- Article
Oligocarbonate Diols as Modifiers of Polyurethane Coatings
- Mariusz Ł. Mamiński,
- Paweł G. Parzuchowski and
- Magdalena Mazurek-Budzyńska
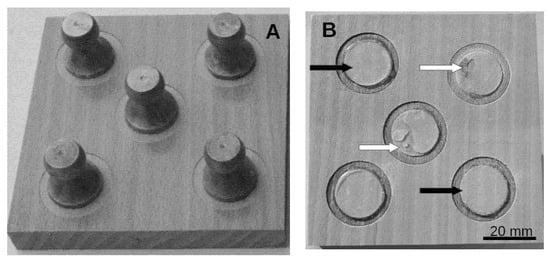
Carbon dioxide-derived oligocarbonate diols (OCDs) represent a promising class of sustainable raw materials that can enhance the environmental profile of polyurethane (PUR) coatings without compromising their performance. In this work, six oligocarbonate diols, differing in chemical structure (aromatic, aliphatic, and cycloaliphatic), were employed as modifiers in solvent-based PUR coatings designed for wood substrates. The study evaluates the influence of OCD’s chemical nature on the mechanical and optical properties of the resulting coatings. The results demonstrate that the structure of the oligocarbonate diol plays a decisive role in determining coating performance. PUR systems containing aliphatic soft segments exhibited the most favorable mechanical response, particularly in terms of wear resistance, outperforming coatings modified with cycloaliphatic and aromatic OCDs—wear reduction ranged between 43% and 71%. In contrast, the highest hardness values (0.46 and 0.41) were observed for the coatings incorporating aromatic moieties, indicating increased rigidity associated with aromatic structures. Importantly, adhesion at the wood–coating interface remained excellent and unaffected by the type of OCD used (cross-cut class I or II), confirming the compatibility of all investigated formulations with wooden substrates. Overall, the findings clearly show that newly developed CO2-based oligocarbonate diols are effective and versatile modifiers for polyurethane wood coatings, enabling the tuning of functional properties while supporting more sustainable coating technologies.
24 January 2026