- Article
Assessing Flight Initiation Distance and Behavioural Tolerance of an Alien Invasive Species, the Sacred Ibis (Threskiornis aethiopicus), in Northern Adriatic Coasts (Italy): Implications for Management of Invasive Waterbirds
- Francesco Scarton and
- Roberto G. Valle
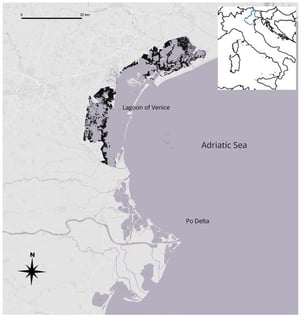
The Sacred Ibis Threskiornis aethiopicus is an invasive alien species (IAS) that has become established in many European countries. Because of its invasive status and its frequent interactions with native species, understanding the behavioural tolerance of this species to human disturbance is relevant for both conservation and management. Here, we analysed Flight Initiation Distances (FID) of T. aethiopicus recorded between 2012 and 2025 across the northern Adriatic coast. The dataset (n = 72) included approaches on foot and by boat in six habitat types (artificial saltmarshes, farmlands, brackish ponds, freshwater wetlands, saltmarshes, tidal flats). Mean FID was 41 m (SD = ± 24); it was affected mainly by group size, whereas habitat, season and approach mode had no clear effect. A cross-species analysis of mean FID versus body mass indicated that, for its size, T. aethiopicus has a much shorter FID than expected from the allometric relationship observed in 20 other waterbirds species for which FID was also collected (n = 1505) at the same sites. The results suggest partial habituation to anthropized environments and a limited flight response compared to native species. These findings may support management actions aimed at monitoring and controlling the expansion of the species while mitigating disturbance to native assemblages.
5 February 2026