimal residual defect. The technique has been concluded to require endoscopic expertise. Conclusions: The endoscopic transorbital approach is a safe, minimally invasive alternative to the bicoronal approach for selected anterior wall frontal sinus fractures. Proper patient selection and surgical experience are essential to achieving favorable outcomes. Studies with longer follow-up are required to assess potential late complications, such as the development of mucoceles.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Towards MRI-Only Mandibular Resection Planning: CT-like Bone Segmentation from Routine T1 MRI Images Using Deep Learning
by
Reinier S. A. ten Brink, Bram J. Merema, Marith E. den Otter, Willemina A. van Veldhuizen, Max J. H. Witjes and Joep Kraeima
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(3), 40; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18030040 - 19 Sep 2025
Abstract
We present a deep learning-based approach for accurate bone segmentation directly from routine T1-weighted MRI scans, with the goal of enabling MRI-only virtual surgical planning in head and neck oncology. Current workflows rely on CT for bone modeling and MRI for tumor delineation,
[...] Read more.
We present a deep learning-based approach for accurate bone segmentation directly from routine T1-weighted MRI scans, with the goal of enabling MRI-only virtual surgical planning in head and neck oncology. Current workflows rely on CT for bone modeling and MRI for tumor delineation, introducing challenges related to image registration, radiation exposure, and resource use. To address this, we trained a deep neural network using CT-based segmentations of the mandible, cranium, and inferior alveolar nerve as ground truth. A dataset of 100 patients with paired CT and MRI scans was collected. MRI scans were resampled to the voxel size of CT, and corresponding CT segmentations were rigidly aligned to MRI. The model was trained on 80 cases and evaluated on 20 cases using Dice similarity coefficient, Intersection over Union (IoU), precision, and recall. The network achieved a mean Dice of 0.86 (SD ± 0.03), IoU of 0.76 (SD ± 0.05), and both precision and recall of 0.86 (SD ± 0.05). Surface deviation analysis between CT- and MRI-derived bone models showed a median deviation of 0.21 mm (IQR 0.05) for the mandible and 0.30 mm (IQR 0.05) for the cranium. These results demonstrate that accurate CT-like bone models can be derived from standard MRI, supporting the feasibility of MRI-only surgical planning.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovation in Oral- and Cranio-Maxillofacial Reconstruction)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of the Upper Airway in Class II Patients Undergoing Maxillary Setback and Counterclockwise Rotation in Orthognatic Surgery
by
Flávio Fidêncio de Lima, Tayná Mendes Inácio De Carvalho, Bianca Pulino, Camila Cerantula, Mônica Grazieli Correa and Raphael Capelli Guerra
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(3), 39; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18030039 - 4 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Introduction: Maxillary setback in orthognathic surgery has been extensively discussed regarding its effects on bone healing and facial soft tissue profile; however, its impact on upper airway volume remains unclear. Objective: We evaluate the influence of maxillary setback combined with counterclockwise (CCW) rotation
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Maxillary setback in orthognathic surgery has been extensively discussed regarding its effects on bone healing and facial soft tissue profile; however, its impact on upper airway volume remains unclear. Objective: We evaluate the influence of maxillary setback combined with counterclockwise (CCW) rotation of the occlusal plane on upper airway dimensions. Methods: A retrospective observational case series was conducted with eight patients diagnosed with Class II malocclusion who underwent orthognathic surgery involving maxillary setback and CCW mandibular rotation. All procedures were performed by the same surgeon. Preoperative (T1) and 6-month postoperative (T2) facial CT scans were analyzed using Dolphin Imaging software11.7 to measure airway volume (VOL), surface area (SA), and linear distances D1, D2 and D3. Statistical analysis was performed using the Wilcoxon test with a 5% significance level. Results: Significant skeletal changes were observed, including 10.2 mm of mandibular advancement, 5.2 mm of hyoid advancement, and 4.1° of CCW rotation. Although increases in airway volume and surface area were noted, they did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.327 and p = 0.050, respectively), but suggesting a favorable trend toward airway adaptation. Conclusions: Maxillary setback combined with CCW rotation appears to safely correct Class II skeletal deformities without compromising upper airway space. These preliminary findings highlight the technique’s potential for both functional and aesthetic outcomes, warranting further long-term studies.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessTechnical Note
Jaw in a Day: How to Perform Your First Case—Our Workflow
by
Camilo Mosquera and Hisham Marwan
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(3), 38; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18030038 - 4 Sep 2025
Abstract
Jaw in a Day (JIAD) reconstruction provides immediate restoration of mandibular form and function through a single-stage procedure that integrates fibula free flap reconstruction, virtual surgical planning (VSP), immediate dental implant placement, and delivery of a prefabricated prosthesis. Although the technique provides significant
[...] Read more.
Jaw in a Day (JIAD) reconstruction provides immediate restoration of mandibular form and function through a single-stage procedure that integrates fibula free flap reconstruction, virtual surgical planning (VSP), immediate dental implant placement, and delivery of a prefabricated prosthesis. Although the technique provides significant benefits in reducing rehabilitation time and improving patient outcomes, its adoption has been limited due to perceived technical complexity and unfamiliarity with dental workflow. This manuscript provides a detailed, step-by-step protocol to guide surgeons through their first JIAD case, from patient selection and data acquisition to VSP execution, intraoperative coordination, and implant positioning. Emphasis is placed on accurate osteotomy design, implant placement using guided protocols, fabrication of patient-specific hardware, and precise prosthesis pickup techniques. This guide also addresses essential OR team preparation and sterile handling of non-sterile components. By breaking down the process into actionable stages and highlighting common pitfalls and technical tips, this resource aims to lower the barrier for early adopters and enhance the success of initial JIAD cases.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovation in Oral- and Cranio-Maxillofacial Reconstruction)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Impact of Therapeutic Alcohol Administration on Perioperative Quality of Life (QoL) and Fracture Healing in Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder Undergoing Surgery for Maxillofacial Trauma—A Randomized Pilot Trial
by
Elavenil Panneerselvam, Rajkumar Krishnan and Jaikumar Velayudham
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(3), 37; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18030037 - 30 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) is common among patients with maxillofacial trauma. Conventional perioperative care recommends complete abstinence. However, abrupt cessation can lead to Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome (AWS), negatively impacting psychological well-being and compliance. This randomized controlled pilot study evaluated the effectiveness of Monitored
[...] Read more.
Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) is common among patients with maxillofacial trauma. Conventional perioperative care recommends complete abstinence. However, abrupt cessation can lead to Alcohol Withdrawal Syndrome (AWS), negatively impacting psychological well-being and compliance. This randomized controlled pilot study evaluated the effectiveness of Monitored Therapeutic Alcohol Administration (MTAA) in reducing perioperative stress and enhancing quality of life without impairing fracture healing. Twenty-four adult male patients with AUD and isolated facial fractures requiring surgery were enrolled. They were assigned to either an intervention group (n = 12) receiving MTAA—oral alcohol at 0.5 g/kg/day for two weeks—or a control group (n = 12) undergoing complete abstinence. Outcomes were assessed over six weeks, including stress (Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale), quality of life (Oral Health Impact Profile-14), soft tissue healing (Landry’s Index), and hard tissue healing (Moed’s Scale, serum osteocalcin). The MTAA group showed significantly reduced stress and improved quality of life (p < 0.001). Healing outcomes were comparable between groups, with no significant differences in soft tissue indices, osteocalcin levels, or radiographic scores. MTAA appears to be a safe and effective strategy to manage AWS-related distress and improve postoperative recovery, offering a practical alternative to strict abstinence in the surgical management of patients with AUD.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Is Simple Reimplantation a Viable Option in Pediculated Auricular Avulsions? A Systematic Review of the Literature
by
Jose Carlos Román Padilla, Luis Ortiz Peces, Pol Alavedra Martínez and Jose Luis Cebrián Carretero
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(3), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18030036 - 27 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Auricular avulsion injuries are rare, and microvascular reimplantation is considered the preferred treatment according to current literature. However, when a small skin pedicle is preserved, non-microvascular reattachment techniques may offer comparable outcomes. This systematic review aims to assess whether these techniques could represent
[...] Read more.
Auricular avulsion injuries are rare, and microvascular reimplantation is considered the preferred treatment according to current literature. However, when a small skin pedicle is preserved, non-microvascular reattachment techniques may offer comparable outcomes. This systematic review aims to assess whether these techniques could represent a viable alternative. We analyzed 32 cases of pedicled auricular avulsion reported in 16 articles, focusing on patient demographics, injury mechanisms, pedicle characteristics, venous congestion, and postoperative management. Venous congestion occurred in 11 patients, with a significantly higher risk in narrower pedicles (mean width 9.82 mm; 95% CI: 4.75–14.89; p = 0.025). Prophylactic heparin significantly reduced this risk (p = 0.007). Other interventions—leech therapy and hyperbaric oxygen—lacked sufficient data for firm conclusions. Most cases achieved graft survival; necrosis occurred in some, and only two patients required additional surgery. Non-microvascular techniques appear to be a viable alternative to microvascular reimplantation, with similar results and potentially fewer complications. Venous congestion remains the main challenge, requiring active management and hospitalization for monitoring. Limited case series and publication bias still hinder the development of standardized guidelines.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Bridging Gaps: Promoting Scientific Research in AOCMF Asia Pacific and Comparison with Latin America
by
Radhika Menon, Takahiro Kanno, Yiu Yan Leung, Yeshaswini Thelekkat and Gopal Krishnan Kulandaswamy
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(3), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18030035 - 22 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Conducting scientific research in craniomaxillofacial surgery presents distinct challenges, particularly in the Asia Pacific region. This study aimed to assess research interests, barriers, and support needs among surgeons in the region through an anonymous online survey conducted via Google Forms from 12 to
[...] Read more.
Conducting scientific research in craniomaxillofacial surgery presents distinct challenges, particularly in the Asia Pacific region. This study aimed to assess research interests, barriers, and support needs among surgeons in the region through an anonymous online survey conducted via Google Forms from 12 to 31 May 2025, with 169 responses collected. The survey included 13 structured questions and an open-ended comment section. Findings were compared with a similar survey done in Latin America in 2024, to identify regional differences. The results revealed a significant gap in research participation, with 18.3% of Asia Pacific respondents having no publications, unlike Latin America, where all had at least one. Familiarity and participation in the Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Osteosynthesefragen Program for Education and Excellence in Research (AO PEER) were lower in Asia Pacific (29% and 6.5%), and greater challenges were reported in establishing topics, research methodology, and data collection. Although interest was high, only 42% conducted research frequently, and 90.5% indicated a need for mentorship. Despite higher awareness of AO grant opportunities (58%), barriers, like inadequate support for scientific research, lack of training, and limited time, persist. These findings highlight the need for AO Craniomaxillofacial surgery (AOCMF) to implement targeted strategies, such as research training, mentorship, promotion of funding opportunities, and support for multi-center collaborations, to enhance research participation across the region.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Advanced Simulation System for Orbitozygomatic Fracture Reconstruction: Multicenter Validation of a Novel Training and Objective Assessment Platform
by
Enrique Vargas, Rodrigo Díaz, Juan Pablo Vargas, Andrés Campolo, Rodrigo Villanueva, Carlos Cortéz and Salvador Valladares-Pérez
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(3), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18030034 - 14 Aug 2025
Abstract
Orbitozygomatic fractures represent a complex surgical challenge. Given the urgent need for validated educational tools that surpass traditional learning models, this multicenter study developed and validated a novel synthetic advanced simulation model for the reconstruction of these fractures. The model integrates platinum-cured silicones
[...] Read more.
Orbitozygomatic fractures represent a complex surgical challenge. Given the urgent need for validated educational tools that surpass traditional learning models, this multicenter study developed and validated a novel synthetic advanced simulation model for the reconstruction of these fractures. The model integrates platinum-cured silicones and 3D-printed bony structures with prefabricated fractures, accurately replicating the anatomy and tactile properties of soft and hard tissues, including simulated herniation of orbital contents. To our knowledge, it is the only available synthetic model combining both tissue types for this training. Ten participants (faculty and residents) completed simulated procedures. Technical performance was assessed using a hand motion tracking system, the global OSATS (Objective Structured Assessment of Technical Skills) scale, and a task-specific error measurement (Specific Fault Measurement, SFM) scale. Statistically significant differences (p = 0.021) were observed in operative time and error count between novices and experts, confirming the model’s construct validity. Faculty completed the surgery in significantly less time (mean 18.16 min vs. 37.01 min for residents) and made fewer errors (mean 12.25 vs. 53.25). Face and content validity were strongly supported by participant surveys, with 100% stating they would use the simulator to practice before real surgery. A strong inverse correlation (r = –0.786, p = 0.021) between OSATS and SFM scores demonstrated concurrent validity. This model enables ethical, repeatable, and cost-effective training, supporting its implementation into surgical curricula to enhance competence and provide objective skill assessment in orbitozygomatic trauma surgery.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovation in Oral- and Cranio-Maxillofacial Reconstruction)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Matrix WaveTM System for Mandibulo-Maxillary Fixation—Just Another Variation on the MMF Theme?—Part II: In Context to Self-Made Hybrid Erich Arch Bars and Commercial Hybrid MMF Systems—Literature Review and Analysis of Design Features
by
Carl-Peter Cornelius, Paris Georgios Liokatis, Timothy Doerr, Damir Matic, Stefano Fusetti, Michael Rasse, Nils Claudius Gellrich, Max Heiland, Warren Schubert and Daniel Buchbinder
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(3), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18030033 - 15 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Study design: Trends in the utilization of Mandibulo-Maxillary Fixation (MMF) are shifting nowadays from tooth-borne devices over specialized screws to hybrid MMF devices. Hybrid MMF devices come in self-made Erich arch bar modifications and commercial hybrid MMF systems (CHMMFSs). Objective: We survey the
[...] Read more.
Study design: Trends in the utilization of Mandibulo-Maxillary Fixation (MMF) are shifting nowadays from tooth-borne devices over specialized screws to hybrid MMF devices. Hybrid MMF devices come in self-made Erich arch bar modifications and commercial hybrid MMF systems (CHMMFSs). Objective: We survey the available technical/clinical data. Hypothetically, the risk of tooth root damage by transalveolar screws is diminished by a targeting function of the screw holes/slots. Methods: We utilize a literature review and graphic displays to disclose parallels and dissimilarities in design and functionality with an in-depth look at the targeting properties. Results: Self-made hybrid arch bars have limitations to meet low-risk interradicular screw insertion sites. Technical/clinical information on CHMMFSs is unevenly distributed in favor of the SMARTLock System: positive outcome variables are increased speed of application/removal, the possibility to eliminate wiring and stick injuries and screw fixation with standoff of the embodiment along the attached gingiva. Inferred from the SMARTLock System, all four CHMMFs possess potential to effectively prevent tooth root injuries but are subject to their design features and targeting with the screw-receiving holes. The height profile and geometry shape of a CHMMFS may restrict three-dimensional spatial orientation and reach during placement. To bridge between interradicular spaces and tooth equators, where hooks or tie-up-cleats for intermaxillary cerclages should be ideally positioned under biomechanical aspects, can be problematic. The movability of their screw-receiving holes according to all six degrees of freedom differs. Conclusion: CHMMFSs allow simple immobilization of facial fractures involving dental occlusion. The performance in avoiding tooth root damage is a matter of design subtleties.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Matrix WaveTM System for Mandibulo-Maxillary Fixation—Just Another Variation on the MMF Theme? Part I: A Review on the Provenance, Evolution and Properties of the System
by
Carl-Peter Cornelius, Paris Georgios Liokatis, Timothy Doerr, Damir Matic, Stefano Fusetti, Michael Rasse, Nils Claudius Gellrich, Max Heiland, Warren Schubert and Daniel Buchbinder
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(3), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18030032 - 12 Jul 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Study design: The advent of the Matrix WaveTM System (Depuy-Synthes)—a bone-anchored Mandibulo-Maxillary Fixation (MMF) System—merits closer consideration because of its peculiarities. Objective: This study alludes to two preliminary stages in the evolution of the Matrix WaveTM MMF System and details its
[...] Read more.
Study design: The advent of the Matrix WaveTM System (Depuy-Synthes)—a bone-anchored Mandibulo-Maxillary Fixation (MMF) System—merits closer consideration because of its peculiarities. Objective: This study alludes to two preliminary stages in the evolution of the Matrix WaveTM MMF System and details its technical and functional features. Results: The Matrix WaveTM System (MWS) is characterized by a smoothed square-shaped Titanium rod profile with a flexible undulating geometry distinct from the flat plate framework in Erich arch bars. Single MWS segments are Omega-shaped and carry a tie-up cleat for interarch linkage to the opposite jaw. The ends at the throughs of each MWS segment are equipped with threaded screw holes to receive locking screws for attachment to underlying mandibular or maxillary bone. An MWS can be partitioned into segments of various length from single Omega-shaped elements over incremental chains of interconnected units up to a horseshoe-shaped bracing of the dental arches. The sinus wave design of each segment allows for stretch, compression and torque movements. So, the entire MWS device can conform to distinctive spatial anatomic relationships. Displaced fragments can be reduced by in-situ-bending of the screw-fixated MWS/Omega segments to obtain accurate realignment of the jaw fragments for the best possible occlusion. Conclusion: The Matrix WaveTM MMF System is an easy-to-apply modular MMF system that can be assembled according to individual demands. Its versatility allows to address most facial fracture scenarios in adults. The option of “omnidirectional” in-situ-bending provides a distinctive feature not found in alternate MMF solutions.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Optimal Duration of Antibiotic Therapy for Space Infections in the Maxillofacial Region: A Systematic Review
by
Abdullah Saleh Alhudaithi, Faris Jaser Almutairi, Abdullah Saleh Almansour, Abdurrahman Abdurrazzaq Aljeadi and Shaul Hameed Kolarkodi
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(3), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18030031 - 3 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objective: This review aimed to examine and highlight the treatment protocols and optimal duration of antibiotic regimens used in managing maxillofacial space infections of odontogenic origin, along with the associated clinical outcomes. Materials and methods: This systematic review followed PRISMA guidelines and was
[...] Read more.
Objective: This review aimed to examine and highlight the treatment protocols and optimal duration of antibiotic regimens used in managing maxillofacial space infections of odontogenic origin, along with the associated clinical outcomes. Materials and methods: This systematic review followed PRISMA guidelines and was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42024621000). A comprehensive search of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar was conducted for studies from January 2003 to October 2024 using relevant MeSH terms. Studies were selected based on PEO criteria, focusing on the antibiotic treatment protocols and duration for odontogenic maxillofacial space infections, with inclusion of original human research and exclusion of non-relevant or unclear studies. Two independent reviewers performed study selection, data extraction, and risk of bias assessments using the Cochrane RoB 2 and ROBINS-I tools, resolving disagreements through discussion. Results: After data extraction, 277 papers were initially identified. Following the removal of duplicates, 141 articles were screened, of which 64 were selected for full-text assessment and 55 were excluded with justification. Ultimately, nine studies met the inclusion criteria for this review. These included two prospective double-blinded randomized clinical trials (RCTs), two prospective RCTs, four retrospective studies, and one prospective study, all involving patients with dentoalveolar orofacial infections. Risk of bias (RoB) assessment using RoB 2 indicated that two RCTs had a high risk of bias, one had a low risk, and one raised some concerns. ROBINS-I assessment showed moderate risk of bias in three studies, while two were not evaluated. Conclusion: This review concludes that prompt incision and drainage combined with a short-course antibiotic regimen of two to five days is generally effective for managing odontogenic maxillofacial space infections, though further high-quality randomized trials are needed to standardize treatment protocols.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Factors Influencing Mandibular Invasion, Lymph Node Metastasis and Extracapsular Spread in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oral Cavity
by
Rathindra Nath Bera and Richik Tripathi
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(3), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18030030 - 27 Jun 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: A number of factors might affect survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Nodal status is one of the most important prognosticators affecting survival. Studies have shown that pattern of invasion is an important aspect related to survival. Study design: retrospective single-center study
[...] Read more.
Background: A number of factors might affect survival in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Nodal status is one of the most important prognosticators affecting survival. Studies have shown that pattern of invasion is an important aspect related to survival. Study design: retrospective single-center study (original article). Objectives: Our study aimed at evaluating the factors affecting mandibular invasion, lymph node metastasis, and extracapsular spread in oral squamous cell carcinoma and the survival factors associated with it. Methods: Patient records were evaluated to identify factors influencing primary outcome and survival. Cox regression analysis and Kaplan Meir were applied to evaluate the outcomes. Youden’s index was used to determine a cut-off value for depth of invasion and lymph node size affecting outcome. A p value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results: The study evaluated 162 patients with oral cancer. The cut-off value for DOI was 6.5 mm, significantly affecting mandibular invasion and cervical metastasis. The cut-off value for lymph node size was 2.95 cm, significantly affecting extracapsular spread and overall survival. An aggressive pattern of invasion significantly affects mandibular invasion, cervical metastasis, and survival. Conclusion: An aggressive pattern of invasion and depth of invasion are independent risk factors for cervical lymph node metastasis and mandibular invasion. The independent risk factor for extracapsular spread is lymph node size. Lymph node metastasis and nodal size, pattern of invasion, mandibular invasion, and extracapsular spread are independent risk factors affecting overall survival.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
The Intraoperative Fabrication of PMMA Patient-Specific Enophthalmos Wedges and Onlays for Post-Traumatic OZC Reconstruction
by
Layton Vosloo
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(2), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18020029 - 29 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Objective: Trauma is a leading cause of enophthalmos, typically resulting from an increase in the volume of the bony orbit. The general consensus is that post-traumatic primary deformity repair should aim to restore the premorbid volume, shape, and cosmesis of the orbitozygomatic complex
[...] Read more.
Objective: Trauma is a leading cause of enophthalmos, typically resulting from an increase in the volume of the bony orbit. The general consensus is that post-traumatic primary deformity repair should aim to restore the premorbid volume, shape, and cosmesis of the orbitozygomatic complex (OZC). This study aims to utilise novel three-dimensional (3D) printed patient-specific moulds to intraoperatively fabricate enophthalmos wedges and onlays using polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) bone cement to reconstruct the OZC. Methods: A total of seven patients underwent digital surgical planning using Freeform software to virtually correct orbitozygomatic complex deformities guided by a design algorithm. Three-dimensionally printed nylon patient-specific moulds were used intraoperatively to fabricate enophthalmos wedges and/or onlays using an industry-standard PMMA bone cement. Clinical examination and application of the proposed design algorithm determined that enophthalmos wedges were indicated for four patients, with one also requiring an onlay; and periorbital onlays were required for the three remaining patients. Results: Hertel exophthalmometry at a mean follow-up of 19.1 months demonstrated good outcomes in the correction of post-traumatic enophthalmos and hypoglobus and with patients reporting good subjective cosmetic results. Patients 5 and 7 had follow-up three-dimensional computed tomography (3D-CT) to confirm correct placement. Conclusion: The use of patient-specific PMMA wedges and onlays, fabricated intraoperatively with the aid of 3D-printed moulds, offers a reliable and effective approach for correcting post-traumatic enophthalmos and hypoglobus. This method allows for the restoration of orbital volume and anatomical contours, addressing both functional and aesthetic concerns. Our results demonstrate that this technique yields favourable outcomes.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessCase Report
A 3D Printed Hydroxyapatite Implant for Temporal Hollowing Reconstruction: A Patient-Specific Approach
by
Lukas B. Seifert, Alexander Aigner, Sead Abazi, Michel Beyer, Jokin Zubizarreta-Oteiza, Neha Sharma and Florian M. Thieringer
Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2025, 18(2), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmtr18020028 - 12 May 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Temporal hollowing, which is a depression in the temple region, often results from trauma, surgical interventions, or neurological conditions. This condition is frequently observed after the resection of encephaloceles, where it can cause esthetic and functional challenges due to temporalis muscle atrophy and
[...] Read more.
Temporal hollowing, which is a depression in the temple region, often results from trauma, surgical interventions, or neurological conditions. This condition is frequently observed after the resection of encephaloceles, where it can cause esthetic and functional challenges due to temporalis muscle atrophy and nerve palsy. We present a case of a 21-year-old female patient who developed temporal hollowing and complete atrophy of the right temporalis muscle following an encephalocele resection in childhood. The patient also suffered from right-sided frontal nerve branch palsy. To address this complex deformity, a patient-specific implant (PSI) made of hydroxyapatite (HA) was digitally designed and produced using 3D printing technology. The postoperative course was uneventful, with the implant securely positioned and the esthetic result highly satisfactory. This case highlights the potential of 3D printed PSIs in craniofacial reconstruction, offering an optimal solution for both functional restoration and esthetic enhancement. HA further ensures the long-term stability and integration of the implant, providing a promising approach for addressing complex craniofacial defects.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
CMTR
Innovation in Oral- and Cranio-Maxillofacial Reconstruction
Guest Editors: Susana Heredero-Jung, Richard Yuxiong Su, Satyesh ParmarDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
CMTR
Advances in Facial Trauma Surgery
Guest Editors: Takahiro Kanno, Yeshaswini Thelekkat, Mohamed Hazem AbdelAzeem, David Bryan PowersDeadline: 31 March 2026









