Journal Description
Computer Sciences & Mathematics Forum
Computer Sciences & Mathematics Forum
is an open access journal dedicated to publishing findings resulting from academic conferences, workshops, and similar events in the area of computer science and mathematics. Each conference proceeding can be individually indexed, is citable via a digital object identifier (DOI), and is freely available under an open access license. The conference organizers and proceedings editors are responsible for managing the peer-review process and selecting papers for conference proceedings.
Latest Articles
Nonlinear Dynamic Inverse Solution of the Diffusion Problem Based on Krylov Subspace Methods with Spatiotemporal Constraints
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 11(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025011005 - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
►
Show Figures
In this work, we propose a nonlinear dynamic inverse solution to the diffusion problem based on Krylov Subspace Methods with spatiotemporal constraints. The proposed approach is applied by considering, as a forward problem, a 1D diffusion problem with a nonlinear diffusion model. The
[...] Read more.
In this work, we propose a nonlinear dynamic inverse solution to the diffusion problem based on Krylov Subspace Methods with spatiotemporal constraints. The proposed approach is applied by considering, as a forward problem, a 1D diffusion problem with a nonlinear diffusion model. The dynamic inverse problem solution is obtained by considering a cost function with spatiotemporal constraints, where the Krylov subspace method named the Generalized Minimal Residual method is applied by considering a linearized diffusion model and spatiotemporal constraints. In addition, a Jacobian-based preconditioner is used to improve the convergence of the inverse solution. The proposed approach is evaluated under noise conditions by considering the reconstruction error and the relative residual error. It can be seen that the performance of the proposed approach is better when used with the preconditioner for the nonlinear diffusion model under noise conditions in comparison with the system without the preconditioner.
Full article
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Time Series Forecasting for Touristic Policies
by
Konstantinos Mavrogiorgos, Athanasios Kiourtis, Argyro Mavrogiorgou, Dimitrios Apostolopoulos, Andreas Menychtas and Dimosthenis Kyriazis
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 11(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025011004 - 30 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The formulation of touristic policies is a time-consuming process that consists of a wide range of steps and procedures. These policies are highly dependent on the number of tourists and visitors to an area to be as effective as possible. The estimation of
[...] Read more.
The formulation of touristic policies is a time-consuming process that consists of a wide range of steps and procedures. These policies are highly dependent on the number of tourists and visitors to an area to be as effective as possible. The estimation of this number is not always easy to achieve, since there is a lack of the corresponding data (i.e., number of visitors per day). Hence, this estimation must be achieved by utilizing alternative data sources. To this end, in this paper, the authors propose a neural network architecture that is trained on waste management data to estimate the number of visitors and tourists in the highly touristic municipality of Vari-Voula-Vouliagmeni, Greece.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Statement of Peer Review
by
Hicham Gibet Tani, Mohamed Kouissi, Mohamed Ben Ahmed, Anouar Boudhir Abdelhakim and Lotfi Elaachak
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010018 - 25 Jul 2025
Abstract
n/a
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Recent Developments in Four-In-Wheel Electronic Differential Systems in Electrical Vehicles
by
Anouar El Mourabit and Ibrahim Hadj Baraka
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010017 - 25 Jul 2025
Abstract
This manuscript investigates the feasibility of Four-In-Wheel Electronic Differential Systems (4 IW-EDSs) within contemporary electric vehicles (EVs), emphasizing their benefits for stability regulation predicated on steering angles. Through an extensive literature review, we conduct a comparative analysis of various in-wheel-motor models in terms
[...] Read more.
This manuscript investigates the feasibility of Four-In-Wheel Electronic Differential Systems (4 IW-EDSs) within contemporary electric vehicles (EVs), emphasizing their benefits for stability regulation predicated on steering angles. Through an extensive literature review, we conduct a comparative analysis of various in-wheel-motor models in terms of power output, efficiency, and torque characteristics. Furthermore, we explore the distinctions between IW-EDSs and steer-by-wire systems, as well as conventional systems, while evaluating recent research findings to determine their implications for the evolution of electric mobility. Moreover, this paper addresses the necessity for fault-tolerant methodologies to boost reliability in practical applications. The findings yield valuable insights into the challenges and impacts associated with the implementation of differential steering control in four-wheel independent-drive electric vehicles. This study aims to explore the interaction between these systems, optimize torque distribution, and discover the most ideal control strategy that will improve maneuverability, stability, and energy efficiency, thereby opening up new frontiers in the development of next-generation electric vehicles with unparalleled performance and safety features.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Detecting Financial Bubbles with Tail-Weighted Entropy
by
Omid M. Ardakani
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 11(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025011003 - 25 Jul 2025
Abstract
This paper develops a novel entropy-based framework to quantify tail risk and detect speculative bubbles in financial markets. By integrating extreme value theory with information theory, I introduce the Tail-Weighted Entropy (TWE) measure, which captures how information scales with extremeness in asset price
[...] Read more.
This paper develops a novel entropy-based framework to quantify tail risk and detect speculative bubbles in financial markets. By integrating extreme value theory with information theory, I introduce the Tail-Weighted Entropy (TWE) measure, which captures how information scales with extremeness in asset price distributions. I derive explicit bounds for TWE under heavy-tailed models and establish its connection to tail index parameters, revealing a phase transition in entropy decay rates during bubble formation. Empirically, I demonstrate that TWE-based signals detect crises in equities, commodities, and cryptocurrencies days earlier than traditional variance-ratio tests, with Bitcoin’s 2021 collapse identified weeks prior to the peak. The results show that entropy decay—not volatility explosions—serves as the primary precursor to systemic risk, offering policymakers a robust tool for preemptive crisis management.
Full article
Open AccessProceeding Paper
An Estimation of Risk Measures: Analysis of a Method
by
Marta Ferreira and Liliana Monteiro
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 11(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025011002 - 25 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Extreme value theory comprises a set of techniques for inference at the tail of distributions, where data are scarce or non-existent. The tail index is the main parameter, with risk measures such as value at risk or expected shortfall depending on it. In
[...] Read more.
Extreme value theory comprises a set of techniques for inference at the tail of distributions, where data are scarce or non-existent. The tail index is the main parameter, with risk measures such as value at risk or expected shortfall depending on it. In this study, we will analyze a method for estimating the tail index through a simulation study. This will allow for an application using real data including the estimation of the mentioned risk measures.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Evaluating Sales Forecasting Methods in Make-to-Order Environments: A Cross-Industry Benchmark Study
by
Marius Syberg, Lucas Polley and Jochen Deuse
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 11(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025011001 - 25 Jul 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Sales forecasting in make-to-order (MTO) production is particularly challenging for small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) due to high product customization, volatile demand, and limited historical data. This study evaluates the practical feasibility and accuracy of statistical and machine learning (ML) forecasting methods in
[...] Read more.
Sales forecasting in make-to-order (MTO) production is particularly challenging for small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) due to high product customization, volatile demand, and limited historical data. This study evaluates the practical feasibility and accuracy of statistical and machine learning (ML) forecasting methods in MTO settings across three manufacturing sectors: electrical equipment, steel, and office supplies. A cross-industry benchmark assesses models such as ARIMA, Holt–Winters, Random Forest, LSTM, and Facebook Prophet. The evaluation considers error metrics (MAE, RMSE, and sMAPE) as well as implementation aspects like computational demand and interpretability. Special attention is given to data sensitivity and technical limitations typical in SMEs. The findings show that ML models perform well under high volatility and when enriched with external indicators, but they require significant expertise and resources. In contrast, simpler statistical methods offer robust performance in more stable or seasonal demand contexts and are better suited in certain cases. The study emphasizes the importance of transparency, usability, and trust in forecasting tools and offers actionable recommendations for selecting a suitable forecasting configuration based on context. By aligning technical capabilities with operational needs, this research supports more effective decision-making in data-constrained MTO environments.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Overview of Training LLMs on One Single GPU
by
Mohamed Ben jouad and Lotfi Elaachak
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010014 - 9 Jul 2025
Abstract
Large language models (LLMs) are developing at a rapid pace, which has made it necessary to better understand how they train, especially when faced with resource limitations. This paper examines in detail how various state-of-the-art LLMs train on a single Graphical Processing Unit
[...] Read more.
Large language models (LLMs) are developing at a rapid pace, which has made it necessary to better understand how they train, especially when faced with resource limitations. This paper examines in detail how various state-of-the-art LLMs train on a single Graphical Processing Unit (GPU), paying close attention to crucial elements like throughput, memory utilization and training time. We find important trade-offs between model size, batch size and computational efficiency through empirical evaluation, offering practical advice for streamlining fine-tuning processes in the face of hardware constraints.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Optimizing Machine Learning for Healthcare Applications: A Case Study on Cardiovascular Disease Prediction Through Feature Selection, Regularization, and Overfitting Reduction
by
Lamiae Eloutouate, Hicham Gibet Tani, Lotfi Elaachak, Fatiha Elouaai and Mohammed Bouhorma
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 13; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010013 - 7 Jul 2025
Abstract
The application of machine learning (ML) to medical datasets offers significant potential for improving disease prediction and patient outcomes. However, challenges such as feature redundancy, overfitting, and suboptimal model performance limit the practical effectiveness of ML algorithms. This study focuses on optimizing ML
[...] Read more.
The application of machine learning (ML) to medical datasets offers significant potential for improving disease prediction and patient outcomes. However, challenges such as feature redundancy, overfitting, and suboptimal model performance limit the practical effectiveness of ML algorithms. This study focuses on optimizing ML techniques for cardiovascular disease prediction using the Kaggle Cardiovascular Disease dataset. We systematically apply feature selection methods, including correlation analysis and regularization techniques (L1/L2), to identify the most relevant attributes and address multicollinearity. Advanced ensemble models such as Random Forest, XGBoost, and LightGBM are employed to mitigate overfitting and enhance predictive performance. Through hyperparameter tuning and stratified k-fold cross-validation, we ensure model robustness and generalizability. The results demonstrate that ensemble methods, particularly gradient boosting algorithms, outperform traditional models, achieving superior predictive accuracy and stability. This study highlights the importance of algorithm optimization in ML applications for healthcare, offering a replicable framework for medical datasets and paving the way for more effective diagnostic tools in cardiovascular health.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
►▼
Show Figures
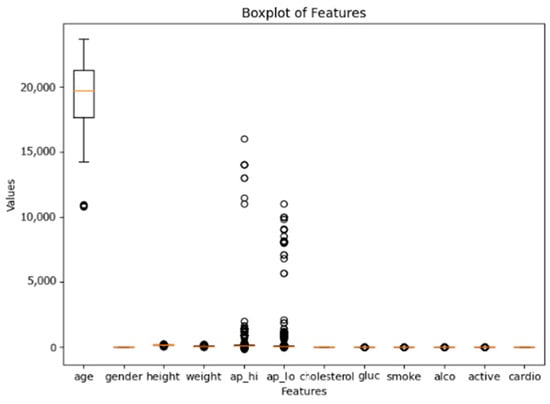
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Integrating Machine Learning with Medical Imaging for Human Disease Diagnosis: A Survey
by
Anass Roman, Chaymae Taib, Ilham Dhaiouir and Haimoudi El Khatir
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 12; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010012 - 7 Jul 2025
Abstract
Machine learning is revolutionizing healthcare by enhancing diagnosis and treatment personalization. This study explores ML applications in medical imaging, analyzing data from X-rays, CT, MRI, and ultrasound for early disease detection. It reviews key ML models, including SVM, ANN, RF, CNN, and other
[...] Read more.
Machine learning is revolutionizing healthcare by enhancing diagnosis and treatment personalization. This study explores ML applications in medical imaging, analyzing data from X-rays, CT, MRI, and ultrasound for early disease detection. It reviews key ML models, including SVM, ANN, RF, CNN, and other methods, demonstrating their effectiveness in detecting cancers such as lung and prostate cancer and other diseases. Despite their accuracy, these methods face challenges such as a reliance on large datasets and significant computational requirements. This study highlights the need for further research to integrate ML into clinical practice, addressing its limitations and unlocking new opportunities for improved patient care.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
►▼
Show Figures
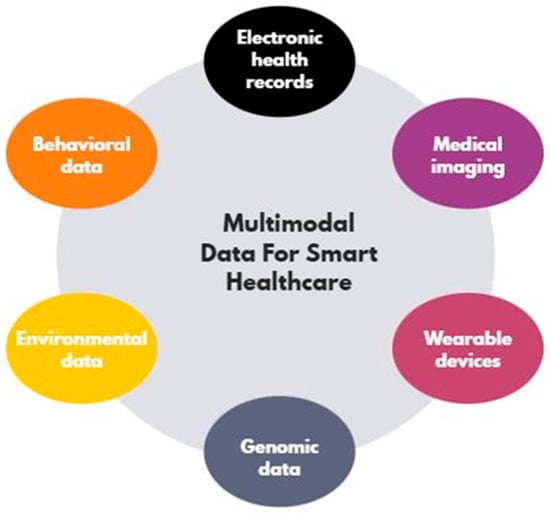
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
The Evolution and Challenges of Real-Time Big Data: A Review
by
Ikram Lefhal Lalaoui, Essaid El Haji and Mohamed Kounaidi
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 11; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010011 - 1 Jul 2025
Abstract
The importance of real-time big data has become crucial in the digital revolution of modern society, in the context of increasing data flows from multiple sources, including social media, internet connected devices (IOT) and financial systems, real-time analysis and processing is becoming a
[...] Read more.
The importance of real-time big data has become crucial in the digital revolution of modern society, in the context of increasing data flows from multiple sources, including social media, internet connected devices (IOT) and financial systems, real-time analysis and processing is becoming a strategic tool for fast and accurate decision making, we find applications in different domains such as healthcare, finance, and digital marketing, which is revolutionizing traditional business models. In this article, we explore the recent advances and future prospects of real-time big data. Our research is based on recent work published between 2020 and 2025, examining the technological advances, the difficulties encountered and suggesting ways of optimizing the efficiency of these technologies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Advancing Stress Detection and Health Monitoring with Deep Learning Approaches
by
Merouane Mouadili, El Mokhtar En-Naimi and Mohamed Kouissi
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010010 - 1 Jul 2025
Abstract
Numerous studies in the healthcare field conducted in recent years have highlighted the impact of stress on health and its role in the development of several critical illnesses. Stress monitoring using wearable technologies, such as smartwatches and biosensors, has shown promising results in
[...] Read more.
Numerous studies in the healthcare field conducted in recent years have highlighted the impact of stress on health and its role in the development of several critical illnesses. Stress monitoring using wearable technologies, such as smartwatches and biosensors, has shown promising results in improving the management of this issue. Data from both physical and mental health can be leveraged to enhance medical decision-making, support research on new treatments, and deepen our understanding of complex diseases. However, traditional machine learning (ML) systems often face limitations, particularly in real-time processing and resource optimization, which restrict their application in critical situations. In this article, we present the development of a deep learning-based approach that leverages models such as 1D CNN (Convolutional Neural Networks), LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory), and Time-Series Transformers, alongside classical deep learning techniques. We then highlight the transformative potential of TinyML for real-time, low-power health monitoring, focusing on Heart Rate Variability (HRV) analysis. This approach aims to optimize personalized health interventions and enhance the accuracy of medical monitoring.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Generative AI Respiratory and Cardiac Sound Separation Using Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
by
Arshad Jamal, R. Kanesaraj Ramasamy and Junaidi Abdullah
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010009 - 1 Jul 2025
Abstract
The separation of respiratory and cardiac sounds is a significant challenge in biomedical signal processing due to their overlapping frequency and time characteristics. Traditional methods struggle with accurate extraction in noisy or diverse clinical environments. This study explores the application of machine learning,
[...] Read more.
The separation of respiratory and cardiac sounds is a significant challenge in biomedical signal processing due to their overlapping frequency and time characteristics. Traditional methods struggle with accurate extraction in noisy or diverse clinical environments. This study explores the application of machine learning, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs), to overcome these obstacles. Advanced machine learning models, denoising algorithms, and domain adaptation strategies address challenges such as frequency overlap, external noise, and limited labeled datasets. This study presents a robust methodology for detecting heart and lung diseases from audio signals using advanced preprocessing, feature extraction, and deep learning models. The approach integrates adaptive filtering and bandpass filtering as denoising techniques and variational autoencoders (VAEs) for feature extraction. The extracted features are input into a CNN, which classifies audio signals into different heart and lung conditions. The results highlight the potential of this combined approach for early and accurate disease detection, contributing to the development of reliable diagnostic tools for healthcare.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Enhanced Lung Disease Detection Using Double Denoising and 1D Convolutional Neural Networks on Respiratory Sound Analysis
by
Reshma Sreejith, R. Kanesaraj Ramasamy, Wan-Noorshahida Mohd-Isa and Junaidi Abdullah
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010007 - 24 Jun 2025
Abstract
The accurate and early detection of respiratory diseases is vital for effective diagnosis and treatment. This study presents a new approach for classifying lung sounds using a double denoising method combined with a 1D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The preprocessing uses Fast Fourier
[...] Read more.
The accurate and early detection of respiratory diseases is vital for effective diagnosis and treatment. This study presents a new approach for classifying lung sounds using a double denoising method combined with a 1D Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). The preprocessing uses Fast Fourier Transform to clean up sounds and High-Pass Filtering to improve the quality of breathing sounds by eliminating noise and low-frequency interruptions. The Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) extracts features that capture localised frequency variations, crucial for distinguishing normal and abnormal respiratory sounds. These features are input into the 1D CNN, which classifies diseases such as bronchiectasis, pneumonia, asthma, COPD, healthy, and URTI. The dual denoising method enhances signal clarity and classification performance. The model achieved 96% validation accuracy, highlighting its reliability in detecting respiratory conditions. The results emphasise the effectiveness of combining signal augmentation with deep learning for automated respiratory sound analysis, with future research focusing on dataset expansion and model refinement for clinical use.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Blockchain for Sustainable Smart Cities: Motivations and Challenges
by
Fatima Zahrae Chentouf, Mohamed El Alami Hasoun and Said Bouchkaren
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010002 - 17 Jun 2025
Abstract
Rapid urbanization and the rising demand for sustainable living have encouraged the growth of smart cities, which incorporate innovative technologies to ameliorate environmental sustainability, optimize resource management, and improve living standards. The convergence of blockchain (BC) technology and the Internet of Things (IoT)
[...] Read more.
Rapid urbanization and the rising demand for sustainable living have encouraged the growth of smart cities, which incorporate innovative technologies to ameliorate environmental sustainability, optimize resource management, and improve living standards. The convergence of blockchain (BC) technology and the Internet of Things (IoT) presents transformative convenience for managing smart cities and achieving sustainability goals. In fact, blockchain technology combined with IoT devices provides a decentralized, transparent, and safe framework for managing massive volumes of data produced by networked sensors and systems. By guaranteeing accountability, minimizing fraud, and maximizing resource use, blockchain not only facilitates the smooth operation of smart city infrastructures but also encourages sustainable habits. The various uses of blockchain technology in smart city management and its contribution to sustainability objectives are examined in this study. Through an examination of important domains like energy distribution, waste management, transportation systems, healthcare, and governance, the research shows how blockchain promotes effective data exchange and data security, builds stakeholder trust, and makes it possible to establish decentralized organizations to improve decision-making.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessEditorial
Preface of Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025)
by
Hicham Gibet Tani, Mohamed Kouissi, Mohamed Ben Ahmed, Anouar Boudhir Abdelhakim and Lotfi Elaachak
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010001 - 17 Jun 2025
Abstract
n/a
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Revolutionizing Distance Learning: The Impact of Ontology and the Semantic Web
by
Camara Alseny, Dhaiouir Ilham and Haimoudi El Khatir
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010016 - 16 Jun 2025
Abstract
The digital age has transformed education, making distance learning essential. With rapid knowledge evolution, flexible and personalized learning is crucial. This article examines how ontology and semantic web technologies enhance e-learning. Ontology structures knowledge in specific domains, while the semantic web enables data
[...] Read more.
The digital age has transformed education, making distance learning essential. With rapid knowledge evolution, flexible and personalized learning is crucial. This article examines how ontology and semantic web technologies enhance e-learning. Ontology structures knowledge in specific domains, while the semantic web enables data automation and integration. Their adoption revolutionizes content organization and personalization. This study explores key concepts, applications, benefits, challenges, and future implications. By analyzing innovations and obstacles, it provides recommendations for educators. Ultimately, it highlights the need for a collaborative approach to leverage these technologies for a more inclusive and adaptive educational environment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
►▼
Show Figures
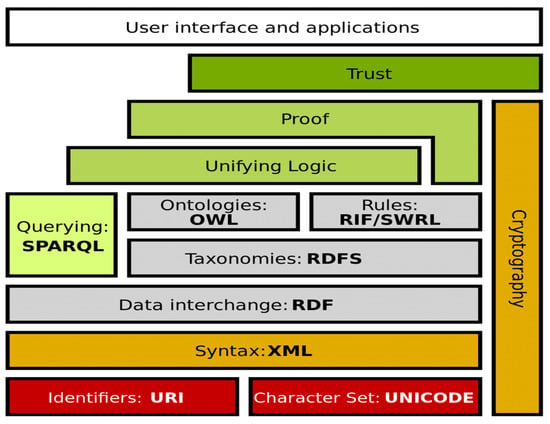
Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Video Surveillance and Artificial Intelligence for Urban Security in Smart Cities: A Review of a Selection of Empirical Studies from 2018 to 2024
by
Abdellah Dardour, Essaid El Haji and Mohamed Achkari Begdouri
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010015 - 16 Jun 2025
Abstract
The rapid growth of information and communication technologies, in particular big data, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT), has made it possible to make smart cities a tangible reality. In this context, real-time video surveillance plays a crucial role in
[...] Read more.
The rapid growth of information and communication technologies, in particular big data, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT), has made it possible to make smart cities a tangible reality. In this context, real-time video surveillance plays a crucial role in improving public safety. This article presents a systematic review of studies focused on the detection of acts of aggression and crime in these cities. By studying 100 indexed scientific articles, dating from 2018 to 2024, we examine the most recent methods and techniques, with an emphasis on the use of machine learning and deep learning for the processing of real-time video streams. The works examined cover several technological axes such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs), fog computing, and integrated IoT systems while also addressing issues such as the challenges related to the detection of anomalies, frequently affected by their contextual and uncertain nature. Finally, this article offers suggestions to guide future research, with the aim of improving the accuracy and efficiency of intelligent monitoring systems.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Enhancing Security and Privacy in IoT Data Streams: Real-Time Anomaly Detection for Threat Mitigation in Traffic Management
by
Oumayma Berraadi, Hicham Gibet Tani and Mohamed Ben Ahmed
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010008 - 16 Jun 2025
Abstract
The rapid expansion of IoT in smart cities has improved traffic management but increased security risks. Traditional IDS struggle with advanced threats, prompting adaptive solutions. This work proposes a framework combining machine learning (ML), Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA), and blockchain authentication. Supervised models
[...] Read more.
The rapid expansion of IoT in smart cities has improved traffic management but increased security risks. Traditional IDS struggle with advanced threats, prompting adaptive solutions. This work proposes a framework combining machine learning (ML), Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA), and blockchain authentication. Supervised models (XGBoost, RF, SVM, LR) detect known anomalies, while a CNN Autoencoder identifies novel threats. Blockchain ensures identity integrity, and compromised devices are isolated automatically. Tests on the IoT-23 dataset demonstrate superior accuracy, fewer false positives, and better scalability than conventional methods. The integration of AI, Zero Trust, and blockchain significantly boosts IoT traffic system security and resilience.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessProceeding Paper
Comparative Analysis of Energy Consumption and Carbon Footprint in Automatic Speech Recognition Systems: A Case Study Comparing Whisper and Google Speech-to-Text
by
Jalal El Bahri, Mohamed Kouissi and Mohammed Achkari Begdouri
Comput. Sci. Math. Forum 2025, 10(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/cmsf2025010006 - 16 Jun 2025
Abstract
This study investigates the energy consumption and carbon footprint of two prominent automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems: OpenAI’s Whisper and Google’s Speech-to-Text API. We evaluate both local and cloud-based speech recognition approaches using a public Kaggle dataset of 20,000 short audio clips in
[...] Read more.
This study investigates the energy consumption and carbon footprint of two prominent automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems: OpenAI’s Whisper and Google’s Speech-to-Text API. We evaluate both local and cloud-based speech recognition approaches using a public Kaggle dataset of 20,000 short audio clips in Urdu, utilizing CodeCarbon, PyJoule, and PowerAPI for comprehensive energy profiling. As a result of our analysis, we expose some substantial differences between the two systems in terms of energy efficiency and carbon emissions, with the cloud-based solution showing substantially lower environmental impact despite comparable accuracy. We discuss the implications of these findings for sustainable AI deployment and minimizing the ecological footprint of speech recognition technologies.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Proceedings of International Conference on Sustainable Computing and Green Technologies (SCGT’2025))
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics












