- Article
NAD-Mediated Protection by Nicotinamide Against UVB-Induced Oxidative Damage in HaCaT Cells
- Lara Camillo,
- Elisa Zavattaro and
- Paola Savoia
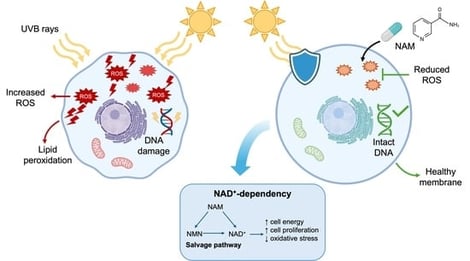
Background/Objectives. Ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation is a key etiological factor for skin cancer, inducing oxidative stress, DNA damage and apoptosis. Nicotinamide (NAM), a NAD+ precursor, has shown photoprotective properties, although the mechanisms underlying this effect have not been fully elucidated. This study sought to elucidate the role of NAM in counteracting UVB-induced oxidative damage in HaCaT cells and to assess the contribution of NAD+ metabolism to these effects. Methods. HaCaT were exposed to low-dose UVB irradiation (40 mJ/cm2) and treated with NAM (25 μM), alone or in combination with the NAMPT inhibitor FK866 (1 nM) for 4 and 24 h. Oxidative stress, lipid peroxidation and DNA damage were evaluated by DCFDA assay, TBARS assay and comet assay, respectively. Cell proliferation, cell cycle progression and apoptosis were assessed using Ki67 immunofluorescence, flow cytometry analysis and Annexin V/PI staining. Transcriptional activity for oxidative stress- and apoptosis-related markers was analyzed by RT-qPCR. Results. NAM significantly reduced UVB-induced ROS production at both 4 and 24 h post-irradiation in an NAD+-dependent manner, as demonstrated by the reversal of its effects following NAMPT inhibition. NAM also decreased oxidative DNA damage accompanied by reduced OGG1 expression, a marker of oxidative stress. Moreover, NAM restored HaCaT proliferation and reduced early apoptosis, particularly at 24 h post-UVB exposure. These protective effects were mediated by NAD+. Conclusions. Our results show that NAM confers robust protection to HaCaT cells from UVB-induced oxidative stress and cellular damage, largely mediated by NAD+-dependent pathways, supporting its potential role as a systemic photoprotective agent in skin cancer prevention.
3 February 2026